|
CIH 541
CIH 541 is a pre-Islamic Arabian inscription dated to 548 CE and written in Sabaic. It was commissioned by Abraha, the ruler of the Himyarite Kingdom, to symbolize the consolidation of his power. It is the last of Abraha's known inscriptions, and also the longest, running up to 136 lines. CIH 541 describes a plague that struck the Himyarite Kingdom, which some have interpreted as evidence for the spread of the Plague of Justinian into pre-Islamic Arabia. The inscription contains the final archaeological reference to the Marib dam before its ultimate demise, describing the lengthy efforts Abraha went to in order to commission its repair including by: supplying 50,806 measures of flour, 26,000 measures of dates, 3,000 cattle worth of meat, 7,200 small stock, 300 camel loads of wine, and 11,000 measures of date wine. The inscription is also known for being the last extant inscription to refer to the family that once ruled Sheba. Abraha's name on the fourth line of the inscription has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Islamic Arabian Inscriptions
Pre-Islamic Arabian inscriptions are Epigraphy, inscriptions that come from the Arabian Peninsula dating to Pre-Islamic Arabia, before the rise of Islam. They were written in both Arabic and other languages, including Sabaic, Hadramautic language, Hadramautic, Minaic, Qatabanian language, Qatabanic. These inscriptions come in two forms: graffiti, "self-authored personal expressions written in a public space", and monumental inscriptions, commissioned to a professional scribe by an elite for an official role. Unlike modern graffiti, the graffiti in these inscriptions are usually signed (and so not anonymous) and were not illicit or subversive. Graffiti are usually just scratchings on the surface of rock, but both graffiti and monumental inscriptions could be produced by painting, or the use of a chisel, charcoal, brush, or other tools. These inscriptions are typically non-portable (being lapidary) and were engraved (and not painted). Both graffiti and monumental inscriptions were als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabaic
Sabaean, also known as Sabaic, was an Old South Arabian language spoken between c. 1000 BC and the 6th century AD, by the Sabaeans. It was used as a written language by some other peoples of the ancient civilization of South Arabia, including the Ḥimyarites, Ḥashidites, Ṣirwāḥites, Humlanites, Ghaymānites, and Radmānites. The Sabaean language belongs to the South Arabian Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Sabaean is distinguished from the other members of the Old South Arabian group by the use of ''h'' to mark the third person, and as a causative prefix; the other languages all use ''s1'' in these cases; Sabaean is therefore called an ''h''-language, and the others ''s''-languages.Norbert Nebes and Peter Stein, "Ancient South Arabian" in ''The Ancient Languages of Syria-Palestine and Arabia''. CUP 2008 Script Sabaean was written in the South Arabian alphabet, and like Hebrew and Arabic marked only consonants, the only indication of vowels being with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraha
Abraha ( Ge’ez: አብርሃ) (also spelled Abreha, died after CE 570;Stuart Munro-Hay (2003) "Abraha" in Siegbert Uhlig (ed.) ''Encyclopaedia Aethiopica: A-C''. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. r. 525–at least 553S. C. Munro-Hay (1991) ''Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity''. Edinburgh: University Press. p. 87. ), also known as Abrahah al-Ashram ( ar, أَبْرَهَة ٱلْأَشْرَم), was an Aksumite army general, then the viceroy of South Arabia for the Kingdom of Aksum, and later declared himself an independent King of Himyar. Abraha ruled much of present-day Arabia and Yemen from at least 531–547 CE to 555–570 CE. Life Dhu Nuwas, the Jewish Himyarite ruler of Yemen, in the period c. 523–525"Abraha." ''Dictionary of African Christian Biographies''. 2007. (last accessed 11 April 2007) or c. 518–20 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
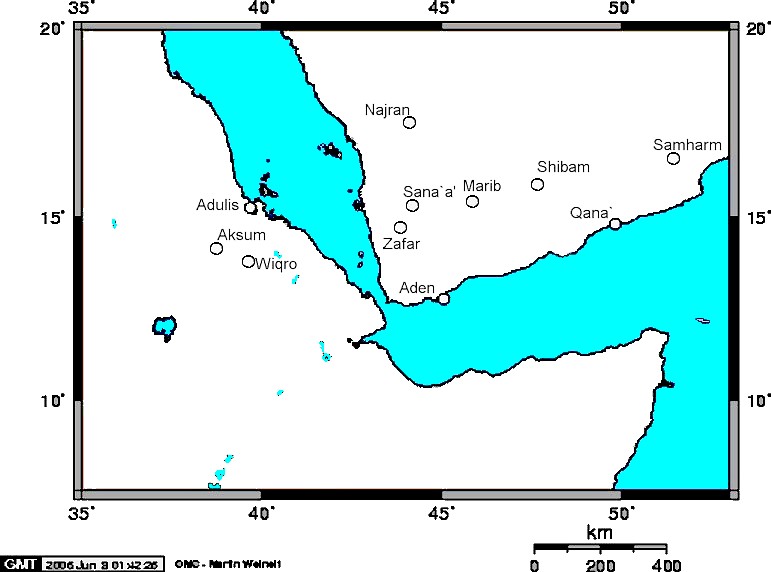
Himyarite Kingdom
The Himyarite Kingdom ( ar, مملكة حِمْيَر, Mamlakat Ḥimyar, he, ממלכת חִמְיָר), or Himyar ( ar, حِمْيَر, ''Ḥimyar'', / 𐩹𐩧𐩺𐩵𐩬) (fl. 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerite Kingdom by the Greeks and the Romans (its subjects being called Homeritae), was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According to classical sources, their capital was the ancient city of Zafar, relatively near the modern-day city of Sana'a. Himyarite power eventually shifted to Sana'a as the population increased in the fifth century. After the establishment of their kingdom, it was ruled by kings from dhū-Raydān tribe. The kingdom was named Raydān.Jérémie Schiettecatte. Himyar. Roger S. Bagnall; Kai Brodersen; Craige B. Champion; Andrew Erskine; Sabine R. Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague Of Justinian
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (541–549 AD) was the first recorded major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. The disease afflicted the entire Mediterranean Basin, Europe, and the Near East, severely affecting the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire and especially Constantinople. The plague is named for the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) who according to his court historian Procopius contracted the disease and recovered in 542, at the height of the epidemic which killed about a fifth of the population in the imperial capital. The contagion arrived in Roman Egypt in 541, spread around the Mediterranean Sea until 544, and persisted in Northern Europe and the Arabian Peninsula, until 549. In 2013, researchers confirmed earlier speculation that the cause of the plague of Justinian was ''Yersinia pestis'', the same bacterium responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Islamic Arabia
Pre-Islamic Arabia ( ar, شبه الجزيرة العربية قبل الإسلام) refers to the Arabian Peninsula before the emergence of Islam in 610 CE. Some of the settled communities developed into distinctive civilizations. Information about these communities is limited and has been pieced together from archaeological evidence, accounts written outside of Arabia, and Arab oral traditions which were later recorded by Islamic historians. Among the most prominent civilizations were the Thamud civilization, which arose around 3000 BCE and lasted to around 300 CE, and the earliest Semitic civilization in the eastern part was Dilmun, which arose around the end of the fourth millennium and lasted to around 600 CE. Additionally, from the second half of the second millennium BCE,Kenneth A. Kitchen The World of "Ancient Arabia" Series. Documentation for Ancient Arabia. Part I. Chronological Framework and Historical Sources p.110 Southern Arabia was the home to a number of kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheba
Sheba (; he, ''Šəḇāʾ''; ar, سبأ ''Sabaʾ''; Ge'ez: ሳባ ''Saba'') is a kingdom mentioned in the Hebrew Bible (Old Testament) and the Quran. Sheba features in Jewish, Muslim, and Christian traditions, particularly the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo tradition. It was the home of the biblical " Queen of Sheba", who is left unnamed in the Bible, but receives the names ''Makeda'' in Ethiopian and ''Bilqīs'' in Arabic tradition. According to Josephus it was also the home of the biblical " Princess Tharbis" said to have been the first wife of Moses when he was still a prince of Egypt. There are competing theories of where this kingdom was, with some placing it in either South Arabia or the Horn of Africa. Encyclopedia Britannica posits that the biblical narrative about the kingdom of Sheba was based on the ancient civilization of Saba ( Old South Arabian: 𐩪𐩨𐩱 ''S-b-ʾ'') in South Arabia. This view is echoed by Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaleb Of Axum
Kaleb (), also known as Saint Elesbaan, was King of Aksum, which was situated in modern-day Eritrea and Ethiopia Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er .... Procopius calls him "Hellestheaeus", a variant of grc-koi, Ελεσβόάς version of his regnal name, gez, እለ አጽብሐ, translit=ʾƎllä ʾAṣbəḥa (''Histories'', 1.20). Variants of his name are Hellesthaeus, Ellestheaeus, Eleshaah, Ellesboas, Elesbaan, and Elesboam. At Aksum, in inscription RIE 191, his name is rendered in unvocalized Gə‘əz as KLB ’L ’ṢBḤ WLD TZN (Kaleb ʾElla ʾAṣbeḥa, son of Tazena). In vocalized Gə‘əz, it is (Kaleb ʾƎllä ʾAṣbəḥa). Kaleb, a name derived from the Biblical character Caleb, was his given name; on both his coins and inscriptions he lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ja 1028
Ja 1028 is a Sabaic inscription dating to the late Himyarite Kingdom. It was commissioned by an army commander of Dhu Nuwas named S²rḥʾl Yqbl in which he celebrated massacring the Christian community of Najran and the burning of their church with the army in a move against the Abyssinian Christians of the Kingdom of Aksum based in Ethiopia. Text The following translation follows that of the Corpus of South Arabian Inscriptions:1 Might, the God, to whom belong the heavens and the earth, bless the king Yusuf ʾs¹ʾr Yṯʾr, the king of all the tribes, and might odbless the qayls ommanders… 2 Lḥyʿt Yrḫm, S¹myfʿ ʾs²wʿ, S²rḥʾl Yqbl, S²rḥbʾl ʾs¹ʿd, the sons of S²rḥbʾl Ykml, of the clan of Yzʾn and Gdnm, 3 the supporters of their lord, the king Yusuf ʾs¹ʾr Yṯʾr, when he burnt the church, killed the Abyssinians in Ẓafār, and moved a war against ʾs²ʿrn, Rkbn, Fr– 4 s¹n, and Mḫwn, and brought the war (against) the defence of Nagr� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DJE 23
DJE 23 is a Hebrew inscription found in the village of Bayt Hadir, 15 km southeast of Sanaa, Yemen. It dates to the period of the Himyarite Kingdom in which the ruling class had converted to Judaism, or sometime between 380 and 530. It is a ''mishmarot'' which lists the priestly divisions based on the list given in 1 Chronicles 24. The priestly divisions refer to the way in which the priests were divided in order to organize their service to the Temple in Jerusalem. Discovery and publication The inscription was discovered twice independently. The first was during the ''Deutsche-Jemen Expedition'' of 1970. It was discovered again by Piotr A. Grjaznevič in 1971. The discovery was first announced in a note by Walter W. Müller in 1973. Rainer Degan fully published the inscription in a 1973 paper in Hebrew and a 1974 paper in German. A seminal study was published on it in 1973 as well, by Ephraim Urbach.Ephraim E. Urbach, ''Mishmarot u-maʻamadot'', Tarbiẕ 42, Jerusalem 1973, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Inscriptions
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himyar
The Himyarite Kingdom ( ar, مملكة حِمْيَر, Mamlakat Ḥimyar, he, ממלכת חִמְיָר), or Himyar ( ar, حِمْيَر, ''Ḥimyar'', / 𐩹𐩧𐩺𐩵𐩬) (fl. 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerite Kingdom by the Greeks and the Romans (its subjects being called Homeritae), was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According to classical sources, their capital was the ancient city of Zafar, relatively near the modern-day city of Sana'a. Himyarite power eventually shifted to Sana'a as the population increased in the fifth century. After the establishment of their kingdom, it was ruled by kings from dhū-Raydān tribe. The kingdom was named Raydān.Jérémie Schiettecatte. Himyar. Roger S. Bagnall; Kai Brodersen; Craige B. Champion; Andrew Erskine; Sabine R. Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)