Scrotal Urethrostomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In most terrestrial
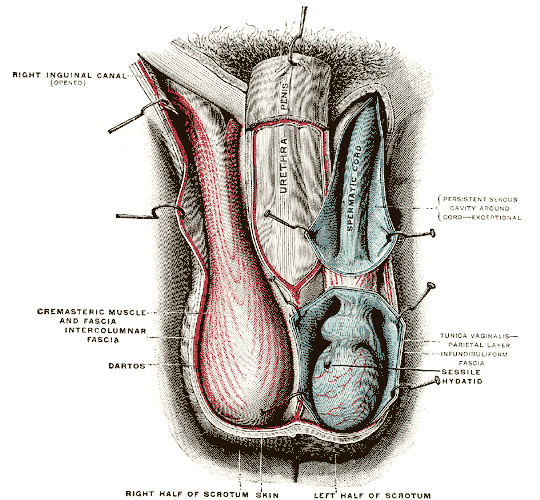 In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of
In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of
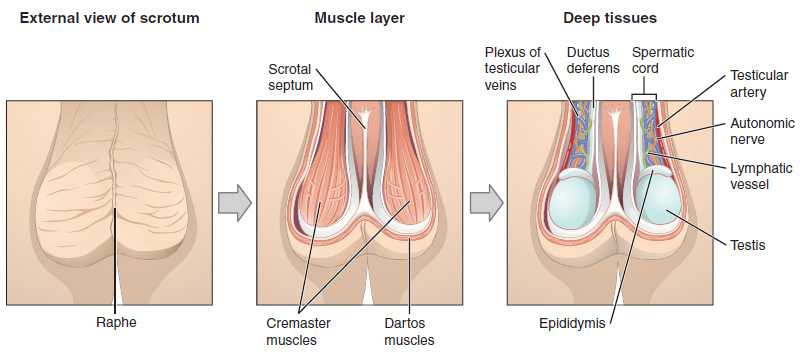 Additional tissues and organs reside inside the scrotum and are described in more detail in the following articles:
* Appendix of epididymidis
*
Additional tissues and organs reside inside the scrotum and are described in more detail in the following articles:
* Appendix of epididymidis
*
 During the fifth week after fertilization, the
During the fifth week after fertilization, the
Testicular of a bulldog cow Hoden eines Ochsen Venezuela P1140356.JPG, Scrotum of a
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
located at the base of the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
. It consists of a sac of skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
containing the external spermatic fascia
The external spermatic fascia (intercrural or intercolumnar fascia) is a thin membrane, prolonged downward around the surface of the spermatic cord and testis. It is separated from the dartos tunic by loose areolar tissue. It is occasionally refe ...
, testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s, epididymides
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
, and vasa deferentia
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididyma ...
. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures.
The scrotum is homologous to the labia majora
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora (: labium majus), also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent Anatomical terms of location, longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis ...
in females.
Structure
 In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of
In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and muscular tissue
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to contract. M ...
containing the testicles and the lower part of the spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
s. It is located behind the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
and above the perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
. The perineal raphe
The perineal raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue on the body that extends from the anus through the perineum to the scrotum (male) or the vulva (female). It is found in both males and females, arises from the fusion of the urogenital folds, ...
is a small, vertical ridge of skin that expands from the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
and runs through the middle of the scrotum front to back. The scrotum is also a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery
The testicular artery (the male gonadal artery, also called the internal spermatic arteries in older texts) is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.
It ...
, testicular vein
The testicular vein (or spermatic vein), the male gonadal vein, carries deoxygenated blood from its corresponding testis to the inferior vena cava or one of its tributaries. It is the male equivalent of the ovarian vein, and is the venous counte ...
, and pampiniform plexus
The pampiniform plexus () is a venous plexus – a network of many small veins found in the human male spermatic cord, and the suspensory ligament of the ovary. In the male, it is formed by the union of multiple testicular veins from the back o ...
.
Nerve supply
Blood supply
Skin and glands
*Sebaceous glands
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in t ...
* Apocrine glands
Apocrine () is a term used to classify the mode of secretion of exocrine glands. In apocrine secretion, secretory cells accumulate material at their apical ends, often forming blebs or "snouts", and this material then buds off from the cells, ...
* Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
The skin on the scrotum is more highly pigmented in comparison to the rest of the body. The septum
In biology, a septum (Latin language, Latin for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a Body cavity, cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Hum ...
is a connective tissue membrane dividing the scrotum into two cavities.
Lymphatic system
The scrotal lymph initially drains into the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, this then drains into the deep inguinal lymph nodes. The deep inguinal lymph nodes channel into the common iliac, which ultimately releases lymph into the cisterna chyli.Asymmetry
One testis is typically lower than the other, which is believed to function to avoid compression in the event of impact; in humans, the left testis is typically lower than the right. An alternative view is that testis descent asymmetry evolved to enable more effective cooling of the testicles.Internal structure
Cremaster muscle
The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testicles and the spermatic cords in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, respo ...
* Dartos fascia
The dartos fascia, dartos tunic or simply dartos is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile shaft, foreskin and scrotum. The penile portion is referred to as the superficial fascia of penis or the subcutaneous tissue of penis, while the ...
* Efferent ductules
The efferent ducts (also efferent ductules, ductuli efferentes, ductus efferentes, or vasa efferentia) connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.Hess 2018
There are two basic designs for efferent ductule structure:
* a ...
* Epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
* Leydig cell
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of the testes and interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle and produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH). They are polyhedral ...
* Lobules of testis
The lobules of testis are of partitions of the testis formed by septa of testis. The lobules of testis contain the tightly coiled seminiferous tubule. There are some hundreds of lobules in a testicle.
Anatomy
They differ in size according to th ...
* Paradidymis
The term paradidymis (: paradidymides; organ of Giraldés) is applied to a small collection of convoluted tubules, situated in front of the lower part of the spermatic cord, above the head of the epididymis.
These tubes are lined with columnar c ...
* Rete testes
* Scrotal septum
The septum of scrotum or scrotal septum is an incomplete vertical wall (septum) that divides the scrotum into two compartments –each containing a single testis. It consists of flexible connective tissue and nonstriated muscle (dartos fascia
...
* Seminiferous tubule
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
Structure
The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells k ...
* Sertoli cell
Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm) as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-sti ...
* Spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
* Testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
* Tunica albuginea of testis
The tunica albuginea is a dense, blue-white layer of fibrous tissue surrounding the testis. It is the middle of three envelopes forming the capsule of the testis; it is deep to the visceral layer of tunica vaginalis, and superficial to the tuni ...
* Tunica vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis is a pouch of serous membrane within the scrotum that lines the testis and epididymis (visceral layer of tunica vaginalis), and the inner surface of the scrotum (parietal layer of tunica vaginalis). It is the outermost of ...
* Tunica vasculosa testis
The tunica vasculosa testis (vascular layer of testis) is the inner-most of the three layers that form the capsule of the testis. It consists of a vascular plexus and loose connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, also known as areolar ti ...
* Vas deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididyma ...
Development
 During the fifth week after fertilization, the
During the fifth week after fertilization, the genital ridge
In embryology, the genital ridge (genital fold or gonadal ridge) is the developmental precursor to the gonads. The genital ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area th ...
grows behind the peritoneal membrane. By the sixth week, string-like tissues called primary sex cords form within the enlarging genital ridge. Externally, a swelling called the genital tubercule appears over the cloacal membrane.
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
secretion starts during week eight, reaches peak levels during week 13 and eventually declines to very low levels by the end of the second trimester. The testosterone causes the masculinization of the labioscrotal folds
The labioscrotal swellings (genital swellings or labioscrotal folds) are paired structures in the mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-pro ...
into the scrotum. The scrotal raphe is formed when the embryonic, urethral groove closes by week 12.
Scrotal growth and puberty
Though the testes and scrotum form early in embryonic life, sexual maturation begins upon enteringpuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
. The increased secretion of testosterone causes the darkening of the skin and development of pubic hair
Pubic hair (or pubes , ) is terminal hair, terminal body hair that is found in the sex organ, genital area and pubic region of adolescent and adult humans. The hair is located on and around the sex organs, and sometimes at the top of the inside ...
on the scrotum.
Function
The scrotum regulates the temperature of the testicles and maintains it at , i.e. two or three degrees below the body temperature of . Higher temperatures affectspermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
. Temperature control is accomplished by the smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
s of the scrotum moving the testicles either closer to or further away from the abdomen dependent upon the ambient temperature. This is accomplished by the cremaster muscle
The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testicles and the spermatic cords in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, respo ...
in the abdomen and the dartos fascia
The dartos fascia, dartos tunic or simply dartos is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile shaft, foreskin and scrotum. The penile portion is referred to as the superficial fascia of penis or the subcutaneous tissue of penis, while the ...
(muscular tissue under the skin that makes the scrotum appear wrinkly).
During sexual arousal
Sexual arousal (also known as sexual excitement) describes the Physiology, physiological and psychological responses in preparation for sexual intercourse or when exposed to Sexual stimulation, sexual stimuli. A number of physiological response ...
, the scrotum will also tighten and thicken in the course of penile erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, a ...
.
Having the scrotum and testicles situated outside the abdominal cavity may provide additional advantages. The external scrotum is not affected by abdominal pressure. This may prevent the emptying of the testes before the sperm were matured sufficiently for fertilization. Another advantage is it protects the testes from jolts and compressions associated with an active lifestyle. The scrotum may provide some friction during intercourse, helping to enhance the activity. The scrotum is also considered to be an erogenous zone
An erogenous zone (from Greek , ''érōs'' "love"; and English ''-genous'' "producing", from Greek , ''-genḗs'' "born") is an area of the human body that has heightened Sensory processing, sensitivity, the sexual stimulation, stimulation of wh ...
.
Society and culture
Common slang terms for the scrotum are ''ballsack'', ''nutsack'', and ''teabag''. Some men will get a piercing on the skin of the scrotum, any of which is called a hafada (e.g., scrotal ladder). Side-to-side or front-to-back piercings that pass through the scrotum are known as transscrotal piercings.Scrotoplasty
Scrotoplasty, also known as oscheoplasty, is a type of surgery to create or repair the scrotum. Scientific research for male genital plastic surgery such as scrotoplasty began to develop in the early 1900s. The development of testicular implants ...
is a sex reassignment surgery
Gender-affirming surgery (GAS) is a surgical procedure, or series of procedures, that alters a person's physical appearance and sexual characteristics to resemble those associated with their gender identity. The phrase is most often associat ...
that creates a scrotum for trans men
A trans man or transgender man is a man who was assigned female at birth. Trans men have a male gender identity, and many trans men undergo Gender transition, medical and social transition to alter their appearance in a way that aligns with th ...
using tissue from the labia majora, or a plastic surgery that repairs or reconstructs the scrotum.
Cock and ball torture
Cock and ball torture (CBT) is a sexual activity involving the application of pain or constriction to the male genitals. This may involve directly painful activities, such as genital piercing, wax play, genital spanking, squeezing, ball- ...
is a kink that may involve bringing pain to the scrotum. Beyond kink, a person (especially a man) may hit someone in the testicles as a gendered cultural practice known as sack tapping. This phenomenon is complex and contains many (often conflicting) meanings: it is used to both strengthen inclusive bonds and reinforce exclusive hierarchies, it is both humorous and violent, and both juvenile and present in male-dominated social spheres beyond those of adolescence.
Other animals
A scrotum is present in allboreoeutheria
Boreoeutheria (, "northern eutherians") is a magnorder of Placentalia, placental mammals that groups together superorders Euarchontoglires and Laurasiatheria. The clade includes groups as diverse as giraffes, Sus (genus), pigs, zebras, Rhinoceros ...
n land mammals except hippopotamus
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Sahar ...
es, rhinoceros
A rhinoceros ( ; ; ; : rhinoceros or rhinoceroses), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls) in the family (biology), famil ...
es, hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are 17 species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introduction. The ...
s, moles, pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises four species found in Asia, while ' ...
s, tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a Suidae, pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk (proboscis). Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South America, South and Centr ...
s, and numerous families of bat
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out ...
s and rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s. The anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
is separated from the scrotum by the perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
in these mammals. The testicles remain in the body cavity in all other vertebrates, including cloaca
A cloaca ( ), : cloacae ( or ), or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, cartilagin ...
l animals.
Unlike placentals
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
, some male marsupials
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a ...
have a scrotum that is anterior to the penis, which is not homologous to the scrotum of placentals, although there are several marsupial species without an external scrotum.
The scrotum is also absent in marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s, such as whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
s, and seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, also called "true seal"
** Fur seal
** Eared seal
* Seal ( ...
s, as well as in lineages of other land mammals, such as the afrotheria
Afrotheria ( from Latin ''Afro-'' "of Africa" + ''theria'' "wild beast") is a superorder of placental mammals, the living members of which belong to groups that are either currently living in Africa or of African origin: golden moles, elephan ...
ns (elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
s, aardvark
Aardvarks ( ; ''Orycteropus afer'') are medium-sized, burrowing, nocturnal mammals native to Africa. Aardvarks are the only living species of the family Orycteropodidae and the order Tubulidentata. They have a long proboscis, similar to a pi ...
s, etc.), xenarthra
Xenarthra (; from Ancient Greek ξένος, xénos, "foreign, alien" + ἄρθρον, árthron, "joint") is a superorder and major clade of placental mammals native to the Americas. There are 31 living species: the anteaters, tree sloths, and ...
ns (armadillo
Armadillos () are New World placental mammals in the order (biology), order Cingulata. They form part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are dis ...
s, anteater
Anteaters are the four extant mammal species in the suborder Vermilingua (meaning "worm tongue"), commonly known for eating ants and termites. The individual species have other names in English and other languages. Together with sloths, they ar ...
s, and sloth
Sloths are a Neotropical realm, Neotropical group of xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant Arboreal locomotion, arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of move ...
s), and monotremes
Monotremes () are mammals of the order Monotremata. They are the only group of living mammals that lay eggs, rather than bearing live young. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and the four species of echidnas. Monotremes are typified ...
.
bull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not Castration, castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e. cows proper), bulls have long been an important symbol cattle in r ...
File:Male-kangaroo.jpg, Scrotum of a kangaroo
Kangaroos are marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use, the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern gre ...
Red deer testicles.jpg, Scrotum of a red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
Jaguar 7374 (5000551901).jpg, Scrotum of a jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large felidae, cat species and the only extant taxon, living member of the genus ''Panthera'' that is native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the biggest cat spe ...
Camel's Testicles (3953363864).jpg, Scrotum of a camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
Chlorocebus-pygerythrus-private-parts.JPG, Scrotum of a vervet monkey
The vervet monkey (''Chlorocebus pygerythrus''), or simply vervet, is an Old World monkey of the family Cercopithecidae native to Africa. The term "vervet" is also used to refer to all the members of the genus '' Chlorocebus''. The five distin ...
File:Giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) male genitals covered with ticks ... (51125861810).jpg, Scrotum of a giraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on ...
Clinical significance
Diseases and conditions
The scrotum and its contents can develop many diseases and can incur injuries. These include: *Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus '' Candida'' (a yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the ...
(yeast infection)
*Sebaceous cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a term commonly used to refer to either:
* Epidermoid cysts (also termed epidermal cysts, infundibular cyst)
* Pilar cysts (also termed trichelemmal cysts, isthmus-catagen cysts)
Both of the above types of cysts contain ...
*Epidermal cyst
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
*Hydrocele testis
A hydrocele testis is an accumulation of clear fluid within the cavum vaginale, the potential space between the layers of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle. It is the most common form of hydrocele and is often referred to simply as a "hydrocele ...
*Hematocele
A hematocele is a collections of blood in a body cavity or potential space. The term most commonly refers to the collection of blood in the tunica vaginalis around the testes, known as a ''scrotal hematocele''. Hematoceles can also occur in t ...
*Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum (MC), sometimes called water warts, is a viral infection of the skin that results in small raised pink lesions with a dimple in the center. They may become itchy or sore, and occur singularly or in groups. Any area of the ...
*Spermatocele
Spermatocele is a fluid-filled cyst that develops in the epididymis. The fluid is usually a clear or milky white color and may contain sperm. Spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa and they can vary in size from several millimeters t ...
*Paget's disease of the scrotum
*Varicocele
A varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum; in a woman, it is an abnormal painful swelling to the List of related male and female reproductive organs, embryologically identical pampiniform venous plexu ...
- enlargement of the pampiniform venous complex
*Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia or groin hernia is a hernia (protrusion) of abdominal cavity contents through the inguinal canal. Symptoms, which may include pain or discomfort especially with or following coughing, exercise, or bowel movements, are absen ...
* Epididymo-orchitis
*Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. The testicle may be higher tha ...
*Pruritus scroti
Pruritus scroti is itchiness of the scrotum that may be secondary to an infectious cause.
See also
* Pruritus vulvae
* Pruritus ani
* Pruritus
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch ...
- irritation of the scrotum (itchiness)
*Genital warts
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). They may be flat or project out from the surface of the skin, and their color may vary; brownish, white, pale yellow, pinkish-red, or gray ...
- sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
*Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.
Risk factors include an c ...
*Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
*Undescended testes
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is . It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boy ...
(also known as cryptorchidism)
*Chyloderma
Chyloderma is swelling of the scrotum resulting from chronic lymphatic obstruction. Obstruction may be caused by a nematode such as '' Wuchereria bancrofti''. This condition is also known as lymphscrotum or elephantiasis scroti.
See also
*Filar ...
- swollen scrotum caused by a lymphatic obstruction
*Mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gen ...
*Scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious human skin infestation by the tiny (0.2–0.45 mm) mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei'', variety ''hominis''. The word is from . The most common symptoms are severe itchiness a ...
*Herpes
Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are oral herpes and genital herp ...
- sexually transmitted infection
*Pubic lice
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
* Chancroid
Chancroid ( ) is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to spread from one individual to another solely through sexual contact. However, there have been reports of accidenta ...
('' Haemophilus ducreyi'') - sexually transmitted infection
* Chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several w ...
(''Chlamydia trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an ...
'') - sexually transmitted infection
* Gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
(''Neisseria gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular) or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria first isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. An obligate human pathog ...
'') - sexually transmitted infection
* Granuloma inguinale
Granuloma inguinale is a bacterial disease caused by '' Klebsiella granulomatis'' (formerly known as ''Calymmatobacterium granulomatis'') characterized by genital ulcers. It is endemic in many less-developed regions. It is also known as donovan ...
or (''Klebsiella granulomatis
''Klebsiella granulomatis'' is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium of the genus ''Klebsiella'' known to cause the sexually transmitted infection granuloma inguinale (or donovanosis). It was formerly called ''Calymmatobacterium granulomatis''.
...
'')
* Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
(''Treponema pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a Microaerophile, microaerophilic, Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic ...
'') - sexually transmitted infection
* Scrotal eczema
* Polyorchidism
Polyorchidism is the incidence of more than two testicles. It is a very rare congenital disorder, with fewer than 200 cases reported in medical literature and six cases (two horses, two dogs and two cats) in veterinary literature.
Polyorchidism ...
- the presence of three or more testicles
* Scrotal psoriasis disease
* Riboflavin deficiency
* Chimney sweeps' carcinoma
Chimney sweeps' cancer, also called soot wart or scrotal cancer, is a squamous cell carcinoma of the scrotum. It has the distinction of being the first reported form of occupational disease, occupational cancer, and was initially identified by P ...
(scrotal cancer)
See also
*Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection
Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) is a surgical procedure to remove abdominal lymph nodes. It is used to treat testicular cancer, as well as to help establish the exact stage and type of the cancer.
Indications
Testicular cancer m ...
* Scrotal infusion
Scrotal inflation or scrotal infusion is a sexual practice in which fluid (typically saline (medicine), saline solution, but sometimes air or another gas) is injected into the scrotum in order to make it balloon in size. It carries a number of r ...
, a temporary form of body modification
* Testicular self-examination
Testicular self-examination (TSE) is a procedure where a man examines his own testicles and scrotum for possible lumps or swelling. It is usually undertaken at home while standing in front of a mirror and after having a warm bath or shower. Month ...
Bibliography
; Books * * * * *References
External links
* {{Authority control Human male reproductive system Integumentary system Mammal male reproductive system Sex organs Testicle