|
Grading Of The Tumors Of The Central Nervous System
The concept of grading of the tumors of the central nervous system, agreeing for such the regulation of the "progressiveness" of these neoplasias (from benign and localized tumors to malignant and infiltrating tumors), dates back to 1926 and was introduced by P. Bailey and H. Cushing, in the elaboration of what turned out the first systematic classification of gliomas. In the following, the grading systems present in the current literature are introduced. Then, through a table, the more relevant are compared. ICD-O scale The first edition of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) dates back to 1893. The current review (ICD-10) dates back to 1994, came into use in the U.S. in 2015, and is revised yearly, being very comprehensive. In 1976 the World Health Organization (WHO) published the first edition of the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O), which is now at the third edition (ICD-O-3, 2000). In this last edition, the Arabic numeral after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Anaplastic astrocytoma is a rare WHO grade III type of astrocytoma, which is a type of cancer of the brain. In the United States, the annual incidence rate for anaplastic astrocytoma is 0.44 per 100,000 people. Signs and symptoms Initial presenting symptoms most commonly are headache, depressed mental status, focal neurological deficits, and/or seizures. The growth rate and mean interval between onset of symptoms and diagnosis is approximately 1.5–2 years but is highly variable, being intermediate between that of low-grade astrocytomas and glioblastomas. Seizures are less common among patients with anaplastic astrocytomas compared to low-grade lesions. Causes The best-known risk factor is exposure to ionizing radiation, and CT scan radiation is an important cause.Smoll NR, Brady Z, Scurrah KJ, Lee C, Berrington de González A, Mathews JD. Computed tomography scan radiation and brain cancer incidence. Neuro-Oncology. 2023 Jan 14;https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noad012Smoll NR, Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness. The cause of most cases of glioblastoma is not known. Uncommon risk factors include genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis and Li–Fraumeni syndrome, and previous radiation therapy. Glioblastomas represent 15% of all brain tumors. They are thought to arise from astrocytes. The diagnosis typically is made by a combination of a CT scan, MRI scan, and tissue biopsy. There is no known method of preventing the cancer. Treatment usually involves surgery, after which chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. The medication temozolomide is frequently used as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, Grade 3
Anaplastic astrocytoma is a rare WHO grade III type of astrocytoma, which is a type of cancer of the brain. In the United States, the annual incidence rate for anaplastic astrocytoma is 0.44 per 100,000 people. Signs and symptoms Initial presenting symptoms most commonly are headache, depressed mental status, focal neurological deficits, and/or seizures. The growth rate and mean interval between onset of symptoms and diagnosis is approximately 1.5–2 years but is highly variable, being intermediate between that of low-grade astrocytomas and glioblastomas. Seizures are less common among patients with anaplastic astrocytomas compared to low-grade lesions. Causes The best-known risk factor is exposure to ionizing radiation, and CT scan radiation is an important cause.Smoll NR, Brady Z, Scurrah KJ, Lee C, Berrington de González A, Mathews JD. Computed tomography scan radiation and brain cancer incidence. Neuro-Oncology. 2023 Jan 14;https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noad012Smoll NR, Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, Grade 2
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord, and it does not usually affect other organs. After glioblastomas, astrocytomas are the second most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord. Within the astrocytomas, two broad classes are recognized in literature, those with: * Narrow zones of infiltration (mostly noninvasive tumors; e.g., pilocytic astrocytoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma), that often are clearly outlined on diagnostic images * Diffuse zones of infiltration (e.g., high-grade astrocytoma), that share various features, including the ability to arise at any location in the central nervous system, but with a preference for the cerebral hemispheres; they occur usually in adults, and have an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
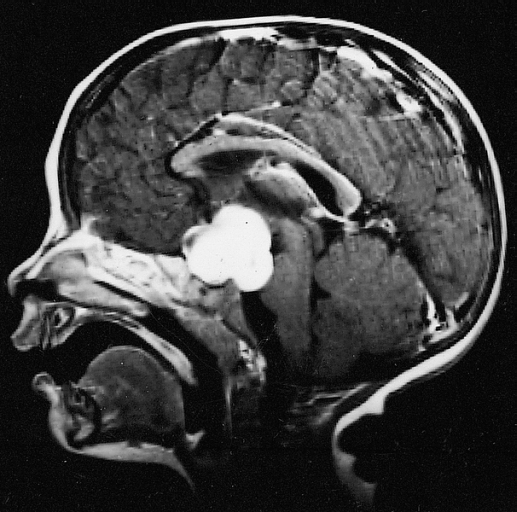
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Pilocytic astrocytoma (and its variant pilomyxoid astrocytoma) is a brain tumor that occurs most commonly in children and young adults (in the first 20 years of life). They usually arise in the cerebellum, near the brainstem, in the hypothalamic region, or the optic chiasm, but they may occur in any area where astrocytes are present, including the cerebral hemispheres and the spinal cord. These tumors are usually slow growing and benign, corresponding to WHO malignancy grade 1. Signs and symptoms Children affected by pilocytic astrocytoma can present with different symptoms that might include failure to thrive (lack of appropriate weight gain/ weight loss), headache, nausea, vomiting, irritability, torticollis (tilt neck or wry neck), difficulty to coordinate movements, and visual complaints (including nystagmus). The complaints may vary depending on the location and size of the neoplasm. The most common symptoms are associated with increased intracranial pressure due to the siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, each with a fixed integer value. The modern style uses only these seven: The use of Roman numerals continued long after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, decline of the Roman Empire. From the 14th century on, Roman numerals began to be replaced by Arabic numerals; however, this process was gradual, and the use of Roman numerals persisted in various places, including on clock face, clock faces. For instance, on the clock of Big Ben (designed in 1852), the hours from 1 to 12 are written as: The notations and can be read as "one less than five" (4) and "one less than ten" (9), although there is a tradition favouring the representation of "4" as "" on Roman numeral clocks. Other common uses include year numbers on monuments and buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilocytic Micro
Pilocytic astrocytoma (and its variant pilomyxoid astrocytoma) is a brain tumor that occurs most commonly in children and young adults (in the first 20 years of life). They usually arise in the cerebellum, near the brainstem, in the hypothalamic region, or the optic chiasm, but they may occur in any area where astrocytes are present, including the cerebral hemispheres and the spinal cord. These tumors are usually slow growing and benign, corresponding to WHO malignancy grade 1. Signs and symptoms Children affected by pilocytic astrocytoma can present with different symptoms that might include failure to thrive (lack of appropriate weight gain/ weight loss), headache, nausea, vomiting, irritability, torticollis (tilt neck or wry neck), difficulty to coordinate movements, and visual complaints (including nystagmus). The complaints may vary depending on the location and size of the neoplasm. The most common symptoms are associated with increased intracranial pressure due to the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, ''apoptosis'' is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates an inflammatory response in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervascularity
Hypervascularity is an increased number or concentration of blood vessels. In Graves disease, the thyroid gland is hypervascular, which can help in differentiating the condition from thyroiditis. 90% of thyroid papillary carcinoma cases are hypervascular. See also * Angiogenesis Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and ... References Hematology Oncology Angiology {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life * Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network * Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Electrochemical cell, a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Cell may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Cell (comics), a Marvel comic book character * Cell (Dragon Ball), Cell (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the manga series ''Dragon Ball'' Literature * Cell (novel), ''Cell'' (novel), a 2006 horror novel by Stephen King * "Cells", poem, about a hungover soldier in gaol, by Rudyard Kipling *The Cell (play), ''The Cell'' (play), an Australian play by Robert Wales Music * Cell (music), a small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a thematic context * Cell (American band) * Cell (Japanese band) * Cell (album), ''Cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelial
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the interior su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |