|
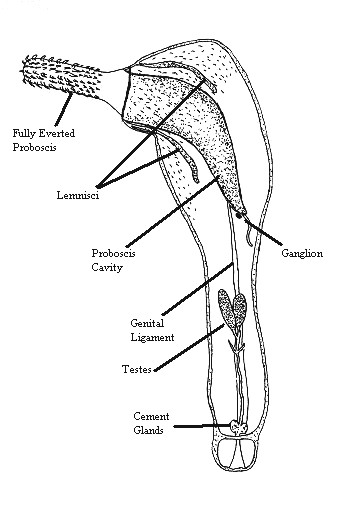
Acanthocephala
Acanthocephala ( Greek , ' 'thorn' + , ' 'head') is a group of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1,420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were long thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is sometimes known as Syndermata, or simply as Rotifera, with the acanthocephalans described as a subclass of a rotifer class Hemirotatoria. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684). In 1771 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archiacanthocephala
Archiacanthocephala is a class within the phylum of Acanthocephala. They are parasitic worms that attach themselves to the intestinal wall of terrestrial vertebrates, including humans. They are characterised by the body wall and the lemnisci (which are a bundle of sensory nerve fibers), which have nuclei that divide without spindle formation, or the appearance of chromosomes, or it has a few amoebae-like giant nuclei. Typically, there are eight separate cement glands in the male, which is one of the few ways to distinguish the dorsal and ventral sides of these organisms. Taxonomy Genetic data are not available for the genus ''Apororhynchus'' in public databases, and ''Apororhynchus'' has not been included in Phylogenetics, phylogenetic analyses thus far due to insufficiency of Morphology (biology), morphological data. However, the lack of features such as an absence of a muscle plate, a wikt:midventral, midventral wikt:longitudinal, longitudinal muscle, wikt:lateral, lateral recep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndermata
Syndermata is a clade of animals that, in some systems, is considered synonymous with Rotifera. Older systems separate Rotifera and Acanthocephala as different phyla, and group them both under Syndermata., p. 788ff. – see particularly p. 804 This clade is placed in the Platyzoa. Phylogeny Phylogenetic analysis of the 18S ribosomal gene has revealed that the Acanthocephala, formerly considered a separate phylum are most closely related to the rotifers. They are possibly closer to the two rotifer classes Bdelloidea and Monogononta than to the other class, Seisonidea, producing the names and relationships shown in the cladogram below. A study of the gene order in the mitochondria suggests that Seisonidea and Acanthocephala are sister clades and that the Bdelloidea are the sister clade to this group. This has since been corroborated by the discovery of a fossil stem-group In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacanthocephala
Polyacanthorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the phylum Acanthocephala. It contains a single genus ''Polyacanthorhynchus''. Taxonomy Phylogenetic analysis has found that polyacanthocephala represents a distinct class of acanthocephalans. Species There are four species in the genus Polyacanthorhynchus. * ''Polyacanthorhynchus caballeroi'' Diaz-ungria and Rodrigo, 1960 The complete genome of the mitochondria has been determined. ''P. caballeroi'' infect South American caimans. * ''Polyacanthorhynchus echiyensis'' * ''Polyacanthorhynchus kenyensis'' Schmidt and Canaris, 1967 ''P. kenyensis'' has been found infecting three freshwater teleosts: the Blue spotted tilapia (''Oreochromis leucostictus''), the Redbelly tilapia (''Tilapia zillii''), and the Largemouth bass (''Micropterus salmoidein'') in Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Samples were found in the liver of ''Tilapia'' and ''Orechromis'' and free in the body cavity in ''Micropterus''Description of morphology available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by John Harris (writer), Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703. Most rotifers are around long (although their size can range from to over ), and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few Seawater, saltwater species. Some rotifers are free swimming and truly planktonic, others move by inchworming along a substrate, and some are Sessility (zoology), sessile, living inside tubes or gelatinous holdfast (biology), holdfasts that are attached to a substrate. About 25 species are colonial (e.g., ''Sinantherina semibullata''), either sessile or planktonic. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton, being a major foodsource and with many specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeacanthocephala
Palaeacanthocephala ("ancient thornheads") is a class within the phylum Acanthocephala. The adults of these parasitic platyzoans feed mainly on fish, aquatic birds and mammals. This order is characterized by the presence of lateral longitudinal lacunar canals and a double-walled proboscis receptacle. The nuclei of the hypodermis (outer layer of skin) are fragmented and the males have two to seven cement glands, unlike their relatives the Archiacanthocephala, which always have eight. There are three orders in the class Palaeacanthocephala: * Echinorhynchida Southwell and Macfie, 1925 * Heteramorphida Amin and Ha, 2008 * Polymorphida Polymorphida are an order of thorny-headed worms (phylum Acanthocephala). The adults of these parasitic platyzoans feed mainly on fish and aquatic birds. This order contains 5 families:Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecu ... Petrochenko, 1956 References Acanthocephalans {{Acanthocephalan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation (literature), latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., Insect mouthparts#Proboscis, moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, Nemertea, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala, the thorny-headed worms or spiny-headed worms, are characterized by the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoacanthocephala
Eoacanthocephala is a class of parasitic worms, within the phylum Acanthocephala. They feed on any aquatic cold-blooded creature such as turtles and fish. Their proboscis spines are arranged radially, with no protonephridia, and with persistent ligament sacs in female. The only reliable way to identify the group is that they only have one cement gland. This is a primitive characteristic and hence the name. The class contains 2 orders Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * H ...: * Gyracanthocephala Van Cleave, 1936 * Neoechinorhynchida Southwell and Macfie, 1925 References *Robert L. Usinger; Storer. 1951. General Zoology. Sixth edition. McGraw-Hill, Inc. Page-437.ITIS - Report: Eoacanthocephala".''www.itis.gov''. Retrieved 2022-10-15. Acanthocephalans { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known Phylum, phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, molluscs, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxon, taxa have a greater number and diversity of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 10 Micrometre, μm (0.0004 in) myxozoans to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are actually sister chordate subphyla to Vertebrata, being more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the "invertebrates" para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynosoma Wegeneri
''Corynosoma'' is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Polymorphidae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution. Species: *''Corynosoma alaskensis'' *''Corynosoma australe'' *''Corynosoma beaglense'' *''Corynosoma bullosum'' *''Corynosoma cameroni'' *''Corynosoma caspicum'' *''Corynosoma cetaceum'' *''Corynosoma curilense'' *''Corynosoma enhydri'' *''Corynosoma erignathi'' *''Corynosoma evae'' *''Corynosoma falcatum'' *''Corynosoma gibsoni'' *''Corynosoma hamanni'' *''Corynosoma hannae'' *''Corynosoma magdaleni'' *''Corynosoma pseudohamanni'' *''Corynosoma rauschi'' *''Corynosoma reductum'' *''Corynosoma semerme'' *''Corynosoma septentrionale'' *''Corynosoma shackletoni'' *''Corynosoma simile'' *''Corynosoma stanleyi'' *''Corynosoma strumosum'' *''Corynosoma validum'' *''Corynosoma ventronudum'' *''Corynosoma villosum'' *''Corynosoma wegeneri'' References Polymorphidae Acanthocephala genera {{acanthocephalan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Worm
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period (geology), Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 161.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations containing land animal fossils include the Forest Marble Formation in England, the Kilmaluag Formation in Scotland,British Geological Survey. 2011Stratigraphic framework for the Middle Jurassic strata of Great Britain and the adjoining continental shelf: research report RR/11/06 British Geological Survey, Keyworth, Nottingham. the Calcaire de Caen of France, the Daohugou Beds in China, the Itat Formation in Russia, the Tiouraren Formation of Niger, and the Isalo III Formation of western Madagascar. Rocks of the Middle Jurassic were formerly (until about 1980s) in Europe called ''Dogger'' or ''Brown Jurassic''. Paleogeography During the Middle Jurassic Epoch, Pangaea began to separate into Laurasia and Gond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |