Types Of Cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following is a list of cancer types. 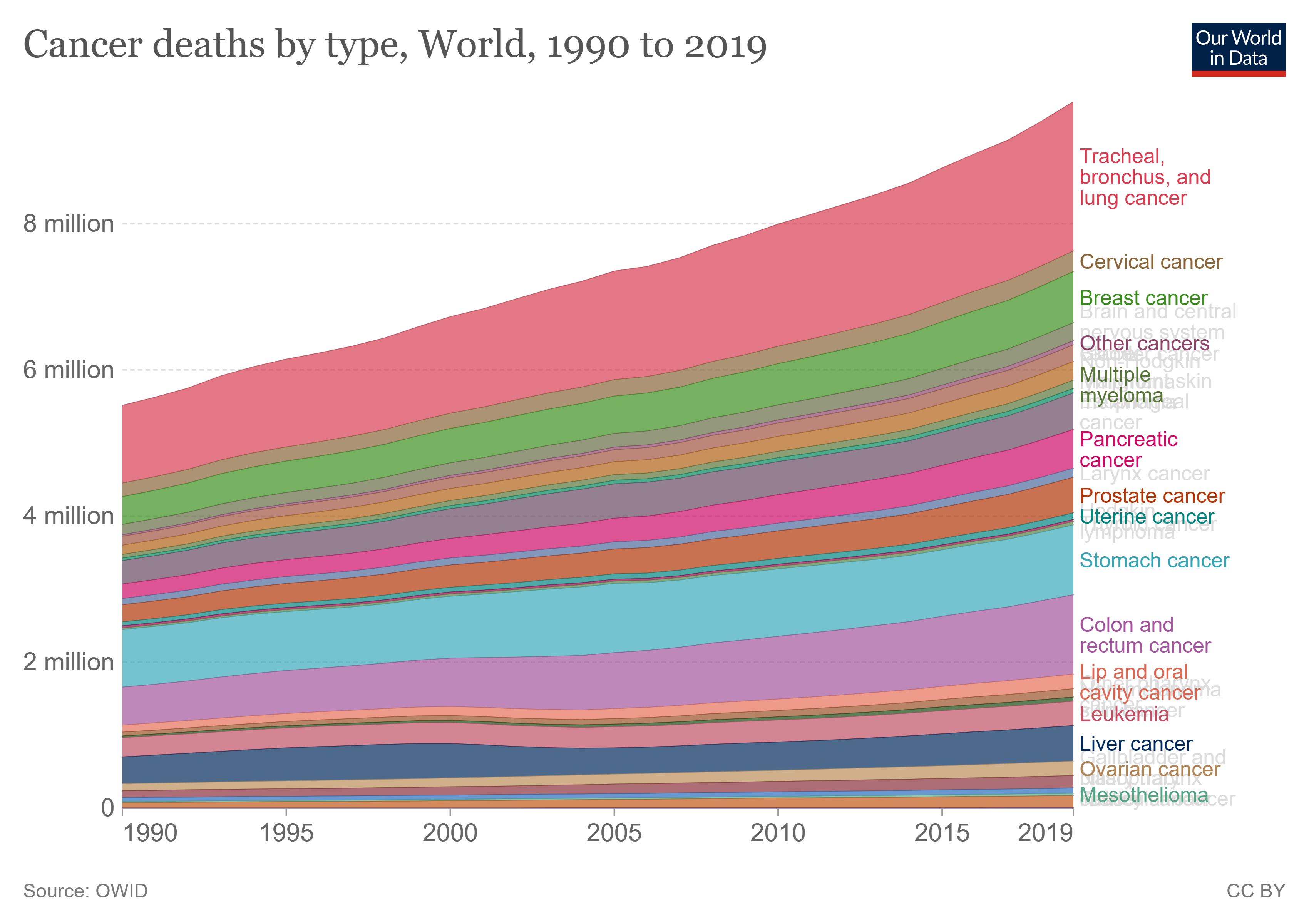 Cancers are usually named using ''-carcinoma'', ''-sarcoma'' or ''-blastoma'' as a suffix, with the Latin or Greek word for the
Cancers are usually named using ''-carcinoma'', ''-sarcoma'' or ''-blastoma'' as a suffix, with the Latin or Greek word for the
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
is a group of diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
that involve abnormal increases in the number of cells, with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Not all tumors or lumps are cancerous; benign tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of Cell (biology), cells (tumor) that does not Cancer invasion, invade neighboring tissue or Metastasis, metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to Cancer, malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally ...
s are not classified as being cancer because they do not spread to other parts of the body. There are over 100 different known cancers that affect humans.
Cancers are often described by the body part that they originated in. However, some body parts contain multiple types of tissue, so for greater precision, cancers are additionally classified by the type of cell that the tumor cells originated from. These types include:
* ''Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoder ...
'': Cancers derived from epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
cells. This group includes many of the most common cancers that occur in older adults. Nearly all cancers developing in the breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is ...
, prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
, lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
, pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, and colon are carcinomas.
* ''Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Originating from mesenchymal cells means that sarcomas are cancers of connective tissues such as bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, or vascular tissues.
Sarcom ...
'': Cancers arising from connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
(i.e. bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
, cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
, fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
, nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
), each of which develop from cells originating in mesenchymal
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
cells outside of the bone marrow.
* ''Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
'' and ''leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
'': These two classes of cancer arise from immature cells that originate in the bone marrow, and are intended to fully differentiate and mature into normal components of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
and the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
, respectively. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is the most common type of cancer in children, accounting for ~30% of cases. However, far more adults than children develop lymphoma and leukemia.
* ''Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from primordial germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cell tumors typically originate from the gonads (ovary and testis), but can arise in other areas of the body. Extragon ...
'': Cancers derived from pluripotent
Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types.
The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum ...
cells, most often presenting in the testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
or the ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
(seminoma
A seminoma is a germ cell tumor of the testicle or, more rarely, the mediastinum or other extra-gonadal locations. It is a Malignancy, malignant neoplasm and is one of the most treatable and curable cancers, with a survival rate above 95% if di ...
and dysgerminoma, respectively).
* '' Blastoma'': Cancers derived from immature "precursor" cells or embryonic tissue. Blastomas are ''generally'' more common in children (e.g. neuroblastoma, retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and 80% of retinoblastoma cas ...
, nephroblastoma, hepatoblastoma, medulloblastoma, etc.) than in older adults.
 Cancers are usually named using ''-carcinoma'', ''-sarcoma'' or ''-blastoma'' as a suffix, with the Latin or Greek word for the
Cancers are usually named using ''-carcinoma'', ''-sarcoma'' or ''-blastoma'' as a suffix, with the Latin or Greek word for the organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
or tissue of origin as the root. For example, the most common cancer of the liver parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
("hepato-" = liver), arising from malignant epithelial cells ("carcinoma"), would be called a '' hepatocarcinoma'', while a malignancy arising from primitive liver precursor cells is called a hepatoblastoma. Similarly, a cancer arising from malignant fat cells would be termed a '' liposarcoma''.
For some common cancers, the English organ name is used. For example, the most common type of breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
is called '' ductal carcinoma of the breast''.
Benign tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of Cell (biology), cells (tumor) that does not Cancer invasion, invade neighboring tissue or Metastasis, metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to Cancer, malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally ...
s (which are not cancers) are usually named using ''-oma'' as a suffix with the organ name as the root. For example, a benign tumor of smooth muscle cells is called a '' leiomyoma'' (the common name of this frequently occurring benign tumor in the uterus is '' fibroid''). Confusingly, some types of cancer use the ''-noma'' suffix, examples including melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
and seminoma
A seminoma is a germ cell tumor of the testicle or, more rarely, the mediastinum or other extra-gonadal locations. It is a Malignancy, malignant neoplasm and is one of the most treatable and curable cancers, with a survival rate above 95% if di ...
.
Some types of cancer are named for the size and shape of the cells under a microscope, such as giant cell carcinoma, spindle cell carcinoma, and small-cell carcinoma.
Bone and muscle sarcoma
* Adamantinoma *Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma is a bone sarcoma, a primary cancer composed of cells derived from transformed cells that produce cartilage. A chondrosarcoma is a member of a category of tumors of bone and soft tissue known as sarcomas. About 30% of bone sarco ...
* Chordoma
Chordoma is a rare slow-growing neoplasm (cancer) that arises from cellular remnants of the notochord in the bones of the skull base and spine. The evidence for the notochordal origin of chordoma is the location of the tumors (along the neuraxis ...
* Ewing's sarcoma
* Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma of bone
* Leiomyosarcoma
* Malignant fibrous histiocytoma
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS), also termed pleomorphic myofibrosarcoma, high-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma, and high-grade myofibrosarcoma, is characterized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a rare, poorly differentiated neopl ...
of bone/osteosarcoma
* Myxosarcoma
* Osteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchyme, mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma) and that exhi ...
* Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the neoplasm, tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts.
The four ...
Brain and nervous system
*Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord, an ...
* Brainstem glioma
* Choroid plexus carcinoma
* Cerebellar astrocytoma
* Cerebral astrocytoma
* Craniopharyngioma
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak inciden ...
* Ependymoma
An ependymoma is a tumor that arises from the ependyma, a tissue of the central nervous system. Usually, in pediatric cases the location is intracranial, while in adults it is spinal. The common location of intracranial ependymomas is the floor ...
* Ganglioneuroma
* Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
* Glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
* Hemangioblastoma
Hemangioblastomas, or haemangioblastomas, are vascular tumors of the central nervous system that originate from the vascular system, usually during middle age. Sometimes, these tumors occur in other sites such as the spinal cord and retina. They m ...
* Medulloblastoma
* Meningioma
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing ...
* Neuroblastoma
* Neurofibroma
* Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a oligodendrocyte progenitor cell, glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults (9.4% of all primary brain and central ne ...
* Paraganglioma
A paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine tumour, neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites (including the head, neck, thorax and abdomen). When the same type of tumor is found in the adrenal gland, they are referred to as a p ...
* Pineal astrocytoma
* Pineocytoma
* Pineoblastoma
* Pituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pilocytic astrocytoma
* Primary central nervous system lymphoma
*
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor is a malignant (cancerous) neural crest tumor. It is a rare tumor, usually occurring in children and young adults under 25 years of age. The overall 5 year survival rate is about 53%.
It gets its name because the ...
* Schwannoma
* Visual pathway and hypothalamic glioma
Breast
*Breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
* Ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a ...
* Inflammatory breast cancer
* Invasive ductal carcinoma
Invasive carcinoma of no special type (invasive carcinoma NST), invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) or invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS ...
* Invasive lobular carcinoma
* Tubular carcinoma
* Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast
Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast (ICCB), also termed invasive cribriform carcinoma, is a rare type of breast cancer that accounts for 0.3% to 0.6% of all carcinomas (i.e. cancers that develop from epithelial cells) in the breast. It o ...
(also termed invasive cribriform carcinoma)
* Medullary carcinoma
* Male breast cancer
Male breast cancer (MBC) is a cancer in males that originates in their breasts. Males account for less than 1% of new breast cancers with about 20,000 new cases being diagnosed
worldwide every year. Its incidence rates in males vs. females are, ...
* Phyllodes tumor
* Mammary secretory carcinoma
* Mucinous carcinoma of the breast
Mucinous carcinoma of the breast is a form of mucinous carcinoma and a breast cancer type. It is a rare form of breast cancer that accounts for 2% of breast carcinomas and most commonly occurs in postmenopausal women over 70 years old. Rare case ...
* Papillary carcinomas of the breast
Endocrine system
* Adrenocortical adenoma * Adrenocortical carcinoma * Carcinoid *Gastrinoma
Gastrinomas are neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), usually located in the duodenum or pancreas, that secrete gastrin and cause a clinical syndrome known as Zollinger–Ellison syndrome (ZES). A large number of gastrinomas develop in the pancreas or duo ...
* Glucagonoma
* Insulinoma
An insulinoma is a tumour of the pancreas that is derived from beta cells and secretes insulin. It is a rare form of a neuroendocrine tumour. Most insulinomas are benign in that they grow exclusively at their origin within the pancreas, but a m ...
* Islet cell carcinoma (endocrine pancreas)
* Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about three people per million members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous APUDoma, Primary tumor, primary neuroendocrine tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma ...
* Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome
* Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of ...
* Parathyroid cancer
* Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they relea ...
* Somatostatinoma
Somatostatinomas are a tumor of the delta cells of the endocrine pancreas that produces somatostatin. Increased levels of somatostatin inhibit pancreatic hormones and gastrointestinal hormones. Thus, somatostatinomas are associated with mild d ...
* Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck, ...
* VIPoma
A VIPoma or vipoma () is a rare endocrine tumor that overproduces vasoactive intestinal peptide (thus ''VIP'' + '' -oma''). The incidence is about 1 per 10,000,000 per year. VIPomas usually (about 90%) originate from the non-β islet cells of ...
Eye
* Conjunctival melanoma * Optic nerve glioma * Orbital lymphoma *Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and 80% of retinoblastoma cas ...
* Uveal melanoma
Uveal melanoma is a type of eye cancer in the uvea of the eye. It is traditionally classed as originating in the iris, choroid, and ciliary body, but can also be divided into class I (low metastatic risk) and class II (high metastatic risk). S ...
Gastrointestinal
* Anal cancer * Appendix cancer * Cholangiocarcinoma * Carcinoid tumor, gastrointestinal *Colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
* Duodenal cancer
* Extrahepatic bile duct cancer
* Gallbladder cancer
* Gastric (stomach) cancer
* Gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor
* Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
* Hepatoblastoma
* Hepatocellular cancer
* Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of ...
, islet cell
* Rectal cancer
* Small intestine cancer
Genitourinary and gynecologic
*Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in thei ...
* Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later sympt ...
* Choriocarcinoma
* Embryonal carcinoma
* Endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the epithelium, lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells (biology), cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first s ...
* Endodermal sinus tumor
* Extragonadal germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from primordial germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cell tumors typically originate from the gonads (ovary and testis), but can arise in other areas of the body. Extragon ...
* Fallopian tube cancer
* Gestational trophoblastic tumor
* Kidney cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, a lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include ...
* Leydig cell tumour
* Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different ...
* Ovarian epithelial cancer ( surface epithelial-stromal tumor)
* Ovarian germ cell tumor
* Penile cancer
Penile cancer, or penile carcinoma, is a cancer that develops in the skin or tissues of the penis. Symptoms may include abnormal growth, an ulcer or sore on the skin of the penis, and bleeding or foul smelling discharge.
Risk factors include phimo ...
* Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
* Renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the Proximal tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cance ...
* Renal pelvis and ureter, transitional cell cancer*
* Seminoma
A seminoma is a germ cell tumor of the testicle or, more rarely, the mediastinum or other extra-gonadal locations. It is a Malignancy, malignant neoplasm and is one of the most treatable and curable cancers, with a survival rate above 95% if di ...
* Serous tumour
* Sertoli cell tumour
* Teratoma
A teratoma is a neoplasia, tumor made up of several types of biological tissue, tissue, such as hair, muscle, Human tooth, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the tailbone (where it is known as a sacrococcygeal teratoma), ovary, or test ...
* Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.
Risk factors include an c ...
* Transitional cell cancer(urothelial carcinoma
Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and ...
)
* Ureter and renal pelvis
* Urethral cancer
Urethral cancer is a rare cancer originating from the urethra. The disease has been classified by the TNM staging system and the World Health Organization.
Symptoms include blood in the urine, lump at end of penis, or bloody penile discharge. ...
* Uterine sarcoma
* Vaginal cancer
Vaginal cancer is an extraordinarily rare form of cancer that develops in the tissue of the vagina. Primary vaginal cancer originates from the vaginal tissue – most frequently Squamous-cell carcinoma of the vagina, squamous cell carcinoma, but p ...
* Vulvar cancer
Vulvar cancer is a cancer of the vulva, the outer portion of the female genitals. It most commonly affects the labia majora. Less often, the labia minora, clitoris, or Bartholin's glands are affected. Symptoms include a lump, itchiness, changes i ...
* Wilms tumor
Wilms' tumor or Wilms tumor, also known as nephroblastoma, is a cancer of the kidneys that typically occurs in children (rarely in adults), and occurs most commonly as a renal tumor in child patients. It is named after Max Wilms, the German surge ...
(nephroblastoma)
Head and neck
*Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weigh ...
* Head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer is a general term encompassing multiple cancers that can develop in the head and neck region. These include cancers of the mouth, tongue, gums and lips (oral cancer), voice box ( laryngeal), throat ( nasopharyngeal, orophary ...
* Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), or nasopharynx cancer, is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx, most commonly in the postero-lateral nasopharynx or pharyngeal recess (fossa of Rosenmüller), accounting for 50% of cases. NPC occurs ...
* Oral cancer
Oral cancer, also known as oral cavity cancer, tongue cancer or mouth cancer, is a cancer of the lining of the lips, mouth, or upper throat. In the mouth, it most commonly starts as a painless red or white patch, that thickens, gets ulcerated ...
* Oropharyngeal cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer, also known as oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and tonsil cancer, is a disease in which abnormal cells with the potential to both grow locally and spread to other parts of the body are found in the oral cavity, in the t ...
* Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer
* Pharyngeal cancer
* Salivary gland cancer
Salivary gland tumours, or neoplasms, are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular gland, submandibular, and subling ...
* Hypopharyngeal cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer is a disease in which malignant cells grow in the hypopharynx (also known as the ''laryngopharynx'') the area where the larynx and esophagus meet.
It first forms in the outer layer (epithelium) of the hypopharynx (last part ...
Hematopoietic
* Acute biphenotypic leukemia * Acute eosinophilic leukemia *Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, ...
* Acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Sympt ...
* Acute myeloid dendritic cell leukemia
* AIDS-related lymphoma
* Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) refers to a group of non-Hodgkin lymphomas in which aberrant T cells proliferate uncontrollably. Considered as a single entity, ALCL is the most common type of peripheral lymphoma and represents ~10% of all per ...
* Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
* B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, referred to as B-PLL, is a rare blood cancer. It is a more aggressive, but still treatable, form of leukemia.
Specifically, B-PLL is a prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL) that affects prolymphocytes – immature forms ...
* Burkitt's lymphoma
Burkitt's lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa ...
* Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. In CLL, the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. In patients with CLL, B cell lymphocytes can begin to colle ...
* Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumula ...
* Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a cancer of B cells, a type of lymphocyte that is responsible for producing antibodies. It is the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among adults, with an annual incidence of 7–8 cases per 100,000 ...
* Follicular lymphoma
* Hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. The incidence of hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is 0.28-0.30 cases per 100,000 people in Europe and the United States and the pre ...
* Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
* Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named a ...
* Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
Intravascular lymphomas (IVL) are rare cancers in which malignant lymphocytes proliferate and accumulate within blood vessels. Almost all other types of lymphoma involve the proliferation and accumulation of malignant lymphocytes in lymph nodes, o ...
* Large granular lymphocytic leukemia
* Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
* Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
* Mantle cell lymphoma
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a type of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, comprising about 6% of cases. It is named for the mantle zone of the lymph nodes where it develops. The term 'mantle cell lymphoma' was first adopted by Raffe ...
* Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma
* Mast cell leukemia
* Mediastinal large B cell lymphoma
* Multiple myeloma/plasma cell neoplasm
* Myelodysplastic syndromes
* Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma
* Mycosis fungoides
* Nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma
Nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma (NMZL) is an uncommon form of marginal-zone lymphoma that can produce colonization of the follicles in the lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the ad ...
* Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredn ...
* Precursor B lymphoblastic leukemia
* Primary central nervous system lymphoma
* Primary cutaneous follicular lymphoma
* Primary cutaneous immunocytoma
* Primary effusion lymphoma
* Plasmablastic lymphoma
* Sézary syndrome
* Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
* T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
Skin
*Basal cell carcinoma
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, basalioma, or rodent ulcer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless, raised area of skin, which may be shiny with Telangiectasia, small blood vessels ru ...
* Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
* Squamous cell skin cancer
* Skin adnexal tumors (e.g. sebaceous carcinoma)
* Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
* Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about three people per million members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous APUDoma, Primary tumor, primary neuroendocrine tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma ...
* Keratoacanthoma
* Sarcomas of primary cutaneous origin (e.g. dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare locally aggressive malignant cutaneous soft-tissue sarcoma. DFSP develops in the connective tissue cells in the middle layer of the skin (dermis). Estimates of the overall occurrence of DFSP in the U ...
)
* Lymphomas of primary cutaneous origin (e.g. mycosis fungoides)
Soft Tissue Sarcoma
*Angiosarcoma
Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that starts in the endothelial cells that line the walls of blood vessels or lymphatic vessels. Since they are made from Endothelium, vascular lining, they can appear anywhere and at any age, but older ...
* Fibrosarcoma
Fibrosarcoma (fibroblastic sarcoma) is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform ...
* Liposarcoma
* Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
A malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is a form of cancer of the connective tissue surrounding peripheral nerves. Given its origin and behavior it is classified as a sarcoma. About half the cases are diagnosed in people with neurofi ...
* Synovial sarcoma
* Blastoma
Thoracic and respiratory
* Adenocarcinoma of the lung * Basaloid squamous cell lung carcinoma * Bronchial adenomas/ carcinoids * Giant-cell carcinoma of the lung *Large-cell lung carcinoma
Large-Cell Lung Carcinoma (LCLC), or Large-Cell Carcinoma (LCC) in short, is a heterogeneous group of undifferentiated malignant neoplasms that lack the cytology and architectural features of small cell carcinoma and glandular or squamous different ...
* Large cell lung carcinoma with rhabdoid phenotype
Large cell lung carcinoma with rhabdoid phenotype (LCLC-RP) is a rare histological form of lung cancer, currently classified as a variant of large-cell lung carcinoma, large cell lung carcinoma (LCLC). In order for a LCLC to be subclassified as th ...
* Laryngeal cancer
Laryngeal cancer is a kind of cancer that can develop in any part of the larynx (voice box). It is typically a squamous-cell carcinoma, reflecting its origin from the epithelium of the larynx.
The prognosis is affected by the location of the tumo ...
* Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lini ...
* Non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitiv ...
*Non-small cell lung carcinoma
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than Small-cell carcinoma#Small-cell lung cancer, small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. ...
* Pleuropulmonary blastoma
* Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
* Small cell lung cancer
* Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung
* Thymoma and thymic carcinoma
HIV/AIDS related
* AIDS-related cancers * Kaposi sarcomaUnsorted (so far)
* Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) * Desmoplastic small round cell tumorSee also
* Lists of diseases * List of oncology-related termsReferences
National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. ...
External links
{{Medicine, state=collapsed Cancer types