|
County Sligo
County Sligo ( , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Northern and Western Region and is part of the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in the county. Sligo County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The population of the county was 70,198 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. It is noted for Benbulben Mountain, one of Ireland's most distinctive natural landmarks. History The county was officially formed in 1585 by Sir Henry Sidney, Lord Deputy of Ireland, but did not come into effect until the chaos of the Nine Years' War (Ireland), Nine Years' War ended, in 1603. Its boundaries reflect the Ó Conchobhair Sligigh confederation of Lower Connacht () as it was at the time of the Elizabethan conquest. This confederation consisted of the tuatha, or territories, of Cairbre Drom Cliabh, Cairbre Drumcliabh, Tír Fhíacr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benbulben
Benbulbin (), sometimes Benbulben or Ben Bulben, is a steep-sided and flat-topped mountain in County Sligo, Ireland. It is part of the Dartry Mountains, in an area sometimes called "William Butler Yeats, Yeats Country". Benbulbin, high, formed as a nunatak during the Last Glacial Period, last Ice Age. Benbulbin is a protected site, designated as a County Geology Site, County Geological Site by Sligo County Council. Etymology "Benbulbin", "Benbulben" and "Ben Bulben" are all anglicisations of the Irish name "Binn Ghulbain". "Binn" means "peak" or "mountain"; "ghulbain" may mean beak or jaw, or may refer to Conall Gulban, a son of Niall of the Nine Hostages, who was associated with the mountain. Geology Formation Benbulbin was shaped during the ice age, when Ireland was under glaciers. Originally it was a large plateau. Glaciers moving from the northeast to southwest shaped it into its present distinct formation. Rock composition Benbulbin, and the Dartry Mountains as a whol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
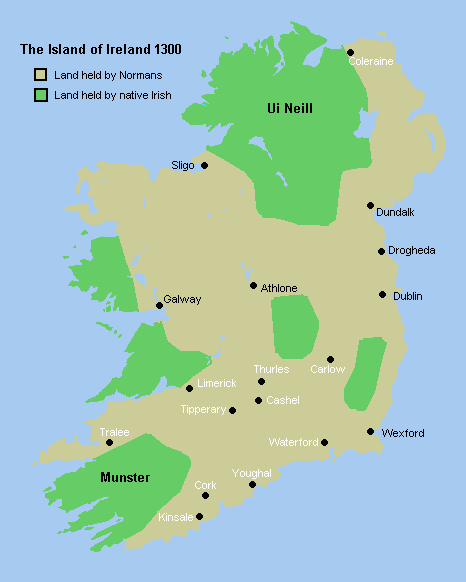
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Normans in Ireland, Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereign State
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may also refer to a constituent country, or a dependent territory. A sovereign state (polity), state is required to have a permanent population, defined territory, a government not under another, and the capacity to International relations, interact with other sovereign states. In actual practice, recognition or non-recognition by other states plays an important role in determining the status of a country. List of states with limited recognition, Unrecognized states often have difficulty engaging in Diplomacy, diplomatic relations with other sovereign states. History Since the end of the 19th century, almost the entire globe has been divided into sections (countries) with more or less defined borders assigned to different sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Deputy Of Ireland
The Lord Deputy was the representative of the monarch and head of the Irish executive (government), executive under English rule, during the Lordship of Ireland and then the Kingdom of Ireland. He deputised prior to 1523 for the Viceroy of Ireland. The plural form is ''Lords Deputy''. List of Lords Deputy Lordship of Ireland Kingdom of Ireland The title subsequently became Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, with the holder also known informally as the Viceroy. References Citations Bibliography * Further reading * Lordship of Ireland Heads of state of Ireland Early modern history of Ireland Long stubs with short prose {{Ireland-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Henry Sidney
Sir Henry Sidney (20 July 1529 – 5 May 1586) was an English soldier, politician and Lord Deputy of Ireland. Background He was the eldest son of Sir William Sidney of Penshurst (1482 – 11 February 1553) and Anne Pakenham (1511 – 22 October 1544). William Sidney prominent politician and courtier during the reigns of Henry VIII and Edward VI, from both of whom he received extensive grants of land, including the manor of Penshurst in Kent, which became the principal residence of the family. Henry Sidney was brought up at court as the companion of Prince Edward, afterwards King Edward VI, and he continued to enjoy the favour of the Crown, serving under Mary I of England and then, particularly, throughout the reign of Queen Elizabeth I. He was instrumental in the Elizabethan conquest of Ireland, serving as Lord Deputy three times. His career was controversial both at home and in Ireland. Career First trip to Ireland In 1556, Sidney served in Ireland with the Lord Deputy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truskmore
Truskmore () is a mountain with a height of on the border of County Sligo and County Leitrim in Ireland. It is the highest summit in the Dartry Mountains and the highest in Sligo. It is in the middle of a plateau whose edges are marked by high cliffs, including Benbulbin (526m), Benwiskin (514m), Slievemore (597m) and Kings Mountain (462m). The top of Truskmore lies in County Sligo, a short distance from the border with County Leitrim; however, the mountain itself is in both counties. Transmission site The Truskmore television transmitter opened on 1 February 1962, the second of the original five main Telefis Éireann transmitters to go on air after Kippure (December 1961). It used as antenna carrier a 135 metretall mast. Initially its transmissions were only in 405-line television system, 405 lines on VHF channel 11, with 625-lines transmissions beginning in November 1963 on Channel I. The new RTÉ Radio VHF FM radio service was added in 1966. The second television service c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eircode
A postal address in Ireland is a place of Delivery (commerce), delivery defined by Irish Standard (IS) EN 14142-1:2011 ("Postal services. Address databases") and serviced by the universal service provider, . Its addressing guides comply with the guidelines of the Universal Postal Union (UPU), the United Nations-affiliated body responsible for promoting standards in the postal industry, across the world. In Ireland, 35% of premises (over 600,000) have non-unique addresses due to an absence of house numbers or names. Before the introduction of a national postcode system (Eircode) in 2015, this required postal workers to remember which family names corresponded to which house in smaller towns, and many townlands. , An Post encourages customers to use Eircode because it ensures that their post person can pinpoint the exact location. Ireland was the last country in the OECD to create a postcode system. In July 2015 all 2.2 million residential and business addresses in Ireland r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In The Republic Of Ireland
Numbers on the Irish telephone numbering plan are regulated and assigned to operators by ComReg. Overview Telephone numbers in Ireland are part of an open numbering plan that allows variations in number length. The Irish format is similar to systems used in many parts of Europe, notably the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany, Belgium and France, where geographical numbers are organised using a logic of large regional prefixes, which are then further subdivided into smaller regions. It differs from UK numbering, which originated as alphanumeric codes based on town names. Irish Mobile and non–geographic numbers are fixed length and do not support local dialling. The trunk prefix 0 is used to access numbers outside the local area and for all mobile calls. This is followed by an area code, referred to as a National Dialling Code (NDC), the first digit of which indicates the geographical area or type of service (e.g. mobile). Calls made from mobile phones and some VoIP systems always ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Standard Time
Ireland uses Irish Standard Time (IST, UTC+01:00; ) in the summer months and Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC+00:00; ) in the winter period. Roughly two-thirds of the Republic is located west of the 7.5°W meridian. Thus the local mean time in most of Ireland is closer to UTC-01:00 time than to GMT. The Standard Time Act 1968 legally established that "the time for general purposes in the State (to be known as standard time) shall be one hour in advance of Greenwich mean time throughout the year". This act was amended by the Standard Time (Amendment) Act 1971, which legally established Greenwich Mean Time as a winter time period. Ireland therefore operates one hour behind its statutory standard time during the winter period, and reverts to standard time in the summer months. This definition contrasts with the practice of other states in the European Union, which operate one hour ahead of their standard time during the summer period, but produces the same result. The net effect is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Time
Western European Time (WET, UTC+00:00) is a time zone covering parts of western Europe and consists of countries using UTC+00:00 (also known as Greenwich Mean Time, abbreviated GMT). It is one of the three standard time zones in the European Union along with Central European Time and Eastern European Time. The following Western European countries and regions use UTC+00:00 in winter months: *Portugal, since 1912 with pauses (except Azores, UTC−01:00) *United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies, since 1847 in England, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, and since 1916 in Northern Ireland, with pauses *Ireland, since 1916, except between 1968 and 1971 *Canary Islands, since 1946 (rest of Spain is CET, UTC+01:00) *Faroe Islands, since 1908 * North Eastern Greenland ( Danmarkshavn and surrounding area) *Iceland, since 1968, without summer time changes All the above countries except Iceland implement daylight saving time in summer (from the last Sunday in March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern And Western Region
The Northern and Western Region has been a region within the Republic of Ireland since 1 January 2015. It is a NUTS Level II statistical region of Ireland (coded IE04). NUTS 2 Regions may be classified as ''less developed regions'', ''transition regions'', or ''more developed regions'' to determine eligibility for funding under the European Regional Development Fund The European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) is one of the European Structural and Investment Funds allocated by the European Union. Its purpose is to transfer money from richer regions (not countries), and invest it in the infrastructure and se ... and the European Social Fund Plus. In 2021, the Northern and Western Region was classified as a ''transition region''. The Northern and Western Regional Assembly is composed of members nominated from the local authorities in the region. It is one of three Regional Assemblies in Ireland established in 2015 following an amendment to the Local Government Act 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Ireland
Ireland uses the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) geocode standard for referencing country subdivisions for statistical purposes. The standard is developed and regulated by the European Union. The NUTS standard is instrumental in delivering European Structural and Investment Funds. The NUTS code for Ireland is ''IE'' and a hierarchy of three levels is established by Eurostat. A further level of geographic organisation, the local administrative unit (LAU), in Ireland is the local electoral area. Overview NUTS levels 1, 2 and 3 The most recent revision of NUTS regions was made in 2016 and took effect in 2018. The eligibility of regions for funding under the European Regional Development Fund and the European Social Fund Plus was revised in 2021. NUTS 2 Regions may be classified as less developed regions, transition regions, or more developed regions. Demographic statistics by NUTS 3 region Local administrative units The local administrative unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |