Southern Ukraine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Southern Ukraine (, ) refers, generally, to the territories in the South of
Southern Ukraine (, ) refers, generally, to the territories in the South of
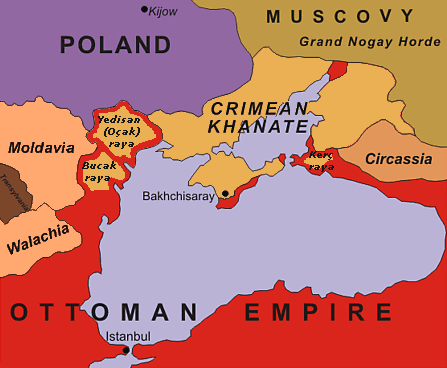 Before the 18th century, the territory known as the Wild Fields (as translated from Polish or Ukrainian) was dominated by Ukrainian Cossack community better known as
Before the 18th century, the territory known as the Wild Fields (as translated from Polish or Ukrainian) was dominated by Ukrainian Cossack community better known as 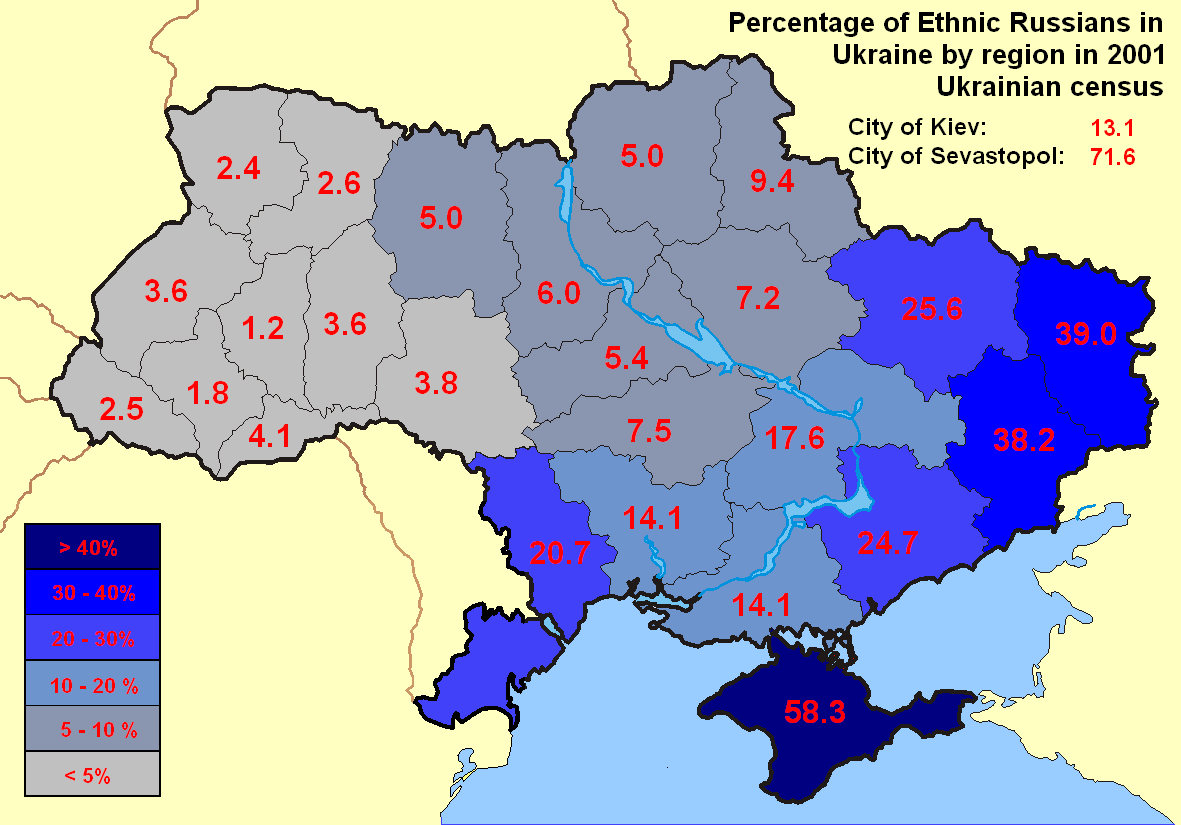

Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (1 March 2013) and more "negative views" of Ukrainian nationalism. In the 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, a lower percentage of the total electorate voted for independence in eastern and southern Ukraine than in the rest of the country.Ukrainian Nationalism in the 1990s: A Minority Faith
by Andrew Wilson,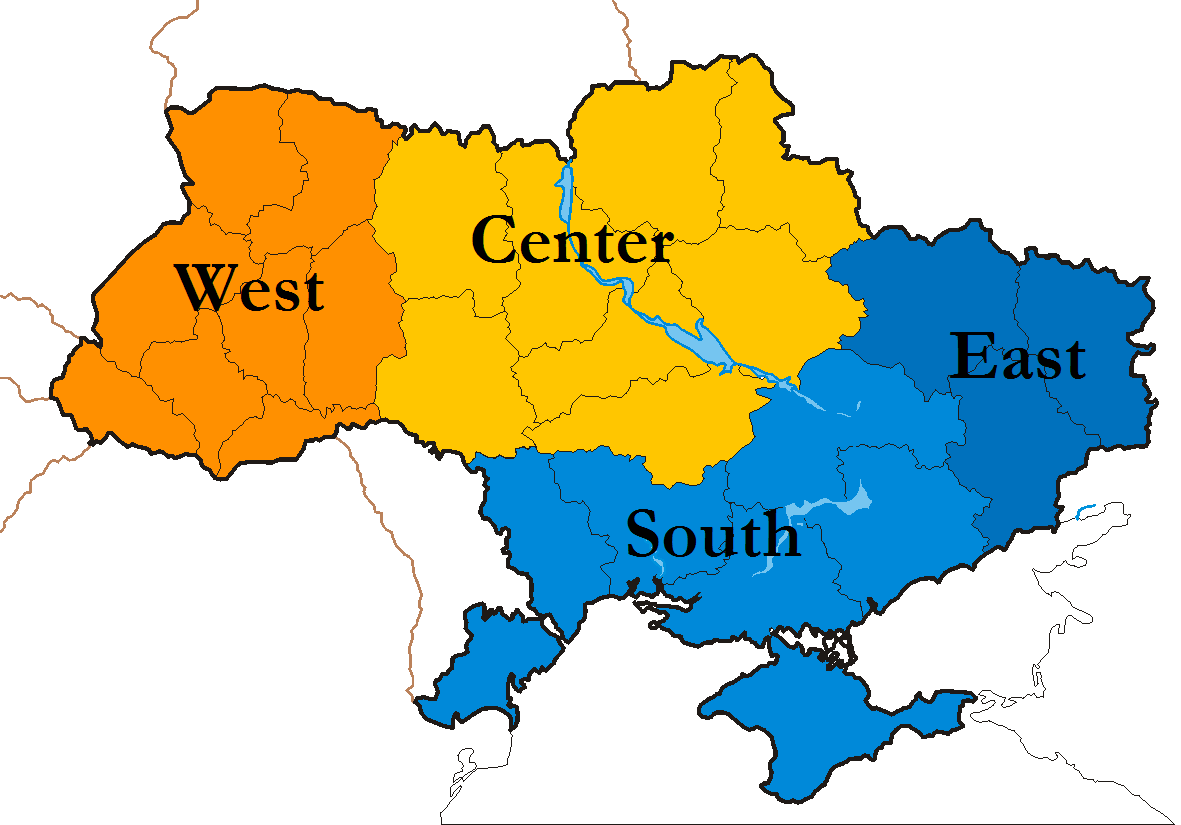 In a poll conducted by Kyiv International Institute of Sociology in the first half of February 2014, 19.4% of those polled in southern Ukraine believed "Ukraine and
In a poll conducted by Kyiv International Institute of Sociology in the first half of February 2014, 19.4% of those polled in southern Ukraine believed "Ukraine and
by Uwe Backes and Patrick Moreau,
openDemocracy.net (January 3, 2011)Eight Reasons Why Ukraine’s Party of Regions Will Win the 2012 Elections
by Taras Kuzio, The Jamestown Foundation (17 October 2012)
UKRAINE: Yushchenko needs Tymoshenko as ally again
by Taras Kuzio, Oxford Analytica (5 October 2007) The electorate of the CPU and the Party of Regions was very loyal to them. But following the
National composition of the population. 2001 Ukrainian Population Census. State Statistics Committee of Ukraine
''
South Ukraine
at
 Southern Ukraine (, ) refers, generally, to the territories in the South of
Southern Ukraine (, ) refers, generally, to the territories in the South of Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
.
The territory usually corresponds with the Soviet economical district, the Southern Economical District of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
. The region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
is completely integrated with a marine and shipbuilding industry.
Southern Ukraine was invaded by the Russian military on February 24, 2022, turning parts of the region into a major theatre of the Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
.
Historical background
The region primarily corresponds to the formerKherson
Kherson (Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and , , ) is a port city in southern Ukraine that serves as the administrative centre of Kherson Oblast. Located by the Black Sea and on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, Kherson is the home to a major ship-bui ...
, Taurida, and most of the Yekaterinoslav Governorate
Yekaterinoslav Governorate} was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Yekaterinoslav. Covering an area of , and being composed of a inhabitant of 2,113,674 by the census of 1897, it bordere ...
s which spanned across the northern coast of Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
after the Russian-Ottoman Wars of 1768–74 and 1787–92.
The Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and part ...
places the Pontic steppes of Ukraine and southern Russia as the linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric ethnolinguistic group of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family.
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from t ...
. The Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya ( ) or Yamna culture ( ), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, is a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic–C ...
is identified with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans. The region has been inhabited for centuries by various nomadic tribes, such as Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
, Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4t ...
, Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
, Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
, Kipchaks
The Kipchaks, also spelled Qipchaqs, known as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Russian annals, were Turkic nomads and then a confederation that existed in the Middle Ages inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe.
First mentioned in the eighth cent ...
, Turco-Mongols and Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
.
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
 Before the 18th century, the territory known as the Wild Fields (as translated from Polish or Ukrainian) was dominated by Ukrainian Cossack community better known as
Before the 18th century, the territory known as the Wild Fields (as translated from Polish or Ukrainian) was dominated by Ukrainian Cossack community better known as Zaporozhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich (, , ; also ) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of Zaporozhian Cossacks that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, for the latter part of that period as an autonomous stratocratic state within the Cossa ...
and the realm of Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of th ...
with its Nogai minions that was a union state of the bigger Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. The Crimean–Nogai slave raids caused considerable devastation and depopulation in the area before the rise of the Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks (in Latin ''Cossacorum Zaporoviensis''), also known as the Zaporozhian Cossack Army or the Zaporozhian Host (), were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids. Along with Registered Cossa ...
.
Encroachment of Muscovy (today Russia) in the region started after the 16th century after its expansion along Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
river after the Moscow-Kazan wars and conquest of Astrakhan
Astrakhan (, ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the Caspian Depression, from the Caspian Se ...
. Further expansion continued also with Moscow-Lithuania armed clashes.
With start of the Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising, also known as the Cossack–Polish War, Khmelnytsky insurrection, or the National Liberation War, was a Cossack uprisings, Cossack rebellion that took place between 1648 and 1657 in the eastern territories of the Poli ...
within Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
in middle of 17th century, Muscovy on pretence of the eastern Orthodoxy protection further expanded its influence down south over Cossack communities of Pontic steppes (lower Don and lower Dnieper) and the Crimean Khan domains.
At the end of 17th century a native Kyivan, bishop Theophan Prokopovych came up with the idea of an all-Russian nation referring to the old Rus state founder of which Volodymyr the Great was baptized and accepted Byzantine Christianity (today known as Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
) in Chersoneses of Taurida (today in Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
).
In 1686 there was signed the Treaty of Perpetual Peace between Muscovy and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, after which Muscovy took control over the Left-bank Ukraine
The Left-bank Ukraine is a historic name of the part of Ukraine on the left (east) bank of the Dnieper River, comprising the modern-day oblasts of Chernihiv, Poltava and Sumy as well as the eastern parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy.
Left-bank Ukrain ...
, Zaporozhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich (, , ; also ) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of Zaporozhian Cossacks that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, for the latter part of that period as an autonomous stratocratic state within the Cossa ...
, and Kyiv
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
with outskirts.
In the 18th century, Ukrainian line was built and the lands of the earlier destroyed Zaporozhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich (, , ; also ) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of Zaporozhian Cossacks that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, for the latter part of that period as an autonomous stratocratic state within the Cossa ...
were resettled by Serbs creating the territories of New Serbia and Slovianoserbia.
At the end of 18th century following the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Empire and the treaty of Jassy (the Ochakiv Region, area of today's Odesa and Mykolaiv oblasts), the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
assumed full control of the northern Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
coast.
Russian Hellenization of Pontic littoral
After the Russian-Ottoman Wars of the second half of 18th century ( 1768–74 and 1787–92) and acquisition of all territory of modern southern Ukraine, number of settlements and cities with Turkic or other names in region were renamed in Greek or Russian manner. * Acidere → Ovidiopol * Hacıbey →Odesa
Odesa, also spelled Odessa, is the third most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern ...
* Orel Sloboda (Catherinine sconce) → Olviopol (today Pervomaisk, Mykolaiv Oblast)
* Domakha → Mariupol
Mariupol is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast (Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius, Kalmius River. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, it was the tenth-largest city in the coun ...
(by Balaklava Greeks from outskirts of Bakhchysarai)
* Bilehowisce (Alexander sconce) → Kherson
Kherson (Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and , , ) is a port city in southern Ukraine that serves as the administrative centre of Kherson Oblast. Located by the Black Sea and on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, Kherson is the home to a major ship-bui ...
* Aqyar → Sebastopol (today Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
)
* Kezlev → Yevpatoria
Yevpatoria (; ; ; ) is a city in western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative center of Yevpatoria Municipality, one of the districts (''raions'') into which Crimea is divided. It had a population of
His ...
* Kiz-yar → Novo-alexandrovka (Novo-olexandrivka) Sloboda → Melitopol
* Caffa (Kefe) → Theodosia (today Feodosia)
* Aqmescit → Simferopol
Simferopol ( ), also known as Aqmescit, is the second-largest city on the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, but controlled by Russia. It is considered the cap ...
* Mykytyn Rih → Slaviansk → Nikopol
* Usivka (Bečej sconce) → Alexandria (today Oleksandriia)
* Sucleia (Sredinnaya fortress) → Tiraspol
Tiraspol (, ; also /; , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Transnistria, a breakaway state of Moldova, where it is the third-largest city. The city is located on the eastern bank of the Dniester River. Tiraspol is a regional hub of cul ...
(in Moldova)
* Czorna → Grigoriopol (in Moldova)
Following the World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
any trace of Crimean Tatar toponymy was predominantly removed in Crimea and Kherson Oblast.
Politics
Russian is spoken by a significant minority in the region, although not to the extent that it is in the three oblasts that comprise eastern Ukraine. Serhy Yekelchyk ''Ukraine: Birth of a Modern Nation'',Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
(2007), , page 187 Effective in August 2012, a new law on regional languages entitles any local language spoken by at least a 10% minority be declared official within that area. Within weeks Russian was declared as a regional language in several southern and eastern oblasts and cities. Russian could then be used in these cities/oblasts' administrative office work and documents.Romanian becomes regional language in Bila Tserkva in Zakarpattia regionKyiv Post
The ''Kyiv Post'' is Ukraine’s first and most prominent English-language newspaper. It was founded in 1995 in Kyiv by American businessman Jed Sunden.
In 2018, the publication was acquired by prominent Ukrainian businessman Adnan Kivan, foun ...
(24 September 2012) On 23 February 2014, the Ukrainian parliament
The Verkhovna Rada ( ; VR), officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameral parliament of Ukraine. It consists of 450 deputies presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovna Rada building in Ukraine's capi ...
voted to repeal the law on regional languages, which would have made Ukrainian the sole state language at all levels even in southern and eastern Ukraine.Ukraine: Speaker Oleksandr Turchynov named interim presidentBBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
(23 February 2014) This vote was vetoed by acting President Turchynov on March 2. Nevertheless the law was repealed by the Constitutional Court of Ukraine on 28 February 2018 when it ruled the law unconstitutional.
Noticeable cultural differences in the region (compared with the rest of Ukraine, except eastern Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine or East Ukraine (; ) is primarily the territory of Ukraine east of the Dnipro (or Dnieper) river, particularly Kharkiv, Luhansk and Donetsk oblasts (provinces). Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts are often also regarded as ...
) are more "positive views" of the Russian language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is ...
The language question, the results of recent research in 2012RATING
A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of a metric (e.g. quality, quantity, a combination of both,...).
Rating or rating system may also refer to:
Business and economics
* Credit rating, estimating the credit worthiness ...
(25 May 2012) and of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
Ставлення населення України до постаті Йосипа Сталіна ''Attitude population Ukraine to the figure of Joseph Stalin''Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (1 March 2013) and more "negative views" of Ukrainian nationalism. In the 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, a lower percentage of the total electorate voted for independence in eastern and southern Ukraine than in the rest of the country.Ukrainian Nationalism in the 1990s: A Minority Faith
by Andrew Wilson,
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessme ...
, 1996, (page 128)
 In a poll conducted by Kyiv International Institute of Sociology in the first half of February 2014, 19.4% of those polled in southern Ukraine believed "Ukraine and
In a poll conducted by Kyiv International Institute of Sociology in the first half of February 2014, 19.4% of those polled in southern Ukraine believed "Ukraine and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
must unite into a single state"; nationwide this percentage was 12.5.
During elections
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated ...
voters of the southern (and eastern) oblasts
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
(provinces) of Ukraine vote for the parties (Communist Party of Ukraine
The Communist Party of Ukraine (CPU or KPU) is a banned political party in Ukraine. It was founded in 1993 and claimed to be the successor to the Soviet-era Communist Party of Ukraine, which had been banned in 1991. In 2002 it held a "unifi ...
, Party of Regions
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will often feature ...
) and the presidential candidates (Viktor Yanukovych
Viktor Fedorovych Yanukovych (born 9 July 1950) is a Ukrainian politician who served as the fourth president of Ukraine from 2010 to 2014. He also served as the prime minister of Ukraine several times between 2002 and 2007 and was a member of t ...
) with a pro-Russian
Russophilia is the identification or solidarity with, appreciation of, or support for the Russia, country, Russians, people, Russian language, language, and history of Russia. One who espouses Russophilia is called a russophile. Its Opposite ...
and status quo
is a Latin phrase meaning the existing state of affairs, particularly with regard to social, economic, legal, environmental, political, religious, scientific or military issues. In the sociological sense, the ''status quo'' refers to the curren ...
platform.Communist and Post-Communist Parties in Europeby Uwe Backes and Patrick Moreau,
Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht
Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht (V&R) is a scholarly publishing house based in Göttingen, Germany. It was founded in 1735 by (1700–1750) in connection with the establishment of the Georg-August-Universität in the same city.
After Abraham Vandenh ...
, 2008, (page 396)Ukraine right-wing politics: is the genie out of the bottle?openDemocracy.net (January 3, 2011)Eight Reasons Why Ukraine’s Party of Regions Will Win the 2012 Elections
by Taras Kuzio, The Jamestown Foundation (17 October 2012)
UKRAINE: Yushchenko needs Tymoshenko as ally again
by Taras Kuzio, Oxford Analytica (5 October 2007) The electorate of the CPU and the Party of Regions was very loyal to them. But following the
Revolution of Dignity
The Revolution of Dignity (), also known as the Maidan Revolution or the Ukrainian Revolution, took place in Ukraine in February 2014 at the end of the Euromaidan protests, when deadly clashes between protesters and state forces in the capit ...
the Party of Regions collapsed and the Communist Party was banned and declared illegal.
Demographics
Ethnic groups and languages
According to the Ukrainian national census in 2001, ethnicUkrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
account for the overwhelming majority of the population in Southern Ukraine, with the only exceptions being central and southern Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
, as well as the southwestern part of the Budjak
Budjak, also known as Budzhak, is a historical region that was part of Bessarabia from 1812 to 1940. Situated along the Black Sea, between the Danube and Dniester rivers, this #Ethnic groups and demographics, multi-ethnic region covers an area ...
in the Odesa region. In terms of spoken languages, Ukrainian is the most common language, although the Russian language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is ...
dominates in many major cities like Odesa
Odesa, also spelled Odessa, is the third most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern ...
, Dnipro
Dnipro is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper River, Dnipro River, from which it takes its name. Dnipro is t ...
, Zaporizhzhia
Zaporizhzhia, formerly known as Aleksandrovsk or Oleksandrivsk until 1921, is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. It is the Capital city, administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia ...
, Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv ( ), also known as Nikolaev ( ) is a List of cities in Ukraine, city and a hromada (municipality) in southern Ukraine. Mykolaiv is the Administrative centre, administrative center of Mykolaiv Raion (Raions of Ukraine, district) and Myk ...
, Melitopol
Melitopol is a city and municipality in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, southeastern Ukraine. It is situated on the Molochna River, which flows through the eastern edge of the city into the Molochnyi Lyman estuary. Melitopol is the second-largest city ...
or Berdiansk
Berdiansk or Berdyansk (, ; , ) is a port city in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, south-eastern Ukraine. It is on the northern coast of the Sea of Azov, which is connected to the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Berdiansk Raion. The c ...
. In Crimea, Russian is most common language, while only rural areas in the north of the peninsula have a Ukrainophone majority. Due to Crimea's ethnic diversity, Russian is also the most common language among the majority of all inhabitants without an ethnic Russian background in the region and serves as the interethnic language in the autonomous republic.
:''SourceNational composition of the population. 2001 Ukrainian Population Census. State Statistics Committee of Ukraine
''
Religion
According to a 2016 survey ofreligion in Ukraine
Christianity is the predominant religion in Ukraine, with 85% of the population identifying as Christian according to a 2022 survey conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS). Seventy-two percent of the population avowed ...
conducted by the Razumkov Center, around 65.7% of the population of southern Ukraine declared to be believers in any religion, while 7.4% declared to be non-believers, and 3.2% declared to be atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
and agnostics. the study also found that 77.6% of the total southern Ukraine population declared to be Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
(71.0% Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
, 5.1% simply Christians, 0.5% Latin Church
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical ...
Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
, 0.53% members of various Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
churches, 0.5% members of the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church
The Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church (UGCC) is a Major archiepiscopal church, major archiepiscopal ''sui iuris'' ("autonomous") Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic church that is based in Ukraine. As a particular church of the Cathol ...
), and 0.5% were Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
. Not religious and other believers not identifying with any of the listed major religious institutions constituted about 24.7% of the population.
Oblasts
The neighbouringKirovohrad Oblast
Kirovohrad Oblast (), also known as Kirovohradshchyna (), is an administrative divisions of Ukraine, oblast (''province'') in central Ukraine. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Kropyvnytskyi. The oblast's population is It is ...
is more often associated with the Central Ukraine. Also Crimea (with Sevastopol City) is reviewed sometimes as a unique region. According to the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
The ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' (), published from 1984 to 2001, is a fundamental work of Ukrainian Studies.
Development
The work was created under the auspices of the Shevchenko Scientific Society in Europe (Sarcelles, near Paris). As the ...
, south Ukraine was considered to consist of the territory of the former Kherson
Kherson (Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and , , ) is a port city in southern Ukraine that serves as the administrative centre of Kherson Oblast. Located by the Black Sea and on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, Kherson is the home to a major ship-bui ...
, Taurida and Yekaterinoslav Governorate
Yekaterinoslav Governorate} was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Yekaterinoslav. Covering an area of , and being composed of a inhabitant of 2,113,674 by the census of 1897, it bordere ...
s.
See also
* Central Ukraine *Dnieper Ukraine
The term Dnieper Ukraine
(), usually refers to territory on either side of the middle course of the Dnieper River. The Ukrainian name derives from ''nad‑'' (prefix: "above, over") + ''Dnipró'' ("Dnieper") + ''‑shchyna'' (suffix denoting a g ...
*Eastern Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine or East Ukraine (; ) is primarily the territory of Ukraine east of the Dnipro (or Dnieper) river, particularly Kharkiv, Luhansk and Donetsk oblasts (provinces). Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts are often also regarded as ...
*Western Ukraine
Western Ukraine or West Ukraine (, ) refers to the western territories of Ukraine. There is no universally accepted definition of the territory's boundaries, but the contemporary Ukrainian administrative regions ( oblasts) of Chernivtsi, I ...
* Wild Fields
References
External links
South Ukraine
at
Encyclopedia of Ukraine
The ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' (), published from 1984 to 2001, is a fundamental work of Ukrainian Studies.
Development
The work was created under the auspices of the Shevchenko Scientific Society in Europe (Sarcelles, near Paris). As the ...
{{Coord missing, Ukraine
Geographic regions of Ukraine