|
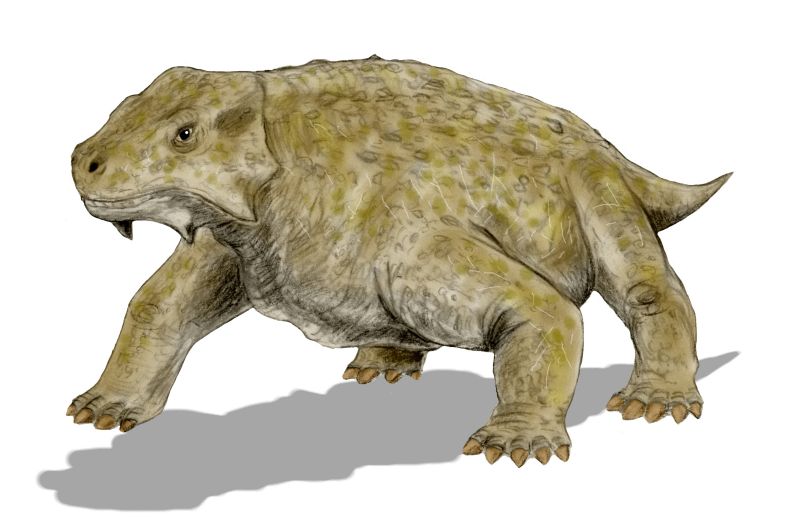
Provelosaurus
''Provelosaurus'' is an extinct Pareiasaur genus of the Late Permian found on the road between Aceguá and Bagé in the Paleorrota, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Found in the Rio do Rasto Formation, aged about 260 million years.http://www.ufrgs.br/geociencias/paleo/pareiassauro2.html Museu da UFRGS The holotype specimen found measures in length.Juan C. Cisneros, Paula Dentzien-Dias and Heitor Francischini. 2021. "The Brazilian Pareiasaur Revisited". ''Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution'' Classification Originally described as a South American representative of the genus ''Pareiasaurus ''Pareiasaurus'' is an extinct genus of pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Descri ...'', it was assigned to a new genus ''Provelosaurus'' by Lee (1997), who noted it shows more affinities with the small, highly derived, South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumiliopareiasauria
Velosauria is a group of pareiasaur reptiles that existed in the late Permian period. They ranged in size from the 50-centimeter-long ''Pumiliopareia'' to the 3-meter-long ''Scutosaurus''. Velosaurs were some of the largest reptiles of their time. Description Velosaurs were large reptiles that were characterized by their short tails, small heads, broad feet, and their legs, which were directly in between sprawling and semi-erect. Velosaurs' bodies were covered in osteoderms and smaller scales all over. Their heads came in all sorts of different shapes; from the cheek-frilled ''Scutosaurus ''Scutosaurus'' ("shield lizard") is an extinct genus of pareiasaur parareptiles. Its genus name refers to large plates of armor scattered across its body. It was a large anapsid reptile that, unlike most reptiles, held its legs underneath its b ...'' to the spiky-headed '' Elginia'' to the nose-horned '' Arganaceras''. They were herbivorous, and it is believed that their large bodies house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species '' Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurs
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species '' Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitanian
In the geologic timescale, the Capitanian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the uppermost or latest of three subdivisions of the Guadalupian Epoch or Series. The Capitanian lasted between and million years ago. It was preceded by the Wordian and followed by the Wuchiapingian.; 2004: ''A Geologic Time Scale 2004'', Cambridge University Press A significant mass extinction event occurred at the end of this stage, which was associated with anoxia and acidification in the oceans and possibly caused by the volcanic eruptions that produced the Emeishan Traps. This extinction event may be related to the much larger Permian–Triassic extinction event that followed about 10 million years later. Stratigraphy The Capitanian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by George Burr Richardson in 1904. The name comes from the Capitan Reef in the Guadalupe Mountains (Texas, United States). The Capitanian was first used as a stratigraphic subdivision of the Guadal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 states and the Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world; and the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of . It borders all other countries and territories in South America except Ecuador and Chile and covers roughly half of the continent's land area. Its Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraná Basin
The Paraná Basin ( pt, Bacia do Paraná, es, Cuenca del Paraná) is a large cratonic sedimentary basin situated in the central-eastern part of South America. About 75% of its areal distribution occurs in Brazil, from Mato Grosso to Rio Grande do Sul states. The remainder area is distributed in eastern Paraguay, northeastern Argentina and northern Uruguay. The shape of the depression is roughly elliptical and covers an area of about . The Paraná River, from which the Paraná Basin derived its name, flows along the central axis of the Paraná Basin and drains it. Description The Paraná Basin stretches from the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso in the north to northern Argentina and Uruguay in the south. The southern portion in Uruguay is locally known as Norte Basin.De Santa Ana et al., 2004, p.88Daners et al., 2006, p.148 Pioneer studies The first study on the Brazilian side of the Paraná Basin dates from 1841, when a Brazilian Imperial Government Mission prospected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Brazil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Brazil
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Reptiles Of South America
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurus
''Pareiasaurus'' is an extinct genus of pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Description ''Pareiasaurus'' is a large quadruped, about long, with elephantine legs, walking in a typically reptilian posture. The skull is broad and the snout short. Its skull had several spine- and wart-like protrusions. ''Pareiasauruss leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for biting through tough plant fibers, indicate it was a herbivore. Even the palate The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly s ... had teeth. Species ''P. nasicornis'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929) is from the ''Tropidostoma'' Zone, Karoo basin, South Africa. This early form is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Do Rasto Formation
The Rio do Rasto Formation is a Late Permian sedimentary geological formation in the South Region of Brazil. The official name is Rio do Rasto, although in some publications it appears as ''Rio do Rastro''. Geography It is found mainly in the Brazilian states of Santa Catarina, Paraná, and Rio Grande do Sul. It was formed during the Late Permian epoch of the Permian period. Fossil content The following fossils have been uncovered from the formation:Langer et al., 2008, p.1 * Flora ** '' Schizoneura'' ** ''Glossopteris'' ** '' Paracalamites'' ** '' Pecopteris'' * Bivalves ** '' Leinzia'' ** '' Palaeomutela'' ** '' Terraia'' * Gastropods ** '' Pseudestheria'' ** '' Monoleiolophus'' ** '' Euestheria'' ** '' Asmussia'' ** '' Liograpta'' * Dicynodonts ** '' Endothiodon'' ** '' Rastodon procurvidens''Boos et al., 2016, p.4 * Amphibians ** ''Australerpeton cosgriffi'' ** '' Bageherpeton longignathus'' ** '' Konzhukovia sangabrielensis'' ** '' Parapytanga catarinensis'' ** '' Ras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagé
Bagé () is a city located in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. In 2020, its population was 121,335 in a total area of 4,096 km2. It was the seventeenth largest city in the state according to the 2011 census. The city was founded in 1811 and given city status in 1859. Due to its strategic border location, Bagé has remained of significant military importance. Prior to official reorganization as a city, Bagé was seized by military forces from Paraguay and Argentina. Primary industries located in the surrounding area are cattle and sheep ranching, as well as meat packing industries and wool depots. Recently, Bagé has become one of the largest wheat-producing areas in the Rio Grande do Sul. Along with wheat, soybeans and are also grown in the surrounding region. Location Bagé is located southwest of the state capital, Porto Alegre and approximately north of the border with Uruguay at Aceguá. The distance to Pelotas to the east on BR 293 is . Other distances from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |