Heroin And Your Veins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a
 In the
In the
 Little research has been focused on the
Little research has been focused on the
 Heroin is classified as a hard drug in terms of
Heroin is classified as a hard drug in terms of
 Users report an intense rush, an acute transcendent state of
Users report an intense rush, an acute transcendent state of
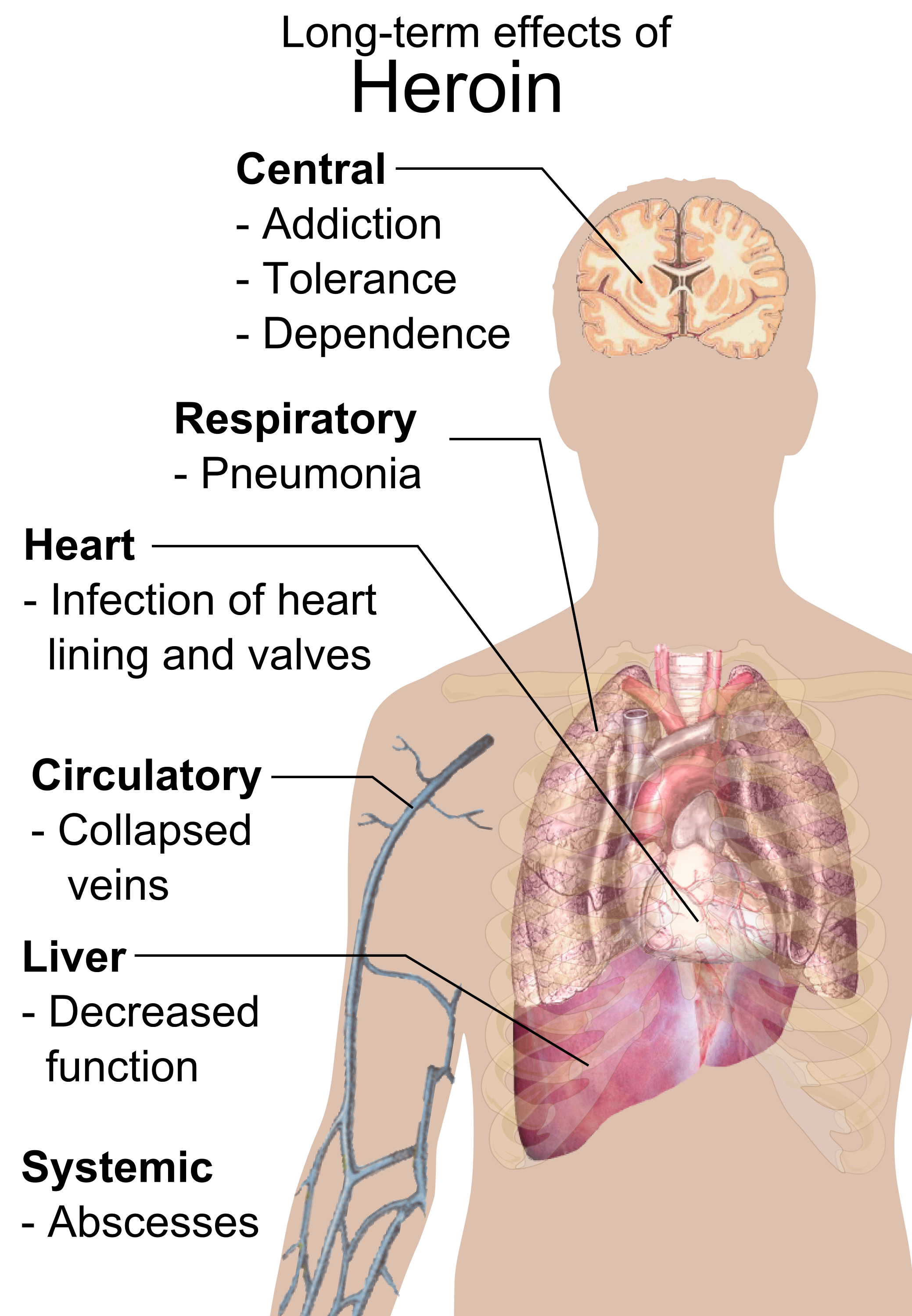 Repeated heroin use changes the physical structure and physiology of the brain, creating long-term imbalances in neuronal and hormonal systems that are not easily reversed. Studies have shown some deterioration of the brain's white matter due to heroin use, which may affect decision-making abilities, the ability to regulate behavior, and responses to stressful situations. Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance occurs when more and more of the drug is required to achieve the same effects. With
Repeated heroin use changes the physical structure and physiology of the brain, creating long-term imbalances in neuronal and hormonal systems that are not easily reversed. Studies have shown some deterioration of the brain's white matter due to heroin use, which may affect decision-making abilities, the ability to regulate behavior, and responses to stressful situations. Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance occurs when more and more of the drug is required to achieve the same effects. With
 The withdrawal syndrome from heroin may begin within as little as two hours of discontinuation of the drug; however, this time frame can fluctuate with the degree of tolerance as well as the amount of the last consumed dose, and more typically begins within 6–24 hours after cessation. Symptoms may include
The withdrawal syndrome from heroin may begin within as little as two hours of discontinuation of the drug; however, this time frame can fluctuate with the degree of tolerance as well as the amount of the last consumed dose, and more typically begins within 6–24 hours after cessation. Symptoms may include

 When taken orally, heroin undergoes extensive
When taken orally, heroin undergoes extensive
 Diamorphine is produced from
Diamorphine is produced from
 Wright's invention did not lead to any further developments, and diamorphine became popular only after it was independently re-synthesized 23 years later by chemist
Wright's invention did not lead to any further developments, and diamorphine became popular only after it was independently re-synthesized 23 years later by chemist
 At present, opium poppies are mostly grown in Afghanistan (), and in Southeast Asia, especially in the region known as the
At present, opium poppies are mostly grown in Afghanistan (), and in Southeast Asia, especially in the region known as the

 The origins of the present international illegal heroin trade can be traced back to laws passed in many countries in the early 1900s that closely regulated the production and sale of opium and its derivatives including heroin. At first, heroin flowed from countries where it was still legal into countries where it was no longer legal. By the mid-1920s, heroin production had been made illegal in many parts of the world. An illegal trade developed at that time between heroin labs in China (mostly in Shanghai and Tianjin) and other nations. The weakness of the government in China and conditions of civil war enabled heroin production to take root there. Chinese
The origins of the present international illegal heroin trade can be traced back to laws passed in many countries in the early 1900s that closely regulated the production and sale of opium and its derivatives including heroin. At first, heroin flowed from countries where it was still legal into countries where it was no longer legal. By the mid-1920s, heroin production had been made illegal in many parts of the world. An illegal trade developed at that time between heroin labs in China (mostly in Shanghai and Tianjin) and other nations. The weakness of the government in China and conditions of civil war enabled heroin production to take root there. Chinese
 The
The
'When Heroin Was Legal'
BBC
Drug-poisoning Deaths Involving Heroin: United States, 2000–2013
Heroin Trafficking in the United States
(2019) US
morphinan
Morphinan is the prototype chemical structure of a large chemical class of psychoactive drugs, consisting of opiate analgesics, cough suppressants, and dissociative hallucinogens, among others. Typical examples include compounds such as morphine, ...
opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
substance synthesized from the dried latex of the opium poppy
''Papaver somniferum'', commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable orname ...
; it is mainly used as a recreational drug
Recreational drug use is the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness, either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an Sub ...
for its euphoric
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and danci ...
effects. Heroin is used medically in several countries to relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy
Opioid agonist therapy (OAT) is a treatment in which prescribed opioid agonists are given to patients who live with opioid use disorder (OUD). In the case of methadone maintenance treatment (MMT), methadone is used to treat dependence on heroin ...
. Medical-grade
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose – either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a diagnostic one. The corresponding f ...
diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative ...
. Various white and brown powders sold illegally around the world as ''heroin'' are routinely diluted with cutting agent
Cutting is the separation or opening of a physical object, into two or more portions, through the application of an acutely directed force.
Implements commonly used for cutting are the knife and saw, or in medicine and science the scalpel and m ...
s. Black tar heroin
Black tar heroin, also known as black dragon, is a form of heroin that is sticky like tar or hard like coal. Its dark color is the result of crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Despite its name, black tar heroin can also be da ...
is a variable admixture of morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM
6-Monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM, 6-acetylmorphine, or 6-AM) is an opioid and also one of three active metabolites of heroin (diacetylmorphine), the others being morphine and the much less active 3-monoacetylmorphine (3-MAM).
Pharmacology
6-MAM oc ...
(6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
during clandestine production of street heroin.
Heroin is typically injected, usually into a vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
, but it can also be snorted, smoked, or inhaled. In a clinical context, the route of administration is most commonly intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
; it may also be given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, as well as orally in the form of tablets. The onset of effects is usually rapid and lasts for a few hours.
Common side effects include respiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapni ...
(decreased breathing), dry mouth, drowsiness, impaired mental function, constipation, and addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
. Use by injection can also result in abscesses
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pres ...
, infected heart valves, blood-borne infections, and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
. After a history of long-term use, opioid withdrawal
Opioid withdrawal is a set of symptoms arising from the sudden cessation or reduction of opioids where previous usage has been heavy and prolonged. Signs and symptoms of withdrawal can include drug craving, anxiety, restless legs syndrome, naus ...
symptoms can begin within hours of the last use. When given by injection into a vein, heroin has two to three times the effect of a similar dose of morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
. It typically appears in the form of a white or brown powder.
Treatment of heroin addiction
Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a substance use disorder characterized by cravings for opioids, continued use despite physical and/or psychological deterioration, increased tolerance with use, and withdrawal symptoms after discontinuing opioids. ...
often includes behavioral therapy
Behaviour therapy or behavioural psychotherapy is a broad term referring to clinical psychotherapy that uses techniques derived from behaviourism and/or cognitive psychology. It looks at specific, learned behaviours and how the environment, or oth ...
and medications. Medications can include buprenorphine
Buprenorphine, sold under the brand name Subutex among others, is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection (intravenous a ...
, methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid used medically to treat chronic pain and opioid use disorder. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and opioid withdrawal sym ...
, or naltrexone
Naltrexone, sold under the brand name Revia among others, is a medication primarily used to manage alcohol use or opioid use disorder by reducing cravings and feelings of euphoria associated with substance use disorder. It has also been ...
. A heroin overdose may be treated with naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand name Narcan among others, is an opioid antagonist, a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. For example, it is used to restore breathing after an opioid overdose. Effects begin within two ...
. As of 2015, an estimated 17 million people use opiates non-medically, of which heroin is the most common, and opioid use resulted in 122,000 deaths; also, as of 2015, the total number of heroin users worldwide is believed to have increased in Africa, the Americas, and Asia since 2000. In the United States, approximately 1.6 percent of people have used heroin at some point. When people die from overdosing on a drug, the drug is usually an opioid and often heroin.
Heroin was first made by C. R. Alder Wright
Charles Romley Alder Wright FCS, FRS (7 September 1844 – 25 June 1894) was an English lecturer in chemistry and physics at St Mary's Hospital Medical School in London, England. He was a founder of the Royal Institute of Chemistry.
Alde ...
in 1874 from morphine, a natural product of the opium poppy
''Papaver somniferum'', commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable orname ...
. Internationally, heroin is controlled under Schedules I and IV of the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs
The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 (Single Convention, 1961 Convention, or C61) is an international treaty that controls activities (cultivation, production, supply, trade, transport) involving specific narcotic drugs and lays down a ...
, and it is generally illegal to make, possess, or sell without a license. About 448 tons of heroin were made in 2016. In 2015, Afghanistan produced about 66% of the world's opium. Illegal heroin is often mixed with other substances such as sugar, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
, quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
, or other opioids like fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medici ...
.
Uses
Recreational
Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
's original trade name of heroin is typically used in non-medical settings. It is used as a recreational drug for the euphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
it induces. Anthropologist
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
Michael Agar once described heroin as "the perfect whatever drug." Tolerance develops quickly, and increased doses are needed in order to achieve the same effects. Its popularity with recreational drug users, compared to morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
, reportedly stems from its perceived different effects.
Short-term addiction studies by the same researchers demonstrated that tolerance developed at a similar rate to both heroin and morphine. When compared to the opioids hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is a morphinan opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may b ...
, fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medici ...
, oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under the brand name Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended-release form) among others, is a semi-synthetic opioid used medically for the treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and is a commonly ...
, and pethidine
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a fully synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Ot ...
(meperidine), former addicts showed a strong preference for heroin and morphine, suggesting that heroin and morphine are particularly susceptible to misuse and causing dependence. Morphine and heroin were also much more likely to produce euphoria and other positive subjective effects when compared to these other opioids.
Medical uses
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, heroin is not accepted as medically useful.
Under the generic name diamorphine, heroin is prescribed
A prescription, often abbreviated or Rx, is a formal communication from physicians or other registered healthcare professionals to a pharmacist, authorizing them to dispense a specific prescription drug for a specific patient. Historically, ...
as a strong pain medication
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in so ...
in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, where it is administered via oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
, subcutaneous, intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles hav ...
, intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space (sin. ''intrathecal space'') so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is useful in several applic ...
, intranasal
Nasal administration, popularly known as snorting, is a route of administration in which drugs are insufflation (medicine), insufflated through the nose. It can be a form of either topical administration or systemic administration, as the drugs t ...
or intravenous routes. It may be prescribed for the treatment of acute pain, such as in severe physical trauma
Injury is physiology, physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether Injury in humans, in humans, Injury in animals, in other animals, or Injury in plants, in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanic ...
, myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
, post-surgical
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery ...
pain and chronic pain
Chronic pain is pain that persists or recurs for longer than 3 months.https://icd.who.int/browse/2025-01/mms/en#1581976053 It is also known as gradual burning pain, electrical pain, throbbing pain, and nauseating pain. This type of pain is in cont ...
, including end-stage terminal illness
Terminal illness or end-stage disease is a disease that cannot be cured or adequately treated and is expected to result in the death of the patient. This term is more commonly used for progressive diseases such as cancer, rather than fatal injur ...
es. In other countries it is more common to use morphine or other strong opioids in these situations. In 2004, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care.
As the national health technology assessment body of England, it is responsible for j ...
produced guidance on the management of caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because va ...
, which recommended the use of intrathecal or epidural
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, "upon" + '' dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians ...
diamorphine for post-operative pain relief
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and health care involving relief of pain (pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from acute and simple to chronic and challenging. Most physicians and other health professionals ...
. For women who have had intrathecal opioids, there should be a minimum hourly observation of respiratory rate, sedation and pain scores for at least 12 hours for diamorphine and 24 hours for morphine. Women should be offered diamorphine (0.3–0.4 mg intrathecally) for intra- and postoperative analgesia because it reduces the need for supplemental analgesia after a caesarean section. Epidural diamorphine (2.5–5 mg) is a suitable alternative.
Diamorphine continues to be widely used in palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
in the UK, where it is commonly given by the subcutaneous route, often via a syringe driver
A syringe driver, also known as a syringe pump, is a small infusion pump, used to gradually administer small amounts of fluid (with or without medication) to a patient or for use in chemical and biomedical research. Some syringe drivers can both ...
if patients cannot easily swallow morphine solution. The advantage of diamorphine over morphine is that diamorphine is more fat soluble and therefore more potent by injection, so smaller doses of it are needed for the same effect on pain. Both of these factors are advantageous if giving high doses of opioids via the subcutaneous route, which is often necessary for palliative care.
It is also used in the palliative management of bone fractures
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''c ...
and other trauma, especially in children. In the trauma context, it is primarily given by nose in hospital; although a prepared nasal spray is available. It has traditionally been made by the attending physician, generally from the same "dry" ampoules as used for injection. In children, Ayendi nasal spray is available at 720 micrograms and 1600 micrograms per 50 microlitres actuation of the spray, which may be preferable as a non-invasive alternative in pediatric care, avoiding the fear of injection in children.
Maintenance therapy
A number of European countries prescribe heroin for treatment ofheroin addiction
Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a substance use disorder characterized by cravings for opioids, continued use despite physical and/or psychological deterioration, increased tolerance with use, and withdrawal symptoms after discontinuing opioids. ...
. The initial Swiss HAT (heroin-assisted treatment
Heroin-assisted treatment (HAT), or diamorphine-assisted treatment, refers to a type of Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) where semi-synthetic heroin is prescribed to opioid addicts who do not benefit from, or cannot tolerate, treatment with on ...
) trial ("PROVE" study) was conducted as a prospective cohort study with some 1,000 participants in 18 treatment centers between 1994 and 1996, at the end of 2004, 1,200 patients were enrolled in HAT in 23 treatment centers across Switzerland. Diamorphine may be used as a maintenance drug to assist the treatment of opiate addiction, normally in long-term chronic intravenous (IV) heroin users. It is only prescribed following exhaustive efforts at treatment via other means. It is sometimes thought that heroin users can walk into a clinic and walk out with a prescription, but the process takes many weeks before a prescription for diamorphine is issued. Though this is somewhat controversial among proponents of a zero-tolerance
A zero-tolerance policy is one which imposes a punishment for every infraction of a stated rule.zero tolerance, n.' (under ''zero, n.''). The Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd Ed. 1989. Retrieved 10 November 2009. Italy, Japan, Singapore China, I ...
drug policy, it has proven superior to methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid used medically to treat chronic pain and opioid use disorder. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and opioid withdrawal sym ...
in improving the social and health situations of addicts.
The UK Department of Health's Rolleston Committee
In 1924, following concerns about the treatment of addicts by doctors, James Smith Whitaker suggested to the Home Office who suggested to the Ministry of Health Departmental Committee on Morphine and Heroin Addiction be formed under the chairman ...
Report in 1926 established the British approach to diamorphine prescription to users, which was maintained for the next 40 years: dealers were prosecuted, but doctors could prescribe diamorphine to users when withdrawing. In 1964, the Brain Committee
The Interdepartmental Committee on Drug Addiction, commonly called the Brain Committee after its chairman Sir Russell Brain, was created by the Home Office in 1958 to consider issues related to drugs and drug addiction in the United Kingdom. The ...
recommended that only selected approved doctors working at approved specialized centres be allowed to prescribe diamorphine and cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
to users. The law was made more restrictive in 1968. Beginning in the 1970s, the emphasis shifted to abstinence and the use of methadone; currently, only a small number of users in the UK are prescribed diamorphine.
In 1994, Switzerland began a trial diamorphine maintenance program for users that had failed multiple withdrawal programs. The aim of this program was to maintain the health of the user by avoiding medical problems stemming from the illicit use of diamorphine. The first trial in 1994 involved 340 users, although enrollment was later expanded to 1000, based on the apparent success of the program. The trials proved diamorphine maintenance to be superior to other forms of treatment in improving the social and health situation for this group of patients. It has also been shown to save money, despite high treatment expenses, as it significantly reduces costs incurred by trials, incarceration, health interventions and delinquency
Delinquent may refer to:
* Delinquent (royalist), Royalists whose estates had been seized during the English Civil War
* A juvenile delinquent
Juvenile delinquency, also known as juvenile offending, is the act of participating in unlawful b ...
. Patients appear twice daily at a treatment center, where they inject their dose of diamorphine under the supervision of medical staff. They are required to contribute about 450 Swiss francs per month to the treatment costs. A national referendum in November 2008 showed 68% of voters supported the plan, introducing diamorphine prescription into federal law. The previous trials were based on time-limited executive ordinances. The success of the Swiss trials led German, Dutch, and Canadian cities to try out their own diamorphine prescription programs. Some Australian cities (such as Sydney) have instituted legal diamorphine supervised injecting centers, in line with other wider harm minimization programs.
Since January 2009, Denmark has prescribed diamorphine to a few addicts who have tried methadone and buprenorphine
Buprenorphine, sold under the brand name Subutex among others, is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection (intravenous a ...
without success. Beginning in February 2010, addicts in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
and Odense
Odense ( , , ) is the third largest city in Denmark (after Copenhagen and Aarhus) and the largest city on the island of Funen. As of 1 January 2025, the city proper had a population of 185,480 while Odense Municipality had a population of 210, ...
became eligible to receive free diamorphine. Later in 2010, other cities including Århus
Aarhus (, , ; officially spelled Århus from 1948 until 1 January 2011) is the second-largest city in Denmark and the seat of Aarhus municipality, Aarhus Municipality. It is located on the eastern shore of Jutland in the Kattegat sea and app ...
and Esbjerg
Esbjerg (, ) is a seaport city and seat of Esbjerg Municipality on the west coast of the Jutland peninsula in southwest Denmark. By road, it is west of Kolding and southwest of Aarhus. With an urban area, urban population of 71,554 (1 January ...
joined the scheme. It was estimated that around 230 addicts would be able to receive free diamorphine.
However, Danish addicts would only be able to inject heroin according to the policy set by Danish National Board of Health. Of the estimated 1500 drug users who did not benefit from the then-current oral substitution treatment, approximately 900 would not be in the target group for treatment with injectable diamorphine, either because of "massive multiple drug abuse of non-opioids" or "not wanting treatment with injectable diamorphine".
In July 2009, the German Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet (assembly), Diet") is the lower house of the Germany, German Federalism in Germany, federal parliament. It is the only constitutional body of the federation directly elected by the German people. The Bundestag wa ...
passed a law allowing diamorphine prescription as a standard treatment for addicts; a large-scale trial of diamorphine prescription had been authorized in the country in 2002.
On 26 August 2016, Health Canada
Health Canada (HC; )Health Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Health (). is the Structure of the Canadian federal government#Departments, with subsidiary units, department of the Gove ...
issued regulations amending prior regulations it had issued under the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controll ...
; the "New Classes of Practitioners Regulations", the "Narcotic Control Regulations", and the "Food and Drug Regulations", to allow doctors to prescribe diamorphine to people who have a severe opioid addiction who have not responded to other treatments. The prescription heroin can be accessed by doctors through Health Canada
Health Canada (HC; )Health Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Health (). is the Structure of the Canadian federal government#Departments, with subsidiary units, department of the Gove ...
's Special Access Programme (SAP) for "emergency access to drugs for patients with serious or life-threatening conditions when conventional treatments have failed, are unsuitable, or are unavailable."
Routes of administration
The onset of heroin's effects depends upon theroute of administration
In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a medication, drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance ...
. Smoking is the fastest route of drug administration, although intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
results in a quicker rise in blood concentration. These are followed by suppository
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver pharmaceutical drug, medications by insertion into a body orifice (any opening in the body), where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, eac ...
(anal or vaginal insertion), insufflation
In religious and magical practice, insufflation and exsufflation are ritual acts of blowing, breathing, hissing, or puffing that signify variously expulsion or renunciation of evil or of the devil (the Evil One), or infilling or blessing with go ...
(snorting), and ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms, inge ...
(swallowing).
A 2002 study suggests that a fast onset of action increases the reinforcing effects of addictive drugs. Ingestion does not produce a rush as a forerunner to the high experienced with the use of heroin, which is most pronounced with intravenous use. While the onset of the rush induced by injection can occur in as little as a few seconds, the oral route of administration requires approximately half an hour before the high sets in. Thus, with both higher the dosage of heroin used and faster the route of administration used, the higher the potential risk for psychological dependence
Psychological dependence is a cognitive disorder and a form of dependence that is characterized by emotional–motivational withdrawal symptoms upon cessation of prolonged drug use or certain repetitive behaviors. Consistent and frequent expos ...
/addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
.
Large doses of heroin can cause fatal respiratory depression, and the drug has been used for suicide or as a murder weapon. The serial killer Harold Shipman
Harold Frederick Shipman (14 January 1946 – 13 January 2004), known to acquaintances as Fred Shipman, was an English doctor in general practice and serial killer. He is considered to be one of the most prolific serial killers in modern ...
used diamorphine on his victims, and the subsequent Shipman Inquiry led to a tightening of the regulations surrounding the storage, prescribing and destruction of controlled drugs in the UK.
Because significant tolerance to respiratory depression develops quickly with continued use and is lost just as quickly during withdrawal, it is often difficult to determine whether a heroin lethal overdose was accidental, suicide or homicide. Examples include the overdose deaths of Sid Vicious
Simon John Ritchie (10 May 1957 – 2 February 1979), better known by his stage name Sid Vicious, was an English musician, best known as the second bassist for the punk rock band Sex Pistols. After his death in 1979 at the age of 21, he remai ...
, Janis Joplin
Janis Lyn Joplin (January 19, 1943 – October 4, 1970) was an American singer and songwriter. One of the most iconic and successful Rock music, rock performers of her era, she was noted for her powerful mezzo-soprano vocals and her "electric" ...
, Tim Buckley
Timothy Charles Buckley III (February 14, 1947 – June 29, 1975) was an American musician. He began his career based in folk rock, but subsequently experimented with genres such as psychedelia, jazz, the avant-garde, and funk paired with his ...
, Hillel Slovak
Hillel Slovak (; April 13, 1962 – June 25, 1988) was an Israeli-American musician, best known as the founding guitarist of the Los Angeles rock band Red Hot Chili Peppers, with whom he recorded two albums. His guitar work was rooted in fun ...
, Layne Staley
Layne Thomas Staley (born Layne Rutherford Staley; August 22, 1967 – April 5, 2002) was an American singer-songwriter and musician. He was the original lead vocalist of Alice in Chains, which rose to international fame in the early 1990s as p ...
, Bradley Nowell
Bradley James Nowell (February 22, 1968 – May 25, 1996) was an American musician and the lead singer of the band Sublime.
Born and raised in Belmont Shore, Long Beach, California, Nowell developed an interest in music at a young age. Nowell ...
, Ted Binion
Lonnie Theodore "Ted" Binion (November 28, 1943 – September 17, 1998), was an American gambling executive and the son of Las Vegas casino magnate Benny Binion, owner of Binion's Horseshoe casino. Ted Binion was involved in multiple criminal cas ...
, and River Phoenix
River Jude Phoenix (; August 23, 1970 – October 31, 1993) was an American actor. He was known as a teen actor before taking on leading roles in critically acclaimed films and becoming one of the most preeminent talents of his generation. Pho ...
.
By mouth
Use of heroin by mouth is less common than other methods of administration, mainly because there is little to no "rush", and the effects are less potent. Heroin is entirely converted tomorphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
by means of first-pass metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism at a specific location in the body which leads to a reduction in the concentration of the active drug before it reaches the ...
, resulting in deacetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
when ingested. Heroin's oral bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
is both dose-dependent (as is morphine's) and significantly higher than oral use of morphine itself, reaching up to 64.2% for high doses and 45.6% for low doses; opiate-naive users showed far less absorption of the drug at low doses, having bioavailabilities of only up to 22.9%. The maximum plasma concentration of morphine following oral administration of heroin was around twice as much as that of oral morphine.
Injection
Injection
Injection or injected may refer to:
Science and technology
* Injective function, a mathematical function mapping distinct arguments to distinct values
* Injection (medicine), insertion of liquid into the body with a syringe
* Injection, in broadca ...
, also known as "slamming", "banging", "shooting up", "digging" or "mainlining", is a popular method which carries relatively greater risks than other methods of administration. Heroin base (commonly found in Europe), when prepared for injection, will only dissolve in water when mixed with an acid (most commonly citric acid powder or lemon juice) and heated. Heroin in the east-coast United States is most commonly found in the hydrochloride salt form, requiring just water (and no heat) to dissolve. Users tend to initially inject in the easily accessible arm veins, but as these veins collapse over time, users resort to more dangerous areas of the body, such as the femoral vein
In the human body, the femoral vein is the vein that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It is a deep vein that begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) as the continuation of the popliteal v ...
in the groin. Some medical professionals have expressed concern over this route of administration, as they suspect that it can lead to deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enl ...
.
Intravenous users can use a variable single dose range using a hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek Language, Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug admini ...
. The dose of heroin used for recreational purposes is dependent on the frequency and level of use.
As with the injection of any drug, if a group of users share a common needle without sterilization procedures, blood-borne diseases, such as HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
or hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
, can be transmitted.
The use of a common dispenser for water for the use in the preparation of the injection, as well as the sharing of spoons and filters can also cause the spread of blood-borne diseases. Many countries now supply small sterile spoons and filters for single use in order to prevent the spread of disease.
Smoking
Smoking heroin refers to vaporizing it to inhale the resulting fumes, rather than burning and inhaling the smoke. It is commonly smoked in glass pipes made from glassblownPyrex
Pyrex (trademarked as ''PYREX'' and ''pyrex'') is a brand introduced by Corning Inc. in 1915, initially for a line of clear, low-thermal-expansion borosilicate glass used for laboratory glassware and kitchenware. It was later expanded in the 1 ...
tubes and light bulbs. Heroin may be smoked from aluminium foil that is heated by a flame underneath it, with the resulting smoke inhaled through a tube of rolled up foil, a method also known as "chasing the dragon
"Chasing the dragon" (CTD) (), or "foily" in Australian English, refers to inhaling the vapor of a powdered psychoactive drug off a heated sheet of aluminium foil. The moving vapor is chased after with a tube (often rolled foil) through which th ...
".
Insufflation
Another popular route to intake heroin isinsufflation
In religious and magical practice, insufflation and exsufflation are ritual acts of blowing, breathing, hissing, or puffing that signify variously expulsion or renunciation of evil or of the devil (the Evil One), or infilling or blessing with go ...
(snorting), where a user crushes the heroin into a fine powder and then gently inhales it (sometimes with a straw or a rolled-up banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
, as with cocaine) into the nose, where heroin is absorbed through the soft tissue in the mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
of the sinus cavity
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
and straight into the bloodstream. This method of administration redirects first-pass metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism at a specific location in the body which leads to a reduction in the concentration of the active drug before it reaches the ...
, with a quicker onset and higher bioavailability than oral administration, though the duration of action is shortened. This method is sometimes preferred by users who do not want to prepare and administer heroin for injection or smoking but still want to experience a fast onset. Snorting heroin becomes an often unwanted route, once a user begins to inject the drug. The user may still get high on the drug from snorting, and experience a nod, but will not get a rush. A "rush" is caused by a large amount of heroin entering the body at once. When the drug is taken in through the nose, the user does not get the rush because the drug is absorbed slowly rather than instantly.
Heroin for pain has been mixed with sterile water on site by the attending physician, and administered using a syringe with a nebulizer tip. Heroin may be used for fractures, burns, finger-tip injuries, suturing, and wound re-dressing, but is inappropriate in head injuries.
Suppository
 Little research has been focused on the
Little research has been focused on the suppository
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver pharmaceutical drug, medications by insertion into a body orifice (any opening in the body), where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, eac ...
(anal insertion), also known as "plugging". These methods of administration are commonly carried out using an oral syringe. Heroin can be dissolved and withdrawn into an oral syringe which may then be lubricated and inserted into the anus or vagina before the plunger is pushed. The rectum or the vaginal canal is where the majority of the drug would likely be taken up, through the membranes lining their walls.
Adverse effects
drug harmfulness
Recreational drug use is the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness, either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an i ...
. Like most opioids
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
, unadulterated heroin may lead to adverse effects
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term complic ...
. The purity of street heroin varies greatly, leading to overdoses when the purity is higher than expected.
Short-term effects
 Users report an intense rush, an acute transcendent state of
Users report an intense rush, an acute transcendent state of euphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
, which occurs while diamorphine is being metabolized into 6-monoacetylmorphine
6-Monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM, 6-acetylmorphine, or 6-AM) is an opioid and also one of three active metabolites of heroin (diacetylmorphine), the others being morphine and the much less active 3-monoacetylmorphine (3-MAM).
Pharmacology
6-MAM oc ...
(6-MAM) and morphine in the brain. Some believe that heroin produces more euphoria than other opioids; one possible explanation is the presence of 6-monoacetylmorphine, a metabolite unique to heroin – although a more likely explanation is the rapidity of onset. While other opioids of recreational use produce only morphine, heroin also leaves 6-MAM, also a psycho-active metabolite
An active metabolite, or pharmacologically active metabolite is a biologically active metabolite of a xenobiotic substance, such as a drug or environmental chemical. Active metabolites may produce therapeutic effects, as well as harmful effects. ...
.
However, this perception is not supported by the results of clinical studies comparing the physiological and subjective effects of injected heroin and morphine in individuals formerly addicted to opioids; these subjects showed no preference for one drug over the other. Equipotent injected doses had comparable action courses, with no difference in subjects' self-rated feelings of euphoria, ambition, nervousness, relaxation, drowsiness, or sleepiness.
The rush is usually accompanied by a warm flushing of the skin, dry mouth, and a heavy feeling in the extremities. Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, and severe itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
ing may also occur. After the initial effects, users usually will be drowsy for several hours; mental function is clouded; heart function slows, and breathing is also severely slowed, sometimes enough to be life-threatening. Slowed breathing can also lead to coma and permanent brain damage
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common ...
. Heroin use has also been associated with myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
.
Long-term effects
 Repeated heroin use changes the physical structure and physiology of the brain, creating long-term imbalances in neuronal and hormonal systems that are not easily reversed. Studies have shown some deterioration of the brain's white matter due to heroin use, which may affect decision-making abilities, the ability to regulate behavior, and responses to stressful situations. Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance occurs when more and more of the drug is required to achieve the same effects. With
Repeated heroin use changes the physical structure and physiology of the brain, creating long-term imbalances in neuronal and hormonal systems that are not easily reversed. Studies have shown some deterioration of the brain's white matter due to heroin use, which may affect decision-making abilities, the ability to regulate behavior, and responses to stressful situations. Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance occurs when more and more of the drug is required to achieve the same effects. With physical dependence
Physical dependence is a physical condition caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug, in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms. Physical dependence can develop from low-dose therapeutic use of certa ...
, the body adapts to the presence of the drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
, and withdrawal symptoms occur if use is reduced abruptly.
Injection
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
use of heroin (and any other substance) with needles and syringes or other related equipment may lead to:
* Contracting blood-borne pathogens
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
such as HIV and hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
via the sharing of needles
* Contracting bacterial or fungal endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
and possibly venous sclerosis
* Abscesses
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pres ...
* Poisoning from contaminants
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
Within the scie ...
added to "cut
Cut or CUT may refer to:
Common uses
* The act of cutting, the separation of an object into two through acutely directed force
** A type of wound
** Cut (archaeology), a hole dug in the past
** Cut (clothing), the style or shape of a garment
** ...
" or dilute heroin
* Decreased kidney function (nephropathy), although it is not currently known if this is because of adulterants or infectious diseases
Smoking
Inhaling heroin appears to rarely lead totoxic leukoencephalopathy
Toxic leukoencephalopathy is a rare condition that is characterized by progressive damage (-pathy) to white matter (-leuko-) in the brain (-encephalo-), particularly myelin, due to causes such as exposure to substance use, environmental toxins, or ...
. There are also documented cases of both severe acute asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
and exacerbation of underlying asthma caused by heroin inhalation, potentially resulting in death.
Withdrawal
 The withdrawal syndrome from heroin may begin within as little as two hours of discontinuation of the drug; however, this time frame can fluctuate with the degree of tolerance as well as the amount of the last consumed dose, and more typically begins within 6–24 hours after cessation. Symptoms may include
The withdrawal syndrome from heroin may begin within as little as two hours of discontinuation of the drug; however, this time frame can fluctuate with the degree of tolerance as well as the amount of the last consumed dose, and more typically begins within 6–24 hours after cessation. Symptoms may include sweating
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the ...
, malaise
In medicine, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. It is considered a vague termdescribing the state of simply not feeling well. The word has exist ...
, anxiety, depression, akathisia
Akathisia (IPA: /æ.kə.ˈθɪ.si.ə/) is a movement disorder characterized by a subjective feeling of inner restlessness accompanied by mental distress and/or an inability to sit still. Usually, the legs are most prominently affected. Those a ...
, priapism
Priapism is a condition in which a penis remains erect for hours in the absence of stimulation or after stimulation has ended. There are three types: ischemic (low-flow), nonischemic (high-flow), and recurrent ischemic (intermittent). Most cases ...
, extra sensitivity of the genitals in females, general feeling of heaviness, excessive yawning or sneezing, rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea (American English), also spelled rhinorrhoea or rhinorrhœa (British English), or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is an extremely common condition. It is a common symptom of allergie ...
, insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low ene ...
, cold sweats, chills, severe muscle and bone aches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramps, watery eyes, fever, cramp-like pains, and involuntary spasms in the limbs (thought to be an origin of the term "kicking the habit").
Overdose

Heroin overdose
An opioid overdose is toxicity due to excessive consumption of opioids, such as morphine, codeine, heroin, fentanyl, tramadol, and methadone. This preventable pathology can be fatal if it leads to Hypoventilation, respiratory depression, a let ...
is usually treated with the opioid antagonist
An opioid antagonist, or opioid receptor antagonist, is a receptor antagonist that acts on one or more of the opioid receptors.
Naloxone and naltrexone are commonly used opioid antagonist drugs which are competitive antagonists that bind to ...
naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand name Narcan among others, is an opioid antagonist, a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. For example, it is used to restore breathing after an opioid overdose. Effects begin within two ...
. This reverses the effects of heroin and causes an immediate return of consciousness but may result in withdrawal symptoms. The half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of naloxone is shorter than some opioids, such that it may need to be given multiple times until the opioid has been metabolized by the body.
Between 2012 and 2015, heroin was the leading cause of drug-related deaths in the United States. Since then, fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medici ...
has been a more common cause of drug-related deaths.
Depending on drug interactions and numerous other factors, death from overdose can take anywhere from several minutes to several hours. Death usually occurs due to lack of oxygen resulting from the lack of breathing caused by the opioid. Heroin overdoses can occur because of an unexpected increase in the dose or purity or because of diminished opioid tolerance. However, many fatalities reported as overdoses are probably caused by interactions with other depressant
Depressants, also known as central nervous system depressants, or colloquially known as "downers", are drugs that lower neurotransmission levels, decrease the electrical activity of brain cells, or reduce arousal or stimulation in various ...
drugs such as alcohol or benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed t ...
s. Since heroin can cause nausea and vomiting, a significant number of deaths attributed to heroin overdose are caused by aspiration of vomit by an unconscious person. Some sources quote the median lethal dose
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for " lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a given substance. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose re ...
(for an average 75 kg opiate-naive individual) as being between 75 and 600 mg. Illicit heroin is of widely varying and unpredictable purity. This means that the user may prepare what they consider to be a moderate dose while actually taking far more than intended. Also, tolerance typically decreases after a period of abstinence. If this occurs and the user takes a dose comparable to their previous use, the user may experience drug effects that are much greater than expected, potentially resulting in an overdose. It has been speculated that an unknown portion of heroin-related deaths are the result of an overdose or allergic reaction to quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
, which may sometimes be used as a cutting agent.
Pharmacology
 When taken orally, heroin undergoes extensive
When taken orally, heroin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism at a specific location in the body which leads to a reduction in the concentration of the active drug before it reaches the ...
via deacetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
, making it a prodrug
A prodrug is a pharmacologically inactive medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be ...
for the systemic delivery of morphine. When the drug is injected, however, it avoids this first-pass effect, very rapidly crossing the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
because of the presence of the acetyl groups, which render it much more fat soluble than morphine itself. Once in the brain, it then is deacetylated variously into the inactive 3-monoacetylmorphine and the active 6-monoacetylmorphine
6-Monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM, 6-acetylmorphine, or 6-AM) is an opioid and also one of three active metabolites of heroin (diacetylmorphine), the others being morphine and the much less active 3-monoacetylmorphine (3-MAM).
Pharmacology
6-MAM oc ...
(6-MAM), and then to morphine, which bind to μ-opioid receptor
The μ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ(''mu'')-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical ...
s, resulting in the drug's euphoric, analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in s ...
(pain relief), and anxiolytic
An anxiolytic (; also antipanic or anti-anxiety agent) is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxie ...
(anti-anxiety) effects; heroin itself exhibits relatively low affinity for the μ receptor. Analgesia follows from the activation of the μ receptor G-protein coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large protein family, group of evoluti ...
, which indirectly hyperpolarizes the neuron, reducing the release of nociceptive
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular ...
neurotransmitters, and hence, causes analgesia and increased pain tolerance.
Unlike hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is a morphinan opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may b ...
and oxymorphone
Oxymorphone (sold under the brand names Numorphan and Opana among others) is a highly potent opioid analgesic indicated for treatment of severe pain. Pain relief after injection begins after about 5–10 minutes; after oral administration it ...
, however, administered intravenously, heroin creates a larger histamine release, similar to morphine, resulting in the feeling of a greater subjective "body high" to some, but also instances of pruritus
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
(itching) when they first start using.
Normally, GABA
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
, which is released from inhibitory neurones, inhibits the release of dopamine. Opiates, like heroin and morphine, decrease the inhibitory activity of such neurones. This causes increased release of dopamine in the brain which is the reason for euphoric and rewarding effects of heroin.
Both morphine and 6-MAM are μ-opioid agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
s that bind to receptors present throughout the brain, spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, and gut of all mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s. The μ-opioid receptor also binds endogenous opioid peptide
Opioid peptides or opiate peptides are peptides that bind to opioid receptors in the brain; opiates and opioids mimic the effect of these peptides. Such peptides may be produced by the body itself, for example endorphins. The effects of these p ...
s such as β-endorphin, leu-enkephalin
Leu-enkephalin is an endogenous opioid peptide neurotransmitter with the amino acid sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu that is found naturally in the brains of many animals, including humans. It is one of the two forms of enkephalin; the other is met ...
, and met-enkephalin
Met-enkephalin, also known as metenkefalin ( INN), sometimes referred to as opioid growth factor (OGF), is a naturally occurring, endogenous opioid peptide that has opioid effects of a relatively short duration. It is one of the two forms of enkep ...
. Repeated use of heroin results in a number of physiological changes, including an increase in the production of μ-opioid receptors (upregulation). These physiological alterations lead to tolerance and dependence, so that stopping heroin use results in uncomfortable symptoms including pain, anxiety, muscle spasms, and insomnia called the opioid withdrawal syndrome. Depending on usage it has an onset 4–24 hours after the last dose of heroin. Morphine also binds to δ- and κ-opioid receptor
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP for its ligand ketazocine, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''OPRK1'' gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four re ...
s.
There is also evidence that 6-MAM binds to a subtype of μ-opioid receptors that are also activated by the morphine metabolite morphine-6β-glucuronide but not morphine itself. The third subtype of third opioid type is the mu-3 receptor, which may be a commonality to other six-position monoesters of morphine. The contribution of these receptors to the overall pharmacology of heroin remains unknown.
A subclass of morphine derivatives, namely the 3,6 esters of morphine, with similar effects and uses, includes the clinically used strong analgesics nicomorphine
Nicomorphine (Vilan, Subellan, Gevilan, MorZet) is the 3,6-dinicotinate ester of morphine. It is a strong opioid agonist analgesic two to three times as potent as morphine with a side effect profile similar to that of dihydromorphine, morphine, a ...
(Vilan), and dipropanoylmorphine
Dipropanoylmorphine (dipropionylmorphine in US English) is an opiate derivative, the 3,6-dipropanoyl ester of morphine. It was developed in 1972 as an analgesic. It is rarely used in some countries for the relief of severe pain such as that caused ...
; there is also the latter's dihydromorphine
Dihydromorphine (Paramorfan, Paramorphan) is a semi-synthetic opioid structurally related to and derived from morphine. The 7,8-double bond in morphine is reduced to a single bond to get dihydromorphine. Dihydromorphine is a moderately strong a ...
analogue, diacetyldihydromorphine
Diacetyldihydromorphine (also known as Paralaudin, dihydroheroin, acetylmorphinol) is a potent opiate derivative developed in Germany in 1928 which is rarely used in some countries for the treatment of severe pain such as that caused by terminal ...
(Paralaudin). Two other 3,6 diesters of morphine invented in 1874–75 along with diamorphine, dibenzoylmorphine
Dibenzoylmorphine is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine. It was developed in the early 1900s after first having been synthesised in 1875 in the UK by the CR Alders Wright organisation at Bayer, along with various other esters of ...
and acetylpropionylmorphine
Acetylpropionylmorphine is an opiate analog that is an ester of morphine. It was developed in the early 1900s after first being synthesized in Great Britain in 1875 but shelved along with heroin and various other esters of morphine. Acetylpropion ...
, were made as substitutes after it was outlawed in 1925 and, therefore, sold as the first "designer drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. ...
" until they were outlawed by the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
in 1930.
Chemistry
acetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
of morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
derived from natural opium sources, generally using acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Commonly abbreviated , it is one the simplest organic acid anhydride, anhydrides of a carboxylic acid and is widely used in the production of c ...
.
The major metabolites of diamorphine, 6-MAM
6-Monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM, 6-acetylmorphine, or 6-AM) is an opioid and also one of three active metabolites of heroin (diacetylmorphine), the others being morphine and the much less active 3-monoacetylmorphine (3-MAM).
Pharmacology
6-MAM oc ...
, morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide
Morphine-3-glucuronide is a metabolite of morphine produced by UGT2B7. It is not active as an opioid agonist, but does have some action as a convulsant, which does not appear to be mediated through opioid receptors, but rather through interacti ...
, and morphine-6-glucuronide
Morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G) is a major active metabolite of morphine. M6G is formed from morphine by the enzyme UGT2B7. It has analgesic effects roughly half that of morphine. M6G can accumulate to toxic levels in kidney failure.
History of di ...
, may be quantitated in blood, plasma or urine to monitor for use, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning, or assist in a medicolegal death investigation. Most commercial opiate screening tests cross-react appreciably with these metabolites, as well as with other biotransformation products likely to be present following usage of street-grade diamorphine such as 6-Monoacetylcodeine and codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
. However, chromatographic
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system ( ...
techniques can easily distinguish and measure each of these substances. When interpreting the results of a test, it is important to consider the diamorphine usage history of the individual, since a chronic user can develop tolerance to doses that would incapacitate an opiate-naive individual, and the chronic user often has high baseline values of these metabolites in his system. Furthermore, some testing procedures employ a hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
step before quantitation that converts many of the metabolic products to morphine, yielding a result that may be 2 times larger than with a method that examines each product individually.
History
Theopium poppy
''Papaver somniferum'', commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable orname ...
was cultivated in lower Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
as long ago as 3400 BC. The chemical analysis of opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
in the 19th century revealed that most of its activity could be ascribed to the alkaloids
Alkaloids are a broad class of naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids.
Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms i ...
codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
and morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
.
Diamorphine was first synthesized in 1874 by C. R. Alder Wright
Charles Romley Alder Wright FCS, FRS (7 September 1844 – 25 June 1894) was an English lecturer in chemistry and physics at St Mary's Hospital Medical School in London, England. He was a founder of the Royal Institute of Chemistry.
Alde ...
, an English chemist working at St. Mary's Hospital Medical School in London who had been experimenting combining morphine with various acids. He boiled anhydrous morphine alkaloid with acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Commonly abbreviated , it is one the simplest organic acid anhydride, anhydrides of a carboxylic acid and is widely used in the production of c ...
for several hours and produced a more potent, acetylated
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite reacti ...
form of morphine which is now called ''diacetylmorphine'' or ''morphine diacetate''. He sent the compound to F. M. Pierce of Owens College in Manchester for analysis. Pierce told Wright:
 Wright's invention did not lead to any further developments, and diamorphine became popular only after it was independently re-synthesized 23 years later by chemist
Wright's invention did not lead to any further developments, and diamorphine became popular only after it was independently re-synthesized 23 years later by chemist Felix Hoffmann
Felix Hoffmann (21 January 1868 – 8 February 1946) was a German chemist notable for re-synthesising diamorphine (independently from C.R. Alder Wright who synthesized it 23 years earlier), which was popularized under the Bayer trade name ...
. Hoffmann was working at Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
pharmaceutical company in Elberfeld
Elberfeld is a municipal subdivision of the Germany, German city of Wuppertal; it was an independent town until 1929.
History
The first official mentioning of the geographic area on the banks of today's Wupper River as "''elverfelde''" was ...
, Germany, and his supervisor Heinrich Dreser
Heinrich Dreser (1 October 1860 – 21 December 1924) was a German chemist responsible for the aspirin and heroin projects at Bayer, Bayer AG. He was also a key figure in creating the widely used modern drug codeine. Dreser was born in Darmsta ...
instructed him to acetylate morphine with the objective of producing codeine, a constituent of the opium poppy that is pharmacologically similar to morphine but less potent and less addictive. Instead, the experiment produced an acetylated form of morphine one and a half to two times more potent than morphine itself. Hoffmann synthesized heroin on 21 August 1897, just eleven days after he had synthesized aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
.
The head of Bayer's research department reputedly coined the drug's new name of "heroin", based on the German ''heroisch'' which means "heroic, strong" (from the ancient Greek word "heros, ήρως"). Bayer scientists were not the first to make heroin, but their scientists discovered ways to make it, and Bayer led the commercialization of heroin.
Bayer marketed diacetylmorphine as an over-the-counter drug
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid pres ...
under the trademark name Heroin. It was developed chiefly as a morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
substitute for cough suppressants that did not have morphine's addictive side-effects. Morphine at the time was a popular recreational drug, and Bayer wished to find a similar but non-addictive substitute to market. However, contrary to Bayer's advertising as a "non-addictive morphine substitute", heroin would soon have one of the highest rates of addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
among its users.
From 1898 through to 1910, diamorphine was marketed under the trademark name Heroin as a non-addictive morphine substitute and cough suppressant. In the 11th edition of ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
'' (1910), the article on morphine states: "In the cough of phthisis minute doses f morphineare of service, but in this particular disease morphine is frequently better replaced by codeine or by heroin, which checks irritable coughs without the narcotism following upon the administration of morphine."
In the US, the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act
The Harrison Narcotics Tax Act (Ch. 1, ) was a United States federal law that regulated and taxed the production, importation, and distribution of opiates and coca products. The act was proposed by Representative Francis Burton Harrison of Ne ...
was passed in 1914 to control the sale and distribution of diacetylmorphine and other opioids, which allowed the drug to be prescribed and sold for medical purposes. In 1924, the United States Congress banned its sale, importation, or manufacture. It is now a Schedule I substance, which makes it illegal for non-medical use in signatory nations of the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs
The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 (Single Convention, 1961 Convention, or C61) is an international treaty that controls activities (cultivation, production, supply, trade, transport) involving specific narcotic drugs and lays down a ...
treaty, including the United States.
The Health Committee of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
banned diacetylmorphine in 1925, although it took more than three years for this to be implemented. In the meantime, the first designer drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. ...
, viz. 3,6 diesters and 6 monoesters of morphine and acetylated analogues of closely related drugs like hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is a morphinan opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may b ...
and dihydromorphine
Dihydromorphine (Paramorfan, Paramorphan) is a semi-synthetic opioid structurally related to and derived from morphine. The 7,8-double bond in morphine is reduced to a single bond to get dihydromorphine. Dihydromorphine is a moderately strong a ...
, were produced in massive quantities to fill the worldwide demand for diacetylmorphine—this continued until 1930 when the Committee banned diacetylmorphine analogues with no therapeutic advantage over drugs already in use, the first major legislation of this type.
Bayer lost some of its trademark rights to heroin (as well as aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
) under the 1919 Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
following the German defeat in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
.
Use of heroin by jazz musicians in particular was prevalent in the mid-twentieth century, including Billie Holiday
Billie Holiday (born Eleanora Fagan; April 7, 1915 – July 17, 1959) was an American jazz and swing music singer. Nicknamed "Lady Day" by her friend and music partner, Lester Young, Holiday made significant contributions to jazz music and pop ...
, saxophonists Charlie Parker
Charles Parker Jr. (August 29, 1920 – March 12, 1955), nicknamed "Bird" or "Yardbird", was an American jazz Saxophone, saxophonist, bandleader, and composer. Parker was a highly influential soloist and leading figure in the development of beb ...
and Art Pepper
Arthur Edward Pepper Jr. (September 1, 1925 – June 15, 1982) was an American jazz musician, most known as an alto saxophonist. He occasionally performed and recorded on tenor saxophone, clarinet (his first instrument) and bass clarinet. Active ...
, trumpeter and vocalist Chet Baker
Chesney Henry "Chet" Baker Jr. (December 23, 1929 – May 13, 1988) was an American jazz trumpeter and vocalist. He is known for major innovations in cool jazz that led him to be nicknamed the "Prince of Cool".
Baker earned much attention and ...
, guitarist Joe Pass
Joe Pass (born Joseph Anthony Jacobi Passalacqua; January 13, 1929 – May 23, 1994) was an American jazz guitarist. Although Pass recorded and performed live with pianist Oscar Peterson, composer Duke Ellington, and vocalist Ella Fitzgerald, he ...
and piano player/singer Ray Charles
Ray Charles Robinson (September 23, 1930 – June 10, 2004) was an American singer, songwriter, and pianist. He is regarded as one of the most iconic and influential musicians in history, and was often referred to by contemporaries as "The Gen ...
; a "staggering number of jazz musicians were addicts". It was also a problem with many rock musicians, particularly from the late 1960s through the 1990s. Pete Doherty
Peter Doherty (born 12 March 1979) is an English musician. He is best known for being co-frontman of the Libertines, which he formed with Carl Barât in 1997. His other musical projects are indie rock, indie bands Babyshambles and Peter Dohert ...
is also a self-confessed user of heroin. Nirvana
Nirvana, in the Indian religions (Jainism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Sikhism), is the concept of an individual's passions being extinguished as the ultimate state of salvation, release, or liberation from suffering ('' duḥkha'') and from the ...
lead singer Kurt Cobain
Kurt Donald Cobain (February 20, 1967 – ) was an American musician. He was the lead vocalist, guitarist, primary songwriter, and a founding member of the grunge band Nirvana (band), Nirvana. Through his angsty songwriting and anti-establis ...
's heroin addiction was well documented. Pantera
Pantera () is an American Heavy metal music, heavy metal band formed in Arlington, Texas in 1981 by the Abbott brothers (guitarist Dimebag Darrell and drummer Vinnie Paul), and currently composed of vocalist Phil Anselmo, bassist Rex Brown, an ...
frontman Phil Anselmo
Philip Hansen Anselmo (born June 30, 1968) is an American musician best known as the lead singer for groove metal band Pantera, southern metal supergroup Down (band), Down, and Hardcore punk, hardcore band Superjoint, amongst other musical proj ...
turned to heroin while touring during the 1990s to cope with his back pain. James Taylor
James Vernon Taylor (born March 12, 1948) is an American singer-songwriter and guitarist. A six-time Grammy Award winner, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2000.
Taylor achieved his breakthrough in 1970 with the single "Fi ...
, Taylor Hawkins
Oliver Taylor Hawkins (February 17, 1972 – March 25, 2022) was an American musician who was the drummer and a vocalist of the rock band Foo Fighters, sharing vocals with Dave Grohl. He joined the band in 1997, and remained the band's drummer ...
, Jimmy Page
James Patrick Page (born 9 January 1944) is an English musician and producer who achieved international success as the guitarist and founder of the Rock music, rock band Led Zeppelin.
Page began his career as a studio session musician in Lo ...
, John Lennon
John Winston Ono Lennon (born John Winston Lennon; 9 October 19408 December 1980) was an English singer-songwriter, musician and activist. He gained global fame as the founder, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of the Beatles. Lennon's ...
, Eric Clapton
Eric Patrick Clapton (born 1945) is an English Rock music, rock and blues guitarist, singer, and songwriter. He is regarded as one of the most successful and influential guitarists in rock music. Clapton ranked second in ''Rolling Stone''s l ...
, Johnny Winter
John Dawson Winter III (February 23, 1944 – July 16, 2014) was an American singer, guitarist, songwriter, and record producer. Winter was known for his high-energy blues rock albums, live performances, and slide guitar playing from the late 1 ...
, Keith Richards
Keith Richards (born 18 December 1943) is an English musician, songwriter, singer and record producer who is an original member, guitarist, secondary vocalist, and co-principal songwriter of the Rolling Stones. His songwriting partnership wi ...
, Shaun Ryder
Shaun William George Ryder (born 23 August 1962) is an English singer, songwriter and poet. As lead singer of Happy Mondays, he was a leading figure in the Madchester cultural scene during the late 1980s and early 1990s. In 1993, he formed Bl ...
, Shane MacGowan
Shane Patrick Lysaght MacGowan (25 December 195730 November 2023) was a British-born Irish singer-songwriter and musician, best known as the lead vocalist and primary lyricist of Celtic punk band the Pogues. He won acclaim for his lyrics, whic ...
and Janis Joplin
Janis Lyn Joplin (January 19, 1943 – October 4, 1970) was an American singer and songwriter. One of the most iconic and successful Rock music, rock performers of her era, she was noted for her powerful mezzo-soprano vocals and her "electric" ...
also used heroin. Many musicians have made songs referencing their heroin usage.
Society and culture
Names
Diamorphine is the international nonproprietary name and theBritish Approved Name
A British Approved Name (BAN) is the official, non-proprietary, or generic name given to a pharmaceutical substance, as defined in the British Pharmacopoeia (BP). The BAN is also the official name used in some countries around the world, because ...
. Other synonyms for heroin include: diacetylmorphine, and morphine diacetate. Heroin is also known by many street names including dope, H, smack, junk, horse, skag, brown, and unga, among others.
Legal status
Asia
In Hong Kong, diamorphine is regulated under Schedule 1 of Hong Kong's Chapter 134 ''Dangerous Drugs Ordinance''. It is available by prescription. Anyone supplying diamorphine without a valid prescription can be fined $5,000,000 ( HKD) and imprisoned for life. The penalty for trafficking or manufacturing diamorphine is a $5,000,000 (HKD) fine and life imprisonment. Possession of diamorphine without a license from the Department of Health is illegal with a $1,000,000 (HKD) fine and seven years of jail time.Europe
In the Netherlands, diamorphine is a List I drug of theOpium Law
The Opium Law (''Opiumwet'' in Dutch) is the section of the Dutch law which covers nearly all psychotropic drugs.
Origin and history
In 1912, the First International Opium Conference took place in The Hague, where agreements were made about ...
. It is available for prescription under tight regulation exclusively to long-term addicts for whom methadone maintenance
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid used medically to treat chronic pain and opioid use disorder. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and opioid withdrawal sy ...
treatment has failed. It cannot be used to treat severe pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
or other illnesses.
In the United Kingdom, diamorphine is available by prescription, though it is a restricted Class A drug
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (c. 38) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It represents action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the ...
. According to the 50th edition of the British National Formulary
The ''British National Formulary'' (BNF) is a United Kingdom (UK) pharmaceutical reference book that contains a wide spectrum of information and advice on prescribing and pharmacology, along with specific facts and details about many medicin ...
(BNF), diamorphine hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternati ...
may be used in the treatment of acute pain, myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
, acute pulmonary oedema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
, and chronic pain
Chronic pain is pain that persists or recurs for longer than 3 months.https://icd.who.int/browse/2025-01/mms/en#1581976053 It is also known as gradual burning pain, electrical pain, throbbing pain, and nauseating pain. This type of pain is in cont ...
. The treatment of chronic non-malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
pain must be supervised by a specialist. The BNF notes that all opioid analgesics cause dependence and tolerance but that this is "no deterrent in the control of pain in terminal illness". When used in the palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
of cancer patients, diamorphine is often injected using a syringe driver
A syringe driver, also known as a syringe pump, is a small infusion pump, used to gradually administer small amounts of fluid (with or without medication) to a patient or for use in chemical and biomedical research. Some syringe drivers can both ...
.
In Switzerland, heroin is produced in injectable or tablet form under the brand name Diaphin by a private company under contract to the Swiss government. Swiss-produced heroin has been imported into Canada with government approval.
Australia
In Australia, diamorphine is listed as a schedule 9 prohibited substance under the Poisons Standard (October 2015).Poisons Standard October 2015 The state ofWestern Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
, in its ''Poisons Act 1964'' (Reprint 6: amendments as at 10 September 2004), described a schedule 9 drug as: "Poisons that are drugs of abuse, the manufacture, possession, sale or use of which should be prohibited by law except for amounts which may be necessary for educational, experimental or research purposes conducted with the approval of the Governor."
North America
In Canada, diamorphine is a controlled substance under Schedule I of theControlled Drugs and Substances Act
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controll ...
(CDSA). Any person seeking or obtaining diamorphine without disclosing authorization 30 days before obtaining another prescription from a practitioner is guilty of an indictable offense and subject to imprisonment for a term not exceeding seven years. Possession of diamorphine for the purpose of trafficking is an indictable offense and subject to imprisonment for life.
In the United States, diamorphine is a Schedule I drug according to the Controlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) is the statute establishing federal government of the United States, federal drug policy of the United States, U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use, and distribution of ...
of 1970, making it illegal to possess without a DEA license. Possession of more than 100 grams of diamorphine or a mixture containing diamorphine is punishable with a minimum mandatory sentence of five years of imprisonment in a federal prison.
In 2021, the US state of Oregon became the first state to decriminalize the use of heroin after voters passed Ballot Measure 110 in 2020. This measure will allow people with small amounts to avoid arrest.
Turkey
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
maintains strict laws against the use, possession or trafficking of illegal drugs. If convicted under these offences, one could receive a heavy fine or a prison sentence of 4 to 24 years.
Misuse of prescription medication
Misused prescription medicine, such as opioids, can lead to heroin use and dependence. The number of death from illegal opioid overdose follows the increasing number of death caused by prescription opioid overdoses. Prescription opioids are relatively easy to obtain. This may ultimately lead to heroin injection because heroin is cheaper than prescribed pills.Pharmaceutical supply chain
Production
= Legal opium production
= Heroin is produced fromopium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
, which is regulated differently around the world. Unlike coca
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine. Coca leaves contain cocaine which acts as a mild stimulant when chewed or ...
leaves in Peru—handled exclusively by the state monopoly, the National Coca Company The National Company of the Coca (Spanish: ''Empresa Nacional de la Coca'', ENACO) is a Peruvian state company dedicated to the commercialization of the coca leaf and derivatives. It is the only state company that has a monopoly on the commercializ ...
(ENACO)—there is no state company dedicated to the commercialization of opium and its derivatives. While international treaties—such as the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961)—require strict state control or monopoly over the legal production and commercialization of opium for medical and scientific purposes, in practice, only a few countries maintain such a state monopoly today. Notably, India operates a state monopoly through the Government Opium and Alkaloid Factories (GOAF), also known as Opium and Alkaloid Works
The Government Opium and Alkaloid Factories (GOAF) is an Indian government-owned organisation. Its headquarter is located in New Delhi. The overall supervision of the organisation comes under the purview of Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finan ...
, which is responsible for processing raw opium into alkaloids for the pharmaceutical industry and managing the legal opium trade for medical and scientific use. Legal opium production in India, as well as in countries such as Turkey, Australia, France, Japan, and the UK, supplies licensed pharmaceutical manufacturers under close supervision to prevent diversion to illicit markets.
= Licensed pharmaceutical manufacturers
= Heroin and its production and distribution are strictly regulated by government health authorities and subject to international drug control treaties. In countries where medical diamorphine (heroin) is legal, a small number of licensed pharmaceutical manufacturers are authorized to produce diamorphine from morphine, which is derived from legally cultivated opium poppy. All manufacturing and handling are conducted by these licensed companies under close government oversight, operating under stringent national and international regulations. Their activities are monitored by agencies such as the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB), and the entire supply chain—from opium cultivation to the final pharmaceutical product—is subject to quotas, licensing, and detailed reporting requirements to prevent diversion to illicit markets.Distribution
Diamorphine produced by licensed manufacturers is distributed to hospitals and clinics for medical use, primarily for pain management and, in some countries, for heroin-assisted treatment of opioid dependence. Distribution within the health care system is tightly controlled, and all use is documented and audited by health authorities. There is no commercial retail market for diamorphine; it is dispensed only by prescription and administered under medical supervision.Illicit supply chain
Production
Diamorphine is produced fromacetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
of morphine derived from natural opium sources. One such method of heroin production involves isolation of the water-soluble components of raw opium, including morphine, in a strongly basic aqueous solution, followed by recrystallization of the morphine base by addition of ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula , also written as . It is an ammonium salt of hydrogen chloride. It consists of ammonium cations and chloride anions . It is a white crystalline salt (chemistry), sal ...
. The solid morphine base is then filtered out. The morphine base is then reacted with acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Commonly abbreviated , it is one the simplest organic acid anhydride, anhydrides of a carboxylic acid and is widely used in the production of c ...
, which forms heroin. This highly impure brown heroin base may then undergo further purification steps, which produces a white-colored product; the final products have a different appearance depending on purity and have different names. Heroin purity has been classified into four grades. No.4 is the purest form – white powder (salt) to be easily dissolved and injected. No.3 is "brown sugar" for smoking (base). No.1 and No.2 are unprocessed raw heroin (salt or base).
Trafficking
Traffic is heavy worldwide, with the biggest producer beingAfghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
. According to a U.N. sponsored survey, in 2004, Afghanistan accounted for production of 87 percent of the world's diamorphine. Afghan opium kills around 100,000 people annually.
In 2003 ''The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publis ...
'' reported:
Opium production in that country has increased rapidly since, reaching an all-time high in 2006. War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC), the conquest of Afghanistan by the Macedonian Empire
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan, a series of campaigns in ...
once again appeared as a facilitator of the trade. Some 3.3 million Afghans are involved in producing opium.
Golden Triangle
Golden Triangle may refer to:
Places
Asia
* Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), named for its opium production
* Golden Triangle (Yangtze), China, named for its rapid economic development
* Golden Triangle (India), comprising the popular tourist sp ...
straddling Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
(), Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
, Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
() and Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
province in China. There is also cultivation of opium poppies in Pakistan (), Mexico () and in Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
(). According to the DEA
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating illicit drug trafficking and distribution within the U.S. It is the lead agency for domes ...
, the majority of the heroin consumed in the United States comes from Mexico (50%) and Colombia (43–45%) via Mexican criminal cartels such as Sinaloa Cartel
The Sinaloa Cartel (, , after the native Sinaloa region), also known as the ''CDS'', the ''Guzmán-Loera Organization'', the ''Federation'', the ''Sinaloa Cartel'', or the Pacific Cartel, is a large, drug trafficking transnational organized cri ...
. However, these statistics may be significantly unreliable, the DEA's 50/50 split between Colombia and Mexico is contradicted by the amount of hectares cultivated in each country and in 2014, the DEA claimed most of the heroin in the US came from Colombia.
, the Sinaloa Cartel is the most active drug cartel
A drug cartel is a criminal organization composed of independent drug lords who collude with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate the illegal drug trade. Drug cartels form with the purpose of controlling the supply of the i ...
involved in smuggling illicit drugs such as heroin into the United States and trafficking them throughout the United States. According to the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; , GRC) is the Law enforcement in Canada, national police service of Canada. The RCMP is an agency of the Government of Canada; it also provides police services under contract to 11 Provinces and terri ...
, 90% of the heroin seized in Canada (where the origin was known) came from Afghanistan. Pakistan is the destination and transit point for 40 percent of the opiates produced in Afghanistan, other destinations of Afghan opiates are Russia, Europe and Iran.
A conviction for trafficking heroin carries the death penalty in most Southeast Asian
Southeast Asia is the geographical southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Australian mainland, which is part of Oceania. Southeast Asia is ...
, some East Asian
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
and Middle Eastern countries (see Use of death penalty worldwide for details), among which Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, Singapore and Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
are the strictest. The penalty applies even to citizens of countries where the penalty is not in place, sometimes causing controversy when foreign visitors are arrested for trafficking, for example, the arrest of nine Australians in Bali, the death sentence
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
given to Nola Blake
Nola Blake is an Australian woman who in 1987 was arrested in Bangkok, Thailand for drug trafficking and subsequently sentenced to death. Her sentence was later commuted to life in prison. Blake resided in Botany, New South Wales and was aged ...
in Thailand in 1987, or the hanging of an Australian citizen Van Tuong Nguyen
Van Tuong Nguyen (Vietnamese: ''Nguyễn Tường Vân'', ; 17 August 1980 – 2 December 2005), baptised Caleb, was an Australian from Melbourne, Victoria convicted of drug trafficking in Singapore. A Vietnamese Australian, he was also add ...
in Singapore.
=Routes
=
The Balkan route The Balkan route remains the principal corridor for trafficking illegal opiates, primarily heroin, from Afghanistan to Western and Central Europe, with criminal networks-often highly organized and adaptable-leveraging both legal businesses and corruption to facilitate the smuggling, storage, and distribution of drugs. These groups generate enormous illicit profits, with the annual gross income from drug trafficking along the Balkan route estimated between $13.9 and $21.4 billion from 2019 to 2022, of which up to half is illegally moved across borders through complex financial flows that include shell companies, cryptocurrencies, and informal systems like
hawala
Hawala or hewala ( , meaning ''transfer'' or sometimes ''trust''), originating in India as havala (), also known as in Persian, and or in Somali, is a popular and informal value transfer system based on the performance and honour of a hug ...
. The majority of these profits, around 90 percent, come from opiates, and the scale of this income rivals or exceeds the GDP of several countries along the route. The movement of these illicit funds not only sustains and expands drug trafficking operations but also undermines economic stability and governance in affected countries, making the Balkan route a persistent and multifaceted challenge for law enforcement and policymakers in the region.
=Trafficking history
=triad
Triad or triade may refer to:
* a group of three
Humanities
* Trichotomy (philosophy), often called triads
* Triad (sociology), a group of three people as a unit of study
* Triad (relationship), or ''ménage à trois''
Music
* Triad (music ...
gangs eventually came to play a major role in the illicit heroin trade. The French Connection
The French Connection was a scheme through which heroin was smuggled from Indochina through Turkey to France and then to the United States and Canada. The operation started in the 1930s, reached its peak in the 1960s, and was dismantled in the 1 ...
route started in the 1930s.
Heroin trafficking was virtually eliminated in the US during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
because of temporary trade disruptions caused by the war. Japan's war with China had cut the normal distribution routes for heroin and the war had generally disrupted the movement of opium. After World War II, the Mafia
"Mafia", as an informal or general term, is often used to describe criminal organizations that bear a strong similarity to the original Mafia in Sicily, to the Italian-American Mafia, or to other organized crime groups from Italy. The central ...
took advantage of the weakness of the postwar Italian government and set up heroin labs in Sicily which was located along the historic route opium took westward into Europe and the United States. Large-scale international heroin production effectively ended in China with the victory of the communists in the civil war in the late 1940s. The elimination of Chinese production happened at the same time that Sicily's role in the trade developed.
Although it remained legal in some countries until after World War II, health risks, addiction, and widespread recreational use led most western countries to declare heroin a controlled substance by the latter half of the 20th century. In the late 1960s and early 1970s, the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
supported anti-Communist Chinese Nationalists settled near the Sino
Sino as a prefix generally refers to:
* China
* Greater China
* Chinese people
* Two Chinas
* Culture of China
* History of China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part ...
-Burmese border and Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related ...
tribesmen in Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
. This helped the development of the Golden Triangle
Golden Triangle may refer to:
Places
Asia
* Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), named for its opium production
* Golden Triangle (Yangtze), China, named for its rapid economic development
* Golden Triangle (India), comprising the popular tourist sp ...
opium production region, which supplied about one-third of heroin consumed in the US after the 1973 American withdrawal from Vietnam. In 1999, Burma, the heartland of the Golden Triangle, was the second-largest producer of heroin, after Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
.
The Soviet-Afghan war led to increased production in the Pakistani-Afghan border regions, as US-backed mujaheddin
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' (), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' (), an Arabic term that broadly refers to people who engage in '' jihad'' (), interpreted in a jurisprudence of Islam as the fight on behalf of God, religion or the commu ...
militants raised money for arms from selling opium, contributing heavily to the modern Golden Crescent
The Golden Crescent is the name given to one of Asia's two principal areas of illicit opium production, with the other being the Golden Triangle. Located at the crossroads of Central, South, and West Asia, this space covers the mountainous per ...
creation. By 1980, 60 percent of the heroin sold in the US originated in Afghanistan. It increased international production of heroin at lower prices in the 1980s. The trade shifted away from Sicily in the late 1970s as various criminal organizations violently fought with each other over the trade. The fighting also led to a stepped-up government law enforcement presence in Sicily.
Following the discovery at a Jordanian airport of a toner cartridge
A toner cartridge, also called laser toner, is the consumable component of a laser printer. Toner cartridges contain toner powder, a fine, dry mixture of plastic particles, carbon, and black or other coloring agents that make the actual image ...
that had been modified into an improvised explosive device
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional warfare, conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached t ...
, the resultant increased level of airfreight scrutiny led to a major shortage (drought) of heroin from October 2010 until April 2011. This was reported in most of mainland Europe and the UK which led to a price increase of approximately 30 percent in the cost of street heroin and increased demand for diverted methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid used medically to treat chronic pain and opioid use disorder. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and opioid withdrawal sym ...
. The number of addicts seeking treatment also increased significantly during this period. Other heroin droughts (shortages) have been attributed to cartels restricting supply in order to force a price increase and also to a fungus that attacked the opium crop of 2009. Many people thought that the American government had introduced pathogens into the Afghanistan atmosphere in order to destroy the opium crop and thus starve insurgents of income.
On 13 March 2012, Haji Bagcho
Haji Bagcho Sherzai, also known as ''Haji Bagh Chagul'' or ''Haji Bagcho'' (born 1954), is a convicted drug trafficker from Afghanistan. He is accused by the United States of having ties with the Taliban. He was convicted on March 13, 2012, by a ...
, with ties to the Taliban
, leader1_title = Supreme Leader of Afghanistan, Supreme leaders
, leader1_name = {{indented plainlist,
* Mullah Omar{{Natural Causes{{nbsp(1994–2013)
* Akhtar Mansour{{Assassinated (2015–2016)
* Hibatullah Akhundzada (2016–present) ...
, was convicted by a US District Court of conspiracy, distribution of heroin for importation into the United States and narco-terrorism. Based on heroin production statistics compiled by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French language, French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention ...
, in 2006, Bagcho's activities accounted for approximately 20 percent of the world's total production for that year.
Street price
 The
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
The European Union Drugs Agency (EUDA), known until 2024 as the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), is an agency of the European Union headquartered in Lisbon, Portugal, and established in 1993.
In June 2022, the ...
reports that the retail price of brown heroin varies from €14.5 per gram in Turkey to €110 per gram in Sweden, with most European countries reporting typical prices of €35–40 per gram. The price of white heroin is reported only by a few European countries and ranged between €27 and €110 per gram.
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French language, French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention ...
claims in its 2008 World Drug Report that typical US retail prices are US$172 per gram.
Research
Researchers are attempting to reproduce the biosynthetic pathway that producesmorphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
in genetically engineered
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including th ...
yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
. In June 2015 the ''S''-reticuline
Reticuline is an alkaloid found in opium and a variety of plants including ''Lindera aggregata'', ''Annona squamosa'', and ''Ocotea#Selected species, Ocotea fasciculata'' (also known as ''Ocotea duckei'').
Experiments in rodents suggest reticuli ...
could be produced from sugar and ''R''-reticuline could be converted to morphine, but the intermediate reaction could not be performed.
See also
* * *References
External links
'When Heroin Was Legal'
BBC
Drug-poisoning Deaths Involving Heroin: United States, 2000–2013
US Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
Heroin Trafficking in the United States
(2019) US
Congressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service (CRS) is a public policy research institute of the United States Congress. Operating within the Library of Congress, it works primarily and directly for members of Congress and their committees and staff on a ...
{{Authority control
1874 introductions
1898 introductions
Acetate esters
Analgesics
Brands that became generic
British inventions
Depressogens
4,5-Epoxymorphinans
Euphoriants
Morphine
Mu-opioid receptor agonists
Nephrotoxins
Opioids
Phenol ethers
Prodrugs
Semisynthetic opioids
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate