|
Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, on the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two period (geology), subperiods of the Carboniferous Period (or the upper of two system (stratigraphy), subsystems of the Carboniferous System). It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronology, geochronologic units, the stratum, rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal Bed (geology), beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian (geology), Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Commission On Stratigraphy
The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), sometimes unofficially referred to as the International Stratigraphic Commission, is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific organization that concerns itself with stratigraphy, stratigraphical, geology, geological, and chronology, geochronological matters, worldwide. It is the largest subordinate body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS). The ICS is essentially a permanent working committee, working subcommittee, which meets far more regularly than the quadrennial meetings scheduled by the IUGS, when it meets as a congress or committee, membership of the whole. Aims One of its main aims, a project begun in 1974, is to establish a multidisciplinary standard and global geologic time scale that will ease paleontology, paleontological and geobiology, geobiological comparisons region to region by benchmarks with stringent and rigorous strata criteria called Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Points ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
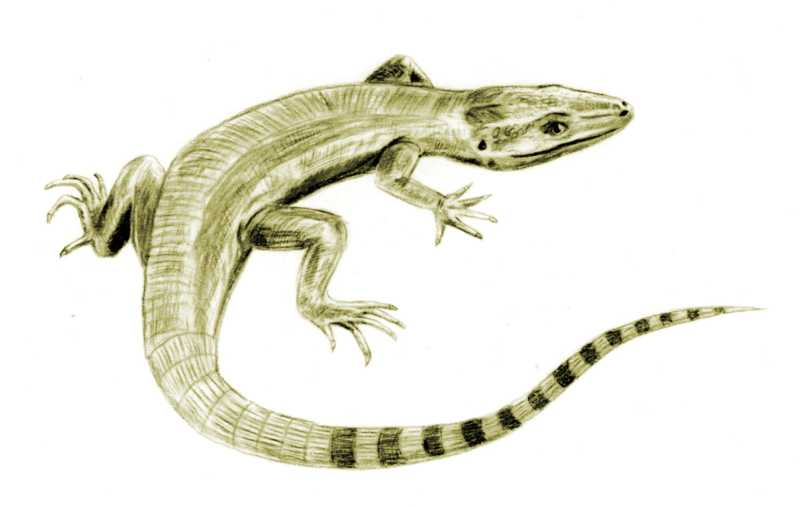
Amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tetrapoda, stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous geologic period, period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the anamniote, non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/toads, salamanders/newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three fetal membranes, extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; rib, costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenal cortex, adrenocortical and chromaffin cell, chromaffin tissues as adrenal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse
The Carboniferous rainforest collapse (CRC) was a minor extinction event that occurred around 305 million years ago in the Carboniferous period. The event occurred at the end of the Moscovian and continued into the early Kasimovian stages of the Pennsylvanian (Upper Carboniferous). It altered the vast coal forests that covered the equatorial region of Euramerica (Europe and North America). This event may have fragmented the forests into isolated refugia or ecological "islands", which in turn encouraged dwarfism and, shortly after, extinction of many plant and animal species. Following the event, coal-forming tropical forests continued in large areas of the Earth, but their extent and composition were changed. Extinction patterns on land In the Carboniferous, the great tropical rainforests of Euramerica supported towering lycopodiophyta, a heterogeneous mix of vegetation, as well as a great diversity of animal life: giant griffinflies, millipedes, blattopterans, smaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant taxon, extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass (biology), subclass Lissamphibia, with three living order (biology), orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater ecosystem, freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their biological life cycle, life cycle typically starts out as aquatic animal, aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meganeura
''Meganeura'' is a genus of extinct insects from the Late Carboniferous (approximately 300 million years ago). It is a member of the extinct order Meganisoptera, which are closely related to and resemble dragonflies and damselflies (with dragonflies, damselflies and meganisopterans being part of the broader group Odonatoptera). Like other odonatopterans, they were predatory, with their diet mainly consisting of other insects. The genus belongs to the Meganeuridae, a family including other similarly giant dragonfly-like insects ranging from the Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian. With single wing length reaching and a wingspan about , ''M. monyi'' is one of the largest-known flying insect species. Fossils of ''Meganeura'' were first discovered in Late Carboniferous ( Stephanian) Coal Measures of Commentry, France in 1880. In 1885, French paleontologist Charles Brongniart described and named the fossil "''Meganeura''" (great-nerved), which refers to the network of vei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffinfly
Meganisoptera is an extinct order of large dragonfly-like insects, informally known as griffenflies or (incorrectly) as giant dragonflies. The order was formerly named Protodonata, the "proto-Odonata", for their similar appearance and supposed relation to modern Odonata (damselflies and dragonflies). They range in Palaeozoic (Late Carboniferous to Late Permian) times. Though most were only slightly larger than modern dragonflies, the order includes the largest known insect species, such as the late Carboniferous '' Meganeura monyi'' and the even larger early Permian '' Meganeuropsis permiana'', with wingspans of up to . The forewings and hindwings are similar in venation (a primitive feature) except for the larger anal (rearwards) area in the hindwing. The forewing is usually slenderer and slightly longer than the hindwing. Unlike the true dragonflies, the Odonata, they had no pterostigmata, and had a somewhat simpler pattern of veins in the wings. Most specimens are known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millipede
Millipedes (originating from the Latin , "thousand", and , "foot") are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery in 2020 of '' Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropleura
''Arthropleura'', from Ancient Greek ἄρθρον (''árthron''), meaning "joint", and πλευρά (''pleurá''), meaning "rib", is an extinct genus of massive myriapoda, myriapod that lived in what is now Europe and North America around 344 to 292 Myr, million years ago, from the Viséan stage of the lower Carboniferous period to the Sakmarian stage of the lower Permian period. It is a millipede, and was capable of reaching at least in length, possibly up to over , making it the largest known land arthropod of all time. ''Arthropleura'' is known from body fossils as well as trace fossils, particularly giant trackways up to wide, and potentially also large burrows. It lived in open, sparsely wooded environments near water, and was possibly amphibious. Classification First discovered in 1849 during construction of a railway near Friedrichsthal in Germany, ''Arthropleura'' has consistently attracted much artistic and scientific attention, yet has historically been known fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Of Life Web Project
The Tree of Life Web Project (ToL) is an Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world. The site has not been updated since 2011, however the pages are still accessible. The pages are linked hierarchically, in the form of the branching evolutionary tree of life, organized cladistically. Each page contains information about one particular group of organisms and is organized according to a branched tree-like form, thus showing hypothetical relationships between different groups of organisms. In 2009 the project ran into funding problems from the University of Arizona. Pages and Treehouses submitted took a considerably longer time to be approved as they were being reviewed by a small group of volunteers, and apparently, around 2011, all activities ended. History The idea of this project started in the late 1980s. David Maddison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meredith Blackwell
Meredith May Blackwell (born 1940) is an American mycologist, known as one of the world's leading experts on fungi associated with arthropods. Education and career Meredith Blackwell graduated in 1961 with B.S. in biology from the University of Southwestern Louisiana, Lafayette and in 1963 with M.S. in biology from the University of Alabama in Tuscaloosa. She graduated in 1973 with Ph.D. in botany from the University of Texas at Austin with thesis "A Developmental and Taxonomic Study of ''Protophysarum phloiogenum''" under the supervision of C. J. Alexopoulos. At the University of Florida, Blackwell was an electron microscopist from 1972 to 1974 and an assistant in botany from 1974 to 1975. She was an assistant professor at Hope College from 1975 to 1981. At Louisiana State University, she was an associate professor of botany from 1981 to 1985, a full professor of botany from 1998 to 1997, and Boyd Professor in the Department of Biological Sciences from 1997 to 2014, when she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |