|
Hydromagnesite
Hydromagnesite is a hydrated magnesium carbonate mineral with the formula Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O. It generally occurs associated with the weathering products of magnesium containing minerals such as serpentine or brucite. It occurs as incrustations and vein or fracture fillings in ultramafic rocks and serpentinites, and occurs in hydrothermally altered dolomite and marble. Hydromagnesite commonly appears in caves as speleothems and " moonmilk", deposited from water that has seeped through magnesium rich rocks. It is the most common cave carbonate after calcite and aragonite. The mineral thermally decomposes, over a temperature range of approximately 220 °C to 550 °C, releasing water and carbon dioxide leaving a magnesium oxide residue. Hydromagnesite was first described in 1836 for an occurrence in Hoboken, New Jersey. Stromatolites in an alkaline ( pH greater than 9) freshwater lake ( Salda Gölü) in southern Turkey are made of hydromagnesite precipitated by diatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Retardant
A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants may also cool the fuel through physical action or endothermic chemical reactions. Fire retardants are available as powder, to be mixed with water, as fire-fighting foams and fire-retardant gels. Fire retardants are also available as coatings or sprays to be applied to an object. Fire retardants are commonly used in fire fighting, where they may be applied aerially or from the ground. Principles of operation In general, fire retardants reduce the flammability of materials by either blocking the fire physically or by initiating a chemical reaction that stops the fire. Physical action There are several ways in which the combustion process can be retarded by physical action: * By cooling: Some chemical reactions actually cool the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Retardant
The term flame retardants subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and are intended to prevent or slow the further development of ignition by a variety of different physical and chemical methods. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or (particularly for textiles) applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive. Classes Both Reactive and Additive Flame retardants types, can be further separated into four distinct classes: * Minerals such as aluminium hydroxide (ATH), magnesium hydroxide (MDH), huntite and hydromagnesite, various hydrates, red phosphorus, and boron compounds, mostly borates. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
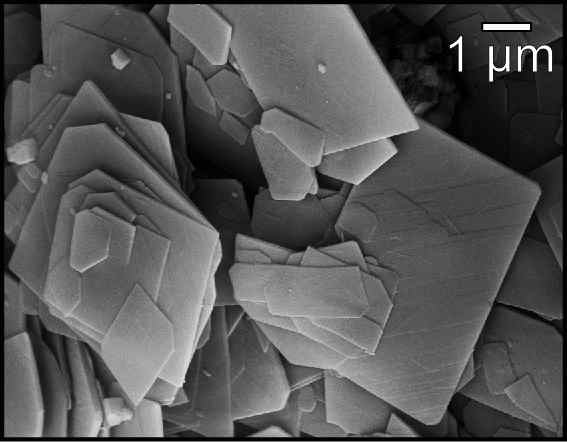
Huntite
Huntite is a carbonate mineral with the chemical formula Mg3Ca(CO3)4. Huntite crystallizes in the trigonal system and typically occurs as platy crystals and powdery masses. For most of recorded history its main use was as a white pigment. Today the most common industrial use of huntite is as a natural mixture with hydromagnesite as a flame retardant or fire retardant additive for polymers. Discovery In 1953 a paper by George Faust announced the discovery of a new carbonate mineral found in Currant Creek, Nevada (US). Faust acknowledged that the mineral probably had been discovered previously, but it had been misidentified as impure magnesite by W. E. Ford in 1917. Faust named the new mineral "huntite" in honour of his former teacher, Walter Frederick Hunt (1882–1975), Professor of Petrology at the University of Michigan. Faust carried out analyses of the mineral, and found amongst others that in differential thermal analysis huntite showed two endothermic peaks, which could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewel Cave National Monument
Jewel Cave National Monument contains Jewel Cave, currently the third longest cave in the world, with of mapped passageways. It is located approximately west of the town of Custer in Black Hills of South Dakota. It became a national monument in 1908. History Frank and Albert Michaud, two local prospectors, discovered the cave in 1900, when they felt cold air blowing out of a small hole in a canyon. It is unknown whether any previous inhabitants of the area were aware of the natural cave opening, which was not large enough for a person to enter.Jewel Cave brochure; National Park Service; GPO, WDC After enlarging the cave entrance with dynamite, the Michaud brothers found a cavern lined with calcite crystals, which led them to name it "Jewel Cave". The brothers tried to capitalize on the discovery, widening the opening, building walkways inside, and opening it to tourists. Although their venture was unsuccessful, news of the discovery eventually reached Washington. President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Mineral
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal ** Calcite CaCO3 ** Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 ** Otavite CdCO3 ** Rhodochrosite MnCO3 ** Siderite FeCO3 ** Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic ** Aragonite CaCO3 ** Cerussite PbCO3 ** Strontianite SrCO3 ** Witherite BaCO3 ** Rutherfordine UO2CO3 ** Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal ** Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 ** Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 ** Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 ** Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 ** Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 ** Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 ** Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 ** Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 ** Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 ** Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 ** Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates * Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brucite
Brucite is the mineral form of magnesium hydroxide, with the chemical formula Mg( OH)2. It is a common alteration product of periclase in marble; a low-temperature hydrothermal vein mineral in metamorphosed limestones and chlorite schists; and formed during serpentinization of dunites. Brucite is often found in association with serpentine, calcite, aragonite, dolomite, magnesite, hydromagnesite, artinite, talc and chrysotile. It adopts a layered CdI2-like structure with hydrogen-bonds between the layers. Discovery Brucite was first described in 1824 by François Sulpice Beudant and named for the discoverer, American mineralogist, Archibald Bruce (1777–1818). A fibrous variety of brucite is called nemalite. It occurs in fibers or laths, usually elongated along 010 but sometimes 120 crystalline directions. Occurrence A notable location in the U.S. is Wood's Chrome Mine, Cedar Hill Quarry, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. Yellow, white and blue Brucite with a botryoidal habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Salda
Lake Salda is a mid-size crater lake in southwestern Turkey, within the boundaries of Yeşilova district of Burdur Province. It lies at a distance of about fifty kilometers to the west from the province seat Burdur. Lake Salda is often included in the Turkish Lakes Region that extends across inner western to southern Anatolia, especially Isparta Province and Afyonkarahisar Province, although Lake Salda is geographically separate from the larger lakes, which are more to the east and, being a crater lake, is morphologically different from these tectonic lakes. The lake area covers 4,370 hectares, and its depth reaches 196 meters, making it one of the deeper lakes in Turkey, if not the deepest. The lake sedimentary records show high resolution climate changes that are related to solar variability during the last millennium. The lake is a popular excursion spot for people across the region or from beyond, the more so due to the hydromagnesite mineral found in its coastal waters, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromatolite
Stromatolites () or stromatoliths () are layered sedimentary formations ( microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota (formerly proteobacteria). These microorganisms produce adhesive compounds that cement sand and other rocky materials to form mineral " microbial mats". In turn, these mats build up layer by layer, growing gradually over time. A stromatolite may grow to a meter or more. Although they are rare today, fossilized stromatolites provide records of ancient life on Earth. Morphology Stromatolites are layered, biochemical, accretionary structures formed in shallow water by the trapping, binding and cementation of sedimentary grains in biofilms (specifically microbial mats), through the action of certain microbial lifeforms, especially cyanobacteria. They exhibit a variety of forms and structures, or morphologies, including conical, stratiform, domal, columnar, and bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CO2 Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through changes in land use and agricultural practices, such as converting crop land into land for non-crop fast growing plants. Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced using subsurface Saline water, saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks, bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, enhanced weathering, Carbon dioxide scrubber, direct air capture and Water capture of CO₂, water capture when combined with storage. Forests, kelp beds, and other forms of plant life absorb carbon dioxide from the air as they grow, and bind it into biomass. However, these biological stores are considered volatile carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, British Columbia, Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver Regional District, Metro Vancouver. The First Nations in Canada, first known human inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Lake
A dry lake bed, also known as a playa, is a basin or depression that formerly contained a standing surface water body, which disappears when evaporation processes exceeds recharge. If the floor of a dry lake is covered by deposits of alkaline compounds, it is known as an alkali flat. If covered with salt, it is known as a '' salt flat.'' Terminology If its basin is primarily salt, then a dry lake bed is called a '' salt pan'', ''pan'', or ''salt flat'' (the latter being a remnant of a salt lake). ''Hardpan'' is the dry terminus of an internally drained basin in a dry climate, a designation typically used in the Great Basin of the western United States. Another term for dry lake bed is ''playa''. The Spanish word ''playa'' () literally means "beach". Dry lakes are known by this name in some parts of Mexico and the western United States. This term is used e.g. on the Llano Estacado and other parts of the Southern High Plains and is commonly used to address paleolake sediments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





