|
Myoblast
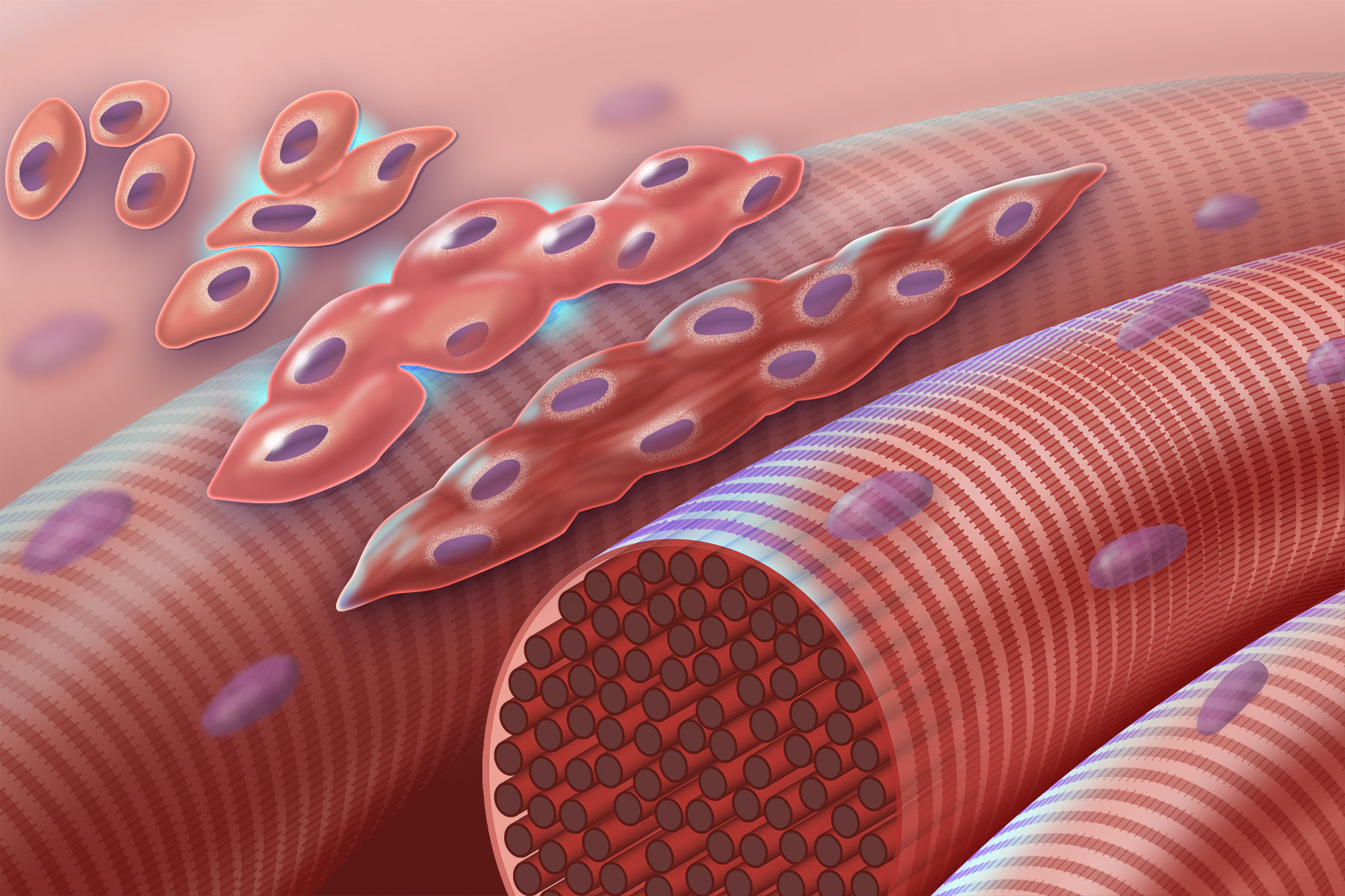
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called myotubes. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoblast Fusion - Myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscle, skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Skeletal muscle#Skeletal muscle cells, Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor cell, precursor myoblasts into Multinucleate, multinucleated fibers called myotubes. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either cell proliferation, proliferate, or Cellular differentiation, differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the align ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MyoD
MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs to a family of proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These bHLH (basic helix loop helix) transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation. Vertebrate MRF family members include MyoD1, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4 (Myf6). In non-vertebrate animals, a single MyoD protein is typically found. MyoD is one of the earliest markers of myogenic commitment. MyoD is expressed at extremely low and essentially undetectable levels in quiescent satellite cells, but expression of MyoD is activated in response to exercise or muscle tissue damage. The effect of MyoD on satellite cells is dose-dependent; high MyoD expression represses cell renewal, promotes terminal differentiation and can induce apoptosis. Although MyoD marks myoblast commitment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADAM12
Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 12 (previously Meltrin) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ADAM12'' gene. ADAM12 has two splice variants: ADAM12-L, the long form, has a transmembrane region and ADAM12-S, a shorter variant, is soluble and lacks the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Function This gene encodes a member of the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease) protein family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins, and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. This gene has two alternatively spliced transcripts: a shorter secreted form and a longer membrane-bound form. The shorter form is found to stimulate myogenesis. Clinical Significance ADAM 12, a metalloprotease that binds insulin growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogenic Regulatory Factor
Myogenic regulatory factors (MRF) are basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors that regulate myogenesis: MyoD, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4. These proteins contain a conserved basic DNA binding domain that binds the E box DNA motif. They dimerize with other HLH containing proteins through an HLH-HLH interaction. MRF Gene Family Evolution There are typically four vertebrate MRF paralogues which are homologous to typically a single MRF gene in non-vertebrates. These four genes are thought to have been duplicated in the two rounds of whole-genome duplication early in vertebrate evolution that played a role in the evolution of more complex vertebrate body plans. The four MRFs have four distinct expression profiles, though with some redundancy, as MyoD MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mef2
In the field of molecular biology, myocyte enhancer factor-2 (Mef2) proteins are a family of transcription factors which through control of gene expression are important regulators of cellular differentiation and consequently play a critical role in embryonic development. In adult organisms, Mef2 proteins mediate the stress response in some tissues. Mef2 proteins contain both MADS-box and Mef2 DNA-binding domains. Discovery Mef2 was originally identified as a transcription factor complex through promoter analysis of the muscle creatine kinase (mck) gene to identify nuclear factors interacting with the mck enhancer region during muscle differentiation. Three human mRNA coding sequences designated RSRF (Related to Serum Response Factor) were cloned and shown to dimerize, bind a consensus sequence similar to the one present in the MCK enhancer region, and drive transcription. RSRFs were subsequently demonstrated to encode human genes now named Mef2A, Mef2B and Mef2D. Spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Fusion
Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells (cells with a single nucleus) combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoclasts and trophoblasts, during embryogenesis, and morphogenesis. Cell fusion is a necessary event in the maturation of cells so that they maintain their specific functions throughout growth. History In 1839, Theodor Schwann, in his '' Microscopical Researches,'' expanded upon the theory that all living organisms are composed of cells when he added that discrete cells are the basis of life. Schwann observed that in certain cells the walls and cavities of the cells coalesce ('' verschmelzen'') together. This observation provided the first hint that cells fuse. It was not until 1960 that cell biologists deliberately fused cells for the first time. To fuse the cells, biologists combined isolated mouse cells and induced fusion of their outer membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAX3
The PAX3 (paired box gene 3) gene encodes a member of the paired box or Pax genes, PAX family of transcription factors. The PAX family consists of nine human (PAX1-PAX9) and nine mouse (Pax1-Pax9) members arranged into four subfamilies. Human PAX3 and mouse Pax3 are present in a subfamily along with the highly homologous human PAX7 and mouse Pax7 genes. The human PAX3 gene is located in the 2q36.1 chromosomal region, and contains 10 exons within a 100 kb region. Transcript splicing Alternative splicing and processing generates multiple PAX3 isoforms that have been detected at the mRNA level. PAX3e is the longest isoform and consists of 10 exons that encode a 505 amino acid protein. In other mammalian species, including mouse, the longest mRNAs correspond to the human PAX3c and PAX3d isoforms, which consist of the first 8 or 9 exons of the PAX3 gene, respectively. Shorter PAX3 isoforms include mRNAs that skip exon 8 (PAX3g and PAX3h) and mRNAs containing 4 or 5 exons (PAX3a and P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Met
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGF receptor) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MET'' gene. The protein possesses tyrosine kinase activity. The primary single chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide linked to form the mature receptor. HGF receptor is a single pass tyrosine kinase receptor essential for embryonic development, organogenesis and wound healing. Hepatocyte growth factor/Scatter Factor (HGF/SF) and its splicing isoform (NK1, NK2) are the only known ligands of the HGF receptor. MET is normally expressed by cells of epithelial origin, while expression of HGF/SF is restricted to cells of mesenchymal origin. When HGF/SF binds its cognate receptor MET it induces its dimerization through a not yet completely understood mechanism leading to its activation. Sometimes MET is misunderstood as of an abbreviation of Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition. It is incorrect. The three letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSX1
Homeobox protein MSX-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSX1'' gene. MSX1 transcripts are not only found in thyrotrope-derived TSH cells, but also in the TtT97 thyrotropic tumor, which is a well differentiated hyperplastic tissue that produces both TSHß- and a-subunits and is responsive to thyroid hormone. MSX1 is also expressed in highly differentiated pituitary cells which until recently was thought to be expressed exclusively during embryogenesis. There is a highly conserved structural organization of the members of the MSX family of genes and their abundant expression at sites of inductive cell–cell interactions in the embryo suggest that they have a pivotal role during early development. Function This gene encodes a member of the muscle segment homeobox gene family. The encoded protein functions as a transcriptional repressor during embryogenesis through interactions with components of the core transcription complex and other homeoproteins. It may also ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LBX1
Transcription factor LBX1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LBX1'' gene. This gene and the orthologous mouse gene were found by their homology to the Drosophila lady bird early and late homeobox genes. In the mouse, this gene is a key regulator of muscle precursor cell migration Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryogenesis, embryonic development, wound healing and immune system, immune responses all require the orchestrated movemen ... and is required for the acquisition of dorsal identities of forelimb muscles. References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |