|
Nalidixic Acid
Nalidixic acid (tradenames Nevigramon, NegGram, Wintomylon and WIN 18,320) is the first of the synthetic quinolone antibiotics. In a technical sense, it is a naphthyridone, not a quinolone: its ring structure is a 1,8-naphthyridine nucleus that contains two nitrogen atoms, unlike quinoline, which has a single nitrogen atom. Synthetic quinolone antibiotics were discovered by George Lesher and coworkers as a byproduct of chloroquine manufacture in the 1960s; nalidixic acid itself was used clinically, starting in 1967. Nalidixic acid is effective primarily against Gram-negative bacteria, with minor anti-Gram-positive activity. In lower concentrations, it acts in a bacteriostatic manner; that is, it inhibits growth and reproduction. In higher concentrations, it is bactericidal, meaning that it kills bacteria instead of merely inhibiting their growth. It has historically been used for treating urinary tract infections, caused, for example, by ''Escherichia coli'', ''Proteus'', ''Shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition where unusually high amount of glucose is present in blood. It is defined as blood glucose level exceeding 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL) after fasting for 8 hours or 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) 2 hours after eating. Blood glucose level indication Patients with diabetes are oriented to avoid exceeding the recommended postprandial threshold of 160 mg/dL (8.89 mmol/L) for optimal glycemic control. Values of blood glucose higher than 160 mg/dL are classified as 'very high' hyperglycemia, a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose (glucotoxicity) circulates in the blood plasma. These values are higher than the renal threshold of 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) up to which glucose reabsorption is preserved at physiological rates and insulin therapy is not necessary. Blood glucose values higher than the cutoff level of 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) are used to diagnose T2DM and strongly associated with metabolic disturbances, although symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amfonelic Acid
Amfonelic acid (AFA; WIN 25,978) is a research chemical and dopaminergic stimulant with antibiotic properties. Limited clinical trials have been conducted, and it is primarily used in scientific research. History The stimulant properties of AFA were discovered incidentally at Sterling-Winthrop during research on the antibiotic nalidixic acid. In addition to behaving as an antibiotic, it was found that many derivatives of nalidixic acid have either stimulant or depressant effects on the central nervous system. Researchers at Sterling-Winthrop found that AFA had a higher potency and therapeutic index than cocaine or amphetamine, leading to further study of the drug. A small number of clinical trials were held in the 1970s, but clinical evaluation of AFA was discontinued after it was found that AFA exacerbated psychotic symptoms in schizophrenic patients and produced undesirable stimulant properties in geriatric depressives. AFA remains a widely used pharmacological tool for study o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of '' Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from ), and suffixed by the (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staphylococcus bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The 348 members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches and hosts. Their ease of culture ''in vitro'' and availability of an increasing number of ''Pseudomonas'' strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include '' P. aeruginosa'' in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen '' P. syringae'', the soil bacterium '' P. putida'', and the plant growth-promoting '' P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae'', and '' P. graminis''. Because of their widespread occurrence in water and plant seeds such as dicots, the pseudomonads were observed early in the history of microbiology. The generic name ''Pseudomonas'' created for these organisms was defined in rather vague terms by Walter Migula i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
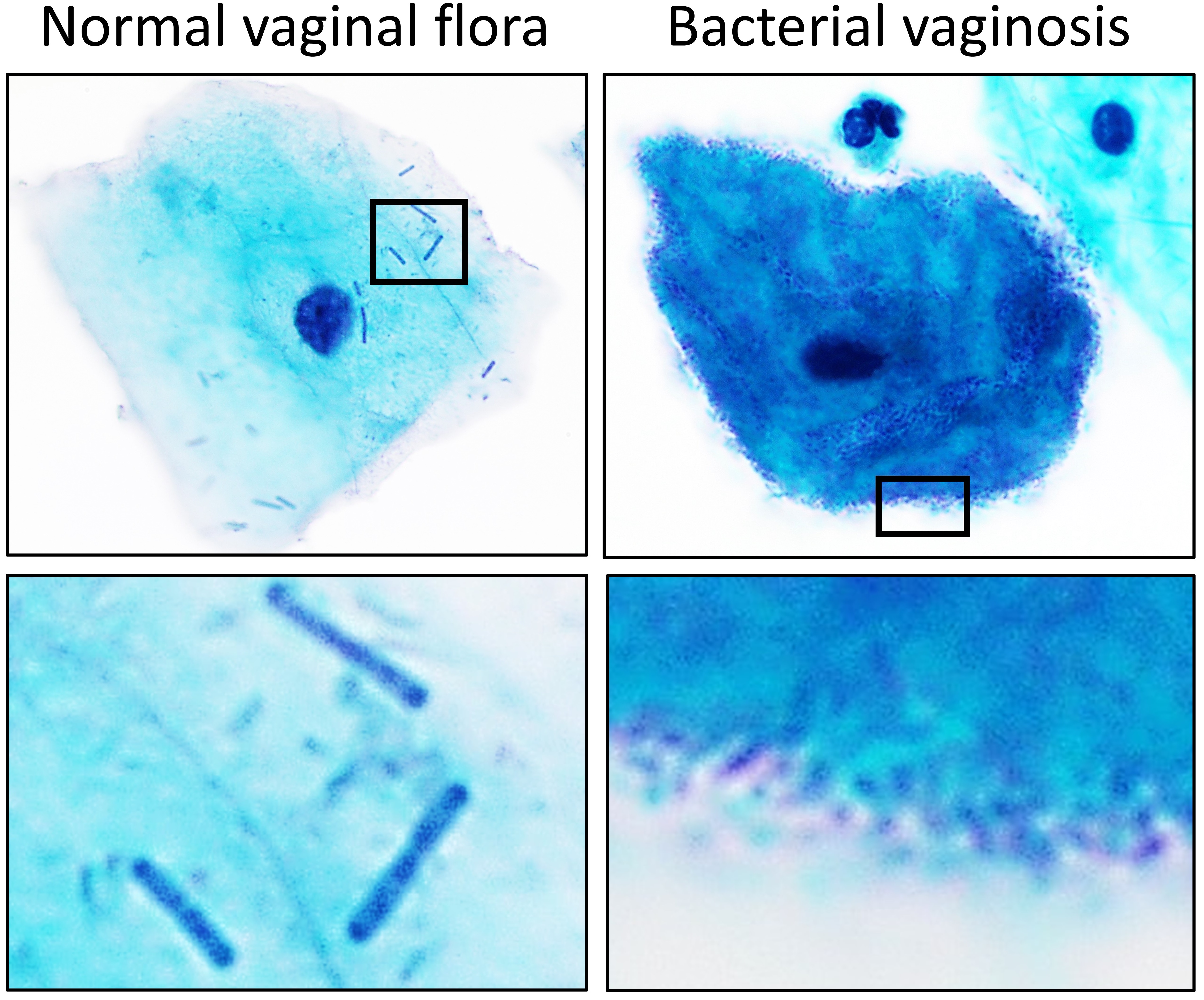
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist in harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacteria
''Bifidobacterium'' is a genus of gram-positive, nonmotile, often branched anaerobic bacteria. They are ubiquitous inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract though strains have been isolated from the vagina and mouth ('' B. dentium'') of mammals, including humans. Bifidobacteria are one of the major genera of bacteria that make up the gastrointestinal tract microbiota in mammals. Some bifidobacteria are used as probiotics. Before the 1960s, ''Bifidobacterium'' species were collectively referred to as ''Lactobacillus bifidus''. History In 1899, Henri Tissier, a French pediatrician at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, isolated a bacterium characterised by a Y-shaped morphology ("bifid") in the intestinal microbiota of breast-fed infants and named it "bifidus". In 1907, Élie Metchnikoff, deputy director at the Pasteur Institute, propounded the theory that lactic acid bacteria are beneficial to human health. Metchnikoff observed that the longevity of Bulgarians was the result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilus
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of the wide range of shapes they occasionally assume. These organisms inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. The genus includes commensal organisms along with some significant pathogenic species such as '' H. influenzae''—a cause of sepsis and bacterial meningitis in young children—and '' H. ducreyi'', the causative agent of chancroid. All members are either aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. This genus has been found to be part of the salivary microbiome. Metabolism Most members of the genus ''Haemophilus'' require at least one of these blood factors for growth: hemin (sometimes called 'X-factor') and/or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD; sometimes called 'V-fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium
''Clostridium'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive bacteria. Species of ''Clostridium'' inhabit soils and the intestinal tracts of animals, including humans. This genus includes several significant human pathogens, including the causative agents of botulism and tetanus. It also formerly included an important cause of diarrhea, '' Clostridioides difficile'', which was reclassified into the '' Clostridioides'' genus in 2016. History In the late 1700s, Germany experienced several outbreaks of an illness connected to eating specific sausages. In 1817, the German neurologist Justinus Kerner detected rod-shaped cells in his investigations into this so-called sausage poisoning. In 1897, the Belgian biology professor Emile van Ermengem published his finding of an endospore-forming organism he isolated from spoiled ham. Biologists classified van Ermengem's discovery along with other known gram-positive spore formers in the genus ''Bacillus''. This classification presented proble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeromonas Hydrophila
''Aeromonas hydrophila'' is a heterotrophic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium mainly found in areas with a warm climate. This bacterium can be found in fresh or brackish water. It can survive in aerobic and anaerobic environments, and can digest materials such as gelatin and hemoglobin. ''A. hydrophila'' was isolated from humans and animals in the 1950s. It is the best known of the species of '' Aeromonas''. It is resistant to most common antibiotics and cold temperatures and is oxidase- and indole-positive. ''Aeromonas hydrophila'' also has a symbiotic relationship as gut flora inside of certain leeches, such as ''Hirudo medicinalis''. Structure ''Aeromonas hydrophila'' bacteria are Gram-negative, straight rods with rounded ends (bacilli to coccibacilli shape) usually from 0.3 to 1.0 μm in width and 1.0 to 3.0 μm in length. They can grow at temperatures as low as 4 °C. These bacteria are motile by a polar flagellum. Pathology Because of its structure, it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, or consciousness. Symptoms vary widely. Some seizures involve subtle changes, such as brief lapses in attention or awareness (as seen in absence seizures), while others cause generalized convulsions with loss of consciousness ( tonic–clonic seizures). Most seizures last less than two minutes and are followed by a postictal period of confusion, fatigue, or other symptoms. A seizure lasting longer than five minutes is a medical emergency known as status epilepticus. Seizures are classified as provoked, when triggered by a known cause such as fever, head trauma, or metabolic imbalance, or unprovoked, when no immediate trigger is identified. Recurrent unprovoked seizures define the neurological condition epilepsy. Clinical features Seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Confusion
In psychology, confusion is the quality or emotional state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"''Confusion Definition'' on . is often used interchangeably with in the '' |