|
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample Cell (biology), cells or Biological tissue, tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then Histopathology, fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, are examined under a microscope (biopsy). The sampling and biopsy considered together are called fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) (the latter to emphasize that any aspiration biopsy involves cytopathology, not histopathology). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe for minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical (excisional or open) biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy instead, eliminating the need for hospitalization. In 1981, the first fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the United States was done at Maimonides Medical Center. The modern procedure is widely used to diagnose cancer and inflammatory conditions. Fine needle aspiration i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologist
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psychological conditions (such as ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
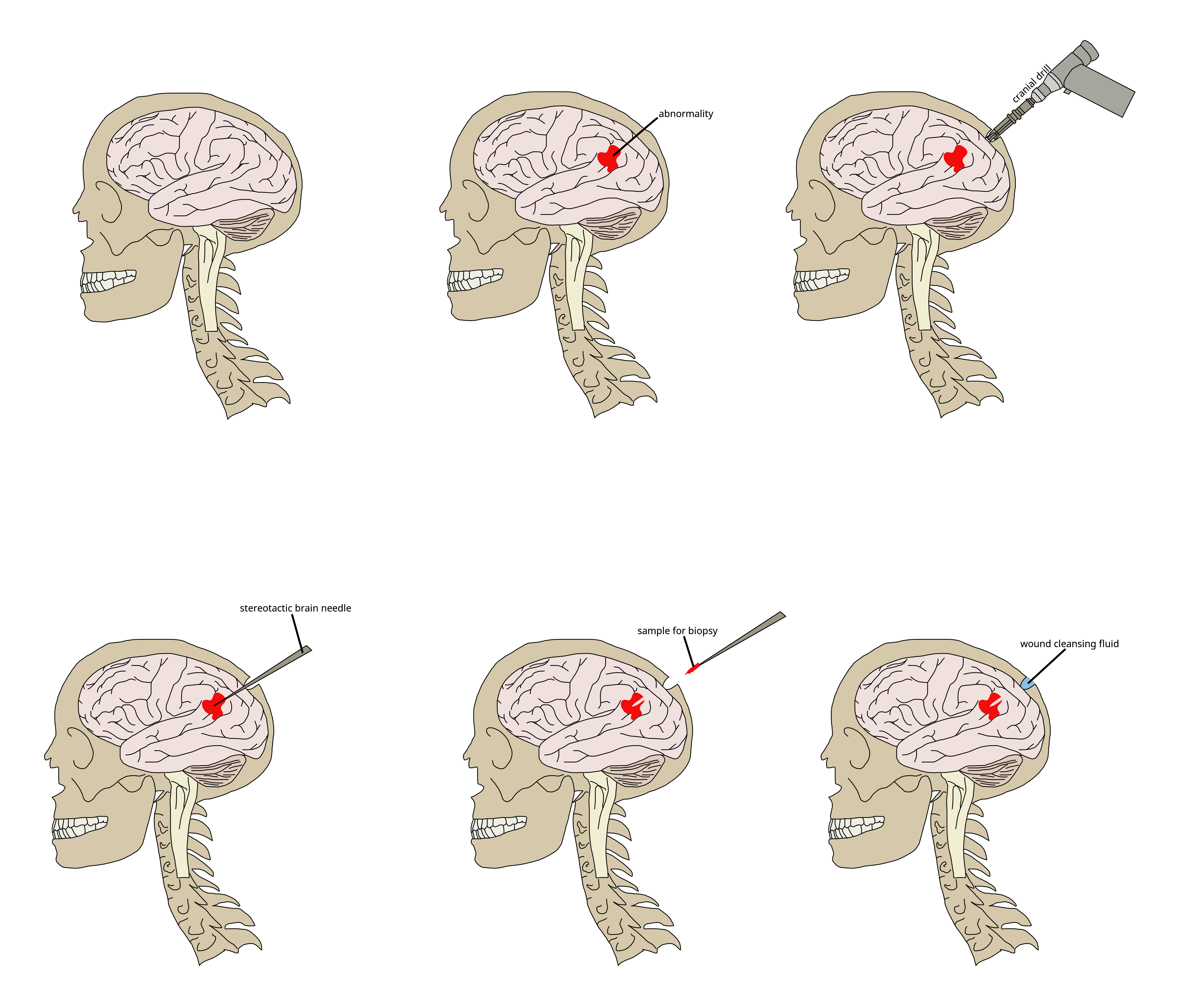
Brain Biopsy
Brain biopsy is the removal of a small piece of brain tissue for the diagnosis of abnormalities of the brain. It is used to diagnose tumors, infection, inflammation, and other brain disorders. By examining the tissue sample under a microscope, the biopsy sample provides information about the appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Indications Given the potential risks surrounding the procedure, cerebral biopsy is indicated only if other diagnostic approaches (e.g. magnetic resonance imaging) have been insufficient in showing the cause of symptoms, and if it is felt that the benefits of histological diagnosis will influence the treatment plan. If the person has a brain tumor, biopsy is 95% sensitive. The procedure can also be valuable in people who are immunocompromised and who have evidence of brain lesions that could be caused by opportunistic infection An opportunistic infection is an infection that occurs most commonly in individuals with an immunodeficiency disorder and acts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guardant Health
Guardant Health, Inc. is an American biotechnology company based in Palo Alto, California. Co-founders Helmy Eltoukhy and AmirAli Talasaz serve as co-chief executive officers. History The American biotechnology company Guardant Health, which produces liquid biopsy tests to detect cancer from mutations and other modifications in blood samples, was co-founded by Helmy Eltoukhy and AmirAli Talasaz during 2012–2013. According to John Dorfman of the ''Pittsburgh Tribune-Review'', Talasaz and Eltoukhy discovered a technique which "involves detecting and monitoring tumor fragments circulating in the patient's bloodstream", as an alternative to traditional tissue biopsies. The duo met at Stanford University in 2002 and worked together at Illumina, until Talasaz left in 2012. Early in its history, Guardant Health acquired multiple patents by Swiss biochemist Maurice Stroun, who became a founding advisor. In 2015, the company had 40 patents and was developing a blood test to "ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling (medicine)
In medicine, sampling is gathering of matter from the body to aid in the process of a medical diagnosis and/or evaluation of an indication (medicine), indication for treatment, further medical tests or other procedures. In this sense, the sample is the gathered matter, and the sampling tool or sampler is the person or material to collect the sample. Sampling is a prerequisite for many medical tests, but generally not for medical history, physical examination and radiologic tests. By sampling technique * Obtaining excretions or materials that leave the body anyway, such as urine, Feces, stool, sputum, or vomitus, by direct collection as they exit. A sample of saliva can also be collected from the mouth. * Surgery#Types of surgery, Excision (cutting out), a surgical method for the removal of solid or soft tissue samples. * Puncture (also called ''centesis'') followed by aspiration is the main method used for sampling of many types of tissues and body fluids. Examples are thoracoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks "). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buffered saline). Preparation for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancerous
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Tumor
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor causing approximately 16–18% of cancers worldwide. These infectious agents include ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HPV, Epstein–Barr virus, Human T-lymphotropic virus 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventional Radiologist
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement (e.g., stents), and angioplasty of narrowed structures. The main benefits of IR techniques are that they can reach the deep structures of the body through a body orifice or tiny incision using small needles and wires. This decreases risks, pain, and recovery compared to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |