Canis Aureus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to
 The golden jackal fills much the same ecological niche in Eurasia as the
The golden jackal fills much the same ecological niche in Eurasia as the
 Some golden jackals carry diseases and parasites harmful to human health. These include
Some golden jackals carry diseases and parasites harmful to human health. These include
 In Transcaucasia, golden jackal pups are born from late March to late April, and in northeastern Italy during late April; they can be born at any time of year in Nepal. The number of pups born in a single litter varies geographically. Jackals in Transcaucasia give birth to 3–8 pups, Tajikistan 3–7 pups,
In Transcaucasia, golden jackal pups are born from late March to late April, and in northeastern Italy during late April; they can be born at any time of year in Nepal. The number of pups born in a single litter varies geographically. Jackals in Transcaucasia give birth to 3–8 pups, Tajikistan 3–7 pups,
 The golden jackal often hunts alone, and sometimes in pairs, but rarely hunts in a
The golden jackal often hunts alone, and sometimes in pairs, but rarely hunts in a
 During British rule in
During British rule in
 The golden jackal may have once been tamed in Neolithic
The golden jackal may have once been tamed in Neolithic
Golden jackal being trained for scent detection
{{Authority control
Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller and has shorter legs, a shorter tail, a more elongated torso, a less-prominent forehead, and a narrower and more pointed muzzle than the Arabian wolf. It is listed as Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
due to its widespread distribution and high density in areas with plenty of available food and optimum shelter.
Despite its name, the golden jackal is not closely related to the African black-backed jackal
The black-backed jackal (''Lupulella mesomelas'') is a medium-sized Caninae, canine native to East Africa, eastern and southern Africa. These regions are separated by roughly .
One region includes the southernmost tip of the continent, includin ...
or side-striped jackal, which are part of the genus '' Lupulella''. It is instead closer to wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
and coyotes. The ancestor of the golden jackal is believed to be the extinct Arno river dog that lived in southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
. It is described as having been a small, jackal-like canine. Genetic studies indicate that the golden jackal expanded from India around 20,000 years ago, towards the end of the last Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
. The oldest golden jackal fossil, found at the Ksar Akil rock shelter near Beirut
Beirut ( ; ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, just under half of Lebanon's population, which makes it the List of largest cities in the Levant region by populatio ...
, Lebanon, is 7,600 years old. The oldest golden jackal fossils in Europe were found in Greece and are 7,000 years old. There are six subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
of the golden jackal. It is capable of producing fertile hybrids with both the gray wolf and the African wolf. Jackal–dog hybrids called Sulimov dogs are in service at the Sheremetyevo Airport
Sheremetyevo International Airport (, , Internal code: ШРМ) is one of four international airports that serve the city of Moscow. It is the busiest airport in Russia and the post-Soviet states, as well as the ninth-busiest airport in Euro ...
near Moscow, where they are deployed by the Russian airline Aeroflot
PJSC AeroflotRussian Airlines (, ), commonly known as Aeroflot ( or ; , , ), is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Russia. Aeroflot is headquartered in the Central Administrative Okrug, Moscow, with its hub being Sheremetyevo Interna ...
for scent-detection.
The golden jackal is abundant in valleys and beside rivers and their tributaries, canals, lakes, and seashores; however, the species is rare in foothills and low mountains. It is a social species, the basic social unit of which consists of a breeding pair and any young offspring. It is very adaptable, with the ability to exploit food ranging from fruit and insects to small ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to b ...
. It attacks domestic fowl and domestic mammals up to the size of domestic water buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called domestic water buffalo, Asian water buffalo and Asiatic water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also kept in Italy, the Balkans ...
calves. Its competitors are the red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
, steppe wolf
The steppe wolf (''Canis lupus campestris''), also known as the Caspian Sea wolf, is a Canis lupus subspecies, subspecies of grey wolf native to the Caspian Sea, Caspian steppes, the steppe regions of the Caucasus, the lower Volga region, souther ...
, jungle cat, Caucasian wildcat, the raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
in the Caucasus and in Central Asia, and the Asiatic wildcat. It is expanding beyond its native grounds in from Southeast Europe into Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
as far as France, and Northeast Europe into areas where there are few or no wolves.
Etymology and naming
The word 'jackal' appeared in theEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples th ...
around 1600. It derives from the Turkish word ''çakal'', which originates from the Persian word ''šagāl''. The golden jackal is also known as the common jackal.
Taxonomy
The biological familyCanidae
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a family (biology), biological family of caniform carnivorans, constituting a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). The family includes three subfamily, subfamilies: the Caninae, a ...
is composed of the South American canids, the fox-like canids, and the wolf-like canids. All species within the wolf-like canids share a similar morphology and possess 78chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s, allowing them potentially to interbreed. Within the wolf-like canids is the jackal group, which includes the three jackals: the black-backed jackal
The black-backed jackal (''Lupulella mesomelas'') is a medium-sized Caninae, canine native to East Africa, eastern and southern Africa. These regions are separated by roughly .
One region includes the southernmost tip of the continent, includin ...
(''Lupulellamesomela''), the side-striped jackal (''Lupulella'' ''adusta''), and the golden jackal (''Canis aureus''). These three species are approximately the same size, possess similar dental and skeletal morphology, and are identified from each other primarily by their coat color. They were once thought to have different distributions across Africa with their ranges overlapping in East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
(Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tanzania). Although the jackal group has traditionally been considered as homogenous, genetic studies show that jackals are not monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
(they do not share a common ancestor), and they are only distantly related. The accuracy of the colloquial name "jackal" to describe all jackals is therefore questionable.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
(mDNA) passes along the maternal line and can date back thousands of years. Thus, phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
of mDNA sequences within a species provides a history of maternal lineages that can be represented as a phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
. A 2005 genetic study of the canids found that the gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
and dog are the most closely related on this tree. The next most closely related are the coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the Wolf, gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the c ...
(''Canis latrans''), golden jackal, and Ethiopian wolf (''Canis simensis''), which have all been shown to hybridize with the dog in the wild. The next closest are the dhole (''Cuon alpinus'') and African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), which are not members of genus ''Canis''. These are followed by the black-backed and side-striped jackals, members of the genus ''Lupulella'' and the most basal members of this clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
.
Results from two recent studies of mDNA from golden jackals indicate that the specimens from Africa are genetically closer to the gray wolf than are the specimens from Eurasia. In 2015 a major DNA study of golden jackals concluded that the six ''C.aureus'' subspecies found in Africa should be reclassified under the new species ''C.anthus'' (African wolf), reducing the number of golden jackal subspecies to seven. The phylogenetic tree generated from this study shows the golden jackal diverging from the wolf/coyote lineage 1.9million years ago and the African wolf diverging 1.3million years ago. The study found that the golden jackal and the African wolf shared a very similar skull and body morphology and that this had confused taxonomists into regarding these as one species. The study proposes that the very similar skull and body morphology is due to both species having originated from a larger common ancestor.
Evolution
The Arno river dog (''Canis arnensis'') is an extinct species of canine that was endemic to Mediterranean Europe during theEarly Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial epoch (geology), sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, representing the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently esti ...
around 1.9million years ago. It is described as a small jackal-like dog and probably the ancestor of modern jackals. Its anatomy and morphology relate it more to the modern golden jackal than to the two African jackal species, the black-backed jackal and the side-striped jackal.
The oldest golden jackal fossil was found at the Ksar Akil rock shelter located northeast of Beirut
Beirut ( ; ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, just under half of Lebanon's population, which makes it the List of largest cities in the Levant region by populatio ...
, Lebanon. The fragment of a single tooth is dated approximately 7,600 years ago. The oldest golden jackal fossils found in Europe are from Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
and Kitsos in Greece and are dated 7,000–6,500 years ago. An unusual fossil of a heel bone found in Azykh Cave, in Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh (, ; ) is a region in Azerbaijan, covering the southeastern stretch of the Lesser Caucasus mountain range. Part of the greater region of Karabakh, it spans the area between Lower Karabakh and Syunik Province, Syunik. Its ter ...
, dates to the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
and is described as probably belonging to the golden jackal, but its classification is not clear. The fossil is described as being slightly smaller and thinner than the cave lynx, similar to the fox, but too large, and similar to the wolf, but too small. As the golden jackal falls between these two in size, the fossil possibly belongs to a golden jackal. The absence of clearly identified golden jackal fossils in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
region and Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
, areas where the species currently resides, indicates that the species is a relatively recent arrival.
A haplotype
A haplotype (haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material (DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA orga ...
is a group of genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
found in an organism that is inherited from one of its parents. A haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a sing ...
is a group of similar haplotypes that share a single mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
inherited from their common ancestor. The mDNA haplotypes of the golden jackal form two haplogroups: the oldest haplogroup is formed by golden jackals from India, and the other, younger, haplogroup diverging from this includes golden jackals from all of the other regions. Indian golden jackals exhibit the highest genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
, and those from northern and western India are the most basal, which indicates that India was the center from which golden jackals spread. The extant golden jackal lineage commenced expanding its population in India 37,000 years ago. During the Last Glacial Maximum, 25,000 to 18,000 years ago, the warmer regions of India and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
provided a refuge from colder surrounding areas. At the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the beginning of the warming cycles, the golden jackal lineage expanded out of India and into Eurasia to reach the Middle East and Europe.
Outside of India, golden jackals in the Caucasus and Turkey demonstrate the next highest genetic diversity, while those in Europe indicate low genetic diversity, confirming their more recent expansion into Europe. Genetic data indicates that the golden jackals of the Peloponnese Peninsula in Greece and the Dalmatian coast in Croatia may represent two ancient European populations from 6,000 years ago that have survived into modern times.
Jackals were absent from most of Europe until the 19th century, when they started to expand slowly. Jackals were recorded in Hungary with the nearest population known at that time being found in Dalmatia, some 300 kilometers away. This was followed by rapid expansion of jackals towards the end of the 20th century. Golden jackals from both Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
and the Caucasus are expanding into the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
. In the Middle East, golden jackals from Israel have a higher genetic diversity than European jackals. This is thought to be due to Israeli jackals having hybridized with dogs, gray wolves, and African golden wolves, creating a hybrid zone in Israel.
Admixture with other ''Canis'' species
Genetic analysis reveals that mating sometimes occurs between female jackals and gray wolves, producing jackal-wolf hybrids that experts cannot visually distinguish from wolves. Hybridization also occurs between female golden jackals and male dogs, which produces fertile offspring, a jackal–dog hybrid. There was 11–13% of ancientgene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
into the golden jackal from the population that was ancestral to wolves and dogs, and an additional 3% from extant wolf populations. Up to 15% of the Israeli wolf genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
is derived from admixture with golden jackals in ancient times.
In 2018, whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's ...
was used to compare members of the genus ''Canis''. The study supports the African wolf being distinct from the golden jackal, and with the Ethiopian wolf being genetically basal to both. There is evidence of gene flow between African golden wolves, golden jackals, and gray wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
. One African wolf from the Egyptian Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
showed high admixture with the Middle Eastern gray wolves and dogs, highlighting the role of the land bridge between the African and Eurasian continents in canid evolution. There was evidence of gene flow between golden jackals and Middle Eastern wolves, less so with European and Asian wolves, and least with North American wolves. The study proposes that the golden jackal ancestry found in North American wolves may have occurred before the divergence of the Eurasian and North American wolves.
Subspecies and populations
The golden jackal was taxonomically subordinated to the genus ''Canis
''Canis'' is a genus of the Caninae which includes multiple extant taxon, extant species, such as Wolf, wolves, dogs, coyotes, and golden jackals. Species of this genus are distinguished by their moderate to large size, their massive, well-develo ...
'' by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
in his 1758 publication ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the Orthographic ligature, ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Sweden, Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the syste ...
''. 13 subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
were described since then.
Description
The golden jackal is similar to the gray wolf but is distinguished by its smaller size, lighter weight, more elongated torso, less-prominent forehead, shorter legs and tail, and a muzzle that is narrower and more pointed. The legs are long in relation to its body, and the feet are slender with small pads. Males measure in body length and females . Males weigh and females weigh . The shoulder height is for both. In comparison, the smallest wolf is the Arabian wolf (''Canis lupus arabs''), which weighs on average . The skull is most like that of the dingo, and is closer to that of the coyote (''C.latrans'') and the gray wolf (''C.lupus'') than to that of the black-backed jackal (''L.mesomalas''), the side-striped jackal (''L.adustus''), and the Ethiopian wolf (''C.simensis''). Compared with the wolf, the skull of the golden jackal is smaller and less massive, with a lower nasal region and shorter facial region; the projections of the skull are prominent but weaker than those of the wolf; the canine teeth are large and strong but relatively thinner; and itscarnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
teeth are weaker. The golden jackal is a less specialized species than the gray wolf, and these skull features relate to the jackal's diet of small bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s, rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s, small vertebrates, insects, carrion, fruit, and some vegetable matter. It was once thought that golden jackals could develop a horny growth on the skull referred to as a " jackal's horn" which usually measured approximately in length and was concealed by fur. Although no evidence of its existence has been found, belief in it remains common in South Asia. This feature was once associated with magical powers by the people of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
.
The jackal's fur is coarse and relatively short, with the base color golden, varying seasonally from a pale creamy yellow to a dark tawny. The fur on the back is composed of a mixture of black, brown, and white hairs, sometimes giving the appearance of the dark saddle like that seen on the black-backed jackal. The underparts are a light pale ginger to cream color. Individual specimens can be distinguished by their unique light markings on the throat and chest. The coats of jackals from high elevations tend to be more buff-colored than those of their lowland counterparts while those of jackals in rocky, mountainous areas may exhibit a grayer shade. The bushy tail has a tan to black tip. Melanism
Melanism is the congenital excess of melanin in an organism resulting in dark pigment.
Pseudomelanism, also called abundism, is another variant of pigmentation, identifiable by dark spots or enlarged stripes, which cover a large part of the bod ...
can cause a dark-colored coat in some golden jackals, a coloring once fairly common in Bengal. Unlike melanistic wolves and coyotes that received their dark pigmentation from interbreeding with domestic dogs, melanism in golden jackals probably stems from an independent mutation that could be an adaptive trait. What is possibly an albino specimen was photographed in southeastern Iran during 2012.
The jackal moults twice a year, in spring and in autumn. In Transcaucasia and Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, the spring moult begins at the end of winter. If the winter has been warm, the spring moult starts in the middle of February; if the winter has been cold, it begins in the middle of March. The spring moult lasts for 60–65 days; if the animal is sick, it loses only half of its winter fur. The spring moult commences with the head and limbs, extends to the flanks, chest, belly and rump, and ends at the tail. Fur on the underparts is absent. The autumn moult occurs from mid-September with the growth of winter fur; the shedding of the summer fur occurs at the same time. The development of the autumn coat starts with the rump and tail and spreads to the back, flanks, belly, chest, limbs and head, with full winter fur being attained at the end of November.
Ecology
The golden jackal inhabits Europe and Southwest, Central, South, and Southeast Asia. The golden jackal's omnivorous diet allows it to eat a large range of foods; this diet, together with its tolerance of dry conditions, enables it to live in different habitats. The jackal's long legs and lithe body allow it to trot over great distances in search of food. It is able to go without water for extended periods and has been observed on islands that have no fresh water. Jackals are abundant in valleys and along rivers and their tributaries, canals, lakes, and seashores, but are rare in foothills and low mountains. In Central Asia they avoid waterless deserts and cannot be found in the Karakum Desert nor the Kyzylkum Desert, but can be found at their edges or in oases. On the other hand, in India they can be found living in theThar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
. They are found in dense thickets of prickly bushes, reed flood-lands and forests. They have been known to ascend over up the slopes of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
; they can withstand temperatures as low as and sometimes . They are not adapted to snow, and in snow country they must travel along paths made by larger animals or humans. In India, they will occupy the surrounding foothills above arable areas, entering human settlements at night to feed on garbage, and have established themselves around hill station
A hill station is a touristic town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The English term was originally used mostly in Western imperialism in Asia, colonial Asia, but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by ...
s at the elevation of .
They generally avoid mountainous forests, but may enter alpine and sub-alpine areas during dispersal. In Turkey, the Caucasus, and Transcaucasia they have been observed up to the elevation of , particularly in areas where the climate supports shrublands in high elevations. The Estonian population, which marks the only population of this species adapted to the boreal region, largely inhabits coastal grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
s, alvars, and reed bed
A reedbed or reed bed is a natural habitat found in floodplains, waterlogged depressions and
estuaries. Reedbeds are part of a succession from young reeds colonising open water or wet ground through a gradation of increasingly dry ground. As ...
s, habitats where wolves are seldom present. In Finland, a golden jackal has been trapped near Sodankylä within the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
.
Diet
 The golden jackal fills much the same ecological niche in Eurasia as the
The golden jackal fills much the same ecological niche in Eurasia as the coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the Wolf, gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the c ...
does in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
; it is both a predator and a scavenger, and an omnivorous and opportunistic forager with a diet that varies according to its habitat and the season. In Keoladeo National Park, India, over 60% of its diet was measured to consist of rodents, birds, and fruit. In the Kanha Tiger Reserve
Kanha Tiger Reserve, also known as Kanha–Kisli National Park, is one of the tiger reserves of India and the largest national park of the state of Madhya Pradesh. It covers an area of in the two districts Mandla and Balaghat.
The park hosts ...
, 80% of its diet consists of rodents, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s and fruit. Vegetable matter forms part of the jackal diet; in India, they feed intensively on the fruits of buckthorn
''Rhamnus'' is a genus of about 140 accepted species of shrubs or small trees, commonly known as buckthorns, in the family Rhamnaceae. Its species range from tall (rarely to ) and are native mainly in east Asia and North America, but found thr ...
, dogbane, Java plum, and the pods of mesquite and the golden rain tree. The jackal scavenges off the kills made by the lion, tiger, leopard, dhole, and gray wolf. In some regions of Bangladesh and India, golden jackals subsist by scavenging on carrion and garbage, and will cache extra food by burying it. The Irish novelist, playwright and poet, Oliver Goldsmith
Oliver Goldsmith (10 November 1728 – 4 April 1774) was an Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish poet, novelist, playwright, and hack writer. A prolific author of various literature, he is regarded among the most versatile writers of the Georgian e ...
, wrote about the golden jackal:
In the Caucasus and Transcaucasia, golden jackals primarily hunt hare
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores and live Solitary animal, solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are precociality, able to fend for themselves ...
s and mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
-like rodents, and also pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera's native range is restricted to Eura ...
s, francolin
Francolins are birds in the tribe Gallini that traditionally have been placed in the genus ''Francolinus'', but now commonly are divided into multiple genera.
As previously defined, they were paraphyletic as the genus '' Pternistis'', which wa ...
s, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family (biology), family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and goose, geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfam ...
s, coots, moorhens, and passerine
A passerine () is any bird of the order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped') which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines generally have an anisodactyl arrangement of their ...
s. Vegetable matter eaten by Jackals in these areas includes fruits, such as pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in late summer into mid-autumn. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the Family (biology), family Rosaceae, bearing the Pome, po ...
s, hawthorn, dogwood
''Cornus'' is a genus of about 30–60 species of woody plants in the family Cornaceae, commonly known as dogwoods or cornels, which can generally be distinguished by their blossoms, berries, and distinctive bark. Most are deciduous ...
, and the cones of common medlars. The jackal is implicated in the destruction of grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
, watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
, muskmelon
Muskmelon may refer to:
*True melon (''Cucumis melo'')
*American cantaloupe
The cantaloupe ( ) is a type of true melon (''Cucumis melo'') with sweet, aromatic, and usually orange flesh. Originally, ''cantaloupe'' refers to the true cantalou ...
, and nut crops. Near the Vakhsh River, their spring diet consists almost exclusively of plant bulbs and the roots of wild sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, while during winter they feed on wild stony olives. Around the edges of the Karakum Desert, jackals feed on gerbils, lizards, snakes, fish, muskrat
The muskrat or common muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America.
The muskrat is found in wetlands over various climates ...
s, the fruits of wild stony olives, mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinat ...
, dried apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus ''Prunus''.
Usually an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also ...
s, watermelons, muskmelons, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, and grapes.
In Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, the golden jackal's diet consists of mammals, fruits, vegetables, insects, birds and their eggs, grasses and leaves. Golden jackals change their diet to more readily available foods. In Serbia, their diet is primarily livestock carcasses that are increasingly prevalent due to a lack of removal, and this may have led to the expansion of their population. In Hungary, 55% of their diet is composed of common vole
The common vole (''Microtus arvalis'') is a European rodent.
Distribution and habitat
The common vole is hardly restricted in means of distribution and habitat and inhabits large areas of Eurasia but, apart from the Orkney vole, not the Br ...
s and bank vole
The bank vole (''Clethrionomys glareolus'') is a small vole with red-brown fur and some grey patches, with a tail about half as long as its body. A rodent, it lives in woodland areas and is around in length. The bank vole is found in much of Eu ...
s, and 41% is composed of wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
carcasses. Information on the diet of the golden jackal in northeastern Italy is scant, but it is known to prey on small roe deer and hares. In Israel, golden jackals are significant predators of snakes; during a poisoning campaign against golden jackals there was an increase in human snakebite reports, but a decrease when the poisoning ceased.
Competition
The jackal's competitors are the red fox, wolf, jungle cat, wildcat, and raccoon in the Caucasus, and the steppe wildcat in Central Asia. Wolves dominate jackals, and jackals dominate foxes. In 2017 in Iran, an Indian wolf under study killed a golden jackal. In Europe, the range of wolves and jackals is mutually exclusive, with jackals abandoning their territory with the arrival of a wolf pack. One experiment used loudspeakers to broadcast the calls of jackals, and this attracted wolves at a trotting pace to chase away the perceived competitors. Dogs responded to these calls in the same way while barking aggressively. Unleashed dogs have been observed to immediately chase away jackals when the jackals were detected. In Europe, there are an estimated 12,000 wolves. The jackal's recent expansion throughout eastern and western Europe has been attributed to the extermination of the local wolf populations. The present diffusion of the jackal into the northern Adriatic hinterland is in areas where the wolf is absent or very rare. In the past, jackals competed with tigers andleopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
s, feeding on the remains of their kills and, in one case, on a dead tiger. Leopards and tigers once hunted jackals, but today, the leopard is rare, and the tiger is extinct in the jackal's range. Eurasian lynx
The Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx'') is one of the four wikt:extant, extant species within the medium-sized wild Felidae, cat genus ''Lynx''. It is widely distributed from Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe to Cent ...
es have also been known to hunt jackals.Mengüllüoğlu, D.; Ambarlı, H.; Berger, A. & Hofer, H. (2018). "Foraging ecology of Eurasian lynx populations in southwest Asia: Conservation implications for a diet specialist". Ecology and Evolution. 8 (18): 9451–9463. doi:10.1002/ece3.4439. PMC 6194280. .
Red foxes and golden jackals share similar diets. Red foxes fear jackals, which are three times bigger than them. Red foxes will avoid close proximity to jackals and fox populations decrease where jackals are abundant. Foxes can be found only at the fringes of jackal territory. There is however one record of a male golden jackal interacting peacefully with multiple red foxes in southwestern Germany.
Striped hyena
The striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena'') is a species of hyena native to North and East Africa, the Middle East, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Hyaena''. It is listed by the IU ...
s prey on golden jackals, and three jackal carcasses were found in one hyena den.
A 2022 study indicated that the presence of golden jackals in portions of Eastern Europe leads to a decrease in the population of invasive raccoon dogs (''Nyctereutes procyonoides''), indicating a potentially positive consequence of the jackal colonization of Europe.
Diseases and parasites
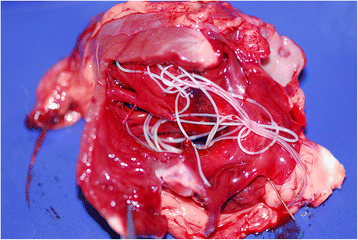
 Some golden jackals carry diseases and parasites harmful to human health. These include
Some golden jackals carry diseases and parasites harmful to human health. These include rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abn ...
, and Donovan's ''Leishmania'' that is harmless to jackals but may cause leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' an ...
in people. Jackals in southwestern Tajikistan can carry up to 16 species of parasitic cestode
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies co ...
s, roundworms, and acanthocephalans, these are: '' Sparganum mansoni'', '' Diphyllobothrium mansonoides'', '' Taenia hydatigena'', '' T.pisiformis'', ''T.ovis'', '' Hydatigera taeniaeformis'', '' Dipylidium caninum'', ''Mesocestoides lineatus'', '' Ancylostoma caninum'', '' Uncinaria stenocephala'', '' Dioctophyma renale'', '' Toxocara canis'', '' Toxascaris leonina'', '' Dracunculus medinensis'', ''Filariata'' and ''Macracanthorhynchus catulinum''. Jackals infected with '' Dracunculus medinensis'' can infect bodies of water with their eggs, which cause dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Guinea worm ('' Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking water contaminated with Guinea-worm larvae that reside inside copepods (a typ ...
in people who drink from them. Golden jackals may also play a large part in spreading coenurosis in sheep and cattle, and canine distemper in dogs. In Tajikistan, jackals may carry up to 12 tick
Ticks are parasitic arachnids of the order Ixodida. They are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, and species, but can become larger when engorged. Ticks a ...
species including '' Ixodes'', '' Rhipicephalus turanicus'', ''R.leporis'', ''R.rossicus'', '' R. sanguineus'', ''R.pumilio'', ''R.schulzei'', '' Hyalomma anatolicum'', ''H.scupense'' and ''H.asiaticum'', the four flea
Flea, the common name for the order (biology), order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by hematophagy, ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult f ...
species '' Pulex irritans'', ''Xenopsylla nesokiae'', '' Ctenocephanlides canis'' and '' C.felis'', and one louse
Louse (: lice) is the common name for any member of the infraorder Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera was previously recognized as an order (biology), order, until a 2021 genetic stud ...
species (''Trichodectes canis'').
In Iran, some golden jackals carry intestinal worms (helminths
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other par ...
) and ''Echinococcus granulosus
''Echinococcus granulosus'', also called the hydatid worm or dog tapeworm, is a cyclophyllid cestode that dwells in the small intestine of canids as an adult, but which has important intermediate hosts such as livestock and humans, where it caus ...
''. In Israel, some jackals are infected with intestinal helminths and '' Leishmania tropica''. In Romania, a jackal was found to be carrying '' Trichinella britovi''. In northeastern Italy, the jackal is a carrier of the tick species '' Ixodes ricinus'' and ''Dermacentor reticulatus
''Dermacentor reticulatus'', also known as the ornate cow tick, ornate dog tick, meadow tick, and marsh tick, is a species of tick from the family Ixodidae. It is the type species for the genus ''Dermacentor''.
''Dermacentor reticulatus'' is an ...
'', and the smallest human fluke ''Metagonimus yokogawai
''Metagonimus yokogawai'', or the Yokogawa fluke, is a species of a Trematoda, trematode, or fluke worm, in the family Heterophyidae.
It is a human parasite causing metagonimiasis. It is among a few species of ''Metagonimus'' that cause metagoni ...
'' that can be caught from ingesting infected raw fish. In Hungary, some jackals carry dog heartworm '' Dirofilaria immitis'', and some have provided the first record in Hungary of ''Trichinella spiralis
''Trichinella spiralis'' is a viviparous nematode parasite, occurring in rodents, pigs, bears, hyenas and humans, and is responsible for the disease trichinosis. It is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm" due to it being typically encount ...
'' and the first record in Europe of ''Echinococcus multilocularis
''Echinococcus multilocularis'', the fox tapeworm, is a small Cyclophyllidea, cyclophyllid Cestoda, tapeworm found extensively in the northern hemisphere. ''E. multilocularis,'' along with other members of the ''Echinococcus'' genus (especially ' ...
''. A golden jackel from Iran was found to be a host of an intestinal acanthocephalan worm, '' Pachysentis canicola''.
Behavior

Social behavior
Golden jackals exhibit flexible social organization depending on the availability of food. The breeding pair is the basic social unit, and they are sometimes accompanied by their current litter of pups. In India, their distributions are a single jackal, 31%, two jackals, 35%, three jackals, 14%, and more than three jackals, 20%. Family groups of up to 4–5 individuals have been recorded. Scent marking through urination and defecation is common around golden jackal den areas and on the trails they most often use. Scent marking is thought to assist in territorial defense. The hunting ranges of several jackals can overlap. Jackals can travel up to during a single night in search of either food or more suitable habitat. Non-breeding members of a pack may stay near a distant food source, such as a carcass, for up to several days before returning to their home range. Home range sizes can vary between , depending on the available food. Social interactions such as greetings, grooming, and grouphowling
Howling is a vocal form of animal communication seen in most canines, particularly wolves, coyotes, foxes, and dogs, as well as cats and some species of monkeys. Howls are lengthy sustained sounds, loud and audible over long distances, often with ...
are common in jackals. Howling is more frequent between December and April when pair bond
In biology, a pair bond is the strong affinity that develops in some species between a mating pair, often leading to the production and rearing of young and potentially a lifelong bond. Pair-bonding is a term coined in the 1940s that is frequently ...
s are being formed and breeding occurs, which suggests howling has a role in the delineation of territory and for defense. Adult jackals howl standing and the young or subordinate jackals howl sitting. Jackals are easily induced to howl and a single howl may solicit replies from several jackals in the vicinity. Howling begins with 2–3 low-pitched calls that rise to high-pitched calls. The howl consists of a wail repeated 3–4 times on an ascending scale, followed by three short yelps. Jackals typically howl at dawn and in the evening, and sometimes at midday. Adults may howl to accompany the ringing of church bells, with their young responding to sirens or the whistles of steam engines and boats. Social canids such as golden jackals, wolves, and coyotes respond to human imitations of their howls. When there is a change in the weather, jackals will produce a long and continuous chorus. Dominant canids defend their territories against intruders with either a howl to warn them off, approach and confront them, or howl followed by an approach. Jackals, wolves and coyotes will always approach a source of howling. Golden jackals give a warning call that is very different from their normal howling when they detect the presence of large carnivores such as wolves and tigers.
Reproduction
Golden jackals are monogamous and will remain with the one partner until death. Female jackals have only one breeding cycle each year. Breeding occurs from October to March in Israel and from February to March in India, Turkmenistan, Bulgaria, and Transcaucasia, with the mating period lasting up to 26–28 days. Females undergoing their first estrus are often pursued by several males that may quarrel among themselves. Mating results in a copulatory tie that lasts for several minutes, as it does with all other canids. Gestation lasts 63 days, and the timing of the births coincides with the annual abundance of food. In India, the golden jackal will take over the dens of the Bengal fox and the Indian crested porcupine, and will use abandoned gray wolf dens. Most breeding pairs are spaced well apart and maintain a core territory around their dens. Den excavations commence from late April to May in India, with dens located in scrub areas. Rivulets, gullies, and road and check-dam embankments are prime denning habitats. Drainage pipes and culverts have been used as dens. Dens are long and deep, with between 1–3 openings. Young pups can be moved between 2–4 dens. The male helps with digging the den and raising the pups. In the Caucasus and Transcaucasia, the burrow is located either in thick shrub, on the slopes of gullies, or on flat surfaces. InDagestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Fede ...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, litters are sometimes located within the hollows of fallen trees, among tree roots, and under stones on river banks. In Central Asia, the golden jackal does not dig burrows but constructs lairs in dense tugai thickets. Jackals in the tugais and cultivated lands of Tajikistan construct lairs in long grass, shrubs, and reed openings. In Transcaucasia, golden jackal pups are born from late March to late April, and in northeastern Italy during late April; they can be born at any time of year in Nepal. The number of pups born in a single litter varies geographically. Jackals in Transcaucasia give birth to 3–8 pups, Tajikistan 3–7 pups,
In Transcaucasia, golden jackal pups are born from late March to late April, and in northeastern Italy during late April; they can be born at any time of year in Nepal. The number of pups born in a single litter varies geographically. Jackals in Transcaucasia give birth to 3–8 pups, Tajikistan 3–7 pups, Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
2–8 pups, and Bulgaria 4–7 pups; in India the average is four pups. The pups are born with closed eyes that open after 8–11 days, with the ears erecting after 10–13 days. Their teeth erupt at 11 days after birth, and the eruption of adult dentition is completed after five months. Pups are born with soft fur that ranges in color from light gray to dark brown. At the age of one month, their fur is shed and replaced with a new reddish-colored pelt with black speckles. The pups have a fast growth rate and weigh at two days of age, at one month, and at four months. Females possess four pairs of teats, and lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process ...
lasts for up to 8–10 weeks. The pups begin to eat meat at the age of 15–20 days.
Dog pups show unrestrained fighting with their siblings from 2 weeks of age, with injury avoided only due to their undeveloped jaw muscles. This fighting gives way to play-chasing with the development of running skills at 4–5 weeks. Wolf pups possess more-developed jaw muscles from 2 weeks of age, when they first show signs of play-fighting with their siblings; serious fighting occurs during 4–6 weeks of age. Compared to wolf and dog pups, golden jackal pups develop aggression at the age of 4–6 weeks, when play-fighting frequently escalates into uninhibited biting intended to harm. This aggression ceases by 10–12 weeks when a hierarchy has formed. Once the lactation period concludes, the female drives off the pups. Pups born late remain with their mother until early autumn, at which time they leave either singly or in groups of two to four individuals. Females reach sexual maturity after 10–11 months and males at 21–22 months.
Foraging
 The golden jackal often hunts alone, and sometimes in pairs, but rarely hunts in a
The golden jackal often hunts alone, and sometimes in pairs, but rarely hunts in a pack
Pack or packs may refer to:
Music
* Packs (band), a Canadian indie rock band
* ''Packs'' (album), by Your Old Droog
* ''Packs'', a Berner album
Places
* Pack, Styria, defunct Austrian municipality
* Pack, Missouri, United States (US)
* ...
. When hunting alone, it trots around an area and occasionally stops to sniff and listen. Once prey is located, the jackal conceals itself, quickly approaches its prey and then pounces on it. Single jackals hunt rodents, hares, and birds. They hunt rodents in grass by locating them with their hearing before leaping into the air and pouncing on them. In India, they can dig Indian gerbils out from their burrows, and they can hunt young, old, and infirm ungulates up to 4–5 times their body weight. Jackals search for hiding blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is a medium-sized antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources.
It stands up to high at the sh ...
calves throughout the day during the calving period. The peak times for their searches are the early morning and the late evening. When hunting in pairs or packs, jackals run parallel to their prey and overtake it in unison. When hunting aquatic rodents or birds, they will run along both sides of narrow rivers or streams and drive their prey from one jackal to another.
Pack-hunting of langurs is recorded in India. Packs of between 5 and 18 jackals scavenging on the carcasses of large ungulates is recorded in India and Israel. Packs of 8–12 jackals consisting of more than one family have been observed in the summer periods in Transcaucasia. In India, the Montagu's harrier and the Pallid harrier roost in their hundreds in grasslands during their winter migration. Jackals stalk close to these roosting harriers and then rush at them, attempting to catch one before the harriers can take off or gain sufficient height to escape.
In Southeastern Asia, golden jackals have been known to hunt alongside dhole packs. They have been observed in the Blackbuck National Park, Velavadar, India, following Indian wolves (''Canis lupus pallipes'') when these are on a hunt, and they will scavenge off wolf kills without any hostility shown from the wolves. In India, lone jackals expelled from their pack have been known to form commensal relationships with tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is a large Felidae, cat and a member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is ...
s. These solitary jackals, known as ''kol-bahl'', will associate themselves with a particular tiger, trailing it at a safe distance to feed on the big cat's kills. A ''kol-bahl'' will even alert a tiger to prey with a loud "pheal". Tigers have been known to tolerate these jackals, with one report describing how a jackal confidently walked in and out between three tigers walking together. Golden jackals and wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
can occupy the same territory.
Conservation
The golden jackal is listed asLeast Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
due to its widespread distribution, with it being common throughout its range and with high densities in those areas where food and shelter are abundant. In Europe, golden jackals are not listed under the 1973 '' Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora'' nor the 1979 Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals. Golden jackals in Europe fall under various international legal instruments. These include the 1979 ''Berne Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats
Bern (), or Berne (), ; ; ; . is the '' de facto'' capital of Switzerland, referred to as the " federal city".; ; ; . According to the Swiss constitution, the Swiss Confederation intentionally has no "capital", but Bern has governmental i ...
'', the '' 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity'', and the 1992 European Union '' Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. The Council Directive provides both guidance and limits on what participating governments can do when responding to the arrival of expanding jackals. These legislative instruments aim to contribute to conserving native wildlife; some governments argue that the golden jackal is not native wildlife but an invading species. The Golden Jackal informal study Group in Europe (GOJAGE) is an organization that is formed by researchers from across Europe to collect and share information on the golden jackal in Europe. The group also has an interest in the golden jackal's relationship with its environment across Eurasia. Membership is open to anyone who has an interest in golden jackals.
In Europe, there are an estimated 70,000 golden jackals. They are fully protected in Albania, North Macedonia, Germany, Italy, Poland and Switzerland. They are unprotected in Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Czech Republic, Estonia, and Greece. They are hunted in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Ukraine. Their protection in Austria and Turkey depends on the part of the country. Their status in Moldova is not known.
The Syrian jackal was common in Israel and Lebanon in the 1930s–40s, but their populations were reduced during an anti-rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abn ...
campaign. Its current status is difficult to ascertain, due to possible hybridisation with pariah dogs and African golden wolves. The jackal population for the Indian subcontinent is estimated to be over 80,000. In India, the golden jackal occurs in all of India's protected areas apart from those in the higher areas of the Himalayas. It is included in CITES
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of inte ...
AppendixIII, and is listed in the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, under ScheduleIII, thus receiving legal protection at the lowest level to help control the trade of pelts and tails in India.
Relationships with humans
In folklore, mythology and literature
Golden jackals appear in Indian folklore and in two ancient texts, the '' Jakatas'' and the ''Panchatantra
The ''Panchatantra'' ( IAST: Pañcatantra, ISO: Pañcatantra, , "Five Treatises") is an ancient Indian collection of interrelated animal fables in Sanskrit verse and prose, arranged within a frame story.
'', where they are portrayed as intelligent and wily creatures. The ancient Hindu text, the ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
'', tells the story of a learned jackal who sets his friends the tiger, wolf, mongoose
A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family has two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to southern Europe, A ...
, and mouse against each other so he can eat a gazelle without sharing it. The ''Panchatantra'' tells the fable of a jackal who cheats a wolf and a lion out of their shares of a camel. In Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
tales, the jackal is regarded as being cunning in a way similar to the fox in European tales. One popular Indian saying describes the jackal as "the sharpest among beasts, the crow among birds, and the barber among men". For a person embarking on an early morning journey, hearing a jackal howl was considered to be a sign of impending good fortune, as was seeing a jackal crossing a road from the left side.
In Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, the jackal is portrayed as the familiar of several deities with the most common being Chamunda, the emaciated, devouring goddess of the cremation grounds. Another deity associated with jackals is Kali
Kali (; , ), also called Kalika, is a major goddess in Hinduism, primarily associated with time, death and destruction. Kali is also connected with transcendental knowledge and is the first of the ten Mahavidyas, a group of goddesses who p ...
, who inhabits the cremation ground and is surrounded by millions of jackals. According to the '' Tantrasara'' scripture, when offered animal flesh, Kali appears in the form of a jackal. The goddess Shivaduti is depicted with a jackal's head. The goddess Durga
Durga (, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around combating evils and demonic ...
was often linked to the jackal. Jackals are considered to be the vahana
''Vāhana'' () or ''vahanam'' () denotes the being, typically an animal or mythical entity, a particular Hindus, Hindu deity is said to use as a vehicle. In this capacity, the vāhana is often called the deity's "mount". Upon the partnership b ...
s (vehicles) of various protective Hindu and Buddhist deities, particularly in Tibet. According to the flood myth
A flood myth or a deluge myth is a myth in which a great flood, usually sent by a deity or deities, destroys civilization, often in an act of divine retribution. Parallels are often drawn between the flood waters of these Mythology, myths and the ...
of the Kamar people in Raipur district
Raipur district is a district in the Chhattisgarh state of India. Its administrative headquarters is the city of Raipur. The district is rich in mineral resources and there are many wildlife sanctuaries. With a population of 2 million, it is the ...
, India, the god Mahadeo (Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
) caused a deluge to dispose of a jackal who had offended him. In Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English journalist, novelist, poet, and short-story writer. He was born in British Raj, British India, which inspired much ...
's Mowgli stories collected in ''The Jungle Book
''The Jungle Book'' is an 1894 collection of stories by the English author Rudyard Kipling. Most of the characters are animals such as Shere Khan the tiger and Baloo the bear, though a principal character is the boy or "man-cub" Mowgli, who ...
'', the character Tabaqui is a jackal despised by the Seeonee wolf pack due to his mock cordiality, his scavenging habits, and his subservience to Shere Khan
Shere Khan () is a fictional Bengal tiger featured in the Mowgli stories of Rudyard Kipling's ''The Jungle Book, Jungle Book''. He is often portrayed as the main antagonist in the book's media adaptations, itself an exaggeration of his role in ...
the tiger.
Attacks on humans
In the Marwahi forest division of theChhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (; ) is a landlocked States and union territories of India, state in Central India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the List ...
state in eastern India, the jackal is of conservation value and there were no jackal attacks reported before 1997. During 1998–2005 there were 220 reported cases of jackal attacks on humans, although none were fatal. The majority of these attacks occurred in villages, followed by forests and crop fields. Jackals build their dens in the bouldery hillocks that surround flat areas, and these areas have been encroached by human agriculture and settlements. This encroachment has led to habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological proces ...
and the need for jackals to enter agricultural areas and villages in search for food, resulting in conflict with humans. People in this region habitually chase jackals from their villages, which leads to the jackals becoming aggressive. Female jackals with pups respond with an attack more often than lone males. In comparison, over twice as many attacks were carried out by sloth bears over the same period. There are no known attacks on humans in Europe.
Livestock, game, and crop predation
The golden jackal can be a harmful pest that attacks domestic animals such as turkeys, lambs,sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of Caprinae, goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the ...
s, domestic water buffalo calves, and valuable game species like newborn roe deer, hare
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores and live Solitary animal, solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are precociality, able to fend for themselves ...
s, coypu, pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera's native range is restricted to Eura ...
s, francolin
Francolins are birds in the tribe Gallini that traditionally have been placed in the genus ''Francolinus'', but now commonly are divided into multiple genera.
As previously defined, they were paraphyletic as the genus '' Pternistis'', which wa ...
s, grey partridges, bustards and waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
. It destroys grape, coffee, maize, sugarcane, and eats watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
s, muskmelons, and nuts. In Greece, golden jackals are not as damaging to livestock as wolves and red foxes but they can become a serious nuisance to small stock when in great numbers. In southern Bulgaria, over 1,000 attacks on sheep and lambs were recorded between 1982 and 1987, along with some damage to newborn deer in game farms. The damage by jackals in Bulgaria was minimal when compared to the livestock losses due to wolves. Approximately 1.5–1.9% of calves born in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
die due to predation, mainly by jackals. The high predation rate by jackals in both Bulgaria and Israel is attributable to the lack of preventative measures in those countries and the availability of food in illegal garbage dumps, leading to jackal population explosions.
Golden jackals are extremely harmful to fur-bearing rodents, such as coypu and muskrat
The muskrat or common muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America.
The muskrat is found in wetlands over various climates ...
s. Coypu can be completely extirpated in shallow water bodies. During 1948–1949 in the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Ku ...
, muskrats constituted 12.3% of jackal fecal contents, and 71% of muskrat houses were destroyed by jackals. Jackals also harm the fur industry by eating muskrats caught in traps or taking skins left out to dry.
Hunting
 During British rule in
During British rule in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, sportsmen conducted golden jackal hunting on horseback with hounds, with jackal coursing
Jackal coursing involves the pursuit of jackals (usually the golden jackal and black-backed jackal) with dogs.
Jackal coursing was an occasional pastime for sportsmen in British India. English Foxhounds were usually imported to India for the pur ...
a substitute for the fox hunting
Fox hunting is an activity involving the tracking, chase and, if caught, the killing of a fox, normally a red fox, by trained foxhounds or other scent hounds. A group of unarmed followers, led by a "master of foxhounds" (or "master of hounds" ...
of their native England. They were not considered as beautiful as English red foxes, but were esteemed for their endurance in the chase with one pursuit lasting hours. India's weather and terrain added further challenges to jackal hunters that were not present in England: the hounds of India were rarely in as good condition as English hounds, and although the golden jackal has a strong odor, the terrain of northern India was not good in retaining scent. Also, unlike foxes, jackals sometimes feigned death when caught and could be ferociously protective of their captured packmates.
Jackals were hunted in three ways: with greyhound
The English Greyhound, or simply the Greyhound, is a dog breed, breed of dog, a sighthound which has been bred for coursing, greyhound racing and hunting. Some are kept as show dogs or pets.
Greyhounds are defined as a tall, muscular, smooth-c ...
s, with foxhounds, and with mixed packs. Hunting jackals with greyhounds offered poor sport because greyhounds were too fast for jackals, and mixed packs were too difficult to control. From 1946 in Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, British diplomats and Iraqi riders conducted jackal coursing together. They distinguished three types of jackal: the "city scavenger", which was described as being slow and so smelly that dogs did not like to follow them; the "village jack", which was described as being faster, more alert, and less odorous; and the "open-country jack", which was described as being the fastest, cleanest, and providing the best sport of all three populations.
Some indigenous people of India, such as the Kolis and Vaghirs of Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
and Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
and the Narikuravas in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
, hunt and eat golden jackals, but the majority of South Asian cultures consider the animal to be unclean. The orthodox ''dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...
'' texts forbid the eating of jackals because they have five nails. In the area of the former Soviet Union, jackals are not actively hunted and are usually captured only incidentally during the hunting of other animals by means of traps or shooting during drives. In Transcaucasia, jackals are captured with large fishing hooks baited with meat and suspended from the ground with wire. The jackals can only reach the meat by jumping, and are then hooked by the lip or jaw.
Fur use
In Russia and the other nations of the former Soviet Union, golden jackals are considered furbearers of low quality because of their sparse, coarse, and monotonously colored fur. Jackal hairs have very little fur fiber; therefore, their pelts have a flat appearance. The jackals of Asia and the Middle East produce the coarsest pelts, though this can be remedied during the dressing process. Elburz in northern Iran produces the softest furs. Jackal skins are not graded to a fur standard, and are made into collars, women's coats, and fur coats. During the 1880s, 200 jackals were captured annually in Mervsk and in the Zakatal area of the Transcaucasus, with 300 jackals being captured there during 1896. In this same period, a total of 10,000 jackals were taken within Russia and their furs sent exclusively to the Nizhegorod fair. In the early 1930s there were 20,000–25,000 jackal skins tanned annually in the Soviet Union, but these could not be utilized within the country, and so the majority were exported to the United States. Commencing from 1949, they were all used within the Soviet Union.Sulimov dog
 The golden jackal may have once been tamed in Neolithic
The golden jackal may have once been tamed in Neolithic Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
11,000 years ago, as there is a sculpture of a man cradling a jackal found in Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe (, ; Kurdish: or , 'Wish Hill') is a Neolithic archaeological site in Upper Mesopotamia (''al-Jazira'') in modern-day Turkey. The settlement was inhabited from around to at least , during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic. It is famou ...
. French explorers during the 19thcentury noted that people in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
kept golden jackals in their homes. The Kalmyk people
Kalmyks (), archaically anglicised as Calmucks (), are the only Mongolic ethnic group living in Europe, residing in the easternmost part of the European Plain.
This dry steppe area, west of the lower Volga River, known among the nomads as ...
near the Caspian Sea were known to frequently cross their dogs with jackals, and Balkan shepherds once crossed their sheepdogs with jackals.
The Russian military established the Red Star kennels in 1924 to improve the performance of working dogs and to conduct military dog research. The Red Star kennel developed "Laikoid" dogs, which were a cross-breed of Spitz-type Russian Laikas with German Shepherds. By the 1980s, the ability of Russia's bomb and narcotic detection dogs were assessed as being inadequate. Klim Sulimov, a research scientist with the DS Likhachev Scientific Research Institute for Cultural Heritage and Environmental Protection, began cross-breeding dogs with their wild relatives in an attempt to improve their scent-detection abilities. The researchers assumed that during domestication dogs had lost some of their scent-detection ability because they no longer had to detect prey. Sulimov crossed European jackals with Laikas, and also with fox terriers to add trainability and loyalty to the mix. He used the jackal because he believed that it was the wild ancestor of the dog, that it had superior scent-detecting ability, and, because it was smaller with more endurance than the dog, it could be housed outdoors in the Russian climate. Sulimov favored a mix of one quarter jackal and three-quarters dog. Sulimov's program continues today with the use of the hybrid Sulimov dogs at the Sheremetyevo Airport
Sheremetyevo International Airport (, , Internal code: ШРМ) is one of four international airports that serve the city of Moscow. It is the busiest airport in Russia and the post-Soviet states, as well as the ninth-busiest airport in Euro ...
near Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
by the Russian airline Aeroflot
PJSC AeroflotRussian Airlines (, ), commonly known as Aeroflot ( or ; , , ), is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Russia. Aeroflot is headquartered in the Central Administrative Okrug, Moscow, with its hub being Sheremetyevo Interna ...
.
The hybrid program has been criticized, with one of Sulimov's colleagues pointing out that in other tests the Laika performed just as well as the jackal hybrids. The assumption that dogs have lost some of their scent-detection ability may be incorrect, in that dogs need to be able to scent-detect and identify the many humans that they come into contact with in their domesticated environment. Another researcher crossed German Shepherds with wolves and claimed that this hybrid had superior scent-detection abilities. The scientific evidence to support the claims of hybrid researchers is minimal, and more research has been called for.
Notes
References
Bibliography
*External links
Golden jackal being trained for scent detection
{{Authority control
golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
Carnivorans of Asia
Carnivorans of Europe
Mammals of Southeast Asia
Mammals of West Asia
Mammals of South Asia
Mammals of Central Asia
Mammals of the Middle East
Least concern biota of Asia
Least concern biota of Europe
golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
Habitats Directive species