|
Glaukerpeton
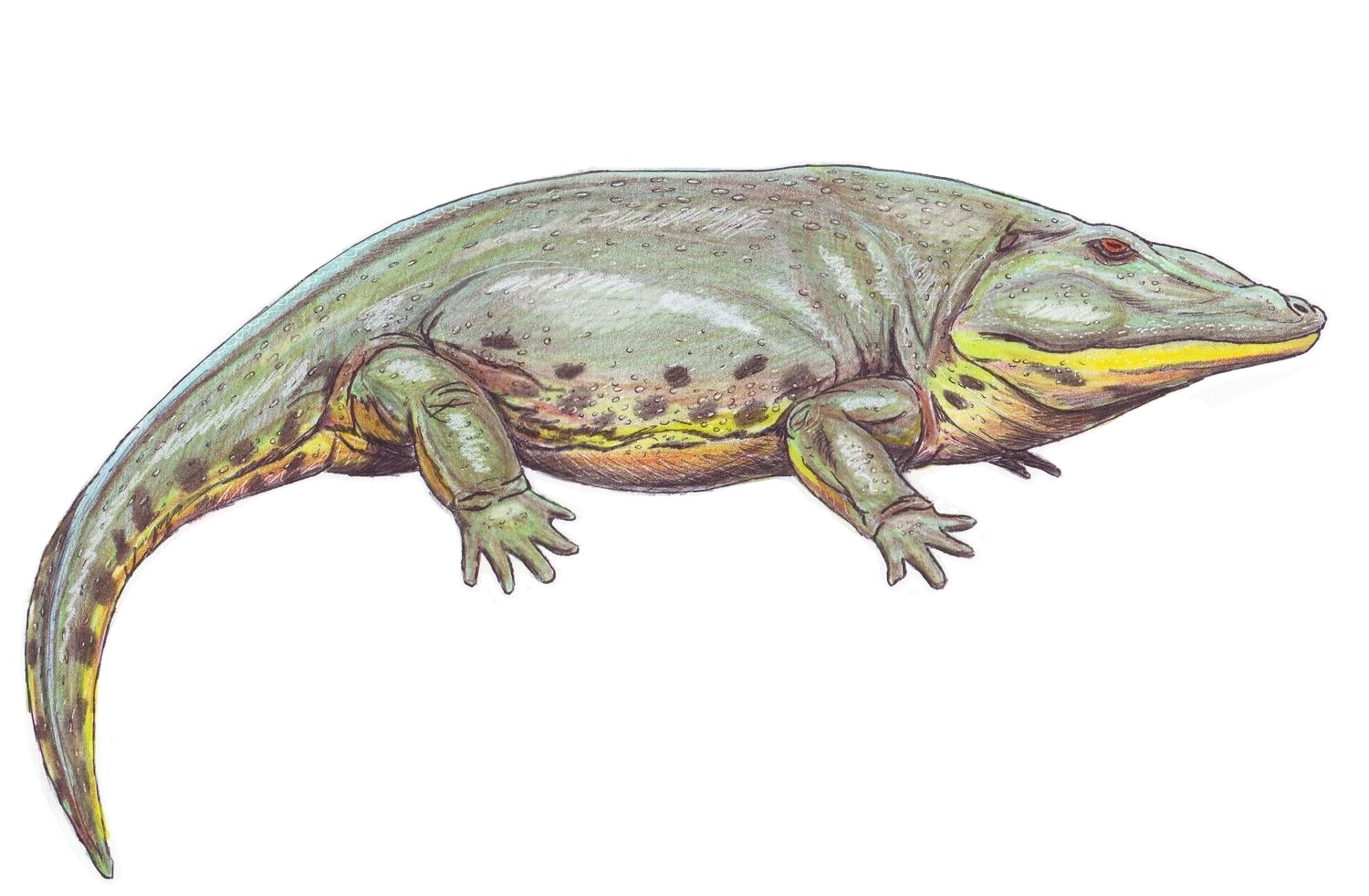
''Eryops'' (; from Greek , , 'drawn-out' + , , 'face', because most of its skull was in front of its eyes) is a genus of extinct, amphibious temnospondyls. It contains the single species , the fossils of which are found mainly in early Permian (about 295 million years ago) rocks of the Texas Red Beds, located in Archer County, Texas. Fossils have also been found in late Carboniferous period rocks from New Mexico. Several complete skeletons of ''Eryops'' have been found in lower Permian rocks, but skull bones and teeth are its most common fossils. Description ''Eryops'' averaged a little over long and could grow up to , making them among the largest land animals of their time. Adults weighed between . The skull was proportionately large, being broad and flat and reaching lengths of . It had an enormous mouth with many curved teeth like the frog. Its teeth had enamel with a folded pattern, leading to its early classification as a " labyrinthodont" ("maze toothed"). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had characteristics, such as scales and armour-like bony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods (or upper of two subsystems) of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal-productive beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian and the Permian. In parts of Europe, the Mississippian and Pennsylvanian are one more-or-less continuous sequence of lowland continental deposits and are grouped t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid
A coracoid (from Greek κόραξ, ''koraks'', raven) is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is not homologous with the coracoid bone of most other vertebrates. In other tetrapods it joins the scapula to the front end of the sternum and has a notch on the dorsal surface which, along with a similar notch on the ventral surface of the scapula, forms the socket in which the proximal end of the humerus (upper arm bone) is located. The acrocoracoid process is an expansion adjacent to this contact surface, to which the shoulderward end of the biceps brachii muscle attaches in these animals. In birds (and generally theropods and related animals), the entire unit is rigid and called scapulocoracoid. This plays a major role in bird flight. In dinosaurs the main bones of the pectoral girdle were the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
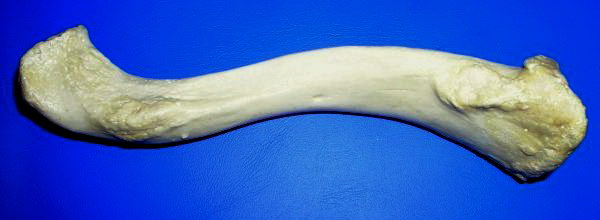
Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes ( trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae ( radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenoid
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from el, gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest. This cavity forms the glenohumeral joint along with the humerus. This type of joint is classified as a synovial, ball and socket joint. The humerus is held in place within the glenoid cavity by means of the long head of the biceps tendon. This tendon originates on the superior margin of the glenoid cavity and loops over the shoulder, bracing humerus against the cavity. The rotator cuff also reinforces this joint more specifically with the supraspinatus tendon to hold the head of the humerus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interclavicle
An interclavicle is a bone which, in most tetrapods, is located between the clavicles. Therian mammals (marsupials and placentals) are the only tetrapods which never have an interclavicle, although some members of other groups also lack one. In therians, it is replaced by the sternum which is similar in shape and function but forms via endochondral ossification (cartilage forming bone). The interclavicle, on the other hand, develops through intramembranous ossification of the skin. Monotreme Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals ( Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brai ...s, although part of the mammalian class, do have interclavicles. References Bones of the upper limb Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleithrum
The cleithrum (plural cleithra) is a membrane bone which first appears as part of the skeleton in primitive bony fish, where it runs vertically along the scapula. Its name is derived from Greek κλειθρον = "key (lock)", by analogy with "clavicle" from Latin ''clavicula'' = "little key". In modern fishes, the cleithrum is a large bone that extends upwards from the base of the pectoral fin and anchors to the cranium above the gills, forming the posterior edge of the gill chamber. The bone has scientific use as a means to determine the age of fishes. The lobe-finned fishes share this arrangement. In the earliest amphibians however, the cleithrum/clavicle complex came free of the skull roof, allowing for a movable neck. The cleithrum disappeared early in the evolution of reptiles, and in amniotes is very small or absent. It has been argued based on position, muscle connectivity, and developmental origin that the nuchal element of the turtle carapace A carapace is a dors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species (such as the dog and the horse) have only the scapula. The pectoral girdles are to the upper limbs as the pelvic girdle is to the lower limbs; the girdles are the parts of the appendicular skeleton that anchor the appendages to the axial skeleton. In humans, the only true anatomical joints between the shoulder girdle and the axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. No anatomical joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection or physiological joint between the two permits great mobility of the shoulder girdle compared to the compact pelvic girdle; because the upper limb is not usually involved in weight bearing, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodont
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group ( clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

