|
Meningeal Carcinomatosis
Leptomeningeal cancer is a rare complication of cancer in which the disease spreads from the original tumor site to the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This leads to an inflammatory response, hence the alternative names neoplastic meningitis (NM), malignant meningitis, or carcinomatous meningitis. The term leptomeningeal (from the Greek ''lepto'', meaning 'fine' or 'slight') describes the thin meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater, between which the cerebrospinal fluid is located. The disorder was originally reported by Eberth in 1870. It is also known as leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, leptomeningeal disease (LMD), leptomeningeal metastasis, meningeal metastasis and meningeal carcinomatosis. It occurs with cancers that are most likely to spread to the central nervous system. The most common cancers to include the leptomeninges are breast cancer, lung cancer, and melanomas because they can metastasize to the subarachnoid space in the brain which offers a hospita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complication (medicine)
A complication in medicine, or medical complication, is an unfavorable result of a disease, health condition, or therapy, treatment. Complications may adversely affect the prognosis, or outcome, of a disease. Complications generally involve a worsening in the severity of the disease or the development of new signs, symptoms, or pathology, pathological changes that may become widespread throughout the body and affect other organ systems. Thus, complications may lead to the development of new diseases resulting from previously existing diseases. Complications may also arise as a result of various treatments. The development of complications depends on a number of factors, including the degree of vulnerability, susceptibility, senescence, age, health status, and immune system condition. Knowledge of the most common and severe complications of a disease, procedure, or treatment allows for prevention and preparation for treatment if they should occur. Complications are not to be confus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatome (anatomy)
A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibres from the dorsal root of any given spinal nerve. There are 8 cervical nerves (C1 being an exception with no dermatome), 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and 5 sacral nerves. Each of these nerves relays sensation (including pain) from a particular region of skin to the brain. The term is also used to refer to a part of an embryonic somite. Along the thorax and abdomen, the dermatomes are like a stack of discs forming a human, each supplied by a different spinal nerve. Along the arms and the legs, the pattern is different: the dermatomes run longitudinally along the limbs. Although the general pattern is similar in all people, the precise areas of innervation are as unique to an individual as fingerprints. An area of skin innervated by a single nerve is called a peripheral nerve field. The word ''dermatome'' is formed from Ancient Greek 'skin, hide' and 'cut'. Clinical significance A derma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracranial
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull is also known as the cranium. The cranial cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in humans includes the skull cap and forms the protective case around the brain. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. The meninges are three protective membranes that surround the brain to minimize damage to the brain in the case of head trauma. Meningitis is the inflammation of meninges caused by bacterial or viral infections. Structure The capacity of an adult human cranial cavity is 1,200–1,700 cm3. The spaces between meninges and the brain are filled with a clear cerebrospinal fluid, increasing the protection of the brain. Facial bones of the skull are not included in the cranial cavity. There are only eight cranial bones: The occipital, sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid, two parietal, and two temporal bones are fused to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
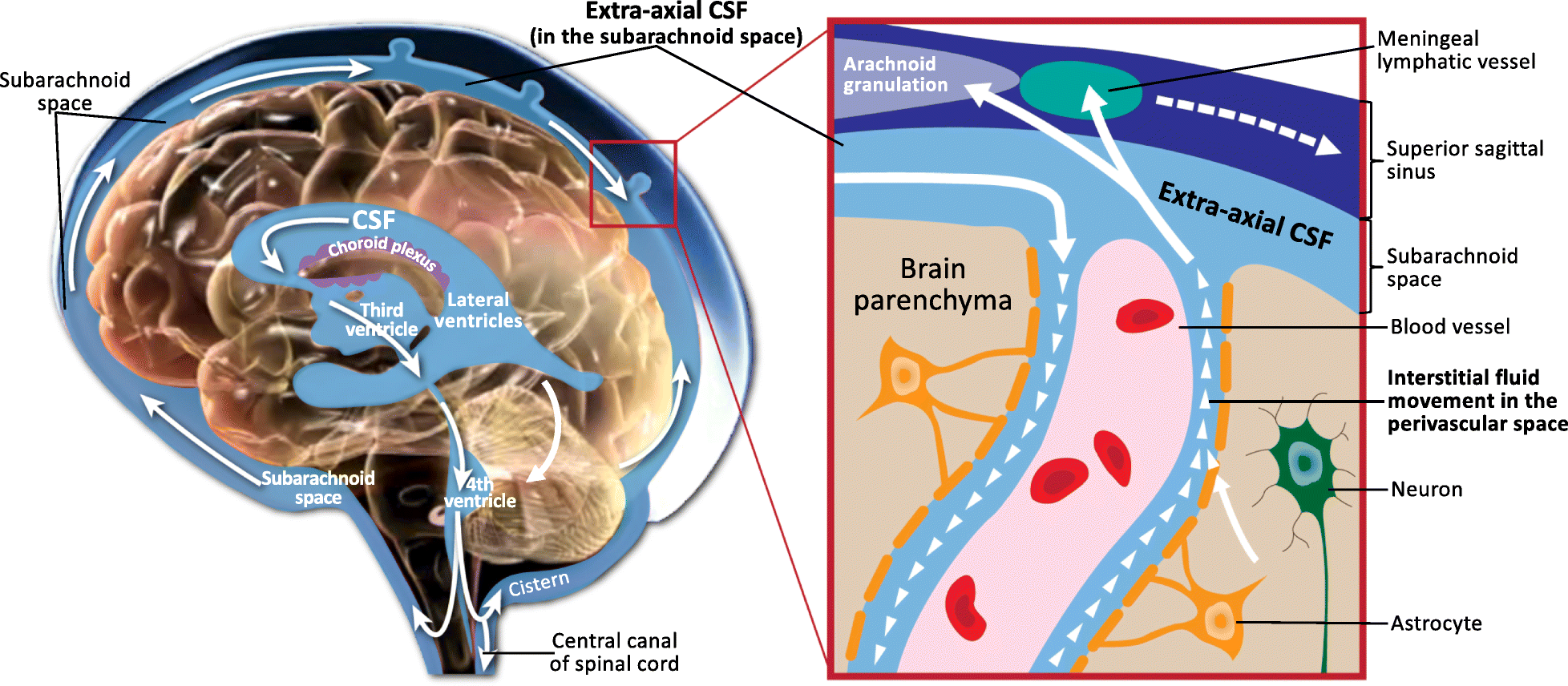
Virchow-Robin Space
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immunological function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space. In the brain, ''perivascular cuffs'' are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with viral encephalitis. Perivascular spaces vary in dimension according to the type of blood vessel. In the brain where most capillaries have an imperceptible perivascular space, select structures of the brain, such as the circumventricular organs, are notable for having large perivascular spaces surrounding highly permeable capillaries, as observed by microscopy. The median eminence, a brain structure at the base of the hypothalamus, contains capillar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as visual perception, vision, hearing, and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing that information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective segmentation (biology), body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a brain vesicle, vesicular enlargement at the rostral (anatomical term), rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Confusion
Delirium (formerly acute confusional state, an ambiguous term that is now discouraged) is a specific state of acute confusion attributable to the direct physiological consequence of a medical condition, effects of a psychoactive substance, or multiple causes, which usually develops over the course of hours to days. As a syndrome, delirium presents with disturbances in attention, awareness, and higher-order cognition. People with delirium may experience other neuropsychiatric disturbances including changes in psychomotor activity (e.g., hyperactive, hypoactive, or mixed level of activity), disrupted sleep-wake cycle, emotional disturbances, disturbances of consciousness, or altered state of consciousness, as well as perceptual disturbances (e.g., hallucinations and delusions), although these features are not required for diagnosis. Diagnostically, delirium encompasses both the syndrome of acute confusion and its underlying organic process known as an acute encephalopathy. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibulocochlear
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea. Structure The vestibulocochlear nerve consists mostly of bipolar neurons and splits into two large divisions: the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve. Cranial nerve 8, the vestibulocochlear nerve, goes to the middle portion of the brainstem called the pons (which then is largely composed of fibers going to the cerebellum). The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons and medulla oblongata (the lower portion of the brainstem). This junction between the pons, medulla, and cerebellum that contains the 8th nerve is called the cerebellopontine angle. The vestibulocochlear nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear, sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures), or the vestibulocochlear nerve (Cranial nerves, cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for about 90% of reported hearing loss. SNHL is usually permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total. Various other descriptors can be used depending on the shape of the audiogram, such as high frequency, low frequency, U-shaped, notched, peaked, or flat. ''Sensory'' hearing loss often occurs as a consequence of damaged or deficient cochlear hair cells. Hair cells may be abnormal at birth or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, including Ear infection, infection, and Ototoxicity, ototoxic drugs, as well as intrinsic causes, including genetic mutations. A common cause or exacerbating factor in SNHL is prolonged exposure to environmental noise, or noise-induced hearing loss. Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Cerebellar Ataxia Of Childhood
Acute cerebellar ataxia of childhood is a childhood condition characterized by an unsteady gait, most likely secondary to an autoimmune response to infection, drug induced or paraneoplastic. The most common viruses causing acute cerebellar ataxia are chickenpox virus and Epstein–Barr virus, leading to a childhood form of post viral cerebellar ataxia. It is a diagnosis of exclusion. Signs and symptoms Acute cerebellar ataxia usually follows 2–3 weeks after an infection. Onset is abrupt. Vomiting may be present at the onset but fever and nuchal rigidity characteristically are absent. Horizontal nystagmus is present in approximately 50% of cases. * Truncal ataxia with deterioration of gait * Slurred speech and nystagmus * Afebrile Cause Possible causes of acute cerebellar ataxia include varicella infection, as well as infection with influenza, Epstein–Barr virus, Coxsackie virus, Echo virus or mycoplasma. Diagnosis Acute Cerebellar ataxia is a diagnosis of exclusion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiparesis
Hemiparesis, also called unilateral paresis, is the weakness of one entire side of the body (''wikt:hemi-#Prefix, hemi-'' means "half"). Hemiplegia, in its most severe form, is the complete paralysis of one entire side of the body. Either hemiparesis or hemiplegia can result from a variety of medical causes, including congenital conditions, trauma, tumors, traumatic brain injury and stroke.Detailed article about hemiparesis at Disabled-World.com Signs and symptoms Different types of hemiparesis can impair different bodily functions. Some effects, such as weakness or partial paralysis of a limb on the affected side, are generally always to be expected. Other impairments can appear, upon external examination, to be unrelated to the limb weakness, but are nevertheless also cau ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of Visual perception, vision, taste, Olfaction, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the Atlas (anatomy), first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including the non-paired cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |