|
Catholic Church In Romania
Romanian Catholics, like Catholics elsewhere, are members of the Catholic Church under the spiritual leadership of the Pope and Roman Curia, Curia in Rome. The administration for the local Latin Church is centered in Bucharest, and comprises two archdioceses and four other dioceses. It is the second largest Romanian denomination after the Romanian Orthodox Church, and one of the 18 state-recognized religions. The 2022 census indicated that there were 741,504 Romanian citizens adhering to the Latin Church (3.89% of the population). Of these, the largest groups were Hungarian minority in Romania, Hungarians (54.7% or 405,212, including Székelys, Székely and Csángó), Romanians (38.2% or 283,092), Germans of Romania, Germans (1.7% or 12,495) and Slovaks of Romania, Slovaks (0.9% or 6,853)."Biserica Romano-Catolică" , at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
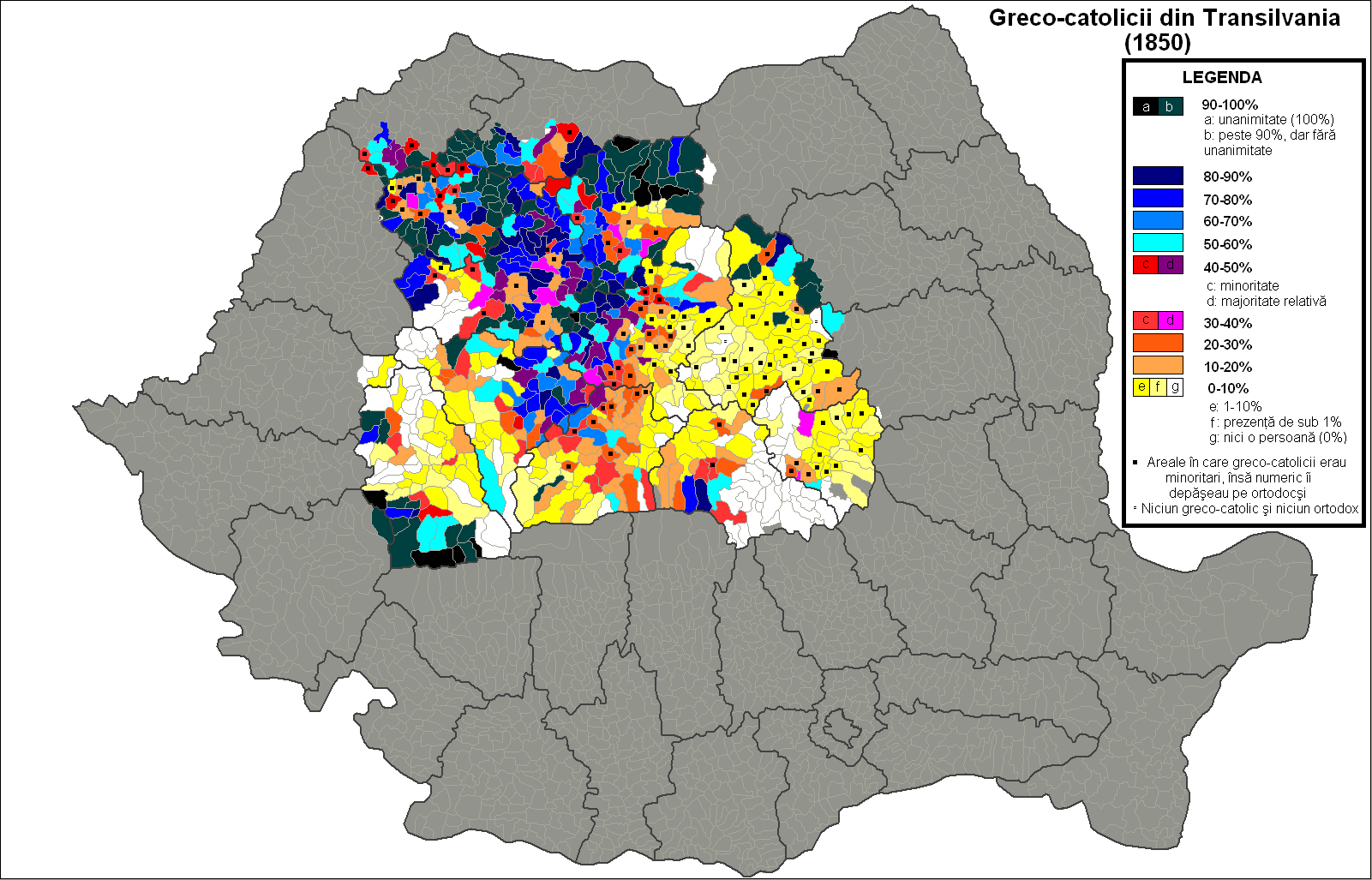
Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border are the Carpathian Mountains and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Historical Transylvania also includes small parts of neighbouring Western Moldavia and even a small part of south-western neighbouring Bukovina to its north east (represented by Suceava County). Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history, coupled with its multi-cultural character. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other very well preserved medieval iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Bistrița, Alba Iuli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, is a liturgical rite that is identified with the wide range of cultural, devotional, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian church of Constantinople. The canonical hours are extended and complex, lasting about eight hours (longer during Great Lent) but are abridged outside of large Monastery, monasteries. An iconostasis, a partition covered with icons, separates Sanctuary#Sanctuary as area around the altar, the area around the altar from the nave. The Sign of the cross#Eastern Orthodoxy, sign of the cross, accompanied by bowing, is made very frequently, e.g., more than a hundred times during the Divine Liturgy#Byzantine Rite, divine liturgy, and there is prominent veneration of icons, a general acceptance of the congregants freely moving within the church and interacting with each other, and distinctive traditions of liturgical chanting. Some traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Iuris
''Sui iuris'' (), also spelled ''sui juris'', is a Latin phrase that literally means "of one's own right". It is used in both the Catholic Church's canon law and secular law. The term church ''sui iuris'' is used in the Catholic ''Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches'' (CCEO) to denote the autonomous churches in Catholic communion. The Catholic Church consists of 24 churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic churches. Etymology and spelling The Latin ''sui iuris'' (the individual words meaning 'self' and 'law') corresponds to the Greek 'αὐτόνομος', from which the English word autonomy is derived. The spelling in Classical Latin is ''sui iuris'', and in Medieval Latin ''sui juris''. English Law gets the term from Medieval Latin, and so spells it ''sui juris''. Catholic canon law Church documents such as the ''Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches'' apply the Latin term ''sui iuris'' to the particular Churches that are together the Catholic Chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Greek Catholic Church
The Romanian Greek Catholic Church or Romanian Church United with Rome is a '' sui iuris'' Eastern Catholic Church, in full union with the Catholic Church. It has the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church and it uses the Byzantine liturgical rite in the Romanian language. It is part of the Major Archiepiscopal Churches of the Catholic Church that are not distinguished with a patriarchal title. Cardinal Lucian Mureșan, Archbishop of Făgăraș and Alba Iulia, has served as the head of the Romanian Greek-Catholic Church since 1994. On December 16, 2005, as the ''Romanian Church United with Rome'', the Greek-Catholic church was elevated to the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church by Pope Benedict XVI, with Lucian Mureșan becoming its first major archbishop. Mureşan was made a cardinal, at the consistory of February 18, 2012. Besides the Archeparchy of Făgăraș and Alba Iulia, there are five more Greek-Catholic eparchies in Romania ( Eparchy of Oradea Mare, Eparchy of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roma Minority In Romania
Romani people in Romania, locally and pejoratively referred to as the (), constitute the second largest ethnic minority in the country (the first being Hungarians in Romania, Hungarians). According to the Demographics of Romania#Censuses in Romania, 2021 census, their number was 569,477 people and 3.4% of the total population. The size of the total population of people with Romani ancestry in Romania is even more, with different estimates varying from 4.6 percent to over 10 percent of the population, because many people of Romani descent do not declare themselves Roma. For example, in 2007 the Council of Europe estimated that approximately 1.85 million Roma lived in Romania, based on an average between the lowest estimate (1.2 to 2.2 million people) and the highest estimate (1.8 to 2.5 million people) available at the time. This figure is equivalent to 8.32% of the population. On the other hand, less than half are native speakers of the Romani language. Origins History, genetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechs Of Romania
The Czechs (; ; ) are an ethnic minority in Romania, Alena Gecse and Dezideriu Gecse, "Istoria și cultura cehilor din Banat", i''Minorităţi în zonele de contact interetnic. Cehii şi slovacii în România şi Ungaria'' p.45-60, ed. Jakab Albert Zsolt and Peti Lehel, Editura Institutului pentru Studierea Problemelor Minorităților Naționale and Editura Kriterion, Cluj-Napoca, 2010, . numbering 3,938 people according to the 2002 census. The majority of Romanian Czechs live in the south-west of the country, with around 60% of them living in Caraș-Severin County, where they make up 0.7% of the population. As an officially recognised ethnic minority, Czechs, together with Slovaks, have one seat reserved in the Romanian Chamber of Deputies associated within Democratic Union of Slovaks and Czechs of Romania. History The Czechs were among the last peoples colonized by the Habsburg Empire in Banat. Their colonization took place in three main waves/stages: 1823, 1827 and 1862, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krashovani
The Krashovani (, ) are a Croat community inhabiting Carașova and Lupac in the Caraș-Severin County within Romanian Banat. They are Catholic by faith and speak a Torlakian dialect. Names In Romanian, they are commonly known as ''Carașoveni''; other variants include ''Carșoveni'', ''Cârșoveni'', ''Cotcoreți'' or ''Cocoși''. In Croatian, they are commonly known as ''Krašovani''; other variants include ''Karašovani'', ''Krašovanje'', ''Karaševci'' and ''Koroševci''. Settlements Krashovani, declared as Croats, form a majority in two communes of Caraș-Severin County: Carașova and Lupac. *Carașova commune **Carașova (Karaševo) **Nermed (Neremić) **Iabalcea (Jabalče) *Lupac commune **Clocotici (Klokotič) **Rafnic (Ravnik) **Vodnic (Vodnik) **Lupac (Lupak) Identity The Krashovani are adhere to the Catholic Church and identify their language as Croatian. Their dialect is regarded a sub-dialect of the Torlak dialect, a transitional dialect spoken in southea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Minority In Romania
According to the 2021 Romanian census, 2,137 Polish people, Poles live in Romania, mainly in the villages of Suceava County (). There are three exclusively Polish villages, as follows: ''Nowy Sołoniec'' (Cacica, Solonețu Nou), ''Plesza'' (Mănăstirea Humorului, Pleșa), and ''Pojana Mikuli'' (Poiana Micului), as well a significant Polish presence in ''Kaczyca'' (Cacica) and ''Paltynosa'' (Păltinoasa). There is also a relatively sizable number of ethnic Poles living in the county seat, Suceava (). Poles in Romania form an officially recognised national minority, having one seat in the Chamber of Deputies (Romania), Chamber of Deputies (currently held by the Union of Poles of Romania) and access to Polish elementary schools and cultural centres (known as "Polish Houses" or "Dom Polski" in Polish). History The first Poles settled in Moldavia in the times of Casimir III of Poland, Casimir III (specifically during the Late Middle Ages). Most of the Poles immigrating after 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italians Of Romania
Italian Romanians (; ) are Romanian-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Romania during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Romania. Italians have been present in Romania since the first half of the 19th century, when they emigrated from some Italian regions (particularly from Veneto and Friuli) to work in the mines, railway yards or construction. Characteristics Italian Romanians are fairly dispersed throughout the country, even though there is a higher number of them in some parts of the country (particularly Suceava County, Bacău County, Galați County, Iași County, Constanța County, Brașov County, Prahova County, Vâlcea County and Timiș County), and in Bucharest. As an officially recognised historical ethnic minority estimated at 9,000 Romanians of Italian ancestry, Italians have one seat reserved in the Romanian Chamber of Deputies. This was held by the Italian Community of Romania b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banat Bulgarians
The Banat Bulgarians ( Banat Bulgarian: ''Palćene'' or ''Banátsći balgare''; common ; ; ), also known as Bulgarian Roman Catholics, Bulgarian Latin Catholics and Bulgarians Paulicians or simply as Paulicians, are a distinct Bulgarian minority group which since the Chiprovtsi Uprising in the late 17th century began to settle in the region of the Banat, which was then ruled by the Habsburgs and after World War I was divided between Romania, Serbia, and Hungary. Unlike most other Bulgarians, they are Roman Catholic by confession and stem from groups of Paulicians (who eventually adopted Catholicism) and Roman Catholics from modern northern and northwestern Bulgaria. Banat Bulgarians speak a distinctive codified form of the Eastern Bulgarian vernacular with much lexical influence from the other languages of the Banat. Although strongly acculturated to the Pannonian region (remote from Bulgaria's mainland), they have preserved their Bulgarian identity; however, they consider the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |