Pampaphoneus Biccai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Pampaphoneus'' is an extinct
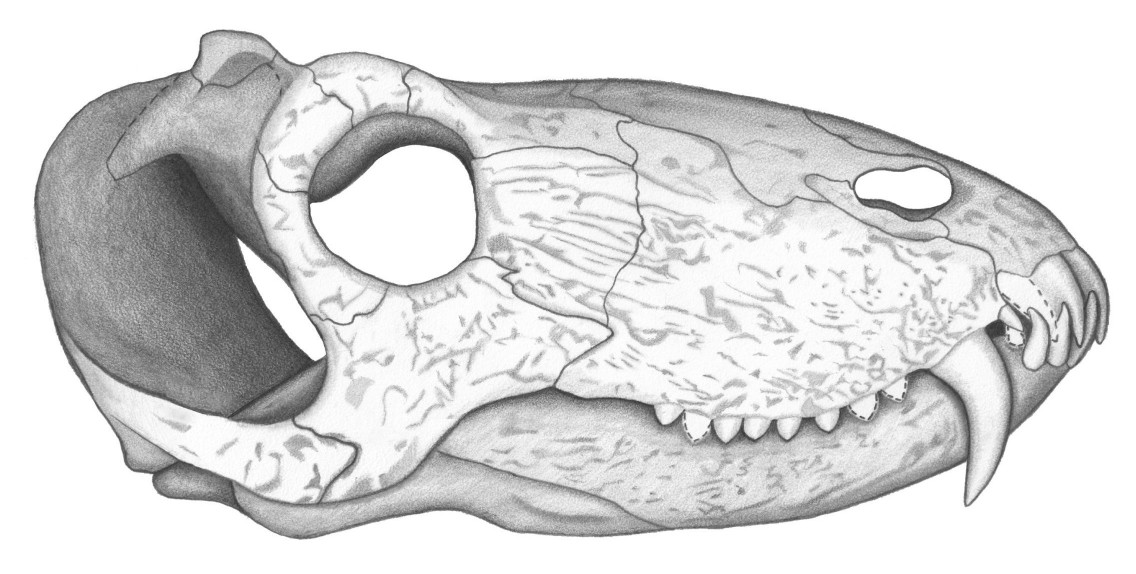 The holotype ( UFRGS PV386P) of ''Pampaphoneus'' is a skull measuring approximately 32 cm in length. As with all anteosaurs, the ventral margin of the
The holotype ( UFRGS PV386P) of ''Pampaphoneus'' is a skull measuring approximately 32 cm in length. As with all anteosaurs, the ventral margin of the
 Remains of ''Pampaphoneus'' comes from the Morro Pelado Member of the
Remains of ''Pampaphoneus'' comes from the Morro Pelado Member of the
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of carnivorous dinocephalia
Dinocephalians (terrible heads) are a clade of large-bodied early therapsids that flourished in the Early and Middle Permian between 279.5 and 260 million years ago (Ma), but became extinct during the Capitanian mass extinction event. ...
n therapsid belonging to the family Anteosauridae
Anteosauridae is an extinct family of large carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids that are known from the Middle Permian of Asia, Africa, and South America.These animals were by far the largest predators of the Permian period, with skulls reachin ...
. It lived 268 to 265 million years ago during the Wordian
In the geologic timescale, the Wordian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is the middle of three subdivisions of the Guadalupian Epoch or Series. The Wordian lasted between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Roadian and fo ...
age
Age or AGE may refer to:
Time and its effects
* Age, the amount of time someone has been alive or something has existed
** East Asian age reckoning, an Asian system of marking age starting at 1
* Ageing or aging, the process of becoming older
...
of the Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle Series (stratigraphy), series/Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico an ...
(= middle Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
) period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Period (punctuation)
* Era, a length or span of time
*Menstruation, commonly referred to as a "period"
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (o ...
in what is now Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. ''Pampaphoneus'' is known by an almost complete skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
with the lower jaw still articulated, discovered on the lands of the Boqueirão Farm, near the city of São Gabriel, in the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
. A second specimen from the same locality was reported in 2019 and 2020 but has not yet been described. It is composed of a skull associated with postcranial remains. It is the first South American species of dinocephalian to have been described. The group was previously known in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
only by a few isolated teeth and a jaw fragment reported in 2000 in the same region of Brazil. Phylogenetic analysis conducted by Cisneros and colleagues reveals that ''Pampaphoneus'' is closely related to anteosaurs from European Russia
European Russia is the western and most populated part of the Russia, Russian Federation. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the country's sparsely populated and vastly larger eastern part, Siberia, which is situated in Asia ...
, indicating a closer faunal relationship between South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
than previously thought, thus promoting a Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia (continent), Siberia during the Carboniferous period ...
B continental reconstruction.
Etymology
The name of the genus comes from thePampas
The Pampas (; from Quechua 'plain'), also known as the Pampas Plain, are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all o ...
, a region of vast plains typical of southern South America, from which the specimen originates, and from the Greek ''phoneus'', meaning "killer", in reference to the predatory habits of the animal. The specific epithet honors José Bicca, the landowner of the farm where the fossil was found.
Description
 The holotype ( UFRGS PV386P) of ''Pampaphoneus'' is a skull measuring approximately 32 cm in length. As with all anteosaurs, the ventral margin of the
The holotype ( UFRGS PV386P) of ''Pampaphoneus'' is a skull measuring approximately 32 cm in length. As with all anteosaurs, the ventral margin of the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals h ...
is inclined upwards and the postorbital bar is strongly curved anteroventrally so that the temporal fenestra
Temporal fenestrae are openings in the temporal region of the skull of some amniotes, behind the orbit (eye socket). These openings have historically been used to track the evolution and affinities of reptiles. Temporal fenestrae are commonly (al ...
undercuts orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
. The skull roof is slightly pachyostosed. The temporal fenestrae open widely on the skull roof
The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes, including land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
In com ...
where the insertion zone of the adductor musculature of the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
extends to the pineal
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep patterns following the diurnal cycles. ...
boss. The frontals contribute to the insertion zone of this musculature and also participate to the anterior edge of the pineal boss. These characteristics indicate that ''Pampaphoneus'' belongs to the clade Syodontinae
Syodontinae is a group of dinocephalian therapsids. It is one of two subfamilies in the family Anteosauridae, the other being Anteosaurinae. They are known from the Middle Permian Period of what is now Russia and South Africa. One of the best kn ...
. Within this group it is with the Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n species ''Syodon
''Syodon'' (from , "close, shut" and , "tooth", "closed-root tooth") is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids that lived approximately 267-260 million years ago during the middle Permian period of the Paleozoic era. These therapsids, disc ...
biarmicum'' that ''Pampaphoneus'' shares the most similarities. Like the latter, it possesses strongly recurved hook-like canine
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* Animals of the family Canidae, more specifically the subfamily Caninae, which includes dogs, wolves, foxes, jackals and coyotes
** ''Canis'', a genus that includes dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Do ...
s and very low postcanines with serrassions. The canines of the holotype are 7 cm in length. ''Pampaphoneus'' however differs from ''Syodon'' by its larger size, more robust snout, thickened postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
forming a supraorbital boss, and a well-developed ridge extending from the pineal boss to the orbital rim. It also differs from other anteosaurs by its squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestra ...
with a jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
extending beyond the anterior edge of the temporal fenestra. Also unlike ''Syodon'', ''Pampaphoneus'' lacked bifurcating anterior processes in its parietals. Its antorbital depression is also more gradual than in ''Syodon'' and excavates the posterior of the maxilla and the postfrontal and not just the lacrimal as it does in ''Syodon''. A peculiarity of the holotype that was thought to be a diagnostic feature is the presence of only four teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
per premaxilla (the fourth incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
, small in size, being however laterally masked by the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
) and eight postcanines. However, a second skull (yet undescribed) was reported showing some differences with the holotype such as the presence of five premaxillary teeth and only seven postcanines. Since the other cranial elements are very similar, these differences are interpreted as intraspecific variation. Although being a Syodontinae, ''Pampaphoneus'' also shares several characters with the more derived Anteosaurinae
Anteosaurinae is an extinct subfamily of dinocephalian therapsids. It is one of two subfamilies in the family Anteosauridae, the other being Syodontinae.
Description
These are very specialized, very large anteosaurs. The postcanine teeth are ...
. It thus has a well-developed medial crest on the skull roof, while a pronounced thickening of each postorbital forms a supraorbital boss similar to that of a subadult individual of the Russian '' Titanophoneus potens''. In addition, the angular bone
The angular is a large bone in the lower jaw (mandible) of amphibians and reptiles (birds included), which is connected to all other lower jaw bones: the dentary (which is the entire lower jaw in mammals), the splenial, the suprangular, and the ...
of the lower jaw bears a boss as in ''Anteosaurus
''Anteosaurus'' (meaning "Antaeus lizard") is an extinct genus of large carnivorous dinocephalian synapsid. It lived at the end of the Guadalupian (= Middle Permian) during the Capitanian age, about 265 to 260 million years ago in what is now Sou ...
'' and the two species of ''Titanophoneus''. This angular boss is however much less developed in ''Pampaphoneus''.
Paleoecology
 Remains of ''Pampaphoneus'' comes from the Morro Pelado Member of the
Remains of ''Pampaphoneus'' comes from the Morro Pelado Member of the Rio do Rasto Formation
The Rio do Rasto Formation is a Late Permian sedimentary geological formation in the South Region, Brazil, South Region of Brazil. The official name is Rio do Rasto, although in some publications it appears as ''Rio do Rastro''.
The strata were d ...
, outcropping on the lands of the Boqueirão farm in the municipality of São Gabriel (district of Catuçaba, State of Rio Grande do Sul). The fossils are preserved there in a fine pinkish sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
and are covered with a dark crust of iron oxide.
Sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s of the Morro Pelado Member were deposited in fluvio-lacustrine and deltaic settings suggesting alluvial conditions with coalescing floodplains. Aeolian facies (fossil dunes) present in the upper part of the Morro Pelado Member attest to a progressive aridification of the environment. Palaeogeographically, southeastern Brazil was located at mid-latitudes between the 35th Military units
*35th Fighter Wing, an air combat unit of the United States Air Force
*35th Infantry Division (United States), a formation of the National Guard since World War I
*35th Infantry Regiment (United States), a regiment created on 1 July 1 ...
and 45th parallel south
Following are circles of latitude between the 40th parallel south and the 45th parallel south:
41st parallel south
The 41st parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 41 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlanti ...
, where a warm temperate climate probably prevailed with a prolonged dry season. The flora included forests of '' Glossopteris communis'' which occupied the floodplains and the overbank channels while the more humid biotopes were covered with dense mats of equisetids including equisetales
Equisetales is an order of subclass Equisetidae with only one living family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relation ...
('' Schizoneura'' and '' Phyllotheca'' ) and sphenophyllales
Sphenophyllales is an extinct order of articulate land plants and a sister group to the present-day Equisetales ( horsetails). They are fossils dating from the Devonian to the Triassic. They were common during the Late Pennsylvanian to Early ...
('' Sphenophyllum paranaense''). Besides ''Pampaphoneus'', the Boqueirão farm site also contains the temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek language, Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') or temnospondyls is a diverse ancient order (biology), order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered Labyrinth ...
'' Konzhukovia sangabrielensis'' and the small dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivores that typically bore a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, t ...
'' Rastodon''. Other localities in the Morro Pelado Member have also yielded tetrapod remains. In Rio Grande do Sul, several sites around Aceguá in the district of Minuano have yielded the most complete fossils of the pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with osteoderms which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Per ...
''Provelosaurus
''Provelosaurus'' is an extinct Pareiasaur genus of the Late Permian found on the road between Aceguá and Bagé in the Paleorrota, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Found in the Rio do Rasto Formation, aged about 260 million years.http://www.ufrgs.br ...
''. The Fagundes farm locality (São Gabriel, Catuçaba district) yielded a fragmentary skull of ''Provelosaurus'', teeth of undetermined Anteosaurid
Anteosauridae is an extinct family of large carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids that are known from the Middle Permian of Asia, Africa, and South America.These animals were by far the largest predators of the Permian period, with skulls reachin ...
, Titanosuchid
Titanosuchidae is an extinct family of dinocephalians known only from the middle Permian ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa.
The titanosuchids were large, omnivorous or herbivorous animals. As with other tapinocephalians, they h ...
and Tapinocephalid
Tapinocephalidae was an advanced family of tapinocephalians. It is defined as the clade containing ''Ulemosaurus'', ''Tapinocaninus'', and the Tapinocephalinae. They are known from both Russia and South Africa. In all probability, the Tapinocepha ...
dinocephalians, and an undetermined amphibian. In the district of Tiarajú (also near São Gabriel) was found the basal anomodont
Anomodontia is an extinct group of non-mammalian therapsids from the Permian and Triassic periods. By far the most speciose group are the dicynodonts, a clade of beaked, tusked herbivores. Anomodonts were very diverse during the Middle Pe ...
''Tiarajudens
''Tiarajudens'' () (" Tiaraju tooth") is an extinct genus of saber-toothed herbivorous anomodonts which lived during the Middle Permian period (Capitanian stage) in what is now Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is known from the holotype UFRGS ...
'' From the Serra do Cadeado area (near Ortigueira
Ortigueira is a seaport and municipality in the province of A Coruña the autonomous community of Galicia in northwestern Spain. It belongs to the comarca of Ortegal. It is located on the northern slope of the Serra da Faladoira, the river Mer ...
, State
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Paraná Paraná, Paranã or Parana may refer to:
Geology
* Paraná Basin, a sedimentary basin in South America
Places In Argentina
*Paraná, Entre Ríos, a city
* Paraná Department, a part of Entre Ríos Province
In Brazil
*Paraná (state), a state ...
), come the amphibian ''Australerpeton
''Australerpeton'' is an extinct genus of stereospondylomorph temnospondyl currently believed to belong to the family Rhinesuchidae. When first named in 1998, the genus was placed within the new family Australerpetontidae. However, studies publ ...
'', an undetermined species of the dicynodont ''Endothiodon
''Endothiodon'' (/ɛndoʊθiːoʊdɔːn/ "inner tooth" from Greek endothi (ἔνδοθῐ), "within", and odon (ὀδών), "tooth", most likely named for the characteristic of the teeth being placed internally to the maxilla) is an extinct genus ...
'', (possibly ''E. bathystoma'') as well as an indeterminate tapinocephalid dinocephalian showing similarities with the genera ''Moschops
''Moschops'' (Greek for "calf face") is an extinct genus of therapsids that lived in the Guadalupian Epoch (geology), epoch, around 265–260 million years ago. They were heavily built plant eaters, and they may have lived partly in water, as hi ...
'' and '' Moschognathus''. However, there are uncertainties about the contemporaneity of all these sites. Vertebrate fossils from the Rio do Rasto Formation occur in scattered, isolated, and discontinuous outcrops due to dense vegetation cover, making it difficult to establish local correlations. The precise location of several ancient discoveries is uncertain and several taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
could come from different stratigraphic
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithost ...
levels within the Rio do Rasto Formation. This is the case of the fossils of Paraná, where tapinocephalid and ''Endothiodon'' remains could come from two distinct levels.
Classification
In describing ''Pampaphoneus'', Cisneros et al. presented severalcladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
s confirming the recognition of the clades Anteosaurinae and Syodontinae erected a year earlier by Christian Kammerer. In all their analyzes, ''Pampaphoneus'' is identified as the most basal Syodontinae:
Palaeobiogeography
During the Permian, most of the landmasses were united into a single supercontinent,Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia (continent), Siberia during the Carboniferous period ...
, which was roughly C-shaped. Its northern (Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
) and southern (Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
) parts were connected to the west but separated to the east by a very large oceanic bay - the Tethys. A long string of microcontinents, grouped under the name of Cimmeria, divided the Tethys in two: the Paleo-Tethys in the north, and the Neo-Tethys in the south. In the northern hemisphere, anteosaurs are known from eastern European Russia
European Russia is the western and most populated part of the Russia, Russian Federation. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the country's sparsely populated and vastly larger eastern part, Siberia, which is situated in Asia ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, territories corresponding to mid-paleolatitudes between the 30th and 40th parallel north
Following are circles of latitude between the 35th parallel north and the 40th parallel north:
36th parallel north
The 36th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 36 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, t ...
. In the southern hemisphere, anteosaur remains are known in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, Zambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ...
and Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Bots ...
, territories which were all located at high paleolatitudes located at the level of the 60th parallel south
The 60th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees south of Earth's equatorial plane. No land lies on the parallel—it crosses nothing but ocean. The closest land is a group of rocks north of Coronation Island (Melson Rocks o ...
. The Brazilian localities were located a little further north, between the 35th Military units
*35th Fighter Wing, an air combat unit of the United States Air Force
*35th Infantry Division (United States), a formation of the National Guard since World War I
*35th Infantry Regiment (United States), a regiment created on 1 July 1 ...
and the 45th parallel south
Following are circles of latitude between the 40th parallel south and the 45th parallel south:
41st parallel south
The 41st parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 41 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlanti ...
. The close relationship of the Brazilian ''Pampaphoneus'' with some South African and Russian anteosaurs suggests dispersal through western Pangea rather than eastern Pangea via the Cathaysian Bridge. The latter included parts of northern and southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, and Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
and played an important role in the dispersal of therapsids
Therapsida is a clade comprising a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors and close relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including li ...
in the late Permian
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Groh ...
and Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
. However, this bridge was probably not yet formed in the Middle Permian and marine barriers broke up the different Cathaysian blocks, making it difficult for animals to disperse from Cathaysia
Cathaysia was a microcontinent or a group of terranes that rifted off Gondwana during the Late Paleozoic. They mostly correspond to the modern territory of China, historically referred to in Europe as Cathay, which was split into the North China ...
to Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
via Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
. Cisneros and colleagues suggest a seemingly easier migration route via western Pangea by favoring a Pangea B-type continental reconstruction where South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
was juxtaposed with the Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
and was thus closer to Russia than in the Pangea A reconstruction. In the latter, the Appalachian and Mauritanides mountains would have been difficult natural barriers to cross. In contrast, in a Pangea B configuration, Brazil was not only closer to Eastern Europe, but the only mountain barrier along the way was the moderately high European Hercynides. Anteosaurs would have migrated from Russia (where the oldest specimens come from) to southern Africa, passing through eastern Europe and western Africa (bypassing the Mauritanides chain) and then through Brazil. The discovery of probable anteosaur footprints in southern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,These footprints, initially named ''Planipes caudatus'' and ''P. brachydactylus'', are now grouped under the name '' Brontopus antecursor'' (cf. references Marchetti et al. 2019). which was then located at low paleolatitude, at the level of the 10th parallel north
Following are circles of latitude between the 15th parallel north and the 20th parallel north:
6th parallel north
The 6th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 6 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Ind ...
, also supports this hypothesis, the south-western Europe being in this migration corridor.
Notes
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q3283954 Anteosaurs Prehistoric therapsid genera Prehistoric synapsids of South America Permian Brazil Fossils of Brazil Paraná Basin Fossil taxa described in 2012