|
European Higher Education Area
The European Higher Education Area (EHEA) was launched in March 2010, during the Budapest-Vienna Ministerial Conference, on the occasion of the 10th anniversary of the Bologna Process. As the main objective of the Bologna Process since its inception in 1999, the EHEA was meant to ensure more comparable, compatible and coherent higher education systems in Europe. Between 1999 and 2010, all the efforts of the Bologna Process members were targeted to creating the European Higher Education Area, which became reality with the Budapest-Vienna Declaration of March 2010. In order to join the EHEA, a country must sign and ratify the European Cultural Convention treaty. Denmark was the first country outside the UK and the US to introduce the 3+2+3 system. General objectives The key objectives are promoting the mobility of students and staff, the employability of graduates and the European dimension in higher education. Coping with the diversity of their national systems, the EHEA mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master's Degree
A master's degree (from Latin ) is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice. A master's degree normally requires previous study at the bachelor's degree, bachelor's level, either as a separate degree or as part of an integrated course. Within the area studied, master's graduates are expected to possess advanced knowledge of a specialized body of theoretical and applied topics; high order skills in analysis [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisbon Recognition Convention
The Lisbon Recognition Convention, officially the Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications concerning Higher Education in the European Region, is an international convention of the Council of Europe elaborated together with the UNESCO. This is the main legal agreement on credential evaluation in Europe. As of 2024, the convention has been ratified by all 47 member states of the Council of Europe in Strasbourg. It has also been ratified by the Council of Europe non-member states Australia, Belarus, Canada, the Holy See, Israel, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and New Zealand. The United States has signed but not ratified the convention. Aims The Convention stipulates that degrees and periods of study must be recognised unless ''substantial differences'' can be proved by the institution that is charged with recognition. Students and graduates are guaranteed fair procedures under the convention. It is named after Lisbon, Portugal, where it was signed in 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEMPUS
The TEMPUS (Trans-European Mobility Programme for University Studies) is a program that encouraged higher education institutions in the EU Member States and partner countries to engage in structured cooperation through the establishment of "consortia". The "consortia" implemented Joint European Projects (JEPs) with a clear set of objectives to promote exchanges and mobility of teaching staff and trainers. Such projects could receive financial aid for two or three years. Tempus also provided Individual Mobility Grants (IMGs) to individuals working in the higher education sector to help them work on certain specified activities in other countries.Syrquin, Ari (16 July 2008)"What's New in the EU: Tempus office opens in Jerusalem" ''Jerusalem Post''. Retrieved 3 June 2013. TEMPUS was adopted on 7 May 1990 by The Council of the European Communities. As of 1 January 2014, Tempus-like activities, namely capacity building activities, became part of a new cooperation programme called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Research Area
The European Research Area (ERA) is a system of scientific research programs integrating the scientific resources of the European Union (EU). Since its inception in 2000, the structure has been concentrated on European cooperation in the fields of medical, environmental, industrial, and socioeconomic research. The ERA can be likened to a research and innovation equivalent of the European " common market" for goods and services. Its purpose is to increase the competitiveness of European research institutions by bringing them together and encouraging a more inclusive way of work, similar to what already exists among institutions in North America and Japan. Increased mobility of knowledge workers and deepened multilateral cooperation among research institutions among the member states of the European Union are central goals of the ERA. Section 1 in article 179 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union states the following: History The creation of a European Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Lists Of Universities And Colleges ...
{{CatAutoTOC * Universities and colleges Universities and colleges Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank defines tertiary education as including universities, colleges, and vocational school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologation
Homologation (Greek language, Greek ''homologeo'', ὁμολογέω, "to agree") is the granting of approval by an official authority. This may be a court of law, a government department, or an academic or professional body, any of which would normally work from a set of rules or standards to determine whether such approval should be given. The word may be considered very roughly synonymous with ''wiktionary:Accreditation, accreditation'', and in fact in French language, French and Spanish language, Spanish may be used with regard to academic degrees (see apostille). ''Certification'' is another possible synonym, while ''to homologate'' is the infinitive verb form. In today's marketplace, for instance, products must often be homologated by some public agency to assure that they meet standards for such things as safety and environmental impact. A court action may also sometimes be homologated by a judicial authority before it can proceed, and the term has a precise legal meaning i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Credit Transfer System
The European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) is a standard means for comparing academic credits, i.e., the "volume of learning based on the defined learning outcomes and their associated workload" for higher education across the European Union The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ... and other collaborating European countries. For successfully completed studies, ECTS credits are awarded. One academic year corresponds to 60 ECTS credits that are normally equivalent to 1500–1800 hours of total workload, irrespective of standard or qualification type. ECTS credits are used to facilitate transfer and progression throughout the Union. ECTS also includes a standard grading scale, intended to be shown in addition to local (i.e. national) standard grades. Curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploma Supplement
The Diploma Supplement is a document accompanying a European higher education diploma, providing a standardised description of the nature, level, context, content and status of the studies completed by its holder. Overview The Diploma Supplement is designed to provide a description of the nature, level, context, content and status of the studies that were successfully completed by the individual named on the original qualification to which the supplement is appended. It should be free from any value judgements, equivalence statements or suggestions about recognition. The Diploma Supplement provides a common structure to translate qualifications across the EU. It is a flexible, non-prescriptive tool which has been shown to save time, money and workload by an EU working party. Diploma Supplements were gradually implemented at European universities as part of the Bologna Process, since approximately 1999. Students graduating from European Universities since this date, and depending o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
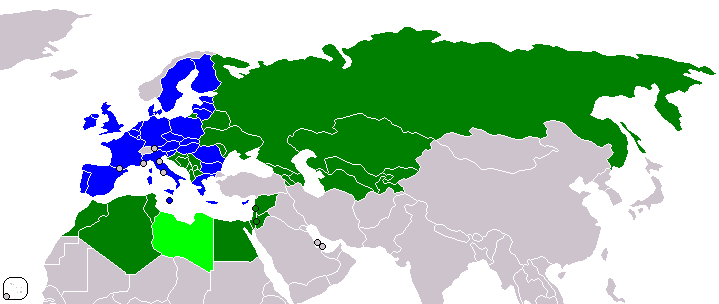
Bologna Process
file:Bologna-Prozess-Logo.svg, 96px, alt=Logo with stylized stars, Logo file:Bologna zone.svg, alt=Map of Europe, encompassing the entire Bologna zone, 256px, Bologna zone The Bologna Process is a series of ministerial meetings and agreements between European countries to ensure comparability in the standards and quality of higher-education qualifications. The process has created the European Higher Education Area under the Lisbon Recognition Convention. It is named after the University of Bologna, where the Bologna declaration was signed by education ministers from 29 European countries in 1999. The process was opened to other countries in the European Cultural Convention of the Council of Europe, and government meetings have been held in Prague (2001), Berlin (2003), Bergen (2005), London (2007), Leuven (2009), Budapest-Vienna (2010), Bucharest (2012), Yerevan (2015), Paris (2018), and Rome (2020). Before the signing of the Bologna declaration, the Magna Charta Universitatum w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directorate-General For Education And Culture
The Directorate-General for Education, Youth, Sport and Culture (DG EAC; formerly the Directorate-General for Education and Culture) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission. The Education, Youth, Sport and Culture Directorate-General is responsible of policies in the field of education, youth, culture, languages, and sport. Structure DG EAC is divided into 5 "directorates": * Directorate A : Policy Strategy and Evaluation * Directorate B : Youth, Education and Erasmus+ * Directorate C : Innovation, International Cooperation and Sport * Directorate D : Culture and Creativity * Directorate R : Performance Management, Supervision and Resources It oversees the European Union's Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA), which handles most operational programmes on DG EAC's behalf. See also * European Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education and Youth * Education in the European Union * European Higher Education Area * Bologna process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |