Verrucae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A plantar wart is a
Veruca right foot detail.jpg, A plantar wart:
"Laser Surgery for Warts"
webmd.com
Plantar warts
at the
Warts
at ''
wart
Warts are non-cancerous viral growths usually occurring on the hands and feet but which can also affect other locations, such as the genitals or face. One or many warts may appear. They are distinguished from cancerous tumors as they are caus ...
occurring on the bottom of the foot
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up o ...
or toe
Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plantigrade''; ...
s. Its color is typically similar to that of the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
. Small black dots often occur on the surface. One or more may occur in an area. They may result in pain with pressure such that walking is difficult.
They are caused by the human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
(HPV). A break in the skin is required for infection to occur. Risk factors include use of communal showers, having had prior warts, and poor immune function. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms.
Treatment is only needed if it is causing symptoms. This may include salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a active metabolite, metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been lis ...
, cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy can be used in many ways, including whole body exposure for therapeutic health benefits or may be used locally to treat ...
, chemo-based fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU, 5-fluorouracil), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stoma ...
or bleomycin
-13- (1''H''-imidazol-5-yl)methyl9-hydroxy-5- 1''R'')-1-hydroxyethyl8,10-dimethyl-4,7,12,15-tetraoxo-3,6,11,14-tetraazapentadec-1-yl}-2,4'-bi-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)carbonyl]amino}propyl)(dimethyl)sulfonium
, C=55 , H=84 , N=17 , O=21 , S=3
, SMI ...
, and surgical removal. The skin atop the lesion should generally be removed before treatment. In about a third to two-thirds of cases, they go away without specific treatment, but this may take a few years. Plantar warts are common. Children and young adults are most often affected.
Signs and symptoms
Their colors are typically similar to that of the nearbyskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
. Small, black dots may occur on their surfaces. One or more may occur in an area. They may result in pain with pressure such that walking may be difficult.
striae
Stretch marks, also known as striae () or striae distensae, are a form of scarring on the skin with an off-color hue. Over time, they may diminish, but will not disappear completely. Striae are caused by tearing of the dermis during periods of ...
(fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
s) go around the lesion.
File:Plantarwartscluster.jpg, Mosaic wart cluster
File:Wart-IMG 1676.JPG, Young plantar warts
File:30 year old plantar wart.jpg, 30-year-old plantar wart
File:Painful plantar warts.jpg, Deep, painful plantar warts
File:Plantar wart at heel.jpg, Deep plantar wart on heel
Cause
Plantar warts are benignepithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
generally caused by infection by human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
types 1, 2, 4, 60, or 63, but also by types 57, 65, 66, and 156. These types are classified as clinical (visible symptoms). The virus attacks compromised skin through direct contact, possibly entering through tiny cuts and abrasions in the stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin language, Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis (skin), epidermis. Consisting of dead tissue, it protects underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress. It is ...
(outermost layer of skin). After infection, warts may not become visible for several weeks or months. Because of pressure on the sole of the foot or finger
A finger is a prominent digit (anatomy), digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (dactyly, pentadact ...
, the wart is pushed inward and a layer of hard skin may form over the wart. A plantar wart can be painful if left untreated.
Warts may spread through autoinoculation Autoinoculation is derived from the Latin root words "autos" and "inoculate" that mean "self implanting" or "self infection" or "implanting something from oneself". Autoinoculation can refer to both beneficial medical procedures (e.g. vaccination) a ...
, by infecting nearby skin, or by contaminated walking surfaces. They may fuse or develop into clusters called mosaic warts.
Diagnosis
A plantar wart is a small lesion that appears on the surface of the skin and typically resembles acauliflower
Cauliflower is one of several vegetables cultivated from the species '' Brassica oleracea'' in the genus '' Brassica'', which is in the Brassicaceae (or mustard) family. Cauliflower usually grows with one main stem that carries a large, rou ...
, with tiny black petechia
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Causes Physical t ...
e (tiny hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
s under the skin) in the center. Pinpoint bleeding may occur when these are scratched. Plantar warts occur on the soles of feet and toes. They may be painful when standing or walking.
Plantar warts are often similar to callus
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, b ...
es or corns
Corn most often refers to maize, the yellow, large-grained crop native to the Americas.
It can also refer to the main cereal crop of a country or region:
* Wheat, barley and oats in England and Wales
* Oats in Scotland and Ireland
Corn may also ...
, but can be differentiated by close observation of skin striations. Feet are covered in friction ridges, which are akin to fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
s of the feet. Friction ridges are disrupted by plantar warts; if the lesion is not a plantar wart, the striations continue across the top layer of the skin. Plantar warts tend to be painful on application of pressure from either side of the lesion rather than direct pressure, unlike corns (which tend to be painful on direct pressure, instead).
Prevention
HPV is spread by direct and indirect contact from an infected host. Avoiding direct contact with contaminated surfaces such as communal changing rooms and shower floors and benches, avoiding sharing of shoes and socks and avoiding contact with warts on other parts of the body and on the bodies of others may help reduce the spread of infection. Infection is less common among adults than children. As all warts are contagious, precautions should be taken to avoid spreading them. Recommendations include: * Cover them with anadhesive bandage
An adhesive bandage, also called a sticking plaster, sticky plaster, medical plaster, or simply plaster in British English, is a small medical dressing used for injuries not serious enough to require a full-size bandage. They are also known by ...
while swimming
* Wear latex swimming socks
* Wear flip-flops
Flip-flops are a type of light sandal-like shoe, typically worn as a form of casual footwear. They consist of a flat sole held loosely on the foot by a Y-shaped strap known as a toe thong that passes between the first and second toes and around ...
when using communal showers
* Do not share towels.
Plantar warts are not prevented by inoculation with HPV vaccine
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines are vaccines intended to provide acquired immunity against infection by certain types of human papillomavirus. The first HPV vaccine became available in 2006. Currently there are six licensed HPV vaccines: ...
s because the warts are caused by different strains of HPV. Gardasil
Gardasil is an HPV vaccine for use in the prevention of certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledg ...
protects against strains 6, 11, 16, and 18, and Cervarix
Cervarix is a vaccine against certain types of cancer-causing human papillomavirus (HPV).
Cervarix is designed to prevent infection from HPV types 16 and 18, that cause about 70% of cervical cancer cases. These types also cause most HPV-induced ...
protects against 16 and 18, whereas plantar warts are caused by strains 1, 2, 4, and 63.
Treatment
A number of treatments have been found to be effective. A 2012 review of different treatments for skin warts in otherwise healthy people concluded modest benefit from salicylic acid, and cryotherapy appears similar to salicylic acid.Medications
Salicylic acid, thetreatment of warts by keratolysis Keratolysis is the removal of dead surface skin cells and is a treatment for several types of wart. The most common keratolytic treatment of warts available over-the-counter involves salicylic acid. These products are readily available at most drugs ...
, involves the peeling away of dead surface skin cells with keratolytic
Keratolytic () therapy is a type of medical treatment to remove warts, calluses and other lesions in which the epidermis produces excess skin. In this therapy, acidic topical medicines, such as Whitfield's ointment or Jessner's solution, are a ...
chemicals such as salicylic acid or trichloroacetic acid
Trichloroacetic acid (TCA; TCAA; also known as trichloroethanoic acid) is an analogue of acetic acid in which the three hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have all been replaced by chlorine atoms. Salts and esters of trichloroacetic acid are cal ...
. These are available in over-the-counter products, but in higher concentrations may need to be prescribed by a physician. A 12-week daily treatment with salicylic acid has been shown to lead to a complete clearance of warts in 10–15% of the cases.
Formic acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . This acid is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some an ...
, topical, is a common treatment for plantar warts, which works by being applied over a period of time, causing the body to reject the wart.
Fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU, 5-fluorouracil), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stoma ...
cream, a chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
agent sometimes used to treat skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
, can be used on particularly resistant warts, by blocking viral
The word ''Viral'' means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
It may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spre ...
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
production and repair.
Bleomycin
-13- (1''H''-imidazol-5-yl)methyl9-hydroxy-5- 1''R'')-1-hydroxyethyl8,10-dimethyl-4,7,12,15-tetraoxo-3,6,11,14-tetraazapentadec-1-yl}-2,4'-bi-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)carbonyl]amino}propyl)(dimethyl)sulfonium
, C=55 , H=84 , N=17 , O=21 , S=3
, SMI ...
, a more potent chemotherapy drug, can be injected into deep warts, destroying the viral DNA or RNA. Bleomycin is notably not US FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
approved for this purpose. Possible side effects include necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the digits, nail loss, and Raynaud syndrome
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rare ...
. The usual treatment is one or two injections.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
, as intralesional injection of antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
s (mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gen ...
, ''candida
Candida, or Cándida (Spanish), may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* ''Candida'' (fungus), a genus of yeasts
** Candidiasis, an infection by ''Candida'' organisms
* Malvasia Candida, a variety of grape
Places
* Candida, Campania, a ''comu ...
'' or trichophytin antigens USP), is a wart treatment that may trigger a host immune response to the wart virus, resulting in wart resolution. It is now recommended as a second-line therapy.
Surgery

Liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose vis ...
and similar cryosurgery
Cryosurgery (with ''cryo'' from the Ancient Greek ) is the use of extreme cold in surgery to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue; thus, it is the surgical application of cryoablation.
Cryosurgery has been historically used to treat a number o ...
methods are common surgical treatments, which act by freezing the external cell structure of the warts, destroying the live tissue.
Electrodesiccation
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or ...
and surgical excision may produce scarring.
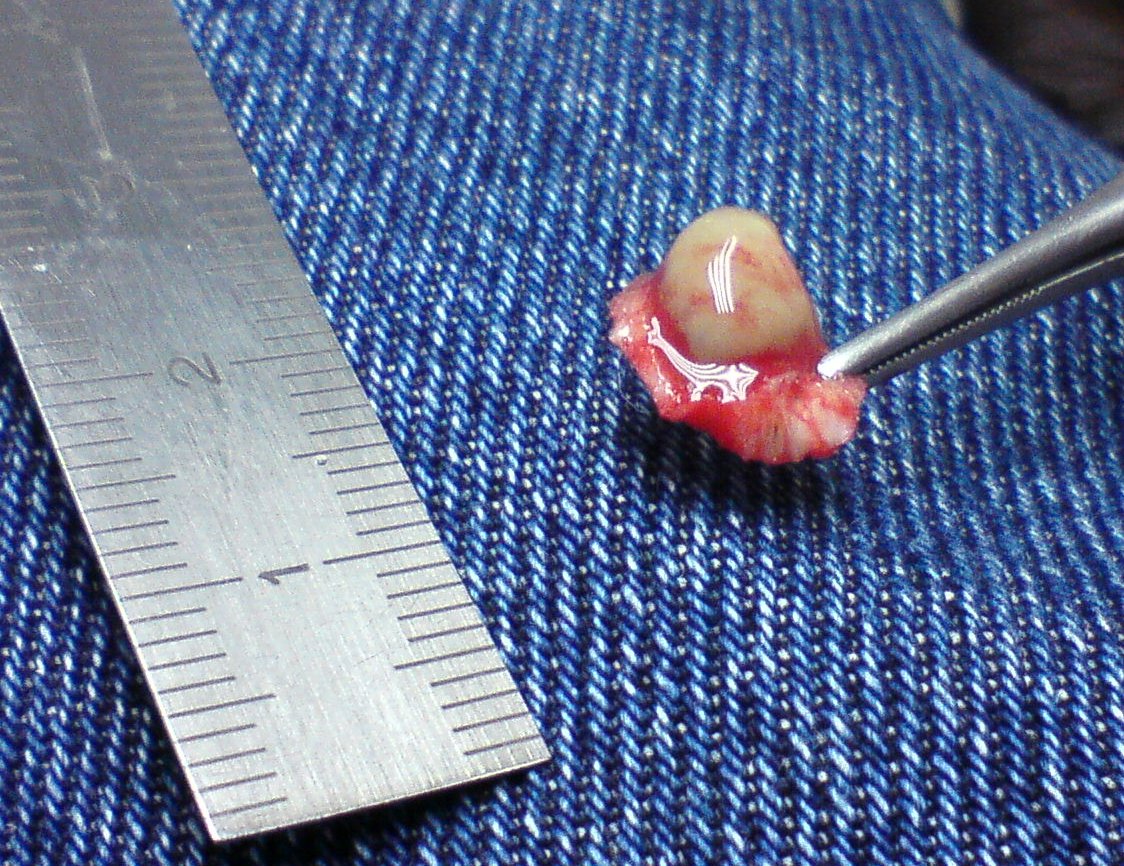
Laser surgery
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that cuts tissue using a laser in contrast to using a scalpel.
Soft-tissue laser surgery is used in a variety of applications in humans ( general surgery, neurosurgery, ENT, dentistry, orthodontics, and ...
is generally a last resort treatment, as it is expensive and painful, but may be necessary for large, hard-to-cure warts.webmd.com
Cauterization
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, o ...
may be effective as a prolonged treatment. As a short-term treatment, cauterization of the base with anesthetic can be effective, but this method risks scarring or keloid
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation t ...
s. Subsequent surgical removal, if necessary, also risks keloids and/or recurrence in the operative scar.
References
External links
Plantar warts
at the
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic () is a Nonprofit organization, private American Academic health science centre, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center focused on integrated health care, healthcare, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science ...
website
Warts
at ''
Merck Manual
''The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy'', referred to as ''The Merck Manual'',
is the world's best-selling medical textbook, and the oldest continuously published English language medical textbook. First published in 1899, the current print e ...
''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Plantar Wart
Virus-related cutaneous conditions
Foot diseases
Papillomavirus-associated diseases
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate