Irish people in Great Britain or British Irish are immigrants from the island of
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
living in
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
as well as their British-born descendants.
Irish migration to Great Britain has occurred from the earliest recorded history to the present. There has been a continuous movement of people between the islands of Ireland and Great Britain due to their proximity. This tide has ebbed and flowed in response to politics, economics and social conditions of both places.
Today, millions of residents of Great Britain are either from Ireland or are entitled to an Irish passport due to having a parent or grandparent who was born in Ireland. It is estimated that as many as six million people living in the UK have at least one Irish grandparent (around 10% of the UK population).
The
Irish diaspora
The Irish diaspora () refers to ethnic Irish people and their descendants who live outside the island of Ireland.
The phenomenon of migration from Ireland is recorded since the Early Middle Ages,Flechner, Roy; Meeder, Sven (2017). The Irish ...
() refers to
Irish people
The Irish ( or ''Na hÉireannaigh'') are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common ancestry, history and Culture of Ireland, culture. There have been humans in Ireland for about 33,000 years, and it has be ...
and their descendants who live outside
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
. This article refers to those who reside in Great Britain, the largest island and principal territory of the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
.
Migration eras
Medieval
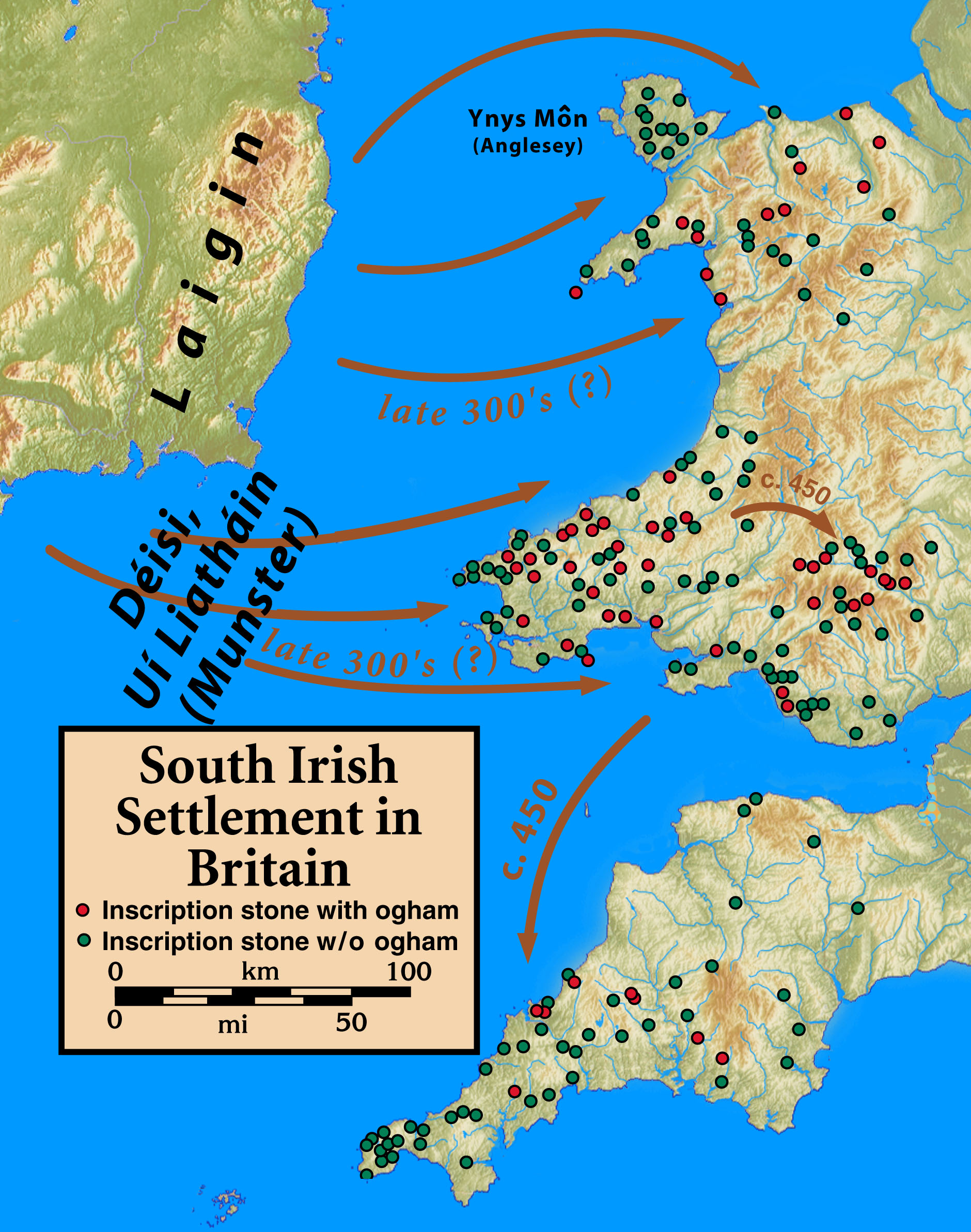
After the
end of Roman rule in Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain occurred as the military forces of Roman Britain withdrew to defend or seize the Western Roman Empire's continental core, leaving behind an autonomous post-Roman Britain. In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus wit ...
, significant Irish settlement of western Britain took place.
The
Déisi
The ''Déisi'' were a social class in Ireland between the ancient and early medieval period. The various peoples listed under the heading ''déis'' shared a similar status in Gaelic Ireland, and had little or no actual kinship, though they were ...
recorded as having founded the
Gwynedd
Gwynedd () is a county in the north-west of Wales. It borders Anglesey across the Menai Strait to the north, Conwy, Denbighshire, and Powys to the east, Ceredigion over the Dyfi estuary to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The ci ...
(Anglesea) and
Dyfed
Dyfed () is a preserved county in southwestern Wales, covering the modern counties Carmarthenshire, Ceredigion and Pembrokeshire. It is mostly rural area with a coastline on the Irish Sea and the Bristol Channel. Between 1974 and 1996, Dyfed w ...
(Pembrokeshire) colonies, with contemporary
Ogham inscription
Roughly 400 inscriptions in the ogham alphabet are known from stone monuments scattered around the Irish Sea, the bulk of them dating to the fifth and sixth centuries. The language of these inscriptions is predominantly Primitive Irish, but a ...
s identifying the genealogies of the colonists, and later echoed in the 8th century, Old Irish work,
The Expulsion of the Déisi
''The Expulsion of the Déisi'' is a medieval Irish narrative of the Cycles of the Kings. It dates approximately to the 8th century, but survives only in manuscripts of a much later date. It describes the fictional history of the Déisi, a group ...
.
Similarly, the traditional view is that
Gaelic language
The Goidelic ( ) or Gaelic languages (; ; ) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically formed a dialect continuum stretching from Ireland through the Isle o ...
and culture was brought to
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, probably in the 4th century, by settlers from Ireland, who founded the Gaelic kingdom of
Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North ...
on Scotland's west coast. This is based mostly on medieval writings from the 9th and 10th centuries. However, recently some archeologists have argued against this view, saying that there is no archeological or placename evidence for a migration or a takeover by a small group of elites.
[Campbell, Ewan.]
Were the Scots Irish?
in ''Antiquity'' #75 (2001). Due to the growth of Dál Riata, in both size and influence, Scotland became almost wholly
Gaelic-speaking. However, in the
Lowlands
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of a ...
– which had been the northernmost part of the
Kingdom of Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
, the
Northumbrian language remained dominant, and formed the basis of the
Scots language. While Scots gradually became more and more widespread, Gaelic remained the dominant language of the
Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Africa
* Highlands, Johannesburg, South Africa
* Highlands, Harare, Zimbab ...
into the 19th century.
Before and during the
Gregorian mission
The Gregorian missionJones "Gregorian Mission" ''Speculum'' p. 335 or Augustinian missionMcGowan "Introduction to the Corpus" ''Companion to Anglo-Saxon Literature'' p. 17 was a Christian mission sent by Pope Pope Gregory I, Gregory the Great ...
of 596 AD, Irish Christians such as
Columba
Columba () or Colmcille (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the important abbey ...
(521–97),
Buriana,
Diuma __NOTOC__
Diuma (or Dwyna or Duma) was the first Bishop of Mercia in the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Mercia, during the Early Middle Ages.
All that is known of Diuma's life is contained in a short account in Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the Engl ...
,
Ceollach
__NOTOC__
Ceollach (or Cellach) was a medieval Bishop of Mercia. His consecration dates and death dates are unknown.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 220 He was Irish by birth and was trained in Ireland.Stenton ''Anglo-Saxon En ...
,
Saint Machar,
Saint Cathan
Saint Cathan, also known as Catan, Cattan, etc., was a 6th-century Irish monk revered as a saint in parts of the Scottish Hebrides.
Source material
This saint appears in the '' Aberdeen Breviary'', Walter Bower's ''Scotichronicon'', and the ...
,
Saint Blane
Saint Blane (Old Irish ''Bláán'', died 590) was a bishop and confessor in Scotland, born on the Isle of Bute, date unknown; died 590. His feast is kept on 10 August.
Origin
Late (medieval) Scottish texts relate that his mother was Irish and ...
,
Jaruman __NOTOC__
Jaruman (or Jarumann; died 669) was the fourth Bishop of Mercia.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 220 He fought against apostasy outside his diocese.Stenton ''Anglo-Saxon England'' p. 130 He served as bishop in the time ...
,
Wyllow
Wyllow was a Cornish people, Cornish hermit saint and martyr whose existence was reported by William Worcester.
He was said to have been born in Ireland but worked in Cornwall.
He was reputedly beheaded by Melyn ys Kynrede ("Melyn's kinfolk") in ...
,
Kessog
Saint Kessog was an Irish people, Irish missionary of the mid-sixth century active in the Lennox (district), Lennox area and southern Perthshire. Son of the king of Cashel, County Tipperary, Cashel in Ireland, Kessog is said to have worked mirac ...
,
St Govan
Saint Govan (; died 586) was a hermit who lived in a fissure on the side of coastal cliff near Bosherston, in the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park, Wales. St. Govan's Chapel was built in the fissure in the 13th century on what is now known as ...
,
Donnán of Eigg
__NOTOC__
Saint Donnán of Eigg (also known as Donan;''The Oxford Dictionary of Saints'', p.135 died 17 April 617) was a Gaelic priest, likely from Ireland, who attempted to introduce Christianity to the Picts of northwestern Scotland during th ...
,
Foillan
Saint Foillan (''Faélán, Faolán, Foélán, '') is an Irish saint of the seventh century.
Family
Foillan was the brother of Saints Ultan and Fursey. He is described as the 'uterine brother' of Fursa, meaning that they had the same mother ...
and
Saint Fursey
Saint Fursey (also known as Fursa, Fursy, Forseus, and Furseus: died 650) was an Irish monk who did much to establish Christianity throughout the British Isles and particularly in East Anglia. He reportedly experienced angelic visions of the a ...
began the conversion of the English and Pictish peoples.
Modwenna and others were significant in the following century.
Some English monarchs, such as
Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu, also known as Oswy or Oswig (; c. 612 – 15 February 670), was King of Bernicia from 642 and of Northumbria from 654 until his death. He is notable for his role at the Synod of Whitby in 664, which ultimately brought the church in Northu ...
(c. 612 – 15 February 670),
Aldfrith
Aldfrith (Early Modern Irish: ''Flann Fína mac Ossu''; Latin: ''Aldfrid'', ''Aldfridus''; died 14 December 704 or 705) was king of Northumbria from 685 until his death. He is described by early writers such as Bede, Alcuin and Stephen of Ripo ...
(died 704 or 705) and
Harold Godwinson
Harold Godwinson ( – 14 October 1066), also called Harold II, was the last crowned Anglo-Saxon King of England. Harold reigned from 6 January 1066 until his death at the Battle of Hastings on 14 October 1066, the decisive battle of the Norman ...
(died 1066) were either raised in or sought refuge in Ireland, as did Welsh rulers such as
Gruffudd ap Cynan
Gruffudd ap Cynan (–1137) was List of rulers of Gwynedd, King of Gwynedd from 1081 until his death in 1137. In the course of a long and eventful life, he became a key figure in Welsh resistance to House of Normandy, Norman rule.
As a descen ...
.
Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfr ...
may have spent some of his childhood in Ireland.
In the year 902 Norsemen who had been forced out of Ireland were given permission by the English to settle in
Wirral, in the north west of England. An Irish historical record known as "
The Three Fragments" refers to a distinct group of settlers living among these Vikings as "Irishmen". Further evidence of this Irish migration to Wirral comes from the name of the village of
Irby Irby may refer to: People
* Irby (given name), a list of people
* Irby (surname), a list of people
Places
* Irby, Merseyside, England, a village
* Irby, Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community
* Irby, Washington, United States, a ...
in Wirral, which means "settlement of the Irish", and St Bridget's church, which is known to have been founded by "Vikings from Ireland". The Irish of the 10th century may have settled as far afield as
Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
and
Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire (), abbreviated ''Lincs'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East Midlands and Yorkshire and the Humber regions of England. It is bordered by the East Riding of Yorkshire across the Humber estuary to th ...
, as place names such as
Irby upon Humber
Irby upon Humber or Irby-on-Humber is a small village and (as just Irby) a civil parish in North East Lincolnshire, England. The village is situated on the A46 road, south-west of Laceby.
Village population at the 2001 census was 124, incr ...
,
Ireleth and
Irton
Irton is a village and civil parish, south-west of Scarborough in the county of North Yorkshire, England. According to the 2011 UK census, Irton parish had a population of 312, a decrease on the 2001 UK census figure of 332. In 2015, North Yor ...
mention the Irish as an ethnic group, while Goidelic personal names appear in some northern English place-names, including
Duggleby
Duggleby is a hamlet in the civil parish of Kirby Grindalythe, in North Yorkshire, England. It was historically part of the East Riding of Yorkshire until 1974. It was part of the Ryedale district from 1974 to 2023.
It is north-eas ...
,
Fixby
Fixby is a suburb in north-west Kirklees bordering neighbouring Calderdale and is traditionally part of Huddersfield in the county of West Yorkshire, England.
The area is now sought after suburban location of Huddersfield for homeowners. The vi ...
and
Melmerby, and in a Viking-age Runic inscription from County Durham.
The island of Ireland was itself claimed as an
Ecclesiastical fief
In the feudal system of the European Middle Ages, an ecclesiastical fief, held from the Catholic Church, followed all the laws laid down for temporal fiefs. The suzerain, e.g. bishop, abbot, or other possessor, granted an estate in perpetuity to a ...
, via the forged, mid 8th century,
Donation of Constantine
The Donation of Constantine () is a forged Roman imperial decree by which the 4th-century emperor Constantine the Great supposedly transferred authority over Rome and the western part of the Roman Empire to the Pope. Composed probably in the ...
, with the feudal
Lordship of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland (), sometimes referred to retrospectively as Anglo-Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman Lords between 1177 and 1542. T ...
later leased to
Henry II of England
Henry II () was King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with the ...
and his heirs, by
Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland (), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181.
A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a Papal election, ...
's, 1171 grant, resulting in the presence and settlement of Irish traders and seamen in English and Welsh ports, as well as the establishment of
The Pale
The Pale ( Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast s ...
, on the island, the Irish settlers being subject to a poll tax, from 1440; in 1542,
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, following his excommunication, would have the Irish Parliament create the
Kingdom, with himself elected as King. Subsequently through offering English titles, and ecclesiastical lands, in a
surrender and regrant
During the Tudor conquest of Ireland (c.1540–1603), "surrender and regrant" was the legal mechanism by which Irish clans were to be converted from a power structure rooted in clan and kin loyalties, to a late-Feudalism, feudal system under t ...
process, would offer Irish clan chiefs, property and political power, in England, as well as Ireland. In 1555,
Pope Paul IV
Pope Paul IV (; ; 28 June 1476 – 18 August 1559), born Gian Pietro Carafa, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 23 May 1555 to his death, in August 1559. While serving as papal nuncio in Spain, he developed ...
, would confirm the existence of the Irish Kingdom, and that it was to be held in
personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with the
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
, via a Papal bull. A personal Union that would later include the
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
, and between 1707 and 1800, the politically united
Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
. The Irish Parliament and Kingdom would be politically united with Great Britain as the
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into one sovereign state, established by the Acts of Union 1800, Acts of Union in 1801. It continued in this form until ...
, between 1801 and 1922, through the
Acts of Union 1800
The Acts of Union 1800 were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland (previously in personal union) to create the United Kingdom of G ...
. Today, Ireland is divided between the independent
Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland, with a population of about 5.4 million. ...
and
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
, a constituent of the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
.
Irish people who made Britain their home in the later medieval era included
Aoife MacMurrough
Aoife MacMurrough (; – ), also known as Eva of Leinster or Red Eva, was an Irish noblewoman. The daughter of King of Leinster Dermot MacMurrough, her marriage to Anglo-Norman nobleman Richard "Strongbow" de Clare on 25 August 1170 is consid ...
, Princess of Leinster (1145–88), the poet
Muireadhach Albanach (fl. 1213), the lawyer
William of Drogheada (died 1245),
Máel Muire Ó Lachtáin (died 1249),
Malachias Hibernicus
Malachy of Ireland (fl. 1279–1300), also known as Malachias Hibernicus, was a theologian and Archbishop of Tuam in 1280.
He was a friar of the Franciscan convent of Limerick and was elected Archbishop of Tuam, though never officially installed ...
(fl. 1279–1300),
Gilbert Ó Tigernaig
Gilbert Ó Tigernaig was the Bishop of Annaghdown from 1306 to 1323.
Ó Tigernaig was a native of Carra, County Mayo, his family belonging to those ruling the area, subject to (or descended from) the Uí Fiachrach Muaidhe. The surname is now ...
(died 1323), Diarmait MacCairbre (executed 1490) and
Germyn Lynch
Germyn Lynch (fl. 1441 – 1483) was a merchant and entrepreneur from Galway, Ireland. His life is notable in that few other commoners in late medieval Ireland are so well-documented.
Lynch was a member of one of Tribes of Galway. He was ...
(fl. 1441–1483), all of whom made successful lives in the various kingdoms of Britain.
16th to 18th centuries
Historically, Irish immigrants to the United Kingdom in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries were considered over-represented amongst those appearing in court. However, research suggests that policing strategy may have put immigrants at a disadvantage by targeting only the most public forms of crime, while locals were more likely able to engage in the types of crimes that could be conducted behind locked doors. An analysis of historical courtroom records suggests that despite higher rates of arrest, immigrants were not systematically disadvantaged by the British court system in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries.
Some notable people born in Ireland who settled in Great Britain between the 16th and 19th centuries:
*
Richard Burke, 4th Earl of Clanricarde
Richard Burke (or de Burgh), 4th Earl of Clanricarde Privy Counsellor, PC (Ire) ( ; 1572 – 12 November 1635), styled Lord Dunkellin ( ) until 1601, was an Irish nobleman and politician.
He was the son of Ulick Burke, 3rd Earl of Clanricarde ...
, died 1635
*
Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, Alchemy, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the foun ...
, FRS, died 1691
*
Laetitia Pilkington
Laetitia Pilkington (born Laetitia van Lewen; ''c.'' 1709 – 29 July 1750) was an Anglo-Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant ...
, died 1750
*
Richard Brinsley Sheridan
Richard Brinsley Butler Sheridan (30 October 17517 July 1816) was an Anglo-Irish playwright, writer and Whig politician who sat in the British House of Commons from 1780 to 1812, representing the constituencies of Stafford, Westminster and I ...
*
George Monro (British Army officer)
Lieutenant-Colonel George Monro (1700 – 3 November 1757) was a British Army officer best known for his unsuccessful defense of Fort William Henry in 1757 during the French and Indian War. After surrendering with full honours of war to Frenc ...
, 1700–57
*
Patrick Brontë
Patrick Brontë (, commonly ; born Patrick Brunty; 17 March 1777 – 7 June 1861) was an Irish Anglican minister and author who spent most of his adult life in England. He was the father of the writers Charlotte Brontë, Charlotte, Emily Bront ...
, 1777–1861
*
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington (; 1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was a British Army officer and statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures in Britain during t ...
*
Thomas Moore
Thomas Moore (28 May 1779 – 25 February 1852), was an Irish writer, poet, and lyricist who was widely regarded as Ireland's "National poet, national bard" during the late Georgian era. The acclaim rested primarily on the popularity of his ''I ...
, died 1852
*
Bram Stoker
Abraham Stoker (8 November 1847 – 20 April 1912), better known by his pen name Bram Stoker, was an Irish novelist who wrote the 1897 Gothic horror novel ''Dracula''. The book is widely considered a milestone in Vampire fiction, and one of t ...
, author of ''
Dracula
''Dracula'' is an 1897 Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish author Bram Stoker. The narrative is Epistolary novel, related through letters, diary entries, and newspaper articles. It has no single protagonist and opens ...
''
*
Oliver Goldsmith
Oliver Goldsmith (10 November 1728 – 4 April 1774) was an Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish poet, novelist, playwright, and hack writer. A prolific author of various literature, he is regarded among the most versatile writers of the Georgian e ...
, author of ''
The Deserted Village
''The Deserted Village'' is a poem by Oliver Goldsmith published in 1770. It is a work of social commentary, and condemns rural depopulation and the pursuit of excessive wealth.
The poem is written in heroic couplets, and describes the decli ...
''
*
Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January ew Style, NS1729 – 9 July 1797) was an Anglo-Irish Politician, statesman, journalist, writer, literary critic, philosopher, and parliamentary orator who is regarded as the founder of the Social philosophy, soc ...
, politician, reformer, writer
*
Mary Burns
*
Robert Tressell
Robert Phillipe Noonan (17 April 1870 – 3 February 1911), born Robert Croker, and best known by the pen name Robert Tressell, was an Irish writer best known for his novel '' The Ragged-Trousered Philanthropists''.
Tressell spent his early adu ...
, author of
The Ragged Trousered Philanthropists
''The Ragged-Trousered Philanthropists'' is a 1914 semi-autobiographical novel by Ireland, Irish house painter and sign writer Robert Noonan, who wrote the book in his spare time under the pen name Robert Tressell. Published after Tressell's de ...
19th century
The most significant exodus followed the worst of a series of potato crop failures in the 1840s – the
Great Irish Famine
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact o ...
. It is estimated that more than one million people died and almost the same again emigrated. A further wave of emigration to England also took place between the 1930s and 1960s by Irish escaping poor economic conditions following the establishment of the
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
. This was furthered by the severe labour shortage in Britain during the mid-20th century, which depended largely on Irish immigrants to work in the areas of construction and domestic labour. The extent of the Irish contribution to Britain's construction industry in the 20th century may be gauged from Sir William MacAlpine's 1998 assertion that the contribution of the Irish to the success of his industry had been "immeasurable". This statement by a member of the British upper class illustrates how Irish migrant labour was regularly employed to discipline and weaken organised English labour unions at the same time as disparaging the contribution of the latter to the development of their own nation. Of this process the German-born philosopher
Karl Marx
Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
wrote in 1870:
"Ireland constantly sends her own surplus to the English labour market, and thus forces down wages and lowers the material and moral position of the English working class... This antagonism is the secret of the impotence of the English working class, despite its organisation. It is the secret by which the capitalist class maintains its power. And the latter is quite aware of this."
Ireland's population fell from more than 8 million to just 6.5 million between 1841 and 1851. A century later it had dropped to 4.3 million. By the late 19th century, emigration was heaviest from Ireland's most rural southern and western counties.
Cork
"Cork" or "CORK" may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Stopper (plug), or "cork", a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
*** Wine cork an item to seal or reseal wine
Places Ireland
* ...
,
Kerry,
Galway
Galway ( ; , ) is a City status in Ireland, city in (and the county town of) County Galway. It lies on the River Corrib between Lough Corrib and Galway Bay. It is the most populous settlement in the province of Connacht, the List of settleme ...
,
Mayo,
Sligo
Sligo ( ; , meaning 'abounding in shells') is a coastal seaport and the county town of County Sligo, Ireland, within the western province of Connacht. With a population of 20,608 in 2022, it is the county's largest urban centre (constituting 2 ...
,
Tipperary and
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. W ...
alone provided nearly half of Ireland's emigrants. Some of this movement was temporary, made up of seasonal harvest labourers working in Britain and returning home for winter and spring.
Some notable people born in Ireland who settled in Great Britain in the 19th century:
*
Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
(1854–1900)
20th to 21st centuries
By the mid-1930s, Great Britain was the choice of many who had to leave Ireland. Britain's wartime economy (1939–45) and post-war boom attracted many Irish people to expanding cities and towns such as
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
,
Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
,
Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
,
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
,
Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
and
Luton
Luton () is a town and borough in Bedfordshire, England. The borough had a population of 225,262 at the 2021 census.
Luton is on the River Lea, about north-west of London. The town's foundation dates to the sixth century as a Saxon settleme ...
. Prior to the 2000s financial crisis, ongoing
sectarian violence
Sectarian violence or sectarian strife is a form of communal violence which is inspired by sectarianism, that is, discrimination, hatred or prejudice between different sects of a particular mode of an ideology or different sects of a religion wi ...
and its economic aftermath was another major factor for immigration.
According to the
UK 2001 Census, white Irish-born residents make up 1.2% of those living in England and Wales. In 1997, the
Irish Government
The Government of Ireland () is the executive authority of Ireland, headed by the , the head of government. The government – also known as the cabinet – is composed of ministers, each of whom must be a member of the , which consists of ...
in its ''White Paper on Foreign Policy'' claimed that there were around two million Irish citizens living in Britain. The 2001 Census also showed that Irish people are more likely to be employed in managerial or professional occupations than those classed as "White British".
As a result of the
Irish financial crisis, emigration from Ireland rose significantly. Data published in June 2011 showed that Irish emigration to Britain had risen by 25 per cent to 13,920 in 2010.
Some notable people born in Ireland who settled in Great Britain between the 20th and 21st centuries include:
Irish broadcasters
BBC broadcaster Sir
Terry Wogan
Sir Michael Terence Wogan (; 3 August 1938 – 31 January 2016) was an Irish radio and television broadcaster who worked for the BBC in Britain for most of his career. Between 1993 and his semi-retirement in 2009, his BBC Radio 2 weekday brea ...
moved to
Buckinghamshire, England in 1969, acquiring
British citizenship
The primary law governing nationality in the United Kingdom is the British Nationality Act 1981, which came into force on 1 January 1983. Regulations apply to the British Islands, which include the UK itself (England, Wales, Scotland, and Nor ...
and a knighthood in 2005, and remained resident in the UK until his death in 2016. Comedians
Ed Byrne and
Dara Ó Briain
Dara Ó Briain ( , ; born 4 February 1972) is an Irish comedian and television presenter based in the United Kingdom. He is noted for performing stand-up comedy shows all over the world and for hosting topical panel shows such as ''Mock the Wee ...
have relocated to Britain from Ireland, and regularly feature on British television.
Black and Asian communities
Since the 1970s some UK organisations, sections of media, and government departments have defined
Black, Asian and minority ethnic
A number of different systems of classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom exist. These schemata have been the subject of debate, including about the nature of ethnicity, how or whether it can be categorised, and the relationship betwe ...
(BAME) in anti-racist efforts and general demography. There are several notable Irish migrants to Great Britain who are
people of colour
The term "person of color" (: people of color or persons of color; abbreviated POC) is used to describe any person who is not considered "white". In its current meaning, the term originated in, and is associated with, the United States. From th ...
, or who might otherwise be considered part of BAME communities. This includes emigrants from Ireland from the
black Irish community, as well as
Asian Irish people.
Irish musician and singer
Phil Lynott
Philip Parris Lynott (, ; 20 August 1949 – 4 January 1986) was an Irish musician, songwriter, and poet. He was the co-founder, lead vocalist, bassist, and primary songwriter for the hard rock band Thin Lizzy. He was known for his distinctive ...
settled in
Surrey
Surrey () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Greater London to the northeast, Kent to the east, East Sussex, East and West Sussex to the south, and Hampshire and Berkshire to the wes ...
,
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
after the commercial success of his
Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
-formed band
Thin Lizzy
Thin Lizzy are an Irish rock band formed in Dublin in 1969. The band initially consisted of bass guitarist, lead vocalist and principal songwriter Phil Lynott, drummer Brian Downey, guitarist Eric Bell and organist Eric Wrixon although Wr ...
. Lynott, who died in 1986, was mixed raced and had
British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies. It was located on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first known Europeans to encounter Guia ...
n ancestry. Irish actor
Christopher Simpson was moved to
London, England
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
as child in 1981. Simpson is of Irish and
Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
n descent.
Irish footballer
Darren Randolph, who has spoken of his experiences growing up black in Ireland, moved to Britain permanently after joining London team
Charlton Athletic F.C.
Charlton Athletic Football Club is a professional association football club based in Charlton, London, Charlton, south-east London, England. The team compete in the EFL Championship, the second level of the English football league system.
Thei ...
in 2003, and has since remained in English football. Model and actress
Layla Flaherty
Layla Flaherty is an Irish Model (person), model and actress who appeared in the ‘scripted-reality’ TV show ''Desperate Scousewives'', which was broadcast on E4 (TV channel), E4 in 2011. More recently, she appeared on an episode of ''Real Hou ...
relocated to
Liverpool, England
Liverpool is a port city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population of (in ), Liverpool is the administrative, c ...
in 2006. Flaherty, who has
Irish and
African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
heritage, has appeared in UK-based
E4 productions, such as ''
Desperate Scousewives
''Desperate Scousewives'' is a British scripted-reality television series based in Liverpool. It premiered on E4 at 10:00pm on 28 November 2011. It ran for eight episodes before being cancelled due to stagnating ratings and a perceived lack of ...
''. Also relocating to England in 2006,
Ethiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
-Irish actress
Ruth Negga
Ruth Negga ( ; born 4 May 1981) is an Irish actress known for her roles in the AMC television series ''Preacher'' (2016–2019) and the film '' Loving'' (2016). For her portrayal of Mildred Loving in the latter, Negga received a nomination for ...
has appeared in films, as well as
RTÉ
(; ; RTÉThe É in RTÉ is pronounced as an English E () and not an Irish É ()) is an Irish public service broadcaster. It both produces and broadcasts programmes on television, radio and online. The radio service began on 1 January 1926, ...
and BBC series. In 2018, Negga, who has been
Academy Award
The Academy Awards, commonly known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit in film. They are presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) in the United States in recognition of excellence ...
-nominated, was featured in the
Evening Standard
The ''London Standard'', formerly the ''Evening Standard'' (1904–2024) and originally ''The Standard'' (1827–1904), is a long-established regional newspaper published weekly and distributed free newspaper, free of charge in London, Engl ...
's ''Progress 1000'' list, which claims to chart the careers of London's most influential people. Irish presenter
Liz Bonnin
Elizabeth Bonnin (born 16 September 1976) is a French-Irish science, wildlife and natural history presenter, who has worked on television in both Ireland and the United Kingdom. She presented morning show '' RI:SE'' and music show ''Top of the ...
has also relocated to London. Bonnin, who has
Indian, Portuguese, and French-
Martiniquan
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
heritage moved to Britain after establishing a science-based broadcasting career with the
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
since 2009.
In 2020, Irish
women's football Women's football most often refers to:
* Women's association football
Women's football may also refer to:
* Women's gridiron football
* Women's Australian rules football
* Ladies' Gaelic football
* Women's rugby league
* Women's rugby union
...
player
Rianna Jarrett relocated to
Brighton
Brighton ( ) is a seaside resort in the city status in the United Kingdom, city of Brighton and Hove, East Sussex, England, south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age, R ...
, England. Jarrett, whose father is
Jamaican, made the move to Britain after joining
Brighton & Hove Albion W.F.C.
Irish footballers
Notable Irish footballers, who were born or raised in Ireland, began moving as young adults to teams based in Great Britain since the post-
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
period. As the sport became more commercially successful, wealthy English clubs in particular pursued Irish talent, which was often seen as detrimental to the game's development in Ireland.
Moving from
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
between 1949 and 1963, players such as
Danny Blanchflower
Robert Dennis Blanchflower (10 February 1926 – 9 December 1993) was a Northern Ireland footballer, football manager and journalist who played for and captained Tottenham Hotspur, including during their double-winning season of 1960–61. H ...
,
Jimmy McIlroy
James McIlroy (25 October 1931 – 20 August 2018) was a Northern Ireland international footballer, who played for Glentoran, Burnley, Stoke City and Oldham Athletic. He was regarded as one of Burnley's greatest players, having played 497 mat ...
,
Billy Bingham
William Laurence Bingham (5 August 1931 – 9 June 2022) was a Northern Ireland international footballer and manager.
As a player, his first professional club was Glentoran, for whom he played between 1948 and 1950. Making a move to England, ...
,
Terry Neill
William John Terence Neill (8 May 1942 – 28 July 2022) was a Northern Irish football player and manager. A centre-back, he captained and later managed Arsenal, guiding the club to a European final in 1980 and three consecutive FA Cup final ...
,
George Best
George Best (22 May 1946 – 25 November 2005) was a Northern Irish professional association football, footballer who played as a winger (association football), winger, spending most of his club career at Manchester United F.C., Manchester Un ...
,
Pat Jennings
Patrick Anthony Jennings (born 12 June 1945) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. He is widely recognised as one of the greatest goalkeepers in the history of the sport and was nominated for the Ball ...
and later, migrating between 1971 and 1981;
Sammy McIlroy
Samuel Baxter McIlroy (born 2 August 1954) is a Northern Irish retired footballer who played for Manchester United, Stoke City, Manchester City, Örgryte (Sweden), Bury, VfB Mödling (Austria), Preston North End and the Northern Ireland na ...
,
Mal Donaghy
Malachy Martin Donaghy (born 13 September 1957 in Belfast) is a former Northern Ireland international footballer who played for Luton Town and Manchester United.
Career
Club career
Originally from West Belfast, began his football career as a g ...
,
Norman Whiteside
Norman Whiteside (born 7 May 1965) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played as a midfielder and striker.
Whiteside began his career at Manchester United, signing professional forms in 1982 at the age of 17 and quickly be ...
,
David McCreery
David McCreery (born 16 September 1957) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played for Newcastle United and many other clubs during his long career.
He mostly played in midfield, but was very versatile, and during his caree ...
,
Nigel Worthington
Nigel Worthington (born 4 November 1961) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who was most recently the manager of York City.
He played a defender and a midfielder, playing his club football for Ballymena United, Notts County ...
,
Jimmy Nicholl
James Michael Nicholl (born 28 December 1956) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played for several clubs, including Manchester United and Rangers. He was mainly a right-back but could also play in other defensive roles. N ...
and
Martin O'Neill
Martin Hugh Michael O'Neill, (born 1 March 1952) is a Northern Irish professional Manager (association football), football manager and former Association football, player who played as a midfielder. After a brief early career in the Irish Leag ...
won titles as players, or managers, in England and Scotland's top competitions.
Moving to Britain from the Republic of Ireland during the 1950s and 60s,
Tony Dunne
Anthony Peter Dunne (24 July 19418 June 2020) was an Irish footballer who played as a left-back. Born in Dublin, he began his career with youth side Stella Maris before signing for Drumcondra-based Shelbourne, with whom he won the FAI Cup in h ...
,
Noel Cantwell
Noel Euchuria Cornelius Cantwell (28 February 1932 – 8 September 2005) was an Irish football player and sometime cricketer.
Club career
Cantwell was born in Cork, Ireland, and was educated at the Roman Catholic Presentation Brothers College ...
,
Johnny Giles
Michael John Giles (born 6 November 1940) is an Irish former association football player and manager best remembered for his time as a midfielder with Leeds United in the 1960s and 1970s. After retiring from management in 1985, Giles served as ...
, and later, in the 1970s and 80s,
Liam Brady
William Brady (born 13 February 1956) is an Irish former footballer and pundit. He found success both in England with Arsenal, where he won an FA Cup in 1979, and in Italy with Juventus, winning two Serie A titles. Brady was capped 72 times for ...
,
Packie Bonner
Patrick Joseph Bonner (born 24 May 1960) is an Irish retired footballer who played as a goalkeeper and spent his entire senior career at Celtic. He earned 80 caps for the Republic of Ireland after making his debut on his 21st birthday. Commonly ...
,
Ronnie Whelan
Ronald Andrew Whelan (; born 25 September 1961) is an Irish former professional football player who played as a midfielder and sometimes as a defender. He played an integral role in the dominant Liverpool side that won a wealth of titles in ...
,
Frank Stapleton
Francis Anthony Stapleton (born 10 July 1956) is an Irish former professional football player and manager. He is best remembered for his time at Arsenal, Manchester United and as a pivotal player for the Republic of Ireland national team. He h ...
,
David O'Leary
David Anthony O'Leary (born 2 May 1958) is a football manager and former player. The majority of his 20-year playing career was spent as a central defender at Arsenal, where his tally of 722 appearances stands as a club record. He played 68 time ...
and
Steve Staunton
Stephen Staunton (born 19 January 1969) is an Irish football manager, scout and former professional footballer.
He played as a defender with two separate spells each with Premier League sides Aston Villa and Liverpool. He also played in the F ...
all won major honours in the Scottish or English top-flights.
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, players also from the Republic, such as
John O'Shea
John Francis O'Shea (; born 30 April 1981) is an Irish professional football coach and former player who is currently assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland men's national team. He was known for his versatility in playing several defensi ...
,
Stephen Carr
Stephen Carr (born 29 August 1976) is an Irish former professional footballer who played as a right-back, sometimes deputising at left-back or centre back. He started his career with Premier League team Tottenham Hotspur in 1993 and remained wi ...
,
Steve Finnan
Stephen John Finnan (born 24 April 1976) is an Irish former international footballer who played as a right-back.
He is the only player to have played in the World Cup, UEFA Champions League, UEFA Cup, Intertoto Cup, all four levels of the Engli ...
,
Denis Irwin
Joseph Denis Irwin (born 31 October 1965) is an Irish former professional footballer and sports television presenter. Irwin is the joint most successful Irish footballer in history, a record he shares with Ronnie Whelan and fellow Manchester U ...
,
Niall Quinn
Niall John Quinn (honorary Order of the British Empire, MBE; born 6 October 1966) is an Irish former professional Association football, footballer, manager, businessman and sports television pundit.
As a player, he was a Striker (association f ...
,
Roy Keane
Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football pundit, former coach, and former professional player. He is best known for his career in the Premier League, in particular his captaincy of Manchester United. He is the joint most ...
,
Shay Given
Séamus John James Given (born 20 April 1976) is an Irish former professional Association football, footballer who played as a Goalkeeper (association football), goalkeeper. Widely regarded as one of the greatest Irish goalkeepers of all time ...
,
Robbie Keane
Robert David Keane (born 8 July 1980) is an Irish professional football coach and former player who played as a striker and is currently the head coach of Ferencváros. Keane served as captain of the Republic of Ireland from March 2006 until h ...
and
Damien Duff
Damien Anthony Duff (born 2 March 1979) is an Irish professional manager (association football), football manager and former Association football, player. He is the manager of League of Ireland club Shelbourne F.C., Shelbourne.
He began his pro ...
, moved to enjoy decades-long careers in English and Scottish football, each winning at least one top-flight competition. In the same era, players who moved from Northern Ireland to Britain, winning competitions in the Scottish and English top-tiers, included
Steven Davis
Steven Davis (born 1 January 1985) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played as a midfielder. He made his full international debut in 2005 and made 140 appearances at senior level, scoring 13 goals, to become the most cappe ...
,
David Healy,
Jonny Evans
Jonathan Grant Evans (born 3 January 1988) is a Northern Irish former professional Association football, footballer who played as a centre-back.
Evans started his career at Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, having progressed throug ...
,
Keith Gillespie
Keith Robert Gillespie ( ; born 18 February 1975) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who plays as a winger for FC Mindwell in the Mid-Ulster Football League.
He began his career at Manchester United after winning the FA Yo ...
,
Roy Carroll
Roy Eric Carroll (born 30 September 1977) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. He is best known for his spells at Wigan Athletic, Manchester United (where he won a Premier League winners medal and the ...
,
Gerry Taggart
Gerald Taggart (born 18 October 1970) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer. He played for Barnsley, Bolton Wanderers, Leicester City, Manchester City and Stoke City as well as the Northern Ireland national team.
A former defend ...
,
Kyle Lafferty
Kyle Joseph George Lafferty (born 16 September 1987) is a Northern Irish professional footballer who plays as a striker for side Johnstone Burgh.
Lafferty began his professional career with English side Burnley, where he made 89 appearances ...
and
Neil Lennon
Neil Francis Lennon (born 25 June 1971) is a Northern Irish professional football manager and former player who played as a midfielder. He currently manages Scottish Championship club Dunfermline Athletic.
During his playing career he represe ...
.
Types of migration
Seasonal workers
Prior to the 19th century, much of Irish migration of the
modern period
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500 ...
had been large-scale movement of temporary labourers to Britain.
These seasonal workers or labourers, known as Spalpeens and Tatie Hookers, were often based on extended family ties, and would involve up to half a year working on farms or in agricultural industry. Up until as late as the 1970s, earnings from this type of employment helped sustain communities in
Western Ireland
The West is a strategic planning area within the Northern and Western Region in Ireland. It is a NUTS Level III statistical region of Ireland (coded IE042) under the Eurostat classification. It consists of the counties of Galway, Mayo and Ro ...
.
Great Famine refugees
The
Great Famine in 1845 triggered a mass exodus from Ireland, with significant numbers of Irish migrants fleeing to Britain to escape severe poverty and starvation.
Regional migration histories
Irish in England
In 2021, there were 505,212 people in England (0.9 per cent of the population), who had been born in Ireland, down from 674,786 in 2001. Of these, 314,674 were born in the Republic of Ireland, and 190,538 born in Northern Ireland. Despite the drop since 2001, this is still the greatest concentration of Irish-born—as distinct from persons of Irish ancestry—abroad anywhere in the world and was equivalent to 7.2% of the population of the island of Ireland (7.1 million) in 2021, or 6.1% of the Republic of Ireland population and 10% of the Northern Irish population.
Barrow-in-Furness
During the
Great Famine of the 19th century,
Barrow-in-Furness
Barrow-in-Furness is a port town and civil parish (as just "Barrow") in the Westmorland and Furness district of Cumbria, England. Historic counties of England, Historically in the county of Lancashire, it was incorporated as a municipal borou ...
was seen as a desirable location that many Irish (along with Scottish and Cornish) fled to. This was in part due to ease of access to reach the town's port from Ireland (particularly from
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
), and secondly because it was a booming town as a result of the Industrial Revolution with guaranteed work, particularly in the emerging steelworks and shipbuilding industries in the town. At its peak, it was estimated that somewhere between 7-11% of Barrow's population were Irish or Scottish. As a result of this, to this day a huge number of Barrow's population are of Irish descent.
Birmingham
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
has a large Irish community, dating back to the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, it is estimated that Birmingham has the largest Irish population per capita in Britain.
Digbeth
Digbeth is an area of central Birmingham, England. Following the remodelling of the Birmingham Inner Ring Road, Inner Ring Road, Digbeth is now considered a district within Birmingham City Centre. As part of the Big City Plan, Digbeth is under ...
is the traditional Irish area in Birmingham. During the 1950s
Sparkhill
Sparkhill is an inner-city area of Birmingham, England, situated between Springfield, Birmingham, Springfield, Hall Green and Sparkbrook.
Historic counties of England, Historically part of Worcestershire, Sparkhill once existed as a Yardley ...
,
Sparkbrook
Sparkbrook is an inner-city area in south-east Birmingham, England. It is one of the four wards forming the Hall Green formal district within Birmingham City Council.
Etymology
The area receives its name from Spark Brook, a small stream that ...
,
Aston
Aston is an area of inner Birmingham, in the county of the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. Located immediately to the north-west of Birmingham city centre, Central Birmingham, Aston constitutes a wards of the United Kingdom, war ...
, and
Nechells
Nechells () is a district ward in central Birmingham, England, whose population in 2011 was 33,957. It is also a ward (politics), ward within the Government of Birmingham, England#Districts, formal district of Ladywood. Nechells local government ...
were the main Irish areas. Today many Irish people live in areas such as
Hall Green
Hall Green is an area in southeast Birmingham, England, synonymous with the B28 postcode. It is also a council constituency of Birmingham City Council, managed by its own district committee. Historic counties of England, Historically it lay wit ...
and
Erdington
Erdington is a suburb and ward of Birmingham, in the county of the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. Historic counties of England, Historically part of Warwickshire, it is located northeast of central Birmingham, bordering Sutt ...
. Birmingham has the UK's largest
St Patricks Day's Parade (and the world's third biggest) and Britain's only
Irish Quarter, with many traditional
Irish pub
In Ireland, a "pub" is an establishment licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. Irish pubs are characterised by a unique culture centred around a casual and friendly atmosphere, hearty food and drink, Irish sports, ...
s and the Birmingham Irish centre. Irish people have always moved to Birmingham for work especially for the construction, factory and industrial work which the city had to offer. Many Irish people moved to Birmingham to build
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
s,
road
A road is a thoroughfare used primarily for movement of traffic. Roads differ from streets, whose primary use is local access. They also differ from stroads, which combine the features of streets and roads. Most modern roads are paved.
Th ...
s and
railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
s in the city's industrial past.
St Chad's Cathedral is one of only two of the minor Basilicas in the UK. It is very important as the first Catholic church built in Britain after the
English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church ...
, and was designed by the architect
Augustus Pugin
Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin ( ; 1 March 1812 – 14 September 1852) was an English architect, designer, artist and critic with French and Swiss origins. He is principally remembered for his pioneering role in the Gothic Revival architecture ...
.
Community relations for the Irish in Birmingham were complicated by the
pub bombings of November 1974. At inquests into the deaths of the 21 victims, "Witness O" named the men responsible as Seamus McLoughlin, Mick Murray, Michael Hayes and James Gavin. He said he had been given permission to reveal the names by the current head of the IRA in Dublin. There were very limited physical attacks on Irish people in the aftermath of the bombings. In November 2018, Birmingham's Irish Association revealed a memorial to those killed outside
Birmingham New Street Station.
Bolton
A large number settled here in the 1950s as work was scarce at home, especially in the South. Many found work in the mills and factories and encouraged other family members to come over as there were jobs waiting for them.
Bradford
Bradford
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in West Yorkshire, England. It became a municipal borough in 1847, received a city charter in 1897 and, since the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 reform, the city status in the United Kingdo ...
largely expanded into the city it is today during the 19th century, due to jobs in the newly built textile mills attracting many immigrants in dire need of work. The population increase, in fact, saw Bradford go from a small town of 6,000 in 1801, to 103,000 by 1851 according to records taken. Many of these newly arriving people were Irish escaping the Great Famine, and could easily take advantage of all the work Bradford had on offer due to the ease to reach there from Ireland. J. B. Hammond once commented on this, saying of the distance from Ireland to Yorkshire, "It was easier to reach Yorkshire from Ireland than from Norfolk or Dorset... Labourers who were sent to Lancashire were taken to London, put on a boat of Pickfords...carried to Manchester in four or five days at a cost of fourteen shillings. But an Irishman could cross to Liverpool in fourteen hours for two shillings and sixpence". In 1851, records showed that Bradford had the highest proportion of Irish-born people in Yorkshire at the time.
In Donald M. MacRaid's book ''Irish Migration in Modern Britain'', he comments on research showing that a large number of Bradford's Irish originally came from
County Mayo
County Mayo (; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. In the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht, it is named after the village of Mayo, County Mayo, Mayo, now ge ...
,
County Sligo
County Sligo ( , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Northern and Western Region and is part of the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in ...
,
County Dublin
County Dublin ( or ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dubli ...
, and
County Laois
County Laois ( ; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and in the province of Leinster. It was known as Queen's County from 1556 to 1922. The modern county takes its name from Loígis, a medieval kingdom. Hist ...
, with records also suggesting that there was a common migration trail at the time from
County Roscommon
County Roscommon () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is part of the province of Connacht and the Northern and Western Region. It is the List of Irish counties by area, 11th largest Irish county by area and Li ...
to Bradford. Many of the Irish from Mayo and Sligo originated from a rural background, and at first struggled to adapt to urban life in Bradford.
To this day, many residents of Bradford and the surrounding area are of Irish descent.
There was an Irish Diaspora Research Unit at the University of Bradford in the early 21st Century under Dr. Patrick O'Sullivan, but the Unit did not continue after he moved to New York University.
Braintree, Essex
In the 1950s many thousands of Irish migrated to Braintree in Essex to meet the demands of the labour shortage primarily in the Courtauld's textile mills, both in Braintree and nearby Halstead. They also helped meet the need for labour both in Critall's main Braintree factory.
Coventry
Coventry had a large influx of Irish from around the middle of the 20th century, when the city's motor industry was booming. To this day, Coventry remains one of the cities in the UK with a higher Irish population, and retains strong Irish links. The city council put the town's Irish population at 2.3% in 2009, higher than the UK national average of 1%, and additionally the Coventry Irish Society estimated that around 10% of the city's population are of Irish descent.
Gateshead
During the 19th century, many of the towns in
County Durham
County Durham, officially simply Durham, is a ceremonial county in North East England.UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. The county borders Northumberland and Tyne an ...
(the county
Gateshead
Gateshead () is a town in the Gateshead Metropolitan Borough of Tyne and Wear, England. It is on the River Tyne's southern bank. The town's attractions include the twenty metre tall Angel of the North sculpture on the town's southern outskirts, ...
historically belongs to), which before that point had mostly been a rural county, began to take advantage of emerging new technology and discovered resources in the wake of the Industrial Revolution. This not only changed the face of the county, urbanizing much of it, but also led to expansion on a massive scale. People from all over the United Kingdom, ranging from the south of England to Ireland, moved to the area to take advantage of the large amount of work that these industries brought in roles such as coal mining and shipbuilding. As in many other instances around this time, it was the Great Famine which caused many from Ireland in particular to be drawn to jobs in the County Durham area, and make the move. A further advantage was that the county was quite straightforward to reach from Ireland, due to easy access by rail to there from the western port of
Whitehaven
Whitehaven is a town and civil parish in the Cumberland (unitary authority), Cumberland district of Cumbria, England. It is a port on the north-west coast, and lies outside the Lake District National parks of England and Wales, National Park. ...
, itself easily accessible by ferry from Ireland itself (in particular, Ulster). Gateshead in particular was one of the towns that changed most significantly due to the events of Industrial Revolution, but moreover took in one of the largest numbers of Irish of all the County Durham towns. In 1871, the town was recorded as having the densest number of Irish-born in County Durham, at 6.7%, and a year later it was recorded that 1 in 4 people in the town were Irish. The town also went through a huge population increase, rising by approximately 100,000 people over the course of the 19th century which the Irish undeniably contributed to. To this day, many people in the town are of Irish descent.
Halifax
Similarly to Bradford, Halifax was a desirable location for Irish escaping the Great Famine due to ease of access to reach, and the fact that its growth into an industrial boomtown over the 19th century coincided with the time of the famine. Many of the jobs on offer in Halifax were in newly opened cotton spinning mills, opened as a result of taking advantage of technological innovation in the then emerging textile industry. There were said to be as many as 24 mills in the town by 1850. The Irish contributed to its population growth from around 9,000 in 1800, to 25,000 by the middle of the century. In 1872, records showed that the Irish numbered "from a sixth to an eighth of the population" in Halifax, with it also being noted that "the political strength of the Irish people in Halifax is considerable". Irish heritage still lives on in Halifax through the likes of the town's football team, ''Halifax Irish F.C.''
Heywood
As
Heywood developed into a mill town during the Industrial Revolution, this brought a large number of new residents to the town, including many Irish escaping the Great Famine. Additionally, many Irish migrants took up jobs in the area working as
navvies on the local railway, a fact that still lives on in the town's legacy as some say that these navvies may have been the influence behind Heywood's nickname, Monkey Town.
Jarrow
Also situated in County Durham, the story behind why many Irish moved to Jarrow is similar to that of Gateshead. Shipbuilding, in particular, drew many of them to Jarrow. The town to this day is still sometimes nicknamed Little Ireland, and has a large Catholic community, as a result of the sheer number of Irish who moved there.
Keighley
During the Industrial Revolution, Keighley flourished in the textile and weaving industries, which encouraged many Irish fleeing the Great Famine and looking for work to move there. This resulted in a significant Irish community, and to this day the town still has a large number of inhabitants of Irish descent. The Irish redefined aspects of Keighley as a town significantly. It was once commented that the (then fairly new) Irish community in Keighley "contributed more to the Home-Rule than
neither of the populous towns of Glasgow or Liverpool". The influence of the Irish also led to there being a large Catholic community in Keighley, which has lived on in both Catholic churches and schools that exist in the town today.
Leeds
There is an Irish community in Leeds, although it is generally smaller than in other large cities in Britain. The Leeds Irish Centre is on York Road on the east side of the city. The nearby area of
East End Park
East End Park, currently named KDM Group East End Park for sponsorship purposes, is a football stadium situated in Dunfermline, Fife, Scotland with a seating capacity of .
The stadium plays host to the home matches of side, Dunfermline Athle ...
is the area most associated with Leeds's Irish community. In the years after the Famine, 3.3% of Leeds's population was Irish-born. There was a particular concentration of migrants from the Irish county of
Mayo. A book on the subject of migration from Ireland to Leeds in the 20th century was published in 2010: ''Taking The Boat: The Irish in Leeds, 1931-81.''
Liverpool
Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
is widely known for having the strongest Irish heritage of any UK city - perhaps alongside Glasgow. This originates from
the city's port being close to Ireland, which made it easy to reach for all those escaping the
Great Famine between 1845 and 1849. More than 20% of Liverpool's population was Irish by 1851. Up to 2 million Irish people travelled to Liverpool within 10 years during this time, though many subsequently
departed for the United States.
It is also
twinned with Dublin. All four of Liverpool's most famous natives,
the Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band formed in Liverpool in 1960. The core lineup of the band comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are widely regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatle ...
, had some Irish ancestry:
John Lennon
John Winston Ono Lennon (born John Winston Lennon; 9 October 19408 December 1980) was an English singer-songwriter, musician and activist. He gained global fame as the founder, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of the Beatles. Lennon's ...
's great-grandparents on his father's side were Irish immigrants from
County Down
County Down () is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the traditional thirty-two counties of Ireland. It covers an area of and has a population of 552,261. It borders County Antrim to the ...
,
Paul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained global fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and the piano, and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John ...
had an Irish grandfather and great-grandfather,
Ringo Starr
Sir Richard Starkey (born 7 July 1940), known professionally as Ringo Starr, is an English musician, songwriter and actor who achieved international fame as the drummer for the Beatles. Starr occasionally sang lead vocals with the group, us ...
had an Irish great-grandmother, and
George Harrison
George Harrison (25 February 1943 – 29 November 2001) was an English musician, singer and songwriter who achieved international fame as the lead guitarist of the Beatles. Sometimes called "the quiet Beatle", Harrison embraced Culture ...
had Irish blood through his mother.
Liverpool's Irish heritage is further highlighted by it being the only English city to have a significant
Orange Order
The Loyal Orange Institution, commonly known as the Orange Order, is an international Protestant fraternal order based in Northern Ireland and primarily associated with Ulster Protestants. It also has lodges in England, Grand Orange Lodge of ...
membership, as well as having a large
Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particul ...
majority and being the most Catholic city in the UK. It remains the only UK city to elect—and continuously re-elect—an
Irish nationalist
Irish nationalism is a nationalist political movement which, in its broadest sense, asserts that the people of Ireland should govern Ireland as a sovereign state. Since the mid-19th century, Irish nationalism has largely taken the form of cult ...
politician (
T. P. O'Connor) and hosts one of the UK's largest
St Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick (), is a religious and cultural holiday held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick (), the foremost patron saint of Ireland.
Saint Patrick's Day was made an official Chris ...
parades. The city has been at odds with
right-wing
Right-wing politics is the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position based on natural law, economics, authority, property ...
politicians since the 1970s, with
a city council that was previously dominated by the right-wing
Conservative Party becoming more
left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social ...
, a relationship that was exacerbated further during the days of Prime Minister
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
, whose Conservative government planned to starve the area of resources. It has also been regarded as a notably European city, and often identifies more with Ireland and the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
than the UK; this intensified in the 1980s during the UK media's mishandling of the
Hillsborough disaster
The Hillsborough disaster was a fatal crowd crush at a football match at Hillsborough Stadium in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England, on 15 April 1989. It occurred during an FA Cup semi-final between Liverpool and Nottingham Forest in the tw ...
, which saw lies being spread about dead Liverpudlians by tabloids such as ''
The Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot Plasma (physics), plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as ...
'', and it is not uncommon to hear a Liverpudlian refer to themselves as "Scouse, not English". Pro-EU sentiment increased again in 2008, when the EU designated Liverpool as a "Capital of Culture" and helped it to regenerate by pouring over
€
The euro sign () is the currency sign used for the euro, the official currency of the eurozone. The design was presented to the public by the European Commission on 12 December 1996. It consists of a stylized letter E (or epsilon), crossed by t ...
1 billion into the economy while the Conservative UK government continued to cut its funding. The Irish have also come to be a staple of Liverpool's surrounding areas; places such as
Birkenhead
Birkenhead () is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. The town is on the Wirral Peninsula, along the west bank of the River Mersey, opposite Liverpool. It lies within the Historic counties of England, historic co ...
,
Bootle
Bootle (pronounced ) is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton, Merseyside, England, which had a population of 51,394 in 2011; the wider Bootle (UK Parliament constituency), Parliamentary constituency had a population of 98,449. It is pa ...
,
Crosby Crosby may refer to:
Places Canada
*Crosby, Ontario, part of the township of Rideau Lakes, Ontario
*Crosby, Ontario, a neighbourhood in the city of Markham, Ontario
England
*Crosby, Cumbria
*Crosby, Lincolnshire
*Crosby, Merseyside
**Crosby (UK P ...
,
Halewood
Halewood is a town and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Knowsley, Merseyside, England, near the city of Liverpool's southeastern boundary, bordered by the suburbs of Netherley, Hunt's Cross and Woolton.
Historically part of Lanca ...
,
Huyton
Huyton ( ) is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Knowsley, Merseyside, England. Part of the Liverpool Urban Area, Liverpool Built-up Area, it borders the Liverpool suburbs of Dovecot, Merseyside, Dovecot, Knotty Ash and Netherley, Liverpool, ...
,
Kirkby
Kirkby ( ) is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Knowsley, Merseyside, England. The town, Historic counties of England, historically in Lancashire, has a size of is north of Huyton and north-east of Liverpool. The population in 2016 wa ...
,
Litherland
Litherland is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton, Merseyside. Until 1899 it was within the historic county of Lancashire. It was an urban district, which included Seaforth and Ford. It neighbours Waterloo to the north, Seaforth t ...
,
Runcorn
Runcorn is an industrial town and Runcorn Docks, cargo port in the Borough of Halton, Cheshire, England. Runcorn is on the south bank of the River Mersey, where the estuary narrows to form the Runcorn Gap. It is upstream from the port of Live ...
,
St Helens and
Wallasey
Wallasey () is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. It is at the mouth of the River Mersey, on the north-eastern corner of the Wirral Peninsula. It lies within the Historic counties of England, historic county bou ...
have many ethnically Irish residents and have also inherited the Liverpool accent.
Between
Liverpool FC
Liverpool Football Club is a professional football club based in Liverpool, England. The club competes in the Premier League, the top tier of English football. Founded in 1892, the club joined the Football League the following year and has ...
and
Everton FC
Everton Football Club () is a professional association football club based in Liverpool, England. The club competes in the Premier League, the top tier of English football league system, English football. Founded in 1878, the club was a foun ...
, the city's two biggest football teams, Everton FC is often cited as the more Irish of the two; some Liverpool FC fans have rejected this view.
London Irish

The term "London Irish" relates to people born in London of Irish descent. London has Great Britain's biggest Irish population and there was a particularly big community in the (affectionately known) "
County Kilburn
''County Kilburn'' is a 2000 British comedy film directed by Elliot Hegarty and starring Ciarán McMenamin, Rick Warden and John Bowe.
Plot
A young man takes a job working at The Waggon and Horses, an Irish bar in Kilburn in North London, whe ...
" area of northwest
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
. With urban
gentrification
Gentrification is the process whereby the character of a neighborhood changes through the influx of more Wealth, affluent residents (the "gentry") and investment. There is no agreed-upon definition of gentrification. In public discourse, it has ...
and higher housing costs, many of London's
working-class
The working class is a subset of employees who are compensated with wage or salary-based contracts, whose exact membership varies from definition to definition. Members of the working class rely primarily upon earnings from wage labour. Most c ...
Irish-Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particul ...
community have moved further out from
Kilburn to
Cricklewood
Cricklewood is a town in North London, England, in the London Boroughs of Camden, Barnet, and Brent. The Crown pub, now the Clayton Crown Hotel, is a local landmark and lies north-west of Charing Cross.
Cricklewood was a small rural hamlet ...
.
Another large Irish community was in the
Archway area, where many Irish
navvies came to work in building railways and roads from the 1830s onwards.
The community grew larger throughout the Famine years and then again after the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
when the
Whittington Hospital
Whittington Hospital is a district general hospital, district general and teaching hospital of UCL Medical School and Middlesex University School of Health and Social Sciences. Located in Archway, London, it is managed by Whittington Health NH ...
in Archway recruited nurses from Ireland.
[ This area became associated with Irish political activism with the election of Michael O'Halloran as MP for ]Islington North
Islington North is a United Kingdom constituencies, constituency in Greater London established for 1885 United Kingdom general election, the 1885 general election. It has been represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of C ...
in 1969. O'Halloran referred to his supporters as "the Irish mafia". In 2017, a new public space outside Archway underground station was named Navigator Square after the Irish navvies.[
The ]Camden Town
Camden Town () is an area in the London Borough of Camden, around north-northwest of Charing Cross. Historically in Middlesex, it is identified in the London Plan as one of 34 major centres in Greater London.
Laid out as a residential distri ...
area of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, as well as Shepherd's Bush
Shepherd's Bush is a suburb of West London, England, within the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham west of Charing Cross, and identified as a major metropolitan centre in the London Plan.
Although primarily residential in character, its ...
, were also known for their large Irish communities. The Irish Cultural Centre is located in Hammersmith
Hammersmith is a district of West London, England, southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, and identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
It ...
, West London. Greenford
Greenford () is a large town in the London Borough of Ealing in West London, Greater London, London, England, lying west from Charing Cross. It has a population of 46,787 inhabitants.
Greenford is served by Greenford station, Greenford Stati ...
in the London Borough of Ealing
The London Borough of Ealing () is a London boroughs, London borough in London, England. It comprises the districts of Acton, London, Acton, Ealing, Greenford, Hanwell, Northolt, Perivale and Southall. With a population of 367,100 inhabitants, i ...
is home to a large Irish community and contains Tir Chonaill Park, home to the Tír Chonaill Gaels Gaelic Football
Gaelic football (; short name '')'', commonly known as simply Gaelic, GAA, or football, is an Irish team sport. A form of football, it is played between two teams of 15 players on a rectangular grass pitch. The objective of the sport is to score ...
club.
Manchester
Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
has strong and long established Irish connections. The earliest large influx of migrants arrived sometime around 1798 according to Peter Ewart, a Manchester cotton manufacturer.Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
's current population has Irish ancestry, although no reliable data exists to evidence this. In November 2012 whilst addressing an audience at the University of Manchester, Michael D. Higgins
Michael Daniel Higgins (; born 18 April 1941) is an Irish politician, poet, broadcaster, and sociologist who has been serving as the president of Ireland since 2011. Entering national politics through the Labour Party, he served as a senator ...
suggested "the Irish connection in Manchester is no less evident than in Liverpool. And where Liverpool was a gateway for so many Irish people, Manchester tended to be for many the end of the journey, a home".Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ;["Engels"](_blank)
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''.[The Condition of the Working Class in England
''The Condition of the Working Class in England'' () is an 1845 book by the German philosopher Friedrich Engels, a study of the industrial working class in Victorian England. Engels' first book, it was originally written in German; an English t ...]
''. Areas concentrated with high levels of Irish were known as Little Ireland around Oxford Road and later Ancoats and Hulme. Manchester was a breeding ground for Irish Republicanism
Irish republicanism () is the political movement for an Irish Republic, Irish republic, void of any British rule in Ireland, British rule. Throughout its centuries of existence, it has encompassed various tactics and identities, simultaneously ...
, supporters known as Fenians
The word ''Fenian'' () served as an umbrella term for the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) and their affiliate in the United States, the Fenian Brotherhood. They were secret political organisations in the late 19th and early 20th centurie ...
, and when three Irish men were hanged accused of murder they became figureheads for Irish nationalism in Britain, Ireland and America and were known as the Manchester Martyrs
The Manchester Martyrs () were three Irish Republicanism, Irish Republicans – William Philip Allen, Michael Larkin, and Michael O'Brien – who were Hanging, hanged in 1867 following their conviction of murder after an attack on a police van i ...
. The reports of these terrible conditions sparked pioneering social changes in Manchester in the 1840s with the city often at the forefront of social reform in Britain.
Manchester was targeted by the IRA in the 1996 Manchester bombing
The 1996 Manchester bombing was an attack carried out by the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) on 15 June 1996. The IRA detonated a lorry bomb on Corporation Street, Manchester, Corporation Street in the Manchester city centre, centre ...
in what was described as the biggest bomb on British soil since World War II. Manchester was targeted in part because security in London was so rigid due to parades in London for the Queen's Trooping of the Colour. However, it was telling that the terrorists warned of the exact location beforehand to save human lives in a city with a rich history of Irish migration, balancing a fine line of shocking Britain and alienating supporters back home. On 20 June 1996, the IRA claimed responsibility for the bombing, and stated that it "sincerely regretted" causing injury to civilians. This stood in sharp contrast to their earlier 1993 bombing of nearby Warrington which killed two English children aged 3 and 12, which the IRA blamed on "the British authorities" for not being able to respond to its imprecise warning that did not even specify Warrington as the target.
The city's residents of Irish heritage have been influential in the music industry. All four members of the Smiths
The Smiths were an English Rock music, rock band formed in Manchester in 1982, composed of Morrissey (vocals), Johnny Marr (guitar), Andy Rourke (bass) and Mike Joyce (musician), Mike Joyce (drums). Morrissey and Marr formed the band's songwrit ...
had Irish roots, as do the Gallagher brothers of the band Oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment[Gary Mounfield
Gary "Mani" Mounfield (born 16 November 1962)Warshaw, AaronMani allmusic.com is an English rock bassist, best known for being a member of the Stone Roses and Primal Scream.
Career
Mounfield attended Xaverian College in Rusholme, Manchester ...]
(Mani), bass player of the Stone Roses
The Stone Roses were an English rock band formed in Manchester in 1983. They were one of the pioneering groups of the Madchester movement in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The band's classic and most prominent lineup consisted of vocalist I ...
had an Irish mother. Manchester holds an annual Irish Festival each March, including one of the UK's largest St Patrick's Day parades. Cheetham is home to the Irish World Heritage Centre.
Due to its connections with the local Irish Catholic population, Manchester United
Manchester United Football Club, commonly referred to as Man United (often stylised as Man Utd) or simply United, is a professional association football, football club based in Old Trafford (area), Old Trafford, Greater Manchester, Engl ...
was almost named Manchester Celtic in 1902 and is the most supported football club in Ireland.
Middlesbrough
Middlesbrough
Middlesbrough ( ), colloquially known as Boro, is a port town in the Borough of Middlesbrough, North Yorkshire, England. Lying to the south of the River Tees, Middlesbrough forms part of the Teesside Built up area, built-up area and the Tees Va ...
during the latter half of the 19th century had the second highest percentage of Irish born migrants in England after Liverpool. In terms of the overall population, 15.6% of Middlesbrough's inhabitants were Irish born in 1861 and 1 in 5 adults (9.2%) were Irish born in the 1871 census. During the late 19th century, Middlesbrough became a world leader in the Steel and Iron industry and with the rapid growth of the town, the expanse of newly opened blast furnaces attracted many workers and their families to the Middlesbrough area. Unlike many other towns in England at the time, Middlesbrough showed no signs of sectarianism or segregation within the various communities that lived alongside each other, there were no "Irish quarters" and the many Irish that settled in Middlesbrough integrated into their adopted home. This was most likely as a result of the town's infancy, it was essentially a migrant town. Although the number of Irish born currently residing in Middlesbrough may not be as substantial as it once was, Middlesbrough retains a strong Irish connection and heritage through the ancestry of many residents.
Sunderland
Sunderland was another place in County Durham that many Irish escaping the famine saw as desirable. Once dubbed "the largest shipbuilding town in the world", the city largely expanded into what it is today as a result of the number of people this work, and the demand for manual labour in other local jobs such as coal mining and chemical works,Peter O'Toole
Peter Seamus O'Toole (; 2 August 1932 – 14 December 2013) was an English actor known for his leading roles on stage and screen. His numerous accolades include the Academy Honorary Award, a BAFTA Award, a Primetime Emmy Award, and four Golde ...
's father was a labourer in Sunderland for many years, which is why Peter O'Toole
Peter Seamus O'Toole (; 2 August 1932 – 14 December 2013) was an English actor known for his leading roles on stage and screen. His numerous accolades include the Academy Honorary Award, a BAFTA Award, a Primetime Emmy Award, and four Golde ...
supported Sunderland A.F.C.
Sunderland Association Football Club is a professional football club based in Sunderland, Tyne and Wear, England. The team compete in the Premier League, the top tier of the English football league system.
Formed in 1879, the club has won si ...
Whitehaven
Due to its port and close proximity to Ireland, similarly to Liverpool, Whitehaven was an easy way of accessing England for the Irish, especially when escaping the Great Famine of the 19th century. Thousands passed through the town to move on to work for themselves elsewhere in England, such as the aforementioned County Durham, however many also stayed in the area and many people in the town still have Irish heritage today.
Widnes
Widnes
Widnes ( ) is an Industrial city, industrial town in the Borough of Halton, Cheshire, England, which at the 2021–2022 United Kingdom censuses, 2021 census had a population of 62,400.
Historic counties of England, Historically in Lancashire, ...
became a boom town during the Industrial Revolution, having a successful chemical industry brought on by a factory opened in the town in 1847, which led to many Irish workers (among others from Wales, Poland and Lithuania) moving there for work. Further making Widnes advantageous for the Irish to move to was its close proximity to Liverpool. Since then, a large number of overspill from the neighbouring city of Liverpool have brought many more people of Irish descent to Widnes too, particularly in areas at the west end of the town such as Ditton and Hough Green, where overspill are still moved.
Wigan
Wigan, being almost equal distance from Liverpool and Manchester received high immigration rates of Irish people in the 1800s. The Wigan districts population doubled from 60,000 in 1841 to 120,000 in 1871 with the immigration of Irish to the town the biggest factor. The Irish mainly settled in the central areas of the town such as Scholes and Ince with the area around Belle Green Lane referred to as Irishtown. St Patrick's church in Scholes was built in 1847 on the back of huge swathes of Irish immigration.
The local amateur rugby league club Wigan St Patricks
Wigan St. Patricks is an amateur rugby league football club based in the Scholes area of Wigan, Greater Manchester. The first team plays in the National Conference League Division One .
In 1986, the club was one of ten founder members of the B ...
has the Irish shamrock on the club badge with green and black being the club colours.
The Wigan accent has even been affected by the great number of Irish coming to the town. The local word "moidered", known elsewhere as " mithered", is said to have derived from pronouncing the word ''mithered'' in an Irish accent.
Wolverhampton
Wolverhampton prospered during the Industrial Revolution, particularly having successful iron and locomotive industries, which attracted many Irish escaping the Great Famine. As well as this, Wolverhampton had a longstanding Roman Catholic community from as early as the 18th century, leading to the city sometimes being nicknamed "Little Rome", which began to attract Irish to the city from an early stage.
Irish in Scotland
There are long standing migration links between Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
and the Province of Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
, especially between County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county of the Republic of Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster and is the northernmost county of Ireland. The county mostly borders Northern Ireland, sharing only a small b ...
, County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, County Antrim, Antrim, ) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, located within the historic Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the c ...
and County Down
County Down () is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the traditional thirty-two counties of Ireland. It covers an area of and has a population of 552,261. It borders County Antrim to the ...
with the west coast of Scotland. Considering the Dal Riada
Dal is a term in the Indian subcontinent for dried, split pulses.
Dal or DAL may also refer to:
Places
Cambodia
*Dal, Ke Chong
Finland
* Laakso, a neighbourhood of Helsinki
India
* Dal Lake, in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
* Dal ...
kingdoms and the gaelicisation
Gaelicisation, or Gaelicization, is the act or process of making something Gaels, Gaelic or gaining characteristics of the ''Gaels'', a sub-branch of Celticisation. The Gaels are an ethno-linguistic group, traditionally viewed as having spread fro ...
of Scotland in the early Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, it is difficult to determine how many Scots have genetic ancestry from Ireland historically or how many were Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples in what is now Scotland north of the Firth of Forth, in the Scotland in the early Middle Ages, Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and details of their culture can be gleaned from early medieval texts and Pic ...
who adopted Irish lifestyles, although the general consensus is that both happened as Pictish culture vanished by the 11th century. In 2001, around 55,000 people in Scotland (1.1 per cent of the Scottish population) had been born in Ireland, while people of Irish (either Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
or Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
) ancestry make up 20% of the Scottish population. Scotland has a greater number of persons born in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
and County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county of the Republic of Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster and is the northernmost county of Ireland. The county mostly borders Northern Ireland, sharing only a small b ...
(0.66 per cent) than people who were born in the rest of Ireland (0.43%). Despite having lower than average numbers of Irish people resident, the Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire, also called the County of Lanark (; ), is a Counties of Scotland, historic county, Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area and registration county in the Central Lowlands and Southern Uplands of Scotland. The county is no l ...
town of Coatbridge
Coatbridge (, ) is a town in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, about east of Glasgow city centre, set in the central Lowlands. Along with neighbouring town Airdrie, North Lanarkshire, Airdrie, Coatbridge forms the area known as the Monklands (popula ...
is more than 50% Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
. The town is populated by the second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth generation children of Irish immigrants, especially immigrants from County Donegal. In 2006 more than 28% of adults in Coatbridge had surnames with Irish origins. Coatbridge holds the largest St. Patrick's Day Festival in Scotland.
Famous Scots of Irish-Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particul ...
ancestry include actors Sean Connery
Sir Thomas Sean Connery (25 August 1930 – 31 October 2020) was a Scottish actor. He was the first actor to Portrayal of James Bond in film, portray the fictional British secret agent James Bond (literary character), James Bond in motion pic ...
, Brian Cox and Gerard Butler
Gerard James Butler (born 13 November 1969) is a Scottish actor and film producer. After studying law, he turned to acting in the mid-1990s with small roles in productions such as '' Mrs Brown'' (1997), the James Bond film ''Tomorrow Never ...
; comedians Billy Connolly
Sir William Connolly (born 24 November 1942) is a Scottish actor, musician, television presenter, artist and retired stand-up comedian. He is sometimes known by the Scots nickname the Big Yin ("the Big One"). Known for his idiosyncratic and of ...
and Frankie Boyle
Francis Martin Patrick Boyle (born 16 August 1972) is a Scottish comedian and writer. Boyle first gained widespread recognition as a regular panellist on the comedy show '' Mock the Week'' from 2005 until 2009. He then created and starred in t ...
; singers Susan Boyle
Susan Magdalane Boyle (born 1 April 1961) is a Scottish singer who rose to fame in 2009 after appearing as a contestant on the third series of '' Britain's Got Talent'', singing " I Dreamed a Dream" from '. As of 2021, Boyle has sold 25 ...
, Gerry Rafferty
Gerald Rafferty (16 April 1947– 4 January 2011) was a Scottish singer, songwriter, musician and record producer. He was a founding member of Stealers Wheel, whose biggest hit was "Stuck in the Middle with You" in 1973. His solo hits in the ...
, Fran Healy and David Byrne
David Byrne (; born May 14, 1952) is an American musician, writer, visual artist, and filmmaker. He was a founding member, principal songwriter, lead singer, and guitarist of the American New wave music, new wave band Talking Heads.
Byrne has ...
; historians Tom Devine
Sir Thomas Martin Devine (born 30 July 1945), usually known as Sir Tom Devine, is a Scottish academic and author who specializes in the history of Scotland. He was knighted and made an Officer of the Order of the British Empire for his contr ...
and Michael Lynch; footballers
A football player or footballer is a sportsperson who plays one of the different types of football. The main types of football are association football, American football, Canadian football, Australian rules football, Gaelic football, rugby le ...
like Jimmy McGrory
James Edward McGrory (26 April 1904 – 20 October 1982) was a Scottish footballer who played for Celtic and Clydebank as a forward. He later managed Kilmarnock and Celtic.
McGrory is also the all-time leading goalscorer in top-flight Bri ...
and Ray Houghton
Raymond James Houghton (born 9 January 1962) is a former professional Association football, footballer and current sports analyst and commentator with RTÉ Sport.
As a player, he was a midfielder, notably playing for Liverpool F.C., Liverpool w ...
; politicians like James Connolly
James Connolly (; 5 June 1868 – 12 May 1916) was a Scottish people, Scottish-born Irish republicanism, Irish republican, socialist, and trade union leader, executed for his part in the Easter Rising, 1916 Easter Rising against British rule i ...
(the trade unionist
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
and Easter Rising
The Easter Rising (), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an ind ...
leader), Jim Murphy
James Francis Murphy (born 23 August 1967) is a Scottish former politician who served as Leader of the Scottish Labour Party from 2014 to 2015 and Secretary of State for Scotland from 2008 to 2010. He was Member of Parliament (MP) for East R ...
(former British Shadow
A shadow is a dark area on a surface where light from a light source is blocked by an object. In contrast, shade occupies the three-dimensional volume behind an object with light in front of it. The cross-section of a shadow is a two-dimensio ...
Defence Secretary), and socialist political figure Tommy Sheridan
Thomas Sheridan (born 7 March 1964) is a Scottish politician who served as convenor of Solidarity from 2019 to 2021. He previously served as convenor of the Scottish Socialist Party (SSP) from 1998 to 2004 and as co-convenor of Solidarity from ...
; television presenter
A television presenter (or television host, some become a "television personality") is a person who introduces or hosts television show, television programs, often serving as a mediator for the program and the audience. It is common for people ...
Lorraine Kelly
Lorraine Kelly (born 30 November 1959) is a Scottish television presenter. She has presented various television shows for ITV and STV, including '' Good Morning Britain'' (1988–1992), ''GMTV'' (1993–2010), ''This Morning'' (2003–2005, ...
; businessmen like Thomas Lipton
Sir Thomas Johnstone Lipton, 1st Baronet (10 May 18482 October 1931) was a Scotsman of Irish parentage who was a self-made man, as company founder of Lipton Tea, merchant, philanthropist and yachtsman who lost 5 straight America's Cup races.
...
; and writers Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Hol ...
, A. J. Cronin
Archibald Joseph Cronin (Cronogue) (19 July 1896 – 6 January 1981) was a Scottish physician and novelist. His best-known novel is ''The Citadel (novel), The Citadel'' (1937), about a Scottish physician who serves in a Welsh coal mining, minin ...
, John Byrne and Andrew O'Hagan
Andrew O'Hagan (born 1968) is a Scottish novelist and non-fiction author. Three of his novels have been nominated for the Booker Prize and he has won several awards, including the ''Los Angeles Times'' Book Prize.
His most recent novel is ''C ...
.
Support for particular football teams often reflects Catholic or Protestant heritage. Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
are overwhelmingly, though not exclusively, supported by people from a Catholic background. Hibernian and Dundee United
Dundee United Football Club is a Scotland, Scottish professional association football, football club based in the city of Dundee. Formed in 1909, originally as Dundee Hibernian, the club changed to the present name in 1923. United are nickname ...
were formed as clubs representing Irish Catholics, however there is little vestige of these founding values today. Teams such as Dundee
Dundee (; ; or , ) is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, fourth-largest city in Scotland. The mid-year population estimate for the locality was . It lies within the eastern central Lowlands on the north bank of the Firt ...
(though founded before Dundee United on entirely secular grounds), Heart of Midlothian and Lanarkshire teams such as Motherwell
Motherwell (, ) is a List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, town and former burgh in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, United Kingdom, south east of Glasgow. It has a population of around 32,120. Shires of Scotland, Historically in the p ...
and Airdrie are contentiously perceived by some as Protestant clubs. Rangers
A ranger is typically someone in a law enforcement or military/paramilitary role specializing in patrolling a given territory, called "ranging" or "scouting". The term most often refers to:
* Park ranger or forest ranger, a person charged with prot ...
are seen as having retained a Protestant identity, despite signing a number of Catholic players since the 1980s.
Today a very small minority of the Irish Catholic community in Scotland take part in Irish republican
Irish republicanism () is the political movement for an Irish republic, void of any British rule. Throughout its centuries of existence, it has encompassed various tactics and identities, simultaneously elective and militant and has been both w ...
marches (mainly in Strathclyde
Strathclyde ( in Welsh language, Welsh; in Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic, meaning 'strath alley
An alley or alleyway is a narrow lane, footpath, path, or passageway, often reserved for pedestrians, which usually runs between, behind, or within buildings in towns and cities. It is also a rear access or service road (back lane), or a path, w ...
of the River Clyde') was one of nine former Local government in Scotland, local government Regions and districts of Scotland, regions of Scotland cre ...
), though these marches do not have exclusively Catholics in attendance, with many Protestants and others of various faiths or none involved, and the Orange Order
The Loyal Orange Institution, commonly known as the Orange Order, is an international Protestant fraternal order based in Northern Ireland and primarily associated with Ulster Protestants. It also has lodges in England, Grand Orange Lodge of ...
has a large membership in Scotland, predominantly in Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
, Lanarkshire and Ayrshire
Ayrshire (, ) is a Counties of Scotland, historic county and registration county, in south-west Scotland, located on the shores of the Firth of Clyde. The lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area of Ayrshire and Arran covers the entirety ...
. As well as Scotland's own parades, many Scottish bands parade in Ulster (chiefly in Northern Ireland and County Donegal) on or around 12 July.
Irish in Wales
Starting in the 4th century AD, Irish raiders settled Wales extensively, their impact being so great that many Irish words were introduced into the Welsh language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales by about 18% of the population, by some in England, and in (the Welsh c ...
. Many Irish emigrants came to Wales as a result of the famine of 1845–52. They were often very poor, and seen as carrying "famine fever" (typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
), but over time they acquired a notable presence—in the thousands, particularly in the Welsh coal mining towns in and around Swansea
Swansea ( ; ) is a coastal City status in the United Kingdom, city and the List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, second-largest city of Wales. It forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area, officially known as the City and County of ...
and Newport.
One of the most famous Welsh nationals of Irish-Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particul ...
ancestry is screen actress Catherine Zeta-Jones
Catherine Zeta-Jones (; born 25 September 1969) is a Welsh actress. Recognised for her versatility, she has received various accolades, including an Academy Award, a British Academy Film Award, and a Tony Award. In 2010, she was appointed Comm ...
.
The Irish language is taught at all levels in the Department of Welsh and Celtic Studies in Aberystwyth University in West Wales, and scholarships offered to students to do intensive summer language courses in Ireland
Cultural impact
Catholic Church
The large-scale migration of Irish people to Britain in the 19th century contributed to the reemergence of the Catholic Church in England
The Catholic Church in England and Wales (; ) is part of the worldwide Catholic Church in full communion with the Holy See. Its origins date from the 6th century, when Pope Gregory I through a Roman missionary and Benedictine monk, Augustine, ...
, which ultimately accelerated tolerance for freedom of religion in the United Kingdom
The right to freedom of religion in the United Kingdom is provided for in all three constituent legal systems, by devolved, national, European, and international law and treaty. Four constituent nations compose the United Kingdom, resulting in ...
. Observed by the Catholic Church, Saint Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick (), is a religious and cultural holiday held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick (), the foremost patron saint of Ireland.
Saint Patrick's Day was made an official Chris ...
is widely celebrated throughout Great Britain, owing to many British people's ancestral links with Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
as well as the general popularity of the event. Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
, and Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
have particularly large parades.
Irish language
The Irish language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous ...
has a long history in Britain. Gaels came to Britain between the 4th to 5th centuries and established Irish speaking communities in the west coast of Scotland that remain to this day. The waves of immigrants from Ireland that settled in British communities in the 19th century included speakers of Irish but English became the norm. However, there are regular gatherings of Irish speakers in London, Glasgow and Manchester and lessons available all over Britain including Glasgow, Milton Keynes, Manchester, Brighton, Lewisham, Hammersmith, Camden, Birmingham, Liverpool, Leeds, Newcastle and Cardiff. While several British universities offer a one-term-long introduction to the Irish language, the Department of Welsh and Celtic Studies in Aberystwyth University in west Wales is the only university to teach the modern Irish language at all levels. Modules in Old, Middle and Early-Modern Irish are also offered, and students can receive scholarships to do intensive summer courses in Ireland.
Access to services in the language
The lack of provision for legal and citizenship services in the Irish language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous ...
, including for the Life in the United Kingdom test
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, organisation, metabolism, growth, adaptation, r ...
, has been met with criticism from the ''Committee of Experts'' of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, t ...
, of which the UK has ratified for the Cornish language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or , ) is a Southwestern Brittonic language, Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. Along with Welsh language, Welsh and Breton language, Breton, Cornish descends from Common Brittonic, ...
, the Irish language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous ...
, Manx Gaelic
Manx ( or , or ), also known as Manx Gaelic, is a Goidelic language, Gaelic language of the insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family. Manx is the heritage language of the Manx ...
, the Scots & Ulster Scots dialect
Ulster Scots or Ulster-Scots (), also known as Ulster Scotch and Ullans, is the dialect (whose proponents assert is a dialect of Scots language, Scots) spoken in parts of Ulster, being almost exclusively spoken in parts of Northern Ireland a ...
s, Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
and the Welsh language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales by about 18% of the population, by some in England, and in (the Welsh c ...
. In a 2014 report detailing the application of the charter in the UK, the Committee were given no justification for the inequality in the treatment of Irish speakers in contrast to that of English, Scottish Gaelic and Welsh speakers, and said that efforts to rectify the inequality were non-existent.
Sport
Sports teams with links to the Irish community exist in England, although this is not as marked as in Scotland.
Football
In football, Aston Villa
Aston Villa Football Club (commonly referred to as simply Villa) is a professional football club based in Aston, Birmingham, England. The club, founded in 1874, compete in the Premier League, the top tier of English football. The team have p ...
, Arsenal
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
, Everton, Manchester United
Manchester United Football Club, commonly referred to as Man United (often stylised as Man Utd) or simply United, is a professional association football, football club based in Old Trafford (area), Old Trafford, Greater Manchester, Engl ...
have a tradition of representing the Irish communities in their area although unlike many clubs in Scotland they were not formed on the basis of representing the Irish community. For example, Arsenal has featured ethnically Irish players such as Liam Brady
William Brady (born 13 February 1956) is an Irish former footballer and pundit. He found success both in England with Arsenal, where he won an FA Cup in 1979, and in Italy with Juventus, winning two Serie A titles. Brady was capped 72 times for ...
, Terry Neill
William John Terence Neill (8 May 1942 – 28 July 2022) was a Northern Irish football player and manager. A centre-back, he captained and later managed Arsenal, guiding the club to a European final in 1980 and three consecutive FA Cup final ...
, Pat Rice
Patrick James Rice, MBE (born 17 March 1949) is a Northern Irish former footballer and coach. As a player, he made nearly 400 appearances for Arsenal, winning the Double, and later made a hundred more appearances for Watford. He also won 49 ...
, Niall Quinn
Niall John Quinn (honorary Order of the British Empire, MBE; born 6 October 1966) is an Irish former professional Association football, footballer, manager, businessman and sports television pundit.
As a player, he was a Striker (association f ...
, David O'Leary
David Anthony O'Leary (born 2 May 1958) is a football manager and former player. The majority of his 20-year playing career was spent as a central defender at Arsenal, where his tally of 722 appearances stands as a club record. He played 68 time ...
and Graham Barrett
Graham Barrett (born 6 October 1981) is an Irish former professional footballer who played as a forward.
He began his footballing career at Arsenal, where he won the FA Youth Cup. He went on to feature for English clubs Bristol Rovers, Crewe ...
. Aston Villa has featured many Irish players such as Steve Staunton
Stephen Staunton (born 19 January 1969) is an Irish football manager, scout and former professional footballer.
He played as a defender with two separate spells each with Premier League sides Aston Villa and Liverpool. He also played in the F ...
, Paul McGrath, Richard Dunne
Richard Patrick Dunne (born 21 September 1979) is an Irish former professional footballer and current television pundit for TNT Sports, who played as a centre-back. He made 431 Premier League appearances, including 253 for Manchester City.
Du ...
and former managers David O'Leary
David Anthony O'Leary (born 2 May 1958) is a football manager and former player. The majority of his 20-year playing career was spent as a central defender at Arsenal, where his tally of 722 appearances stands as a club record. He played 68 time ...
and Martin O'Neill
Martin Hugh Michael O'Neill, (born 1 March 1952) is a Northern Irish professional Manager (association football), football manager and former Association football, player who played as a midfielder. After a brief early career in the Irish Leag ...
. Aston Villa has a large Irish following in the West Midlands which has the highest proportion of Irish people in England. Both Everton and Liverpool have roots in a Methodist church
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
but Everton F.C.
Everton Football Club () is a professional association football club based in Liverpool, England. The club competes in the Premier League, the top tier of English football. Founded in 1878, the club was a founding member of the Football Lea ...
was often described as Liverpool's Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particul ...
team, probably because Everton had a number of Irish internationals in the 1950s. Liverpool F.C.
Liverpool Football Club is a professional Football club (association football), football club based in Liverpool, England. The club competes in the Premier League, the top tier of English football league system, English football. Founded in ...
was formed by a prominent Orangeman but this fact did not deter Liverpool people from a Catholic background supporting the team. Everton has notably produced Wayne Rooney
Wayne Mark Rooney (born 24 October 1985) is an English professional Manager (association football), football manager and former Association football, player who was most recently the head coach of EFL Championship club Plymouth Argyle F.C., Pl ...
who is of Irish descent and have recently featured promising Irish international Séamus Coleman
Séamus Coleman ( ; born 11 October 1988) is an Irish professional footballer who plays as a right-back for and captains both club Everton and the Republic of Ireland national team.
Originally a Gaelic footballer, Coleman started his associa ...
; as were prominent Liverpool players who were Everton fans in their youth such as Jamie Carragher
James Lee Duncan Carragher ( ; born 28 January 1978) is an English football analyst and former player who played as a defender for Premier League club Liverpool during a career which spanned 17 years. A one-club man, he was Liverpool's vice ...
and Steve McManaman
Steven McManaman (born 11 February 1972) is an English former professional footballer who played as a winger. He is one of the most decorated English footballers to have played for a club abroad, with the UEFA website stating in 2012 that "of al ...
. Recently Jonjo Shelvey
Jonjo Shelvey (born 27 February 1992) is an English professional footballer who most recently played as a central midfielder for EFL Championship club Burnley.
Shelvey began his career at Charlton Athletic, becoming their youngest-ever player ...
has become the latest in a line of Liverpool players with Irish heritage, going back to the days of Mark Lawrenson
Mark Thomas Lawrenson (born 2 June 1957) is an English former professional association football, footballer who played as a Defender (association football), defender for Liverpool F.C., Liverpool, among others, during the 1970s and 1980s. After ...
, Ronnie Whelan
Ronald Andrew Whelan (; born 25 September 1961) is an Irish former professional football player who played as a midfielder and sometimes as a defender. He played an integral role in the dominant Liverpool side that won a wealth of titles in ...
and Ray Houghton
Raymond James Houghton (born 9 January 1962) is a former professional Association football, footballer and current sports analyst and commentator with RTÉ Sport.
As a player, he was a midfielder, notably playing for Liverpool F.C., Liverpool w ...
. Neither Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
nor Everton have a sectarian
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism a ...
affiliation and many families are split in support of the clubs.
Under the management of Sir Matt Busby, Manchester United
Manchester United Football Club, commonly referred to as Man United (often stylised as Man Utd) or simply United, is a professional association football, football club based in Old Trafford (area), Old Trafford, Greater Manchester, Engl ...
also emerged as a club with a considerable Irish following both in Great Britain and in Ireland itself, as well as having notable Irish stars like George Best
George Best (22 May 1946 – 25 November 2005) was a Northern Irish professional association football, footballer who played as a winger (association football), winger, spending most of his club career at Manchester United F.C., Manchester Un ...
, Norman Whiteside
Norman Whiteside (born 7 May 1965) is a Northern Irish former professional footballer who played as a midfielder and striker.
Whiteside began his career at Manchester United, signing professional forms in 1982 at the age of 17 and quickly be ...
, Mal Donaghy
Malachy Martin Donaghy (born 13 September 1957 in Belfast) is a former Northern Ireland international footballer who played for Luton Town and Manchester United.
Career
Club career
Originally from West Belfast, began his football career as a g ...
, Denis Irwin
Joseph Denis Irwin (born 31 October 1965) is an Irish former professional footballer and sports television presenter. Irwin is the joint most successful Irish footballer in history, a record he shares with Ronnie Whelan and fellow Manchester U ...
, Roy Keane
Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football pundit, former coach, and former professional player. He is best known for his career in the Premier League, in particular his captaincy of Manchester United. He is the joint most ...
, and recently John O'Shea
John Francis O'Shea (; born 30 April 1981) is an Irish professional football coach and former player who is currently assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland men's national team. He was known for his versatility in playing several defensi ...
.
Rugby
In rugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as rugby league in English-speaking countries and rugby 13/XIII in non-Anglophone Europe, is a contact sport, full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular Rugby league playin ...
, Dewsbury Celtic
Dewsbury Celtic is a rugby league club in the town of Dewsbury, West Yorkshire. They play in the NCL Division Two under Head Coach Scott Dyson. Mark Brierley also coaches alongside, adding to the coaching expertise.
Boasting a strong amateur ...
represented the large Irish community in Dewsbury
Dewsbury is a market town in the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees in West Yorkshire, England. It lies on the River Calder, West Yorkshire, River Calder and on an arm of the Calder and Hebble Navigation waterway. It is to the west of Wakefield, ...
, and St. Helens represent communities on Merseyside
Merseyside ( ) is a ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial and metropolitan county in North West England. It borders Lancashire to the north, Greater Manchester to the east, Cheshire to the south, the Wales, Welsh county of Flintshire across ...
. Wigan St Patricks
Wigan St. Patricks is an amateur rugby league football club based in the Scholes area of Wigan, Greater Manchester. The first team plays in the National Conference League Division One .
In 1986, the club was one of ten founder members of the B ...
amateur rugby league club is borne out of the St Patricks Catholic Church in Scholes, Wigan, that was built in 1847 after huge swathes of Irish moved to the town.
The rugby union club London Irish
London Irish RFC is a professional rugby union club that most recently competed in the Premiership Rugby, Premiership, the top division of rugby union in England. The club also participated in the European Rugby Champions Cup, European Champion ...
represents the community in London.
Gaelic Games
The British GAA
The British Council of the Gaelic Athletic Association () or Britain GAA is the only provincial council of the Gaelic Athletic Association outside the island of Ireland, and is responsible for Gaelic games in Great Britain. The board is also r ...
is responsible for Gaelic games
Gaelic games () are a set of sports played worldwide, though they are particularly popular in Ireland, where they originated. They include Gaelic football, hurling, Gaelic handball and rounders. Football and hurling, the most popular of the s ...
in Britain. There are seven GAA counties within Britain and a number of hurling, football and camogie clubs operate within each county.
Brexit
Ever since the Brexit
Brexit (, a portmanteau of "Britain" and "Exit") was the Withdrawal from the European Union, withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU).
Brexit officially took place at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February ...
vote in 2016, over 400,000 British persons with ties to Ireland – mainly that of Irish diaspora – applied for an Irish passport
An Irish passport () is the passport issued to Irish nationality law, citizens of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. An Irish passport enables the bearer to travel internationally and serves as evidence of Irish nationality and citizenship of the Eu ...
as of 2021. This phenomenon further adds on to the growing demand for Irish identity, but is also attributed to rising popularity in European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
citizenship.
Perceptions of Irish immigration
Effect on the British trade union movement
In 1870, Karl Marx
Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
examined how the migration of Irish labour into the British labour market caused significant problems for the nascent English trade union movement since an over-supply of workers enabled employers to lower wages and threaten organised British workers with replacement by Irish migrants. Marx wrote in a letter that "the ordinary English worker hates the Irish worker as a competitor who lowers his standard of life", in addition to noting that "every industrial and commercial centre in England now possesses a working class divided into two hostile camps", consisting of the English and Irish working class.
Criminality
Perceptions of Irish immigration in Victorian Britain
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed th ...
led to negative stereotypes. Settling in large numbers, at a time of unprecedented economic development, Irish people, and especially those living in poverty, were seen as innately criminal by elements of British society. It was even a widespread belief that Irish migrants formed the core of what were described as the "dangerous classes", and represented a threat to law and order. The Vagrancy Act 1824
The Vagrancy Act 1824 ( 5 Geo. 4. c. 83) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that makes it an offence to sleep rough or beg in England and Wales. The legislation was passed in Georgian England to combat the increasing number o ...
was, in part, a reaction to significant levels of perceived vagrancy from Irish people "searching for generous local welfare in England".
Disease and poverty
The results of Irish migration during the 19th century were also perceived as bringing disease and poverty into urban centres, in particular cities such as Manchester, Liverpool and Glasgow.
Social and health issues
Health
A 2009 study published in '' Ethnicity & Health'' demonstrated that the grouping self-reported higher rates of poor general health than the White British populace. This was found to be particularly the case in Northern Ireland, for those who had designated themselves as White, and with an "Irish" national identity. In 2020, a UCL study based in NHS England
NHS England, formally the NHS Commissioning Board for England, is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care. It oversees the budget, planning, delivery and day-to-day operation of the commissioning si ...
data, showed that the White Irish group was around 50 per cent less at risk of death from COVID-19 than other black, Asian and minority ethnic
A number of different systems of classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom exist. These schemata have been the subject of debate, including about the nature of ethnicity, how or whether it can be categorised, and the relationship betwe ...
(BAME) groups. This was significantly lower than the White British group, which were 12 per cent lower than the average risk for BAME communities.
Identity
In 2015 research, University of Southampton
The University of Southampton (abbreviated as ''Soton'' in post-nominal letters) is a public university, public research university in Southampton, England. Southampton is a founding member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universit ...
fellow Dr Rosalind Willis explored the social fragility of the White Irish ethnicity, particularly in England where distinctions between White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the White population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population was 49 ...
and White Irish are, at times, openly denied.
In July 2019, the East Ham
East Ham is a district of the London Borough of Newham, England, 8 miles (12.8 km) east of Charing Cross. Within the boundaries of the Historic counties of England, historic county of Essex, East Ham is identified in the London Plan as a ...
constituency Labour branch was criticised for its election of a white Irish woman as the women’s officer for its Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic
A number of different systems of classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom exist. These schemata have been the subject of debate, including about the nature of ethnicity, how or whether it can be categorised, and the relationship betwe ...
(BAME) forum. The woman in question self-identified as being an ethnic minority and no objections within the branch were raised against her election. Branch secretary, Syed Taqi Shah commented that "if somebody self-declares s BAME and the Labour Party allows them to do so, they should be respected."
Police discrimination
In a 1995 study, sociologist Jock Young
Jock Young (4 March 1942 – 16 November 2013) was a British sociologist and an influential criminologist.
Biography
Jock Young was educated at the London School of Economics. His PhD was an ethnography of drug use in Notting Hill, West L ...
found that of 1000 randomly selected residents of Finsbury Park when were asked if they had been stopped by the police over the past year, the White Irish population was disproportionately large with 14.3%, in contrast to 12.8% of Black Caribbean and 5.8% of White British people. The researchers found the Police tactic of "lurking and larking", whereby constables would wait outside Irish pubs and clubs to make arrests to be to blame for the high statistics, which was labelled a form of "institutional racism".
Census
2001 Census
The 2001 UK census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
was the first which allowed British citizen
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality ...
s to identify an Irish ethnicity. In all previous British censuses, figures for the Irish community were based on Irish birthplace. The percentage claiming White Irish descent in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Th ...
was 1.2 per cent, with the highest concentration found in the London Borough of Brent
Brent () is a London boroughs, borough in north-west London, England. It is known for landmarks such as Wembley Stadium, the BAPS Shri Swaminarayan Mandir London, Swaminarayan Temple and the Kiln Theatre. It also contains the Brent Reservoir, W ...
, where they made up 6.9 per cent of the population, while the figure for Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
was 0.98 per cent. The Irish have been the largest source of immigrants to Britain for over 200 years and as many as six million people in the UK are estimated to have at least one Irish grandparent.[
]
2011 census
As of 2011, the highest concentration was in the London Borough of Brent where they made up 4.0 per cent of the population. This was followed by the Inner London boroughs of Islington
Islington ( ) is an inner-city area of north London, England, within the wider London Borough of Islington. It is a mainly residential district of Inner London, extending from Islington's #Islington High Street, High Street to Highbury Fields ...
, Hammersmith and Fulham
Hammersmith is a district of West London, England, southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, and identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London. ...
and Camden, and the Outer London boroughs of Ealing
Ealing () is a district in west London (sub-region), west London, England, west of Charing Cross in the London Borough of Ealing. It is the administrative centre of the borough and is identified as a major metropolitan centre in the London Pl ...
and Harrow
Harrow may refer to:
Places
* Harrow, Victoria, Australia
* Harrow, Ontario, Canada
* The Harrow, County Wexford, a village in Ireland
* London Borough of Harrow, England
* Harrow, London, a town in London
* Harrow (UK Parliament constituency)
* ...
(all above 3.0 per cent). The highest concentration outside London was the city of Manchester, at 2.4 per cent.
2021 census
The 2021 census (2022 in Ireland and Scotland) was the first time since detailed records have been available that the Irish-born population comprised less than 1% of the population of Great Britain, and the first time since 1841 that it was less than 10% of the population of Ireland.
Profile of Irish in England in 2021
The age profile of the Irish-born is shown below. The population is aging, with 63% aged over 50 (compared to 39% among those born in England). 50.4% of those born in the Republic of Ireland arrived before 1981. Since those born in Northern Ireland are counted as UK citizens, information on when they moved is not available.
Almost two thirds of Irish people under 50 in England are now full time students (ages 16-24) or working in professional, administrative, and management positions. This is in comparison to 49% of 16-24 year olds in full time education, and 43% of the population in professional, administrative and management positions in the English-born.
Similarly, a significantly higher percentage of Irish-born people hold a degree or equivalent, compared to England overall. Nearly 75% of 25-34 year olds and 66% of 35–44 year olds hold a degree, compared to 43–45% of English people. It is higher across all age groups under 75.
There are few significant differences between those born in Northern Ireland and those born in the Republic, among the Irish-born in England under 50. However those born in Northern Ireland and over 50 are more likely to have a degree and to be in a professional occupation.
Profile of Irish in Scotland in 2022
The 2022 Scottish census reports 59,343 residents (1.1% of the Scottish population) who were born in Ireland, of which 37,260 (2% of the population of Northern Ireland) were born in Northern Ireland and 22,083 born in the Republic of Ireland (0.4% of its population).
The age profile of the Irish-born in Scotland from the 2022 Census is shown below. Compared to the population in England, the Irish-born living in Scotland are much younger, with fewer than half over 50 and a median age in the mid-40s.
Similar to the Irish in England, the majority are either full time students (72% of 16-24 year olds) or in managerial, administrative and professional occupations (60% of those between 25 and 50). Irish-born are twice as likely to be in upper managerial, administrative and professional occupations as those born in Scotland.
Similarly, a significantly higher percentage of Irish-born people hold a degree or equivalent, compared to Scotland overall. More than 75% of 25-34 year olds and nearly 70% of 35–49 year olds hold a degree. Irish-born are twice as likely to have a degree than those born in Scotland
Britons of Irish ancestry
See: ''British people of Irish descent
Irish people in Great Britain or British Irish are immigrants from the island of Ireland living in Great Britain as well as their British-born descendants.
Irish migration to Great Britain has occurred from the earliest recorded history to t ...
''
See also
* Anglo-Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the State rel ...
* Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
* Ireland–United Kingdom relations
Ireland–United Kingdom relations are the international relations between the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. British rule in Ireland dates back to the Anglo-Norman invasion on behalf of the En ...
* Irish in Britain (charity)
* Irish military diaspora#Britain
* James II of England
James II and VII (14 October 1633 – 16 September 1701) was King of England and Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1 ...
* Lilliburlero
* St Giles in the Fields
St Giles in the Fields is the Anglican parish church of the St Giles district of London. The parish stands within the London Borough of Camden and forms part of the Diocese of London. The church, named for St Giles the Hermit, began as the c ...
Explanatory notes
# The article "More Britons applying for Irish passports" states that 6 million British nationals have either an Irish grandfather or grandmother and are thus able to apply for Irish citizenship.
Citations
General and cited references
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Gannon, Darragh. (2014) "The Rise of the Rainbow Chasers: Advanced Irish Political Nationalism in Britain, 1916–22." ''Éire-Ireland'' 49.3 (2014): 112-142
online
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* McBride, Terence. "Ribbonmen and radicals: the cultivation of Irishness and the promotion of active citizenship in mid-Victorian Glasgow." ''Irish Studies Review'' 23.1 (2015): 15-32.
* MacRaild, Donald. (2013) "‘No Irish Need Apply’: The Origins and Persistence of a Prejudice." ''Labour History Review'' 78.3 (2013): 269-299.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Reid, Colin W. (2016) "Citizens of Nowhere: longing, belonging and exile among Irish Protestant writers in Britain, c. 1830–1970." ''Irish Studies Review'' 24.3 (2016): 255-274.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
Conradh na Gaeilge i Londain
British Association for Irish Studies
*
The Archive of the Irish in Britain at London Metropolitan University
BBC News article 16 March, 2003: "City celebrates Irish influence"
One in four Britons claim Irish roots
One in four Britons claim Irish roots
Photo Gallery: Liverpool's streets broad and narrow
Statistics Online
*
Reassessing what we collect website – Irish London
History of Irish London with objects and images
Communities - Irish London - Central Criminal Court
* ttp://www.victorianweb.org/authors/dickens/bleakhouse/carter.html The Slum of All Fears: Dickens's Concern with Urban Poverty and Sanitation
{{Irish diaspora
+
+
+
+
Ireland–United Kingdom relations
 After the
After the  The term "London Irish" relates to people born in London of Irish descent. London has Great Britain's biggest Irish population and there was a particularly big community in the (affectionately known) "
The term "London Irish" relates to people born in London of Irish descent. London has Great Britain's biggest Irish population and there was a particularly big community in the (affectionately known) "