Hepatic Perfusion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The liver is a major
 The liver is a dark reddish brown, wedge-shaped
The liver is a dark reddish brown, wedge-shaped
 The liver is grossly divided into two parts when viewed from above – a right and a left lobe – and four parts when viewed from below (left, right, caudate, and
The liver is grossly divided into two parts when viewed from above – a right and a left lobe – and four parts when viewed from below (left, right, caudate, and
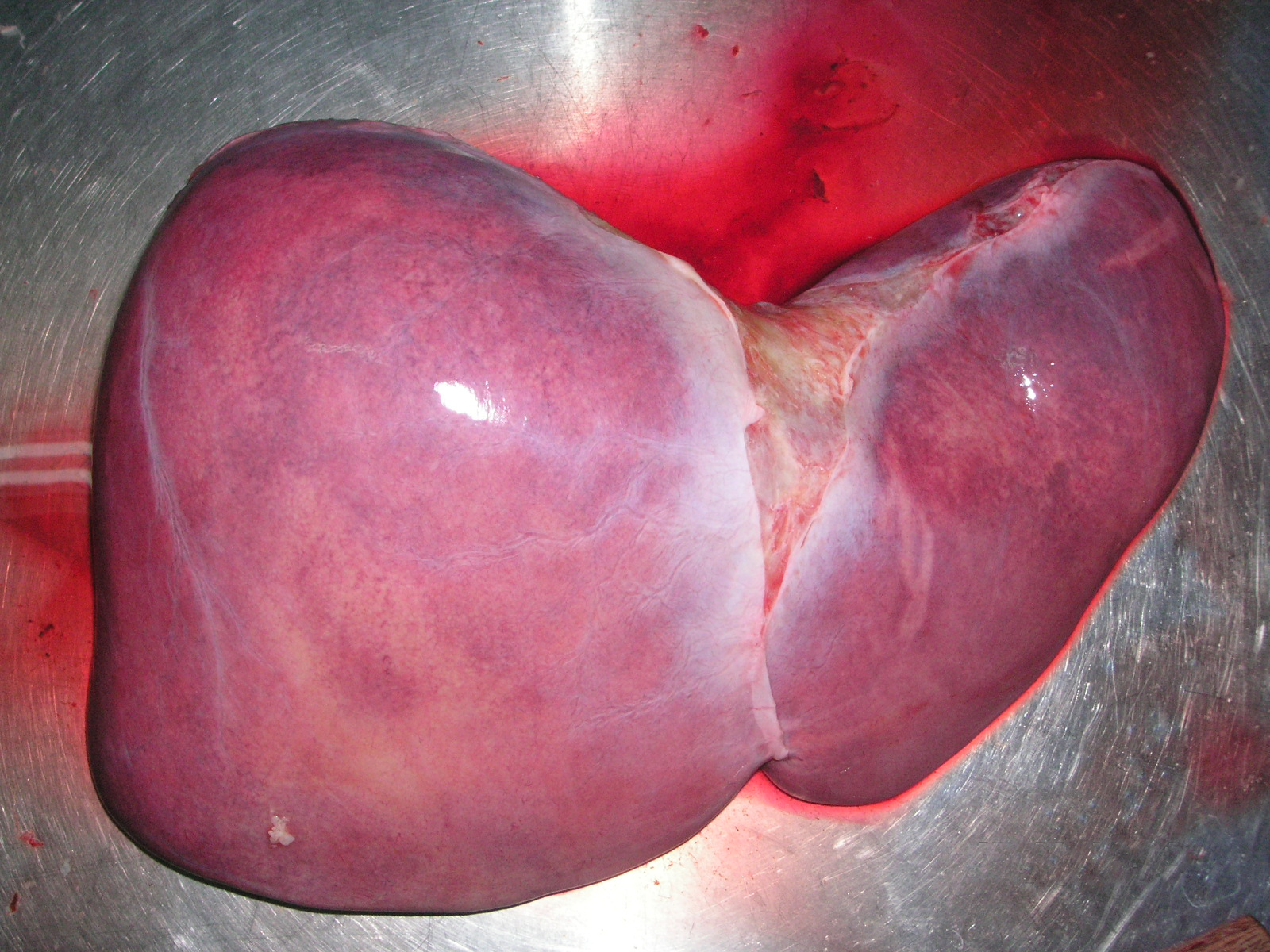 On the diaphragmatic surface, apart from a triangular bare area where it connects to the diaphragm, the liver is covered by a thin, double-layered membrane, the
On the diaphragmatic surface, apart from a triangular bare area where it connects to the diaphragm, the liver is covered by a thin, double-layered membrane, the
 Several impressions on the surface of the liver accommodate the various adjacent structures and organs. Underneath the right lobe and to the right of the gallbladder fossa are two impressions, one behind the other and separated by a ridge. The one in front is a shallow colic impression, formed by the
Several impressions on the surface of the liver accommodate the various adjacent structures and organs. Underneath the right lobe and to the right of the gallbladder fossa are two impressions, one behind the other and separated by a ridge. The one in front is a shallow colic impression, formed by the
 Microscopically, each liver lobe is seen to be made up of
Microscopically, each liver lobe is seen to be made up of
2423 Microscopic Anatomy of Liver.jpg, Microscopic anatomy of the liver
2104 Three Major Capillary Types.jpg, Types of capillaries–sinusoid on right
3D Medical Animation liver parts.jpg, alt=3D Medical Animation Still Shot Depicting parts of liver, 3D medical animation still shot depicting parts of liver
 The central area or hepatic hilum, includes the opening known as the porta hepatis which carries the
The central area or hepatic hilum, includes the opening known as the porta hepatis which carries the
 In the widely used Couinaud system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein. The caudate lobe is a separate structure that receives blood flow from both the right- and left-sided vascular branches. The Couinaud classification divides the liver into eight functionally independent liver segments. Each segment has its own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage. In the centre of each segment are branches of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. In the periphery of each segment is vascular outflow through the hepatic veins. The classification system uses the vascular supply in the liver to separate the functional units (numbered I to VIII) with unit 1, the caudate lobe, receiving its supply from both the right and the left branches of the portal vein. It contains one or more hepatic veins which drain directly into the inferior vena cava. The remainder of the units (II to VIII) are numbered in a clockwise fashion:
In the widely used Couinaud system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein. The caudate lobe is a separate structure that receives blood flow from both the right- and left-sided vascular branches. The Couinaud classification divides the liver into eight functionally independent liver segments. Each segment has its own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage. In the centre of each segment are branches of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. In the periphery of each segment is vascular outflow through the hepatic veins. The classification system uses the vascular supply in the liver to separate the functional units (numbered I to VIII) with unit 1, the caudate lobe, receiving its supply from both the right and the left branches of the portal vein. It contains one or more hepatic veins which drain directly into the inferior vena cava. The remainder of the units (II to VIII) are numbered in a clockwise fashion:

 At birth, the liver comprises roughly 4% of body weight and weighs on average about . Over the course of further development, it will increase to but will only take up 2.5–3.5% of body weight.
Hepatosomatic index (HSI) is the ratio of liver weight to body weight.
At birth, the liver comprises roughly 4% of body weight and weighs on average about . Over the course of further development, it will increase to but will only take up 2.5–3.5% of body weight.
Hepatosomatic index (HSI) is the ratio of liver weight to body weight.
 The
The
 The liver is a vital organ and supports almost every other organ in the body. Because of its strategic location and multidimensional functions, the liver is prone to many diseases. The bare area of the liver is a site that is vulnerable to the passing of infection from the abdominal cavity to the
The liver is a vital organ and supports almost every other organ in the body. Because of its strategic location and multidimensional functions, the liver is prone to many diseases. The bare area of the liver is a site that is vulnerable to the passing of infection from the abdominal cavity to the
 Humans commonly eat the livers of mammals, fowl, and fish as food. Domestic pig, ox, lamb, calf, chicken, and goose livers are widely available from butchers and supermarkets. In the
Humans commonly eat the livers of mammals, fowl, and fish as food. Domestic pig, ox, lamb, calf, chicken, and goose livers are widely available from butchers and supermarkets. In the
 The liver is found in all
The liver is found in all
Liver at the Human Protein Atlas
VIRTUAL Liver – online learning resource
Liver enzymes
* with several diagrams. * {{Authority control Organs (anatomy)
metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
exclusively found in vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s, which performs many essential biological function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-orie ...
s such as detoxification
Detoxification or detoxication (detox for short) is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism, including the human body, which is mainly carried out by the liver. Additionally, it can refer to the period o ...
of the organism, and the synthesis of various proteins and various other biochemical
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, ...
s necessary for digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
and growth. In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great ve ...
. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism
Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemistry, biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic anabolism, formation, catabolism, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in life, living organisms.
Carbohydrates are central t ...
, the production of a number of hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
, and the decomposition of red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word for liver, such as hepatology
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion ...
, and hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
The liver is also an accessory digestive organ
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
that produces bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
, an alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
fluid containing cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
and bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver in peroxisomes. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile ...
s, which emulsifies
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although ...
and aids the breakdown of dietary fat. The gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, a small hollow pouch that sits just under the right lobe of liver, stores and concentrates the bile produced by the liver, which is later excreted to the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
to help with digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
. The liver's highly specialized tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
s, regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex organic molecules, many of which are necessary for normal vital functions. Estimates regarding the organ's total number of functions vary, but is generally cited as being around 500. For this reason, the liver has sometimes been described as the body's chemical factory.
It is not known how to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although liver dialysis
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins (liver dialysis), or providing additional replacement of the m ...
techniques can be used in the short term. Artificial livers have not been developed to promote long-term replacement in the absence of the liver. , liver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
is the only option for complete liver failure
Liver failure is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic functions as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic (cirrhosis). Recently, a third form of liver failure known as acute- ...
.
Structure
 The liver is a dark reddish brown, wedge-shaped
The liver is a dark reddish brown, wedge-shaped organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
with two lobes of unequal size and shape. A human liver normally weighs approximately and has a width of about . There is considerable size variation between individuals, with the standard reference range
In medicine and health-related fields, a reference range or reference interval is the range or the interval of values that is deemed normal for a physiological measurement in healthy persons (for example, the amount of creatinine in the blood ...
for men being and for women . It is both the heaviest internal organ and the largest gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also funct ...
in the human body. It is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contain Organ (anatomy), organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roo ...
, resting just below the diaphragm, to the right of the stomach, and overlying the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
.
The liver is connected to two large blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s: the hepatic artery
The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder.
It arises from the celiac artery and has the following branches:
Additional images
...
and the portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approxima ...
. The hepatic artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the aorta via the celiac trunk
The celiac () artery (also spelled coeliac in British English), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vert ...
, whereas the portal vein carries blood rich in digested nutrients from the entire gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
and also from the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
and pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
. These blood vessels subdivide into small capillaries known as liver sinusoid
A liver sinusoid is a type of capillary known as a sinusoidal capillary, discontinuous capillary or sinusoid, that is similar to a Capillary#Fenestrated, fenestrated capillary, having discontinuous endothelium that serves as a location for mixing ...
s, which then lead to hepatic lobules.
Hepatic lobules are the functional units of the liver. Each lobule is made up of millions of hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
s, which are the basic metabolic cells. The lobules are held together by a fine, dense, irregular, fibroelastic connective tissue layer extending from the fibrous capsule covering the entire liver known as ''Glisson's capsule'' after British doctor Francis Glisson
Francis Glisson (1597 – 14 October 1677) was a British physician, anatomist, and writer on medical subjects. He did important work on the anatomy of the liver, and he wrote an early pediatric text on rickets. An experiment he performed he ...
. This tissue extends into the structure of the liver by accompanying the blood vessels, ducts, and nerves at the hepatic hilum. The whole surface of the liver, except for the bare area
The bare area of the liver (nonperitoneal area) is a large triangular area on the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragmatic surface of the liver. It is the only part of the liver with no peritoneal covering, although it is still covered by Glisson's caps ...
, is covered in a serous
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fl ...
coat derived from the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
, and this firmly adheres to the inner Glisson's capsule.
Gross anatomy
Lobes
 The liver is grossly divided into two parts when viewed from above – a right and a left lobe – and four parts when viewed from below (left, right, caudate, and
The liver is grossly divided into two parts when viewed from above – a right and a left lobe – and four parts when viewed from below (left, right, caudate, and quadrate lobe
In human anatomy, the liver is divided Gross anatomy, grossly into four parts or Lobe (anatomy), lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragmatic surface ...
s).
The falciform ligament
In human anatomy, the falciform ligament () is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being dire ...
makes a superficial division of the liver into a left and right lobe. From below, the two additional lobes are located between the right and left lobes, one in front of the other. A line can be imagined running from the left of the vena cava
In anatomy, the ''venae cavae'' (; ''vena cava'' ; ) are two large veins ( great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into t ...
and all the way forward to divide the liver and gallbladder into two halves. This line is called Cantlie's line.
Other anatomical landmarks include the ligamentum venosum
The ligamentum venosum, also known as Arantius' ligament, is the fibrous remnant of the ductus venosus of the fetal circulation. Usually, it is attached to the left branch of the portal vein within the porta hepatis. It may be continuous with the ...
and the round ligament of the liver, which further divide the left side of the liver in two sections. An important anatomical landmark, the porta hepatis
The porta hepatis or transverse fissure of the liver is a short but deep fissure, about 5 cm long, extending transversely beneath the left portion of the right lobe of the liver, nearer its posterior surface than its anterior border.
It join ...
, divides this left portion into four segments, which can be numbered starting at the caudate lobe as I in an anticlockwise manner. From this parietal view, seven segments can be seen, because the eighth segment is only visible in the visceral
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an o ...
view.
Surfaces
 On the diaphragmatic surface, apart from a triangular bare area where it connects to the diaphragm, the liver is covered by a thin, double-layered membrane, the
On the diaphragmatic surface, apart from a triangular bare area where it connects to the diaphragm, the liver is covered by a thin, double-layered membrane, the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
, that helps to reduce friction against other organs. This surface covers the convex shape of the two lobes where it accommodates the shape of the diaphragm. The peritoneum folds back on itself to form the falciform ligament
In human anatomy, the falciform ligament () is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being dire ...
and the right
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
and left triangular ligament
The left triangular ligament is a large peritoneal fold. It connects the posterior part of the upper surface of the left lobe of the liver to the thoracic diaphragm.
Structure
The left triangular ligament connects the posterior part of the u ...
s.
These peritoneal ligament
Peritoneal ligaments are folds of peritoneum that are used to connect viscera to viscera or the abdominal wall.
There are multiple named ligaments that usually are named in accordance with what they are.
* Gastrocolic ligament, connects the stom ...
s are not related to the anatomic ligaments in joints, and the right and left triangular ligaments have no known functional importance, though they serve as surface landmarks. The falciform ligament functions to attach the liver to the posterior portion of the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
body wall.
The visceral surface or inferior surface is uneven and concave. It is covered in peritoneum apart from where it attaches the gallbladder and the porta hepatis. The fossa of gallbladder lies to the right of the quadrate lobe, occupied by the gallbladder with its cystic duct close to the right end of porta hepatis.
Impressions
 Several impressions on the surface of the liver accommodate the various adjacent structures and organs. Underneath the right lobe and to the right of the gallbladder fossa are two impressions, one behind the other and separated by a ridge. The one in front is a shallow colic impression, formed by the
Several impressions on the surface of the liver accommodate the various adjacent structures and organs. Underneath the right lobe and to the right of the gallbladder fossa are two impressions, one behind the other and separated by a ridge. The one in front is a shallow colic impression, formed by the hepatic flexure
In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure.
S ...
and the one behind is a deeper renal impression accommodating part of the right kidney and part of the suprarenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex whic ...
.
The suprarenal impression is a small, triangular, depressed area on the liver. It is located close to the right of the fossa, between the bare area and the caudate lobe, and immediately above the renal impression. The greater part of the suprarenal impression is devoid of peritoneum and it lodges the right suprarenal gland.
Medial to the renal impression is a third and slightly marked impression, lying between it and the neck of the gall bladder. This is caused by the descending portion of the duodenum, and is known as the duodenal impression.
The inferior surface of the left lobe of the liver presents behind and to the left of the gastric impression. This is moulded over the upper front surface of the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
, and to the right of this is a rounded eminence, the tuber omentale, which fits into the concavity of the lesser curvature of the stomach and lies in front of the anterior layer of the lesser omentum
The lesser omentum (small omentum or gastrohepatic omentum) is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into t ...
.
Microscopic anatomy
hepatic lobule
In histology (microscopic anatomy), the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver Tissue (biology), tissue, consisting of portal tr ...
s. The lobules are roughly hexagonal, and consist of plates of hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
s, and sinusoids
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the inn ...
radiating from a central vein towards an imaginary perimeter of interlobular portal triads. The central vein joins to the hepatic vein to carry blood out from the liver. A distinctive component of a lobule is the portal triad
In histology (microscopic anatomy), the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of portal triads, hepatocytes ...
, which can be found running along each of the lobule's corners. The portal triad consists of the hepatic artery, the portal vein, and the common bile duct. The triad may be seen on a liver ultrasound, as a Mickey Mouse sign Mickey Mouse sign is a medical sign resembling the head of Mickey Mouse, the Walt Disney character. Presented for the very first time at the CHIVA's Meeting, Berlin 2002 by Dr. Lurdes Cerol, this sign has been described as the image at the groin wh ...
with the portal vein as the head, and the hepatic artery, and the common bile duct as the ears.
Histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
, the study of microscopic anatomy, shows two major types of liver cell: parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
l cells and nonparenchymal cells. About 70–85% of the liver volume is occupied by parenchymal hepatocytes. Nonparenchymal cells constitute 40% of the total number of liver cells but only 6.5% of its volume. The liver sinusoid
A liver sinusoid is a type of capillary known as a sinusoidal capillary, discontinuous capillary or sinusoid, that is similar to a Capillary#Fenestrated, fenestrated capillary, having discontinuous endothelium that serves as a location for mixing ...
s are lined with two types of cell, sinusoidal endothelial cells, and phagocytic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs ph ...
Kupffer cell
Kupffer cells, also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer–Browicz cells, are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. K ...
s. Hepatic stellate cell
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier ''lipocytes'' or ''fat-storing cells''), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between ...
s are nonparenchymal cells found in the perisinusoidal space, between a sinusoid and a hepatocyte.
Additionally, intrahepatic lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
are often present in the sinusoidal lumen.
Functional anatomy
 The central area or hepatic hilum, includes the opening known as the porta hepatis which carries the
The central area or hepatic hilum, includes the opening known as the porta hepatis which carries the common bile duct
The common bile duct (also bile duct) is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the ampulla of Vater (hepatopancreatic ampulla). ...
and common hepatic artery
The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder.
It arises from the celiac artery and has the following branches:
Additional images
...
, and the opening for the portal vein. The duct, vein, and artery divide into left and right branches, and the areas of the liver supplied by these branches constitute the functional left and right lobes. The functional lobes are separated by the imaginary plane, Cantlie's line, joining the gallbladder fossa to the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
. The plane separates the liver into the true right and left lobes. The middle hepatic vein also demarcates the true right and left lobes. The right lobe is further divided into an anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and posterior segment by the right hepatic vein. The left lobe is divided into the medial
Medial may refer to:
Mathematics
* Medial magma, a mathematical identity in algebra Geometry
* Medial axis, in geometry the set of all points having more than one closest point on an object's boundary
* Medial graph, another graph that repr ...
and lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
segments by the left hepatic vein.
The hilum of the liver is described in terms of three ''plates'' that contain the bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).
Bile is requ ...
s and blood vessels. The contents of the whole plate system are surrounded by a sheath. The three plates are the ''hilar plate'', the ''cystic plate'' and the ''umbilical plate'' and the plate system is the site of the many anatomical variations to be found in the liver.
Couinaud classification system
 In the widely used Couinaud system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein. The caudate lobe is a separate structure that receives blood flow from both the right- and left-sided vascular branches. The Couinaud classification divides the liver into eight functionally independent liver segments. Each segment has its own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage. In the centre of each segment are branches of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. In the periphery of each segment is vascular outflow through the hepatic veins. The classification system uses the vascular supply in the liver to separate the functional units (numbered I to VIII) with unit 1, the caudate lobe, receiving its supply from both the right and the left branches of the portal vein. It contains one or more hepatic veins which drain directly into the inferior vena cava. The remainder of the units (II to VIII) are numbered in a clockwise fashion:
In the widely used Couinaud system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein. The caudate lobe is a separate structure that receives blood flow from both the right- and left-sided vascular branches. The Couinaud classification divides the liver into eight functionally independent liver segments. Each segment has its own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage. In the centre of each segment are branches of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. In the periphery of each segment is vascular outflow through the hepatic veins. The classification system uses the vascular supply in the liver to separate the functional units (numbered I to VIII) with unit 1, the caudate lobe, receiving its supply from both the right and the left branches of the portal vein. It contains one or more hepatic veins which drain directly into the inferior vena cava. The remainder of the units (II to VIII) are numbered in a clockwise fashion:
Gene and protein expression
About 20,000 protein coding genes are expressed in human cells and 60% of these genes are expressed in a normal, adult liver. Over 400 genes are more specifically expressed in the liver, with some 150 genes highly specific for liver tissue. A large fraction of the corresponding liver-specific proteins are mainly expressed in hepatocytes and secreted into the blood and constitute plasma proteins andhepatokines
Hepatokines (Greek ''heapto-'', liver; and ''-kinos'', movement) are proteins produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) that are secreted into the circulation and function as hormones across the organism. Research is mostly focused on hepatokines tha ...
. Other liver-specific proteins are certain liver enzymes such as HAO1 and RDH16
Retinol dehydrogenase 16 (all-trans) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RDH16'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in ...
, proteins involved in bile synthesis such as BAAT
Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BAAT'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the bile acid moiety from the acyl-CoA thioester to eithe ...
and SLC27A5
Bile acyl-CoA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC27A5'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase ( VLCS). It is capable of activating very long-chain fatty-acids cont ...
, and transporter proteins involved in the metabolism of drugs, such as ABCB11
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B member 11 (ABCB11), also known as the bile salt export pump (BSEP), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the gene.
Function
The product of the ''ABCB11'' gene is an ABC transporter named BSEP (bile s ...
and SLC2A2. Examples of highly liver-specific proteins include apolipoprotein A II, coagulation factors F2 and F9, complement factor related proteins, and the fibrinogen beta chain
Fibrinogen beta chain, also known as FGB, is a gene found in humans and most other vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the sp ...
protein.
Development

Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal org ...
, the development of the organs, takes place from the third to the eighth week during embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
. The origins of the liver lie in both the ventral portion of the foregut
The foregut in humans is the anterior part of the alimentary canal, from the distal esophagus to the first half of the duodenum, at the entrance of the bile duct. Beyond the stomach, the foregut is attached to the abdominal walls by mesentery. ...
endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastr ...
(endoderm being one of the three embryonic germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cell (biology), cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce tw ...
s) and the constituents of the adjacent septum transversum
The septum transversum is a thick mass of cranial mesenchyme, formed in the embryo, that gives rise to parts of the thoracic diaphragm and the ventral mesentery of the foregut in the developed human being and other mammals.
Origins
The septum t ...
mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
. In the human embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
, the hepatic diverticulum
The hepatic diverticulum (or liver bud) is a primordial cellular extension of the embryonic foregut endoderm that gives rise to the parenchyma of the liver and the bile duct. It typically differentiates from the endoderm in the third or fourth we ...
is the tube of endoderm that extends out from the foregut into the surrounding mesenchyme. The mesenchyme of septum transversum induces this endoderm to proliferate, to branch, and to form the glandular epithelium of the liver. A portion of the hepatic diverticulum (that region closest to the digestive tube) continues to function as the drainage duct of the liver, and a branch from this duct produces the gallbladder. Besides signals from the septum transversum mesenchyme, fibroblast growth factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by the macrophages. They are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in ...
from the developing heart also contributes to hepatic competence, along with retinoic acid
Retinoic acid (simplified nomenclature for all-''trans''-retinoic acid) is a metabolite of vitamin A1 (all-''trans''-retinol) that is required for embryonic development, male fertility, regulation of bone growth and immune function. All-''trans ...
emanating from the lateral plate mesoderm
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow r ...
. The hepatic endodermal cells undergo a morphological transition from columnar to pseudostratified resulting in thickening into the early liver bud. Their expansion forms a population of the bipotential hepatoblasts. Hepatic stellate cells are derived from mesenchyme.
After migration of hepatoblasts into the septum transversum mesenchyme, the hepatic architecture begins to be established, with liver sinusoids and bile canaliculi appearing. The liver bud separates into the lobes. The left umbilical vein
The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus. The umbilical vein provides convenient access to the central circulation of a neonate for restoration of blood vo ...
becomes the ductus venosus
In the fetus, the ''ductus venosus'' (''"DV"''; Arantius' duct after Julius Caesar Aranzi) shunts a portion of umbilical vein blood flow directly to the inferior vena cava. Thus, it allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the liver. ...
and the right vitelline vein
The vitelline veins are veins that drain blood from the yolk sac and the gut tube during gestation.
Path
They run upward at first in front, and subsequently on either side of the intestinal canal. They unite on the ventral aspect of the canal.
...
becomes the portal vein. The expanding liver bud is colonized by hematopoietic cells
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten b ...
. The bipotential hepatoblasts begin differentiating into biliary epithelial cells and hepatocytes. The biliary epithelial cells differentiate from hepatoblasts around portal veins, first producing a monolayer, and then a bilayer of cuboidal cells. In ductal plate, focal dilations emerge at points in the bilayer, become surrounded by portal mesenchyme, and undergo tubulogenesis into intrahepatic bile ducts. Hepatoblasts not adjacent to portal veins instead differentiate into hepatocytes and arrange into cords lined by sinusoidal epithelial cells and bile canaliculi. Once hepatoblasts are specified into hepatocytes and undergo further expansion, they begin acquiring the functions of a mature hepatocyte, and eventually mature hepatocytes appear as highly polarized epithelial cells with abundant glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
accumulation. In the adult liver, hepatocytes are not equivalent, with position along the portocentrovenular axis within a liver lobule dictating expression of metabolic genes involved in drug metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism
Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemistry, biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic anabolism, formation, catabolism, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in life, living organisms.
Carbohydrates are central t ...
, ammonia detoxification, and bile production and secretion. WNT/β-catenin has now been identified to be playing a key role in this phenomenon.
 At birth, the liver comprises roughly 4% of body weight and weighs on average about . Over the course of further development, it will increase to but will only take up 2.5–3.5% of body weight.
Hepatosomatic index (HSI) is the ratio of liver weight to body weight.
At birth, the liver comprises roughly 4% of body weight and weighs on average about . Over the course of further development, it will increase to but will only take up 2.5–3.5% of body weight.
Hepatosomatic index (HSI) is the ratio of liver weight to body weight.
Fetal blood supply
In the growing fetus, a major source of blood to the liver is the umbilical vein, which supplies nutrients to the growing fetus. The umbilical vein enters the abdomen at the umbilicus and passes upward along the free margin of the falciform ligament of the liver to the inferior surface of the liver. There, it joins with the left branch of the portal vein. The ductus venosus carries blood from the left portal vein to the left hepatic vein and then to the inferior vena cava, allowing placental blood to bypass the liver. In the fetus, the liver does not perform the normal digestive processes and filtration of the infant liver because nutrients are received directly from the mother via theplacenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
. The fetal liver releases some blood stem cells that migrate to the fetal thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
, creating the (or T lymphocytes). After birth, the formation of blood stem cells shifts to the red bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
. After 2–5 days, the umbilical vein and ductus venosus are obliterated; the former becomes the round ligament of liver
The round ligament of the liver, ligamentum teres or ligamentum teres hepatis is a ligament that forms part of the free edge of the falciform ligament of the liver. It connects the liver to the umbilicus. It is the remnant of the left umbilical ...
and the latter becomes the ligamentum venosum. In the disorders of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
and portal hypertension
Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Normal portal pressure is 1–4 mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5� ...
, the umbilical vein can open up again.
Unlike eutherian mammals, in marsupials the liver remains haematopoietic well after birth.
Functions
The various functions of the liver are carried out by the liver cells or hepatocytes. The liver is thought to be responsible for up to 500 separate functions, usually in combination with other systems and organs. Currently, noartificial organ
An artificial organ is a human-made organ device or Tissue (biology), tissue that is Implant (medicine), implanted or integrated into a humaninterfacing with living tissueto replace a natural Organ (anatomy), organ, to duplicate or augment a spec ...
or device is capable of reproducing all the functions of the liver. Some functions can be carried out by liver dialysis
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins (liver dialysis), or providing additional replacement of the m ...
, an experimental treatment for liver failure
Liver failure is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic functions as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic (cirrhosis). Recently, a third form of liver failure known as acute- ...
. The liver also accounts for about 20% of resting total body oxygen consumption.
Blood supply
The liver gets its blood supply from the hepatic portal vein and hepatic arteries. The hepatic portal vein delivers around 75% of the liver's blood supply and carriesvenous blood
Venous blood is deoxygenated blood which travels from the peripheral blood vessels, through the venous system into the right atrium of the heart. Deoxygenated blood is then pumped by the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary artery whi ...
drained from the spleen, gastrointestinal tract, and its associated organs. The hepatic arteries supply arterial blood to the liver, accounting for the remaining quarter of its blood flow. Oxygen is provided from both sources; about half of the liver's oxygen demand is met by the hepatic portal vein, and half is met by the hepatic arteries. The hepatic artery also has both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors; therefore, flow through the artery is controlled, in part, by the splanchnic nerves of the autonomic nervous system.
Blood flows through the liver sinusoids and empties into the central vein of each lobule. The central veins coalesce into hepatic veins, which leave the liver and drain into the inferior vena cava.
Biliary flow
biliary tract
The biliary tract (also biliary tree or biliary system) refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids an ...
is derived from the branches of the bile ducts. The biliary tract, also known as the biliary tree, is the path by which bile is secreted by the liver then transported to the first part of the small intestine, the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
. The bile produced in the liver is collected in bile canaliculi
A bile canaliculus (: bile canaliculi; also called bile capillaries) is a thin tube that collects bile secreted by hepatocytes. The bile canaliculi empty into a series of progressively larger bile ductules and ducts, which eventually become commo ...
, small grooves between the faces of adjacent hepatocytes. The canaliculi radiate to the edge of the liver lobule, where they merge to form bile ducts. Within the liver, these ducts are termed intrahepatic bile ducts, and once they exit the liver, they are considered extrahepatic. The intrahepatic ducts eventually drain into the right and left hepatic ducts, which exit the liver at the transverse fissure, and merge to form the common hepatic duct. The cystic duct
The cystic duct is the duct that (typically) joins the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct; the union of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct forms the bile duct (formerly known as the common bile duct). Its length varies.
Anatomy
...
from the gallbladder joins with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct. The biliary system and connective tissue is supplied by the hepatic artery alone.
Bile either drains directly into the duodenum via the common bile duct, or is temporarily stored in the gallbladder via the cystic duct. The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct enter the second part of the duodenum together at the hepatopancreatic ampulla, also known as the ampulla of Vater
The ampulla of Vater, hepatopancreatic ampulla or hepatopancreatic duct is the common duct that is usually formed by a union of the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct within the wall of the duodenum. This common duct usually features a di ...
.
Metabolism
The liver plays a major role in carbohydrate, protein, amino acid, and lipid metabolism.Carbohydrate metabolism
The liver performs several roles in carbohydrate metabolism. * The liver synthesizes and stores around 100g of glycogen viaglycogenesis
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis or the process of converting glucose into glycogen in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycl ...
, the formation of glycogen from glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
.
* When needed, the liver releases glucose into the blood by performing glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanis ...
, the breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
* The liver is also responsible for gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
, which is the synthesis of glucose from certain amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, lactate, or glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
. Adipose and liver cells produce glycerol by breakdown of fat, which the liver uses for gluconeogenesis.
* Liver also does glyconeogenesis which is synthesis of glycogen from lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula C3H6O3. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as wel ...
.
Protein metabolism
The liver is responsible for the mainstay of proteinmetabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
, synthesis as well as degradation. All plasma proteins except Gamma-globulins are synthesised in the liver. It is also responsible for a large part of amino acid synthesis
Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of biochemical processes (metabolic pathways) by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to ...
. The liver plays a role in the production of clotting factors, as well as red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
production. Some of the proteins synthesized by the liver include coagulation factors
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of coagulation ...
I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, XIII, as well as protein C
Protein C, also known as autoprothrombin IIA and blood coagulation factor XIV, is a zymogen, that is, an inactive enzyme. The activated form plays an important role in regulating anticoagulation, inflammation, and cell death and maintaini ...
, protein S
Protein S (also known as PROS) is a vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein synthesized in the liver. In the circulation, Protein S exists in two forms: a free form and a complex form bound to complement protein C4b-binding protein (C4BP). In h ...
and antithrombin
Antithrombin (AT) is a small glycoprotein that inactivates several enzymes of the coagulation system. It is a 464-amino-acid protein produced by the liver. It contains three disulfide bonds and a total of four possible glycosylation sites. α-An ...
. The liver is a major site of production for thrombopoietin
Thrombopoietin (THPO) also known as megakaryocyte growth and development factor (MGDF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''THPO'' gene.
Thrombopoietin is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the liver and kidney which regulates the pro ...
, a glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
hormone that regulates the production of platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
s by the bone marrow.
Lipid metabolism
The liver plays several roles inlipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
metabolism: it performs cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
synthesis, lipogenesis
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into Adipose tissue, fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in adipose, fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty aci ...
, and the production of triglyceride
A triglyceride (from '' tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates ...
s, and a bulk of the body's lipoproteins are synthesized in the liver. The liver plays a key role in digestion, as it produces and excretes bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
(a yellowish liquid) required for emulsifying fats and help the absorption of vitamin K from the diet. Some of the bile drains directly into the duodenum, and some is stored in the gallbladder. The liver produces insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in tertiary structure, molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has Anabolism, anabolic effects in adults. In the ...
, a polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty ...
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
hormone that plays an important role in childhood growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults.
Breakdown
The liver is responsible for the breakdown ofinsulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
and other hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s. The liver breaks down bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
via glucuronidation
Glucuronidation is often involved in drug metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids. These linkages involve gly ...
, facilitating its excretion into bile.
The liver is responsible for the breakdown and excretion of many waste products. It plays a key role in breaking down or modifying toxic substances (e.g., methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replac ...
) and most medicinal products in a process called drug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set o ...
. This sometimes results in toxication
Toxication, toxification or toxicity exaltation is the conversion of a chemical compound into a more toxic form in living organisms or in substrates such as soil or water. The conversion can be caused by enzyme, enzymatic metabolism in the organism ...
, when the metabolite is more toxic than its precursor. Preferably, the toxins are conjugated to avail excretion in bile or urine. The liver converts ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
into urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
as part of the ornithine cycle or the urea cycle, and the urea is excreted in the urine.
Blood reservoir
Because the liver is an expandable organ, large quantities of blood can be stored in its blood vessels. Its normal blood volume, including both that in the hepatic veins and that in the hepatic sinuses, is about 450 milliliters, or almost 10 percent of the body's total blood volume. When high pressure in the right atrium causes backpressure in the liver, the liver expands, and 0.5 to 1 liter of extra blood is occasionally stored in the hepatic veins and sinuses. This occurs especially incardiac failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pre ...
with peripheral congestion. Thus, in effect, the liver is a large, expandable, venous organ capable of acting as a valuable blood reservoir in times of excess blood volume and capable of supplying extra blood in times of diminished blood volume.
Lymph production
Because the pores in the hepatic sinusoids are very permeable and allow ready passage of both fluid and proteins into the perisinusoidal space, thelymph
Lymph () is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the ori ...
draining from the liver usually has a protein concentration of about 6 g/dl, which is only slightly less than the protein concentration of plasma.
Also, the high permeability of the liver sinusoid epithelium allows large quantities of lymph to form. Therefore, about half of all the lymph formed in the body under resting conditions arises in the liver.
Other
* The liver stores a multitude of substances, includingvitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
(1–2 years' supply), vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
(1–4 months' supply), vitamin B12 (3–5 years' supply), vitamin K
Vitamin K is a family of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-translational modification, post-synthesis modification of certain proteins ...
, vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds related in molecular structure that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The tocopherols function as fat-soluble antioxidants which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen speci ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, etc.
* Haemopoiesis - The formation of blood cells is called haemopoiesis. In the embryonic stage, RBCs and WBCs are formed by liver. In the first trimester fetus, the liver is the main site of red blood cell production. By the 32nd week of gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregn ...
, the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
has almost completely taken over that task.
*The liver helps in the purification of blood. The Kupffer cell
Kupffer cells, also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer–Browicz cells, are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. K ...
s of liver are phagocytic cells
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ...
that help in the phagocytosis of dead blood cells and bacteria from the blood.
* The liver is responsible for immunological effects – the mononuclear phagocyte system
In immunology, the mononuclear phagocyte system or mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS), also known as the macrophage system, is a part of the immune system that consists of the Phagocyte, phagocytic cells located in reticular connective tissue. T ...
of the liver contains many immunologically active cells, acting as a 'sieve' for antigens carried to it via the portal system.
* The liver produces albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Alb ...
, the most abundant protein in blood serum
Serum () is the fluid and solvent component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum contains all proteins ex ...
. Albumin is essential in the maintenance of oncotic pressure
Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a type of osmotic pressure induced by the plasma proteins, notably albumin, in a blood vessel's plasma (or any other body fluid such as blood and lymph) that causes a pull on fluid back into ...
and acts as a transport for fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s and steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
s.
* The liver synthesizes angiotensinogen
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adr ...
, a hormone that is responsible for raising the blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
when activated by renin
Renin ( etymology and pronunciation), also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an aspartic protease protein and enzyme secreted by the kidneys that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—also known as the reni ...
, an enzyme that is released when the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
senses low blood pressure.
* The liver produces the enzyme catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting ...
to break down hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
, a toxic oxidising agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
, into water and oxygen.
Clinical significance
Disease
thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. Ther ...
. Liver diseases may be diagnosed by liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial ...
–blood tests that can identify various markers. For example, acute-phase reactants are produced by the liver in response to injury or inflammation.
The most common chronic liver disease is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which affects an estimated one-third of the world population.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
is a common condition of inflammation of the liver. The most usual cause of this is viral, and the most common of these infections are hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Some of these infections are sexually transmitted. Inflammation can also be caused by other viruses in the family Herpesviridae
''Orthoherpesviridae'', previously named and more widely known as ''Herpesviridae'', is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are commonly known as herp ...
such as the herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
. Chronic (rather than acute) infection with hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus is the main cause of liver cancer
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy, is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary in which the cancer starts in the liver, or it can be liver metastasis, or secondar ...
. Globally, about 248 million individuals are chronically infected with hepatitis B (with 843,724 in the U.S.), and 142 million are chronically infected with hepatitis C (with 2.7 million in the U.S.). Globally there are about 114 million and 20 million cases of hepatitis A and hepatitis E respectively, but these generally resolve and do not become chronic. Hepatitis D virus is a "satellite" of hepatitis B virus (it can only infect in the presence of hepatitis B), and co-infects nearly 20 million people with hepatitis B, globally.
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an altered level of consciousness as a result of liver failure. Its onset may be gradual or sudden. Other symptoms may include movement problems, changes in mood, or changes in personality. In the advanced stag ...
is caused by an accumulation of toxins in the bloodstream that are normally removed by the liver. This condition can result in coma and can prove fatal. Budd–Chiari syndrome
Budd–Chiari syndrome is a condition when an occlusion or obstruction in the hepatic veins prevent normal outflow of blood from the liver.
The symptoms are non-specific and vary widely, but it may present with the classical triad of abdomin ...
is a condition caused by blockage of the hepatic veins
In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava (as opposed to the hepatic portal vein which conveys blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver). There are usually thr ...
(including thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
) that drain the liver. It presents with the classical triad of abdominal pain, ascites
Ascites (; , meaning "bag" or "sac") is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdo ...
and liver enlargement. Many diseases of the liver are accompanied by jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving ...
caused by increased levels of bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
in the system. The bilirubin results from the breakup of the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
of dead red blood cells; normally, the liver removes bilirubin from the blood and excretes it through bile.
Other disorders caused by excessive alcohol consumption are grouped under alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosi ...
s and these include alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association wi ...
, fatty liver
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis and steatotic liver disease (SLD), is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper r ...
, and cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
. Factors contributing to the development of alcoholic liver diseases are not only the quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption, but can also include gender, genetics, and liver insult. Liver damage can also be caused by drugs, particularly paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
and drugs used to treat cancer. A rupture of the liver can be caused by a liver shot
A liver shot or liver punch is a punch, kick, or knee strike to the right side of the ribcage that damages the liver. Blunt force to the liver can be excruciatingly painful, but mostly lasts only about 30 seconds to one minute. An especially ef ...
used in combat sports.
Primary biliary cholangitis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to buil ...
is an autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
of the liver. It is marked by slow progressive destruction of the small bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).
Bile is requ ...
s of the liver, with the intralobular ducts (Canals of Hering
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flo ...
) affected early in the disease. When these ducts are damaged, bile and other toxins build up in the liver (cholestasis
Cholestasis is a condition where the flow of bile from the liver to the duodenum is impaired. The two basic distinctions are:
* obstructive type of cholestasis, where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallston ...
) and over time damages the liver tissue in combination with ongoing immune related damage. This can lead to scarring (fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, ch ...
) and cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
. Cirrhosis increases the resistance to blood flow in the liver, and can result in portal hypertension
Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Normal portal pressure is 1–4 mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5� ...
. Congested anastomoses between the portal venous system
In the circulatory system of vertebrates, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them ar ...
and the systemic circulation, can be a subsequent condition.
There are also many pediatric liver diseases, including biliary atresia
Biliary atresia, also known as extrahepatic ductopenia and progressive obliterative cholangiopathy, is a childhood disease of the liver in which one or more bile ducts are abnormally narrow, blocked, or absent. It can be congenital or acquired. ...
, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an inc ...
, alagille syndrome
Alagille syndrome (ALGS) is a genetic disorder that affects primarily the liver and the heart. Problems associated with the disorder generally become evident in infancy or early childhood. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant patter ...
, progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a group of Genetic disorder, familial cholestasis, cholestatic conditions caused by defects in bile, biliary Epithelium, epithelial transporters. The clinical presentation usually occurs firs ...
, Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is an abnormal clonal proliferation of Langerhans cells, abnormal cells deriving from bone marrow and capable of migrating from skin to lymph nodes.
Symptoms range from isolated bone lesions to multisystem d ...
and hepatic hemangioma a benign tumour the most common type of liver tumour, thought to be congenital. A genetic disorder causing multiple cysts to form in the liver tissue, usually in later life, and usually asymptomatic, is polycystic liver disease. Diseases that interfere with liver function will lead to derangement of these processes. However, the liver has a great capacity to regenerate and has a large reserve capacity. In most cases, the liver only produces symptoms after extensive damage.
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is enlargement of the liver. It is a non-specific sign (medicine), medical sign, having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, hepatic tumours, and metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly presents as an abdomin ...
refers to an enlarged liver and can be due to many causes. It can be palpated
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
in a liver span measurement.
Consuming caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
regularly may help safeguard individuals from liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
. Additionally, it has been shown to slow the advancement of liver disease in those already affected, lower the risk of liver fibrosis, and provide a protective benefit against liver cancer for moderate coffee drinkers. A 2017 study revealed that the positive effects of caffeine on the liver were evident regardless of the coffee preparation method.
Symptoms
The classic symptoms of liver damage include the following: * Pale stools occur whenstercobilin
Stercobilin is a tetrapyrrolic bile pigment and is one end-product of heme catabolism. It is the chemical responsible for the brown color of human feces and was originally isolated from feces in 1932. Stercobilin (and related urobilin) can be ...
, a brown pigment, is absent from the stool. Stercobilin is derived from bilirubin metabolites produced in the liver.
* Dark urine occurs when bilirubin mixes with urine
* Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving ...
(yellow skin and/or whites of the eyes) This is where bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
deposits in skin, causing an intense itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
. Itching is the most common complaint by people who have liver failure. Often this itch cannot be relieved by drugs.
* Swelling of the abdomen, and swelling of the ankles and feet occurs because the liver fails to make albumin.
* Excessive fatigue occurs from a generalized loss of nutrients, minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): M ...
and vitamins.
* Bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
and easy bleeding are other features of liver disease. The liver makes clotting factors
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of coagulatio ...
, substances which help prevent bleeding. When liver damage occurs, these factors are no longer present and severe bleeding can occur.
* Pain in the upper right quadrant can result from the stretching of Glisson's capsule in conditions of hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
and pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the new onset of hypertension, high blood pressure and often a significant amount of proteinuria, protein in the urine or by the new onset of high blood pressure a ...
.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis ofliver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Liver diseases
File:Ground gla ...
is made by liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial ...
, groups of blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s, that can readily show the extent of liver damage. If infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
is suspected, then other serological
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given mi ...
tests will be carried out. A physical examination of the liver can only reveal its size and any tenderness, and some form of imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
such as an ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
or CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
may also be needed.
Sometimes a liver biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy (removal of a small sample of tissue) from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.
Medica ...
will be necessary, and a tissue sample is taken through a needle inserted into the skin just below the rib cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great ve ...
. This procedure may be helped by a sonographer providing ultrasound guidance to an interventional radiologist.
Liver regeneration
The liver is the only human internal organ capable of natural regeneration of lost tissue; as little as 25% of a liver can regenerate into a whole liver. This is, however, not true regeneration but rather compensatory growth in mammals. The lobes that are removed do not regrow and the growth of the liver is a restoration of function, not original form. This contrasts with true regeneration where both original function and form are restored. In some other species, such as zebrafish, the liver undergoes true regeneration by restoring both shape and size of the organ. In the liver, large areas of the tissues are formed but for the formation of new cells there must be sufficient amount of material so the circulation of the blood becomes more active. This is predominantly due to thehepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
s re-entering the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
. That is, the hepatocytes go from the quiescent G0 phase
The G0 phase describes a cellular state outside of the replicative cell cycle. Classically, cells were thought to enter G0 primarily due to environmental factors, like nutrient deprivation, that limited the resources necessary for proliferation ...
to the G1 phase
The G1 phase, gap 1 phase, or growth 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes Messenger RNA, mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequ ...
and undergo mitosis. This process is activated by the p75 receptors. There is also some evidence of bipotential
Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types.
The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum ...
stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
s, called hepatic oval cells or ovalocytes (not to be confused with oval red blood cells of ovalocytosis), which are thought to reside in the canals of Hering
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flo ...
. These cells can differentiate into either hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
s or cholangiocyte
Cholangiocytes are the epithelial cells of the bile duct. They are cuboidal epithelium in the small interlobular bile ducts, but become columnar and carbonate-secreting in larger bile ducts approaching the porta hepatis and the extrahepatic du ...
s. Cholangiocytes are the epithelial lining cells of the bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).
Bile is requ ...
s. They are cuboidal epithelium in the small interlobular bile ducts, but become columnar and mucus secreting in larger bile ducts approaching the porta hepatis and the extrahepatic ducts. Research is being carried out on the use of stem cells for the generation of an artificial liver.
Scientific and medical works about liver regeneration often refer to the Greek Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
who was chained to a rock in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
where, each day, his liver was devoured by an eagle, only to grow back each night. The myth suggests the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically re ...
may have known about the liver's remarkable capacity for self-repair.
Liver transplantation
Human liver transplants were first performed by Thomas Starzl in theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Roy Calne
Sir Roy Yorke Calne (30 December 1930 – 6 January 2024) was a British surgeon and pioneer in organ transplantation. He was part of the team that performed the first liver transplantation operation in Europe in 1968, the world's first liver, ...
in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
, England in 1963 and 1967, respectively.
Liver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
is the only option for those with irreversible liver failure. Most transplants are done for chronic liver diseases leading to cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
, such as chronic hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include ...
, alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
, and autoimmune hepatitis. Less commonly, liver transplantation is done for fulminant hepatic failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs (such as jaundice) of liver disease, and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complicati ...
, in which liver failure occurs rapidly over a period of days or weeks.
Liver allograft
Allotransplant (''allo-'' meaning "other" in Ancient Greek, Greek) is the Organ transplant, transplantation of cell (biology), cells, Biological tissue, tissues, or Organ (anatomy), organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of ...
s for transplant usually come from donors who have died from fatal brain injury
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common ...
. Living donor liver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
is a technique in which a portion of a living person's liver is removed (hepatectomy
Hepatectomy is the surgical resection (removal of all or part) of the liver. While the term is often employed for the removal of the liver from a liver transplant donor, this article will focus on Segmental resection, partial resections of hepatic ...
) and used to replace the entire liver of the recipient. This was first performed in 1989 for pediatric liver transplantation. Only 20 percent of an adult's liver (Couinaud segments 2 and 3) is needed to serve as a liver allograft for an infant or small child.
More recently, adult-to-adult liver transplantation has been done using the donor's right hepatic lobe, which amounts to 60 percent of the liver. Due to the ability of the liver to regenerate, both the donor and recipient end up with normal liver function if all goes well. This procedure is more controversial, as it entails performing a much larger operation on the donor, and indeed there were at least two donor deaths out of the first several hundred cases. A 2006 publication addressed the problem of donor mortality and found at least fourteen cases. The risk of postoperative complications (and death) is far greater in right-sided operations than that in left-sided operations.
With the recent advances of noninvasive imaging, living liver donors usually have to undergo imaging examinations for liver anatomy to decide if the anatomy is feasible for donation. The evaluation is usually performed by multidetector row computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(MDCT) and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI). MDCT is good in vascular anatomy and volumetry. MRI is used for biliary tree anatomy. Donors with very unusual vascular anatomy, which makes them unsuitable for donation, could be screened out to avoid unnecessary operations.
Society and culture
Some cultures regard the liver as the seat of thesoul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that ...
. In Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, the gods punished Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
for revealing fire to humans by chaining him to a rock where a vulture
A vulture is a bird of prey that scavenges on carrion. There are 23 extant species of vulture (including condors). Old World vultures include 16 living species native to Europe, Africa, and Asia; New World vultures are restricted to Nort ...
(or an eagle
Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family of the Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of Genus, genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus ''Aquila ( ...
) would peck out his liver, which would regenerate overnight (the liver is the only human internal organ that actually can regenerate itself to a significant extent). Many ancient peoples of the Near East and Mediterranean areas practiced a type of divination
Divination () is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic ritual or practice. Using various methods throughout history, diviners ascertain their interpretations of how a should proceed by reading signs, ...
called haruspicy
In the religion of ancient Rome, a haruspex was a person trained to practise a form of divination called haruspicy, the inspection of the entrails of sacrificed animals, especially the livers of sacrificed sheep and poultry.
Various ancient ...
or hepatomancy
In the religion of ancient Rome, a haruspex was a person trained to practise a form of divination called haruspicy, the inspection of the entrails of sacrificed animals, especially the livers of sacrificed sheep and poultry.
Various ancient ...
, where they tried to obtain information by examining the livers of sheep and other animals.
In Plato, and in later physiology, the liver was thought to be the seat of the darkest emotions (specifically wrath, jealousy and greed) which drive men to action. The Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
(tractate ''Berakhot 61b'') refers to the liver as the seat of anger
Anger, also known as wrath ( ; ) or rage (emotion), rage, is an intense emotional state involving a strong, uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt, or threat.
A person experiencing anger will often experie ...
, with the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
counteracting this. The Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
, and Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
languages ( or or ) refer to the liver in figurative speech to indicate courage and strong feelings, or "their best"; e.g., "This Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
has thrown to you the pieces of its liver!". The term , literally "the strength (power) of my liver", is a term of endearment in Urdu. In Persian slang, is used as an adjective for any object which is desirable, especially women. In the Zulu language
Zulu ( ), or isiZulu as an endonym, is a Southern Bantu languages, Southern Bantu language of the Nguni languages, Nguni branch spoken in, and indigenous to, Southern Africa. Nguni dialects are regional or social varieties of the Nguni language, ...
, the word for liver () is the same as the word for courage. In English the term 'lily-livered' is used to indicate cowardice from the medieval belief that the liver was the seat of courage.
Spanish also means "courage".
However the secondary meaning of Basque is "indolence".
In biblical Hebrew, the word for liver, (, stemmed or , similar to Arabic ), also means heavy and is used to describe the rich ("heavy" with possessions) and honor (presumably for the same reason). In the Book of Lamentations (2:11) it is used to describe the physiological responses to sadness by "my liver spilled to earth" along with the flow of tears and the overturning in bitterness of the intestines. On several occasions in the book of Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( , ; ; ; ; , in Islam also called Zabur, ), also known as the Psalter, is the first book of the third section of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) called ('Writings'), and a book of the Old Testament.
The book is an anthology of ...
(most notably 16:9), the word is used to describe happiness in the liver, along with the heart (which beats rapidly) and the flesh (which appears red under the skin). Further usage as the self (similar to "your honor") is widely available throughout the old testament, sometimes compared to the breathing soul (Genesis 49:6, Psalms 7:6, etc.). An honorable hat was also referred to with this word (Job 19:9, etc.) and under that definition appears many times along with - grandeur. These four meanings were used in preceding ancient Afro-Asiatic languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of th ...
such as Akkadian and Ancient Egyptian preserved in classical Ethiopic Ge'ez language.
Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word for liver, such as hepatology
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion ...
, and hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
Food
Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, the anatomical word for "liver" ( French ''foie'', Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
''hígado'', etc.) derives not from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
anatomical term, ''jecur'', but from the culinary term ''ficatum'', literally "stuffed with figs
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Moraceae, native to the Mediterranean region, together with western and southern Asia. It has been cultivated since ancient times and i ...
", referring to the livers of geese that had been fattened on figs. Animal livers are rich in iron, vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
and vitamin B12; and cod liver oil
Cod liver oil is a dietary supplement derived from liver of Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua''). As with most fish oils, it contains the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and also vitamin A and vita ...
is commonly used as a dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill (pharmacy), pill, capsule (pharmacy), capsule, tablet (pharmacy), tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients eithe ...
.
Liver can be baked, boiled, broiled, fried, stir-fried, or eaten raw (''asbeh nayeh'' or ''sawda naye'' in Lebanese cuisine
Lebanese cuisine is the culinary traditions and practices originating from Lebanon. It includes an abundance of Whole grain#Varieties, whole grains, Fruit#Food uses, fruits, Vegetable#Cultivation, vegetables, fresh Fish (food), fish and seafood. ...
, or liver sashimi
is a Japanese cuisine, Japanese delicacy consisting of fresh raw fish or Raw meat, meat sliced into thin pieces and often eaten with soy sauce.
Origin
The word ''sashimi'' means 'pierced body', i.e., "wikt:刺身, 刺身" = ''sashimi'', whe ...
in Japanese cuisine
Japanese cuisine encompasses the regional and traditional foods of Japan, which have developed through centuries of political, economic, and social changes. The traditional cuisine of Japan (Japanese language, Japanese: ) is based on rice with m ...
). In many preparations, pieces of liver are combined with pieces of meat or kidneys, as in the various forms of Middle Eastern mixed grill (e.g. ''meurav Yerushalmi
Jerusalem mixed grill () is a grilled meat dish considered a specialty of Jerusalem. It consists of chicken hearts, spleens and liver mixed with bits of lamb cooked on a flat grill, seasoned with onion, garlic, black pepper, cumin, turmeric, oli ...
''). Well-known examples include liver pâté
Liver pate is a pâté and meat spread popular in Northern and Eastern Europe. Made from finely or coarsely ground pork liver and lard, it is similar to certain types of French and Belgian pâtés.
Scandinavia
Liver pâté is a popular foo ...
, foie gras
; (, ) is a specialty food product made of the liver of a Domestic duck, duck or Domestic goose, goose. According to French law, ''foie gras'' is defined as the liver of a duck or goose fattened by ''gavage'' (force feeding).
''Foie gras'' i ...
, chopped liver
Chopped liver (, ''gehakte leber'') is a liver pâté popular in Ashkenazi Jewish cuisine. This dish is a common menu item in kosher Jewish delicatessens in Britain, Canada, South Africa, Argentina and the United States.
Preparation and servin ...
, and leverpastej. Liver sausage
A sausage is a type of meat product usually made from ground meat—often pork, beef, or poultry—along with salt, spices and other flavourings. Other ingredients, such as grains or breadcrumbs, may be included as fillers or extenders.
...
s, such as Braunschweiger and liverwurst
Liverwurst, leberwurst, or liver sausage is a kind of sausage made from liver (food), liver. It is eaten throughout Europe, as well as North and South America, notably in Argentina and Chile.
Some liverwurst varieties are spreadable. Liverwurst ...
, are also a valued meal. Liver sausage
Liverwurst, leberwurst, or liver sausage is a kind of sausage made from liver. It is eaten throughout Europe, as well as North and South America, notably in Argentina and Chile.
Some liverwurst varieties are spreadable. Liverwurst usually contai ...
s may also be used as spreads. A traditional South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
n delicacy, skilpadjies
Skilpadjies is a traditional South African food, also known by other names such as and .
The dish is lamb's liver wrapped in (caul fat), which is the fatty membrane that surrounds the kidneys. Most cooks mince the liver, add coriander, choppe ...
, is made of minced lamb's liver wrapped in ''netvet'' (caul fat), and grilled over an open fire. Traditionally, some fish livers were valued as food, especially the stingray
Stingrays are a group of sea Batoidea, rays, a type of cartilaginous fish. They are classified in the suborder Myliobatoidei of the order Myliobatiformes and consist of eight families: Hexatrygonidae (sixgill stingray), Plesiobatidae (deepwate ...
liver. It was used to prepare delicacies, such as poached skate liver on toast in England, as well as the ''beignets de foie de raie'' and ''foie de raie en croute'' in French cuisine
French cuisine is the cooking traditions and practices of France. In the 14th century, Guillaume Tirel, a Court (royal), court chef known as "Taillevent", wrote ''Le Viandier'', one of the earliest recipe collections of medieval France. In ...
.
Giraffe liver
The Humr are one of the tribes in theBaggara
The Baggāra ( "heifer herder"), also known as Chadian Arabs, are a nomadic confederation of people of mixed Arab and Arabized indigenous African ancestry, inhabiting a portion of the Sahel mainly between Lake Chad and the Nile river near sou ...
ethnic group, native to southwestern Kordofan
Kordofan ( ') is a former province of central Sudan. In 1994 it was divided into three new federal states: North Kordofan, South Kordofan and West Kordofan. In August 2005, West Kordofan State was abolished and its territory divided between N ...
in Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
who speak ''Shuwa'' (Chadian Arabic
Chadian Arabic (), also known as Shuwa Arabic, Western Sudanic Arabic, or West Sudanic Arabic (WSA), is a variety of Arabic and the first language of 1.9 million people in Chad, both town dwellers and Baggara, nomadic cattle herders. Most of its ...
), make a non-alcoholic drink from the liver and bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
of the giraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on ...
, which they call ''umm nyolokh''. They claim it is intoxicating (Arabic سكران ''sakran''), causing dreams and even waking hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ...
s. Anthropologist Ian Cunnison accompanied the Humr on one of their giraffe-hunting expeditions in the late 1950s, and noted that:
:It is said that a person, once he has drunk ''umm nyolokh'', will return to giraffe again and again. Humr, being Mahdists, are strict abstainers rom alcohol
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* R ...
and a Humrawi is never drunk (''sakran'') on liquor
Liquor ( , sometimes hard liquor), spirits, distilled spirits, or spiritous liquor are alcoholic drinks produced by the distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar that have already gone through ethanol fermentation, alcoholic ferm ...
or beer. But he uses this word to describe the effects which ''umm nyolokh'' has upon him.
Cunnison's remarkable account of an apparently psychoactive mammal found its way from a somewhat obscure scientific paper into more mainstream literature through a conversation between W. James of the Institute of Social and Cultural Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
at the University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest un ...
and specialist on the use of hallucinogen
Hallucinogens, also known as psychedelics, entheogens, or historically as psychotomimetics, are a large and diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mo ...
s and intoxicants in society, and R. Rudgley, who discussed it in a book on psychoactive drugs for general readers. He speculated that a hallucinogenic compound N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), also known as ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (''N'',''N''-DMT), is a serotonergic hallucinogen and investigational drug of the tryptamine family that occurs naturally in many plants and animals, including humans. ...
in the giraffe liver might account for the intoxicating properties claimed for ''umm nyolokh''.
Cunnison, on the other hand, writing in 1958 found it hard to believe in the literal truth of the Humr's assertion that the drink was intoxicating:
:I can only assume that there is no intoxicating substance in the drink, and that the effect it produces is simply a matter of convention, although it may be brought about subconsciously.
The study of entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances used in spiritual and religious contexts to induce altered states of consciousness. Hallucinogens such as the psilocybin found in so-called "magic" mushrooms have been used in sacred contexts since ancie ...
s in general – including entheogens of animal origin (e.g. hallucinogenic fish
Several species of fish are claimed to produce hallucinogenic effects when consumed, a condition known as '' ichthyoallyeinotoxism''. For example, '' Sarpa salpa'', a species of sea bream referred to as the "dream-fish", is commonly claimed to ...
and toad venom) – has, however, made considerable progress in the sixty-odd years since Cunnison's report; the idea that some intoxicating substance might reside in giraffe livers may no longer be as far-fetched as it seemed to Cunnison. However, to date, proof (or disproof) still waits on detailed analyses of the organ and the beverage made from it.
Arrow/bullet poison
CertainTungusic peoples
Tungusic peoples are an ethnolinguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia, Mongolia and China.
The Tungusic language family is divided into two main branches, Northern ...
of northeast Asia formerly prepared a type of arrow poison
Arrow poisons are used to poison arrow heads or darts for the purposes of hunting and warfare. They have been used by indigenous peoples worldwide and are still in use in areas of South America, Africa and Asia. Notable examples are the poisons se ...
from rotting animal livers, which was, in later times, also applied to bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constru ...
s. Russian anthropologist S. M. Shirokogoroff
Sergei Mikhailovich Shirokogorov (; , 1887-1939) was a Russian anthropologist. A White émigré, he lived in China from 1922 until his death.
Early life and education
Shirokogoroff was born in Suzdal. He went to France in 1906 to study at the Uni ...
wrote that:
:Formerly the using of poisoned arrows was common. For instance, among the Kumarčen, OroqenOther animals
 The liver is found in all
The liver is found in all vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s and is typically the largest internal organ. The internal structure of the liver is broadly similar in all vertebrates, though its form varies considerably in different species, and is largely determined by the shape and arrangement of the surrounding organs. Nonetheless, in most species, it is divided into right and left lobes; exceptions to this general rule include snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
s, where the shape of the body necessitates a simple cigar-like form.
In neonatal marsupials, it is responsible for the production of blood cells.
An organ sometimes referred to as a liver is found associated with the digestive tract of the primitive chordate amphioxus
The lancelets ( ), also known as amphioxi (: amphioxus ), consist of 32 described species of somewhat fish-like benthic filter feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata, class Leptocardii, and family Branchiostomatidae.
Lancelets div ...
. Although it performs many functions of a liver, it is not considered a "true" liver but rather a ''homolog'' of the vertebrate liver.
The amphioxus hepatic caecum produces the liver-specific proteins vitellogenin, antithrombin
Antithrombin (AT) is a small glycoprotein that inactivates several enzymes of the coagulation system. It is a 464-amino-acid protein produced by the liver. It contains three disulfide bonds and a total of four possible glycosylation sites. α-An ...
, plasmin
Plasmin is an important enzyme () present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin thrombus, clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein (in the zymogen form of plasminogen) i ...
ogen, alanine aminotransferase
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT or ALAT), formerly alanine transaminase (ALT), and even earlier referred to as serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), is a transaminase enzyme () that was first ch ...
, and insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
/insulin-like growth factor
The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) are proteins with high sequence similarity to insulin. IGFs are part of a complex system that cells use to communicate with their physiologic environment. This complex system (often referred to as the IGF ...
.
See also
*Porphyria
Porphyria ( or ) is a group of disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, adversely affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as Porphyria#Acute porphyrias, acute p ...
*Johann Joseph Dömling
Johann Joseph Dömling (13 January 1771 – 7 March 1803) was a German physician, pauper's doctor and professor of physiology at the University of Würzburg. He was the son of a farmer who was unable to afford further education himself, but as a ...
(published ''Is the liver a purifying organ'' in 1798)
References
Works cited
* *External links
Liver at the Human Protein Atlas
VIRTUAL Liver – online learning resource
Liver enzymes
* with several diagrams. * {{Authority control Organs (anatomy)