Ethnic Romanian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Romanians (, ; dated
U.S. Library of Congress
: "however it is one interpretation of census data results. The subject of Moldovan vs Romanian ethnicity touches upon the sensitive topic of
Moldova's national identity
page 108 sqq. Romanians also form an ethnic minority in several nearby countries situated in Central, Southeastern, and Eastern Europe, most notably in
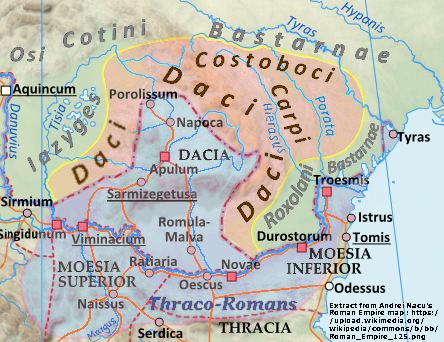 The territories of modern-day
The territories of modern-day  The Diocese of Dacia (circa 337–602) was a
The Diocese of Dacia (circa 337–602) was a
 After the
After the
 Eventually the entire
Eventually the entire 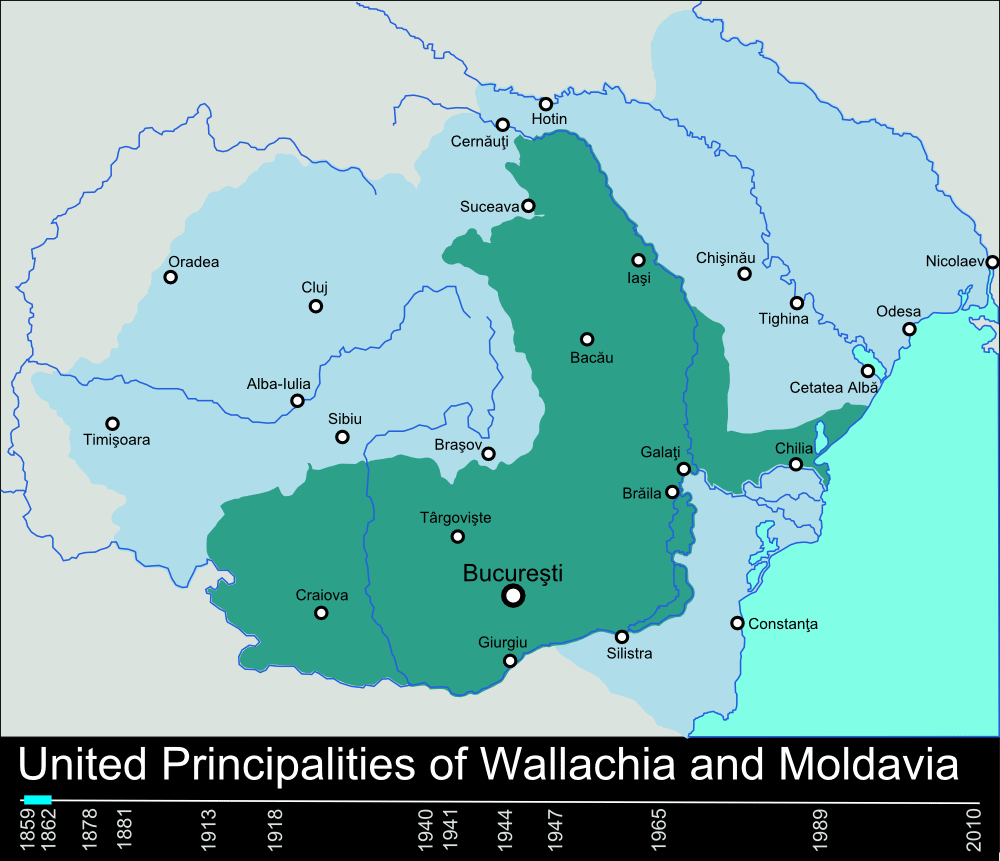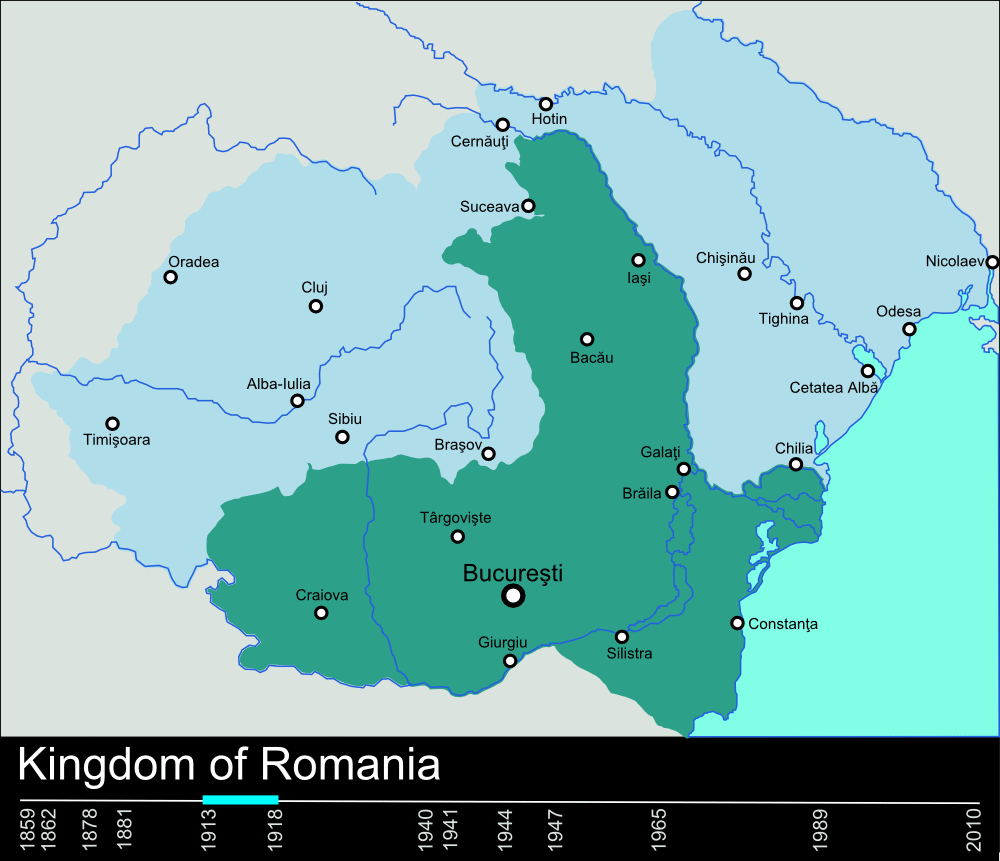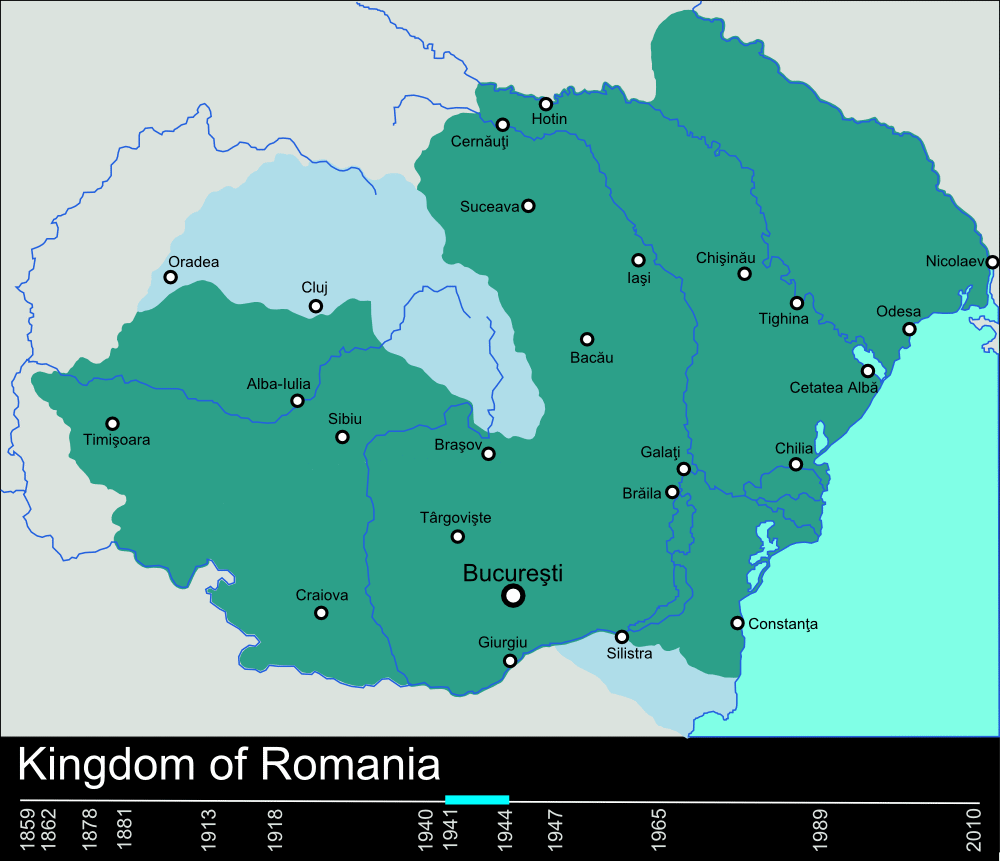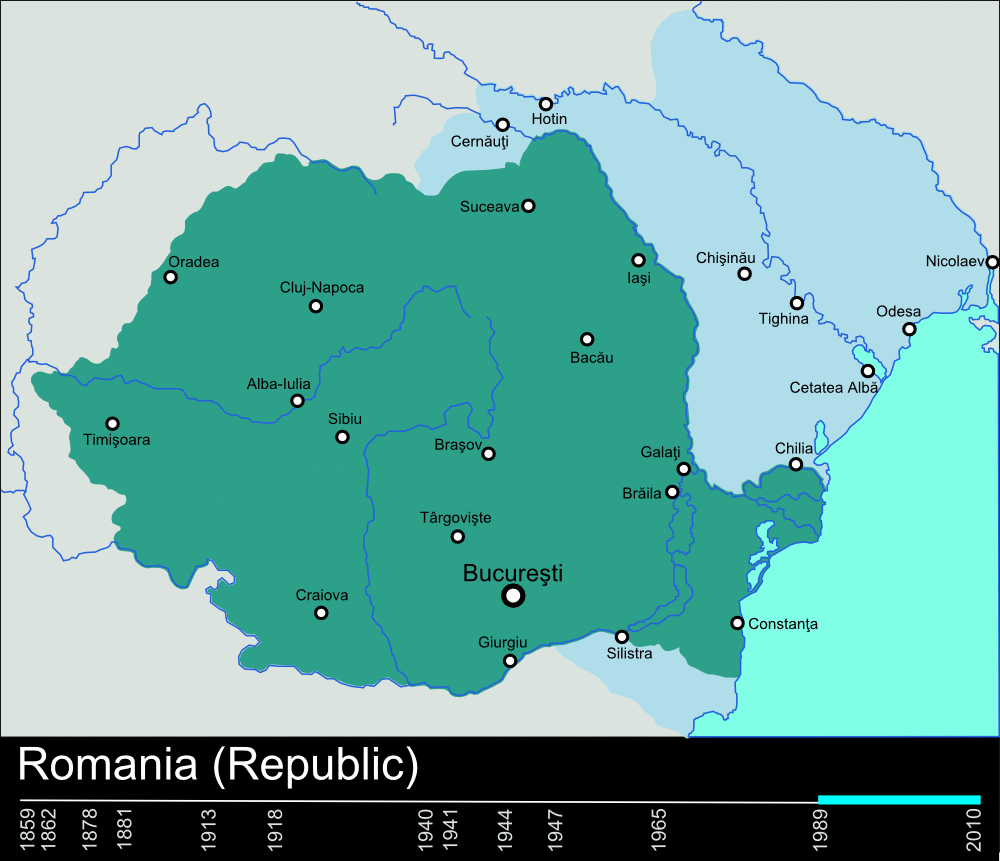 In the context of the 1848 Romanticist and liberal revolutions across Europe, the events that took place in the Grand Principality of Transylvania were the first of their kind to unfold in the Romanian-speaking territories. On the one hand, the
In the context of the 1848 Romanticist and liberal revolutions across Europe, the events that took place in the Grand Principality of Transylvania were the first of their kind to unfold in the Romanian-speaking territories. On the one hand, the
 During the Middle Ages, Romanian was isolated from the other Romance languages, and borrowed words from the nearby
During the Middle Ages, Romanian was isolated from the other Romance languages, and borrowed words from the nearby  Since 2013, the Romanian Language Day is officially celebrated on
Since 2013, the Romanian Language Day is officially celebrated on
 The name ''Romanian'' is derived from
The name ''Romanian'' is derived from

 Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia,
Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia,  For example, the decennial US Census of 2000 calculated (based on a
For example, the decennial US Census of 2000 calculated (based on a
File:Biserica „Sf. Nicolae” sat Densuș, comuna Densuș, jud. Hunedoara.jpg, Romano-Gothic Densuș Church, Hunedoara, Transylvania
File:Strei HD.NV.jpg, Romano-Gothic Strei Church, Hunedoara, Transylvania
File:Biserica Sfantu Nicolae.JPG, St. Nicholas Church, Brașov, Transylvania
File:Biserica Sf.Ioan Botezatorul.jpg, Nativity of St. John the Baptist Church, Piatra Neamț, Moldavia
File:Catedrala Mitropolitana02.JPG, Metropolitan Cathedral, Iași, Moldavia
File:Manastirea putna1.jpg, Putna Monastery, Bukovina
Romanian Catholics are present in
File:19, Strada General Henri Mathias Berthelot, Bucharest (Romania).jpg, Roman Catholic Saint Joseph Cathedral, Bucharest, Wallachia
File:Alba Iulia - Catedrala Sf.Mihail Aprilie 2013.JPG, Roman Catholic St. Michael's Cathedral, Alba Iulia, Transylvania
File:Blaj Catedrala greco catolica (3).jpg, Greek Catholic Cathedral of the Holy Trinity, Blaj, Transylvania
File:Centrul Vechi Baia Mare.jpg, Greek Catholic Assumption of Mary Cathedral, Baia Mare, Transylvania
File:Roman Catholic church in Suceava by day.jpg, Roman Catholic St. John of Nepomuk Church,
There are no official dates for the adoption of religions by the Romanians. Based on linguistic and archaeological findings, historians suggest that the Romanians' ancestors acquired polytheistic religions in the Roman era, later adopting Christianity, most likely by the 4th century AD when decreed by Emperor
File:43. TKB - Martis Orul z Kluż-Napoki (Rumunia) 03.JPG, Romanians from
 A Bulgarian study from 2013 shows genetic similarity between
A Bulgarian study from 2013 shows genetic similarity between  According to a Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a, is a
According to a Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a, is a
File:Roumanophones 1856.jpeg, Mid-19th century French map depicting Romanians in Central and Eastern Europe
File:RomaniansInBalkans.png, Modern distribution of the Eastern Romance-speaking ethnic groups (including, most notably, the Romanians)
File:Austria-Hungary (ethnic).jpg, Romanians in Central Europe (coloured in blue), 1880
File:Austro-Ungaria si Romania (harta etnica).jpg, Ethnic map of Austria-Hungary and Romania, 1892
File:Romanians before WW1.jpg, British map depicting territories inhabited by Eastern Romance peoples before the outbreak of World War I
File:Sprachatlas Weigand 67.JPG, Romanian speakers in Central and Eastern Europe, early 20th century
File:GreaterRomaniaHistoricRegions.png, Map of the Kingdom of Romania at its greatest extent (1920–1940)
File:SE Europe Romanians.png, Geographic distribution of ethnic Romanians in the early 21st century
File:Map-balkans-vlachs.png, Notable regions with inhabited by Eastern Romance speakers at the beginning of the 21st century
File:Daco-Romanians (subgroups).PNG, Map highlighting the three main sub-groups of Daco-Romanians
File:Romania harta etnica 2011.PNG, Geographic distribution of Romanians in Romania (coloured in purple) at commune level (2011 census)
File:Harta etnica 2011 JUD.png, Geographic distribution of Romanian in Romania (coloured in purple) at county level (2011 census)
A Concise History of Romanians
The Romanian nation in the beginning of the 20th century
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Romania Ethnic groups in Moldova Ethnic groups in Ukraine Ethnic groups in Serbia Ethnic groups in Vojvodina Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Hungary Ethnic groups divided by international borders Eastern Romance people
exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
''Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
'') are a Romance-speaking
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic branch of the Indo-European language family.
The fi ...
ethnic group and nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
native to Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
. Sharing a common culture and ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder, or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from ...
, they speak the Romanian language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved fr ...
and live primarily in Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
. The 2021 Romanian census
The 2021 Romanian census () was a census held in Romania between 1 February and 31 July 2022, with the reference day for the census data set at 1 December 2021. The census was supposed to be done in 2021, but it was postponed due to the COVID-19 ...
found that 89.3% of Romania's citizens identified themselves as ethnic Romanians.
In one interpretation of the 1989 census results in Moldova, the majority of Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians (, , ), are an ethnic group native to Moldova, who mostly speak the Romanian language, also referred to locally as Moldovan language, Moldovan. Moldovans form significant communities in Romania, It ...
were counted as ethnic Romanians as well.''Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook By'' David Levinson, Published 1998 – Greenwood Publishing Group.At the time of the 1989 census, Moldova's total population was 4,335,400. The largest nationality in the republic, ethnic Romanians, numbered 2,795,000 persons, accounting for 64.5 percent of the population. Source U.S. Library of Congress
: "however it is one interpretation of census data results. The subject of Moldovan vs Romanian ethnicity touches upon the sensitive topic of
Moldova's national identity
page 108 sqq. Romanians also form an ethnic minority in several nearby countries situated in Central, Southeastern, and Eastern Europe, most notably in
Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
(including Timok), and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
.
Estimates of the number of Romanian people worldwide vary from 24 to 30 million, in part depending on whether the definition of the term "Romanian" includes natives of both Romania and Moldova, their respective diasporas, and native speakers of both Romanian and other Eastern Romance languages
The Eastern Romance languages are a group of Romance languages. The group comprises the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian), the Aromanian language and two other related minor languages, Megleno-Romanian and Istro-Romanian.
The extinct Dalmat ...
. Other speakers of the latter languages are the Aromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
, the Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites (), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs (), are an Eastern Romance ethnic group, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis regional units of Central ...
, and the Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( or ) are a Romance languages, Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istria, Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. Howe ...
(native to Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
), all of them unevenly distributed throughout the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, which may be considered either Romanian subgroups or separated but related ethnicities.
History
Antiquity
 The territories of modern-day
The territories of modern-day Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
were inhabited by the ancient Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of informa ...
and Dacian tribes. King Burebista who reigned from 82/61 BC to 45/44 BC, was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers. King Decebalus
Decebalus (; ), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a R ...
who reigned from 87 to 106 AD was the last king of the Dacian kingdom before it was conquered by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in 106, after two wars between Decebalus' army and Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
's army. Prior to the two wars, Decebalus defeated a Roman invasion during the reign of Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a r ...
between 86 and 88 AD.Brian W. Jones, ''The Emperor Domitian'', (London: Routledge, 1992), p. 150
The Roman administration retreated from Dacia between 271 and 275 AD, during the reign of emperor Aurelian
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disinte ...
under the pressure of the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
and the Dacian Carpi tribe. The later Roman province '' Dacia Aureliana'', was organized inside former Moesia Superior. It was reorganized as Dacia Ripensis
Dacia Ripensis () was the name of a Roman province in the northern Balkan peninsula, immediately south of the Middle Danube. Its capital was Ratiaria (modern Archar, Bulgaria). It was a district less urban than neighbouring Dacia Mediterranea ...
(as a military province, devastated by an Avars invasion in 586) : "When founded as a colony by Trajan, Ratiaria was within Moesia Superior: when Aurelian withdrew from the old Dacia north of the Danube and established a new province of the same name on the south (Dacia Ripensis), Ratiaria became the capital. As such it was the seat of the military governor (dux), and the base of the legion XIII Gemina. It flourished in the fourth and fifth centuries, and according to the historian Priscus was ("very great and with numerous inhabitants") when it was captured by the Huns in the early 440s. It appears to have recovered from this sack, but was finally destroyed by the Avars in 586, though the name survives in the modern Arcar." and Dacia Mediterranea (as a civil province, devastated by an Avar invasion in 602).
 The Diocese of Dacia (circa 337–602) was a
The Diocese of Dacia (circa 337–602) was a diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
of the later Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, in the area of modern-day Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
. The Diocese of Dacia was composed of five provinces, the northernmost provinces were Dacia Ripensis
Dacia Ripensis () was the name of a Roman province in the northern Balkan peninsula, immediately south of the Middle Danube. Its capital was Ratiaria (modern Archar, Bulgaria). It was a district less urban than neighbouring Dacia Mediterranea ...
(the Danubian portion of Dacia Aureliana, one of the cities of Dacia Ripensis in today Romania is Sucidava) and Moesia Prima (today in Serbia, near the border between Romania and Serbia). The territory of the diocese was devastated by the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
in the middle of 5th century and finally overrun by the Avars and Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
in late 6th and early 7th century.
Scythia Minor (c. 290 – c. 680) was a Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
corresponding to the lands between the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, today's Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
divided between Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
.Kazhdan, Alexander (1991). "Scythia Minor". In Kazhdan, Alexander (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. . The capital of the province was Tomis (today Constanța
Constanța (, , ) is a city in the Dobruja Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Romania. A port city, it is the capital of Constanța County and the country's Cities in Romania, fourth largest city and principal port on the Black ...
). According to the ''Laterculus Veronensis
The ''Laterculus Veronensis'' or Verona List is a list of Roman provinces and barbarian peoples from the time of the emperors Diocletian and Constantine I, most likely from AD 314.
The list is transmitted only in a 7th-century manuscript preser ...
'' of and the ''Notitia Dignitatum
The (Latin for 'List of all dignities and administrations both civil and military') is a document of the Late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very ...
'' of , Scythia belonged to the Diocese of Thrace
The Diocese of Thrace (, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the eastern Balkan Peninsula (comprising territories in modern south-eastern Romania, central and eastern Bulgaria, and Greek and Turkish Thrace) ...
. The indigenous population of Scythia Minor was Dacian and their material culture is apparent archaeologically into the sixth century. Roman fortifications mostly date to the Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their junior colleagues and designated successors, the ''caesares''.
I ...
or the Constantinian dynasty
The Constantinian dynasty is an informal name for the ruling family of the Roman Empire from Constantius Chlorus (died 306) to the death of Julian in 363. It is named after its most famous member, Constantine the Great, who became the sole rule ...
. The province ceased to exist around 679–681, when the region was overrun by the Bulgars, which the Emperor Constantine IV
Constantine IV (); 650 – 10 July 685), called the Younger () and often incorrectly the Bearded () out of confusion with Constans II, his father, was Byzantine emperor from 668 to 685. His reign saw the first serious check to nearly 50 years ...
was forced to recognize in 681.
Early Middle Ages to Late Middle Ages
During theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
Romanians were mostly known as Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
, a blanket term ultimately of Germanic origin, from the word Walha
*''Walhaz'' is a reconstructed Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic word meaning 'foreigner', or more specifically 'Roman', 'Romance-speaker' or '(romanized) Celt', and survives in the English words of 'Wales/Welsh people, Welsh' and 'Corn ...
, used by ancient Germanic peoples to refer to Romance-speaking and Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
neighbours. Besides the separation of some groups (Aromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
, Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites (), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs (), are an Eastern Romance ethnic group, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis regional units of Central ...
, and Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( or ) are a Romance languages, Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istria, Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. Howe ...
) during the Age of Migration, many Vlachs could be found all over the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, across Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
as far north as Poland and as far west as the regions of Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
(part of the modern Czech Republic), some went as far east as Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in ...
of western Ukraine, and the present-day Croatia where the Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, Морлаци; ; ) is an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach pastoralist community in the mountain ...
gradually disappeared, while the Catholic and Orthodox Vlachs took Croat and Serb national identity.
The first written record about a Romance language
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
spoken in the Middle Ages in the Balkans, near the Haemus Mons
The Balkan mountain range is located in the eastern part of the Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border between Bulgaria and Serbia. It then runs f ...
is from 587 AD. A Vlach muleteer accompanying the Byzantine army noticed that the load was falling from one of the animals and shouted to a companion ''Torna, torna, fratre!'' (meaning "Return, return, brother!"). Theophanes the Confessor recorded it as part of a 6th-century military expedition by Comentiolus and Priscus
Priscus of Panium (; ; 410s/420s AD – after 472 AD) was an Eastern Roman diplomat and Greek historian and rhetorician (or sophist)...: "For information about Attila, his court and the organization of life generally in his realm we have the ...
against the Avars. Historian Gheorghe I. Brătianu considers that these words "represent an expression from the Romanian language, as it was formed at that time in the Balkan and Danube regions"; "they probably belong to one and the most significant of the substrates on which our (''Romanian'') language was built".
 After the
After the Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empi ...
collapsed in the 790s, the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northe ...
became the dominant power of the region, occupying lands as far as the river Tisa. The First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northe ...
had a mixed population consisting of the Bulgar conquerors, Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
and Vlachs (Romanians) but the Slavicisation of the Bulgar elite had already begun in the 9th century. Following the conquest of Southern and Central Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
around 830, people from the Bulgar Empire mined salt from mines in Turda
Turda (; , ; ; ) is a Municipiu, city in Cluj County, Transylvania, Romania. It is located in the southeastern part of the county, from the county seat, Cluj-Napoca, to which it is connected by the European route E81, and from nearby Câmpia ...
, Ocna Mureș, Sărățeni and Ocnița. They traded and transported salt throughout the Bulgar Empire.
A series of Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
historians from the 10th century are some of the first to mention Vlachs in Eastern/South Eastern Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
: Mutahhar al-Maqdisi (c.945-991) writes: "They say that in the Turkic neighborhood there are the Khazars, Russians, Slavs, ''Waladj'' (Vlachs), Alans, Greeks and many other peoples". Ibn al-Nadīm (early 932–998) published in 998 the work '' Kitāb al-Fihrist'' mentioning "Turks, Bulgars and Vlahs" (using ''Blagha'' for Vlachs).
The Byzantine chronicler Niketas Choniates writes that in 1164, Andronikos I Komnenos
Andronikos I Komnenos (; – 12 September 1185), Latinized as Andronicus I Comnenus, was Byzantine emperor from 1183 to 1185. A nephew of John II Komnenos (1118–1143), Andronikos rose to fame in the reign of his cousin Manuel I Komne ...
, the emperor Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos (; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Latinized as Comnenus, also called Porphyrogenitus (; " born in the purple"), was a Byzantine emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history o ...
's cousin, tried without success, to usurp the throne. Failing in his attempt, the Byzantine prince sought refuge in Halych
Halych (, ; ; ; ; , ''Halitsch'' or ''Galitsch''; ) is a historic List of cities in Ukraine, city on the Dniester River in western Ukraine. The city gave its name to the Principality of Halych, the historic province of Galicia (Eastern Europe), ...
but Andronikos I Komnenos
Andronikos I Komnenos (; – 12 September 1185), Latinized as Andronicus I Comnenus, was Byzantine emperor from 1183 to 1185. A nephew of John II Komnenos (1118–1143), Andronikos rose to fame in the reign of his cousin Manuel I Komne ...
was "captured by the ''Vlachs'', to whom the rumor of his escape had reached, he was taken back to the emperor".
The Byzantine chronicler John Kinnamos
John Kinnamos or ''Joannes Kinnamos'' or ''John Cinnamus'' ( or Κίναμος; born shortly after 1143, died after 1185), was a Byzantine historian. He was imperial secretary (Greek "grammatikos", most likely a post connected with the military ad ...
, presenting the campaign of Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos (; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Latinized as Comnenus, also called Porphyrogenitus (; " born in the purple"), was a Byzantine emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history o ...
against Hungary in 1166, reports that General Leon Vatatzes had under his command "a great multitude of Vlachs, who are said to be ancient colonies of those in Italy", an army that attacked the Hungarian possessions "about the lands near the Pontus called the Euxine", respectively the southeastern regions of Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, "destroyed everything without sparing and trampled everything it encountered in its passage".
By the 9th and 10th centuries, the nomadic Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
conquered much of the steppes of Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
and the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrai ...
.The Pecheneg wars against the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
caused some of the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
and Vlachs from North of the Danube to gradually migrate north of the Dniestr
The Dniester ( ) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and then through Moldova (from which it more or less separates the breakaway territory of Transnistria), finally discharging into the Black Sea on Ukr ...
in the 10th and 11th centuries.
The Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1422. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
founded by the Asen dynasty consisting of Bulgarians and Vlachs was founded in 1185 and lasted until 1396. Early rulers from the Asen dynasty (particularly Kaloyan
Kaloyan or Kalojan, also known as Ivan I, Ioannitsa or Johannitsa (; 1170 – October 1207), the Roman Slayer, was emperor or tsar of Bulgaria from 1196 to 1207. He was the younger brother of Theodor and Asen, who led the anti-Byzantine upr ...
) referred to themselves as "Emperors of Bulgarians and Vlachs". Later rulers, especially Ivan Asen II
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II (, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I of Bulgaria, Ivan Asen I one of the founders of th ...
, styled themselves "Tsars (Emperors) of Bulgarians and Romans". An alternative name used in connection with the pre-mid Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1422. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
13th century period is the ''Empire of Vlachs and Bulgarians''; variant names include the "Vlach–Bulgarian Empire", the "Bulgarian–Wallachian Empire".
Royal charters wrote of the "Vlachs' land" in southern Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
in the early 13th century, indicating the existence of autonomous Romanian communities. Papal correspondence mentions the activities of Orthodox prelates among the Romanians in Muntenia
Muntenia (, also known in English as Greater Wallachia) is a historical region of Romania, part of Wallachia (also, sometimes considered Wallachia proper, as ''Muntenia'', ''Țara Românească'', and the rarely used ''Valahia'' are synonyms in Ro ...
in the 1230s. Béla IV of Hungary
Béla IV (1206 – 3 May 1270) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1235 and 1270, and Duke of Styria from 1254 to 1258. As the oldest son of Andrew II of Hungary, King Andrew II, he was crowned upon the initiative of a group ...
's land grant to the Knights Hospitallers in Oltenia
Oltenia (), also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions – with the alternative Latin names , , and between 1718 and 1739 – is a historical province and geographical region of Romania in western Wallachia. It is situated between the Da ...
and Muntenia
Muntenia (, also known in English as Greater Wallachia) is a historical region of Romania, part of Wallachia (also, sometimes considered Wallachia proper, as ''Muntenia'', ''Țara Românească'', and the rarely used ''Valahia'' are synonyms in Ro ...
shows that the local Vlach rulers were subject to the king's authority in 1247.
The late 13th-century Hungarian chronicler Simon of Kéza states that the Vlachs were "shepherds and husbandmen" who "remained in Pannonia". An unknown author's ''Description of Eastern Europe'' from 1308 likewise states that the Vlachs "were once the shepherds of the Romans" who "had over them ten powerful kings in the entire Messia and Pannonia".
In the 14th century the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
emerged to fight the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. During the late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
, prominent medieval Romanian monarchs such as Bogdan of Moldavia, Stephen the Great
Stephen III, better known as Stephen the Great (; ; died 2 July 1504), was List of rulers of Moldavia, Voivode (or Prince) of Moldavia from 1457 to 1504. He was the son of and co-ruler with Bogdan II of Moldavia, Bogdan II, who was murdered in ...
, Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder (, ; 1355 – 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited the throne.
After the dea ...
, Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvani ...
, or Vlad the Impaler
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ) or Vlad Dracula (; ; 1428/31 – 1476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most important rulers in Wallachian hi ...
took part actively in the history of Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
by waging tumultuous wars and leading noteworthy crusades against the then continuously expanding Ottoman Empire, at times allied with either the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
or the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
in these causes.
Early Modern Age to Late Modern Age
 Eventually the entire
Eventually the entire Balkan peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
was annexed by the Ottoman Empire. However, Moldavia and Wallachia (extending to Dobruja and Bulgaria) were not entirely subdued by the Ottomans as both principalities became autonomous (which was not the case of other Ottoman territorial possessions in Europe). Transylvania, a third region inhabited by an important majority of Romanian speakers, was a vassal state of the Ottomans until 1687, when the principality became part of the Habsburg possessions. The three principalities were united for several months in 1600 under the authority of Wallachian Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The ...
Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvani ...
.
Up until 1541, Transylvania was part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, later (due to the conquest of Hungary by the Ottoman Empire) was a self-governed Principality governed by the Hungarian nobility. In 1699 it became a part of the Habsburg lands. By the end of the 18th century, the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
was awarded by the Ottomans with the region of Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
and, in 1812, the Russians occupied the eastern half of Moldavia, known as Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
through the Treaty of Bucharest of 1812.
 In the context of the 1848 Romanticist and liberal revolutions across Europe, the events that took place in the Grand Principality of Transylvania were the first of their kind to unfold in the Romanian-speaking territories. On the one hand, the
In the context of the 1848 Romanticist and liberal revolutions across Europe, the events that took place in the Grand Principality of Transylvania were the first of their kind to unfold in the Romanian-speaking territories. On the one hand, the Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen'' or simply ''Soxen'', singularly ''Sox'' or ''Soax''; Transylvanian Landler dialect, Transylvanian Landler: ''Soxn'' or ''Soxisch''; ; seldom ''sa ...
and the Transylvanian Romanians (with consistent support on behalf of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
) successfully managed to oppose the goals of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848, also known in Hungary as Hungarian Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many Revolutions of 1848, European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in ...
, with the two noteworthy historical figures leading the common Romanian-Saxon side at the time being Avram Iancu and Stephan Ludwig Roth.
On the other hand, the Wallachian revolutions of 1821 and 1848 as well as the Moldavian Revolution of 1848
The Moldavian Revolution of 1848 is the name used for the unsuccessful Romanian liberal and Romantic nationalist movement inspired by the Revolutions of 1848 in the principality of Moldavia. Initially seeking accommodation within the political ...
, which aimed for independence from Ottoman and Russian foreign rulership, represented important impacts in the process of spreading the liberal ideology in the eastern and southern Romanian lands, in spite of the fact that all three eventually failed. Nonetheless, in 1859, Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
elected the same ruler, namely Alexander John Cuza (who reigned as '' Domnitor'') and were thus unified ''de facto'', resulting in the United Romanian Principalities for the period between 1859 and 1881.
During the 1870s, the United Romanian Principalities (then led by Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen () was a principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to the junior House of Hohenzollern#Swabian branch, Swabian branch of the House of Hohenzollern. The Swabian Hohenzollerns were elevated to princes in 162 ...
Domnitor Carol I
Carol I or Charles I of Romania (born Karl Eitel Friedrich Zephyrinus Ludwig von Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen; 20 April 1839 – ), was the monarch of Romania from 1866 to his death in 1914, ruling as Prince (''Domnitor'') from 1866 to 1881, and as ...
) fought a War of Independence
Wars of national liberation, also called wars of independence or wars of liberation, are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against foreign powers (or at least those perceived as foreign) ...
against the Ottomans, with Romania's independence being formally recognised in 1878 at the Treaty of Berlin.
Although the relatively newly founded Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania () was a constitutional monarchy that existed from with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King of Romania, King Carol I of Romania, Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian royal family), until 1947 wit ...
initially allied with Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
, Romania refused to enter World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
on the side of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
, because it was obliged to wage war only if Austria-Hungary was attacked. In 1916, Romania joined the war on the side of the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was built upon th ...
.
As a result, at the end of the war, Transylvania, Bessarabia, and Bukovina were awarded to Romania, through a series of international peace treaties, resulting in an enlarged and far more powerful kingdom under King Ferdinand I. As of 1920, the Romanian people was believed to number over 15 million solely in the region of the Romanian kingdom, a figure larger than the populations of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, and the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
combined.
During the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, two additional monarchs came to the Romanian throne, namely Carol II
Carol II (4 April 1953) was King of Romania from 8 June 1930, until his forced abdication on 6 September 1940. As the eldest son of Ferdinand I of Romania, King Ferdinand I, he became crown prince upon the death of his grand-uncle, King Carol I, ...
and Michael I Michael I may refer to:
* Pope Michael I of Alexandria, Coptic Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark in 743–767
* Michael I Rangabe, Byzantine Emperor (died in 844)
* Michael I Cerularius, Patriarch Michael I of Constantinop ...
. This short-lived period was marked, at times, by political instabilities and efforts of maintaining a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
in favour of other, totalitarian regimes such as an absolute monarchy or a military dictatorship
A military dictatorship, or a military regime, is a type of dictatorship in which Power (social and political), power is held by one or more military officers. Military dictatorships are led by either a single military dictator, known as a Polit ...
.
Contemporary Era
During World War II, the Kingdom of Romania lost territory both to the east and west, asNorthern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania (, ) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary (1920-1946), Kingdom ...
became part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
through the Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and the Kingdom of Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Cri ...
, while Bessarabia and northern Bukovina were taken by the Soviets and included in the Moldavian SSR
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic or Moldavian SSR (, mo-Cyrl, Република Советикэ Сочиалистэ Молдовеняскэ), also known as the Moldovan Soviet Socialist Republic, Moldovan SSR, Soviet Moldavia, Sovie ...
, respectively Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
. The eastern territory losses were facilitated by the Molotov–Ribbentrop Nazi-Soviet non-aggression pact.
After the end of the war, the Romanian Kingdom managed to regain territories lost westward but was nonetheless not given Bessarabia and northern Bukovina back, the aforementioned regions being forcefully incorporated into the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(USSR). Subsequently, the Soviet Union imposed a communist government and King
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
Michael was forced to abdicate and leave for exile, subsequently settling in Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, while Petru Groza
Petru Groza (7 December 1884 – 7 January 1958) was a Romanian politician, best known as the first Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister of the Romanian Communist Party, Communist Party-dominated government under Soviet Union, Soviet Sovie ...
remained the head of the government of the Socialist Republic of Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania (, RSR) was a Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist One-party state, one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989 (see Revolutions of 1989). From 1947 to 1965, the state was ...
(RSR). Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( ; ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian politician who was the second and last Communism, communist leader of Socialist Romania, Romania, serving as the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 u ...
became the head of the Romanian Communist Party
The Romanian Communist Party ( ; PCR) was a communist party in Romania. The successor to the pro-Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave an ideological endorsement to a communist revolution that would replace the social system ...
(PCR) in 1965 and his severe rule of the 1980s was ended by the Romanian Revolution of 1989.
The chaos of the 1989 revolution brought to power the dissident communist Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu (; born 3 March 1930) is a Romanian politician and engineer who served as the second president of Romania from 1989 until 1996 and from 2000 until 2004. Between 1996 and 2000 and also from 2004 to 2008, the year in which he retired, ...
as president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
(largely supported by the FSN). Iliescu remained in power as head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
until 1996, when he was defeated by CDR-supported Emil Constantinescu
Emil Constantinescu (; born 19 November 1939) is a Romanian professor and politician, who served as the President of Romania, from 1996 to 2000.
After the Romanian Revolution, Romanian Revolution of 1989, Constantinescu became a founding member ...
in the 1996 general elections, the first in post-communist Romania that saw a peaceful transition of power
A peaceful transition or transfer of power is a concept important to democracy, democratic governments in which the leadership of a government peacefully hands over control of government to a newly elected leadership. This may be after elections o ...
. Following Constantinescu's single term as president from 1996 to 2000, Iliescu was re-elected in late 2000 for another term of four years. In 2004, Traian Băsescu, the PNL- PD candidate of the Justice and Truth Alliance (DA), was elected president. Five years later, Băsescu (solely supported by the PDL this time) was narrowly re-elected for a second term in the 2009 presidential elections.
In 2014, the PNL- PDL candidate (as part of the larger Christian Liberal Alliance or ACL for short; also endorsed by the Democratic Forum of Germans in Romania
The Democratic Forum of Germans in Romania (, DFDR; , FDGR; in short or ) is a political party (legally recognized as an association of public utility according to the governmental decision HG 599 as per 4 June 2008) organised on ethnic criteria ...
, FDGR/DFDR for short respectively) Klaus Iohannis
Klaus Werner Iohannis (; ; born 13 June 1959) is a Romanian politician, physicist, and former teacher who served as the fifth president of Romania from 2014 until his resignation in 2025. Prior to entering Politics of Romania, national politics, ...
won a surprise victory over former Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
and PSD-supported contender Victor Ponta in the second round of the 2014 presidential elections. Thus, Iohannis became the first Romanian president stemming from an ethnic minority of the country (as he belongs to the Romanian-German community, being a Transylvanian Saxon). In 2019, the PNL-supported Iohannis was re-elected for a second term as president after a second round landslide victory in the 2019 Romanian presidential election (being also supported in that round by PMP and USR as well as by the FDGR/DFDR in both rounds).
In the meantime, Romania's major foreign policy achievements were the alignment with Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
by joining the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental transnational military alliance of 32 member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermat ...
(NATO) back in 2004 and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
three years later, in 2007. Current national objectives of Romania include adhering to the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
, the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
as well as the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
(i.e. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development).
Language
 During the Middle Ages, Romanian was isolated from the other Romance languages, and borrowed words from the nearby
During the Middle Ages, Romanian was isolated from the other Romance languages, and borrowed words from the nearby Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavs, Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic language, Proto- ...
(see Slavic influence on Romanian). Later on, it borrowed a number of words from German, Hungarian, and Turkish. During the modern era, most neologisms were borrowed from French and Italian, though the language has increasingly begun to adopt English borrowings.
The origins of the Romanian language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved fr ...
, a Romance language
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, can be traced back to the Roman colonisation of the region. The basic vocabulary is of Latin origin, although there are some substratum
Substrata, plural of substratum, may refer to:
*Earth's substrata, the geologic layering of the Earth
*''Hypokeimenon'', sometimes translated as ''substratum'', a concept in metaphysics
*Substrata (album), a 1997 ambient music album by Biosphere
* ...
words that are assumed to be of Dacian origin. It is the most spoken Eastern Romance language and is closely related to Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian, all three part of the same sub-branch of Romance languages.
31 August
Events Pre-1600
* 1056 – After a sudden illness a few days previously, Byzantine Empress Theodora dies childless, thus ending the Macedonian dynasty.
* 1057 – Abdication of Byzantine Emperor Michael VI Bringas after just one yea ...
in Romania. In Moldova, it is officially celebrated on the same day since 2023.
As of 2017, an Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
estimation puts the (worldwide) number of Romanian speakers at approximately 24.15 million. The 24.15 million, however, represent only speakers of Romanian, not all of whom are necessarily ethnic Romanians. Also, this number does not include ethnic-Romanians who no longer speak the Romanian language.
Names for Romanians
In English, Romanians are usually called Romanians and very rarely Rumanians or Roumanians, except in some historical texts, where they are called Roumans orVlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
.
Etymology of the name ''Romanian'' ()
 The name ''Romanian'' is derived from
The name ''Romanian'' is derived from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''romanus'', meaning " Roman". Under regular phonetical changes that are typical to the Romanian language, the name over the centuries transformed into . An older form of was still in use in some regions. Socio-linguistic evolutions in the late 18th century led to a gradual preponderance of the spelling form, which was then generalised during the National awakening of Romania of early 19th century.Vladimír Baar, Daniel Jakubek, (2017) Divided National Identity in Moldova, Journal of Nationalism, Memory & Language Politics, Volume 11: Issue 1, .
Several historical sources show the use of the term "Romanian" among the medieval or early modern Romanian population. One of the earliest examples comes from the '' Nibelungenlied'', a German epic poem
In poetry, an epic is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. With regard to ...
from before 1200 in which a "Duke Ramunc from the land of Vlachs (Wallachia)" is mentioned. "Vlach" was an exonym used almost exclusively for the Romanians during the Middle Ages. It has been argued by some Romanian researchers that "Ramunc" was not the name of the duke, but a name that highlighted his ethnicity. Other old documents, especially Byzantine or Hungarian ones, make a correlation between the old Romanians as Romans or their descendants. Several other documents, notably from Italian travelers into Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania, speak of the self-identification, language and culture of the Romanians, showing that they designated themselves as "Romans" or related to them in up to 30 works. One example is Tranquillo Andronico's 1534 writing that states that the Vlachs "now call themselves Romans". Another one is Francesco della Valle's 1532 manuscripts that state that the Romanians from Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania preserved the name "Roman" and cites the sentence "''Sti Rominest?''" (''?'', "do you speak Romanian?"). Authors that travelled to modern Romania who wrote about it in 1574, 1575 and 1666 also noted the use of the term "Romanian". From the Middle Ages, Romanians bore two names, the exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
(one given to them by foreigners) ''Wallachians'' or ''Vlachs'', under its various forms (''vlah'', ''valah'', ''valach'', ''voloh'', ''blac'', ''olăh'', ''vlas'', ''ilac'', ''ulah'', etc.), and the endonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
(the name they used for themselves) ''Romanians'' (/). The first mentions by Romanians of the endonym are contemporary with the earliest writings in Romanian from the sixteenth century.
According to Tomasz Kamusella
Tomasz Kamusella (born 24 December 1967) is a Polish scholar pursuing interdisciplinary research in language politics, nationalism, and ethnicity.
Education
Kamusella was educated at the University of Silesia in Katowice, Faculty of Philolog ...
, at the time of the rise of Romanian nationalism during the early 19th century, the political leaders of Wallachia and Moldavia were aware that the name ''România'' was identical to ''Romania'', a name that had been used for the former Byzantine Empire by its inhabitants. Kamusella continues by stating that they preferred this ethnonym in order to stress their presumed link with Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
and that it became more popular as a nationalistic form of referring to all Romanian-language speakers as a distinct and separate nation during the 1820s. Raymond Detrez asserts that , derived from the Latin , acquired at a certain point the same meaning of the Greek ; that of Orthodox Christian. Wolfgang Dahmen claims that the meaning of ''romanus'' (Roman) as "Christian", as opposed to "pagan", which used to mean "non-Roman", may have contributed to the preservation of this word as an ethonym of the Romanian people, under the meaning of "Christian".
Daco-Romanian
To distinguish Romanians from the other Romanic peoples of the Balkans (Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, and Istro-Romanians), the term Daco-Romanian is sometimes used to refer to those who speak the standardRomanian language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved fr ...
and live in the former territory of ancient Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
(today comprising mostly Romania and Moldova) and its surroundings (such as Dobruja or the Timok Valley, the latter region part of the former Roman province of Dacia Ripensis
Dacia Ripensis () was the name of a Roman province in the northern Balkan peninsula, immediately south of the Middle Danube. Its capital was Ratiaria (modern Archar, Bulgaria). It was a district less urban than neighbouring Dacia Mediterranea ...
).
Etymology of the term Vlach
The name of "Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
" is an exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
that was used by Slavs to refer to all Romanized natives of the Balkans. It holds its origin from ancient Germanic—being a cognate to "Welsh" and "Walloon"—and perhaps even further back in time, from the Roman name Volcae, which was originally a Celt
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
ic tribe. From the Slavs, it was passed on to other peoples, such as the Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
(''Oláh'') and Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
(''Vlachoi'') (see the Etymology section of Vlachs). Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
, the Southern region of Romania, takes its name from the same source.
Nowadays, the term Vlach is more often used to refer to the Romanized populations of the Balkans who speak Daco-Romanian, Aromanian, Istro-Romanian, and Megleno-Romanian.
Romanians outside Romania
 Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia,
Most Romanians live in Romania, where they constitute a majority; Romanians also constitute a minority in the countries that neighbour Romania. Romanians can also be found in many countries, notably in the other EU countries, particularly in Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and France; in North America in the United States and Canada; in Israel; as well as in Brazil, Australia, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, and New Zealand among many other countries. Italy and Spain have been popular emigration destinations, due to a relatively low language barrier, and both are each now home to about a million Romanians. With respect to geopolitical identity, many individuals of Romanian ethnicity in Moldova prefer to identify themselves as Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians (, , ), are an ethnic group native to Moldova, who mostly speak the Romanian language, also referred to locally as Moldovan language, Moldovan. Moldovans form significant communities in Romania, It ...
.
The contemporary total population of ethnic Romanians cannot be stated with any degree of certainty. A disparity can be observed between official sources (such as census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
counts) where they exist, and estimates which come from non-official sources and interested groups. Several inhibiting factors (not unique to this particular case) contribute towards this uncertainty, which may include:
* A degree of overlap may exist or be shared between Romanian and other ethnic identities in certain situations, and census or survey respondents may elect to identify with one particular ancestry but not another, or instead identify with multiple ancestries;In an ever more globalized world the incredibly diverse and widespread phenomenon of migration has played a significant role in the ways in which notions such as "home," "membership" or "national belonging" have constantly been disputed and negotiated in both sending and receiving societies. – ''Rogers Brubaker, Citizenship and Nationhood '' (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1994).
* Counts and estimates may inconsistently distinguish between Romanian nationality and Romanian ethnicity (i.e. not all Romanian nationals identify with Romanian ethnicity, and vice versa);
* The measurements and methodologies employed by governments to enumerate and describe the ethnicity and ancestry of their citizens vary from country to country. Thus the census definition of "Romanian" might variously mean Romanian-born, of Romanian parentage, or also include other ethnic identities as Romanian which otherwise are identified separately in other contexts.
 For example, the decennial US Census of 2000 calculated (based on a
For example, the decennial US Census of 2000 calculated (based on a statistical sampling
In this statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole ...
of household data) that there were 367,310 respondents indicating Romanian ancestry (roughly 0.1% of the total population).
The actual total recorded number of foreign-born Romanians was only 136,000. However, some non-specialist organisations have produced estimates which are considerably higher: a 2002 study by the Romanian-American Network Inc. mentions an estimated figure of 1,200,000 for the number of Romanian Americans. Which makes the United States home to the largest Romanian community outside Romania.
This estimate notes however that "...other immigrants of Romanian national minority groups have been included such as: Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Gypsies, Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
, Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, and Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
". It also includes an unspecified allowance for second- and third-generation Romanians, and an indeterminate number living in Canada. An error range for the estimate is not provided. For the United States 2000 Census figures, almost 20% of the total population did not classify or report an ancestry, and the census is also subject to undercounting, an incomplete (67%) response rate, and sampling error in general.
In Republika Srpska
Republika Srpska ( sr-Cyrl, Република Српска, ; also referred to as the Republic of Srpska or Serb Republic) is one of the two Political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, entities within Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other bein ...
, one of the two entities constituting Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
together with the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Serbo-Croatian: ''Federacija Bosne i Hercegovine'' / ''Федерација Босне и Херцеговине'') is one of the two Political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, entities composing Bo ...
, Romanians are legally recognized as an ethnic minority.
Culture
Contributions to contemporary culture
Romanians have played and contributed a major role in the advancement of thearts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creativity, creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive ...
, culture, sciences
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
, technology and engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
.
In the history of aviation, Traian Vuia
Traian Vuia or Trajan Vuia (; 17 August 1872 – 3 September 1950) was a Romanian inventor and List of aviation pioneers, aviation pioneer who designed, built, and tested the first tractor configuration, tractor monoplane. He was the first to de ...
and Aurel Vlaicu built and tested some of the earliest aircraft designs, while Henri Coandă discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics. Victor Babeș discovered more than 50 germs and a cure for a disease named after him, babesiosis
Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a ''Babesia'' or '' Theileria'', in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via ...
; biologist Nicolae Paulescu
Nicolae Constantin Paulescu (; 30 October 1869 (O.S.) – 17 July 1931) was a Romanians, Romanian physiologist, professor of medicine, and politician, most famous for his work on diabetes, including patenting ''pancreine'' (a pancreatic extract ...
was among the first scientists to identify insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
. Another biologist, Emil Palade
George Emil Palade (; November 19, 1912 – October 7, 2008) was a Romanian-American cell biology, cell biologist. ...
, received the Nobel Prize for his contributions to cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
. George Constantinescu created the theory of sonics
The theory of sonics is a branch of continuum mechanics which describes the transmission of mechanical energy through oscillation, vibrations. The birth of the theory of sonics is the publication of the book ''A treatise on transmission of power b ...
, while mathematician Ștefan Odobleja has been claimed as "the ideological father behind cybernetics
Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions (its outputs) return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with ...
" – his work ''The Consonantist Psychology'' (Paris, 1938) was supposedly the main source of inspiration for N. Wiener's ''Cybernetics'' (Paris, 1948). Lazăr Edeleanu was the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
and also invented the modern method of refining
Refining is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, but which is more useful in its pure form. For instance, most types of natural petroleum w ...
crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring u ...
.
In the arts and culture, prominent figures were George Enescu
George Enescu (; – 4 May 1955), known in France as Georges Enesco, was a Romanians, Romanian composer, violinist, pianist, conductor, teacher and statesman. He is regarded as one of the greatest musicians in Romanian history.
Biography
En ...
(music composer, violinist, professor of Sir Yehudi Menuhin
Yehudi Menuhin, Baron Menuhin (22 April 191612 March 1999), was an American-born British violinist and conductor who spent most of his performing career in Britain. He is widely considered one of the greatest violinists of the 20th century. ...
), Constantin Brâncuși
Constantin Brâncuși (; February 19, 1876 – March 16, 1957) was a Romanian sculptor, painter, and photographer who made his career in France. Considered one of the most influential sculptors of the 20th century and a pioneer of modernism ...
(sculptor), Eugène Ionesco
Eugène Ionesco (; ; born Eugen Ionescu, ; 26 November 1909 – 28 March 1994) was a Romanian-French playwright who wrote mostly in French, and was one of the foremost figures of the French avant-garde theatre#Avant-garde, French avant-garde th ...
(playwright), Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanian History of religion, historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. One of the most influential scholars of religion of the 20th century and in ...
(historian of religion and novelist), Emil Cioran (essayist, Prix de l'Institut Français for stylism) and Angela Gheorghiu (soprano). More recently, filmmakers such as Cristi Puiu and Cristian Mungiu have attracted international acclaim, as has fashion designer Ioana Ciolacu.
In sports, Romanians have excelled in a variety of fields, such as football ( Gheorghe Hagi), gymnastics ( Nadia Comăneci, Lavinia Miloșovici etc.), tennis ( Ilie Năstase, Ion Țiriac
Ion Țiriac
(; born 9 May 1939), also known as the "Brașov Bulldozer", is a Romanian businessman and former professional tennis and ice hockey player. He has been president of the Romanian Tennis Federation.
A former singles top 10 player o ...
, Simona Halep), rowing ( Ivan Patzaichin) and handball (four times men's World Cup
A world cup is a global sporting competition in which the participant entities – usually international teams or individuals representing their countries – compete for the title of world champion. The event most associated with the name is ...
winners).
Count Dracula
Count Dracula () is the title character of Bram Stoker's 1897 gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. He is considered the prototypical and archetypal vampire in subsequent works of fiction. Aspects of the character are believed by some to have been i ...
is a worldwide icon of Romania. This character was created by the Irish fiction writer Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912), better known by his pen name Bram Stoker, was an Irish novelist who wrote the 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. The book is widely considered a milestone in Vampire fiction, and one of t ...
, based on some stories spread in the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
by the frustrated German tradesmen of Kronstadt (Brașov
Brașov (, , ; , also ''Brasau''; ; ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the county seat (i.e. administrative centre) of Brașov County.
According to the 2021 Romanian census, ...
) and on some vampire folk tales about the historic Romanian figure of Prince Vlad Țepeș.
Religion
Almost 90% of all Romanians consider themselves religious. The vast majority areEastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
Christians, belonging to the Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; , ), or Romanian Patriarchate, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates in the East ...
(a branch of Eastern Orthodoxy, or Eastern Orthodox Church, together with the Greek Orthodox, Orthodox Church of Georgia and Russian Orthodox Churches, among others). Romanians form the third largest ethno-linguistic group among Eastern Orthodox in the world.
According to the 2022 census, 91.5% of ethnic Romanians in Romania identified themselves as Romanian Orthodox (in comparison to 73.6% of Romania's total population, including other ethnic groups), followed by 3.6% as Protestants and 2.5% as Catholics. However, the actual rate of church attendance is significantly lower and many Romanians are only nominally believers. For example, according to a 2006 Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of public opinion statistical survey, surveys conducted regularly on behalf of the European Commission and other Institutions of the European Union, EU institutions since 1974. These surveys address a wide variety of to ...
poll, only 23% of Romanians attend church once a week or more. A 2006 poll conducted by the Open Society Foundations
Open Society Foundations (OSF), formerly the Open Society Institute, is an American grantmaking network founded by business magnate George Soros. Open Society Foundations financially supports civil society groups around the world, with the s ...
found that only 33% of Romanians attended church once a ''month'' or more.
Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
, Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
, and parts of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
, belonging to both the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
(297,246 members) and the Romanian Greek Catholic Church (124,563 members). According to the 2011 Romanian census
The 2011 Romanian census was a census held in Romania between 20 and 31 October 2011. It was performed by some 120,000 census takers in around 101,000 statistic sectors throughout the country established by the National Institute of Statistics ( ...
, 2.5% of ethnic Romanians in Romania identified themselves as Catholic (in comparison to 5% of Romania's total population, including other ethnic groups). Around 1.6% of ethnic Romanians in Romania identify themselves as Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
, with the population numbering 276,678 members. Smaller percentages are Protestant, Jews, Muslims, agnostic, atheist, or practice a traditional religion.
Suceava
Suceava () is a Municipiu, city in northeastern Romania. The seat of Suceava County, it is situated in the Historical regions of Romania, historical regions of Bukovina and Western Moldavia, Moldavia, northeastern Romania. It is the largest urban ...
, Bukovina
File:Timisoara - Catholic Dome in Union Square.jpg, Roman Catholic St. George Cathedral in Timișoara, Banat
Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
as the official religion of the Roman Empire. Like in all other Romance languages, the basic Romanian words related to Christianity are inherited from Latin, such as ''God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
'' ( < ), ''church'' ( < ), ''cross
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of t ...
'' ( < , -), ''angel'' ( < ), ''saint'' (regional: < ), ''Christmas'' ( < , -), ''Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
'' ( < ), ''Easter'' ( < ), ''sin'' ( < ), ''to baptise'' ( < ), ''priest'' ( < ), ''to pray'' ( < ), ''faith'' ( < ), and so on.
After the Roman Catholic-Eastern Orthodox Schism of 1054, there existed a Roman Catholic Diocese of Cumania for a short period of time, from 1228 to 1241. However, this seems to be the exception, rather than the rule, as in both Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
and Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
the state religion was Eastern Orthodox. Until the 17th century, the official language of the liturgy was Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
(a.k.a. Middle Bulgarian). Then, it gradually changed to Romanian.
Symbols
In addition to the colours of the Romanian flag, each historical province of Romania has its own characteristic symbol: *Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
: Trajan's Bridge
Trajan's Bridge (; ), also called Bridge of Apollodorus over the Danube, was a Roman segmental arch bridge, the first bridge to be built over the lower Danube and considered one of the greatest achievements in Roman architecture. Though it was ...
* Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
: Dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
* Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
(including Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
and Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
): Aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
/Wisent
The European bison (: bison) (''Bison bonasus'') or the European wood bison, also known as the wisent ( or ), the zubr (), or sometimes colloquially as the European buffalo, is a European species of bison. It is one of two extant species of bi ...
* Oltenia
Oltenia (), also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions – with the alternative Latin names , , and between 1718 and 1739 – is a historical province and geographical region of Romania in western Wallachia. It is situated between the Da ...
: Lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
* Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
(including Crișana
Crișana (, , ) is a geographical and historical region of Romania named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Romania, the term is sometimes extended to include areas ...
and Maramureș
( ; ; ; ) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, along parts of the upper Tisza River drainage basin; it covers the Maramureș Depression and the ...
): Black eagle or Turul
* Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
: Eagle
Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family of the Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of Genus, genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus ''Aquila ( ...
The coat of arms of Romania combines these together.
Customs
Traditional costumes
Cluj-Napoca
Cluj-Napoca ( ; ), or simply Cluj ( , ), is a city in northwestern Romania. It is the second-most populous city in the country and the seat of Cluj County. Geographically, it is roughly equidistant from Bucharest (), Budapest () and Belgrade ( ...
, Cluj County
Cluj County () is a county () of Romania, in Transylvania. Its seat is Cluj-Napoca.
Name
In Hungarian language, Hungarian it is known as ''Kolozs megye''. Under the Kingdom of Hungary, a county with an identical name (Kolozs County, ) existed s ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, in traditional folk costumes, dancing on the occasion of the Mărțișor holiday (2006).
File:Ion Theodorescu-Sion - Tarani din Abrud.jpg, Painting of Transylvanian Romanian peasants from Abrud by Ion Theodorescu-Sion
File:Costumes of Peasants from Romania, Hungary, Slovakia and Germany.jpg, Traditional Romanian peasant costumes to the left, followed from left to right by Hungarian, Slavic, and German ones
File:Bucovina.jpg, Romanian peasant costume from Bukovina, early 20th century
File:Bukovynski rumuny.jpg, Romanians from Bukovina, early 20th century postcard
File:Ipolit Strambu - Ciobanas.jpg, Painting of a young Wallachian shepherd in the early 20th century by Ipolit Strâmbu
File:Roumanians in New York 1891.JPG, Romanian immigrants in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, late 19th century
Relationship to other ethnic groups
The closest ethnic groups to the Romanians are the other Romanic peoples of Southeastern Europe: theAromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
( Macedo-Romanians), the Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites (), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs (), are an Eastern Romance ethnic group, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis regional units of Central ...
, and the Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( or ) are a Romance languages, Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istria, Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. Howe ...
. The Istro-Romanians are the closest ethnic group to the Romanians, and it is believed they left Maramureș
( ; ; ; ) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, along parts of the upper Tisza River drainage basin; it covers the Maramureș Depression and the ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
about a thousand years ago and settled in Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Croatia. Numbering about 500 people still living in the original villages of Istria while the majority left for other countries after World War II (mainly to Italy, United States, Canada, Spain, Germany, France, Sweden, Switzerland, Romania, and Australia), they speak the Istro-Romanian language
The Istro-Romanian language () is an Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance language, spoken in a few villages and hamlets in the peninsula of Istria in Croatia, as well as in the diaspora of this people. It is sometimes abbreviated to IR. ...
, the closest living relative of Romanian. On the other hand, the Aromanians and the Megleno-Romanians are Romance peoples who live south of the Danube, mainly in Greece, Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria although some of them migrated to Romania in the 20th century. It is believed that they diverged from the Romanians in the 7th to 9th century, and currently speak the Aromanian language
The Aromanian language (, , , , , or , , ), also known as Vlach or Macedo-Romanian, is an Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance language, similar to Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian an ...
and Megleno-Romanian language
Megleno-Romanian (known as by its speakers, and Megleno-Romanian or Meglenitic and sometimes Moglenitic or Meglinitic by linguists) is an Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance language, similar to Aromanian language, Aromanian. It is spo ...
, both of which are Eastern Romance languages, like Romanian, and are sometimes considered by traditional Romanian linguists to be dialects of Romanian.
Genetics
 A Bulgarian study from 2013 shows genetic similarity between
A Bulgarian study from 2013 shows genetic similarity between Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
(8-6 century BC), medieval Bulgarians (8–10 century AD), and modern Bulgarians, highlighting highest resemblance between them and Romanians, Northern Italians and Northern Greeks. A genetic study published in ''Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely ...
'' in 2019 examined the mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the DNA contained in ...
of 25 Thracian remains in Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
from the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC. They were found to harbor a mixture of ancestry from Western Steppe Herders (WSHs) and Early European Farmers (EEFs), supporting the idea that Southeast Europe was the link between Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean.
The prevailing Y-chromosome in Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
(Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a Municipiu, city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest.
The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Ble ...
, Dolj), Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
(Piatra Neamț
Piatra Neamț (; ; ) is the capital city of Neamț County, in the historical region of Western Moldavia, in northeastern Romania. Because of its very privileged location in the Divisions of the Carpathians, Eastern Carpathian mountains, it is con ...
, Buhuși
Buhuși (; ; ) is a town in Bacău County, Romania with a population of 14,152 as of 2021. It was first mentioned in the 15th century when it was named "Bodești" and was a property of an important family of Boyars named "Buhuș".
The town had ...
), Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
(Constanța
Constanța (, , ) is a city in the Dobruja Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Romania. A port city, it is the capital of Constanța County and the country's Cities in Romania, fourth largest city and principal port on the Black ...
), and northern Republic of Moldova is recorded to be Haplogroup I. Subclades I1 and I2 can be found in most present-day European populations, with peaks in some Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
an and Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
an countries. Haplogroup I occurs at 32% in Romanians. The frequency of I2a1 (I-P37) in the Balkans today is owed to indigenous European tribes, and was present before the Slavic migrations to Southeastern Europe
Early Slavs began mass migrating to Southeastern Europe between the first half of the 6th and 7th century in the Early Middle Ages. The rapid demographic spread of the Slavs was followed by a population exchange, mixing and language shift to and ...
. A similar result was cited in a study investigating the genetic pool of people from Republic of Moldova, concluded about the representative samples taken for comparison from Romanians from the towns of Piatra-Neamț and Buhuși that "the most common Y haplogroup in this population was I-M423 (40.7%). This is the highest frequency of the I-M423 haplogroup reported so far outside of the northwest Balkans. The next most frequent among Romanian males was haplogroup R-M17* (16.7%), followed by R-M405 (7.4%), E-v13 and R-M412* (both 5.6%)." The I-M423 haplogroup is a subclade of I2a, a haplogroup prosperous in the Starcevo culture and its possible offshoot Cucuteni–Trypillia culture (4800-3000 BCE). The high concentration of I2a1b-L621, the main subclade, is attributed to Bronze Age and Early Iron Age migrations (Dacians, Thracians, Illyrians) and the medieval Slavic migrations.
 According to a Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a, is a
According to a Y-chromosome analysis of 335 sampled Romanians, 15% of them belong to R1a. Haplogroup R1a, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by specific mutations in the non-Genetic recombination, recombining portions of DNA on the male-specific Y chromosome (Y-DNA). Individuals within a haplogroup share ...
which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
, extending from Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
to southern Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. Haplogroup R1a among Romanians is entirely from the Eastern European variety Z282 and may be a result of Baltic, Thracian or Slavic descent. 12% of the Romanians belong to Haplogroup R1b, the Alpino-Italic branch of R1b is at 2% a lower frequency recorded than other Balkan peoples. The eastern branches of R1b represent 7%, they prevail in parts of Eastern and Central Europe as a result of Ancient Greek colonisation
Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ag ...
– in parts of Sicily as well. Other studies analyzing the haplogroup frequency among Romanians came to similar results.
Delving into the regional differences of Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
of Romanians, a 2014 study emphasised the different position of North and South Romanian populations (ie inside and outside of the Carpathian range) in terms of mitochondrial haplotype variability. The population within the Carpathian range was found to have haplogroup H at 59.7% frequency, U at 11.3%, K and HV at 3.23% each, and M, X and A at 1.61% each. The South Romanian population also showed the highest frequency in haplogroup H at 47% (lower than in the sample from the North of Romania), haplogroup U showed a noticeable frequency at 17% (higher than in the sample from North Romania), haplogroups HV and K at 10.61% and 7.58%, respectively, while haplogroups M, X and A were absent. Comparing the results to European and international samples, the study proposes a weak differentiated distribution of mitochondrial haplogroups between inner and outer Carpathian population (rather than North-South boundary) based on higher frequency for the haplogroup J and haplogroup K2a in the Southern Romanian sample - considered as markers of the Neolithic expansion in Europe from the Near East, the absence of K2a and the presence of haplogroup M in Northern Romanian sample - with higher frequency in Western and Southern Asia, and the inclusion of both Romanian populations within the range of the European mitochondrial variability, rather than being closer to the Near Eastern populations. The North Romanian sample was also found to be slightly separated from the other samples included in the study.
A 2017 paper concentrated on the Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
of Romanians, showed how Romania has been "a major crossroads between Asia and Europe" and thus "experienced continuous migration and invasion episodes"; while stating that previous studies show Romanians "exhibit genetic similarity with other Europeans". The paper also mentions how "signals of Asian maternal lineages were observed in all Romanian historical provinces, indicating gene flow along the migration routes through East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
and Europe, during different time periods, namely, the Upper Paleolithic period and/or, with a likely greater preponderance, the Middle Ages", at low frequency (2.24%). The study analysed 714 samples, representative to the 41 counties of Romania, and grouped them in 4 categories corresponding to historical Romanian provinces: Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, and Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
. The majority was classified within 9 Eurasian mitochondrial haplogroups (H, U, K, T, J, HV, V, W, and X), while also finding sequences that belonged to the most frequent Asian haplogroups (haplogroups A, C, D, I - at 2.24% overall frequency, and M and N) and African haplogroup L (two samples in Wallachia and one in Dobruja). The H, V, and X haplogroups were detected at higher frequencies in Transylvania, while the frequency of U and N was lower, with M being absent, interpreted as an indicator of genetic proximity of Transylvania to Central European populations, in contrast to the other three provinces, which showed resemblance to Balkan populations. The Dobrujan samples showed a larger contribution of genes from Southwestern Asia which the authors attributed to a larger Asian influence historically and/or its smaller sample size compared to that of the other populations included.
Ethnogenesis
Three theories account for the ethnogenesis of the Romanian people. One, known as the Daco-Roman continuity theory, posits that they are descendants of Romans and Romanized indigenous peoples (Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
) living in the Roman Province of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
, while the other posits that the Romanians are descendants of Romans and Romanized indigenous populations of the former Roman provinces of Illyricum, Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
, Thracia
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkans, Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical Greece, Classical and Hellenistic period, Hellenis ...
, and Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
, and the ancestors of Romanians later migrated from these Roman provinces south of the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
into the area which they inhabit today.
The third theory also known as the admigration theory, proposed by Dimitrie Onciul (1856–1923), posits that the formation of the Romanian people occurred in the former "Dacia Traiana" province, and in the central regions of the Balkan Peninsula. However, the Balkan Vlachs' northward migration ensured that these centers remained in close contact for centuries. This theory is a compromise between the immigrationist and the continuity theories.
Demographics
The largest ethnic group in Romania is ethnic Romanians, followed byHungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
and Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
.
Maps
See also
* List of notable Romanians * List of Romanian inventors and discoverers *Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
* Slavic influence on Romanian
* Legacy of the Roman Empire
* Romanian diaspora
The Romanian diaspora is the Romanians, ethnically Romanian population outside Romania and Moldova. The concept does not usually include the ethnic Romanians who live as natives in nearby states, chiefly those Romanians who live in Ukraine, Hun ...
* Romanians in Germany
* Romanian British
* Romanian French
* Romanians of Italy
* Romanians of Spain
* Romanian Australians
* Romanian Americans
* Romanian Canadians
* Romanians of Serbia
* Romanian language in Serbia
* Romanians of Ukraine
* Romanians of Hungary
* Romanians of Bulgaria
* History of Romania
The Romanian state was formed in 1859 through a personal union of the United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. The new state, officially named Romania since 1866, gained independence ...
* Thraco-Roman
The term Thraco-Roman describes the Romanization (cultural), Romanized culture of Thracians under the rule of the Roman Empire.
The Odrysian kingdom of Thrace became a Roman client kingdom c. 20 BC, while the Greek city-states on the Black Sea coa ...
* Daco-Roman
The term Daco-Roman describes the Romanization (cultural), Romanized culture of Dacia under the rule of the Roman Empire.
Etymology
The Daco-Roman mixing theory, as an origin for the Romanian people, was formulated by the earliest Romanian scho ...
* Brodnici
The Brodnici (, ) were a tribe of disputed origin.
Etymology
In some opinions, the name, as used by foreign chronicles, means a person in charge of a ford (water crossing) in Slavic language (cf. Slavic ''brodŭ''). The probable reason for the n ...
* Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, Морлаци; ; ) is an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach pastoralist community in the mountain ...
* Gorals
The Gorals (; Goral ethnolect: ''Górole''; ; Cieszyn Silesian dialect, Cieszyn Silesian: ''Gorole''), also anglicized as the Highlanders, are an ethnographic group with historical ties to the Vlachs. The Goral people are primarily found in thei ...
* Moravian Wallachia
Moravian Wallachia (, or simply ''Valašsko''; ) is a mountainous ethnoregion located in the easternmost part of Moravia in the Czech Republic, near the Slovakia, Slovak border, roughly centered on the cities Vsetín, Valašské Meziříčí and ...
* Culture of Romania
The culture of Romania is an umbrella term used to encapsulate the ideas, customs and social behaviours of the people of Romania that developed due to the country's distinct geopolitical history and evolution. It is theorized that Romanians an ...
* Art of Romania
* Geography of Romania
With an area of , Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe. It is a country located at the crossroads of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeast Europe. It is bordered on the Black Sea, the country is halfway between the ...
* Folklore of Romania
The folklore of Romania is the collection of traditions of the Romanians. A feature of Culture of Romania, Romanian culture is the special relationship between folklore and the learned culture, determined by two factors. First, the rural chara ...
* Music of Romania
* Sport in Romania
* Name of Romania
* Romanian cuisine
Romanian cuisine () is a diverse blend of different dishes from several traditions with which it has come into contact, but it also maintains its own character. It has been influenced mainly by Ottoman cuisine, Ottoman and Turkish cuisine but a ...
* Romanian literature
* Minorities in Romania
Notes and references
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
A Concise History of Romanians
The Romanian nation in the beginning of the 20th century
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Romania Ethnic groups in Moldova Ethnic groups in Ukraine Ethnic groups in Serbia Ethnic groups in Vojvodina Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Hungary Ethnic groups divided by international borders Eastern Romance people