|
Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air, as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be used either in medicine, medical examination as a test of cardiac function and autonomic nervous system, autonomic nervous control of the heart (because the maneuver raises the pressure in the lungs), or to clear the ears and paranasal sinuses, sinuses (that is, to equalize pressure between them) when ambient pressure changes, as in scuba diving, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or air travel. A modified version is done by expiring against a closed glottis. This will elicit the cardiovascular responses described below but will not force air into the Eustachian tubes. History The technique is named after Antonio Maria Valsalva, a 17th-century physician and anatomist from Bologna whose principal scientific interest was the human ear. He descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otoscope
An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device used by healthcare professionals to examine the ear canal and eardrum. This may be done as part of routine Physical examination, physical examinations, or for evaluating specific ear complaints, such as earaches, sense of fullness in the ear, or hearing loss. Usage Function An otoscope enables viewing and examination of the ear canal and tympanic membrane (eardrum). Otoscopic examination can help diagnose conditions such as acute otitis media (infection of the middle ear), traumatic Perforated eardrum, perforation of the eardrum, and cholesteatoma. The presence of cerumen (earwax), shed skin, pus, canal skin edema, Foreign body, foreign bodies, and various ear diseases, can obscure the view of the eardrum and thus compromise the value of otoscopy done with a common otoscope, but can confirm the presence of obstructing symptoms. Otoscopes can also be used to examine patients' noses (avoiding the need for a separate Specu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by a single Ventricle (heart), ventricle of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula: :CO = HR \times SV Values for cardiac output are usually denoted as L/min. For a healthy individual weighing 70 kg, the cardiac output at rest averages about 5 L/min; assuming a heart rate of 70 beats/min, the stroke volume would be approximately 70 mL. Because cardiac output is related to the quantity of blood delivered to various parts of the body, it is an important com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Tympani Muscle
The tensor tympani is a muscle within the middle ear, located in the bony canal above the bony part of the auditory tube, and connects to the malleus bone. Its role is to dampen loud sounds, such as those produced from chewing, shouting, or thunder. Because its reaction time is not fast enough, the muscle cannot protect against hearing damage caused by sudden loud sounds, like explosions or gunshots, however some individuals have voluntary control over the muscle, and may tense it pre-emptively. Structure The tensor tympani is a muscle that is present in the middle ear. It arises from the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube, and the adjacent great wing of the sphenoid. It then passes through its own canal, and ends in the tympanic cavity as a slim tendon that connects to the handle of the malleus. The tendon makes a sharp bend around the ''processus cochleariformis'', part of the wall of its cavity, before it joins with the malleus. The tensor tympani receives blood from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yawn
A yawn is a reflex in vertebrate animals characterized by a long inspiratory phase with gradual mouth gaping, followed by a brief climax (or acme) with muscle stretching, and a rapid expiratory phase with muscle relaxation, which typically lasts a few seconds. For fish and birds, this is described as gradual mouth gaping, staying open for at least three seconds and subsequently a rapid closure of the mouth. Almost all vertebrate animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and even fish, experience yawning. The study of yawning is called chasmology. Yawning (oscitation) most often occurs in adults immediately before and after sleep, during tedious activities and as a result of its contagious quality. It is commonly associated with tiredness, stress, sleepiness, boredom, or even hunger. In humans, yawning is often triggered by the perception that others are yawning (for example, seeing a person yawning, or talking to someone on the phone who is yawning). This is a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal
The South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society (SPUMS) is a primary source of information for diving and hyperbaric medicine physiology worldwide. History The SPUMS was founded on May 3, 1971 in the wardroom of HMAS ''Penguin''. The founding members of SPUMS were Carl Edmonds, Bob Thomas, Douglas Walker, Ian Unsworth, and Cedric Deal and they were joined by approximately 20 others as "charter members". The society was incorporated in 1990. Purpose The aims of SPUMS have never changed since its inception: * To promote and facilitate the study of all aspects of underwater and hyperbaric medicine; * To provide information on underwater and hyperbaric medicine; * To publish a journal and; * To convene members of each Society annually at a scientific conference. Training SPUMS offers a Diploma of Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine. This certification, was the first non-naval certification and for years the only postgraduate education available. The first Diplomas by examinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mouth to the pharynx and then into the esophagus. In colloquial English, the term "swallowing" is also used to describe the action of ''gulping'', i.e. taking in a large mouthful of food without any biting. Swallowing is performed by an initial push from back part of the tongue (with the tongue tip contacting the hard palate for mechanical anchorage) and subsequent coordinated muscle contraction, contractions of the pharyngeal muscles. The portion of food, drink and/or other material (e.g. mucus, secretions and medications) that moves into the gullet in one swallow is called a bolus, which is then propelled through to the stomach for further digestion by autonomic peristalsis of the esophagus. Swallowing is an important part of eating and dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caisson (engineering)
In geotechnical engineering, a caisson (; borrowed , , an augmentative of ) is a watertight retaining structure. It is used, for example, to work on the foundation (architecture), foundations of a bridge pier (architecture), pier, for the construction of a concrete dam, or for the repair of ships. Caissons are constructed in such a way that the water can be pumped out, keeping the work environment dry. When piers are being built using an open caisson, and it is not practical to reach suitable soil, Deep foundation, friction pilings may be driven to form a suitable sub-foundation. These piles are connected by a foundation pad upon which the column pier is erected. Caisson engineering has been used since at least the 19th century, with three prominent examples being the Royal Albert Bridge (completed in 1859), the Eads Bridge (completed in 1874), and the Brooklyn Bridge (completed in 1883). Types To install a caisson in place, it is brought down through soft mud until a suitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwater Diving
Underwater diving, as a human activity, is the practice of descending below the water's surface to interact with the environment. It is also often referred to as diving (other), diving, an ambiguous term with several possible meanings, depending on context. Immersion in water and exposure to high ambient pressure have Physiology, physiological effects that limit the depths and duration possible in ambient pressure diving. Humans are not physiologically and anatomically well-adapted to the environmental conditions of diving, and various equipment has been developed to extend the depth and duration of human dives, and allow different types of work to be done. In ambient pressure diving, the diver is directly exposed to the pressure of the surrounding water. The ambient pressure diver may dive on breath-hold (freediving) or use breathing apparatus for scuba diving or surface-supplied diving, and the saturation diving technique reduces the risk of decompression sickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
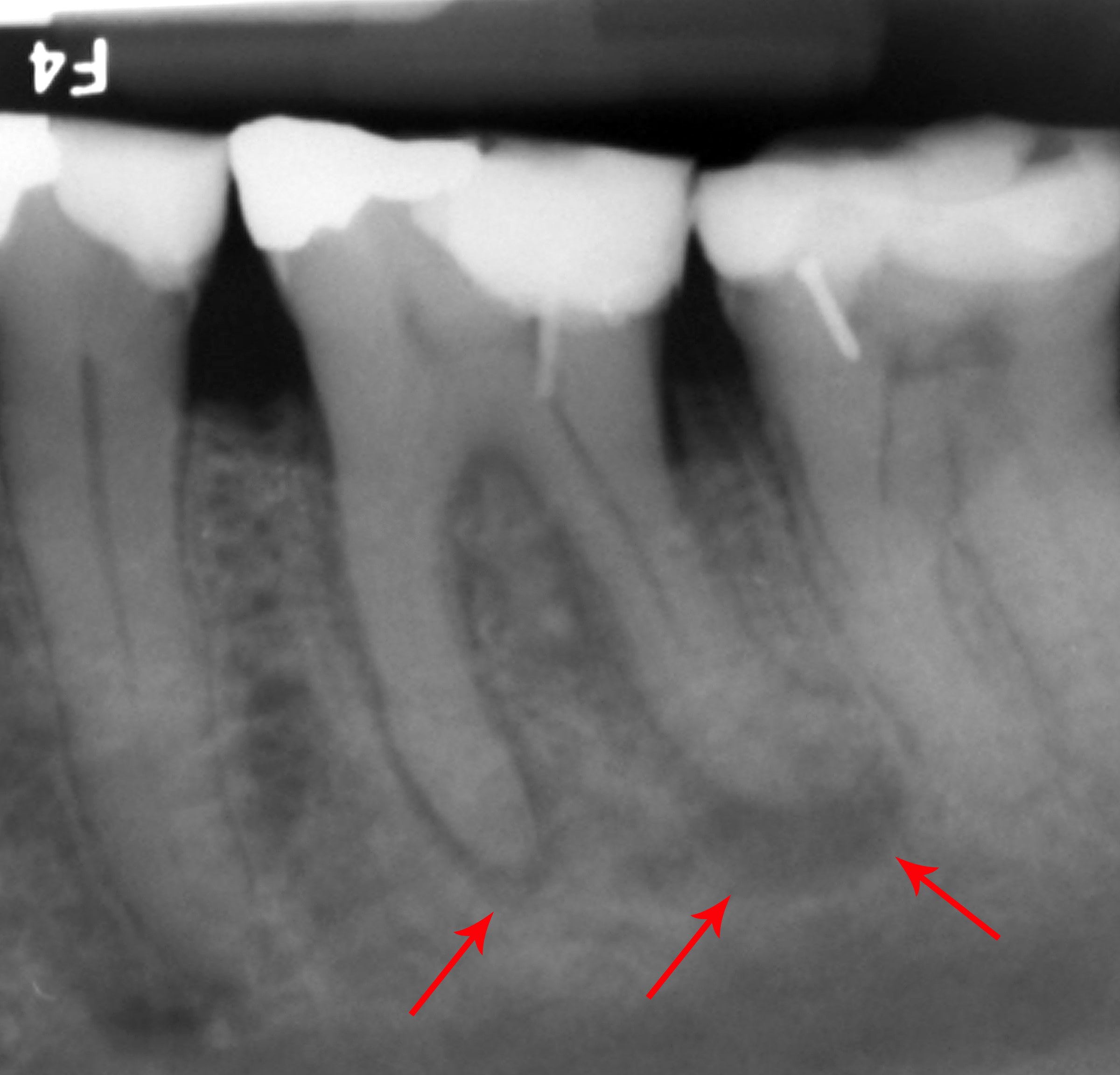
Antral Communication
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum ( pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perforation
A perforation is a small hole in a thin material or web. There is usually more than one perforation in an organized fashion, where all of the holes collectively are called a ''perforation''. The process of creating perforations is called perforating, which involves removing bits of the workpiece with a tool. Old-fashioned lick-and-stick postage stamps are perforated. When a tool makes small cuts in the material (without removing anything) it is called 'rouletting', because that tool often resembles a roulette wheel, with blades around the edge. Raffle tickets are a good example of rouletting. Perforations are usually used to allow easy separation of two sections of the material, such as allowing paper to be torn easily along the line. Packaging with perforations in paperboard or plastic film is easy for consumers to open. Other purposes include filtrating fluids, sound deadening, allowing light or fluids to pass through, and to create an aesthetic design. Various applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
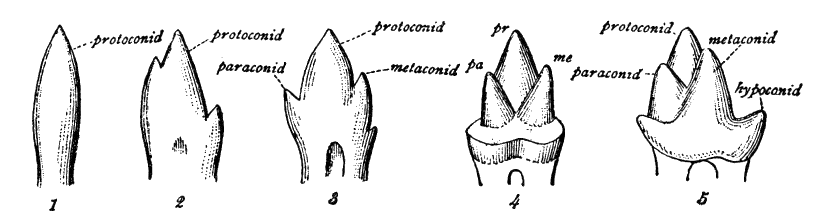
Maxillary Molar
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third molar, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its Myocardial contractility, force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary dilation, pupillary response, Micturition, urination, and Animal sexual behaviour, sexual arousal. The fight-or-flight response, also known as the acute stress response, is set into action by the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is regulated by integrated reflexes through the brainstem to the spinal cord and organ (anatomy), organs. Autonomic functions include control of respiration, heart rate, cardiac regulation (the cardiac control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex, reflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |