|
Itga7
Alpha-7 integrin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITGA7'' gene. Alpha-7 integrin is critical for modulating cell-matrix interactions. Alpha-7 integrin is highly expressed in cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and smooth muscle cells, and localizes to Z-disc and costamere structures. Mutations in ''ITGA7'' have been associated with congenital myopathies and noncompaction cardiomyopathy, and altered expression levels of alpha-7 integrin have been identified in various forms of muscular dystrophy. Structure ''ITGA7'' encodes the protein alpha-7 integrin. Alpha-7 integrin is 128.9 kDa in molecular weight and 1181 amino acids in length. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. Alpha-7 integrin undergoes post-translational cleavage within the extracellular domain to yield disulfide-linked light and heavy chains that join with beta 1 to form an integrin that binds to the extracellular matrix protein laminin-1. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene. Interactions Laminin, alpha 1 has been shown to interact with FBLN2 Fibulin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FBLN2'' gene. This gene encodes an extracellular matrix protein, which belongs to the fibulin family. This protein binds various extracellular ligands and calcium. It may play a role dur .... Role in pathology Mutations of the LAMA1 gene cause the Poretti–Boltshauser syndrome. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-18-stub Laminins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITGA6
Integrin alpha-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITGA6'' gene. Function The ITGA6 protein product is the integrin alpha chain alpha 6. Integrins are integral cell-surface proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. A given chain may combine with multiple partners resulting in different integrins. For example, alpha 6 may combine with beta 4 in the integrin referred to as TSP180, or with beta 1 in the integrin VLA-6. Integrins are known to participate in cell adhesion as well as cell-surface mediated signalling. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Specific loss of this integrin chain in the intestinal epithelium, and thus of their hemidesmosomes, induces long-standing colitis and infiltrating adenocarcinomas. Interactions ITGA6 has been shown to interact with TSPAN4 and GIPC1. See also * Cluster of differentiation * Integrin Integrins are transmembrane receptors that help cell–cell and cell– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITGA5
Integrin alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITGA5'' gene. The product of this gene belongs to the integrin alpha chain family. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. This gene encodes the integrin alpha 5 chain. Alpha chain 5 undergoes post-translational cleavage in the extracellular domain to yield disulfide-linked light and heavy chains that join with beta 1 to form a fibronectin receptor. In addition to adhesion, integrins are known to participate in cell-surface mediated signalling. Interactions ITGA5 has been shown to interact with GIPC1. See also * Cluster of differentiation * Integrin Integrins are transmembrane receptors that help cell–cell and cell–extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, o ... References Further reading * * * * External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoblast
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called myotubes. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminin
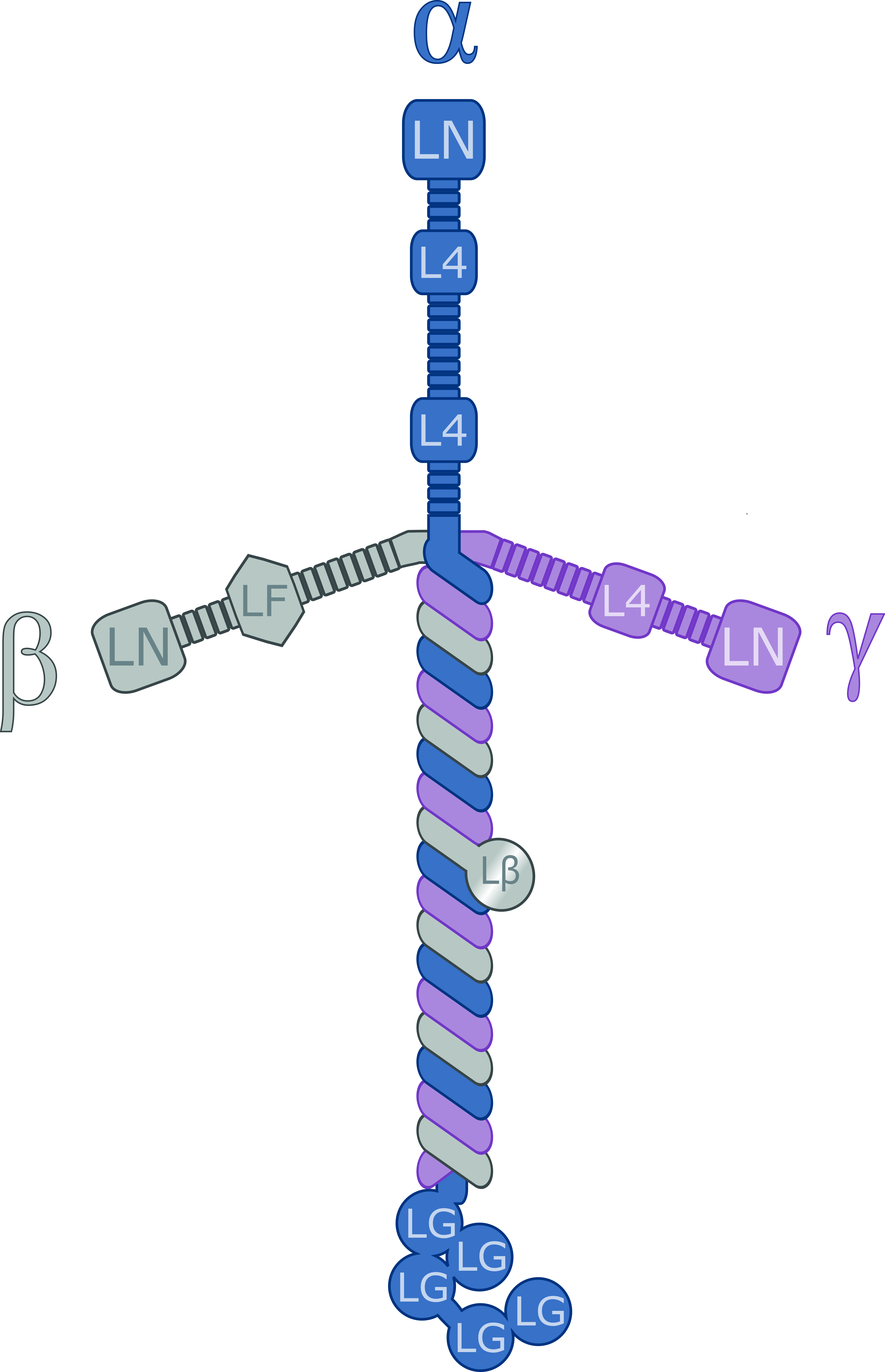
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina (the protein network foundation for most cells and organs). Laminins are vital to biological activity, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa) and possess three different chains (α, β, and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition, e.g. laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect, composing a cruciform structure that is able to bind to other molecules of the extracellular matrix and cell membrane. The three short arms have an affinity for binding to other laminin molecules, conducing sheet formation. The long ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striated Muscle
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. Under the microscope, sarcomeres are visible along muscle fibers, giving a striated appearance to the tissue. The two types of striated muscle are skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. Structure Striated muscle tissue contains T-tubules which enables the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle includes skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Skeletal muscle is wrapped in epimysium, allowing structural integrity of the muscle despite contractions. The perimysium organizes the muscle fibers, which are encased in collagen and endomysium, into fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, and sarcoplasmic reticulum. The functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a sarcomere. Each muscle cell contains myofibrils composed of actin and myosin myofilaments repeated as a sarcomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splice Variant
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants are due to spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITGB1
Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1), also known as CD29, is a cell surface receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''ITGB1'' gene. This integrin associates with integrin alpha 1 and integrin alpha 2 to form integrin complexes which function as collagen receptors. It also forms dimers with integrin alpha 3 to form integrin receptors for netrin 1 and reelin. These and other integrin beta 1 complexes have been historically known as very late activation (VLA) antigens. Integrin beta 1 is expressed as at least four different isoforms. In cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle, the integrin beta-1D isoform is specifically expressed, and localizes to costameres, where it aids in the lateral force transmission from the Z-discs to the extracellular matrix. Abnormal levels of integrin beta-1D have been found in limb girdle muscular dystrophy and polyneuropathy. Structure Integrin beta-1 can exist as different isoforms via alternative splicing. Six alternatively spliced variants have been found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LAMB2
Laminin subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB2'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... Function Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide variety of biological processes including cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, signaling, neurite outgrowth and metastasis. Laminins are composed of 3 non identical chains: laminin alpha, beta and gamma (formerly A, B1, and B2, respectively) and they form a cruciform structure consisting of 3 short arms, each formed by a different chain, and a long arm composed of all 3 chains. Each laminin chain is a multidomain protein encoded by a distinct gene. Several isoforms of eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |