|
Whole Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of DNA sequencing, gene sequencing at Single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
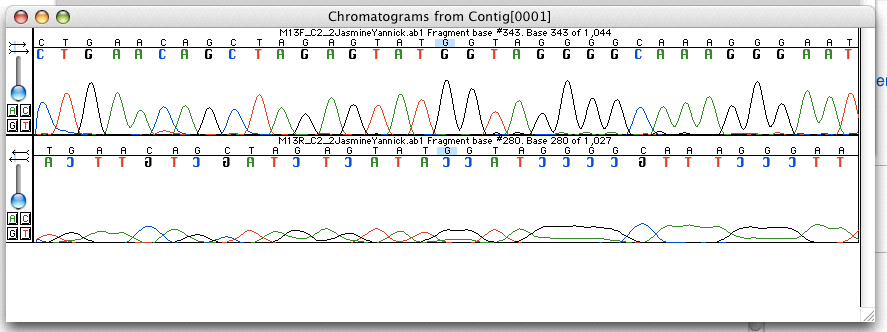
Chromatogram
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be ''preparative'' or ''analytical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNP Genotyping
SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is > 1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci ( QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase of interest in SNPs has been ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social Amoeba, amoebae such as the genus ''Dictyostelium''. Multicellular organisms arise in various ways, for example by cell division or by aggregation of many single cells. Colonial organisms are the result of many identical individuals joining together to form a colony (biology), colony. However, it can often be hard to separate colonial protists from true multicellular organisms, because the two concepts are not distinct; colonial protists have been dubbed "pluricellular" rather than "multicellular". There are also macroscopic organisms that are multinucleate though technically unicellular, such as the Xenophyophorea that can reach 20 cm. Evolutionary history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early organisms emerging 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Although some prokaryotes live in colonies, they are not specialised cells with differing functions. These organisms live together, and each cell must carry out all life processes to survive. In contrast, even the simplest multicellular organisms have cells that depend on each other to survive. Most multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. Gametes, for example, are reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal kingdom Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as flagellated cells. The leading evolutionary theory is they were created by symbiogenesis between an anaerobic Promethearchaeati archaean and an aerobic proteobacterium, which form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even though the domain Archaea Cladistics, cladistically includes eukaryotes, the term "archaea" (: archaeon , from the Greek "ἀρχαῖον", which means ancient) in English still generally refers specifically to prokaryotic members of Archaea. Archaea were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (, in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been Isolation (microbiology), isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their Gene, gene s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilus Influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria are Mesophile, mesophilic and grow best at temperatures between 35 and 37 °C. ''H. influenzae'' was first described in 1893 by Richard Friedrich Johannes Pfeiffer, Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic when he incorrectly identified it as the causative microbe, which is why the bacteria was given the name "influenzae". ''H. influenzae'' is responsible for a wide range of localized and invasive infections, typically in infants and children, including pneumonia, meningitis, or bloodstream infections. Treatment consists of antibiotics; however, ''H. influenzae'' is often resistant to the penicillin family, but amoxicillin/clavulanic acid can be used in mild cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage MS2
Bacteriophage MS2 (''Emesvirus zinderi''), commonly called MS2, is an icosahedral, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that infects the bacterium ''Escherichia coli'' and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. MS2 is a member of a family of closely related bacterial viruses that includes bacteriophage f2, bacteriophage Qβ, R17, and GA. It is small and contains a maturation protein, coat protein, and genomic RNA. It also has one of the smallest known genomes, encoding four proteins. The MS2 lifecycle involves infecting bacteria with the fertility factor, enabling the virus to attach to the pilus, though the mechanism by which the virus's RNA enters the bacterium remains unknown. Once inside, the viral RNA starts functioning as a messenger RNA to produce viral proteins. MS2 replicates its plus-strand genome by creating a minus strand RNA as a template. The virus then assembles, and the bacterial cell lyses, releasing new viruses. The virus was isolated in 1961 and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanger Sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Frederick Sanger and colleagues in 1977, it became the most widely used sequencing method for approximately 40 years. An automated instrument using slab gel electrophoresis and fluorescent labels was first commercialized by Applied Biosystems in March 1987. Later, automated slab gels were replaced with automated capillary array electrophoresis. Recently, higher volume Sanger sequencing has been replaced by next generation sequencing methods, especially for large-scale, automated genome analyses. However, the Sanger method remains in wide use for smaller-scale projects and for validation of deep sequencing results. It still has the advantage over short-read sequencing technologies (like Illumina) in that it can produce DNA sequence reads of > ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxam–Gilbert Sequencing
Maxam–Gilbert sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing developed by Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbert in 1976–1977. This method is based on nucleobase-specific partial chemical modification of DNA and subsequent cleavage of the DNA backbone at sites adjacent to the modified nucleotides. Maxam–Gilbert sequencing was the first widely adopted method for DNA sequencing, and, along with the Sanger dideoxy method, represents the first generation of DNA sequencing methods. Maxam–Gilbert sequencing is no longer in widespread use, having been supplanted by next-generation sequencing methods. History Although Maxam and Gilbert published their chemical sequencing method two years after Frederick Sanger and Alan Coulson published their work on plus-minus sequencing, Maxam–Gilbert sequencing rapidly became more popular, since purified DNA could be used directly, while the initial Sanger method required that each read start be cloned for production of single-stranded DNA. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaeis Guineensis MS 3467
''Elaeis'' () is a genus of palms, called oil palms, containing two species, native to Africa and the Americas. They are used in commercial agriculture in the production of palm oil. Description Mature palms are single-stemmed, and can grow well over tall. The leaves are pinnate, and reach between long. The flowers are produced in dense clusters; each individual flower is small, with three sepals and three petals. The palm fruit is reddish, about the size of a large plum, and grows in large bunches. Each fruit is made up of an oily, fleshy outer layer (the pericarp), with a single seed (the palm kernel), also rich in oil. Species The two species, '' E. guineensis'' (Africa) and '' E. oleifera'' (Americas) can produce fertile hybrids. The genome of ''E. guineensis'' has been sequenced, which has important implications for breeding improved strains of the crop plants. Distribution and habitat ''E. guineensis'' is native to west and southwest Africa, occurri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |