Brain tumor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the
 The brain is divided into lobes and each lobe or area has its own function. A tumour in any of these lobes may affect the area's performance. The symptoms experienced are often linked to the location of the tumour, but each person may experience something different.
*
The brain is divided into lobes and each lobe or area has its own function. A tumour in any of these lobes may affect the area's performance. The symptoms experienced are often linked to the location of the tumour, but each person may experience something different.
*
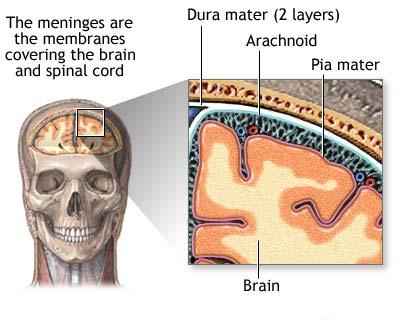 Human brains are surrounded by a system of
Human brains are surrounded by a system of
brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a mass. There are two main types of tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
(non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumor
A primary tumor is a tumor growing at the anatomical site where tumor progression began and proceeded to yield a cancerous mass. Most solid cancers develop at their primary site but may then go on to metastasize or spread to other parts of the b ...
s, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis
A brain metastasis is a cancer that has metastasis, metastasized (spread) to the brain from another location in the body and is therefore considered a brain tumor, secondary brain tumor. The metastasis typically shares a Cancer cell, cancer cell ...
tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s, problems with vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness
Unconsciousness is a state in which a living individual exhibits a complete, or near-complete, inability to maintain an awareness of self and environment or to respond to any human or environmental stimulus. Unconsciousness may occur as the r ...
.
The cause of most brain tumors is unknown, though up to 4% of brain cancers may be caused by CT scan radiation. Uncommon risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
s include exposure to vinyl chloride
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C =CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. It is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Vinyl chloride is a ...
, Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is one of the nine known Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human herpesvirus types in the Herpesviridae, herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in ...
, ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
, and inherited syndromes such as neurofibromatosis, tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combinatio ...
, and von Hippel-Lindau Disease. Studies on mobile phone exposure have not shown a clear risk. The most common types of primary tumors in adults are meningiomas (usually benign) and astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord, an ...
s such as glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
s. In children, the most common type is a malignant medulloblastoma. Diagnosis is usually by medical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
along with computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT) or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI). The result is then often confirmed by a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
. Based on the findings, the tumors are divided into different grades of severity.
Treatment may include some combination of surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
and chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
. If seizures occur, anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatme ...
medication may be needed. Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a fluorinated glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye su ...
and furosemide
Furosemide, sold under the brand name Lasix among others, is a loop diuretic medication used to treat edema due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. Furosemide may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can ...
are medications that may be used to decrease swelling around the tumor. Some tumors grow gradually, requiring only monitoring and possibly needing no further intervention. Treatments that use a person's immune system are being studied. Outcomes for malignant tumors vary considerably depending on the type of tumor and how far it has spread at diagnosis. Although benign tumors only grow in one area, they may still be life-threatening depending on their size and location. Malignant glioblastomas usually have very poor outcomes, while benign meningiomas usually have good outcomes. The average five-year survival rate for all (malignant) brain cancers in the United States is 33%.
Secondary, or metastatic, brain tumors are about four times as common as primary brain tumors, with about half of metastases coming from lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged ...
. Primary brain tumors occur in around 250,000 people a year globally, and make up less than 2% of cancers. In children younger than 15, brain tumors are second only to acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, ...
as the most common form of cancer. In New South Wales, Australia in 2005, the average lifetime economic cost of a case of brain cancer was AU$1.9 million, the greatest of any type of cancer.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of brain tumors are broad. People may experience symptoms regardless of whether the tumor is benign (not cancerous) or cancerous. Primary and secondary brain tumors present with similar symptoms, depending on the location, size, and rate of growth of the tumor. For example, larger tumors in the frontal lobe can cause changes in the ability to think. However, a smaller tumor in an area such asWernicke's area
Wernicke's area (; ), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech, the other being Broca's area. It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language, in contrast to ...
(small area responsible for language comprehension) can result in a greater loss of function.
Headaches
Headaches as a result of raisedintracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
can be an early symptom of brain cancer. However, isolated headache without other symptoms is rare, and other symptoms including visual abnormalities may occur before headaches become common. Certain warning signs for headache exist which make the headache more likely to be associated with brain cancer. These are defined as "abnormal neurological examination, headache worsened by Valsalva maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air, as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be ...
, headache causing awakening from sleep, new headache in the older population, progressively worsening headache, atypical headache features, or patients who do not fulfill the strict definition of migraine". Other associated signs are headaches that are worse in the morning or that subside after vomiting.
Location-specific symptoms
 The brain is divided into lobes and each lobe or area has its own function. A tumour in any of these lobes may affect the area's performance. The symptoms experienced are often linked to the location of the tumour, but each person may experience something different.
*
The brain is divided into lobes and each lobe or area has its own function. A tumour in any of these lobes may affect the area's performance. The symptoms experienced are often linked to the location of the tumour, but each person may experience something different.
* Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
: Tumours may contribute to poor reasoning, inappropriate social behavior, personality changes, poor planning, lower inhibition, and decreased production of speech (Broca's area
Broca's area, or the Broca area (, also , ), is a region in the frontal lobe of the dominant Cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere, usually the left, of the Human brain, brain with functions linked to speech production.
Language processing in the brai ...
).
* Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
: Tumours in this lobe may contribute to poor memory, loss of hearing, and difficulty in language comprehension (Wernicke's area
Wernicke's area (; ), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech, the other being Broca's area. It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language, in contrast to ...
is located in this lobe).
* Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integra ...
: Tumours here may result in poor interpretation of languages, difficulty with speaking, writing, drawing, naming, and recognizing, and poor spatial and visual perception.
* Occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
: Damage to this lobe may result in poor vision or loss of vision.
* Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
: Tumours in this area may cause poor balance, muscle movement, and posture.
* Brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
: Tumours on the brainstem can cause seizures, endocrine problems, respiratory changes, visual changes, headaches and partial paralysis.
* Leptomeninges: Tumours that spread to the leptomeninges, the lining of the brain, may cause cranial nerve palsies such as facial paralysis, abnormalities of eye movement, abnormalities of facial sensation or swallowing difficulty, depending on which cranial nerves are involved.
Behaviour changes
A person's personality may be altered due to the tumor-damaging lobes of the brain. Since the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes control inhibition, emotions, mood, judgement, reasoning, and behavior, a tumor in those regions can cause inappropriate social behavior, temper tantrums, laughing at things which merit no laughter, and even psychological symptoms such as depression and anxiety. More research is needed into the effectiveness and safety of medication for depression in people with brain tumors. Personality changes can have damaging effects such as unemployment, unstable relationships, and a lack of control.Cause
A known cause of brain cancers isionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
. Approximately 4% of brain cancers in the general population are caused by CT-scan radiation. For brain cancers that follow a CT scan at lags of 2 years or more, it has been estimated that 40% are attributable to CT-scan radiation. The risk of brain cancer is dose dependent, with the relative risk increasing by 0.8 for each 100 gray of ionizing radiation received. At this dose, approximately 6391 people would have to be exposed to cause 1 case of brain cancer. Ionizing radiation to the head as part of treatment for other cancers is also a risk factor for developing brain cancer.
Mutations and deletions of tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results ...
s, such as P53, are thought to be the cause of some forms of brain tumor. Inherited conditions, such as Von Hippel–Lindau disease, tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combinatio ...
, multiple endocrine neoplasia, and neurofibromatosis type 2 carry a high risk for the development of brain tumors. People with celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
have a slightly increased risk of developing brain tumors. Smoking may increase the risk, but evidence of this remains unclear.
Although studies have not shown any link between cell-phone or mobile-phone radiation and the occurrence of brain tumors, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
has classified mobile-phone radiation on the IARC scale into Group 2B – possibly carcinogenic.
The claim that cell-phone usage may cause brain cancer is likely based on epidemiological studies which observed a slight increase in glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
risk among heavy users of wireless phones. When those studies were conducted, GSM (2G) phones were in use. Modern, third-generation (3G) phones emit, on average, about 1% of the energy emitted by those GSM (2G) phones, and therefore the finding of an association between cell-phone usage and increased risk of brain cancer is not based upon current phone usage.
Pathophysiology
Meninges
 Human brains are surrounded by a system of
Human brains are surrounded by a system of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
membranes called meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
that separate the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
from the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. This three-layered covering is composed of (from the outside in) the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
subarachnoid space which contains
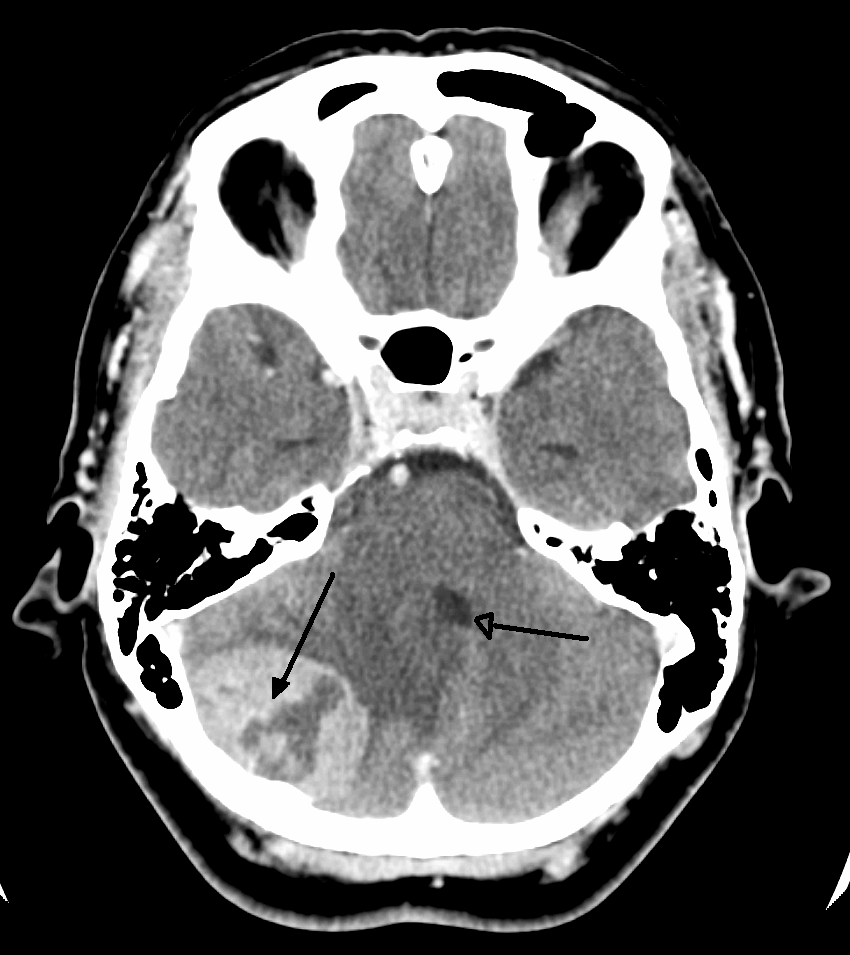 There are no specific signs or symptoms for brain cancer, but the presence of a combination of symptoms and the lack of alternative causes may indicate a brain tumor. A
There are no specific signs or symptoms for brain cancer, but the presence of a combination of symptoms and the lack of alternative causes may indicate a brain tumor. A

 Maximal safe surgical resection (to preserve as much neurological function as possible) and histologic examination of the tumor is also required to aid in the diagnosis. Cancer cells may have specific characteristics.
Atypia: an indication of abnormality of a cell (which may be indicative of malignancy). Significance of the abnormality is highly dependent on context.
Neoplasia: the (uncontrolled) division of cells that is characteristic of cancer.
Maximal safe surgical resection (to preserve as much neurological function as possible) and histologic examination of the tumor is also required to aid in the diagnosis. Cancer cells may have specific characteristics.
Atypia: an indication of abnormality of a cell (which may be indicative of malignancy). Significance of the abnormality is highly dependent on context.
Neoplasia: the (uncontrolled) division of cells that is characteristic of cancer.
 The most common primary brain tumors are:
*
The most common primary brain tumors are:
*
 Led by Prof. Nori Kasahara, researchers from
Led by Prof. Nori Kasahara, researchers from
Brain tumour information
from
Neuro-Oncology:
Cancer Management Guidelines
MR Scans of Primary Brain Lymphoma, etc. {{Authority control Disorders causing seizures Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Tumor localization
in
subarachnoid space which contains
cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
(CSF). This fluid circulates in the narrow spaces between cells and through the cavities in the brain called ventricles, to support and protect the brain tissue. Blood vessels
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the tissues of a body. They also take waste an ...
enter the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
through the perivascular space above the pia mater. The cells in the blood vessel walls are joined tightly, forming the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
which protects the brain from toxins that might enter through the blood.
Tumors of the meninges are meningiomas and are often benign. Though not technically a tumor of brain tissue, they are often considered brain tumors since they protrude into the space where the brain is, causing symptoms. Since they are usually slow-growing tumors, meningiomas can be quite large by the time symptoms appear.
Brain matter
The three largest divisions of the brain are thecerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
, cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
and the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
. These areas are composed of two broad classes of cells: neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
and glia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up ...
. These two cell types are equally numerous in the brain as a whole, although glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up ...
outnumber neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
roughly 4 to 1 in the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
. Glia come in several types, which perform a number of critical functions, including structural support, metabolic support, insulation, and guidance of development. Primary tumors of the glial cells are called glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
s and often are malignant by the time they are diagnosed.
The thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
and hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
are major divisions of the diencephalon
In the human brain, the diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as t ...
, with the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
and pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
attached at the bottom; tumors of the pituitary and pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
are often benign.
The brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
lies between the large cerebral cortex and the spinal cord. It is divided into the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
Diagnosis
 There are no specific signs or symptoms for brain cancer, but the presence of a combination of symptoms and the lack of alternative causes may indicate a brain tumor. A
There are no specific signs or symptoms for brain cancer, but the presence of a combination of symptoms and the lack of alternative causes may indicate a brain tumor. A medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
aids in the diagnosis. Clinical and laboratory investigations will serve to exclude infections as the cause of the symptoms.
Brain tumors, when compared to tumors in other areas of the body, pose a challenge for diagnosis. Commonly, radioactive tracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide (a radioactive atom). By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to ...
s are uptaken in large volumes in tumors due to the high activity of tumor cells, allowing for radioactive imaging of the tumor. However, most of the brain is separated from the blood by the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
(BBB), a membrane that exerts a strict control over what substances are allowed to pass into the brain. Therefore, many tracers that may reach tumors in other areas of the body easily would be unable to reach brain tumors until there was a disruption of the BBB by the tumor. Disruption of the BBB is well imaged via MRI or CT scan, and is therefore regarded as the main diagnostic indicator for malignant gliomas, meningiomas, and brain metastases.
Imaging

Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
plays a central role in the diagnosis of brain tumors. Early imaging methods – invasive and sometimes dangerous – such as pneumoencephalography
Pneumoencephalography (sometimes abbreviated PEG; also referred to as an "air study") was a common medical procedure in which most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was drained from around the brain by means of a lumbar puncture and replaced with ...
and cerebral angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfo ...
have been replaced by non-invasive, high-resolution techniques, especially magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) and computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT) scans. MRI with contrast enhancement is the preferred imaging test in the diagnosis of brain tumors. Glioblastomas usually enhance with contrast on T1 MRI weighted MRI imaging, and on T2 with FLAIR imaging showing hyperintense cerebral edema. Low grade gliomas are usually hypointense on T1 MRI, and hyperintense with T2 with FLAIR MRI. Meningiomas are usually homogenously enhanced with dural thickening on MRI.
Treatment with radiation can lead to treatment induced changes in the brain, including radiation necrosis (death of brain tissue due to radiation treatments) visible on brain imaging and which can be difficult to differentiate from tumor recurrence.
Different Types of MRI Scans
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) looks at the blood vessels in the brain. In the diagnosis of brain tumor, MRAs are typically carried out before surgery to help surgeons get a better understanding of the tumor vasculature. For example, a study was done where surgeons were able to separate benign brain tumors from malignant ones by analyzing the shapes of the blood vessels that were extracted from MRA. Although not required, some MRA may inject contrast agent, gadolinium, into the patient to get an enhanced image Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) measures the metabolic changes or chemical changes inside the tumor. The most common MRS is proton spectroscopy with its frequency measured in parts per million (ppm). Gliomas or malignant brain tumors have different spectra from normal brain tissue in that they have greater choline levels and lower N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) signals. Using MRS in brain tumor diagnosis can help doctors identify the type of tumor and its aggressiveness. For example, benign brain tumors or meningioma have increased alanine levels. It can also help to distinguish brain tumors from scar tissues or dead tissues caused by previous radiation treatment, which does not have increased choline levels that brain tumors have, and from tumor-mimicking lesions such as abscesses or infarcts. Perfusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging (pMRI) assess the blood volume and blood flow of different parts of the brain and brain tumors. pMRI requires the injection of contrast agent, usually gadopentetate dimeglumine (Gd-DTPA) into the veins in order to enhance the contrast. pMRI provides a cerebral blood volume map that shows the tumor vascularity and angiogenesis. Brain tumors would require a larger blood supply and thus, would show a high cerebral blood volume on the pMRI map. The vascular morphology and degree of angiogenesis from pMRI help to determine the grade and malignancy of brain tumors. For brain tumor diagnosis, pMRI is useful in determining the best site to perform biopsy and to help reduce sampling error. pMRI is also valuable for after treatment to determine if the abnormal area is a remaining tumor or a scar tissue. For patients that are undergoing anti-angiogenesis cancer therapy, pMRI can give the doctors a better sense of efficacy of the treatment by monitoring tumor cerebral blood volume. Functional MRI (fMRI) measures blood flow changes in active parts of the brain while the patient is performing tasks and provides specific locations of the brain that are responsible for certain functions. Before performing a brain tumor surgery on patients, neurosurgeons would use fMRI to avoid damage to structures of the brain that correspond with important brain functions while resecting the tumor at the same time. Preoperative fMRI is important because it is often difficult to distinguish the anatomy near the tumor as it distorts its surrounding regions. Neurosurgeons would use fMRI to plan whether to perform a resection where tumor is surgically removed as much as possible, a biopsy where they take a surgical sampling amount to provide a diagnosis, or to not undergo surgery at all. For example, a neurosurgeon may be opposed to resecting a tumor near the motor cortex as that would affect the patient's movements. Without preoperative fMRI, the neurosurgeon would have to perform an awake-craniotomy where the patient would have to interact during open surgery to see if tumor removal would affect important brain functions. Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) a form of MRI that measures random Brownian motion of water molecules along a magnetic field gradient. For brain tumor diagnosis, measurement of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in brain tumors allow doctors to categorize tumor type. Most brain tumors have higher ADC than normal brain tissues and doctors can match the observed ADC of the patient's brain tumor with a list of accepted ADC to identify tumor type. DWI is also useful for treatment and therapy purposes where changes in diffusion can be analyzed in response to drug, radiation, or gene therapy. Successful response results in apoptosis and increase in diffusion while failed treatment results in unchanged diffusion values.Other Types of Imaging Techniques
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan uses x-rays to take pictures from different angles and computer processing to combine the pictures into a 3D image. A CT scan usually serves as an alternative to MRI in cases where the patient cannot have an MRI due to claustrophobia or pacemaker. Compared to MRI, a CT scan shows a more detailed image of the bone structures near the tumor and can be used to measure the tumor's size. Like an MRI, a contrast dye may also be injected into the veins or ingested by mouth before a CT scan to better outline any tumors that may be present. CT scans use contrast materials that are iodine-based and barium sulfate compounds. The downside of using CT scans as opposed to MRI is that some brain tumors do not show up well on CT scans because some intra-axial masses are faint and resemble normal brain tissue. In some scenarios, brain tumors in CT scans may be mistaken for infarction, infection, and demyelination. To suspect that an intra-axial mass is a brain tumor instead of other possibilities, there must be unexplained calcifications in the brain, preservation of the cortex, and disproportionate mass effect. CT Angiography (CTA) provides information about the blood vessels in the brain using X-rays. A contrast agent is always required to be injected into the patient in the CT scanner. CTA serves as an alternative to MRA. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan uses radiolabelled substances, such as FDG which taken up by cells that are actively dividing. Tumor cells are more actively dividing so they would absorb more of the radioactive substance. After injection, a scanner would be used to create an image of the radioactive areas in the brain. PET scans are used more often for high-grade tumors than for low-grade tumors. It is useful after treatment to help doctors determine if the abnormal area on an MRI image is a remaining tumor or a scar tissue. Scar tissues will not show up on PET scans while tumors would.Pathology
 Maximal safe surgical resection (to preserve as much neurological function as possible) and histologic examination of the tumor is also required to aid in the diagnosis. Cancer cells may have specific characteristics.
Atypia: an indication of abnormality of a cell (which may be indicative of malignancy). Significance of the abnormality is highly dependent on context.
Neoplasia: the (uncontrolled) division of cells that is characteristic of cancer.
Maximal safe surgical resection (to preserve as much neurological function as possible) and histologic examination of the tumor is also required to aid in the diagnosis. Cancer cells may have specific characteristics.
Atypia: an indication of abnormality of a cell (which may be indicative of malignancy). Significance of the abnormality is highly dependent on context.
Neoplasia: the (uncontrolled) division of cells that is characteristic of cancer.
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
: the (premature) death of cells, caused by external factors such as infection, toxin or trauma. Necrotic cells send the wrong chemical signals which prevent phagocyte
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ...
s from disposing of the dead cells, leading to a buildup of dead tissue, cell debris and toxins at or near the site of the necrotic cells
Local hypoxia, or the deprivation of adequate oxygen supply to certain areas of the brain, including within the tumor, as the tumor grows and recruits local blood vessels.
Classification
Tumors can bebenign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
or malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
, can occur in different parts of the brain, and may be classified as primary or secondary. A primary tumor is one that has started in the brain, as opposed to a metastatic tumor, which is one that has spread to the brain from another area of the body. The incidence of metastatic tumors is approximately four times greater than primary tumors. Tumors may or may not be symptomatic: some tumors are discovered because the patient has symptoms, others show up incidentally on an imaging scan, or at an autopsy.
Grading of the tumors of the central nervous system commonly occurs on a 4-point scale (I-IV) created by the World Health Organization in 1993. Grade I tumors are the least severe and commonly associated with long-term survival, with severity and prognosis worsening as the grade increases. Low-grade tumors are often benign, while higher grades are aggressively malignant and/or metastatic. Other grading scales do exist, many based upon the same criteria as the WHO scale and graded from I-IV.
Primary
 The most common primary brain tumors are:
*
The most common primary brain tumors are:
* Gliomas
A glioma is a type of primary tumor, primary Neoplasm, tumor that starts in the glial cells of the Human brain, brain or spinal cord. They are Malignancy, malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain ...
(50.4%)
* Meningiomas (20.8%)
* Pituitary adenomas (15%)
* Nerve sheath tumors (10%)
These common tumors can also be organized according to tissue of origin as shown below:
Secondary
Secondary tumors of the brain are metastatic and have spread to the brain fromcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s originating in another organ. Metastatic spread is usually by the blood. The most common types of cancers that spread to the brain are lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged ...
(accounting for over half of all cases), breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
, melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
skin cancer, kidney cancer and colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
.
=By behavior
= Brain tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). However, the definitions of malignant or benign neoplasms differ from those commonly used in other types of cancerous or non-cancerous neoplasms in the body. In cancers elsewhere in the body, three malignant properties differentiate benign tumors from malignant forms of cancer: benign tumors are self-limited and do not invade or metastasize. Characteristics of malignant tumors include: * uncontrolled mitosis (growth by division beyond the normal limits) *anaplasia
Anaplasia () is a condition of cell (biology), cells with poor cellular differentiation, losing the morphology (biology), morphological characteristics of mature cells and their orientation with respect to each other and to endothelium, endotheli ...
: the cells in the neoplasm have an obviously different form (in size and shape). Anaplastic cells display marked pleomorphism. The cell nuclei are characteristically extremely hyperchromatic (darkly stained) and enlarged; the nucleus might have the same size as the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
of the cell (nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio may approach 1:1, instead of the normal 1:4 or 1:6 ratio). Giant cells – considerably larger than their neighbors – may form and possess either one enormous nucleus or several nuclei (syncytia
A syncytium (; : syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus), ...
). Anaplastic nuclei are variable and bizarre in size and shape.
* invasion or infiltration:
** Invasion or invasiveness is the spatial expansion of the tumor through uncontrolled mitosis, in the sense that the neoplasm invades the space occupied by adjacent tissue, thereby pushing the other tissue aside and eventually compressing the tissue. Often these tumors are associated with clearly outlined tumors in imaging.
** Infiltration is the behavior of the tumor either to grow (microscopic) tentacles that push into the surrounding tissue (often making the outline of the tumor undefined or diffuse) or to have tumor cells "seeded" into the tissue beyond the circumference of the tumorous mass.
* metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
(spread to other locations in the body via lymph or blood).
By genetics
In 2016, the WHO restructured their classifications of some categories ofglioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
s to include distinct genetic mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
that have been useful in differentiating tumor types, prognoses, and treatment responses. Genetic mutations are typically detected via immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Alber ...
, a technique that visualizes the presence or absence of a targeted protein via staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic ...
.
* Mutations in IDH1 and IDH2 genes are commonly found in low-grade gliomas
* Loss of both IDH genes combined with loss of chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
arms 1p and 19q indicates the tumor is an oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a oligodendrocyte progenitor cell, glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults (9.4% of all primary brain and central ne ...
* Loss of TP53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
and ATRX characterizes astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord, an ...
s
* Genes EGFR, TERT, and PTEN, are commonly altered in gliomas and are useful in differentiating tumor grade and biology
Specific types
Anaplastic astrocytoma, Anaplastic oligodendroglioma,Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord, an ...
, Central neurocytoma, Choroid plexus carcinoma, Choroid plexus papilloma, Choroid plexus tumor, Colloid cyst
A colloid cyst is a non-malignant tumor in the brain. It consists of a gelatinous material contained within a membrane of epithelial tissue. It is almost always found just posterior to the foramen of Monro in the anterior aspect of the third v ...
, Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour, Ependymal tumor, Fibrillary astrocytoma, Giant-cell glioblastoma, Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
, Gliomatosis cerebri, Gliosarcoma, Hemangiopericytoma, Medulloblastoma, Medulloepithelioma, Meningeal carcinomatosis, Neuroblastoma, Neurocytoma, Oligoastrocytoma, Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a oligodendrocyte progenitor cell, glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults (9.4% of all primary brain and central ne ...
, Optic nerve sheath meningioma, Pediatric ependymoma, Pilocytic astrocytoma, Pinealoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the pineal gland. A pineoblastoma is a supratentorial midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Pineoblastoma can present at any age, but is most common in young children. They account for 0.001% of all prima ...
, Pineocytoma, Pleomorphic anaplastic neuroblastoma, Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, Primary central nervous system lymphoma, Sphenoid wing meningioma, Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, Subependymoma
A subependymoma is a type of brain tumor; specifically, it is a rare form of ependymal tumor. They are usually in middle aged people. Earlier, they were called subependymal astrocytomas.
The prognosis for a subependymoma is better than for most ...
, Trilateral retinoblastoma.
Treatment
A medical team generally assesses the treatment options and presents them to the person affected and their family. Various types of treatment are available depending on tumor type and location, and may be combined to produce the best chances of survival: * Surgery: complete or partial resection of the tumor with the objective of removing as many tumor cells as possible. * Radiotherapy: the most commonly used treatment for brain tumors; the tumor is irradiated with beta, x rays or gamma rays. * Chemotherapy: a treatment option for cancer, however, it is not always used to treat brain tumors as the blood–brain barrier can prevent some drugs from reaching the cancerous cells. * A variety of experimental therapies are available through clinical trials. Survival rates in primary brain tumors depend on the type of tumor, age, functional status of the patient, the extent of surgical removal and other factors specific to each case. Standard care for anaplastic oligodendrogliomas and anaplastic oligoastrocytomas is surgery followed by radiotherapy. One study found a survival benefit for the addition of chemotherapy to radiotherapy after surgery, compared with radiotherapy alone.Surgery
Surgical resection of the greatest extent of contrast enhancing tumor possible (gross total resection) is associated with increased overall and progression free survival in those with glioblastoma. Gross total resection is often required in other brain tumors. Minimally invasive techniques are becoming the dominant trend in neurosurgical oncology. The main objective of surgery is to remove as many tumor cells as possible, with complete removal being the best outcome and cytoreduction ("debulking") of the tumor may otherwise be done. Due to the infiltrative nature of glioblastomas, total resection is usually unachievable and progression after surgery usually occurs, with progression occurring about 7 months after surgery. Many meningiomas, with the exception of some tumors located at the skull base, can be successfully removed surgically. Most pituitary adenomas can be removed surgically, often using a minimally invasive approach through thenasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
and skull base (trans-nasal, trans-sphenoidal approach). Large pituitary adenomas require a craniotomy
A craniotomy is a surgery, surgical operation in which a bone flap is temporarily removed from the Human skull, skull to access the Human brain, brain. Craniotomies are often critical operations, performed on patients who are suffering from brain ...
(opening of the skull) for their removal. Radiotherapy, including stereotactic
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, ...
approaches, is reserved for inoperable cases.
Postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy are integral parts of the therapeutic standard for malignant tumors.
Multiple metastatic tumors are generally treated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy rather than surgery and the prognosis in such cases is determined by the primary tumor, and is generally poor.
Radiation therapy
The goal of radiation therapy is to kill tumor cells while leaving normal brain tissue unharmed. In standard external beam radiation therapy, multiple treatments of standard-dose "fractions" of radiation are applied to the brain. This process is repeated for a total of 10 to 30 treatments, depending on the type of tumor. This additional treatment provides some patients with improved outcomes and longer survival rates.Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually us ...
is a treatment method that uses computerized calculations to focus radiation at the site of the tumor while minimizing the radiation dose to the surrounding brain. Radiosurgery may be an adjunct to other treatments, or it may represent the primary treatment technique for some tumors. Forms used include stereotactic
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, ...
radiosurgery, such as Gamma knife, Cyberknife or Novalis Tx radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually us ...
.
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
is the most common treatment for secondary brain tumors. The amount of radiotherapy depends on the size of the area of the brain affected by cancer. Conventional external beam "whole-brain radiotherapy treatment" (WBRT) or "whole-brain irradiation" may be suggested if there is a risk that other secondary tumors will develop in the future. Stereotactic radiotherapy is usually recommended in cases involving fewer than three small secondary brain tumors. Radiotherapy may be used following, or in some cases in place of, resection of the tumor. Forms of radiotherapy used for brain cancer include external beam radiation therapy, the most common, and brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation, radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. The word "brachytherapy" comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word , meaning "short-distance" or "s ...
and proton therapy
In medicine, proton therapy, or proton radiotherapy, is a type of particle therapy that uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often to treat cancer. The chief advantage of proton therapy over other types of external beam ...
, the last especially used for children.
People who receive stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for the treatment of metastatic brain tumors have more than twice the risk of developing learning and memory problems than those treated with SRS alone. Results of a 2021 systematic review found that when using SRS as the initial treatment, survival or death related to brain metastasis was not greater than alone versus SRS with WBRT.
Postoperative conventional daily radiotherapy improves survival for adults with good functional well-being and high grade glioma compared to no postoperative radiotherapy. Hypofractionated radiation therapy has similar efficacy for survival as compared to conventional radiotherapy, particularly for individuals aged 60 and older with glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
.
Chemotherapy
Patients undergoingchemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
are administered drugs designed to kill tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
cells. Although chemotherapy may improve overall survival in patients with the most malignant primary brain tumors, it does so in only about 20 percent of patients. Chemotherapy is often used in young children instead of radiation, as radiation may have negative effects on the developing brain. The decision to prescribe this treatment is based on a patient's overall health, type of tumor, and extent of cancer. The toxicity and many side effects of the drugs, and the uncertain outcome of chemotherapy in brain tumors puts this treatment further down the line of treatment options with surgery and radiation therapy preferred.
UCLA Neuro-Oncology publishes real-time survival data for patients with a diagnosis of glioblastoma. They are the only institution in the United States that displays how brain tumor patients are performing on current therapies. They also show a listing of chemotherapy agents used to treat high-grade glioma tumors.
Genetic mutations have significant effects on the effectiveness of chemotherapy. Gliomas with IDH1 or IDH2 mutations respond better to chemotherapy than those without the mutation. Loss of chromosome arms 1p and 19q also indicate better response to chemoradiation.
Other
A shunt may be used to relieve symptoms caused byintracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
, by reducing the build-up of fluid (hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with n ...
) caused by the blockage of the free flow of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
.
For those with brain tumors, anti-seizure prophylactic (preventative) medications are not usually recommended. However, anti-epileptics are used in those with seizures.
Cerebral edema secondary to brain tumors is managed by corticosteroids. Dexamethasone is the preferred corticosteroid due to its long half life and reduced effect on water retention (mineralcorticoid activity). Bevacizumab (an anti-VEGFA antibody) may improve cerebral edema in those that are unresponsive to steroids.
Prognosis
The prognosis of brain cancer depends on the type of cancer diagnosed. Medulloblastoma has a good prognosis with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical resection while glioblastoma has a median survival of only 15 months even with aggressive chemoradiotherapy and surgery. Brainstem gliomas have the poorest prognosis of any form of brain cancer, with most patients dying within one year, even with therapy that typically consists of radiation to the tumor along withcorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s. However, one type, focal brainstem gliomas in children, seems open to exceptional prognosis and long-term survival has frequently been reported.
Prognosis is also affected by presentation of genetic mutations. Certain mutations provide better prognosis than others. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
s, as well as deletion of chromosome arms 1p and 19q, generally indicate better prognosis. TP53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
, ATRX, EGFR, PTEN, and TERT mutations are also useful in determining prognosis.
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
is the most aggressive ( grade 4) and most common form of a malignant primary brain tumor. Even when aggressive multimodality therapy consisting of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgical excision is used, median survival is only 15–18 months. Standard therapy for glioblastoma consists of maximal surgical resection of the tumor, followed by radiotherapy between two and four weeks after the surgical procedure
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
to remove the cancer, then by chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, such as temozolomide. Most patients with glioblastoma take a corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
, typically dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a fluorinated glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye su ...
, during their illness to relieve symptoms. Experimental treatments include targeted therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy (oncology), hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medici ...
, gamma knife radiosurgery, boron neutron capture therapy, gene therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
The first attempt at modifying human DNA ...
, and chemowafer implants.
Oligodendrogliomas
Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a oligodendrocyte progenitor cell, glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults (9.4% of all primary brain and central ne ...
s are incurable but slowly progressive malignant brain tumors. They can be treated with surgical resection, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
or a combination. For some suspected low-grade (grade II) tumors, only a course of watchful waiting and symptomatic therapy is opted for. These tumors show co-deletions of the p and q arms of chromosome 1 and chromosome 19
Chromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 61.7 million base pairs, the building material of DNA. It is considered the most Gene density, gene-ri ...
respectively (1p19q co-deletion) and have been found to be especially chemosensitive with one report claiming them to be one of the most chemosensitive tumors. A median survival of up to 16.7 years has been reported for grade II oligodendrogliomas.
Acoustic neuroma
Acoustic neuromas are non-cancerous tumors. They can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy, or observation. Early intervention with surgery or radiation is recommended to prevent progressive hearing loss.Epidemiology
The incidence of brain tumors is higher in developed countries. This could be explained by undiagnosed tumor-related deaths in resource limited or lower income countries or by early deaths caused by other poverty-related causes that preempt a patient's life before tumors develop. The incidence of CNS tumors in the United States, Israel, and the Nordic countries is relatively high, while Japan and Asian countries have a lower incidence.United States
In the United States in 2015, approximately 166,039 people were living with brain or other central nervous system tumors. Over 2018, it was projected that there would be 23,880 new cases of brain tumors and 16,830 deaths in 2018 as a result, accounting for 1.4 percent of all cancers and 2.8 percent of all cancer deaths. Median age of diagnosis was 58 years old, while median age of death was 65. Diagnosis was slightly more common in males, at approximately 7.5 cases per 100 000 people, while females saw 2 fewer at 5.4. Deaths as a result of brain cancer were 5.3 per 100 000 for males, and 3.6 per 100 000 for females, making brain cancer the 10th leading cause of cancer death in the United States. Overall lifetime risk of developing brain cancer is approximated at 0.6 percent for men and women.UK
Brain, other CNS or intracranial tumors are the ninth most common cancer in the UK (around 10,600 people were diagnosed in 2013), and it is the eighth most common cause of cancer death (around 5,200 people died in 2012). White British patients with brain tumour are 30% more likely to die within a year of diagnosis than patients from other ethnicities. The reason for this is unknown.Children
In the United States more than 28,000 people under 20 are estimated to have a brain tumor. About 3,720 new cases of brain tumors are expected to be diagnosed in those under 15 in 2019. Higher rates were reported in 1985–1994 than in 1975–1983. There is some debate as to the reasons; one theory is that the trend is the result of improved diagnosis and reporting, since the jump occurred at the same time that MRIs became available widely, and there was no coincident jump in mortality. Central nervous system tumors make up 20–25 percent of cancers in children. The average survival rate for all primary brain cancers in children is 74%. Brain cancers are the most common cancer in children under 19, are result in more death in this group thanleukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
. Younger people do less well.
The most common brain tumor types in children (0–14) are: pilocytic astrocytoma, malignant glioma, medulloblastoma, neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors, and ependymoma.
In children under 2, about 70% of brain tumors are medulloblastomas, ependymomas, and low-grade glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
s. Less commonly, and seen usually in infants, are teratoma
A teratoma is a neoplasia, tumor made up of several types of biological tissue, tissue, such as hair, muscle, Human tooth, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the tailbone (where it is known as a sacrococcygeal teratoma), ovary, or test ...
s and atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors. Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from primordial germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cell tumors typically originate from the gonads (ovary and testis), but can arise in other areas of the body. Extragon ...
s, including teratomas, make up just 3% of pediatric primary brain tumors, but the worldwide incidence varies significantly.
In the UK, 429 children aged 14 and under are diagnosed with a brain tumour on average each year, and 563 children and young people under the age of 19 are diagnosed.
Research
Immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the basic research, fundamental research of cancer im ...
is being actively studied. For malignant gliomas no therapy has been shown to improve life expectancy as of 2015.
Vesicular stomatitis virus
In 2000, researchers used the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) to infect and kill cancer cells without affecting healthy cells.Retroviral replicating vectors
USC USC may refer to:
Education
United States
* Universidad del Sagrado Corazón, Santurce, Puerto Rico
* University of South Carolina, Columbia, South Carolina
** University of South Carolina System, a state university system of South Carolina
* ...
, who are now at UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...
, reported in 2001 the first successful example of applying the use of retroviral replicating vectors towards transducing cell lines derived from solid tumors. Building on this initial work, the researchers applied the technology to ''in vivo'' models of cancer and in 2005 reported a long-term survival benefit in an experimental brain tumor animal model. Subsequently, in preparation for human clinical trials, this technology was further developed by Tocagen (a pharmaceutical company primarily focused on brain cancer treatments) as a combination treatment ( Toca 511 & Toca FC). This has been under investigation since 2010 in a Phase I/II clinical trial for the potential treatment of recurrent high-grade glioma including glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. No results have yet been published.
Non-invasive detection
Efforts to detect and monitor development and treatment response of brain tumors by liquid biopsy from blood, cerebrospinal fluid or urine, are in the early stages of development.See also
*Brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
* Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
* Nervous system neoplasm
* List of brain tumor cases
References
External links
Brain tumour information
from
Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK (CRUK) is the world's largest independent cancer research organisation. It is registered as a charity in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man, and was formed on 4 February 2002 by the merger of The Cancer Research Campaign and t ...
Neuro-Oncology:
Cancer Management Guidelines
MR Scans of Primary Brain Lymphoma, etc. {{Authority control Disorders causing seizures Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Tumor localization