|
Testicular Artery
The testicular artery (the male gonadal artery, also called the internal spermatic arteries in older texts) is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles. It is the male equivalent of the ovarian artery. Because the testis is found in a different location than that of its female equivalent, it has a different course than the ovarian artery. They are two slender vessels of considerable length, and arise from the front of the aorta a little below the renal arteries. Each passes obliquely downward and lateralward behind the peritoneum, resting on the psoas major, the right lying in front of the inferior vena cava and behind the middle colic and ileocolic arteries and the terminal part of the ileum, the left behind the left colic and sigmoid arteries and the iliac colon. Each crosses obliquely over the ureter and the lower part of the external iliac artery to reach the abdominal inguinal rin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Aorta
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax). Structure The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the diaphragm, crossing it via the aortic hiatus, technically behind the diaphragm, at the vertebral level of T12. It travels down the posterior wall of the abdomen, anterior to the vertebral column. It thus follows the curvature of the lumbar vertebrae, that is, convex anteriorly. The peak of this convexity is at the level of the third lumbar vertebra (L3). It runs parallel to the inferior vena cava, which is located just to the right of the abdominal aorta, and becomes smaller in diameter as it gives off branches. This is thought to be due to the large size of its principal branches. At the 11th rib, the diameter is 122mm long and 55mm wide and this is because of the constant pressure. The abdominal aorta is clinically divided into 2 segments: # Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmoid Arteries
The sigmoid arteries are 2–5 branches of the inferior mesenteric artery that are distributed to the distal descending colon and the sigmoid colon. Anatomy Course and relations The sigmoid arteries course obliquely inferior-ward and to the left, passing posterior to the peritoneum and in anterior to the psoas major, ureter, and Gonadal artery. Anastomoses The sigmoid arteries anastomose with the left colic superiorly, and with the superior rectal artery The superior rectal artery (superior hemorrhoidal artery) is an artery that descends into the pelvis to supply blood to the rectum. Structure The superior rectal artery is the continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery. It descends into the ... inferiorly. References External links * - "Intestines and Pancreas: Branches of the Inferior Mesenteric Artery" * Arteries of the abdomen {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Vein
The ovarian vein, the female gonadal vein, carries deoxygenated blood from its corresponding ovary to inferior vena cava or one of its tributaries. It is the female equivalent of the testicular vein, and is the venous counterpart of the ovarian artery. It can be found in the suspensory ligament of the ovary. Structure It is a paired vein, each one supplying an ovary. * The right ovarian vein travels through the suspensatory ligament of the ovary and generally joins the inferior vena cava. * The left ovarian vein, unlike the right, often joins the left renal vein instead of the inferior vena cava.Lampmann LE, Smeets AJ, Lohle PN. Uterine fibroids: targeted embolization, an update on technique. Abdom Imaging. 2003 Oct 31; . Pathology Thrombosis of ovarian vein is associated with postpartum endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, diverticulitis, appendicitis Appendicitis is inflammation of the Appendix (anatomy), appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Hernia Repair
Inguinal hernia surgery is an operation to repair a weakness in the abdominal wall that abnormally allows abdominal contents to slip into a narrow tube called the inguinal canal in the groin region. There are two different clusters of hernia: groin and ventral (abdominal) wall. Groin hernia includes femoral, obturator, and inguinal. Inguinal hernia is the most common type of hernia and consist of about 75% of all hernia surgery cases in the US. Inguinal hernia, which results from lower abdominal wall weakness or defect, is more common among men with about 90% of total cases. In the inguinal hernia, fatty tissue or a part of the small intestine gets inserted into the inguinal canal. Other structures that are uncommon but may get stuck in inguinal hernia can be the appendix, caecum, and transverse colon. Hernias can be asymptomatic, incarcerated, or strangled. Incarcerated hernia leads to impairment of intestinal flow, and strangled hernia obstructs blood flow in addition to intest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
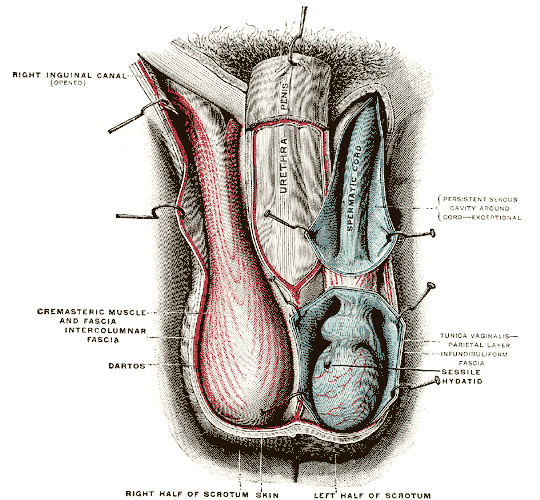
Cremaster Muscle
The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testicles and the spermatic cords in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, responsible for the cremasteric reflex; a protective and physiologic superficial reflex of the testicles. The reflex raises and lowers the testicles in order to keep them protected. Along with the dartos muscle of the scrotum, it regulates testicular temperature, thus aiding the process of spermatogenesis. Structure In human males, the cremaster muscle is a thin layer of striated muscle found in the inguinal canal and scrotum between the external and internal layers of spermatic fascia, surrounding the testis and spermatic cord. The cremaster muscle is a paired structure, there being one on each side of the body. Anatomically, the lateral cremaster muscle originates from the internal oblique muscle, just superior to the inguinal canal, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children. The ureters have been identified for at least two thousand years, with the word "ureter" stemming from the stem relating to urinating and seen in written records since at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Albuginea Of Testis
The tunica albuginea is a dense, blue-white layer of fibrous tissue surrounding the testis. It is the middle of three envelopes forming the capsule of the testis; it is deep to the visceral layer of tunica vaginalis, and superficial to the tunica vasculosa testis (vascular layer of testis). The connective tissue of the tunica albuginea testis extends into the substance of the testis to form fibrous partitions - the septa testis. At the posterior aspect of the testis (where the serosa of testis is deficient to allow for the attachment of the epididymis), the tunica albuginea extends into the testis to form the mediastinum testis. Anatomy It is thicker than the tunica albuginea of the ovary. Histology It is composed of bundles of white fibrous connective tissue (from which it derives its name '' albuginea'') which interlace in every direction. Additional images File:Gray1145.png, Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis. File:Gray111 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
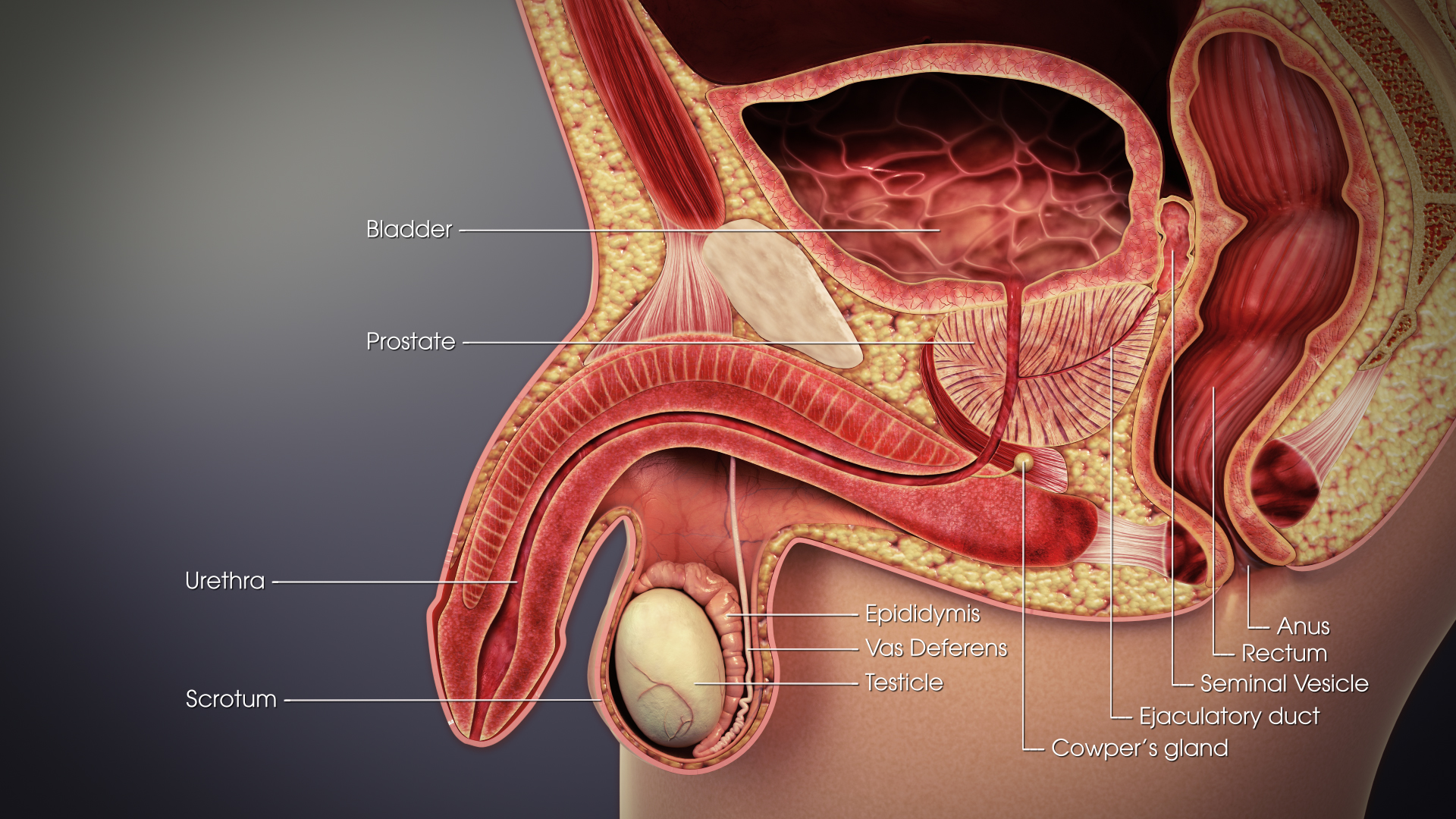
Epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; uncoiled the tube would be approximately 6 m (20 feet) long. It connects the testicle to the vas deferens in the male reproductive system. The epididymis serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Its primary function is the storage, maturation and transport of sperm cells. Structure The human epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head (). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductus Deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididymal duct. The end of the epididymis is connected to the vas deferens. The vas deferens ends with an opening into the ejaculatory duct at a point where the duct of the seminal vesicle also joins the ejaculatory duct. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel" while ''ductus deferens'', also Latin, means "carrying-away duct". Structure The human vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis, and exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms a dilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortuous
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures. The scrotum is homologous to the labia majora in females. Structure In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of skin and muscular tissue containing the testicles and the lower part of the spermatic cords. It is located behind the penis and above the perineum. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical ridge of skin that expands from the anus and runs through the middle of the scrotum front to back. The scrotum is also a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Canal
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body (one on each side of the midline), which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. Structure The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. The canals are approximately 4 to 6 cm long, angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.The diameter has been estimated to be ±2.2cm ±1.08cm in Africans, and 2.1 cm ±0.41cm in Europeans. A first-order approximation is to visualize each canal as a cylinder. Walls To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usually called the "anterior wall", "inferior wall ("floor")", "superior wall ("roof")", and "po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |