|
Dinocephalia
Dinocephalians (terrible heads) are a clade of large-bodied early therapsids that flourished in the Early and Middle Permian between 279.5 and 260 million years ago (Ma), but became extinct during the Capitanian mass extinction event. Dinocephalians included herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous forms. Many species had thickened skulls with many knobs and bony projections. Dinocephalians were the first non-mammalian therapsids to be scientifically described and their fossils are known from Russia, China, Brazil, South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Tanzania. Description Apart from the Biarmosuchians, the dinocephalians are the least advanced therapsids, although still uniquely specialised in their own way. They retain a number of primitive characteristics (e.g. no secondary palate, small dentary) shared with their pelycosaur ancestors, although they are also more advanced in possessing therapsid adaptations like the expansion of the ilium and more erect limbs. They include carniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteosaurus
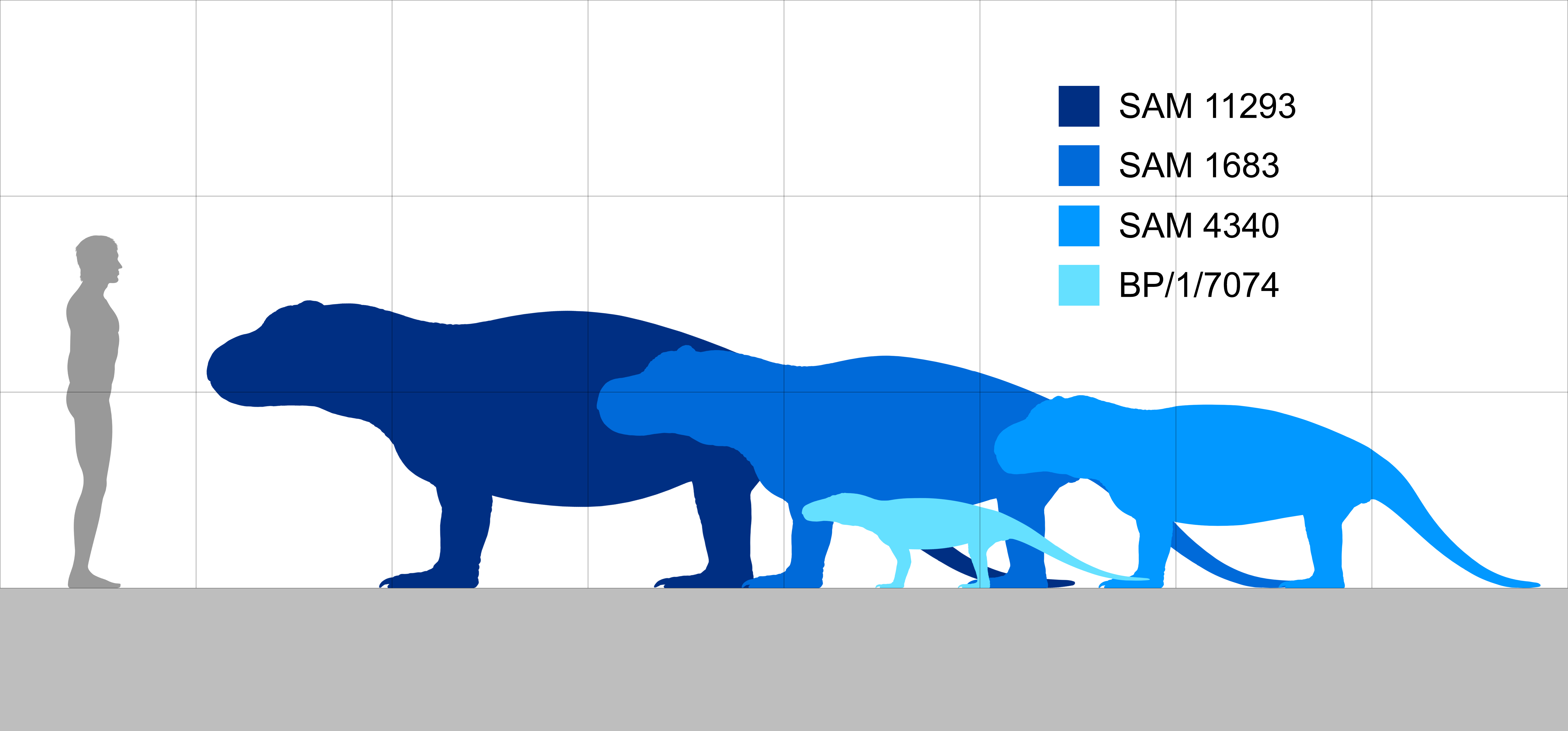
''Anteosaurus'' (meaning "Antaeus reptile") is an extinct genus of large carnivorous dinocephalian synapsid. It lived at the end of the Guadalupian (= Middle Permian) during the Capitanian stage, about 265 to 260 million years ago in what is now South Africa. It is mainly known by cranial remains and few postcranial bones. With its skull reaching in length and a body size estimated at more than in length, and in weight, ''Anteosaurus'' was the largest known carnivorous non-mammalian synapsid and the largest terrestrial predator of the Permian period. Occupying the top of the food chain in the Middle Permian, its skull, jaws and teeth show adaptations to capture large prey like the giants titanosuchids and tapinocephalids dinocephalians and large pareiasaurs. As in many other dinocephalians the cranial bones of ''Anteosaurus'' are pachyostosed, but to a lesser extent than in tapinocephalid dinocephalians. In ''Anteosaurus'', pachyostosis mainly occurs in the form of horn-sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitanian Mass Extinction Event
The Capitanian mass extinction event, also known as the end-Guadalupian extinction event or the pre-Lopingian crisis was an extinction event that predated the end-Permian extinction event and occurred around 260 million years ago during a period of decreased species richness and increased extinction rates in the late Middle Permian during the Guadalupian epoch. It is often called the end-Guadalupian extinction event because of its initial recognition between the Guadalupian and Lopingian series; however, more refined stratigraphic study suggests that extinction peaks in many taxonomic groups occurred within the Guadalupian, in the latter half of the Capitanian age.Bond, D. P. G., Wignall, P. B., Wang, W., Izon, G., Jiang, H. S., Lai, X. L., Sund, Y.-D., Newtona, R.J., Shaoe, L.-Y., Védrinea, S. & Cope, H. (2010). "The mid-Capitanian (Middle Permian) mass extinction and carbon isotope record of South China". ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'', 292 (1-2), pp. 282 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. Therapsids evolved from " pelycosaurs", specifically within the Sphenacodontia, more than 279.5 million years ago. They replaced the "pelycosaurs" as the dominant large land animals in the Middle Permian through to the Early Triassic. In the aftermath of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, therapsids declined in relative importance to the rapidly diversifying reptiles during the Middle Triassic. The therapsids include the cynodonts, the group that gave rise to mammals ( Mammaliaformes) in the Late Triassic, around 225 million years ago. Of the non-mammalian therapsids, only cynodonts survived beyond the end of the Triassic, with the only ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteosaur
Anteosaurs are a group of large, primitive carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids with large canines and incisors and short limbs, that are known from the Middle Permian of South Africa, Russia, China, and Brazil. Some grew very large, with skulls long, and were the largest predators of their time. They died out at the end of the Middle Permian, possibly as a result of the extinction of the herbivorous Tapinocephalia on which they may have fed. Description The Anteosauria are distinguished from the Tapinocephalia by a number of features, such as very large canines, cheek teeth with bulbous crowns, and an upturning of the premaxilla, so that the front of mouth curves strongly upwards. There is a tendency especially in more advanced forms such as '' Anteosaurus'' towards thickening of the bones of the top of the skull, indicating head-butting behaviour. There is a large canal for the pineal organ (third eye); probably tied in with the animal's diurnal and seasonal cycles. The shou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caseidae
Caseidae are an Extinction, extinct Family (biology), family of Basal (phylogenetics), basal synapsids that lived from the Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian between about 300 and 265 million years ago. Fossils of these animals come from the south-central part of the United States (Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas), from various parts of Europe (European Russia, France, Germany, Sardinia, and Poland), and possibly from South Africa if the genus ''Eunotosaurus'' is indeed a caseid as some authors proposed in 2021. Caseids show great Taxonomy, taxonomic and morphological diversity. The most basal taxa were small Insectivore, insectivorous and Omnivore, omnivorous forms that lived mainly in the Upper Carboniferous and Lower Permian, such as ''Eocasea'', ''Callibrachion'', and ''Martensius''. This type of caseid persists until the Guadalupian, middle Permian with ''Phreatophasma'' and may be ''Eunotosaurus''. During the early Permian, the clade is mainly represented by many species that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalia
The Tapinocephalia are one of the major groups of dinocephalian therapsids and the major herbivorous group. Tapinocephalia has been found to consist of three clades: Styracocephalidae, Titanosuchidae, and the very successful Tapinocephalidae. Notable tapinocephalians include '' Moschops'', '' Tapinocephalus'', and '' Titanosuchus''. Description Unlike anteosaurs and estemmenosuchids, tapinocephalians are primarily an African group. The estemmenosuchids and pareiasaurs may have occupied this paleo-bovine niche in the north. Only one tapinocephalian, '' Ulemosaurus'', is known from Russia. Earlier tapinocephalians were carnivorous or omnivorous. One such group was Titanosuchidae, which consisted of long-tailed predators that hunted herbivorous therapsids Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moschops BW
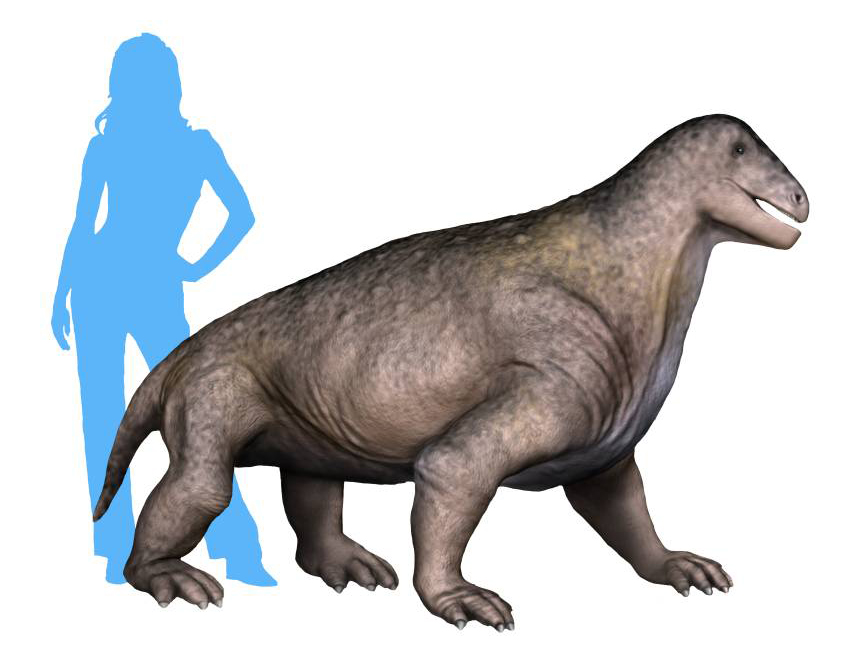
''Moschops'' (Greek for "calf face") is an extinct genus of therapsids that lived in the Guadalupian The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ... Epoch (geology), epoch, around 265–260 million years ago. They were heavily built plant eaters, and they may have lived partly in water, as hippopotamuses do. They had short, thick heads and might have competed by head-butting each other. Their elbow joints allowed them to walk with a more mammal-like gait rather than crawling. Their remains were found in the Karoo region of South Africa, belonging to the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone. Therapsids, such as ''Moschops'', are synapsids, the dominant land animals in the Permian period, which ended 252 million years ago. Description ''Moschops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalus
''Tapinocephalus'' ("humble head") is an extinct genus of large herbivorous dinocephalians that lived during the Middle Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Pale ... Period (geology), Period. These stocky, barrel-bodied animals were characterised by a massive bony skull roof and short weak snout. It is thought that, like the rest of the members of its family (biology), family, the animals engaged in head-butting agonistic behavior, intraspecific behavior, possibly for territory (animal), territory or mates. The fossil remains (skull and postcrania, postcranial elements) of ''Tapinocephalus'' are known from the Lower, Middle, and Upper part of the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone ( Capitanian, Capitanian age) of the Beaufort Group, Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanosuchus
''Titanosuchus ferox'' ("Fierce titan crocodile") is an extinct species of dinocephalian therapsids that lived in the Middle Permian epoch in South Africa. Along with its close relatives, '' Jonkeria'' and ''Moschops'', ''Titanosuchus'' inhabited present-day South Africa around 265 million years ago, in the Late Permian. ''Titanosuchus'' was a carnivore which measured over 2.5 m long and might have eaten both ''Jonkeria'' and ''Moschops'', among other vertebrates. Its teeth included sharp incisors and fang-like canines, perfect for biting prey. ''Titanosuchus'' should not be confused with the therapsid ''Eotitanosuchus'', which belonged to a different family. ''Parascapanodon'' and ''Scapanodon'' were once thought to be distinct genera, but are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Titanosuchus''.Boonstra, L. D., 1969, The fauna of the Tapinocephalus zone (Beaufort beds of the Karoo): Annals of the South African Museum, v. 56, part 1, p. 1-73. See also * List of therapsid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biarmosuchia
Biarmosuchians are an extinct clade of non-mammalian synapsids from the Permian. They are the most basal group of the therapsids. All of them were moderately-sized, lightly-built carnivores, intermediate in form between basal sphenacodont " pelycosaurs" and more advanced therapsids. Biarmosuchians were rare components of Permian ecosystems, and the majority of species belong to the clade Burnetiamorpha, which are characterized by elaborate cranial ornamentation. Characteristics The biarmosuchian skull is very similar to the sphenacodontid skull, differing only in the larger temporal fenestra (although these are still small relative to later therapsids), slightly backward-sloping occiput (the reverse of the pelycosaur condition), reduced number of teeth, and single large canine teeth in both upper and lower jaws, and other features (Carroll 1988 pp. 370, Benton 2000 p. 114). In later specialised Biarmosuchia, these resemble the enlarged canines of the Gorgonopsia. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
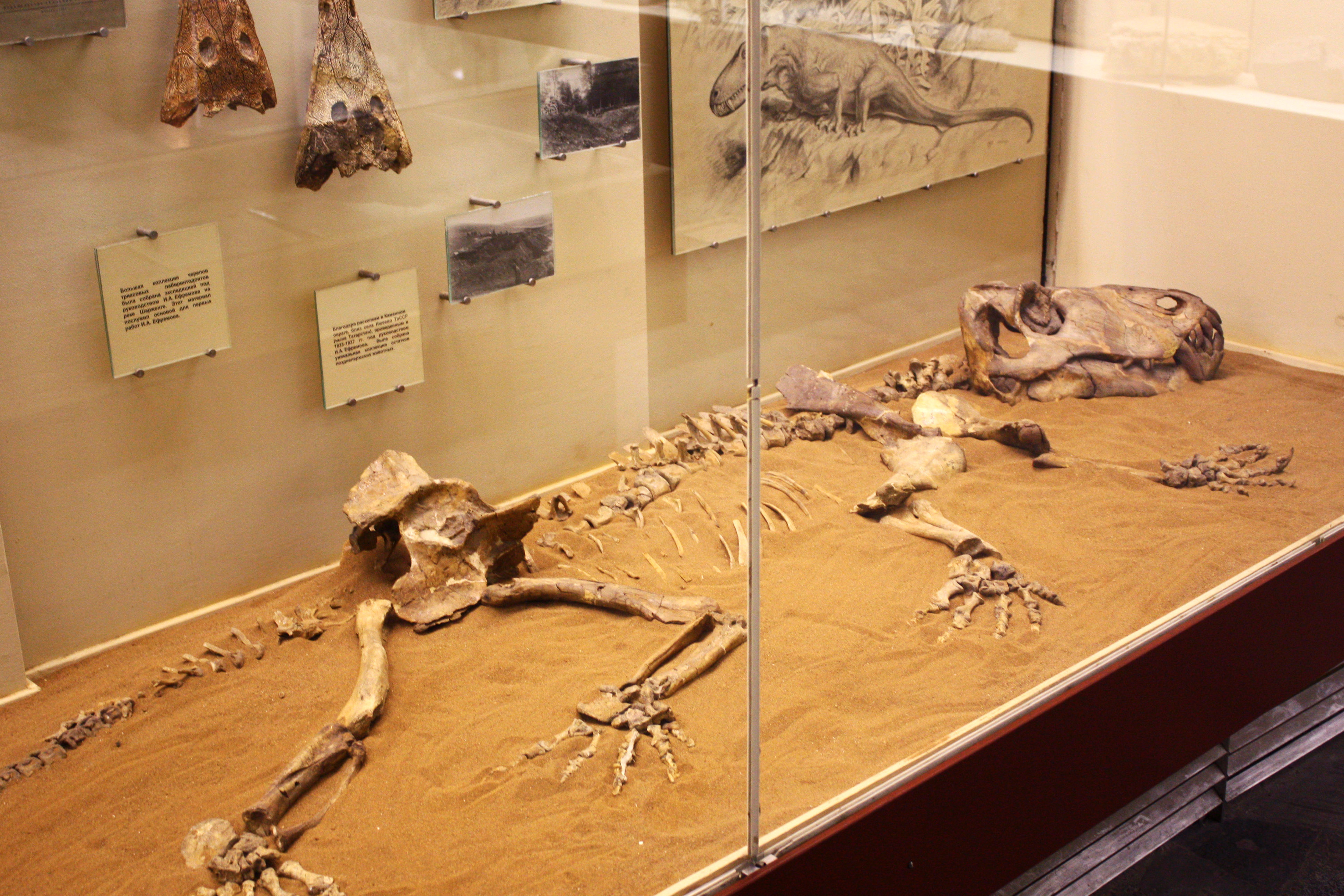
Ulemosaurus
''Ulemosaurus'' is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids that lived 265 to 260 million years ago, at Isheevo in Russian Tatarstan. It was a tapinocephalid, a group of bulky herbivores which flourished in the Middle Permian. ''Ulemosaurus'' and other tapinocephalians disappeared at the end of the Middle Permian. Description Only several partial skeletons and skulls have been found. The skull bones are extremely dense: about at its thickest. This thickening is possibly related to head-butting behavior, as some researchers suggest. The species is considered a herbivore, but because the mandible is heavily constructed some palaeontologists consider it a carnivore, with the species being able to use muscle power to cut prey up with its incisors. Classification ''Ulemosaurus'' is a large ''Moschops''-like form from Russia; it is probably similar enough to be included as a separate species of ''Moschops''. Despite its advanced characteristics, it lived slightly before the Karoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |