Typhoid inoculation2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''


 The Widal test is used to identify specific antibodies in the serum of people with typhoid by using antigen-antibody interactions.
In this test, the serum is mixed with a dead bacterial suspension of ''Salmonella'' with specific antigens. If the patient's serum contains antibodies against those antigens, they get attached to them, forming clumps. If clumping does not occur, the test is negative. The Widal test is time-consuming and prone to significant false positives. It may also be falsely negative in recently infected people. But unlike the Typhidot test, the Widal test quantifies the specimen with titres.
The Widal test is used to identify specific antibodies in the serum of people with typhoid by using antigen-antibody interactions.
In this test, the serum is mixed with a dead bacterial suspension of ''Salmonella'' with specific antigens. If the patient's serum contains antibodies against those antigens, they get attached to them, forming clumps. If clumping does not occur, the test is negative. The Widal test is time-consuming and prone to significant false positives. It may also be falsely negative in recently infected people. But unlike the Typhidot test, the Widal test quantifies the specimen with titres.
 Sanitation and hygiene are important to prevent typhoid. It can spread only in environments where human feces can come into contact with food or drinking water. Careful food preparation and washing of hands are crucial to prevent typhoid. Industrialization contributed greatly to the elimination of typhoid fever, as it eliminated the public health hazards associated with having horse manure in public streets, which led to a large number of flies, which are vectors of many pathogens, including ''Salmonella'' spp. According to statistics from the U.S.
Sanitation and hygiene are important to prevent typhoid. It can spread only in environments where human feces can come into contact with food or drinking water. Careful food preparation and washing of hands are crucial to prevent typhoid. Industrialization contributed greatly to the elimination of typhoid fever, as it eliminated the public health hazards associated with having horse manure in public streets, which led to a large number of flies, which are vectors of many pathogens, including ''Salmonella'' spp. According to statistics from the U.S.
 To help decrease rates of typhoid fever in
To help decrease rates of typhoid fever in
 In 2000, typhoid fever caused an estimated 21.7 million illnesses and 217,000 deaths. It occurs most often in children and young adults between 5 and 19 years old. In 2013, it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990. Infants, children, and adolescents in south-central and Southeast Asia have the highest rates of typhoid. Outbreaks are also often reported in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. In 2000, more than 90% of morbidity and mortality due to typhoid fever occurred in Asia. In the U.S., about 400 cases occur each year, 75% of which are acquired while traveling internationally.
Before the antibiotic era, the
In 2000, typhoid fever caused an estimated 21.7 million illnesses and 217,000 deaths. It occurs most often in children and young adults between 5 and 19 years old. In 2013, it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990. Infants, children, and adolescents in south-central and Southeast Asia have the highest rates of typhoid. Outbreaks are also often reported in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. In 2000, more than 90% of morbidity and mortality due to typhoid fever occurred in Asia. In the U.S., about 400 cases occur each year, 75% of which are acquired while traveling internationally.
Before the antibiotic era, the
 There were several occurrences of milk delivery men spreading typhoid fever throughout the communities they served. Although typhoid is not spread through milk itself, there were several examples of milk distributors in many locations watering their milk down with contaminated water, or cleaning the glass bottles the milk was placed in with contaminated water.
There were several occurrences of milk delivery men spreading typhoid fever throughout the communities they served. Although typhoid is not spread through milk itself, there were several examples of milk distributors in many locations watering their milk down with contaminated water, or cleaning the glass bottles the milk was placed in with contaminated water. 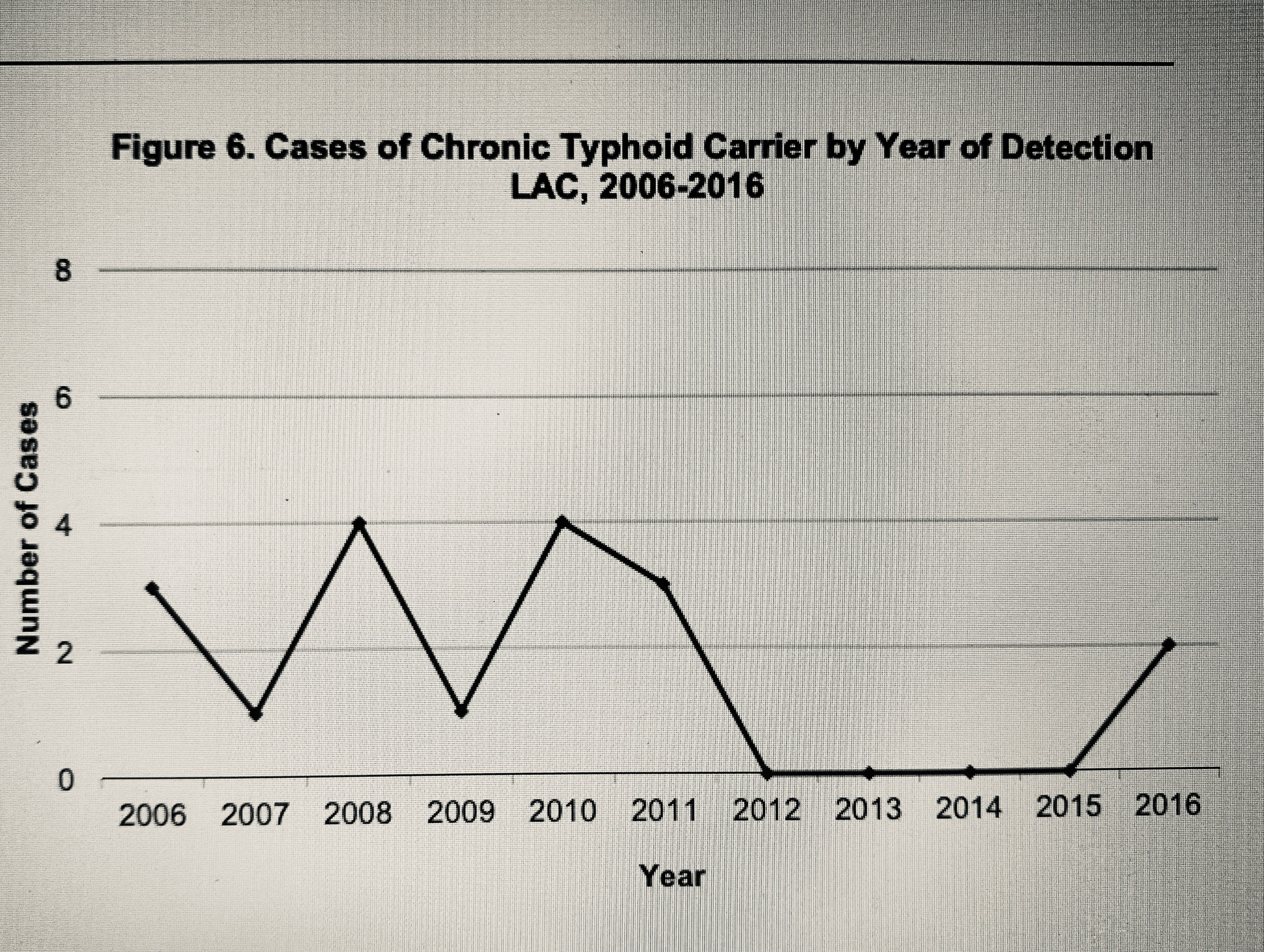 Today, typhoid carriers exist all over the world, but the highest incidence of
Today, typhoid carriers exist all over the world, but the highest incidence of
 British bacteriologist Almroth Edward Wright first developed an effective typhoid vaccine at the Army Medical School in Netley,
British bacteriologist Almroth Edward Wright first developed an effective typhoid vaccine at the Army Medical School in Netley,
Salmonella enterica
''Salmonella enterica'' (formerly ''Salmonella choleraesuis'') is a rod-shaped, flagellate, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus ''Salmonella''. It is divided into six subspecies, arizonae (IIIa), diarizonae ...
'' serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or Cell (biology), cells are classified together based on their shared reactivity ...
Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
, constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The Human feces, stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the ...
, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry it without being affected, but are still contagious. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever
Paratyphoid fever, also known simply as paratyphoid, is a bacterial infection caused by one of three types of '' Salmonella enterica''. Symptoms usually begin 6–30 days after exposure and are the same as those of typhoid fever. Often, a gradu ...
. ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans.
Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their shared reactivity between their ...
Typhi growing in the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. T ...
s, Peyer's patch
Peyer's patches or aggregated lymphoid nodules are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer.
* Reprinted as:
* Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (cl ...
es, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
, liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
and blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
of an infected person. Risk factors include limited access to clean drinking water and poor sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
. Those who have not yet been exposed to it and ingest contaminated drinking water or food are most at risk for developing symptoms. Only humans can be infected; there are no known animal reservoirs. Salmonella Typhi which causes typhoid fever is different from the other ''Salmonella'' bacteria that usually cause salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is a symptomatic infection caused by bacteria of the ''Salmonella'' type. It is the most common disease to be known as food poisoning (though the name refers to food-borne illness in general). These are defined as diseases, usuall ...
, a common type of food poisoning.
Diagnosis is performed by culturing and identifying ''S.'' Typhi from patient samples or detecting an immune response to the pathogen from blood samples. Recently, new advances in large-scale data collection and analysis have allowed researchers to develop better diagnostics, such as detecting changing abundances of small molecules in the blood that may specifically indicate typhoid fever. Diagnostic tools in regions where typhoid is most prevalent are quite limited in their accuracy and specificity, and the time required for a proper diagnosis, the increasing spread of antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis ...
, and the cost of testing are also hardships for under-resourced healthcare systems.
A typhoid vaccine
Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a (a live oral vaccine) and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS) (an injectable subunit vaccine). Dep ...
can prevent about 40–90% of cases during the first two years. The vaccine may have some effect for up to seven years. For those at high risk or people traveling to areas where it is common, vaccination is recommended. Other efforts to prevent it include providing clean drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
, good sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
, and handwashing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to the han ...
. Until an infection is confirmed as cleared, the infected person should not prepare food for others. Typhoid is treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s such as azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes otitis media, middle ear infections, strep throa ...
, fluoroquinolones
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic molecule, bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-Quinolone, 4-quinolone. They are used in human and ve ...
, or third-generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment more difficult.
In 2015, 12.5 million new typhoid cases were reported. The disease is most common in India. Children are most commonly affected. Typhoid decreased in the developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and the use of antibiotics. Every year about 400 cases are reported in the U.S. and an estimated 6,000 people have typhoid. In 2015, it resulted in about 149,000 deaths worldwide – down from 181,000 in 1990. Without treatment, the risk of death may be as high as 20%. With treatment, it is between 1% and 4%.
Typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
is a different disease, caused by unrelated species of bacteria. Owing to their similar symptoms, they were not recognized as distinct diseases until the 1800s. "Typhoid" means "resembling typhus".
Signs and symptoms
Classically, the progression of untreated typhoid fever has three distinct stages, each lasting about a week. Over the course of these stages, the patient becomes exhausted and emaciated. * In the first week, the body temperature rises slowly, and fever fluctuations are seen with relativebradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
( Faget sign), malaise
In medicine, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. It is considered a vague termdescribing the state of simply not feeling well. The word has exist ...
, headache, and cough. A bloody nose (epistaxis
A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is an instance of bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significan ...
) is seen in a quarter of cases, and abdominal pain is also possible. A decrease in the number of circulating white blood cells (leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
) occurs with eosinopenia and relative lymphocytosis; blood cultures are positive for ''S. enterica'' subsp. enterica serovar Typhi. The Widal test
The Widal test, developed in 1896 and named after its inventor, Georges-Fernand Widal, is an indirect agglutination test for enteric fever or undulant fever whereby bacteria causing typhoid fever are mixed with a serum containing specific anti ...
is usually negative.
* In the second week, the person is often too tired to get up, with high fever in plateau around and bradycardia (sphygmothermic dissociation or Faget sign), classically with a dicrotic pulse wave. Delirium
Delirium (formerly acute confusional state, an ambiguous term that is now discouraged) is a specific state of acute confusion attributable to the direct physiological consequence of a medical condition, effects of a psychoactive substance, or ...
can occur, where the patient is often calm, but sometimes becomes agitated. This delirium has given typhoid the nickname "nervous fever". Rose spots
Rose spots are blanching red macules 2-4 millimeters in diameter occurring in patients with enteric fever (which includes typhoid and paratyphoid). These fevers occur following infection by ''Salmonella typhi'' and ''Salmonella paratyphi'' re ...
appear on the lower chest and abdomen in around a third of patients. Rhonchi (rattling breathing sounds) are heard in the base of the lungs. The abdomen is distended and painful in the right lower quadrant, where a rumbling sound can be heard. Diarrhea can occur in this stage, but constipation is also common. The spleen and liver are enlarged ( hepatosplenomegaly) and tender, and liver transaminases are elevated. The Widal test is strongly positive, with antiO and antiH antibodies. Blood cultures are sometimes still positive.
* In the third week of typhoid fever, possible complications include:
** The fever is still very high and oscillates very little over 24 hours. Dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
ensues along with malnutrition, and the patient is delirious. A third of affected people develop a macular rash on the trunk.
** Intestinal haemorrhage due to bleeding in congested Peyer's patches
Peyer's patches or aggregated lymphoid nodules are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer.
* Reprinted as:
* Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (cl ...
occurs; this can be very serious but is usually not fatal.
** Intestinal perforation in the distal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may ...
is a critical complication and often fatal. It may occur without alarming symptoms until sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
or diffuse peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and covering of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One pa ...
sets in.
** Respiratory diseases such as pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
and acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis, also known as a chest cold, is short-term bronchitis – inflammation of the bronchus, bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) of the lungs. The most common symptom is a cough. Other symptoms include sputum, coughing up mucus, ...
** Encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
** Neuropsychiatric symptoms (described as "muttering delirium" or "coma vigil"), with picking at bedclothes or imaginary objects.
** Metastatic abscesses, cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include Right upper quadrant (abdomen), right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks (biliary colic) precede ...
, endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
, and osteitis
Osteitis is inflammation of bone. More specifically, it can refer to one of the following conditions:
* Osteomyelitis, or ''infectious osteitis'', mainly ''bacterial osteitis''
* Alveolar osteitis or "dry socket"
* Condensing osteitis (or Osteit ...
.
** Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
) is sometimes seen.
Causes

Bacteria
TheGram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
bacterium that causes typhoid fever is ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. enterica serovar Typhi. Based on the MLST subtyping scheme, the two main sequence types of the ''S.'' Typhi are ST1 and ST2, which are widespread globally. Global phylogeographical analysis showed dominance of a haplotype 58 (H58), which probably originated in India during the late 1980s and is now spreading through the world with multi-drug resistance. A more detailed genotyping scheme was reported in 2016 and is now widely used. This scheme reclassified the nomenclature of H58 to genotype 4.3.1.
Transmission
Unlike other strains of ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
'', humans are the only known typhoid carriers. ''S. enterica'' subsp. enterica serovar Typhi is spread by the fecal-oral route from people who are infected and from asymptomatic carriers
An asymptomatic carrier is a person or other organism that has become infection, infected with a pathogen, but shows no signs or symptoms.
Although unaffected by the pathogen, carriers can transmit it to others or develop symptoms in later stage ...
of the bacterium. An asymptomatic human carrier is someone who is still excreting typhoid bacteria in stool a year after the acute stage of the infection.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by anyblood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
, bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
, or stool culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
s and with the Widal test
The Widal test, developed in 1896 and named after its inventor, Georges-Fernand Widal, is an indirect agglutination test for enteric fever or undulant fever whereby bacteria causing typhoid fever are mixed with a serum containing specific anti ...
(demonstration of antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
against ''Salmonella'' antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
An ...
O-somatic and H-flagellar). In epidemics and less wealthy countries, after excluding malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehyd ...
, or pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
, a therapeutic trial time with chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
is generally undertaken while awaiting the results of the Widal test and blood and stool cultures.
Widal test
 The Widal test is used to identify specific antibodies in the serum of people with typhoid by using antigen-antibody interactions.
In this test, the serum is mixed with a dead bacterial suspension of ''Salmonella'' with specific antigens. If the patient's serum contains antibodies against those antigens, they get attached to them, forming clumps. If clumping does not occur, the test is negative. The Widal test is time-consuming and prone to significant false positives. It may also be falsely negative in recently infected people. But unlike the Typhidot test, the Widal test quantifies the specimen with titres.
The Widal test is used to identify specific antibodies in the serum of people with typhoid by using antigen-antibody interactions.
In this test, the serum is mixed with a dead bacterial suspension of ''Salmonella'' with specific antigens. If the patient's serum contains antibodies against those antigens, they get attached to them, forming clumps. If clumping does not occur, the test is negative. The Widal test is time-consuming and prone to significant false positives. It may also be falsely negative in recently infected people. But unlike the Typhidot test, the Widal test quantifies the specimen with titres.
Rapid diagnostic tests
Rapid diagnostic tests such as Tubex, Typhidot, and Test-It have shown moderate diagnostic accuracy.Typhidot
Typhidot is based on the presence of specific IgM and IgG antibodies to a specific 50 Kd OMP antigen. This test is carried out on a cellulose nitrate membrane where a specific ''S. typhi'' outer membrane protein is attached as fixed test lines. It separately identifies IgM and IgG antibodies. IgM shows recent infection; IgG signifies remote infection. The sample pad of this kit contains colloidal gold-anti-human IgG or gold-anti-human IgM. If the sample contains IgG and IgM antibodies against those antigens, they will react and turn red. The typhidot test becomes positive within 2–3 days of infection. Two colored bands indicate a positive test. A single control band indicates a negative test. A single first fixed line or no band at all indicates an invalid test. Typhidot's biggest limitation is that it is not quantitative, just positive or negative.Tubex test
The Tubex test contains two types of particles: brown magnetic particles coated with antigen and blue indicator particles coated with O9 antibody. During the test, if antibodies are present in the serum, they will attach to the brown magnetic particles and settle at the base, while the blue indicator particles remain in the solution, producing a blue color, which means the test is positive. If the serum does not have an antibody in it, the blue particles attach to the brown particles and settle at the bottom, producing a colorless solution, which means the test is negative.Prevention
 Sanitation and hygiene are important to prevent typhoid. It can spread only in environments where human feces can come into contact with food or drinking water. Careful food preparation and washing of hands are crucial to prevent typhoid. Industrialization contributed greatly to the elimination of typhoid fever, as it eliminated the public health hazards associated with having horse manure in public streets, which led to a large number of flies, which are vectors of many pathogens, including ''Salmonella'' spp. According to statistics from the U.S.
Sanitation and hygiene are important to prevent typhoid. It can spread only in environments where human feces can come into contact with food or drinking water. Careful food preparation and washing of hands are crucial to prevent typhoid. Industrialization contributed greatly to the elimination of typhoid fever, as it eliminated the public health hazards associated with having horse manure in public streets, which led to a large number of flies, which are vectors of many pathogens, including ''Salmonella'' spp. According to statistics from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
, the chlorination of drinking water has led to dramatic decreases in the transmission of typhoid fever.
Vaccination
Twotyphoid vaccine
Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a (a live oral vaccine) and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS) (an injectable subunit vaccine). Dep ...
s are licensed for use in the prevention of typhoid: the live, oral Ty21a vaccine (sold as Vivotif by Crucell Switzerland AG) and the injectable typhoid polysaccharide vaccine (sold as Typhim Vi by Sanofi Pasteur
Sanofi Pasteur is the vaccines division of the French multinational pharmaceutical company Sanofi. Sanofi Pasteur is the largest company in the world devoted entirely to vaccines. It is one of four global producers of the yellow fever vaccin ...
and Typherix by GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc (an acronym from its former name GlaxoSmithKline plc) is a British Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutics, pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with headquarters in London. It was established in 2000 by a Mergers an ...
). Both are efficacious and recommended for travelers to areas where typhoid is endemic. Boosters are recommended every five years for the oral vaccine and every two years for the injectable form. An older, killed whole-cell vaccine is still used in countries where the newer preparations are not available, but this vaccine is no longer recommended for use because it has more side effects (mainly pain and inflammation at the site of the injection).
developing nation
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
s, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) endorsed the use of a vaccination program starting in 1999. Vaccination has proven effective at controlling outbreaks in high-incidence areas and is also very cost-effective: prices are normally less than US$1 per dose. Because the price is low, poverty-stricken communities are more willing to take advantage of the vaccinations. Although vaccination programs for typhoid have proven effective, they alone cannot eliminate typhoid fever. Combining vaccines with public health efforts is the only proven way to control this disease.
Since the 1990s, the WHO has recommended two typhoid fever vaccines. The ViPS vaccine is given by injection and the Ty21a by capsules. Only people over age two are recommended to be vaccinated with the ViPS vaccine, and it requires a revaccination after 2–3 years, with a 55–72% efficacy. The Ty21a vaccine is recommended for people five and older, lasting 5–7 years with 51–67% efficacy. The two vaccines have proved safe and effective for epidemic disease control in multiple regions.
A version of the vaccine combined with a hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious liver disease caused by Hepatitis A virus (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is ...
vaccine is also available.
Results of a phase 3 trial of typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV) in December 2019 reported 81% fewer cases among children.
Treatment
Oral rehydration therapy
The rediscovery oforal rehydration therapy
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) also officially known as Oral Rehydration Solution is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salt ...
in the 1960s provided a simple way to prevent many of the deaths of diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
l diseases in general.
Antibiotics
Where resistance is uncommon, the treatment of choice is a fluoroquinolone such asciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
. Otherwise, a third-generation cephalosporin such as ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joi ...
or cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is an antibiotic used to treat several bacterial infections in humans, other animals, and plant tissue culture. Specifically in humans it is used to treat joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urin ...
is the first choice. Cefixime is a suitable oral alternative.
Properly treated, typhoid fever is not fatal in most cases. Antibiotics such as ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic belonging to the aminopenicillin class of the penicillin family. The drug is used to prevent and treat several bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, s ...
, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, amoxicillin, and ciprofloxacin have been commonly used to treat it. Treatment with antibiotics reduces the case-fatality rate to about 1%.
Without treatment, some patients develop sustained fever, bradycardia, hepatosplenomegaly, abdominal symptoms, and occasionally pneumonia. In white-skinned patients, pink spots, which fade on pressure, appear on the skin of the trunk in up to 20% of cases. In the third week, untreated cases may develop gastrointestinal and cerebral complications, which may prove fatal in 10–20% of cases. The highest case fatality rates are reported in children under 4. Around 2–5% of those who contract typhoid fever become chronic carriers, as bacteria persist in the biliary tract
The biliary tract (also biliary tree or biliary system) refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids an ...
after symptoms have resolved.
Surgery
Surgery is usually indicated if intestinal perforation occurs. One study found a 30-day mortality rate of 9% (8/88), and surgical site infections at 67% (59/88), with the disease burden borne predominantly by low-resource countries. For surgical treatment, most surgeons prefer simple closure of the perforation with drainage of theperitoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
. Small bowel resection is indicated for patients with multiple perforations. If antibiotic treatment fails to eradicate the hepatobiliary carriage, the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
should be resected. Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed i ...
is sometimes successful, especially in patients with gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s, but is not always successful in eradicating the carrier state because of persisting hepatic
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
infection.
Resistance
As resistance to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, andstreptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, ''Burkholderia'' i ...
is now common, these agents are no longer used as first-line treatment of typhoid fever. Typhoid resistant to these agents is known as multidrug-resistant typhoid.
Ciprofloxacin resistance is an increasing problem, especially in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. Many centres are shifting from ciprofloxacin to ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joi ...
as the first line for treating suspected typhoid originating in South America, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Thailand, or Vietnam. Also, it has been suggested that azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes otitis media, middle ear infections, strep throa ...
is better at treating resistant typhoid than both fluoroquinolone drugs and ceftriaxone. Azithromycin can be taken by mouth and is less expensive than ceftriaxone, which is given by injection.
A separate problem exists with laboratory testing for reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin; current recommendations are that isolates should be tested simultaneously against ciprofloxacin (CIP) and against nalidixic acid (NAL), that isolates sensitive to both CIP and NAL should be reported as "sensitive to ciprofloxacin", and that isolates sensitive to CIP but not to NAL should be reported as "reduced sensitivity to ciprofloxacin". But an analysis of 271 isolates found that around 18% of isolates with reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic molecule, bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-Quinolone, 4-quinolone. They are used in human and ve ...
, the class to which CIP belongs ( MIC 0.125–1.0 mg/L), would not be detected by this method.
Epidemiology
 In 2000, typhoid fever caused an estimated 21.7 million illnesses and 217,000 deaths. It occurs most often in children and young adults between 5 and 19 years old. In 2013, it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990. Infants, children, and adolescents in south-central and Southeast Asia have the highest rates of typhoid. Outbreaks are also often reported in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. In 2000, more than 90% of morbidity and mortality due to typhoid fever occurred in Asia. In the U.S., about 400 cases occur each year, 75% of which are acquired while traveling internationally.
Before the antibiotic era, the
In 2000, typhoid fever caused an estimated 21.7 million illnesses and 217,000 deaths. It occurs most often in children and young adults between 5 and 19 years old. In 2013, it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990. Infants, children, and adolescents in south-central and Southeast Asia have the highest rates of typhoid. Outbreaks are also often reported in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. In 2000, more than 90% of morbidity and mortality due to typhoid fever occurred in Asia. In the U.S., about 400 cases occur each year, 75% of which are acquired while traveling internationally.
Before the antibiotic era, the case fatality rate
In epidemiology, case fatality rate (CFR) – or sometimes more accurately case-fatality risk – is the proportion of people who have been diagnosed with a certain disease and end up dying of it. Unlike a disease's mortality rate, the CFR does ...
of typhoid fever was 10–20%. Today, with prompt treatment, it is less than 1%, but 3–5% of people who are infected develop a chronic infection in the gall bladder. Since ''S. enterica'' subsp. enterica serovar Typhi is human-restricted, these chronic carriers become the crucial reservoir, which can persist for decades for further spread of the disease, further complicating its identification and treatment. Lately, the study of ''S. enterica'' subsp. enterica serovar Typhi associated with a large outbreak and a carrier at the genome level provides new insight into the pathogenesis of the pathogen.
In industrialized nations, water sanitation and food handling improvements have reduced the number of typhoid cases. Third world nations have the highest rates. People in these areas often lack access to clean water, proper sanitation systems, and proper healthcare facilities. In these areas, such access to basic public-health needs is not expected in the near future.
In 2004–2005, an outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
resulted in more than 42,000 cases and 214 deaths. Since November 2016, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
has had an outbreak of extensively drug-resistant
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, ...
(XDR) typhoid fever.
In Europe, a report based on data for 2017 retrieved from The European Surveillance System (TESSy) on the distribution of confirmed typhoid and paratyphoid fever
Paratyphoid fever, also known simply as paratyphoid, is a bacterial infection caused by one of three types of '' Salmonella enterica''. Symptoms usually begin 6–30 days after exposure and are the same as those of typhoid fever. Often, a gradu ...
cases found that 22 EU/EEA countries reported a total of 1,098 cases, 90.9% of which were travel-related, mainly acquired during travel to South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
.Outbreaks
*Plague of Athens
The Plague of Athens (, ) was an epidemic that devastated the city-state of Athens in ancient Greece during the second year (430 BC) of the Peloponnesian War when an Athenian victory still seemed within reach. The plague killed an estimated 75, ...
(suspected)
* Cocoliztli epidemics (suspected)
* "Burning Fever" outbreak among indigenous Americans. Between 1607 and 1624, 85% of the population at the James River
The James River is a river in Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows from the confluence of the Cowpasture and Jackson Rivers in Botetourt County U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowli ...
died from a typhoid epidemic. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
estimates the death toll was over 6,000 during this time.
* Maidstone
Maidstone is the largest Town status in the United Kingdom, town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, l ...
, Kent outbreak in 1897–1898: 1,847 patients were recorded to have typhoid fever. This outbreak is notable because it was the first time a typhoid vaccine was deployed during a civilian outbreak. Almoth Edward Wright's vaccine was offered to 200 healthcare providers, and of the 84 individuals who received the vaccine, none developed typhoid whereas 4 who had not been vaccinated became ill.
* American army in the Spanish-American war: government records estimate over 21,000 troops had typhoid, resulting in 2,200 deaths.
* In 1902, guests at mayoral banquets in Southampton and Winchester, England became ill and four died, including the Dean of Winchester, after consuming oysters. The infection was due to oysters sourced from Emsworth, where the oyster beds had been contaminated with raw sewage.
* Jamaica Plain
Jamaica Plain is a Neighborhoods in Boston, neighborhood of in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Settled by Puritans seeking farmland to the south, it was originally part of Roxbury, Massachusetts, Roxbury. The community seceded from Roxbur ...
neighborhood, Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
in 1908 – linked to milk delivery. See the history section, "carriers" for further details.
* Outbreak in upper-class New Yorkers who employed Mary Mallon
Mary Mallon (September 23, 1869 – November 11, 1938), commonly known as Typhoid Mary, was an Irish Americans, Irish-born American cook who is believed to have infected between 51 and 122 people with typhoid fever. The infections caused ...
– 51 cases and 3 deaths from 1907 to 1915.
* Aberdeen
Aberdeen ( ; ; ) is a port city in North East Scotland, and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, third most populous Cities of Scotland, Scottish city. Historically, Aberdeen was within the historic county of Aberdeensh ...
, Scotland, in summer 1964 – traced back to contaminated canned beef sourced from Argentina sold in markets. More than 500 patients were quarantined in the hospital for a minimum of four weeks, and the outbreak was contained without any deaths.
* Dushanbe
Dushanbe is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 1,564,700, with this population being largely Tajiks, Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe, and from 1929 to 1961 as St ...
, Tajikistan, in 1996–1997: 10,677 cases reported, 108 deaths.
* Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ), formerly named Léopoldville from 1881–1966 (), is the Capital city, capital and Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kinshasa is one of the world's fastest-grow ...
, Democratic Republic of the Congo, in 2004: 43,000 cases and over 200 deaths. A prospective study of specimens collected in the same region between 2007 and 2011 revealed about one-third of samples obtained from patient samples were resistant to multiple antibiotics.
* Kampala
Kampala (, ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Uganda. The city proper has a population of 1,875,834 (2024) and is divided into the five political divisions of Kampala Central Division, Kampala, Kawempe Division, Kawempe, Makindy ...
, Uganda in 2015: 10,230 cases reported.
History
Early descriptions
Theplague of Athens
The Plague of Athens (, ) was an epidemic that devastated the city-state of Athens in ancient Greece during the second year (430 BC) of the Peloponnesian War when an Athenian victory still seemed within reach. The plague killed an estimated 75, ...
, during the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, was most likely an outbreak of typhoid fever. During the war, Athenians
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
retreated into a walled-in city to escape attack from the Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
ns. This massive influx of humans into a concentrated space overwhelmed the water supply and waste infrastructure, likely leading to unsanitary conditions as fresh water became harder to obtain and waste became more difficult to collect and remove beyond the city walls. In 2006, examining the remains of a mass burial site from Athens from around the time of the plague (~430 B.C.) revealed that fragments of DNA similar to that of modern-day ''S.'' Typhi were detected, whereas ''Yersinia pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly ''Pasteurella pestis'') is a Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, non-motile bacteria, non-motile, coccobacillus Bacteria, bacterium without Endospore, spores. It is related to pathogens ''Yer ...
'' (plague), '' Rickettsia prowazekii'' (typhus), ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
'', cowpox virus
Cowpox is an infectious disease caused by Cowpox virus (CPXV). It presents with large vesicle (dermatology), blisters in the skin, a fever and lymphadenopathy, swollen glands, historically typically following contact with an infected cow, though ...
, and '' Bartonella henselae'' were not detected in any of the remains tested.
Definition and evidence of transmission
The French doctors Pierre-Fidele Bretonneau and Pierre-Charles-Alexandre Louis are credited with describing typhoid fever as a specific disease, unique fromtyphus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
. Both doctors performed autopsies on individuals who died in Paris due to fever – and indicated that many had lesions on the Peyer's patch
Peyer's patches or aggregated lymphoid nodules are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer.
* Reprinted as:
* Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (cl ...
es which correlated with distinct symptoms before death. British medics were skeptical of the differentiation between typhoid and typhus because both were endemic to Britain at that time. However, in France, only typhoid was present circulating in the population. Pierre-Charlles-Alexandre Louis also performed case studies and statistical analysis to demonstrate that typhoid was contagious – and that persons who already had the disease seemed to be protected. Afterward, several American doctors confirmed these findings, and then Sir William Jenner convinced any remaining skeptics that typhoid is a specific disease recognizable by lesions in the Peyer's patches by examining sixty-six autopsies from fever patients and concluding that the symptoms of headaches, diarrhea, rash spots, and abdominal pain were present only in patients who were found to have intestinal lesions after death; these observations solidified the association of the disease with the intestinal tract and gave the first clue to the route of transmission.
In 1847, William Budd learned of an epidemic of typhoid fever in Clifton, and identified that all 13 of 34 residents who had contracted the disease drew their drinking water from the same well. Notably, this observation was two years before John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology and early germ theory, in part because of hi ...
first published an early version of his theory that contaminated water was the central conduit for transmitting cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
. Budd later became health officer of Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
ensured a clean water supply, and documented further evidence of typhoid as a water-borne illness throughout his career.
Cause
Polish scientist Tadeusz Browicz described a short bacillus in the organs and feces of typhoid victims in 1874. Browicz was able to isolate and grow the bacilli but did not go as far as to insinuate or prove that they caused the disease. In April 1880, three months before Eberth's publication, Edwin Klebs described short and filamentous bacilli in thePeyer's patch
Peyer's patches or aggregated lymphoid nodules are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer.
* Reprinted as:
* Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (cl ...
es in typhoid victims. The bacterium's role in disease was speculated but not confirmed.
In 1880, Karl Joseph Eberth described a bacillus that he suspected was the cause of typhoid. Eberth is given credit for discovering the bacterium definitively by successfully isolating the same bacterium from 18 of 40 typhoid victims and failing to discover the bacterium present in any "control" victims of other diseases. In 1884, pathologist Georg Theodor August Gaffky (1850–1918) confirmed Eberth's findings. Gaffky isolated the same bacterium as Eberth from the spleen of a typhoid victim, and was able to grow the bacterium on solid media. The organism was given names such as Eberth's bacillus, ''Eberthella'' Typhi, and Gaffky-Eberth bacillus. Today, the bacillus that causes typhoid fever goes by the scientific name ''Salmonella enterica
''Salmonella enterica'' (formerly ''Salmonella choleraesuis'') is a rod-shaped, flagellate, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus ''Salmonella''. It is divided into six subspecies, arizonae (IIIa), diarizonae ...
'' serovar Typhi.
Chlorination of water
Most developed countries had declining rates of typhoid fever throughout the first half of the 20th century due to vaccinations and advances in public sanitation and hygiene. In 1893, attempts were made to chlorinate the water supply inHamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
, Germany, and in 1897 Maidstone
Maidstone is the largest Town status in the United Kingdom, town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, l ...
, England, was the first town to have its entire water supply chlorinated. In 1905, following an outbreak of typhoid fever, the City of Lincoln, England
Lincoln () is a cathedral city and non-metropolitan district, district in Lincolnshire, England, of which it is the county town. In the 2021 Census, the city's district had a population of 103,813. The 2021 census gave the Lincoln Urban Area, u ...
, instituted permanent water chlorination. The first permanent disinfection of drinking water in the US was made in 1908 to the Jersey City, New Jersey
Jersey City is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, second-most populous
, water supply. Credit for the decision to build the chlorination system has been given to John L. Leal. The chlorination facility was designed by George W. Fuller.
Outbreaks in traveling military groups led to the creation of the Lyster bag in 1915: a bag with a faucet that can be hung from a tree or pole, filled with water, and comes with a chlorination tablet to drop into the water. The Lyster bag was essential for the survival of American soldiers in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
.
Direct transmission and carriers
 There were several occurrences of milk delivery men spreading typhoid fever throughout the communities they served. Although typhoid is not spread through milk itself, there were several examples of milk distributors in many locations watering their milk down with contaminated water, or cleaning the glass bottles the milk was placed in with contaminated water.
There were several occurrences of milk delivery men spreading typhoid fever throughout the communities they served. Although typhoid is not spread through milk itself, there were several examples of milk distributors in many locations watering their milk down with contaminated water, or cleaning the glass bottles the milk was placed in with contaminated water. Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
had two such cases around the turn of the 20th century. In 1899, there were 24 cases of typhoid traced to a single milkman, whose wife had died of typhoid fever a week before the outbreak. In 1908, J.J. Fallon, who was also a milkman, died of typhoid fever. Following his death and confirmation of the typhoid fever diagnosis, the city conducted an investigation of typhoid symptoms and cases along his route and found evidence of a significant outbreak. A month after the outbreak was first reported, the ''Boston Globe'' published a short statement declaring the outbreak over, stating " Jamaica Plain there is a slight increase, the total being 272 cases. Throughout the city, there is a total of 348 cases." There was at least one death reported during this outbreak: Mrs. Sophia S. Engstrom, aged 46. Typhoid continued to ravage the Jamaica Plain
Jamaica Plain is a Neighborhoods in Boston, neighborhood of in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Settled by Puritans seeking farmland to the south, it was originally part of Roxbury, Massachusetts, Roxbury. The community seceded from Roxbur ...
neighborhood in particular throughout 1908, and several more people were reported dead due to typhoid fever, although these cases were not explicitly linked to the outbreak. The Jamaica Plain neighborhood at that time was home to many working-class and poor immigrants, mostly from Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
.
The most notorious carrier of typhoid fever, but by no means the most destructive, was Mary Mallon
Mary Mallon (September 23, 1869 – November 11, 1938), commonly known as Typhoid Mary, was an Irish Americans, Irish-born American cook who is believed to have infected between 51 and 122 people with typhoid fever. The infections caused ...
, known as Typhoid Mary. Although other cases of human-to-human spread of typhoid were known at the time, the concept of an asymptomatic carrier, who was able to transmit disease, had only been hypothesized and not yet identified or proven. Mary Mallon became the first known example of an asymptomatic carrier
An asymptomatic carrier is a person or other organism that has become infected with a pathogen, but shows no signs or symptoms.
Although unaffected by the pathogen, carriers can transmit it to others or develop symptoms in later stages of the d ...
of an infectious disease, making typhoid fever the first known disease being transmissible through asymptomatic hosts. The cases and deaths caused by Mallon were mainly upper-class families in New York City. At the time of Mallon's tenure as a personal cook for upper-class families, New York City reported 3,000 to 4,500 cases of typhoid fever annually. In the summer of 1906, two daughters of a wealthy family and maids working in their home became ill with typhoid fever. After investigating their home water sources and ruling out water contamination, the family hired civil engineer George Soper to conduct an investigation of the possible source of typhoid fever in the home. Soper described himself as an "epidemic fighter". His investigation ruled out many sources of food, and led him to question if the cook the family hired just prior to their household outbreak, Mallon, was the source. Since she had already left and begun employment elsewhere, he proceeded to track her down in order to obtain a stool sample. When he was able to finally meet Mallon in person he described her by saying "Mary had a good figure and might have been called athletic had she not been a little too heavy." In recounts of Soper's pursuit of Mallon, his only remorse appears to be that he was not given enough credit for his relentless pursuit and publication of her personal identifying information, stating that the media "rob me of whatever credit belongs to the discovery of the first typhoid fever carrier to be found in America." Ultimately, 51 cases and 3 deaths were suspected to be caused by Mallon.
In 1924, the city of Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
, experienced an outbreak of typhoid fever, consisting of 26 cases and 5 deaths, all deaths due to intestinal hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
. All cases were concluded to be due to a single milk farm worker, who was shedding large amounts of the typhoid pathogen in his urine. Misidentification of the disease, due to inaccurate Widal test results, delayed identification of the carrier and proper treatment. Ultimately, it took four samplings of different secretions from all of the dairy workers in order to successfully identify the carrier. Upon discovery, the dairy worker was forcibly quarantined for seven weeks, and regular samples were taken, most of the time the stool samples yielding no typhoid and often the urine yielding the pathogen. The carrier was reported as being 72 years old and appearing in excellent health with no symptoms. Pharmaceutical treatment decreased the amount of bacteria secreted, however, the infection was never fully cleared from the urine, and the carrier was released "under orders never again to engage in the handling of foods for human consumption." At the time of release, the authors noted "for more than fifty years he has earned his living chiefly by milking cows and knows little of other forms of labor, it must be expected that the closest surveillance will be necessary to make certain that he does not again engage in this occupation."
Overall, in the early 20th century the medical profession began to identify disease carriers and evidence of transmission independent of water contamination. In a 1933 American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is an American professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. This medical association was founded in 1847 and is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was 271,660 ...
publication, physicians' treatment of asymptomatic carriers is best summarized by the opening line "Carriers of typhoid bacilli are a menace". Within the same publication, the first official estimate of typhoid carriers is given: 2–5% of all typhoid patients, and distinguished between temporary carriers and chronic carriers. The authors further estimate that there are four to five chronic female carriers to every one male carrier, although offered no data to explain this assertion of a gender difference in the rate of typhoid carriers. As far as treatment, the authors suggest: "When recognized, carriers must be instructed as to the disposal of excreta as well as to the importance of personal cleanliness. They should be forbidden to handle food or drink intended for others, and their movements and whereabouts must be reported to the public health officers".
 Today, typhoid carriers exist all over the world, but the highest incidence of
Today, typhoid carriers exist all over the world, but the highest incidence of asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
infection is likely to occur in South/Southeast Asian and Sub-Saharan countries. The Los Angeles County department of public health tracks typhoid carriers and reports the number of carriers identified within the county yearly; between 2006 and 2016 0–4 new cases of typhoid carriers were identified per year. Cases of typhoid fever must be reported within one working day from identification. As of 2018, chronic typhoid carriers must sign a "Carrier Agreement" and are required to test for typhoid shedding twice yearly, ideally every 6 months. Carriers may be released from their agreements upon fulfilling "release" requirements, based on completion of a personalized treatment plan designed with medical professionals. Fecal or gallbladder carrier release requirements: 6 consecutive negative feces and urine specimens submitted at 1-month or greater intervals beginning at least 7 days after completion of therapy. Urinary or kidney carrier release requirements: 6 consecutive negative urine specimens submitted at 1-month or greater intervals beginning at least 7 days after completion of therapy.
Due to the nature of asymptomatic cases, many questions remain about how individuals can tolerate infection for long periods, how to identify such cases, and efficient options for treatment. Researchers are working to understand asymptomatic infection with ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
'' species by studying infections in laboratory animals, which will ultimately lead to improved prevention and treatment options for typhoid carriers. In 2002, John Gunn described the ability of ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
'' sp. to form biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
s on gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s in mice, providing a model for studying carriage in the gallbladder. Denise Monack and Stanley Falkow described a mouse model of asymptomatic intestinal and systemic infection in 2004, and Monack went on to demonstrate that a subpopulation of superspreaders are responsible for the majority of transmission to new hosts, following the 80/20 rule of disease transmission, and that the intestinal microbiota likely plays a role in transmission. Monack's mouse model allows long-term carriage of ''Salmonella'' in mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
and liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
.
Vaccine development
 British bacteriologist Almroth Edward Wright first developed an effective typhoid vaccine at the Army Medical School in Netley,
British bacteriologist Almroth Edward Wright first developed an effective typhoid vaccine at the Army Medical School in Netley, Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Berkshire to the north, Surrey and West Sussex to the east, the Isle of Wight across the Solent to the south, ...
. It was introduced in 1896 and used successfully by the British during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic and ...
in South Africa. At that time, typhoid often killed more soldiers at war than were lost due to enemy combat. Wright further developed his vaccine at a newly opened research department at St Mary's Hospital Medical School in London in 1902, where he established a method for measuring protective substances (opsonin
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed (i.e. ...
) in human blood. Wright's version of the typhoid vaccine was produced by growing the bacterium at body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
in broth, then heating the bacteria to 60 °C to "heat inactivate" the pathogen, killing it, while keeping the surface antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
s intact. The heat-killed bacteria was then injected into a patient. To show evidence of the vaccine's efficacy, Wright then collected serum samples from patients several weeks post-vaccination, and tested their serum's ability to agglutinate live typhoid bacteria. A "positive" result was represented by clumping of bacteria, indicating that the body was producing anti-serum (now called antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
) against the pathogen.
Citing the example of the Second Boer War, during which many soldiers died from easily preventable diseases, Wright convinced the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
that 10 million vaccine doses should be produced for the troops being sent to the Western Front, thereby saving up to half a million lives during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The British Army was the only combatant at the outbreak of the war to have its troops fully immunized against the bacterium. For the first time, their casualties due to combat exceeded those from disease.
In 1909, Frederick F. Russell, a U.S. Army physician, adopted Wright's typhoid vaccine for use with the Army, and two years later, his vaccination program became the first in which an entire army was immunized. It eliminated typhoid as a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in the U.S. military. Typhoid vaccination for members of the American military became mandatory in 1911. Before the vaccine, the rate of typhoid fever in the military was 14,000 or greater per 100,000 soldiers. By World War I, the rate of typhoid in American soldiers was 37 per 100,000.
During the Second World War, the United States Army authorized the use of a trivalent vaccine – containing heat-inactivated Typhoid, Paratyphi A and Paratyphi B pathogens.
In 1934, the discovery of the Vi capsular antigen by Arthur Felix and Miss S. R. Margaret Pitt enabled the development of the safer Vi Antigen vaccine – which is widely in use today. Arthur Felix and Margaret Pitt also isolated the strain Ty2, which became the parent strain of Ty21a, the strain used as a live-attenuated vaccine for typhoid fever today.
Antibiotics and resistance
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
was isolated from ''Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'', from στρεπτός (''streptós''), meaning "twisted", and μύκης (''múkés''), meaning "fungus", is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of ''St ...
'' by David Gotlieb during the 1940s. In 1948, American army doctors tested its efficacy in treating typhoid patients in Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur (KL), officially the Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur, is the capital city and a Federal Territories of Malaysia, federal territory of Malaysia. It is the largest city in the country, covering an area of with a census population ...
, Malaysia. Individuals who received a full course of treatment cleared the infection, whereas patients given a lower dose had a relapse. Asymptomatic carriers continued to shed bacilli despite chloramphenicol treatment – only ill patients were improved with chloramphenicol. Resistance to chloramphenicol became frequent in Southeast Asia by the 1950s, and today chloramphenicol is only used as a last resort due to the high prevalence of resistance.
Terminology
The disease has been referred to by various names, often associated with symptoms, such as gastric fever, enteric fever, abdominal typhus, infantile remittent fever, slow fever, nervous fever, phytogenic fever, drain fever, and low fever.Society and culture
Notable people
*Emperor Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
of Rome – suspected based on historical record but not confirmed. He had either a liver abscess or typhoid fever, and survived by using ice baths and cold compresses as a means of treatment for his fever. The idea for this treatment was provided by Greek physician Antonius Musa.
* Albert, Prince Consort
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (Franz August Karl Albert Emanuel; 26 August 1819 – 14 December 1861) was the husband of Queen Victoria. As such, he was consort of the British monarch from their marriage on 10 February 1840 until his ...
, husband of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
of the United Kingdom, died 24 days after the first record of "feeling horribly ill". Died 14 December 1861 after suffering loss of appetite, insomnia, fever, chills, profuse sweating, vomiting, rash spots, delusions, inability to recognize family members, worsening rash on abdomen, a change in tongue color, then finally a state of extreme fatigue. Attending physician William Jenner, an expert on typhoid fever at the time, diagnosed him.
* Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second child ...
of the UK, son of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
, while still Prince of Wales, had a near-fatal case of typhoid fever.
* Tsar Nicholas II of Russia, survived, illness was circa 1900–1901.
* Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands
Wilhelmina (; Wilhelmina Helena Pauline Maria; 31 August 1880 – 28 November 1962) was List of monarchs of the Netherlands, Queen of the Netherlands from 1890 until her abdication in 1948. She reigned for nearly 58 years, making her the longest- ...
may have had an abortion in 1902 because of a typhoid infection she survived.
* William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was the ninth president of the United States, serving from March 4 to April 4, 1841, the shortest presidency in U.S. history. He was also the first U.S. president to die in office, causin ...
, the ninth President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
of the United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguo ...
, died 32 days into his term, in 1841. This is the shortest term served by a United States President.
* Wilbur Wright
The Wright brothers, Orville Wright (August 19, 1871 – January 30, 1948) and Wilbur Wright (April 16, 1867 – May 30, 1912), were American aviation List of aviation pioneers, pioneers generally credited with inventing, building, and flyin ...
, co-inventor of the airplane with his brother Orville, died from typhoid in 1912 at the age of 45. Orville had typhoid in 1896, during which time Wilbur would read aloud to him, books by Otto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making t ...
, a German pioneer in human flight. This started the two men on their own pursuit of creating an airplane.
* Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas (né Douglass; April 23, 1813 – June 3, 1861) was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. As a United States Senate, U.S. senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party (United States) ...
, a political opponent of Abraham Lincoln in 1858 and 1860, died of typhoid on June 3, 1861.
* Ignacio Zaragoza
Ignacio Zaragoza Seguín (March 24, 1829 – September 8, 1862) was a Mexican Army officer and politician. He is best known for leading a Mexican army of 3,791 men which defeated a 5,730-strong force of French troops at the battle of Puebla ...
, a Mexican general and politician, died at the age of 33 of typhoid fever on September 8, 1862.
* Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; ; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical period (music), Classical and early Romantic music, Romantic eras. Despite his short life, Schubert left behind a List of compositions ...
, songwriter and composer died of typhoid at age 31 on November 19, 1828.
* William Wallace Lincoln, the son of US president Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
and Mary Todd Lincoln, died at the age of 11 years of typhoid in 1862.
* Princess Leopoldina of Brazil, daughter of Emperor Pedro II, died of typhoid in 1871.
* Martha Bulloch Roosevelt, mother of president Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
and paternal grandmother of Eleanor Roosevelt
Anna Eleanor Roosevelt ( ; October 11, 1884November 7, 1962) was an American political figure, diplomat, and activist. She was the longest-serving First Lady of the United States, first lady of the United States, during her husband Franklin D ...
, died of typhoid fever in 1884.
* Mary Mallon
Mary Mallon (September 23, 1869 – November 11, 1938), commonly known as Typhoid Mary, was an Irish Americans, Irish-born American cook who is believed to have infected between 51 and 122 people with typhoid fever. The infections caused ...
, "Typhoid Mary" – see history section, "carriers" for further details
* Leland Stanford Jr., son of American tycoon and politician A. Leland Stanford
Amasa Leland Stanford (March 9, 1824June 21, 1893) was an American attorney, industrialist, philanthropist, and Republican Party (United States), Republican Party politician from Watervliet, New York. He served as the eighth governor of Calif ...
and eponym of Leland Stanford Junior University, died of typhoid fever in 1884 at the age of 15.
* Three of Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, Fermentation, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the la ...
's five children died of typhoid fever.
* Gerard Manley Hopkins
Gerard Manley Hopkins (28 July 1844 – 8 June 1889) was an English poet and Society of Jesus, Jesuit priest, whose posthumous fame places him among the leading English poets. His Prosody (linguistics), prosody – notably his concept of sprung ...
, an English poet, died of typhoid fever in 1889.
* Lizzie van Zyl, South African child inmate of the Bloemfontein
Bloemfontein ( ; ), also known as Bloem, is the capital and the largest city of the Free State (province), Free State province in South Africa. It is often, and has been traditionally, referred to as the country's "judicial capital", alongsi ...
concentration camp during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic and ...
, died of typhoid fever in 1901.
* Dr HJH 'Tup' Scott, captain of the 1886 Australian cricket team that toured England, died of typhoid in 1910.
* Arnold Bennett
Enoch Arnold Bennett (27 May 1867 – 27 March 1931) was an English author, best known as a novelist, who wrote prolifically. Between the 1890s and the 1930s he completed 34 novels, seven volumes of short stories, 13 plays (some in collaborati ...
, English novelist, died in 1932 of typhoid, two months after drinking a glass of water in a Paris hotel to prove it was safe.
* Hakaru Hashimoto, a Japanese medical scientist, died of typhoid fever in 1934. Hakaru Hashimoto#Biography
* John Buford
John Buford Jr. (March 4, 1826 – December 16, 1863) was a United States Army cavalry officer. He fought for the Union Army, Union during the American Civil War, rising to the rank of brigadier general. Buford is best known for his actions in th ...
, Union cavalry officer during the Civil War, died of typhoid fever on December 16, 1863.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * {{Authority control Conditions diagnosed by stool test Intestinal infectious diseases Vaccine-preventable diseases Waterborne diseases Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate