Melbourne on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/ Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the

 In May and June 1835, John Batman, a leading member of the Port Phillip Association in Van Diemen's Land, explored the Melbourne area, and later claimed to have negotiated a purchase of with eight Wurundjeri elders. However, the nature of the treaty has been heavily disputed, as none of the parties spoke the same language, and the elders likely perceived it as part of the gift exchanges which had taken place over the previous few days amounting to a tanderrum ceremony which allows temporary, not permanent, access to and use of the land. Batman selected a site on the northern bank of the
In May and June 1835, John Batman, a leading member of the Port Phillip Association in Van Diemen's Land, explored the Melbourne area, and later claimed to have negotiated a purchase of with eight Wurundjeri elders. However, the nature of the treaty has been heavily disputed, as none of the parties spoke the same language, and the elders likely perceived it as part of the gift exchanges which had taken place over the previous few days amounting to a tanderrum ceremony which allows temporary, not permanent, access to and use of the land. Batman selected a site on the northern bank of the
 The discovery of gold in Victoria in mid-1851 sparked a gold rush, and Melbourne, the colony's major port, experienced rapid growth. Within months, the city's population had nearly doubled from 25,000 to 40,000 inhabitants. Exponential growth ensued, and by 1865 Melbourne had overtaken Sydney as Australia's most populous city.
An influx of intercolonial and international migrants, particularly from Europe and China, saw the establishment of slums, including Chinatown and a temporary "tent city" on the southern banks of the Yarra. In the aftermath of the 1854 Eureka Rebellion, mass public support for the plight of the miners resulted in major political changes to the colony, including improvements in working conditions across mining, agriculture, manufacturing and other local industries. At least twenty nationalities took part in the rebellion, giving some indication of immigration flows at the time.
With the wealth brought in from the gold rush and the subsequent need for public buildings, a program of grand civic construction soon began. The 1850s and 1860s saw the commencement of
The discovery of gold in Victoria in mid-1851 sparked a gold rush, and Melbourne, the colony's major port, experienced rapid growth. Within months, the city's population had nearly doubled from 25,000 to 40,000 inhabitants. Exponential growth ensued, and by 1865 Melbourne had overtaken Sydney as Australia's most populous city.
An influx of intercolonial and international migrants, particularly from Europe and China, saw the establishment of slums, including Chinatown and a temporary "tent city" on the southern banks of the Yarra. In the aftermath of the 1854 Eureka Rebellion, mass public support for the plight of the miners resulted in major political changes to the colony, including improvements in working conditions across mining, agriculture, manufacturing and other local industries. At least twenty nationalities took part in the rebellion, giving some indication of immigration flows at the time.
With the wealth brought in from the gold rush and the subsequent need for public buildings, a program of grand civic construction soon began. The 1850s and 1860s saw the commencement of
 The 1880s saw extraordinary growth: consumer confidence, easy access to credit, and steep increases in land prices led to an enormous amount of construction. During this "land boom", Melbourne reputedly became the richest city in the world, and the second-largest (after London) in the
The 1880s saw extraordinary growth: consumer confidence, easy access to credit, and steep increases in land prices led to an enormous amount of construction. During this "land boom", Melbourne reputedly became the richest city in the world, and the second-largest (after London) in the
 At the time of Australia's
At the time of Australia's
 Height limits in the CBD were lifted in 1958, after the construction of ICI House, transforming the city's skyline with the introduction of skyscrapers. Suburban expansion then intensified, served by new indoor malls beginning with Chadstone Shopping Centre. The post-war period also saw a major renewal of the CBD and St Kilda Road which significantly modernised the city. New fire regulations and redevelopment saw most of the taller pre-war CBD buildings either demolished or partially retained through a policy of facadism. Many of the larger suburban mansions from the boom era were also either demolished or subdivided.
To counter the trend towards low-density suburban residential growth, the government began a series of controversial public housing projects in the inner city by the Housing Commission of Victoria, which resulted in the demolition of many neighbourhoods and a proliferation of high-rise towers. In later years, with the rapid rise of motor vehicle ownership, the investment in freeway and highway developments greatly accelerated the outward suburban sprawl and declining inner-city population. The Bolte government sought to rapidly accelerate the modernisation of Melbourne. Major road projects including the remodelling of St Kilda Junction, the widening of Hoddle Street and then the extensive 1969 Melbourne Transportation Plan changed the face of the city into a car-dominated environment.
Australia's financial and mining booms during 1969 and 1970 resulted in establishment of the headquarters of many major companies ( BHP and Rio Tinto, among others) in the city. Nauru's then booming economy resulted in several ambitious investments in Melbourne, such as Nauru House. Melbourne remained Australia's main business and financial centre until the late 1970s, when it began to lose this primacy to Sydney.
Melbourne experienced an economic downturn between 1989 and 1992, following the collapse of several local financial institutions. In 1992, the newly elected Kennett government began a campaign to revive the economy with an aggressive development campaign of public works coupled with the promotion of the city as a tourist destination with a focus on major events and sports tourism. During this period the Australian Grand Prix moved to Melbourne from
Height limits in the CBD were lifted in 1958, after the construction of ICI House, transforming the city's skyline with the introduction of skyscrapers. Suburban expansion then intensified, served by new indoor malls beginning with Chadstone Shopping Centre. The post-war period also saw a major renewal of the CBD and St Kilda Road which significantly modernised the city. New fire regulations and redevelopment saw most of the taller pre-war CBD buildings either demolished or partially retained through a policy of facadism. Many of the larger suburban mansions from the boom era were also either demolished or subdivided.
To counter the trend towards low-density suburban residential growth, the government began a series of controversial public housing projects in the inner city by the Housing Commission of Victoria, which resulted in the demolition of many neighbourhoods and a proliferation of high-rise towers. In later years, with the rapid rise of motor vehicle ownership, the investment in freeway and highway developments greatly accelerated the outward suburban sprawl and declining inner-city population. The Bolte government sought to rapidly accelerate the modernisation of Melbourne. Major road projects including the remodelling of St Kilda Junction, the widening of Hoddle Street and then the extensive 1969 Melbourne Transportation Plan changed the face of the city into a car-dominated environment.
Australia's financial and mining booms during 1969 and 1970 resulted in establishment of the headquarters of many major companies ( BHP and Rio Tinto, among others) in the city. Nauru's then booming economy resulted in several ambitious investments in Melbourne, such as Nauru House. Melbourne remained Australia's main business and financial centre until the late 1970s, when it began to lose this primacy to Sydney.
Melbourne experienced an economic downturn between 1989 and 1992, following the collapse of several local financial institutions. In 1992, the newly elected Kennett government began a campaign to revive the economy with an aggressive development campaign of public works coupled with the promotion of the city as a tourist destination with a focus on major events and sports tourism. During this period the Australian Grand Prix moved to Melbourne from
 Melbourne is in the southeastern part of mainland Australia, within the state of Victoria. Geologically, it is built on the confluence of Quaternary lava flows to the west,
Melbourne is in the southeastern part of mainland Australia, within the state of Victoria. Geologically, it is built on the confluence of Quaternary lava flows to the west,
Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. Retrieved 6 September 2022. Melbourne extends along the
 Melbourne has a temperate
Melbourne has a temperate
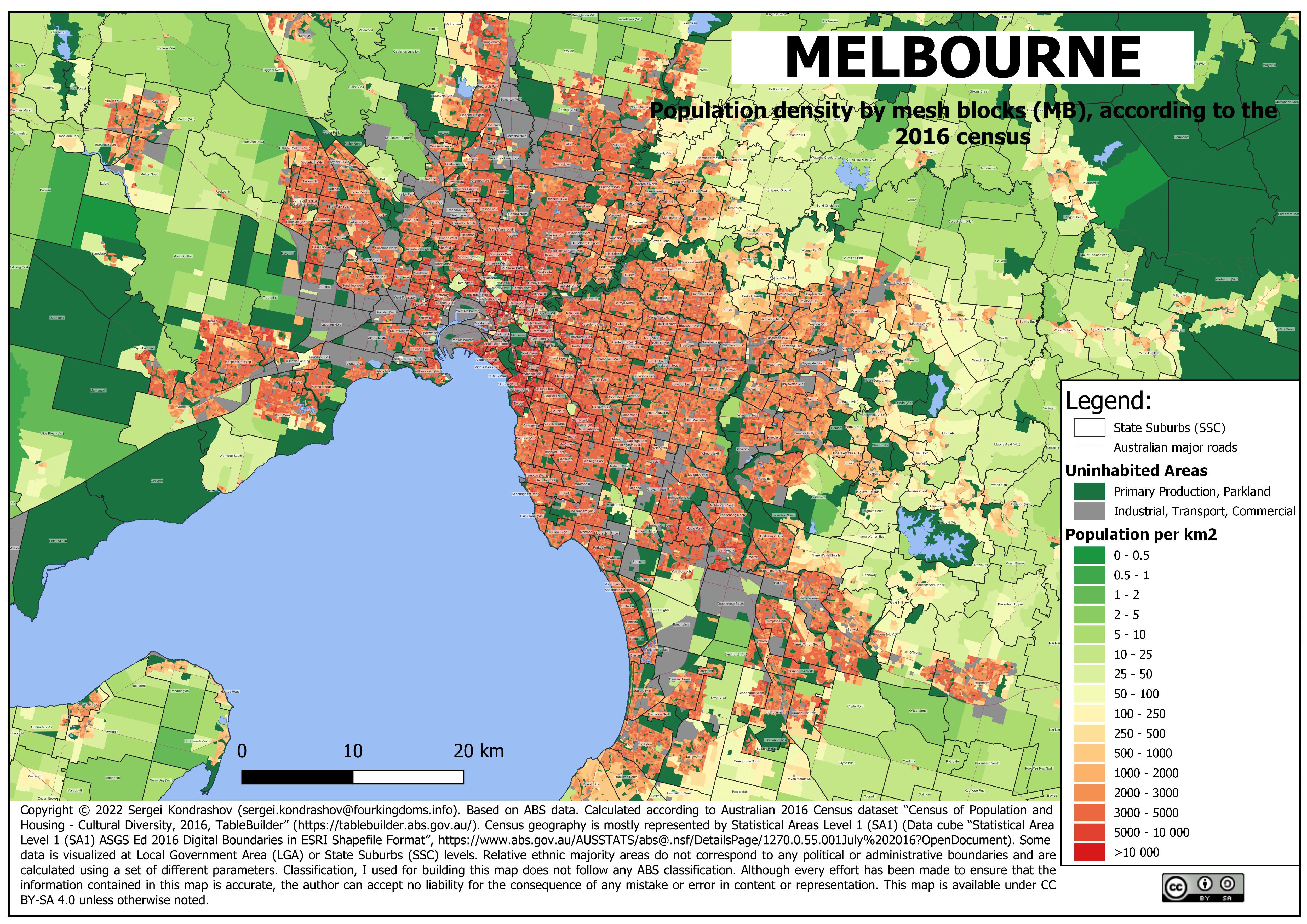

 Melbourne's
Melbourne's
 Melbourne has minimal public housing and high demand for rental housing, which is becoming unaffordable for some. Public housing is managed and provided by the Victorian Government's
Melbourne has minimal public housing and high demand for rental housing, which is becoming unaffordable for some. Public housing is managed and provided by the Victorian Government's
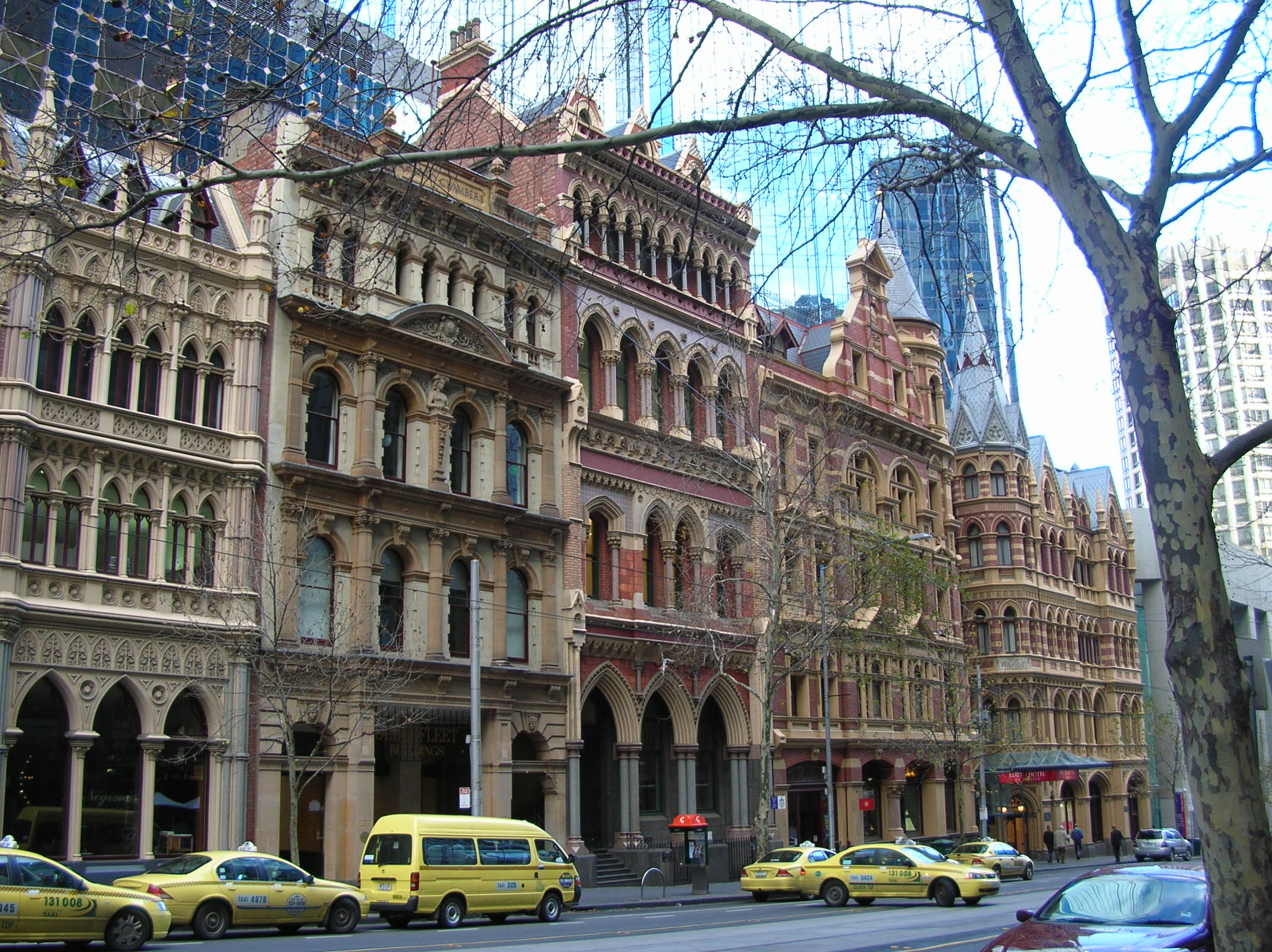 On the back of the 1850s gold rush and 1880s land boom, Melbourne became renowned as one of the world's great Victorian-era cities, a reputation that persists due to its diverse range of
On the back of the 1850s gold rush and 1880s land boom, Melbourne became renowned as one of the world's great Victorian-era cities, a reputation that persists due to its diverse range of  The city also features the Shrine of Remembrance, which was built as a memorial to the men and women of Victoria who served in
The city also features the Shrine of Remembrance, which was built as a memorial to the men and women of Victoria who served in
 Often referred to as Australia's cultural capital, Melbourne is recognised globally as a centre of sport, music, theatre, comedy, art, literature, film and television. For much of the 2010s, it held the top position in '' The Economist Intelligence Unit'' list of the world's most liveable cities, partly due to its cultural attributes.
The city celebrates a wide variety of annual cultural events and festivals of all types, including the Melbourne International Arts Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival,
Often referred to as Australia's cultural capital, Melbourne is recognised globally as a centre of sport, music, theatre, comedy, art, literature, film and television. For much of the 2010s, it held the top position in '' The Economist Intelligence Unit'' list of the world's most liveable cities, partly due to its cultural attributes.
The city celebrates a wide variety of annual cultural events and festivals of all types, including the Melbourne International Arts Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival,  Ray Lawler's play '' Summer of the Seventeenth Doll'' is set in Carlton and debuted in 1955, the same year that Edna Everage, Barry Humphries' Moonee Ponds housewife character, first appeared on stage, both sparking international interest in Australian theatre. Melbourne's East End Theatre District is known for its Victorian era theatres, such as the Athenaeum, Her Majesty's and the
Ray Lawler's play '' Summer of the Seventeenth Doll'' is set in Carlton and debuted in 1955, the same year that Edna Everage, Barry Humphries' Moonee Ponds housewife character, first appeared on stage, both sparking international interest in Australian theatre. Melbourne's East End Theatre District is known for its Victorian era theatres, such as the Athenaeum, Her Majesty's and the  Established in 1861, the National Gallery of Victoria is Australia's oldest and largest art museum. Several art movements originated in Melbourne, most famously the Heidelberg School of impressionists, named after a suburb where they camped to paint '' en plein air'' in the 1880s. The Australian tonalists followed, some of whom founded Montsalvat, Australia's oldest surviving art colony. During World War II, the Angry Penguins, a group of avant-garde artists, convened at a Bulleen dairy farm, now the Heide Museum of Modern Art. The city is also home to the
Established in 1861, the National Gallery of Victoria is Australia's oldest and largest art museum. Several art movements originated in Melbourne, most famously the Heidelberg School of impressionists, named after a suburb where they camped to paint '' en plein air'' in the 1880s. The Australian tonalists followed, some of whom founded Montsalvat, Australia's oldest surviving art colony. During World War II, the Angry Penguins, a group of avant-garde artists, convened at a Bulleen dairy farm, now the Heide Museum of Modern Art. The city is also home to the
 Melbourne has long been regarded as Australia's sporting capital due to the role it has played in the development of Australian sport, the range and quality of its sporting events and venues, and its high rates of spectatorship and participation. The city is also home to 27 professional sports teams competing at the national level, the most of any Australian city. Melbourne's sporting reputation was recognised in 2016 when, after being ranked as the world's top sports city three times biennially, the Ultimate Sports City Awards in Switzerland named it 'Sports City of the Decade'.
The city has hosted a number of major international sporting events, most notably the
Melbourne has long been regarded as Australia's sporting capital due to the role it has played in the development of Australian sport, the range and quality of its sporting events and venues, and its high rates of spectatorship and participation. The city is also home to 27 professional sports teams competing at the national level, the most of any Australian city. Melbourne's sporting reputation was recognised in 2016 when, after being ranked as the world's top sports city three times biennially, the Ultimate Sports City Awards in Switzerland named it 'Sports City of the Decade'.
The city has hosted a number of major international sporting events, most notably the
 Melbourne has a highly diversified economy with particular strengths in finance, manufacturing, research, IT, education, logistics, transportation and tourism. Melbourne houses the headquarters of many of Australia's largest corporations, including five of the ten largest in the country (based on revenue), and five of the largest seven in the country (based on market capitalisation)
Melbourne has a highly diversified economy with particular strengths in finance, manufacturing, research, IT, education, logistics, transportation and tourism. Melbourne houses the headquarters of many of Australia's largest corporations, including five of the ten largest in the country (based on revenue), and five of the largest seven in the country (based on market capitalisation)  It is the Australian base for a number of significant manufacturers including Boeing Australia, truck-makers Kenworth and Iveco, Cadbury as well as Alstom and Jayco, among many others. It is also home to a wide variety of other manufacturers, ranging from petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals to fashion garments, paper manufacturing and food processing. The south-eastern suburb of Scoresby is home to Nintendo's Australian headquarters. The city also has a research and development hub for Ford Australia, as well as a global design studio and technical centre for General Motors and Toyota Australia respectively.
CSL, one of the world's top five biotech companies, and
It is the Australian base for a number of significant manufacturers including Boeing Australia, truck-makers Kenworth and Iveco, Cadbury as well as Alstom and Jayco, among many others. It is also home to a wide variety of other manufacturers, ranging from petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals to fashion garments, paper manufacturing and food processing. The south-eastern suburb of Scoresby is home to Nintendo's Australian headquarters. The city also has a research and development hub for Ford Australia, as well as a global design studio and technical centre for General Motors and Toyota Australia respectively.
CSL, one of the world's top five biotech companies, and
 Melbourne is the second most visited city in Australia and the seventy-third most visited city in the world. In 2018, 10.8 million domestic overnight tourists and 2.9 million international overnight tourists visited Melbourne. The most visited attractions are Federation Square, Queen Victoria Market,
Melbourne is the second most visited city in Australia and the seventy-third most visited city in the world. In 2018, 10.8 million domestic overnight tourists and 2.9 million international overnight tourists visited Melbourne. The most visited attractions are Federation Square, Queen Victoria Market,
 According to the 2021 Australian Census, the population of the Greater Melbourne area was 4,917,750.
Although Victoria's net interstate migration has fluctuated, the population of the Melbourne statistical division has grown by about 70,000 people a year since 2005. Melbourne has now attracted the largest proportion of international overseas immigrants (48,000) finding it outpacing Sydney's international migrant intake on percentage, as well as having strong interstate migration from Sydney and other capitals due to more affordable housing and cost of living.
In recent years, Melton, Wyndham and Casey, part of the Melbourne statistical division, have recorded the highest growth rate of all local government areas in Australia. Melbourne is on track to overtake Sydney in population between 2028 and 2030.
After a trend of declining population density since World War II, the city has seen increased density in the inner and western suburbs, aided in part by Victorian Government planning, such as Postcode 3000 and Melbourne 2030, which have aimed to curtail urban sprawl. , the CBD is the most densely populated area in Australia with more than 19,000 residents per square kilometre, and the inner city suburbs of Carlton, South Yarra, Fitzroy and
According to the 2021 Australian Census, the population of the Greater Melbourne area was 4,917,750.
Although Victoria's net interstate migration has fluctuated, the population of the Melbourne statistical division has grown by about 70,000 people a year since 2005. Melbourne has now attracted the largest proportion of international overseas immigrants (48,000) finding it outpacing Sydney's international migrant intake on percentage, as well as having strong interstate migration from Sydney and other capitals due to more affordable housing and cost of living.
In recent years, Melton, Wyndham and Casey, part of the Melbourne statistical division, have recorded the highest growth rate of all local government areas in Australia. Melbourne is on track to overtake Sydney in population between 2028 and 2030.
After a trend of declining population density since World War II, the city has seen increased density in the inner and western suburbs, aided in part by Victorian Government planning, such as Postcode 3000 and Melbourne 2030, which have aimed to curtail urban sprawl. , the CBD is the most densely populated area in Australia with more than 19,000 residents per square kilometre, and the inner city suburbs of Carlton, South Yarra, Fitzroy and
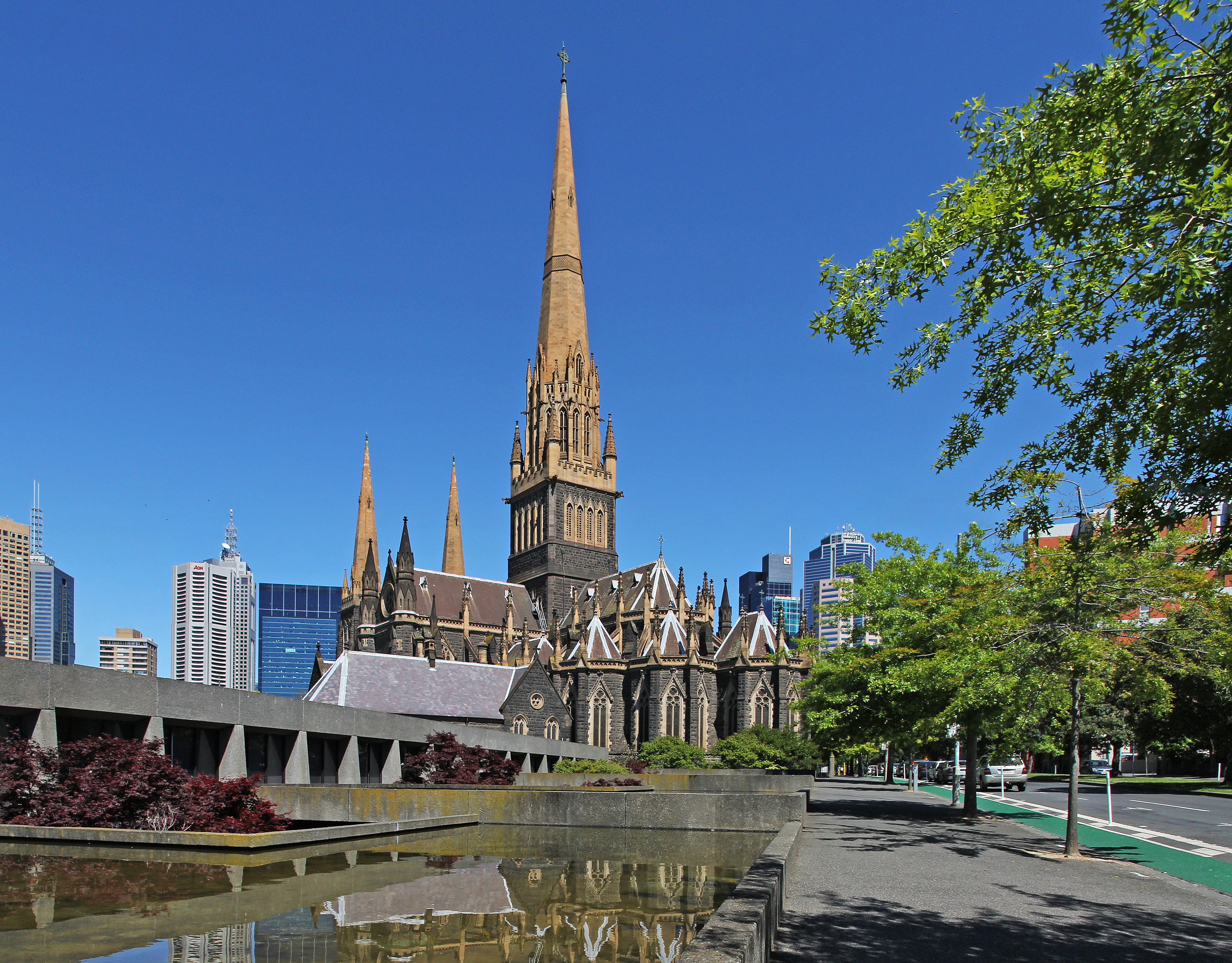 Melbourne has a wide range of religious faiths, the most widely held of which is
Melbourne has a wide range of religious faiths, the most widely held of which is
 Some of Australia's most prominent and well-known schools are based in Melbourne. Of the top twenty high schools in Australia according to th
Some of Australia's most prominent and well-known schools are based in Melbourne. Of the top twenty high schools in Australia according to th
My Choice Schools Ranking
five are in Melbourne. There has also been a rapid increase in the number of International students studying in the city. Furthermore, Melbourne was ranked the world's fourth top university city in 2008 after London, Boston and Tokyo in a poll commissioned by
 The governance of Melbourne is split between the government of Victoria and the 27 cities and four shires that make up the metropolitan area. There is no ceremonial or political head of Melbourne, but the Lord Mayor of the City of Melbourne often fulfils such a role as a first among equals.
The local councils are responsible for providing the functions set out in the ''Local Government Act'' 1989 such as
The governance of Melbourne is split between the government of Victoria and the 27 cities and four shires that make up the metropolitan area. There is no ceremonial or political head of Melbourne, but the Lord Mayor of the City of Melbourne often fulfils such a role as a first among equals.
The local councils are responsible for providing the functions set out in the ''Local Government Act'' 1989 such as
 The Victorian Government's Department of Health oversees about 30 public hospitals in the Melbourne metropolitan region and 13 health services organisations.
Major medical,
The Victorian Government's Department of Health oversees about 30 public hospitals in the Melbourne metropolitan region and 13 health services organisations.
Major medical,
 Like many Australian cities, Melbourne has a high dependency on the automobile for transport, particularly in the outer suburban areas where the largest number of cars are bought, with a total of 3.6 million private vehicles using of road, and one of the highest lengths of road per capita in the world. The early 20th century saw an increase in popularity of automobiles, resulting in large-scale suburban expansion and a tendency towards the development of
Like many Australian cities, Melbourne has a high dependency on the automobile for transport, particularly in the outer suburban areas where the largest number of cars are bought, with a total of 3.6 million private vehicles using of road, and one of the highest lengths of road per capita in the world. The early 20th century saw an increase in popularity of automobiles, resulting in large-scale suburban expansion and a tendency towards the development of
 The Melbourne metropolitan rail network dates back to the 1850s gold rush era, and today consists of 222 suburban stations on 16 lines which radiate from the City Loop, a mostly-underground subway system around the CBD. Flinders Street station, one of Australia's busiest rail hubs, serves the entire network, and remains a prominent Melbourne landmark and meeting place. The city has rail connections with regional Victorian cities run by V/Line, as well as direct interstate rail services which depart from Melbourne's other major rail terminus, Southern Cross station, in Docklands. '' The Overland'' to
The Melbourne metropolitan rail network dates back to the 1850s gold rush era, and today consists of 222 suburban stations on 16 lines which radiate from the City Loop, a mostly-underground subway system around the CBD. Flinders Street station, one of Australia's busiest rail hubs, serves the entire network, and remains a prominent Melbourne landmark and meeting place. The city has rail connections with regional Victorian cities run by V/Line, as well as direct interstate rail services which depart from Melbourne's other major rail terminus, Southern Cross station, in Docklands. '' The Overland'' to
 Melbourne's tram network dates from the 1880s land boom and, as of 2021, consists of of double track, 475 trams, 25 routes, and 1,763 tram stops, making it the largest in the world. In 2017–2018, 206.3 million passenger trips were made by tram. Around 75 per cent of Melbourne's tram network shares road space with other vehicles, while the rest of the network is separated or are light rail routes. Melbourne's trams are recognised as iconic cultural assets and a tourist attraction. Heritage trams operate on the free City Circle route around the CBD. Trams are free within the central city Free Tram Zone and run 24-hours on weekends.
Melbourne's tram network dates from the 1880s land boom and, as of 2021, consists of of double track, 475 trams, 25 routes, and 1,763 tram stops, making it the largest in the world. In 2017–2018, 206.3 million passenger trips were made by tram. Around 75 per cent of Melbourne's tram network shares road space with other vehicles, while the rest of the network is separated or are light rail routes. Melbourne's trams are recognised as iconic cultural assets and a tourist attraction. Heritage trams operate on the free City Circle route around the CBD. Trams are free within the central city Free Tram Zone and run 24-hours on weekends.
 Water storage and supply for Melbourne is managed by Melbourne Water, which is owned by the Victorian Government. The organisation is also responsible for management of sewerage and the major water catchments in the region as well as the
Water storage and supply for Melbourne is managed by Melbourne Water, which is owned by the Victorian Government. The organisation is also responsible for management of sewerage and the major water catchments in the region as well as the
 Melbourne has a moderately low crime rate, ranking 18th for Personal Security and 9th in the overall Safe City Index in ''
Melbourne has a moderately low crime rate, ranking 18th for Personal Security and 9th in the overall Safe City Index in ''
Official tourist board site of Melbourne
* {{Authority control 1835 establishments in Australia 1835 establishments in Oceania Australian capital cities Cities in Victoria (Australia) Coastal cities in Australia Former national capitals Metropolitan areas of Australia Populated places established in 1835 Port cities in Victoria (Australia) Regions of Victoria (Australia)
Australian state
The states and territories are federated administrative divisions in Australia, ruled by regional governments that constitute the second level of governance between the federal government and local governments. States are self-governing ...
of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
. Its name generally refers to a metropolitan area known as Greater Melbourne, comprising an urban agglomeration
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
of 31 local municipalities, although the name is also used specifically for the local municipality of City of Melbourne based around its central business area. The metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big c ...
occupies much of the northern and eastern coastlines of Port Phillip Bay and spreads into the Mornington Peninsula, part of West Gippsland, as well as the hinterlands towards the Yarra Valley, the Dandenong and Macedon Ranges. It has a population over 5 million (19% of the population of Australia, as per 2021 census), mostly residing to the east side of the city centre, and its inhabitants are commonly referred to as "Melburnians".
The area of Melbourne has been home to Aboriginal Victorians for over 40,000 years and serves as an important meeting place for local Kulin nation clans. Of the five peoples of the Kulin nation, the traditional custodians of the land encompassing Melbourne are the Boonwurrung, Wathaurong
The Wathaurong nation, also called the Wathaurung, Wadawurrung and Wadda Wurrung, are an Aboriginal Australian people living in the area near Melbourne, Geelong and the Bellarine Peninsula in the state of Victoria. They are part of the Kulin ...
and the Wurundjeri
The Wurundjeri people are an Australian Aboriginal people of the Woiwurrung language group, in the Kulin nation. They are the Traditional Owners of the Birrarung (Yarra River) Valley, covering much of the present location of Narrm (Melbo ...
peoples. A short-lived penal settlement was built at Port Phillip, then part of the British colony of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, in 1803, but it was not until 1835, with the arrival of free settlers from Van Diemen's Land (modern-day Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
), that Melbourne was founded. It was incorporated as a Crown settlement in 1837, and named after the then British Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern ...
, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne. In 1851, four years after Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
declared it a city, Melbourne became the capital of the new colony of Victoria. During the 1850s Victorian gold rush, the city entered a lengthy boom period that, by the late 1880s, had transformed it into one of the world's largest and wealthiest metropolises. After the federation of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia (which also governed what is now the Northern Territory), and Western ...
in 1901, it served as the interim seat of government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government ...
of the new nation until Canberra became the permanent capital in 1927. Today, it is a leading financial centre in the Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Russian Far East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia and Pacific Isla ...
region and ranks 32nd globally in the March 2022 Global Financial Centres Index.
Melbourne is home to many of Australia's best-known landmark
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances.
In modern use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures or f ...
s, such as the Melbourne Cricket Ground, the National Gallery of Victoria and the World Heritage-listed Royal Exhibition Building. Noted for its cultural heritage, the city gave rise to Australian rules football, Australian impressionism and Australian cinema, and has more recently been recognised as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
City of Literature and a global centre for street art
Street art is visual art created in public locations for public visibility. It has been associated with the terms "independent art", "post-graffiti", "neo-graffiti" and guerrilla art.
Street art has evolved from the early forms of defiant graff ...
, live music and theatre. It hosts major annual international events, such as the Australian Grand Prix and the Australian Open, and also hosted the 1956 Summer Olympics
The 1956 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVI Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, from 22 November to 8 December 1956, with the exception of the equestrian events, wh ...
. Melbourne consistently ranked as the world's most liveable city for much of the 2010s.
Melbourne Airport
Melbourne Airport , colloquially known as Tullamarine Airport, is the primary airport serving the city of Melbourne, and the second busiest airport in Australia. It opened in 1970 to replace the nearby Essendon Airport. Melbourne Airport is ...
, also known as the Tullamarine Airport, is the second-busiest airport in Australia, and the Port of Melbourne is the nation's busiest seaport. Its main metropolitan rail terminus is Flinders Street station and its main regional rail
Regional rail, also known as local trains and stopping trains, are passenger rail services that operate between towns and cities. These trains operate with more stops over shorter distances than inter-city rail, but fewer stops and faster ser ...
and road coach terminus is Southern Cross station. It also has Australia's most extensive freeway network and the largest urban tram network in the world.
History
Early history and foundation
Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the T ...
have lived in the Melbourne area for at least 40,000 years. When European settlers arrived in the 19th century, at least 20,000 Kulin people
The Kulin nation is an alliance of five Aboriginal nations in south central Victoria, Australia. Their collective territory extends around Port Phillip and Western Port, up into the Great Dividing Range and the Loddon and Goulburn River va ...
from three distinct language groups – the Wurundjeri
The Wurundjeri people are an Australian Aboriginal people of the Woiwurrung language group, in the Kulin nation. They are the Traditional Owners of the Birrarung (Yarra River) Valley, covering much of the present location of Narrm (Melbo ...
, Bunurong and Wathaurong
The Wathaurong nation, also called the Wathaurung, Wadawurrung and Wadda Wurrung, are an Aboriginal Australian people living in the area near Melbourne, Geelong and the Bellarine Peninsula in the state of Victoria. They are part of the Kulin ...
– resided in the area. It was an important meeting place for the clans of the Kulin nation alliance and a vital source of food and water.Isabel Ellender and Peter Christiansen, ''People of the Merri Merri. The Wurundjeri in Colonial Days'', Merri Creek Management Committee, 2001 In June 2021, the boundaries between the land of two of the traditional owner groups, the Wurundjeri and Bunurong, were agreed after being drawn up by the Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Council. The borderline runs across the city from west to east, with the CBD, Richmond and Hawthorn included in Wurundjeri land, and Albert Park, St Kilda and Caulfield on Bunurong land. However, this change in boundaries is still disputed by people on both sides of the dispute including N'arweet Carolyn Briggs. The name ''Narrm'' is commonly used by the broader Aboriginal community to refer to the city, stemming from the traditional name recorded for the area on which the Melbourne city centre is built. The word is closely related to ''Narm-narm'', being the Boonwurrung word for Port Phillip Bay. Narrm means scrub in Eastern Kulin languages which reflects the Creation Story of how the Bay was filled by the creation of the Birrarung (Yarra River). Before this, the dry Melbourne region extended out into the Bay and the Bay was filled with teatree scrub where boordmul (emu) and marram (kangaroo) were hunted.
The first British settlement in Victoria, then part of the penal colony of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, was established by Colonel David Collins in October 1803, at Sullivan Bay, near present-day Sorrento. The following year, due to a perceived lack of resources, these settlers relocated to Van Diemen's Land (present-day Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
) and founded the city of Hobart. It would be 30 years before another settlement was attempted.

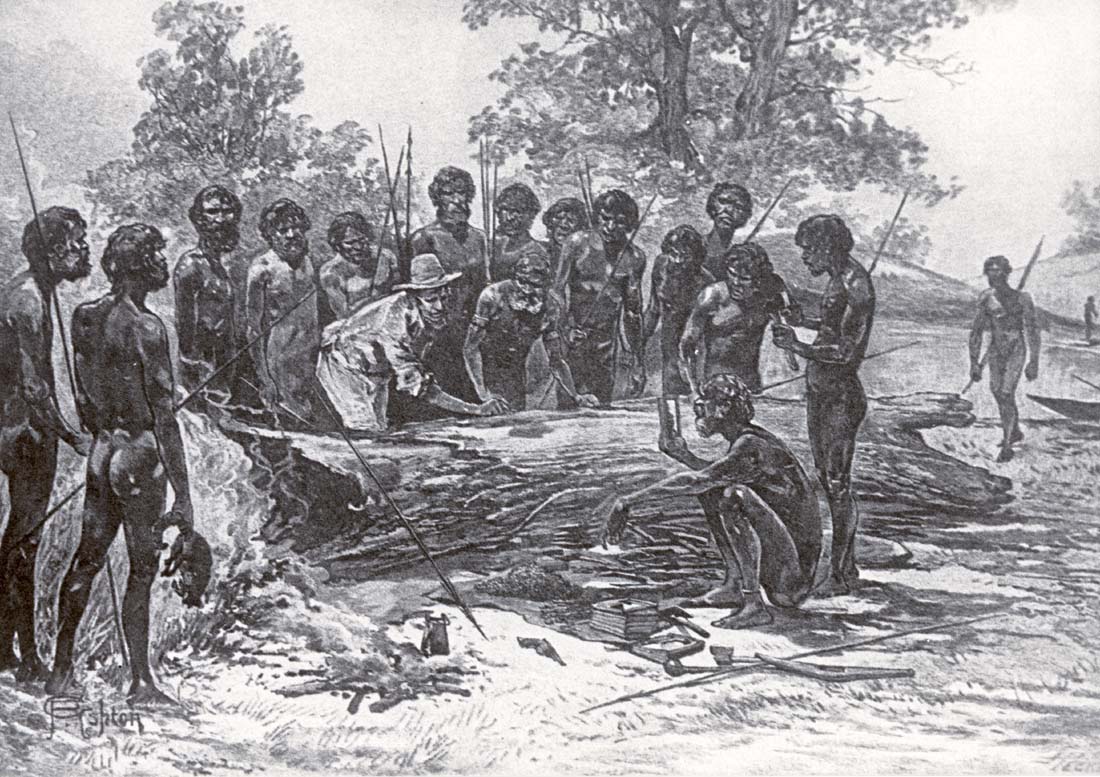
 In May and June 1835, John Batman, a leading member of the Port Phillip Association in Van Diemen's Land, explored the Melbourne area, and later claimed to have negotiated a purchase of with eight Wurundjeri elders. However, the nature of the treaty has been heavily disputed, as none of the parties spoke the same language, and the elders likely perceived it as part of the gift exchanges which had taken place over the previous few days amounting to a tanderrum ceremony which allows temporary, not permanent, access to and use of the land. Batman selected a site on the northern bank of the
In May and June 1835, John Batman, a leading member of the Port Phillip Association in Van Diemen's Land, explored the Melbourne area, and later claimed to have negotiated a purchase of with eight Wurundjeri elders. However, the nature of the treaty has been heavily disputed, as none of the parties spoke the same language, and the elders likely perceived it as part of the gift exchanges which had taken place over the previous few days amounting to a tanderrum ceremony which allows temporary, not permanent, access to and use of the land. Batman selected a site on the northern bank of the Yarra River
The Yarra River or historically, the Yarra Yarra River, ( Kulin languages: ''Berrern'', ''Birr-arrung'', ''Bay-ray-rung'', ''Birarang'', ''Birrarung'', and ''Wongete'') is a perennial river in south-central Victoria, Australia.
The lower ...
, declaring that "this will be the place for a village" before returning to Van Diemen's Land. In August 1835, another group of Vandemonian settlers arrived in the area and established a settlement at the site of the current Melbourne Immigration Museum. Batman and his group arrived the following month and the two groups ultimately agreed to share the settlement, initially known by the native name of Dootigala.
Batman's Treaty with the Aboriginal elders was annulled by Richard Bourke, the Governor of New South Wales (who at the time governed all of eastern mainland Australia), with compensation paid to members of the association. In 1836, Bourke declared the city the administrative capital of the Port Phillip District of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, and commissioned the first plan for its urban layout, the Hoddle Grid, in 1837. Known briefly as Batmania, the settlement was named Melbourne on 10 April 1837 by Governor Richard Bourke after the British Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern ...
, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne, whose seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
was Melbourne Hall in the market town
A market town is a Human settlement, settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular marketplace, market; this distinguished it from a village or ...
of Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/ Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a me ...
, Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the no ...
. That year, the settlement's general post office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state mail, postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II of En ...
officially opened with that name.
Between 1836 and 1842, Victorian Aboriginal groups were largely dispossessed of their land by European settlers. By January 1844, there were said to be 675 Aborigines resident in squalid camps in Melbourne. The British Colonial Office appointed five Aboriginal Protectors for the Aborigines of Victoria, in 1839, however, their work was nullified by a land policy that favoured squatters who took possession of Aboriginal lands. By 1845, fewer than 240 wealthy Europeans held all the pastoral licences then issued in Victoria and became a powerful political and economic force in Victoria for generations to come.
Letters patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, t ...
of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
, issued on 25 June 1847, declared Melbourne a city. On 1 July 1851, the Port Phillip District separated from New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
to become the Colony of Victoria, with Melbourne as its capital.
Victorian gold rush

 The discovery of gold in Victoria in mid-1851 sparked a gold rush, and Melbourne, the colony's major port, experienced rapid growth. Within months, the city's population had nearly doubled from 25,000 to 40,000 inhabitants. Exponential growth ensued, and by 1865 Melbourne had overtaken Sydney as Australia's most populous city.
An influx of intercolonial and international migrants, particularly from Europe and China, saw the establishment of slums, including Chinatown and a temporary "tent city" on the southern banks of the Yarra. In the aftermath of the 1854 Eureka Rebellion, mass public support for the plight of the miners resulted in major political changes to the colony, including improvements in working conditions across mining, agriculture, manufacturing and other local industries. At least twenty nationalities took part in the rebellion, giving some indication of immigration flows at the time.
With the wealth brought in from the gold rush and the subsequent need for public buildings, a program of grand civic construction soon began. The 1850s and 1860s saw the commencement of
The discovery of gold in Victoria in mid-1851 sparked a gold rush, and Melbourne, the colony's major port, experienced rapid growth. Within months, the city's population had nearly doubled from 25,000 to 40,000 inhabitants. Exponential growth ensued, and by 1865 Melbourne had overtaken Sydney as Australia's most populous city.
An influx of intercolonial and international migrants, particularly from Europe and China, saw the establishment of slums, including Chinatown and a temporary "tent city" on the southern banks of the Yarra. In the aftermath of the 1854 Eureka Rebellion, mass public support for the plight of the miners resulted in major political changes to the colony, including improvements in working conditions across mining, agriculture, manufacturing and other local industries. At least twenty nationalities took part in the rebellion, giving some indication of immigration flows at the time.
With the wealth brought in from the gold rush and the subsequent need for public buildings, a program of grand civic construction soon began. The 1850s and 1860s saw the commencement of Parliament House
Parliament House may refer to:
Australia
* Parliament House, Canberra, Parliament of Australia
* Parliament House, Adelaide, Parliament of South Australia
* Parliament House, Brisbane, Parliament of Queensland
* Parliament House, Darwin, Parliame ...
, the Treasury Building, the Old Melbourne Gaol, Victoria Barracks, the State Library, University of Melbourne
The University of Melbourne is a public research university located in Melbourne, Australia. Founded in 1853, it is Australia's second oldest university and the oldest in Victoria. Its main campus is located in Parkville, an inner suburb n ...
, General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state mail, postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II of En ...
, Customs House, the Melbourne Town Hall, St Patrick's cathedral, though many remained uncompleted for decades, with some still not finished .
The layout of the inner suburbs on a largely one-mile grid pattern, cut through by wide radial boulevards and parklands surrounding the central city, was largely established in the 1850s and 1860s. These areas rapidly filled with the ubiquitous terrace houses, as well as with detached houses and grand mansions, while some of the major roads developed as shopping streets. Melbourne quickly became a major finance centre, home to several banks, the Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's oldest company and the official maker of British coins.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly owned by His Majesty's Treasury and is under an exclu ...
, and (in 1861) Australia's first stock exchange.
In 1855, the Melbourne Cricket Club secured possession of its now famous ground, the MCG. Members of the Melbourne Football Club codified Australian football
Australian football, also called Australian rules football or Aussie rules, or more simply football or footy, is a contact sport played between two teams of 18 players on an oval field, often a modified cricket ground. Points are scored by k ...
in 1859, and in 1861, the first Melbourne Cup race was held. Melbourne acquired its first public monument, the Burke and Wills statue, in 1864.
With the gold rush largely over by 1860, Melbourne continued to grow on the back of continuing gold-mining, as the major port for exporting the agricultural products of Victoria (especially wool) and with a developing manufacturing sector protected by high tariffs. An extensive radial railway network spread into the countryside from the late 1850s. Construction started on further major public buildings in the 1860s and 1870s, such as the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
, Government House, and the Queen Victoria Market. The central city filled up with shops and offices, workshops, and warehouses. Large banks and hotels faced the main streets, with fine townhouses in the east end of Collins Street, contrasting with tiny cottages down laneways within the blocks. The Aboriginal population continued to decline, with an estimated 80% total decrease by 1863, due primarily to introduced diseases (particularly smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
), frontier violence and dispossession of their lands.
Land boom and bust
 The 1880s saw extraordinary growth: consumer confidence, easy access to credit, and steep increases in land prices led to an enormous amount of construction. During this "land boom", Melbourne reputedly became the richest city in the world, and the second-largest (after London) in the
The 1880s saw extraordinary growth: consumer confidence, easy access to credit, and steep increases in land prices led to an enormous amount of construction. During this "land boom", Melbourne reputedly became the richest city in the world, and the second-largest (after London) in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
.
The decade began with the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880, held in the large purpose-built Exhibition Building. A telephone exchange was established that year, and the foundations of St Paul's were laid. In 1881, electric light was installed in the Eastern Market, and a generating station capable of supplying 2,000 incandescent lamps was in operation by 1882. The Melbourne cable tramway system opened in 1885 and became one of the world's most extensive systems by 1890.
In 1885, visiting English journalist George Augustus Henry Sala coined the phrase "Marvellous Melbourne", which stuck long into the twentieth century and has come to refer to the opulence and energy of the 1880s, during which time large commercial buildings, grand hotels, banks, coffee palaces, terrace housing and palatial mansions proliferated in the city. The establishment of a hydraulic facility in 1887 allowed for the local manufacture of elevators, resulting in the first construction of high-rise buildings. This period also saw the expansion of a major radial rail-based transport network.
Melbourne's land-boom peaked in 1888, the year it hosted the Centennial Exhibition. A brash boosterism that had typified Melbourne during this time ended in the early 1890s with a severe economic depression, sending the local finance- and property-industries into a period of chaos. Sixteen small "land banks" and building societies collapsed, and 133 limited companies went into liquidation. The Melbourne financial crisis was a contributing factor in the Australian economic depression of the 1890s and in the Australian banking crisis of 1893. The effects of the depression on the city were profound, with virtually no new construction until the late 1890s.
Temporary capital of Australia and World War II
 At the time of Australia's
At the time of Australia's federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
on 1 January 1901 Melbourne became the seat of government of the federated Commonwealth of Australia. The first federal parliament convened on 9 May 1901 in the Royal Exhibition Building, subsequently moving to the Victorian Parliament House, where it sat until it moved to Canberra in 1927. The Governor-General of Australia resided at Government House in Melbourne until 1930, and many major national institutions remained in Melbourne well into the twentieth century.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the city hosted American military forces who were fighting the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
, and the government requisitioned the Melbourne Cricket Ground for military use.
Post-war period
In the immediate years afterWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Melbourne expanded rapidly, its growth boosted by post-war immigration to Australia, primarily from Southern Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
. While the "Paris End" of Collins Street began Melbourne's boutique shopping and open air cafe cultures, the city centre was seen by many as stale—the dreary domain of office workers—something expressed by John Brack in his famous painting '' Collins St., 5 pm'' (1955). Up until the 21st century, Melbourne was considered Australia's "industrial heartland".
 Height limits in the CBD were lifted in 1958, after the construction of ICI House, transforming the city's skyline with the introduction of skyscrapers. Suburban expansion then intensified, served by new indoor malls beginning with Chadstone Shopping Centre. The post-war period also saw a major renewal of the CBD and St Kilda Road which significantly modernised the city. New fire regulations and redevelopment saw most of the taller pre-war CBD buildings either demolished or partially retained through a policy of facadism. Many of the larger suburban mansions from the boom era were also either demolished or subdivided.
To counter the trend towards low-density suburban residential growth, the government began a series of controversial public housing projects in the inner city by the Housing Commission of Victoria, which resulted in the demolition of many neighbourhoods and a proliferation of high-rise towers. In later years, with the rapid rise of motor vehicle ownership, the investment in freeway and highway developments greatly accelerated the outward suburban sprawl and declining inner-city population. The Bolte government sought to rapidly accelerate the modernisation of Melbourne. Major road projects including the remodelling of St Kilda Junction, the widening of Hoddle Street and then the extensive 1969 Melbourne Transportation Plan changed the face of the city into a car-dominated environment.
Australia's financial and mining booms during 1969 and 1970 resulted in establishment of the headquarters of many major companies ( BHP and Rio Tinto, among others) in the city. Nauru's then booming economy resulted in several ambitious investments in Melbourne, such as Nauru House. Melbourne remained Australia's main business and financial centre until the late 1970s, when it began to lose this primacy to Sydney.
Melbourne experienced an economic downturn between 1989 and 1992, following the collapse of several local financial institutions. In 1992, the newly elected Kennett government began a campaign to revive the economy with an aggressive development campaign of public works coupled with the promotion of the city as a tourist destination with a focus on major events and sports tourism. During this period the Australian Grand Prix moved to Melbourne from
Height limits in the CBD were lifted in 1958, after the construction of ICI House, transforming the city's skyline with the introduction of skyscrapers. Suburban expansion then intensified, served by new indoor malls beginning with Chadstone Shopping Centre. The post-war period also saw a major renewal of the CBD and St Kilda Road which significantly modernised the city. New fire regulations and redevelopment saw most of the taller pre-war CBD buildings either demolished or partially retained through a policy of facadism. Many of the larger suburban mansions from the boom era were also either demolished or subdivided.
To counter the trend towards low-density suburban residential growth, the government began a series of controversial public housing projects in the inner city by the Housing Commission of Victoria, which resulted in the demolition of many neighbourhoods and a proliferation of high-rise towers. In later years, with the rapid rise of motor vehicle ownership, the investment in freeway and highway developments greatly accelerated the outward suburban sprawl and declining inner-city population. The Bolte government sought to rapidly accelerate the modernisation of Melbourne. Major road projects including the remodelling of St Kilda Junction, the widening of Hoddle Street and then the extensive 1969 Melbourne Transportation Plan changed the face of the city into a car-dominated environment.
Australia's financial and mining booms during 1969 and 1970 resulted in establishment of the headquarters of many major companies ( BHP and Rio Tinto, among others) in the city. Nauru's then booming economy resulted in several ambitious investments in Melbourne, such as Nauru House. Melbourne remained Australia's main business and financial centre until the late 1970s, when it began to lose this primacy to Sydney.
Melbourne experienced an economic downturn between 1989 and 1992, following the collapse of several local financial institutions. In 1992, the newly elected Kennett government began a campaign to revive the economy with an aggressive development campaign of public works coupled with the promotion of the city as a tourist destination with a focus on major events and sports tourism. During this period the Australian Grand Prix moved to Melbourne from Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater A ...
. Major projects included the construction of a new facility for the Melbourne Museum, Federation Square, the Melbourne Convention & Exhibition Centre, Crown Casino
Crown Melbourne (also referred to as Crown Casino and Entertainment Complex) is a casino and resort located on the south bank of the Yarra River, in Melbourne, Australia. Crown Casino is a unit of Crown Limited, and the first casino of the n ...
and the CityLink tollway. Other strategies included the privatisation of some of Melbourne's services, including power and public transport, and a reduction in funding to public services such as health, education and public transport infrastructure.
Contemporary Melbourne
Since the mid-1990s, Melbourne has maintained significant population and employment growth. There has been substantial international investment in the city's industries and property market. Major inner-city urban renewal has occurred in areas such as Southbank, Port Melbourne, Melbourne Docklands and more recently, South Wharf. Melbourne sustained the highest population increase and economic growth rate of any Australian capital city from 2001 to 2004. From 2006, the growth of the city extended into "green wedges" and beyond the city's urban growth boundary. Predictions of the city's population reaching 5 million people pushed the state government to review the growth boundary in 2008 as part of its Melbourne @ Five Million strategy. In 2009, Melbourne was less affected by the late-2000s financial crisis in comparison to other Australian cities. At this time, more new jobs were created in Melbourne than any other Australian city—almost as many as the next two fastest growing cities, Brisbane and Perth, combined, and Melbourne's property market remained highly priced, resulting in historically high property prices and widespread rent increases. In 2020, Melbourne was classified as an Alpha city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. Out of all major Australian cities, Melbourne was the worst affected by theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
and spent a long time under lockdown restrictions, with Melbourne experiencing six lockdowns totalling 262 days.
Geography
 Melbourne is in the southeastern part of mainland Australia, within the state of Victoria. Geologically, it is built on the confluence of Quaternary lava flows to the west,
Melbourne is in the southeastern part of mainland Australia, within the state of Victoria. Geologically, it is built on the confluence of Quaternary lava flows to the west, Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoi ...
mudstones to the east, and Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
sand accumulation to the southeast along Port Phillip
Port Phillip (Kulin: ''Narm-Narm'') or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel known as The Rip, and is completel ...
. The southeastern suburbs are situated on the Selwyn fault, which transects Mount Martha and Cranbourne. The western portion of the metropolitan area lies within the Victorian Volcanic Plain grasslands
The Victorian Volcanic Plain Grasslands are a critically endangered temperate grasslands that occur in the Australian state of Victoria, stretching from Hamilton in the northwest to the city of Melbourne. Part of the Southern Volcanic Plain and ...
vegetation community, and the southeast falls in the Gippsland Plains Grassy Woodland zone.Gippsland Red Gum Grassy Woodland and Associated Native GrasslandEnvironment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. Retrieved 6 September 2022. Melbourne extends along the
Yarra River
The Yarra River or historically, the Yarra Yarra River, ( Kulin languages: ''Berrern'', ''Birr-arrung'', ''Bay-ray-rung'', ''Birarang'', ''Birrarung'', and ''Wongete'') is a perennial river in south-central Victoria, Australia.
The lower ...
towards the Yarra Valley and the Dandenong Ranges to the east. It extends northward through the undulating bushland valleys of the Yarra's tributaries— Moonee Ponds Creek (toward Tullamarine Airport), Merri Creek, Darebin Creek and Plenty River—to the outer suburban growth corridors of Craigieburn and Whittlesea.
The city reaches southeast through Dandenong to the growth corridor of Pakenham towards West Gippsland, and southward through the Dandenong Creek valley and the city of Frankston. In the west, it extends along the Maribyrnong River and its tributaries north towards Sunbury and the foothills of the Macedon Ranges, and along the flat volcanic plain country towards Melton in the west, Werribee at the foothills of the You Yangs granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
ridge southwest of the CBD. The Little River, and the township of the same name, marks the border between Melbourne and neighbouring Geelong city.
Melbourne's major bayside beaches are in the various suburbs along the shores of Port Phillip Bay, in areas like Port Melbourne, Albert Park, St Kilda, Elwood Elwood may refer to any one of the following::
Places
;In Australia
*Elwood, Victoria
;In the United States of America
*Elwood, Illinois
*Elwood, Indiana
*Elwood, Kansas
* Elwood, Missouri
*Elwood, Nebraska
* Elwood-Magnolia, New Jersey
*Elwood, N ...
, Brighton, Sandringham, Mentone, Frankston, Altona, Williamstown and Werribee South. The nearest surf beaches are south of the Melbourne CBD in the back-beaches of Rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe (Triticeae) and is closely related to both wheat (''Triticum'') and barley (genus ''Hordeum''). Rye grain is u ...
, Sorrento and Portsea Portsea may refer to:
* Portsea, Victoria, a seaside town in Australia
* Portsea Island, an island on the south coast of England contained within the city of Portsmouth
* Portsea, Portsmouth
Portsea Island is a flat and low-lying natural i ...
.
Climate
 Melbourne has a temperate
Melbourne has a temperate oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
''Cfb'') with warm summers and cool winters. Melbourne is well known for its changeable weather conditions, mainly due to it being located on the boundary of hot inland areas and the cool southern ocean. This temperature differential is most pronounced in the spring and summer months and can cause strong cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Northern ...
s to form. These cold fronts can be responsible for varied forms of severe weather from gales to thunderstorms and hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
, large temperature drops and heavy rain. Winters, however, are usually very stable, but rather damp and often cloudy—though not as cloudy as inland areas or places farther west like Warrnambool
Warrnambool ( Maar: ''Peetoop'' or ''Wheringkernitch'' or ''Warrnambool'') is a city on the south-western coast of Victoria, Australia. At the 2021 census, Warrnambool had a population of 35,743. Situated on the Princes Highway, Warrnambool (A ...
due to Melbourne's downwind placement relative to the prevailing westerlies, as evident by its dry winters by southern Victorian standards. The city, however, is exposed to southerly and southwesterly systems as manifested by the overcast, drizzly winters.
Port Phillip
Port Phillip (Kulin: ''Narm-Narm'') or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel known as The Rip, and is completel ...
is often warmer than the surrounding oceans and/or the land mass, particularly in spring and autumn; this can set up a "bay effect", similar to the " lake effect" seen in colder climates, where showers are intensified leeward of the bay. Relatively narrow streams of heavy showers can often affect the same places (usually the eastern suburbs) for an extended period, while the rest of Melbourne and surrounds stays dry. Overall, the area around Melbourne is, owing to the rain shadow of the Otway Ranges, nonetheless drier than average for southern Victoria. Within the city and surrounds, rainfall varies widely, from around at Little River to on the eastern fringe at Gembrook. Melbourne receives 48.6 clear days annually. Dewpoint temperatures in the summer range from .
Melbourne is also prone to isolated convective showers forming when a cold pool crosses the state, especially if there is considerable daytime heating. These showers are often heavy and can include hail, squalls, and significant drops in temperature, but they often pass through very quickly with a rapid clearing trend to sunny and relatively calm weather and the temperature rising back to what it was before the shower. This can occur in the space of minutes and can be repeated many times a day, giving Melbourne a reputation for having "four seasons in one day", a phrase that is part of local popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in ...
. The lowest temperature on record is , on 21 July 1869. The highest temperature recorded in Melbourne city was , on 7 February 2009. While snow is occasionally seen at higher elevations in the outskirts of the city, it has not been recorded in the Central Business District since 1986.
The average temperature of the sea ranges from in September to in February; at Port Melbourne, the average sea temperature range is the same.
Urban structure


 Melbourne's
Melbourne's urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
is approximately 2,453 km2, slightly larger than that of London and Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley of ...
, while its metropolitan area is 9,993 km2 (3,858 sq mi)—larger than Jakarta (at 7,063 km2), but smaller than New York City (at 11,875 km2). The Hoddle Grid, a grid of streets measuring approximately , forms the nucleus of Melbourne's central business district
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business centre of a city. It contains commercial space and offices, and in larger cities will often be described as a financial district. Geographically, it often coincides with the " cit ...
(CBD). The grid's southern edge fronts onto the Yarra River. More recent office, commercial and public developments in the adjoining districts of Southbank and Docklands have made these areas into extensions of the CBD in all but name. A byproduct of the CBD's layout is its network of lanes and arcades, such as Block Arcade
The Block Arcade is an historic shopping arcade in the central business district of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Constructed between 1891 and 1893, it is considered one of the late Victorian era's finest shopping arcades and ranks among Melbou ...
and Royal Arcade.
Melbourne has become Australia's most densely populated area, with approximately 19,500 residents per square kilometre, and is home to more skyscrapers than any other Australian city, the tallest being Australia 108, situated in Southbank. Melbourne's newest planned skyscraper, Southbank By Beulah
STH BNK by Beulah is a dual skyscraper development proposed for Melbourne developed by Beulah and designed by architectural firms UNStudio and Cox Architecture. The site currently hosts a BMW dealership.
History Site
The site for the develop ...
(also known as "Green Spine"), has recently been approved for construction and will be the tallest structure in Australia by 2025.
The CBD and surrounds also contain many significant historic buildings such as the Royal Exhibition Building, the Melbourne Town Hall and Parliament House
Parliament House may refer to:
Australia
* Parliament House, Canberra, Parliament of Australia
* Parliament House, Adelaide, Parliament of South Australia
* Parliament House, Brisbane, Parliament of Queensland
* Parliament House, Darwin, Parliame ...
.
Although the area is described as the ''centre'', it is not actually the demographic centre of Melbourne at all, due to an urban sprawl to the southeast, the demographic centre being located at Glen Iris.
Melbourne is typical of Australian capital cities in that after the turn of the 20th century, it expanded with the underlying notion of a 'quarter acre home and garden' for every family, often referred to locally as the Australian Dream
The Australian Dream or Great Australian Dream is, in its narrowest sense, a belief that in Australia, home ownership can lead to a better life and is an expression of success and security. The term is derived from the American Dream, which f ...
. This, coupled with the popularity of the private automobile after 1945, led to the auto-centric urban structure now present today in the middle and outer suburbs. Much of metropolitan
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
Melbourne is accordingly characterised by low-density sprawl, whilst its inner-city areas feature predominantly medium-density, transit-oriented urban forms. The city centre, Docklands, St. Kilda Road and Southbank areas feature high-density forms.
Melbourne is often referred to as Australia's garden city, and the state of Victoria was once known as ''the garden state''. There is an abundance of parks and gardens in Melbourne, many close to the CBD with a variety of common and rare plant species amid landscaped vistas, pedestrian pathways and tree-lined avenues. Melbourne's parks are often considered the best public parks in all of Australia's major cities. There are also many parks in the surrounding suburbs of Melbourne, such as in the municipalities of Stonnington, Boroondara and Port Phillip
Port Phillip (Kulin: ''Narm-Narm'') or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel known as The Rip, and is completel ...
, southeast of the central business district. Several national park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
s have been designated around the urban area of Melbourne, including the Mornington Peninsula National Park, Port Phillip Heads Marine National Park and Point Nepean National Park in the southeast, Organ Pipes National Park to the north and Dandenong Ranges National Park to the east. There are also a number of significant state parks just outside Melbourne. The extensive area covered by urban Melbourne is formally divided into hundreds of suburbs (for addressing and postal purposes), and administered as local government areas 31 of which are located within the metropolitan area.
Housing
 Melbourne has minimal public housing and high demand for rental housing, which is becoming unaffordable for some. Public housing is managed and provided by the Victorian Government's
Melbourne has minimal public housing and high demand for rental housing, which is becoming unaffordable for some. Public housing is managed and provided by the Victorian Government's Department of Families, Fairness and Housing
The Department of Families, Fairness and Housing (DFFH) is a department of the Government of Victoria. Formed from the splitting of Department of Health and Human Services in the ongoing response to the COVID-19 pandemic, DFFH holds responsibility ...
, and operates within the framework of the Commonwealth-State Housing Agreement, by which both federal and state governments provide funding for housing.
Melbourne is experiencing high population growth, generating high demand for housing. This housing boom has increased house prices and rents, as well as the availability of all types of housing. Subdivision regularly occurs in the outer areas of Melbourne, with numerous developers offering house and land packages. However, since the release of Melbourne 2030 in 2002, planning policies have encouraged medium-density and high-density development in existing areas with good access to public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typic ...
and other services. As a result of this, Melbourne's middle and outer-ring suburbs have seen significant brownfields redevelopment.
Architecture
 On the back of the 1850s gold rush and 1880s land boom, Melbourne became renowned as one of the world's great Victorian-era cities, a reputation that persists due to its diverse range of
On the back of the 1850s gold rush and 1880s land boom, Melbourne became renowned as one of the world's great Victorian-era cities, a reputation that persists due to its diverse range of Victorian architecture
Victorian architecture is a series of architectural revival styles in the mid-to-late 19th century. ''Victorian'' refers to the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901), called the Victorian era, during which period the styles known as Victorian w ...
. High concentrations of well-preserved Victorian-era buildings can be found in the inner suburbs, such as Carlton, East Melbourne and South Melbourne. Outstanding examples of Melbourne's built Victorian heritage include the World Heritage-listed Royal Exhibition Building (1880), the General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state mail, postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II of En ...
(1867), Hotel Windsor (1884) and the Block Arcade
The Block Arcade is an historic shopping arcade in the central business district of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Constructed between 1891 and 1893, it is considered one of the late Victorian era's finest shopping arcades and ranks among Melbou ...
(1891). Comparatively little remains of Melbourne's pre-gold rush architecture; St James Old Cathedral (1839) and St Francis' Church (1845) are among the few examples left in the CBD. Many of the CBD's Victorian boom-time landmarks were also demolished in the decades after World War II, including the Federal Coffee Palace (1888) and the APA Building (1889), one of the tallest early skyscrapers upon completion. Heritage listings and heritage overlays have since been introduced in an effort to prevent further losses of the city's historic fabric.
In line with the city's expansion during the early 20th century, suburbs such as Hawthorn and Camberwell are defined largely by Federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
and Edwardian
The Edwardian era or Edwardian period of British history spanned the reign of King Edward VII, 1901 to 1910 and is sometimes extended to the start of the First World War. The death of Queen Victoria in January 1901 marked the end of the Victori ...
architectural styles. The City Baths, built in 1903, are a prominent example of the latter style in the CBD. The 1926 Nicholas Building is the city's grandest example of the Chicago School style, while the influence of Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
is apparent in the Manchester Unity Building, completed in 1932.
 The city also features the Shrine of Remembrance, which was built as a memorial to the men and women of Victoria who served in
The city also features the Shrine of Remembrance, which was built as a memorial to the men and women of Victoria who served in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and is now a memorial to all Australians who have served in war.
Residential architecture is not defined by a single architectural style, but rather an eclectic mix of large McMansion
In suburban communities, McMansion is a pejorative term for a large "mass-produced" dwelling marketed to the upper middle class mainly in the United States. Virginia Savage McAlester, who also gave a first description of the common features w ...
-style houses (particularly in areas of urban sprawl), apartment buildings, condominiums, and townhouses which generally characterise the medium-density inner-city neighbourhoods. Freestanding dwellings with relatively large gardens are perhaps the most common type of housing outside inner city Melbourne. Victorian terrace housing, townhouses and historic Italianate
The Italianate style was a distinct 19th-century phase in the history of Classical architecture. Like Palladianism and Neoclassicism, the Italianate style drew its inspiration from the models and architectural vocabulary of 16th-century Italia ...
, Tudor revival and Neo-Georgian mansions are all common in inner-city neighbourhoods such as Carlton, Fitzroy and further into suburban enclaves like Toorak Toorak may refer to:
* Toorak, Victoria, an inner south-eastern suburb of Melbourne
*Toorak College, Mount Eliza, approximately 40 km south of Melbourne
* Toorak Gardens, South Australia, an inner eastern suburb of Adelaide initially named Toorak
* ...
.
Culture
 Often referred to as Australia's cultural capital, Melbourne is recognised globally as a centre of sport, music, theatre, comedy, art, literature, film and television. For much of the 2010s, it held the top position in '' The Economist Intelligence Unit'' list of the world's most liveable cities, partly due to its cultural attributes.
The city celebrates a wide variety of annual cultural events and festivals of all types, including the Melbourne International Arts Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival,
Often referred to as Australia's cultural capital, Melbourne is recognised globally as a centre of sport, music, theatre, comedy, art, literature, film and television. For much of the 2010s, it held the top position in '' The Economist Intelligence Unit'' list of the world's most liveable cities, partly due to its cultural attributes.
The city celebrates a wide variety of annual cultural events and festivals of all types, including the Melbourne International Arts Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival, Melbourne Fringe Festival
The Melbourne Fringe Festival is an annual independent arts festival in Melbourne, Australia, usually over three weeks from late September to early October. Held since 1982, the Festival includes a wide variety of art forms, including theatre, com ...
and Moomba, Australia's largest free community festival.
The State Library of Victoria, founded in 1854, is one of the world's oldest free public libraries and, as of 2018, the fourth most-visited library globally. Between the gold rush and the crash of 1890, Melbourne was Australia's literary capital, famously referred to by Henry Kendall as "that wild bleak Bohemia south of the Murray". At this time, Melbourne-based writers and poets Marcus Clarke, Adam Lindsay Gordon and Rolf Boldrewood produced classic visions of colonial life. Fergus Hume's '' The Mystery of a Hansom Cab'' (1886), the fastest-selling crime novel of the era, is set in Melbourne, as is Australia's best-selling book of poetry, C. J. Dennis' '' The Songs of a Sentimental Bloke'' (1915). Contemporary Melbourne authors who have written award-winning books set in the city include Peter Carey, Helen Garner and Christos Tsiolkas. Melbourne has Australia's widest range of bookstores, as well as the nation's largest publishing sector. The city is also home to the Melbourne Writers Festival and hosts the Victorian Premier's Literary Awards. In 2008, it became the second city to be named a UNESCO City of Literature.
 Ray Lawler's play '' Summer of the Seventeenth Doll'' is set in Carlton and debuted in 1955, the same year that Edna Everage, Barry Humphries' Moonee Ponds housewife character, first appeared on stage, both sparking international interest in Australian theatre. Melbourne's East End Theatre District is known for its Victorian era theatres, such as the Athenaeum, Her Majesty's and the
Ray Lawler's play '' Summer of the Seventeenth Doll'' is set in Carlton and debuted in 1955, the same year that Edna Everage, Barry Humphries' Moonee Ponds housewife character, first appeared on stage, both sparking international interest in Australian theatre. Melbourne's East End Theatre District is known for its Victorian era theatres, such as the Athenaeum, Her Majesty's and the Princess
Princess is a regal rank and the feminine equivalent of prince (from Latin '' princeps'', meaning principal citizen). Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or for the daughter of a king or prince.
Princess as a subs ...
, as well as the Forum
Forum or The Forum (plural forums or fora) may refer to:
Common uses
*Forum (legal), designated space for public expression in the United States
*Forum (Roman), open public space within a Roman city
**Roman Forum, most famous example
*Internet ...
and the Regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state ''pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy, ...
. Other heritage-listed theatres include the art deco landmarks The Capitol and St Kilda's Palais Theatre
The Palais Theatre (originally Palais Pictures) is a historic picture palace located in St Kilda, an inner suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. With a capacity of nearly 3,000 people, it is the largest seated theatre in Australia.
Repl ...
, Australia's largest seated theatre with a capacity of 3,000 people. The Arts Precinct in Southbank is home to Arts Centre Melbourne (which includes the State Theatre and Hamer Hall), as well as the Melbourne Recital Centre and Southbank Theatre
Southbank Theatre is a performing arts venue located in the Southbank region of Melbourne, Victoria
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung–Taungurung language, Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the List of Austra ...
, home of the Melbourne Theatre Company, Australia's oldest professional theatre company. The Australian Ballet, Opera Australia and Melbourne Symphony Orchestra are also based in the precinct.
Melbourne has been called "the live music capital of the world"; one study found it has more music venues per capita than any other world city sampled, with 17.5 million patron visits to 553 venues in 2016. The Sidney Myer Music Bowl in Kings Domain
Kings Domain is an area of parklands in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It surrounds Government House Reserve, the home of the governors of Victoria, the Sidney Myer Music Bowl, and the Shrine Reserve incorporating the Shrine of Remembrance. ...
hosted the largest crowd ever for a music concert in Australia when an estimated 200,000 attendees saw Melbourne band The Seekers in 1967. Airing between 1974 and 1987, Melbourne's '' Countdown'' helped launch the careers of Crowded House, Men at Work and Kylie Minogue
Kylie Ann Minogue (; born 28 May 1968) is an Australian singer, songwriter and actress. She is the highest-selling female Australian artist of all time, having sold over 80 million records worldwide. She has been recognised for reinve ...
, among other local acts. Several distinct post-punk
Post-punk (originally called new musick) is a broad genre of punk music that emerged in the late 1970s as musicians departed from punk's traditional elements and raw simplicity, instead adopting a variety of avant-garde sensibilities and non-r ...
scenes flourished in Melbourne during the late 1970s, including the Fitzroy-based Little Band scene and the St Kilda scene centred at the Crystal Ballroom, which gave rise to Dead Can Dance and Nick Cave and the Bad Seeds
Nick Cave and the Bad Seeds are an Australian rock band formed in 1983 by vocalist Nick Cave, multi-instrumentalist Mick Harvey and guitarist-vocalist Blixa Bargeld. The band has featured international personnel throughout its career and p ...
, respectively. More recent independent acts from Melbourne to achieve global recognition include The Avalanches, Gotye and King Gizzard and the Lizard Wizard. Melbourne is also regarded as a centre of EDM
EDM or E-DM may refer to:
Music
* Electronic dance music
* Early Day Miners, American band
Science and technology
* Electric dipole moment
* Electrical discharge machining
* Electronic distance measurement
*Entry, Descent, and landing demonstra ...
, and lends its name to the Melbourne Bounce genre and the Melbourne Shuffle dance style, both of which emerged from the city's underground rave scene.
 Established in 1861, the National Gallery of Victoria is Australia's oldest and largest art museum. Several art movements originated in Melbourne, most famously the Heidelberg School of impressionists, named after a suburb where they camped to paint '' en plein air'' in the 1880s. The Australian tonalists followed, some of whom founded Montsalvat, Australia's oldest surviving art colony. During World War II, the Angry Penguins, a group of avant-garde artists, convened at a Bulleen dairy farm, now the Heide Museum of Modern Art. The city is also home to the
Established in 1861, the National Gallery of Victoria is Australia's oldest and largest art museum. Several art movements originated in Melbourne, most famously the Heidelberg School of impressionists, named after a suburb where they camped to paint '' en plein air'' in the 1880s. The Australian tonalists followed, some of whom founded Montsalvat, Australia's oldest surviving art colony. During World War II, the Angry Penguins, a group of avant-garde artists, convened at a Bulleen dairy farm, now the Heide Museum of Modern Art. The city is also home to the Australian Centre for Contemporary Art
The Australian Centre For Contemporary Art (ACCA) is a contemporary art gallery in Melbourne, Australia. The gallery is located on Sturt Street in the Melbourne Arts Precinct, in the inner suburb of Southbank. Designed by Wood Marsh Architects ...
. In the 2000s, Melbourne street art became globally renowned and a major tourist drawcard, with "laneway galleries" such as Hosier Lane attracting more Instagram hashtags than some of the city's traditional attractions, such as the Melbourne Zoo.
A quarter century after bushranger
Bushrangers were originally escaped convicts in Australia, convicts in the early years of the History of Australia (1788–1850), British settlement of Australia who used The bush#Australia, the bush as a refuge to hide from the authorities. B ...
Ned Kelly's execution at Old Melbourne Gaol, the Melbourne-produced '' The Story of the Kelly Gang'' (1906), the world's first feature-length narrative film, premiered at the above-named Athenaeum, spurring Australia's first cinematic boom. Melbourne remained a world leader in filmmaking until the mid-1910s, when several factors, including a ban on bushranger films, contributed to a decades-long decline of the industry. A notable film shot and set in Melbourne during this lull was '' On the Beach'' (1959). Melbourne filmmakers led the Australian Film Revival with ocker comedies such as '' Stork'' (1971) and '' Alvin Purple'' (1973). Other films shot and set in Melbourne include '' Mad Max'' (1979), '' Romper Stomper'' (1992), '' Chopper'' (2000) and '' Animal Kingdom'' (2010). The Melbourne International Film Festival
The Melbourne International Film Festival (MIFF) is an annual film festival held over three weeks in Melbourne, Australia. It was founded in 1952 and is one of the oldest film festivals in the world following the founding of the Venice Film Fes ...
began in 1952 and is one of the world's oldest film festivals. The AACTA Awards
The Australian Academy of Cinema and Television Arts Awards, known as the AACTA Awards, are presented annually by the Australian Academy of Cinema and Television Arts (AACTA). The awards recognise excellence in the film and television indust ...
, Australia's top screen awards, were inaugurated by the festival in 1958. Melbourne is also home to Docklands Studios Melbourne (the city's largest film and television studio complex), the Australian Centre for the Moving Image
ACMI, formerly the Australian Centre for the Moving Image, is Australia's national museum of film, television, videogames, and art. ACMI was established in 2002 and is based at Federation Square in Melbourne, Victoria.
During the 2014-15 finan ...
and the headquarters of Village Roadshow Pictures, Australia's largest film production company.
Sport
 Melbourne has long been regarded as Australia's sporting capital due to the role it has played in the development of Australian sport, the range and quality of its sporting events and venues, and its high rates of spectatorship and participation. The city is also home to 27 professional sports teams competing at the national level, the most of any Australian city. Melbourne's sporting reputation was recognised in 2016 when, after being ranked as the world's top sports city three times biennially, the Ultimate Sports City Awards in Switzerland named it 'Sports City of the Decade'.
The city has hosted a number of major international sporting events, most notably the
Melbourne has long been regarded as Australia's sporting capital due to the role it has played in the development of Australian sport, the range and quality of its sporting events and venues, and its high rates of spectatorship and participation. The city is also home to 27 professional sports teams competing at the national level, the most of any Australian city. Melbourne's sporting reputation was recognised in 2016 when, after being ranked as the world's top sports city three times biennially, the Ultimate Sports City Awards in Switzerland named it 'Sports City of the Decade'.
The city has hosted a number of major international sporting events, most notably the 1956 Summer Olympics
The 1956 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVI Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, from 22 November to 8 December 1956, with the exception of the equestrian events, wh ...
, the first Olympic Games held outside Europe and the United States. Melbourne also hosted the 2006 Commonwealth Games, will host the 2026 Commonwealth Games along with a number a number of regional areas of Victoria, and is home to several major annual international events, including the Australian Open, the first of the four Grand Slam tennis tournaments. First held in 1861 and declared a public holiday for all Melburnians in 1873, the Melbourne Cup is the world's richest handicap horse race, and is known as "the race that stops a nation". The Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship ...
Australian Grand Prix has been held at the Albert Park Circuit since 1996.
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
was one of the first sports to become organised in Melbourne with the Melbourne Cricket Club forming within three years of settlement. The club manages one of the world's largest stadiums, the 100,000 capacity Melbourne Cricket Ground (MCG). Established in 1853, the MCG is notable for hosting the first Test match and the first One Day International, played between Australia and England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
in 1877 and 1971, respectively. It is also the home of the National Sports Museum, and serves as the home ground of the Victoria cricket team. At Twenty20
Twenty20 (T20) is a shortened game format of cricket. At the professional level, it was introduced by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB) in 2003 for the county cricket, inter-county competition. In a Twenty20 game, the two teams have ...
level, the Melbourne Stars and Melbourne Renegades compete in the Big Bash League.
Australian rules football, Australia's most popular spectator sport, traces its origins to matches played in parklands next to the MCG in 1858. Its first laws were codified the following year by the Melbourne Football Club, also a founding member, in 1896, of the Australian Football League (AFL), the sport's elite professional competition. Headquartered at Docklands Stadium, the AFL fields a further eight Melbourne-based clubs: Carlton, Collingwood Collingwood, meaning "wood of disputed ownership", may refer to:
Educational institutions
* Collingwood College, Victoria, an Australian state Prep to Year 12 school
* Collingwood College, Durham, college of Durham University, England
* Collingw ...
, Essendon, Hawthorn, North Melbourne, Richmond, St Kilda, and the Western Bulldogs
The Western Bulldogs are a professional Australian rules football team that competes in the Australian Football League (AFL), the sport's premier competition.
Founded in 1877 as the Footscray Football Club, and based in West Footscray in the ...
. The city hosts up to five AFL matches per round during the home and away season, attracting an average of 40,000 spectators per game. The AFL Grand Final, traditionally held at the MCG, is the highest attended club championship event in the world.
In soccer, Melbourne is represented in the A-League by Melbourne Victory, Melbourne City FC and Western United FC. The rugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as just rugby league and sometimes football, footy, rugby or league, is a full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular field measuring 68 metres (75 yards) wide and 112 ...
team Melbourne Storm plays in the National Rugby League
The National Rugby League (NRL) is an Australasian rugby league club competition which contains clubs from New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, the Australian Capital Territory and New Zealand. The NRL formed in 1998 as a joint partnership ...
, and in rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a Contact sport#Terminology, close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the Comparison of rugby league and rugby union, two codes of ru ...
, the Melbourne Rebels and Melbourne Rising
The Melbourne Rising is an Australian rugby union team based in Melbourne that competes in the National Rugby Championship (NRC). The team represents the rugby community in Victoria and is organised and managed by Rugby Victoria with the ...
compete in the Super Rugby and National Rugby Championship competitions, respectively. North American sports have also gained popularity in Melbourne: basketball sides South East Melbourne Phoenix and Melbourne United play in the NBL; Melbourne Ice
The Melbourne Ice is an Australian semi-professional ice hockey team from Melbourne, Victoria, based at the Icehouse in the Docklands precinct of central Melbourne. Founded in 2000, the Ice have been a member of the Australian Ice Hockey Lea ...
and Melbourne Mustangs
The Melbourne Mustangs (formally ''Mustangs IHC'') is an Australian semi-professional ice hockey team from Melbourne, Victoria. Formed in 2010, the Mustangs have been a member of the Australian Ice Hockey League (AIHL) since 2011. The Mustangs ...
play in the Australian Ice Hockey League; and Melbourne Aces plays in the Australian Baseball League. Rowing also forms part of Melbourne's sporting identity, with a number of clubs located on the Yarra River, out of which many Australian Olympians trained.
Economy
 Melbourne has a highly diversified economy with particular strengths in finance, manufacturing, research, IT, education, logistics, transportation and tourism. Melbourne houses the headquarters of many of Australia's largest corporations, including five of the ten largest in the country (based on revenue), and five of the largest seven in the country (based on market capitalisation)
Melbourne has a highly diversified economy with particular strengths in finance, manufacturing, research, IT, education, logistics, transportation and tourism. Melbourne houses the headquarters of many of Australia's largest corporations, including five of the ten largest in the country (based on revenue), and five of the largest seven in the country (based on market capitalisation) ANZ
ANZ may refer to:
People
* Anz (musician), a British DJ and electronic musician
Banks
* ANZ (bank), Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited, the fourth-largest bank in Australia
** ANZ Bank New Zealand, the largest bank in New Zealand
* ...
, BHP, the National Australia Bank, CSL and Telstra
Telstra Group Limited is an Australian telecommunications company that builds and operates telecommunications networks and markets voice, mobile, internet access, pay television and other products and services. It is a member of the S&P/ASX ...
, as well as such representative bodies and think tanks as the Business Council of Australia and the Australian Council of Trade Unions. Melbourne's suburbs also have the head offices of Coles Group (owner of Coles Supermarkets
Coles Supermarkets Australia Pty Ltd, trading as Coles, is an Australian supermarket, retail and consumer services chain, headquartered in Melbourne as part of the Coles Group.
Founded in 1914 in Collingwood by George Coles, Coles operate ...
) and Wesfarmers companies Bunnings
Bunnings Group Limited, trading as Bunnings Warehouse or Bunnings, is an Australian household hardware chain. The chain has been owned by Wesfarmers since 1994, and has stores in Australia and New Zealand.
Bunnings was founded in Perth, West ...
, Target, K-Mart and Officeworks. The city is home to Australia's second busiest seaport
A port is a maritime law, maritime facility comprising one or more Wharf, wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge Affreightment, cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can a ...
, after Port Botany in Sydney. Melbourne Airport
Melbourne Airport , colloquially known as Tullamarine Airport, is the primary airport serving the city of Melbourne, and the second busiest airport in Australia. It opened in 1970 to replace the nearby Essendon Airport. Melbourne Airport is ...
provides an entry point for national and international visitors, and is Australia's second busiest airport.
Melbourne is also an important financial centre. In the 2022 Global Financial Centres Index, Melbourne was ranked as having the 32nd most competitive financial centre in the world. Two of the big four Big Four or Big 4 may refer to:
Groups of companies
* Big Four accounting firms: Deloitte, Ernst & Young, KPMG, PwC
* Big Four (airlines) in the U.S. in the 20th century: American, Eastern, TWA, United
* Big Four (banking), several groupings ...
banks, the ANZ and National Australia Bank, are headquartered in Melbourne. The city has carved out a niche as Australia's leading centre for superannuation (pension) funds, with 40% of the total, and 65% of industry super-funds including the AU$109 billion-dollar Federal Government Future Fund
The Future Fund is an independently managed sovereign wealth fund established in 2006 to strengthen the Australian Government's long-term financial position by making provision for unfunded superannuation liabilities for politicians and other p ...
. The city was rated 41st within the top 50 financial cities as surveyed by the MasterCard Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index (2008), second only to Sydney (12th) in Australia. Melbourne is Australia's second-largest industrial centre.
 It is the Australian base for a number of significant manufacturers including Boeing Australia, truck-makers Kenworth and Iveco, Cadbury as well as Alstom and Jayco, among many others. It is also home to a wide variety of other manufacturers, ranging from petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals to fashion garments, paper manufacturing and food processing. The south-eastern suburb of Scoresby is home to Nintendo's Australian headquarters. The city also has a research and development hub for Ford Australia, as well as a global design studio and technical centre for General Motors and Toyota Australia respectively.
CSL, one of the world's top five biotech companies, and
It is the Australian base for a number of significant manufacturers including Boeing Australia, truck-makers Kenworth and Iveco, Cadbury as well as Alstom and Jayco, among many others. It is also home to a wide variety of other manufacturers, ranging from petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals to fashion garments, paper manufacturing and food processing. The south-eastern suburb of Scoresby is home to Nintendo's Australian headquarters. The city also has a research and development hub for Ford Australia, as well as a global design studio and technical centre for General Motors and Toyota Australia respectively.
CSL, one of the world's top five biotech companies, and Sigma Pharmaceuticals
Sigma Healthcare Limited is an Australian, ASX-listed company SX:SIG with a focus on the pharmacy industry. In addition to its wholesale and distribution arms, Sigma Healthcare also owns Australian retail pharmacy brands: Amcal and Discount Dr ...
have their headquarters in Melbourne. The two are the largest listed Australian pharmaceutical companies. Melbourne has an important ICT
ICT may refer to:
Sciences and technology
* Information and communications technology
* Image Constraint Token, in video processing
* Immunochromatographic test, a rapid immunoassay used to detect diseases such as anthrax
* In-circuit test, in ...
industry that employs over 60,000 people (one third of Australia's ICT workforce), with a turnover of AU$19.8 billion and export revenues of AU615 million. In addition, tourism also plays an important role in Melbourne's economy, with about 7.6 million domestic visitors and 1.88 million international visitors in 2004. Melbourne has been attracting an increasing share of domestic and international conference markets. Construction began in February 2006 of an AU$1 billion 5000-seat international convention centre, Hilton Hotel
Hilton Hotels & Resorts (formerly known as Hilton Hotels) is a global brand of full-service hotels and resorts and the flagship brand of American multinational hospitality company Hilton.
The original company was founded by Conrad Hilton. As ...
and commercial precinct adjacent to the Melbourne Convention & Exhibition Centre to link development along the Yarra River
The Yarra River or historically, the Yarra Yarra River, ( Kulin languages: ''Berrern'', ''Birr-arrung'', ''Bay-ray-rung'', ''Birarang'', ''Birrarung'', and ''Wongete'') is a perennial river in south-central Victoria, Australia.
The lower ...
with the Southbank precinct and multibillion-dollar Docklands redevelopment.
The Economist Intelligence Unit ranks Melbourne as the fourth most expensive city in the world to live in according to its worldwide cost of living index in 2013.
Tourism
 Melbourne is the second most visited city in Australia and the seventy-third most visited city in the world. In 2018, 10.8 million domestic overnight tourists and 2.9 million international overnight tourists visited Melbourne. The most visited attractions are Federation Square, Queen Victoria Market,
Melbourne is the second most visited city in Australia and the seventy-third most visited city in the world. In 2018, 10.8 million domestic overnight tourists and 2.9 million international overnight tourists visited Melbourne. The most visited attractions are Federation Square, Queen Victoria Market, Crown Casino
Crown Melbourne (also referred to as Crown Casino and Entertainment Complex) is a casino and resort located on the south bank of the Yarra River, in Melbourne, Australia. Crown Casino is a unit of Crown Limited, and the first casino of the n ...
, Southbank, Melbourne Zoo, Melbourne Aquarium, Docklands, National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Museum, Melbourne Observation Deck
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung–Taungurung language, Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the St ...
, Arts Centre Melbourne, and the Melbourne Cricket Ground. Luna Park, a theme park modelled on New York's Coney Island
Coney Island is a peninsular neighborhood and entertainment area in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Brighton Beach and Manhattan Beach to its east, Lower New York Bay to th ...
and Seattle's Luna Park, is also a popular destination for visitors. In its annual survey of readers, the Condé Nast Traveler magazine found that both Melbourne and Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
were considered the world's friendliest cities in 2014. The magazine highlighted the connection the city inhabitants have to public art and the many parks across the city. Its high liveability rankings make it one of the safest world cities for travellers.
Demographics
 According to the 2021 Australian Census, the population of the Greater Melbourne area was 4,917,750.
Although Victoria's net interstate migration has fluctuated, the population of the Melbourne statistical division has grown by about 70,000 people a year since 2005. Melbourne has now attracted the largest proportion of international overseas immigrants (48,000) finding it outpacing Sydney's international migrant intake on percentage, as well as having strong interstate migration from Sydney and other capitals due to more affordable housing and cost of living.
In recent years, Melton, Wyndham and Casey, part of the Melbourne statistical division, have recorded the highest growth rate of all local government areas in Australia. Melbourne is on track to overtake Sydney in population between 2028 and 2030.
After a trend of declining population density since World War II, the city has seen increased density in the inner and western suburbs, aided in part by Victorian Government planning, such as Postcode 3000 and Melbourne 2030, which have aimed to curtail urban sprawl. , the CBD is the most densely populated area in Australia with more than 19,000 residents per square kilometre, and the inner city suburbs of Carlton, South Yarra, Fitzroy and
According to the 2021 Australian Census, the population of the Greater Melbourne area was 4,917,750.
Although Victoria's net interstate migration has fluctuated, the population of the Melbourne statistical division has grown by about 70,000 people a year since 2005. Melbourne has now attracted the largest proportion of international overseas immigrants (48,000) finding it outpacing Sydney's international migrant intake on percentage, as well as having strong interstate migration from Sydney and other capitals due to more affordable housing and cost of living.
In recent years, Melton, Wyndham and Casey, part of the Melbourne statistical division, have recorded the highest growth rate of all local government areas in Australia. Melbourne is on track to overtake Sydney in population between 2028 and 2030.
After a trend of declining population density since World War II, the city has seen increased density in the inner and western suburbs, aided in part by Victorian Government planning, such as Postcode 3000 and Melbourne 2030, which have aimed to curtail urban sprawl. , the CBD is the most densely populated area in Australia with more than 19,000 residents per square kilometre, and the inner city suburbs of Carlton, South Yarra, Fitzroy and Collingwood Collingwood, meaning "wood of disputed ownership", may refer to:
Educational institutions
* Collingwood College, Victoria, an Australian state Prep to Year 12 school
* Collingwood College, Durham, college of Durham University, England
* Collingw ...
make up Victoria's top five.
Ancestry and immigration
At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated ancestries were: At the 2021 census, 0.7% of Melbourne's population identified as being Indigenous —Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the T ...
and Torres Strait Islanders
Torres Strait Islanders () are the Indigenous Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal people of the rest of Australia, they are often grou ...
.
Melbourne has the 10th largest immigrant population among world metropolitan areas. In Greater Melbourne at the 2021 census, 59.9% of residents were born in Australia. The other most common countries of birth were India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
(4.9%), Mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater Chin ...
(3.4%), England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
(2.7%), Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
(1.8%) and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
(1.7%).
Language
At the time of the 2021 census, 61.1% of Melburnians speak only English at home.Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
(4.3%), Vietnamese (2.3%), Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(2.1%), Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
(2%), and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
(1.8%) were the most common foreign languages spoken at home by residents of Melbourne.
Religion
 Melbourne has a wide range of religious faiths, the most widely held of which is
Melbourne has a wide range of religious faiths, the most widely held of which is Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
. This is signified by the city's two large cathedrals— St Patrick's (Roman Catholic), and St Paul's (Anglican). Both were built in the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edward ...
and are of considerable heritage significance as major landmarks of the city. In recent years, Greater Melbourne's irreligious community has grown to be one of the largest in Australia.
According to the 2021 Census, persons stating that they had no religion constituted 36.9% of the population. Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
was the most popular religious affiliation at 40.1%. The largest Christian denominations were Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(20.8%) and Anglicanism (5.5%). The most popular non-Christian religious affiliations were Islam (5.3%), Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
(4.1%), Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
(3.9%), Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit= Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fr ...
(1.7%) and Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
(0.9%).
Over 180,000 Muslims live in Melbourne. Muslim religious life in Melbourne is centred on about 25 mosques and a number of prayer rooms at university campuses, workplaces and other venues.
, Melbourne had the largest population of Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the lon ...
in Australia. The city was also home to the largest number of Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
survivors of any Australian city, indeed the highest per capita outside Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
itself. Reflecting this community, Melbourne has a number of Jewish cultural, religious and educational institutions, including over 40 synagogues and 7 full-time parochial day schools, along with a local Jewish newspaper.
Education
 Some of Australia's most prominent and well-known schools are based in Melbourne. Of the top twenty high schools in Australia according to th
Some of Australia's most prominent and well-known schools are based in Melbourne. Of the top twenty high schools in Australia according to thMy Choice Schools Ranking
five are in Melbourne. There has also been a rapid increase in the number of International students studying in the city. Furthermore, Melbourne was ranked the world's fourth top university city in 2008 after London, Boston and Tokyo in a poll commissioned by
the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology
RMIT University, officially the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology,, section 4(b) is a public research university in Melbourne, Australia.
Founded in 1887 by Francis Ormond, RMIT began as a night school offering classes in art, scienc ...
. Eight public universities operate in Melbourne: the University of Melbourne
The University of Melbourne is a public research university located in Melbourne, Australia. Founded in 1853, it is Australia's second oldest university and the oldest in Victoria. Its main campus is located in Parkville, an inner suburb n ...
, Monash University
Monash University () is a public research university based in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Named for prominent World War I general Sir John Monash, it was founded in 1958 and is the second oldest university in the state. The university h ...
, Swinburne University of Technology, Deakin University
Deakin University is a public university in Victoria, Australia. Founded in 1974, the university was named after Alfred Deakin, the second Prime Minister of Australia.
Its main campuses are in Melbourne's Burwood suburb, Geelong Waurn P ...
, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT University), La Trobe University
La Trobe University is a public university, public research university based in Melbourne, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia. Its main campus is located in the suburb of Bundoora, Victoria, Bundoora. The university was established in 196 ...
, Australian Catholic University (ACU) and Victoria University (VU).
Melbourne universities have campuses all over Australia and some internationally. Swinburne University and Monash University have campuses in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, while Monash has a research centre based in Prato, Italy. The University of Melbourne, the second oldest university in Australia, was ranked first among Australian universities in the 2016 THES
''Thes'' is a genus of beetles in the family Latridiidae, containing the following species:Rucker, Wolfgang H. (2010). �Checklist Latridiidae & Merophysiinae of the World. Checklist Latridiidae & Merophysiinae of the World.�� . Retrieved on 15 ...
international rankings. In 2018 Times Higher Education Supplement ranked the University of Melbourne the 32nd best university in the world which is higher than the rankings in 2016 and 2017, Monash University was ranked 80th best. Both are members of the Group of Eight
The Group of Eight (G8) was an inter-governmental political forum from 1997 until 2014. It had formed from incorporating Russia into the Group of Seven, or G7, and returned to its previous name after Russia left in 2014.
The forum originate ...
, a coalition of leading Australian tertiary institutions offering comprehensive and leading education.
As of 2017 RMIT University is ranked 17th in the world in art & design, and 28th in architecture. The Swinburne University of Technology, based in the inner-city Melbourne suburb of Hawthorn, was as of 2014 ranked 76th–100th in the world for physics by the Academic Ranking of World Universities. Deakin University
Deakin University is a public university in Victoria, Australia. Founded in 1974, the university was named after Alfred Deakin, the second Prime Minister of Australia.
Its main campuses are in Melbourne's Burwood suburb, Geelong Waurn P ...
maintains two major campuses in Melbourne and Geelong, and is the third largest university in Victoria. In recent years, the number of international students at Melbourne's universities has risen rapidly, a result of an increasing number of places being made available for them. Education in Melbourne is overseen by the Victorian Department of Education (DET), whose role is to 'provide policy and planning advice for the delivery of education'.
Media
Three daily newspapers serve Melbourne: the '' Herald Sun'' (tabloid), ''The Age
''The Age'' is a daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, that has been published since 1854. Owned and published by Nine Entertainment, ''The Age'' primarily serves Victoria, but copies also sell in Tasmania, the Australian Capital Territo ...
'' (compact) and ''The Australian
''The Australian'', with its Saturday edition, ''The Weekend Australian'', is a broadsheet newspaper published by News Corp Australia since 14 July 1964.Bruns, Axel. "3.1. The active audience: Transforming journalism from gatekeeping to gatewat ...
'' (national broadsheet). There are six primary free-to-air digital television
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advanc ...
stations operating in Greater Melbourne and Geelong: ABC Victoria, ( ABV), SBS Victoria (SBS), Seven Melbourne ( HSV), Nine Melbourne ( GTV), Ten
Ten, TEN or 10 may refer to:
* 10, an even natural number following 9 and preceding 11
* one of the years 10 BC, AD 10, 1910 and 2010
* October, the tenth month of the year
Places
* Mount Ten, in Vietnam
* Tongren Fenghuang Airport (IATA code ...
Melbourne (ATV
ATV may refer to:
Broadcasting
* Amateur television
*Analog television
Television stations and companies
* Ràdio i Televisió d'Andorra
* ATV (Armenia)
* ATV (Aruba), NBC affiliate
* ATV (Australian TV station), Melbourne
* ATV (Austria)
* AT ...
), C31 Melbourne (MGV) – community television. Each station (excluding C31) broadcasts a primary channel and several multichannels. Some digital media companies such as Broadsheet are based in and primarily serve Melbourne.
Many AM and FM radio stations broadcast to greater Melbourne. These include public (i.e., state-owned ABC and SBS) and community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, villag ...
stations. Many commercial stations are networked-owned: Nova Entertainment owns Nova 100 and Smooth; ARN controls Gold 104.3
Gold 104.3 (call sign: 3KKZ) is a radio station broadcasting in Melbourne, Australia. Gold 104.3 is part of the Pure Gold Network (which itself is a part of the Australian Radio Network) and broadcasts on the 104.3 MHz frequency.
History
3K ...
and KIIS 101.1; and Southern Cross Austereo runs both Fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelv ...
and Triple M. Youth stations include ABC Triple J
Triple J (stylised in all lowercase) is a government-funded, national Australian radio station intended to appeal to listeners of alternative music, which began broadcasting in January 1975. The station also places a greater emphasis on broad ...
and youth-run SYN. Triple J, and community stations PBS and Triple R, strive to play under represented music. JOY 94.9 caters for gay, lesbian, bisexual and transgender audiences. 3MBS
3MBS was the first FM (frequency modulation) radio station in Victoria, Australia, and began transmitting to Melbourne and surrounding areas on 1 July 1975. Since then it has operated successfully as a non-profit community-based organisation broa ...
and ABC Classic FM play classical music. Light FM is a contemporary Christian station. AM stations include ABC: 774, Radio National, and News Radio
All-news radio is a radio format devoted entirely to the discussion and broadcast of news.
All-news radio is available in both local and syndicated forms, and is carried on both major US satellite radio networks. All-news stations can run the ...
; also Nine Entertainment affiliates 3AW ( talk) and Magic (easy listening
Easy listening (including mood music) is a popular music genre and radio format that was most popular during the 1950s to 1970s. It is related to middle-of-the-road (MOR) music and encompasses instrumental recordings of standards, hit songs, ...
). SEN 1116 broadcasts sports coverage. Melbourne has many community run stations that serve alternative interests, such as 3CR and 3KND (Indigenous). Many suburbs have low powered community run stations serving local audiences.
Governance
 The governance of Melbourne is split between the government of Victoria and the 27 cities and four shires that make up the metropolitan area. There is no ceremonial or political head of Melbourne, but the Lord Mayor of the City of Melbourne often fulfils such a role as a first among equals.
The local councils are responsible for providing the functions set out in the ''Local Government Act'' 1989 such as
The governance of Melbourne is split between the government of Victoria and the 27 cities and four shires that make up the metropolitan area. There is no ceremonial or political head of Melbourne, but the Lord Mayor of the City of Melbourne often fulfils such a role as a first among equals.
The local councils are responsible for providing the functions set out in the ''Local Government Act'' 1989 such as urban planning
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water ...
and waste management. Most other government services are provided or regulated by the Victorian state government, which governs from Parliament House
Parliament House may refer to:
Australia
* Parliament House, Canberra, Parliament of Australia
* Parliament House, Adelaide, Parliament of South Australia
* Parliament House, Brisbane, Parliament of Queensland
* Parliament House, Darwin, Parliame ...
in Spring Street. These include services associated with local government in other countries and include public transport, main roads, traffic control, policing, education above preschool level, health and planning of major infrastructure projects.
Infrastructure
Health
 The Victorian Government's Department of Health oversees about 30 public hospitals in the Melbourne metropolitan region and 13 health services organisations.
Major medical,
The Victorian Government's Department of Health oversees about 30 public hospitals in the Melbourne metropolitan region and 13 health services organisations.
Major medical, neuroscience
Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, an ...
and biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
research institutions located in Melbourne include the St. Vincent's Institute of Medical Research
St Vincent's Institute of Medical Research (SVI) is an independent Australian medical research institute located in , Melbourne, Victoria. The Institute conducts medical research into the cause, prevention and treatment of diseases that are commo ...
, Australian Stem Cell Centre, the Burnet Institute
The Burnet Institute is an Australian medical institute that combines medical research in the laboratory and the field, with public health action to address major health issues affecting disadvantaged communities in Australia, and internationa ...
, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute, Victorian Institute of Chemical Sciences, Brain Research Institute, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
The Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, also known as the Peter MacCallum Cancer Institute and commonly abbreviated as Peter Mac, is an Australian oncology research institute, cancer treatment and professional oncologist training centre located in M ...
, the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, and the Melbourne Neuropsychiatry Centre
The Melbourne Neuropsychiatry Centre (MNC), is a joint centre of University of Melbourne and Melbourne Health in Australia. It brings together clinical and research teams at Sunshine and Royal Melbourne Hospitals, with a dedicated brain imaging a ...
. The headquarters of Australian pharmaceutical company CSL Limited is located in the Melbourne Biomedical Precinct in Parkville, which contains over 40 biomedical and research institutions. It was announced in 2021 that a new Australian Institute for Infectious Disease would also be built in Parkville.
Other institutions include the Howard Florey Institute, the Murdoch Childrens Research Institute
The Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) is an Australian paediatric medical research institute located in Melbourne, Victoria, affiliated with the Royal Children's Hospital and the University of Melbourne. The institute has six rese ...
, Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute
The Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute, commonly known as the Baker Institute, is an Australian independent medical research research institute, institute headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria (Australia), Victoria. Established in 1926, the instit ...
, and the Australian Synchrotron
ANSTO's Australian Synchrotron is a 3 GeV national synchrotron radiation facility located in Clayton, in the south-eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, which opened in 2007.
ANSTO's Australian Synchrotron is a light source facility (in co ...
. Many of these institutions are associated with and located near to universities. Melbourne is also home to the Royal Children's Hospital and the Monash Children's Hospital.
Among Australian capital cities, Melbourne ties with Canberra in first place for the highest male life expectancy (80.0 years) and ranks second behind Perth in female life expectancy (84.1 years).
Roads
 Like many Australian cities, Melbourne has a high dependency on the automobile for transport, particularly in the outer suburban areas where the largest number of cars are bought, with a total of 3.6 million private vehicles using of road, and one of the highest lengths of road per capita in the world. The early 20th century saw an increase in popularity of automobiles, resulting in large-scale suburban expansion and a tendency towards the development of
Like many Australian cities, Melbourne has a high dependency on the automobile for transport, particularly in the outer suburban areas where the largest number of cars are bought, with a total of 3.6 million private vehicles using of road, and one of the highest lengths of road per capita in the world. The early 20th century saw an increase in popularity of automobiles, resulting in large-scale suburban expansion and a tendency towards the development of urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
—like all Australian cities, inhabitants would live in the suburbs and commute to the city for work. By the mid-1950s there was just under 200 passenger vehicles per 1000 people, and by 2013 there was 600 passenger vehicles per 1000 people.
The road network in Victoria is managed by Vicroads, as part of the Department of Transport, who oversee the planning and integration. Maintenance of roads is undertaken by different bodies, depending on the road. Local roads are maintained by local councils, while secondary and main roads are the responsibility of Vicroads. Major national freeways and roads integral to national trade are overseen by the Federal Government.
Today Melbourne has an extensive network of freeways and arterial roadways. These are used by private vehicles, including road freight vehicles, as well as road-based public transport modes like buses and taxis. Major highways feeding into the city include the Eastern Freeway, Monash Freeway and West Gate Freeway (which spans the large West Gate Bridge). Other freeways include the Calder Freeway
Calder Highway is a rural highway in Australia, linking Mildura and the Victoria/New South Wales border to Bendigo, in North Central Victoria. South of Bendigo, where the former highway has been upgraded to freeway-standard, Calder Freeway l ...
, Tullamarine Freeway, which is the main airport link, and the Hume Freeway, which connects Melbourne to Canberra and Sydney. Melbourne's middle suburbs are connected via an orbital freeway, the M80 Ring Road
The M80 Ring Road (also known as simply the Ring Road or by the name of its constituent parts: Western Ring Road and Metropolitan Ring Road) is a currently incomplete urban freeway ring road around Melbourne, Australia. This article will deal ...
, which will be completed when the North East Link
The North East Link is an under construction 26–kilometre tolled motorway scheme in Melbourne, Australia. Its stated objective is to connect the Metropolitan Ring Road at Greensborough with the Eastern Freeway at Bulleen, where the freewa ...
opens.
Out of Melbourne’s 20 declared freeways open or under construction, 6 are electronic toll roads. This includes the M1 and M2 CityLink (which includes the large Bolte Bridge
The Bolte Bridge is a large twin cantilever road bridge in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. The Bolte Bridge carries a total of eight lanes of traffic – four lanes northbound and four lanes southbound. While officially only 490 metres in leng ...
), Eastlink, North East Link, and the West Gate Tunnel. Apart from Eastlink which is owned and operated by ConnectEast
ConnectEast is an Australian limited corporation responsible for the finance, design, construction and operation of Melbourne's EastLink tollway project.
Previously listed in the Australian Stock Exchange as The ConnectEast Group (stock symbol ...
, the toll roads in Melbourne are run by Transurban. In Melbourne, tollways have blue and yellow signage compared to the green signs used for free roads.
Public transport
Melbourne has an integrated public transport system based around extensive train, tram, bus and taxi systems. Flinders Street station was the world's busiest passenger station in 1927 and Melbourne's tram network overtook Sydney's to become the world's largest in the 1940s. From the 1940s, public transport use in Melbourne declined due to a rapid expansion of the road and freeway network, with the largest declines in tram and bus usage. This decline quickened in the early 1990s due to large public transport service cuts. The operations of Melbourne's public transport system was privatised in 1999 through a franchising model, with operational responsibilities for the train, tram and bus networks licensed to private companies. After 1996 there was a rapid increase in public transport patronage due to growth in employment in central Melbourne, with the mode share for commuters increasing to 14.8% and 8.4% of all trips. A target of 20% public transport mode share for Melbourne by 2020 was set by the state government in 2006. Since 2006 public transport patronage has grown by over 20% and a number of projects have commenced aimed at expanding public transport usage.Train
 The Melbourne metropolitan rail network dates back to the 1850s gold rush era, and today consists of 222 suburban stations on 16 lines which radiate from the City Loop, a mostly-underground subway system around the CBD. Flinders Street station, one of Australia's busiest rail hubs, serves the entire network, and remains a prominent Melbourne landmark and meeting place. The city has rail connections with regional Victorian cities run by V/Line, as well as direct interstate rail services which depart from Melbourne's other major rail terminus, Southern Cross station, in Docklands. '' The Overland'' to
The Melbourne metropolitan rail network dates back to the 1850s gold rush era, and today consists of 222 suburban stations on 16 lines which radiate from the City Loop, a mostly-underground subway system around the CBD. Flinders Street station, one of Australia's busiest rail hubs, serves the entire network, and remains a prominent Melbourne landmark and meeting place. The city has rail connections with regional Victorian cities run by V/Line, as well as direct interstate rail services which depart from Melbourne's other major rail terminus, Southern Cross station, in Docklands. '' The Overland'' to Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater A ...
departs twice a week, while the XPT to Sydney departs twice daily. In the 2017–2018 financial year, the Melbourne metropolitan rail network recorded 240.9 million passenger trips, the highest ridership in its history. Many rail lines, along with dedicated lines and rail yards
A rail yard, railway yard, railroad yard (US) or simply yard, is a series of Track (rail transport), tracks in a rail network for storing, sorting, or loading and unloading rail vehicles and locomotives. Yards have many tracks in parallel for kee ...
, are also used for freight.
An assortment of new railways are under construction in Melbourne. A new heavy rail corridor through the inner city, the Metro Tunnel
The Metro Tunnel (previously known during planning as the Melbourne Metro Rail Project) is a metropolitan rail infrastructure project currently under construction in Melbourne, Australia. It includes the construction of twin 9-kilometre rail tun ...
, is set to open by 2025, and will reduce congestion on the City Loop. The ongoing Level Crossing Removal Project is grade separating much of the network, and rebuilding many older stations. In June 2022, early works commenced on the Suburban Rail Loop, a 90-kilometre underground automated orbital loop line through Melbourne's middle suburbs. An airport rail connection is currently in the planning phase.
Tram
 Melbourne's tram network dates from the 1880s land boom and, as of 2021, consists of of double track, 475 trams, 25 routes, and 1,763 tram stops, making it the largest in the world. In 2017–2018, 206.3 million passenger trips were made by tram. Around 75 per cent of Melbourne's tram network shares road space with other vehicles, while the rest of the network is separated or are light rail routes. Melbourne's trams are recognised as iconic cultural assets and a tourist attraction. Heritage trams operate on the free City Circle route around the CBD. Trams are free within the central city Free Tram Zone and run 24-hours on weekends.
Melbourne's tram network dates from the 1880s land boom and, as of 2021, consists of of double track, 475 trams, 25 routes, and 1,763 tram stops, making it the largest in the world. In 2017–2018, 206.3 million passenger trips were made by tram. Around 75 per cent of Melbourne's tram network shares road space with other vehicles, while the rest of the network is separated or are light rail routes. Melbourne's trams are recognised as iconic cultural assets and a tourist attraction. Heritage trams operate on the free City Circle route around the CBD. Trams are free within the central city Free Tram Zone and run 24-hours on weekends.
Bus
Melbourne's bus network consists of almost 300 routes which mainly service the outer suburbs and fill the gaps in the network between rail and tram services. 127.6 million passenger trips were recorded on Melbourne's buses in 2013–2014, an increase of 10.2 percent on the previous year.Airports
Melbourne has four airports.Melbourne Airport
Melbourne Airport , colloquially known as Tullamarine Airport, is the primary airport serving the city of Melbourne, and the second busiest airport in Australia. It opened in 1970 to replace the nearby Essendon Airport. Melbourne Airport is ...
, at Tullamarine, is the city's main international and domestic gateway and second busiest in Australia. The airport, which comprises four terminals, is home base for passenger airline Jetstar and cargo airlines Australian airExpress and Toll Priority, and is a major hub for Qantas
Qantas Airways Limited ( ) is the flag carrier of Australia and the country's largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations. It is the List of airlines by foundation date, world's third-oldest airline sti ...
and Virgin Australia. Avalon Airport
Avalon Airport is an international airport located in Avalon in the City of Greater Geelong in Victoria, Australia. While located outside the Melbourne metropolitan area, it is the second busiest of the four airports serving the state capit ...
, located between Melbourne and Geelong, is a secondary hub of Jetstar. It is also used as a freight and maintenance facility. Buses and taxis are the only forms of public transport to and from the city's main airports. A rail link to Tullamarine is planned to open by 2029. Air Ambulance facilities are available for domestic and international transportation of patients. Melbourne also has a significant general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation service ...
airport, Moorabbin Airport in the city's southeast that also handles a small number of passenger flights. Essendon Airport, which was once the city's main airport also handles passenger flights, general aviation and some cargo flights.
Water transport
Ship transport is an important component of Melbourne's transport system. The Port of Melbourne is Australia's largest container and general cargo port and also its busiest. The port handled two million shipping containers in a 12-month period during 2007, making it one of the top five ports in the Southern Hemisphere. Station Pier on Port Phillip Bay is the main passenger ship terminal with cruise ships and theSpirit of Tasmania
TT-Line Company Pty Ltd, better known by its trading name Spirit of Tasmania is a company which has been operating ferries from mainland Australia to Tasmania since July 1985. The company was separated from the Tasmanian Government's Depar ...
ferries which cross Bass Strait to Devonport, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
docking there. Ferries and water taxis run from berths along the Yarra River as far upstream as South Yarra and across Port Phillip Bay.
Utilities
 Water storage and supply for Melbourne is managed by Melbourne Water, which is owned by the Victorian Government. The organisation is also responsible for management of sewerage and the major water catchments in the region as well as the
Water storage and supply for Melbourne is managed by Melbourne Water, which is owned by the Victorian Government. The organisation is also responsible for management of sewerage and the major water catchments in the region as well as the Wonthaggi desalination plant
The Victorian Desalination Plant (also referred to as the Victorian Desalination Project or Wonthaggi desalination plant) is a water desalination plant in Dalyston, on the Bass Coast in southern Victoria, Australia. The project was announced by ...
and North–South Pipeline
The North–South Pipeline, also known as the Sugarloaf Pipeline, is a water pipeline in Central Victoria, Australia, northeast of Melbourne that is part of Victoria's water system, acting as a link between Melbourne's water grid and the Murray- ...
. Water is stored in a series of reservoirs located within and outside the Greater Melbourne area. The largest dam, the Thomson River Dam, located in the Victorian Alps, is capable of holding around 60% of Melbourne's water capacity, while smaller dams such as the Upper Yarra Dam, Yan Yean Reservoir, and the Cardinia Reservoir carry secondary supplies.
Gas is provided by three distribution companies:
*AusNet Services
AusNet Services (previously SP AusNet) is an Australian energy delivery services business, owning and operating more than $11 billion of electricity and gas network assets. It is a privately held, and was formerly listed on the Australian Securi ...
, which provides gas from Melbourne's inner western suburbs to southwestern Victoria.
* Multinet Gas, which provides gas from Melbourne's inner eastern suburbs to eastern Victoria. (owned by SP AusNet after acquisition, but continuing to trade under the brand name Multinet Gas)
* Australian Gas Networks, which provides gas from Melbourne's inner northern suburbs to northern Victoria, as well as the majority of southeastern Victoria.
Electricity is provided by five distribution companies:
* Citipower, which provides power to Melbourne's CBD, and some inner suburbs
* Powercor, which provides power to the outer western suburbs, as well as all of western Victoria (Citipower and Powercor are owned by the same entity)
* Jemena, which provides power to the northern and inner western suburbs
* United Energy, which provides power to the inner eastern and southeastern suburbs, and the Mornington Peninsula
*AusNet Services
AusNet Services (previously SP AusNet) is an Australian energy delivery services business, owning and operating more than $11 billion of electricity and gas network assets. It is a privately held, and was formerly listed on the Australian Securi ...
, which provides power to the outer eastern suburbs and all of the north and east of Victoria.
Numerous telecommunications companies provide Melbourne with terrestrial and mobile telecommunications services and wireless internet service
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the telecommunication, transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided transmission med ...
s and at least since 2016 Melbourne offers a free public WiFi which allows for up to 250 MB per device in some areas of the city.
Crime
 Melbourne has a moderately low crime rate, ranking 18th for Personal Security and 9th in the overall Safe City Index in ''
Melbourne has a moderately low crime rate, ranking 18th for Personal Security and 9th in the overall Safe City Index in ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econ ...
'' 2021 Safe Cities Index, placing it in the second best category of "high safety" level. Reports of crime in Victoria fell by 13 per cent in 2021 to its lowest in three years, with 5,358.1 cases per 100,000 people and a total of 496,260 offences. Melbourne's city centre (CBD) reported the highest incident rate of local government areas in Victoria, followed by Latrobe and Yarra.
See also
* Naval Base Melbourne * Australian Grand PrixLists
* List of Melbourne suburbs *List of museums in Melbourne
Melbourne, Australia, is home to a large number of cultural institutions, museums and historic sites, some of which are known worldwide:
See also
*Culture of Melbourne
* List of museums in Victoria (Australia)
References
{{MuseumVictoria
...
* List of people from Melbourne
*List of songs about Melbourne
The music of Australia and most particularly the rock, pop, Hip hop and indie rock music of Australia has had a long fascination with the local environment be it urban or rural. This is a list of songs which mention or are about Melbourne the ca ...
* Local government in Victoria
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Official tourist board site of Melbourne
* {{Authority control 1835 establishments in Australia 1835 establishments in Oceania Australian capital cities Cities in Victoria (Australia) Coastal cities in Australia Former national capitals Metropolitan areas of Australia Populated places established in 1835 Port cities in Victoria (Australia) Regions of Victoria (Australia)