Sankirtana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sikh ''kirta''n with Indian harmoniums and '' tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)">Kenya.html" ;"title="tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya">tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)
''Kirtana'' (; ), also rendered as ''Kiirtan'', ''Kirtan'' or ''Keertan'', is a
Sikh ''kirta''n with Indian harmoniums and '' tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)">Kenya.html" ;"title="tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya">tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)
''Kirtana'' (; ), also rendered as ''Kiirtan'', ''Kirtan'' or ''Keertan'', is a
 The term ''kirtana'' (
The term ''kirtana'' (
 A modern kirtan performance
Musical recitation of hymns, mantras and the praise of deities has ancient roots in Hinduism, and may be found in the
A modern kirtan performance
Musical recitation of hymns, mantras and the praise of deities has ancient roots in Hinduism, and may be found in the
Indian Music: A Vast Ocean of Promise
', Routledge. Regarding the southern (Carnatic) traditions of kirtan, they are generally "less ornate" than northern kirtan, making less use of "
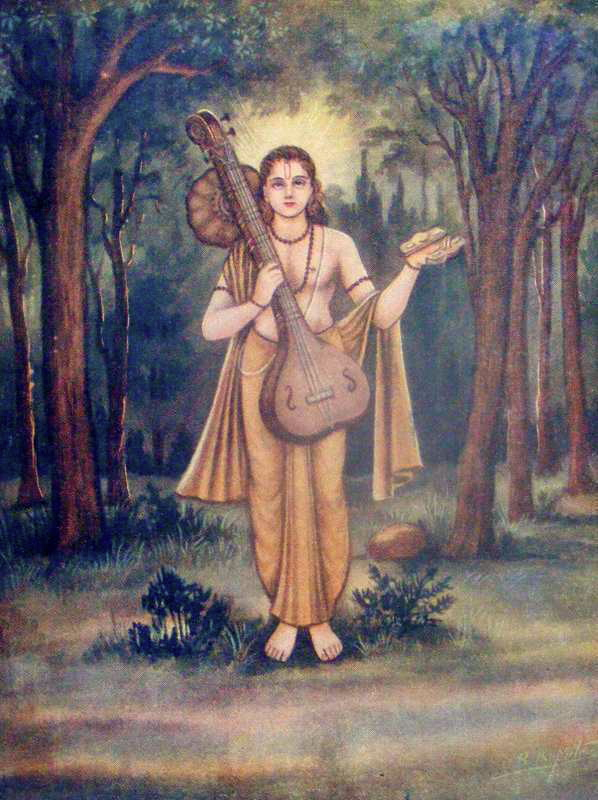
 One important promoter of Vaishnava kirtan in Bengal was
One important promoter of Vaishnava kirtan in Bengal was
"The Vaisnava Sahajiya Traditions of Medieval Bengal"
in ''Religions of India in Practice'', edited by Donald S. Lopez, Jr., Princeton Readings in Religions, Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1995: 333-351. The Vaiṣṇava Sahajiyā tradition produced many great Bengali language poets and singers.Young, Mary (2014). ''The Baul Tradition: Sahaj Vision East and West,'' pp. 27-36. SCB Distributors. The 16th century CE saw an explosion of Vaishnava kirtan in the north. During this time,
 Numerous Buddhist traditions use vocal music with instrumental accompaniment as part of their rituals and devotional practices. Buddhist vocal music and chanting is often part of Buddhist
Numerous Buddhist traditions use vocal music with instrumental accompaniment as part of their rituals and devotional practices. Buddhist vocal music and chanting is often part of Buddhist
 Sikh ''kirta''n with Indian harmoniums and '' tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)">Kenya.html" ;"title="tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya">tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)
''Kirtana'' (; ), also rendered as ''Kiirtan'', ''Kirtan'' or ''Keertan'', is a
Sikh ''kirta''n with Indian harmoniums and '' tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)">Kenya.html" ;"title="tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya">tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)
''Kirtana'' (; ), also rendered as ''Kiirtan'', ''Kirtan'' or ''Keertan'', is a Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
word that means "narrating, Bhajan, reciting, telling, describing" of an idea or story, specifically in Indian religions. It also refers to a genre of religious performance arts, connoting a musical form of narration, shared recitation, or devotional singing, particularly of spiritual or religious ideas, native to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. A person performing kirtan is known as a ''kirtankara'' (or ''kirtankar,'' कीर्तनकार).
With roots in the Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
''anukirtana'' tradition, a kirtan is a call-and-response
Call and response is a form of interaction between a speaker and an audience in which the speaker's statements ("calls") are punctuated by responses from the listeners. This form is also used in music, where it falls under the general category of ...
or antiphonal
An antiphonary or antiphonal is one of the liturgical books intended for use (i.e. in the liturgical choir), and originally characterized, as its name implies, by the assignment to it principally of the antiphons used in various parts of the L ...
style song or chant
A chant (from French ', from Latin ', "to sing") is the iterative speaking or singing of words or sounds, often primarily on one or two main pitches called reciting tones. Chants may range from a simple melody involving a limited set of no ...
, set to music, wherein multiple singers recite the names of a deity, describe a legend, express loving devotion to a deity, or discuss spiritual ideas. It may include dancing or direct expression of ''bhavas'' (emotive states) by the singer. Many kirtan performances are structured to engage the audience where they either repeat the chant,Sara Brown (2012), ''Every Word Is a Song, Every Step Is a Dance'', PhD Thesis, Florida State University (Advisor: Michael Bakan), pages 25-26, 87-88, 277 or reply to the call of the singer.
A kirtan performance includes an accompaniment of regionally popular musical instruments, especially Indian instruments like the Indian harmonium
file:Harmonium 20151009 (23914086965).jpg, A Delhi style Bina brand Indian harmonium with a built in suitcase for easy transport and with 9 Organ stop, air stop knobs (stops 2, 4, 6, 8 are drones).
file:Kathmandu-21.JPG, Musicians in Kathmandu, ...
, the veena
The ''veena'', also spelled ''vina'' ( IAST: vīṇā), is any of various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps.
, sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau K ...
, or ektara
The ''ektara'' (, , , , , ; literally 'one-string', also called ''actara'', ''iktar'', ''ektar'', , ''yaktaro'', ''gopichand'', ''gopichant'', ''golki'' , ''gopijiantra'', ''tun tuna'') is a one-stringed musical instrument used in the traditio ...
(strings
String or strings may refer to:
*String (structure), a long flexible structure made from threads twisted together, which is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Strings'' (1991 film), a Canadian anim ...
), the tabla
A ''tabla'' is a pair of hand drums from the Indian subcontinent. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as an accompaniment with other instruments a ...
(one-sided drums
The drum is a member of the percussion instrument, percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel–Sachs classification system, it is a membranophones, membranophone. Drums consist of at least one Acoustic membrane, membrane, c ...
), the mrdanga
The ''khol'' is a terracotta two-sided drum used in northern and eastern India for accompaniment with devotional music (''bhakti''). It is also known as a ''mridanga'' (< Sanskrit + , ), not to be confused with ''mridangam''. It originates ...
or pakhawaj
The ''pakhavaj'' is a barrel-shaped, two-headed drum, originating from the Indian subcontinent, kendang of Maritime Southeast Asia and other South Asian double-headed drums. Its older forms were made with clay.
It is the percussion instrumen ...
(two-sided drum), flute
The flute is a member of a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, producing sound with a vibrating column of air. Flutes produce sound when the player's air flows across an opening. In th ...
(woodwinds
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments.
Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and re ...
), and karatalas
The ''taal'' or ''manjira'' (also spelled ''manjīrā'' or ''manjeera''), ''jalra'', ''karatala'', ''kartal'' or ''gini'' is a pair of clash cymbals, originating in the Indian subcontinent, which make high-pitched percussion sounds. In its ...
or talas (cymbals
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sou ...
). It is a major practice in Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, Vaisnava
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the major Hindu denominations along with S ...
devotionalism, Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
, the Sant traditions, and some forms of Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, as well as other religious groups. Kirtan is sometimes accompanied by story-telling and acting. Texts typically cover religious, mythological or social subjects.
Etymology and nomenclature
 The term ''kirtana'' (
The term ''kirtana'' (Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
: कीर्तन) generally means "telling, narrating, describing, enumerating, reporting". The Sanskrit root of kirtan is ''kirt'' (). The term is found in the Samhita
Samhita (IAST: ''Saṃhitā'') literally means "put together, joined, union", a "collection", and "a methodical, rule-based combination of text or verses".
s, the Brahmanas
The Brahmanas (; Sanskrit: , International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''Brāhmaṇam'') are Vedas, Vedic śruti works attached to the Samhitas (hymns and mantras) of the Rigveda, Rig, Samaveda, Sama, Yajurveda, Yajur, and Athar ...
, and other Vedic literature, as well as the Vedanga
The Vedanga ( ', "limb of the Veda-s"; plural form: वेदाङ्गानि ') are six auxiliary disciplines of Vedic studies that developed in Vedic and post-Vedic times.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Vedanga" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia o ...
and Sutra
''Sutra'' ()Monier Williams, ''Sanskrit English Dictionary'', Oxford University Press, Entry fo''sutra'' page 1241 in Indian literary traditions refers to an aphorism or a collection of aphorisms in the form of a manual or, more broadly, a ...
s literature. ''Kirt'', according to Monier-Williams
Sir Monier Monier-Williams (; né Williams; 12 November 1819 – 11 April 1899) was a British scholar who was the second Boden Professor of Sanskrit at Oxford University, England. He studied, documented and taught Asian languages, especially ...
, contextually means "to mention, make mention of, tell, name, call, recite, repeat, relate, declare, communicate, commemorate, celebrate, praise, glorify".
The term kirtan is found as ''anukirtan'' (or ''anukrti'', ''anukarana'', literally "retelling") in the context of a Yajna
In Hinduism, ''Yajna'' or ''Yagna'' (, Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐd͡ʒɲə ) also known as Hawan, is a ritual done in front of a sacred fire, often with mantras. Yajna has been a Vedas, Vedic tradition, described in a layer of Vedic literature ...
(Vedic ritual offering), which meant a dual recitation of Vedic hymns in a dialogue style that was part of a ritual dramatic performance.
The Sanskrit verses in the ''Shatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana (, , abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Yajurveda, Śukla Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the ...
'' (chapter 13.2, c. 800–700 BCE), for example, are written in the form of a riddle play between two actors. According to Louis Renou, in this text, "the Vedic sacrifice (''yajna
In Hinduism, ''Yajna'' or ''Yagna'' (, Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐd͡ʒɲə ) also known as Hawan, is a ritual done in front of a sacred fire, often with mantras. Yajna has been a Vedas, Vedic tradition, described in a layer of Vedic literature ...
'') is presented as a kind of drama, with its actors, its dialogues, its portion to be set to music, its interludes, and its climaxes."ML Varadpande (1990), History of Indian Theatre, Volume 1, Abhinav, , pages 45–47
Generally speaking, kirtan, sometimes called ''sankirtana'' (literally, "collective performance"), is a kind of collective chanting or musical conversation. As a genre of religious performance art, it developed in the Indian bhakti movements as a devotional religious practice (i.e. bhakti yoga
Bhakti yoga (), also called Bhakti marga (, literally the path of '' bhakti''), is a spiritual path or spiritual practice within Hinduism focused on loving devotion towards any personal deity.Karen Pechelis (2014), The Embodiment of Bhakti, ...
). But it is a heterogeneous practice that varies regionally, according to Christian Novetzke, and includes varying mixtures of musical instruments, dance, oration, theatre, audience participation, and moral narration.
In Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
for example, Novetzke says, a kirtan is a call-and-response style performance, ranging from devotional dancing and singing by a lead singer and audience to an "intricate scholarly treatise, a social commentary or a philosophical/linguistic exposition" that includes narration, allegory, humor, erudition and entertainment—all an aesthetic part of ''ranga'' (beauty, color) of the kirtan.
Kirtan is locally known by various names, including ''Abhang'', ''Samaj Gayan'', ''Haveli Sangeet'', ''Vishnupad'', ''Harikatha, and Padabali''. Vaishnava temples in Assam and northeastern Indian have large worship halls called ''kirtan ghar''—a name derived from their being used for congregational singing and performance arts. Kirtan is also sometimes called ''harinam'' (Sanskrit: harināma) in some Vaishnava traditions, which means " hantingthe names of God (Hari
Hari () is among the primary epithets of the Hindu preserver deity Vishnu, meaning 'the one who takes away' (sins). It refers to the one who removes darkness and illusion, the one who removes all obstacles to spiritual progress.
The name Ha ...
)."
In regional languages, kirtan is scripted as ; Nepali and ; ; ; / ; Sindhi: / ; ; .
Bhajan and kirtan
Kirtans and ''bhajans
Bhajan is an Indian term for any devotional song with a religious theme or spiritual ideas, specifically among Dharmic religions, in any language. The term bhajanam (Sanskrit: भजनम्) means ''reverence'' and originates from the root w ...
'' are closely related, sharing common aims (devotion, faith, spiritual uplift and liberation), subjects, and musical themes. A ''bhajan'' is freer, and can be a single melody performed by a single singer with or without musical instruments. ''Kirtan'', in contrast, is generally a group performance, typically with a call and response
Call and response is a form of interaction between a speaker and an audience in which the speaker's statements ("calls") are punctuated by responses from the listeners. This form is also used in music, where it falls under the general category of ...
or antiphonal
An antiphonary or antiphonal is one of the liturgical books intended for use (i.e. in the liturgical choir), and originally characterized, as its name implies, by the assignment to it principally of the antiphons used in various parts of the L ...
musical structure, similar to an intimate conversation or gentle sharing of ideas. Kirtan also generally includes two or more musical instruments, and has roots in Sanskrit prosody and poetic meter.
Many ''kirtans'' are structured for more audience participation, where the singer calls a spiritual chant, a hymn or a devotional theme, the audience responds by repeating the chant or by chanting back a reply of their shared beliefs.
Hindu kirtan
 A modern kirtan performance
Musical recitation of hymns, mantras and the praise of deities has ancient roots in Hinduism, and may be found in the
A modern kirtan performance
Musical recitation of hymns, mantras and the praise of deities has ancient roots in Hinduism, and may be found in the Vedic literature
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of relig ...
. A key feature of popular Hindu kirtan is that it is mostly sung in vernacular languages like Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
and Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
(unlike Vedic chanting
The oral tradition of the Vedas () consists of several pathas, "recitations" or ways of chanting the Vedic mantras. Such traditions of Vedic chant are often considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition in existence, the fixation of the Vedic text ...
, which is done in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
), though this may include Sanskrit mantras.Arnold et al (1998). ''The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music: South Asia : the Indian subcontinent,'' p. 247. Taylor & Francis. This style of vernacular singing became popular during the medieval era
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and t ...
(1300–1550) and the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
(1550–1750).
Hindu kirtan is influenced by the practices and teachings of the various devotional Bhakti movements, who emphasized emotional loving relationship with a personal God, and also by the figures of the Sant tradition (like Kabir
Kabir ( 15th century) was a well-known Indian devotional mystic poet and sant. His writings influenced Hinduism's Bhakti movement, and his verses are found in Sikhism's scripture Guru Granth Sahib, the Satguru Granth Sahib of Saint Gar ...
, Ravidas
Ravidas or Raidas was an Indian mystic poet-saint of the Bhakti movement during the 15th to 16th century CE. Venerated as a ''guru'' (spiritual teacher) in the modern regions of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya P ...
, and Namdev
Namdev (Pronunciation: aːmdeʋ, also transliterated as Nam Dayv, Namdeo, Namadeva, (traditionally, ) was a Marathi Vaishnava saint from Narsi, Hingoli, Maharashtra, Medieval India within the Varkari tradition of Hinduism. He was as a devo ...
). Beginning with the Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
People, culture and language
* Tamils, an ethno-linguistic group native to India, Sri Lanka, and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka
** Myanmar or Burmese Tamils, Tamil people of Ind ...
Alvars
The Alvars () are the Tamil poet-saints of South India who espoused '' bhakti'' (devotion) to the Hindu preserver deity Vishnu, in their songs of longing, ecstasy, and service. They are venerated in Vaishnavism, which regards Vishnu as the ...
and Nayanars
The Nayanars (or Nayanmars; , and later 'teachers of Shiva') were a group of 63 Tamils, Tamil Hindu saints living during the 6th to 8th centuries CE who were devoted to the Hindu god Shiva. Along with the Alvars, their contemporaries who were de ...
in around the 6th century, bhakti spread outside Tamilakam
Tamilakam () also known as ancient Tamil country as was the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covering the southernmost region of the Indian subcontinent. Tamilakam covered today's Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Puducherry, La ...
after the 12th century. The foundations of the kirtan traditions are also found in works like the ''Bhagavad-gita
The Bhagavad Gita (; ), often referred to as the Gita (), is a Hindu scripture, dated to the second or first century BCE, which forms part of the epic poem Mahabharata. The Gita is a synthesis of various strands of Indian religious thought, i ...
'' which describes the bhakti marga (path of loving devotion to god) as a means to moksha
''Moksha'' (; , '), also called ''vimoksha'', ''vimukti'', and ''mukti'', is a term in Jainism, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism for various forms of emancipation, liberation, '' nirvana'', or release. In its soteriological and eschatologic ...
. References to kirtan as a musical recitation are also found in the ''Bhagavata Purana
The ''Bhagavata Purana'' (; ), also known as the ''Srimad Bhagavatam (Śrīmad Bhāgavatam)'', ''Srimad Bhagavata Mahapurana'' () or simply ''Bhagavata (Bhāgavata)'', is one of Hinduism's eighteen major Puranas (''Mahapuranas'') and one ...
'', an important Vaishnava text. The story of Prahlada
Prahlada () is an asura king in Hindu scriptures. He is known for his staunch devotion to the preserver deity, Vishnu. He appears in the narrative of Narasimha, the lion avatara of Vishnu, who rescues Prahlada by disimboweling and killing hi ...
in the ''Avatara Katha'' mentions kirtan as one of nine forms of bhakti.
Bhakti
''Bhakti'' (; Pali: ''bhatti'') is a term common in Indian religions which means attachment, fondness for, devotion to, trust, homage, worship, piety, faith, or love.See Monier-Williams, ''Sanskrit Dictionary'', 1899. In Indian religions, it ...
poets and musicians like Jayadeva
Jayadeva (; born ), also spelt Jaideva, was a Sanskrit poet during the 12th century. He is most known for his epic poem ''Gita Govinda'' which concentrates on Krishna's love with the ''gopi'', Radha, in a rite of spring. This poem, which presen ...
(the 12th century author of the Sanskrit ''Gita Govinda
The ''Gita Govinda'' (; IAST: ''gītagovindam'') is a work composed by the 12th-century Hindu poet, Jayadeva. It describes the relationship between Krishna, Radha and ''gopis'' (female cow herders) of Vrindavan.
The ''Gita Govinda'' is organiz ...
'') were influential in the development of Indian devotional music genres like kirtan (which, though written in the vernacular, often imitated the style of Sanskrit bhakti poems).Arnold et al (1998). ''The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music: South Asia : the Indian subcontinent,'' pp. 249, 845. Taylor & Francis. Jayadeva was a great classical composer and wrote devotional music in the dhruvapada style (which is similar to dhrupad
Dhrupad is a genre in Hindustani classical music from the Indian subcontinent. It is the oldest known style of major vocal styles associated with Hindustani classical music (for example in the Haveli Sangeet of Pushtimarg Sampradaya), and is als ...
).
There are various forms of Hindu kirtan, including northern traditions (often influenced by Hindustani music
Hindustani classical music is the Indian classical music, classical music of the Indian subcontinent's northern regions. It may also be called North Indian classical music or ''Uttar Bhartiya shastriya sangeet''. The term ''shastriya sangeet'' ...
and Bengali music
Bengali music () comprises a long tradition of religious and secular song-writing over a period of almost a millennium. Composed with lyrics in the Bengali language, Bengali music spans a wide variety of styles.
History
The earliest mus ...
) and southern ( Carnatic) traditions. Speaking of the Bengali kirtan tradition, Peggy Holroyde writes that "kirtans do not strictly adhere to the raga
A raga ( ; , ; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a musical mode, melodic mode. It is central to classical Indian music. Each raga consists of an array of melodic structures with musical motifs; and, fro ...
scale and they incorporate a chorus led by a leader. Much of the musical value is subordinated to the sentimental emotion expressed in the words of the song."Holroyde, Peggy (2017). Indian Music: A Vast Ocean of Promise
', Routledge. Regarding the southern (Carnatic) traditions of kirtan, they are generally "less ornate" than northern kirtan, making less use of "
grace
Grace may refer to:
Places United States
* Grace, Idaho, a city
* Grace (CTA station), Chicago Transit Authority's Howard Line, Illinois
* Little Goose Creek (Kentucky), location of Grace post office
* Grace, Carroll County, Missouri, an uni ...
, trills and arabesques
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foliate ...
", but they are also much more structured musical forms.
While kirtan is influenced by the practice of Indian classical music, they are much simpler than the complicated instrumental and vocal compositions of Indian classical ensembles. The focus of kirtan is on the lyrics or mantras, which deliver religious messages and stories. Guy Beck, writing on the northern kirtan tradition, states that "melody and rhythm are important, but devotional singers normally deplore musical virtuosity for its own sake, in contrast with the classical Hindustani and Karnatak traditions, which emphasize improvisation
Improvisation, often shortened to improv, is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. The origin of the word itself is in the Latin "improvisus", which literally means un-foreseen. Improvis ...
and technical mastery
A skill is the learned or innate
ability to act with determined results with good execution often within a given amount of time, energy, or both.
Skills can often be divided into domain-general and domain-specific skills. Some examples of gene ...
. A large variety of musical styles and forms exist, and no single formula has ever been mandated by custom to the exclusion of others. Musicians and religious leaders thus freely compose religious and devotional songs."Arnold et al (1998). ''The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music: South Asia : the Indian subcontinent,'' p. 248. Taylor & Francis. However, some kirtan styles ''are'' highly refined and technical, like dhrupad
Dhrupad is a genre in Hindustani classical music from the Indian subcontinent. It is the oldest known style of major vocal styles associated with Hindustani classical music (for example in the Haveli Sangeet of Pushtimarg Sampradaya), and is als ...
and Bengali padavali kirtan, which is considered by Bengalis
Bengalis ( ), also rendered as endonym and exonym, endonym Bangalee, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The current population is divi ...
to be the most cultured religious music.
Regarding the arrangement, most kirtan performances are done by a group, with a choir led by a lead singer sitting on the floor, though sometimes, kirtan is done by standing group in temples, religious processions, or on the street.
Generally speaking, the performance may begin with recitations of Sanskrit mantras, like Om, names of deities, and may also include some Sanskrit prayers.Arnold et al (1998). ''The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music: South Asia : the Indian subcontinent,'' p. 255. Taylor & Francis. Then the lead singer
The lead vocalist in popular music is typically the member of a group or band whose voice is the most prominent melody in a performance where multiple voices may be heard. The lead singer sets their voice against the accompaniment parts of the ...
sings a song or a mantra while accompanying himself with a versatile instrument (like a harmonium
The pump organ or reed organ is a type of organ that uses free reeds to generate sound, with air passing over vibrating thin metal strips mounted in a frame. Types include the pressure-based harmonium, the suction reed organ (which employs a va ...
or a sarangi
The sārangī is a bowed, short-necked three-stringed instrument played in traditional music from South Asia – Punjabi folk music, Rajasthani folk music, Sindhi folk music, Haryanvi folk music, Braj folk music, and Boro folk music (the ...
), and the chorus (which may include the audience as well) repeats the lines and provides musical accompaniment and keeps the rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular r ...
(with percussion instruments like the tabla
A ''tabla'' is a pair of hand drums from the Indian subcontinent. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as an accompaniment with other instruments a ...
). Sometimes the lead may have some solo lines, and the chorus can accompany them with a refrain
A refrain (from Vulgar Latin ''refringere'', "to repeat", and later from Old French ''refraindre'') is the Line (poetry)">line or lines that are repeated in poetry or in music">poetry.html" ;"title="Line (poetry)">line or lines that are repeat ...
. The performance may be punctuated by short sermons or stories. The song repertoire is generally drawn from medieval authors, but may include more recent additions. In temples, a formal worship ceremony (arati
''Arti'' () or ''Aarati'' () is a Hindu ritual employed in worship, part of a '' puja'', in which light from a flame (fuelled by camphor, ghee, or oil) is ritually waved to venerate deities. ''Arti'' also refers to the hymns sung in praise of t ...
) may also follow.
Styles of Hindu kirtan
Northern Vaishnava kirtan

 One important promoter of Vaishnava kirtan in Bengal was
One important promoter of Vaishnava kirtan in Bengal was Chandidas
Chandidas (1339–1399, ) was a medieval Bengali poet from India, or possibly more than one. He wrote over 1250 poems related to the love of Radha and Krishna in medieval Bengali. The poems of Chandidas with ''bhanita'' are found with three di ...
(1339–1399), who introduced Vaishnava kirtan in Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
and was very influential on later Vaishnava northern kirtan. Chandidas was instrumental in the Bengali Vaiṣṇava Sahajiyā tradition, a form of tantric Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole Para Brahman, supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the majo ...
focused on Radha and Krishna which flourished in Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
, Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, Orissa
Odisha (), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is a state located in Eastern India. It is the eighth-largest state by area, and the eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the thir ...
, and Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
.Hayes, Glen A"The Vaisnava Sahajiya Traditions of Medieval Bengal"
in ''Religions of India in Practice'', edited by Donald S. Lopez, Jr., Princeton Readings in Religions, Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1995: 333-351. The Vaiṣṇava Sahajiyā tradition produced many great Bengali language poets and singers.Young, Mary (2014). ''The Baul Tradition: Sahaj Vision East and West,'' pp. 27-36. SCB Distributors. The 16th century CE saw an explosion of Vaishnava kirtan in the north. During this time,
Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
Chaitanya Mahaprabhu (; ), born Vishvambhara Mishra () (18 February 1486 – 14 June 1534), was an Indian Hindus, Hindu saint from Bengal and the founder of Gaudiya Vaishnavism. Chaitanya Mahaprabhu's mode of worshipping Krishna with bha ...
popularized Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
based kirtan in Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
, promoting and teaching the singing of Vaishnava songs which celebrate the love between Radha
Radha (, ), also called Radhika, is a Hindu goddess and the chief consort of the god Krishna. She is the goddess of love, tenderness, compassion, and devotion. In scriptures, Radha is mentioned as the avatar of Lakshmi and also as the Prak� ...
and Krishna, understood as being the love between the soul and God. Chaitanya is also known as the father of padavali singing, a highly developed and complex musical tradition. Padavali kirtan is further linked to process of devotional visualization in Gaudiya Vaisnava practice through a specific musical form that uses slow tempos and large tals (meters) in performance.
About the same time, Shankaradeva (1449–1568) in Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
inspired the Ekasarana Dharma
''Ekasarana Dharma'' () is a Vaishnavism#Later medieval period, Vaishnavite religion propagated by Srimanta Sankardeva in the 15th-16th century in the Indian state of Assam. It reduced focus on Vedic ritualism and focuses on devotion (''bhak ...
bhakti movement that emphasized Advaita Vedanta philosophy within the Vaishnava
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, '' Mahavishnu''. It is one of the major Hindu denominations along wit ...
framework of the ''Bhagavata Purana
The ''Bhagavata Purana'' (; ), also known as the ''Srimad Bhagavatam (Śrīmad Bhāgavatam)'', ''Srimad Bhagavata Mahapurana'' () or simply ''Bhagavata (Bhāgavata)'', is one of Hinduism's eighteen major Puranas (''Mahapuranas'') and one ...
''. Shankaradeva helped establish ''Sattras'' (Hindu temples and monasteries) with ''kirtan-ghar'' (also called ''Namghar
''Namghar'' ( ) is a place for congregational worship associated with the entire Assamese community and the ''Ekasarana'' sect of Hinduism, in particular, that is native to Assam. Besides forming the primary structure used for worship, they a ...
''), for Krishnaite singing and dramatic performance.
Meanwhile, in the Braj
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhumi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura-Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal, Ballabhgarh and Nuh in ...
region, Vallabha acharya
Vallabha, also known as Vallabhācārya or Vallabha Dīkṣita (May 7, 1478 – July 7, 1530 CE), was the founder of the Kr̥ṣṇa-centered Puṣṭimārga sect of Vaishnavism, and propounded the philosophy of Śuddhādvaita.
His biography ...
launched a devotional movement which focused on kirtan songs about baby Krishna and his early childhood. One ofshoot of this tradition is the Radha
Radha (, ), also called Radhika, is a Hindu goddess and the chief consort of the god Krishna. She is the goddess of love, tenderness, compassion, and devotion. In scriptures, Radha is mentioned as the avatar of Lakshmi and also as the Prak� ...
-centered Radha-vallabha Sampradaya, whose singing style known as Haveli Sangeet Haveli Sangeet is a form of Hindustani classical music sung in ''havelis''. The essential component is dhrupad. It originated in Govardhan,Mathura in Braj, northern India. It takes the form of devotional songs sung daily to Krishna by the Pushtimarg ...
is based on Hindustani classical forms like "dhrupad
Dhrupad is a genre in Hindustani classical music from the Indian subcontinent. It is the oldest known style of major vocal styles associated with Hindustani classical music (for example in the Haveli Sangeet of Pushtimarg Sampradaya), and is als ...
" and " dhamar". Another kirtan style shared by the Braj traditions like the Vallabha, Haridasi, and Nimbarka
Nimbarka, also known as Nimbarkacharya, Nimbaditya or Niyamananda, was a Hindu philosopher, theologian and the chief proponent of the theology of Svabhavika Bhedabheda, Dvaitādvaita (dvaita–advaita) or dualistic–non-dualistic sometimes kn ...
is samaj gayan, which is a kind of collective singing.
Kirtan as a genre of religious music has been a major part of the Vaishnavism tradition, particularly starting with the Alvars
The Alvars () are the Tamil poet-saints of South India who espoused '' bhakti'' (devotion) to the Hindu preserver deity Vishnu, in their songs of longing, ecstasy, and service. They are venerated in Vaishnavism, which regards Vishnu as the ...
of Sri Vaishnavism
Sri Vaishnavism () is a denomination within the Vaishnavism tradition of Hinduism, predominantly practiced in South India. The name refers to goddess Lakshmi (also known as Sri), as well as a prefix that means "sacred, revered", and the god Vi ...
sub-tradition between the 7th to 10th century CE. After the 13th-century, two subgenres of kirtan emerged in Vaishnavism, namely the '' Nama-kirtana'' wherein the different names or aspects of god (a Vishnu avatar) are extolled, and the ''Lila- kirtana'' wherein the deity's life and legends are narrated.
In the modern era, north Indian styles of kirtan are widely practiced in the modernist movements of Swami Sivananda
Swami Sivananda Saraswati (; 8 September 1887 – 14 July 1963), also called Swami Sivananda, was a Modern yoga gurus, yoga guru, a Hinduism, Hindu spiritual teacher, and a proponent of ''Vedanta''. Sivananda was born in Pattamadai, in the Ti ...
, Anandamayi Ma
Anandamayi Ma (born Nirmala Sundari; 30 April 1896 – 27 August 1982) was an Indian saint, teacher, and mystic. She was revered as an incarnation of Hindu goddess Durga.
She was described by Sivananda Saraswati (of the Divine Life Society) ...
, Sri Aurobindo
Sri Aurobindo (born Aurobindo Ghose; 15 August 1872 – 5 December 1950) was an Indian Modern yoga gurus, yogi, maharishi, and Indian nationalist. He also edited the newspaper Bande Mataram (publication), ''Bande Mataram''.
Aurobindo st ...
, and A. C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada
Abhay Charanaravinda Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada (; ) (1 September 1896 – 14 November 1977) was a spiritual, philosophical, and religious teacher from India who spread the Hare Krishna mantra and the teachings of "Krishna consciousness" ...
.
Carnatic traditions
InAndhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
, the compositions of the Tallapaka Annamacharya
Tallapaka Annamacharya () (09 May 1408 – 23 February 1503), also popularly known as Annamayya, was a Telugu musician, composer, and a Hindu saint. He is the earliest known Indian musician to compose songs called '' samkirtanas.'' His devoti ...
, a 14th-century Vaishnava mystic, represent the earliest known southern music called "sankirtana". He wrote in praise of Lord Venkateswara, the deity of Seven Hills in Tirumala
Tirumala is a Hindu religious temple town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the neighbourhoods of the Tirupati city. The town is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority and located in Tirupat ...
. During his long and prolific career, he reputedly composed and sang 32,000 Sankirtanas and 12 Shatakas (sets of hundred verses) in both Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of South India
** Telugu literature, is the body of works written in the Telugu language.
* Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Tel ...
and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
.
Marathi kirtan
Maharashtri musicians at Veerabhadra Devasthan, Vadhav A kirtan circle in Maharashtra There are three main styles of Marathi kirtan, Varkari, Naradiya and Jugalbandi. Varkari Kirtan was pioneered by Sant Namdev (1270–1350) inMaharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
. It is usually based on the works of seven famous Maharashtri saints: Saint Nivruttinath, Sant Dnyaneshwar
Sant Dnyaneshwar (Marathi pronunciation: ̪ɲaːn̪eʃʋəɾ, (Devanagari : सन्त ज्ञानेश्वर), also referred to as Jñāneśvara, Jñānadeva, Dnyandev or Mauli or Dnyaneshwar Vitthal Kulkarni (1275–1296 (living ...
, Sopandev, Muktabai, saint Eknath, Saint Namdev, and Saint Tukaram. Marathi kirtan is typically performed by one or two main performers, accompanied by harmonium
The pump organ or reed organ is a type of organ that uses free reeds to generate sound, with air passing over vibrating thin metal strips mounted in a frame. Types include the pressure-based harmonium, the suction reed organ (which employs a va ...
and ''tabla
A ''tabla'' is a pair of hand drums from the Indian subcontinent. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as an accompaniment with other instruments a ...
''. It involves singing, acting, dancing, and story-telling.
The show goes for two or three hours as time permits and is not divided into parts like "Naradiya Kirtan". This form was effectively performed for years by personalities like Hari Bhakti Parayan (sincere devotee of god) Sonopant (mama) Dandekar, Dhunda maharaj Deglurkar, Babamaharaj Satarkar, Dekhanebuwa, and many others in modern times. An institute at Alandi near Pune
Pune ( ; , ISO 15919, ISO: ), previously spelled in English as Poona (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1978), is a city in the state of Maharashtra in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan plateau in Western ...
offers training in this form of Kirtan.
Naradiya Kirtan is divided into five main parts: naman (prayer), Purvaranga (the main spiritual lesson), chanting the names of God, katha or Akhyan (a story to support the lesson), final prayer. The Naradiya Marathi Kirtan popular in Maharashtra is most often performed by a single performer, and contains the poetry of saints of Maharashtra such as Dnyaneshwar
Sant Dnyaneshwar (Marathi pronunciation: ̪ɲaːn̪eʃʋəɾ, (Devanagari : सन्त ज्ञानेश्वर), also referred to as Jñāneśvara, Jñānadeva, Dnyandev or Mauli or Dnyaneshwar Vitthal Kulkarni (1275–1296 (living ...
, Eknath
Eknath (IAST: Eka-nātha, Marathi pronunciation: knath (1533–1599), was an Indian Hindu Vaishnava saint, philosopher and poet. He was a devotee of the Hindu deity Vitthal and is a major figure of the Warkari movement. Eknath is often vie ...
, Namdev
Namdev (Pronunciation: aːmdeʋ, also transliterated as Nam Dayv, Namdeo, Namadeva, (traditionally, ) was a Marathi Vaishnava saint from Narsi, Hingoli, Maharashtra, Medieval India within the Varkari tradition of Hinduism. He was as a devo ...
and Tukaram
Tukaram (Marathi pronunciation: ̪ukaːɾam, also known as Tuka, Tukobaraya and Tukoba, was a Hindu Marathi saint of the Warkari sampradaya in Dehu village, Maharashtra in the 17th century. He was a '' bhakt'' of the god Vithoba, also kn ...
. Learned poets from 17th and 18th century such as Shridhar, Mahipati
Mahipati (1715 - 1790) was an 18th century Marathi language hagiographer who wrote biographies of prominent Hindu Vaishnava sants who had lived between the 13th and the 17th centuries in Maharashtra and other regions of India.
Early life
Mahi ...
, and Moropant contributed to develop this form of kirtan. A Naradiya kirtan performance can last for period of any length, from half an hour to three hours. Attendees may wear traditional clothing and the performers use instruments like the Indian harmonium, drums, and string instruments of various types mostly "Zanz", "chipali", "Tal" or "Chimata". Naradiya kirtan performers are usually very learned in literature, music, dance, acting and comedy.
Jugalbandi Kirtan is performed by two persons, allowing question-answer, dialogue and debate. Performance requires skill in music, dance, comedy, oratory, debate, memory, general knowledge and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
literature. Training takes place at the Kirtan Kul in Sangli, the Akhil Bharatiya Kirtan Sanstha in Dadar, Mumbai, the Narad Mandir at Sadashiv Peth, Pune and the Kalidas Mahavidyalay in Ramtek
Ramtek is a city and municipal council in Nagpur district of Maharashtra, India.
Religious significance
Ramtek hosts a historic temple of Rama. It is believed that Ramtek was the place where Rama, the Hindu god, rested while he was in exile, ...
, Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Nāgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
as well as at smaller schools in Goa, Beed and Ujjain.
Sikhism
file:Photograph of Bhai Jawala Singh Ragi playing accordion (vaaja), Bhai Gurcharn Singh on Jori, and Bhai Avtar Singh on Taus at Gurdwara Dehra Sahib, Lahore, ca.1935.jpg, Bhai Jawala Singh Ragi playingharmonium
The pump organ or reed organ is a type of organ that uses free reeds to generate sound, with air passing over vibrating thin metal strips mounted in a frame. Types include the pressure-based harmonium, the suction reed organ (which employs a va ...
, Bhai Gurcharn Singh on Jori, and Bhai Avtar Singh on Taus at Gurdwara Dera Sahib, Gurdwara Dehra Sahib, Lahore, 1935
''Kirtan'' (Gurmukhi: ਕੀਰਤਨ ''Kīratana'') refers to devotional singing in Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
. It is typically performed at Gurdwaras
A gurdwara or gurudwara () is a place of assembly and worship in Sikhism, but its normal meaning is "place of guru" or "home of guru". Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths and religions are welcomed in gurd ...
(Sikh temples). Sikh scriptures and legends are usually recited in a song, to a certain ''raga
A raga ( ; , ; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a musical mode, melodic mode. It is central to classical Indian music. Each raga consists of an array of melodic structures with musical motifs; and, fro ...
'' and accompanied with musical instruments. The Gurus themselves created numerous musical instruments including the Taus, the Sarangi
The sārangī is a bowed, short-necked three-stringed instrument played in traditional music from South Asia – Punjabi folk music, Rajasthani folk music, Sindhi folk music, Haryanvi folk music, Braj folk music, and Boro folk music (the ...
, the Saranda and a modification of the Pakhawaj
The ''pakhavaj'' is a barrel-shaped, two-headed drum, originating from the Indian subcontinent, kendang of Maritime Southeast Asia and other South Asian double-headed drums. Its older forms were made with clay.
It is the percussion instrumen ...
(called Jori) creating an early form of the Tabla
A ''tabla'' is a pair of hand drums from the Indian subcontinent. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as an accompaniment with other instruments a ...
.
A ''Shabad Kirtan'' refers to the musical recitation of the Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib (, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth (), its first rendition, w ...
, the primary scripture in the Sikhism tradition which is arranged according to ''raga
A raga ( ; , ; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a musical mode, melodic mode. It is central to classical Indian music. Each raga consists of an array of melodic structures with musical motifs; and, fro ...
''. ''Shabad Kirtan'' can be listened to silently or sung along with the gathered congregation.
''Kirtan'' in Sikh history has been the musical analog of ''Kathas'' recitation, both preferably performed by ''ragi jatha'', or professional trained performers. A Sikh Kirtan is a religious, aesthetic and social event, usually held in a congregational setting on Sundays or over certain festivals to honor the historical Gurus, but major temples in the Sikh tradition recite ''Kirtan'' every day as a mark of daily bhakti
''Bhakti'' (; Pali: ''bhatti'') is a term common in Indian religions which means attachment, fondness for, devotion to, trust, homage, worship, piety, faith, or love.See Monier-Williams, ''Sanskrit Dictionary'', 1899. In Indian religions, it ...
(devotional remembrance) of God's name.
This congregational setting is called a ''Sangat'' or ''Satsang'', a word that in ancient Indian texts means "like minded individuals, or fellow travelers on a spiritual journey".
Buddhism
 Numerous Buddhist traditions use vocal music with instrumental accompaniment as part of their rituals and devotional practices. Buddhist vocal music and chanting is often part of Buddhist
Numerous Buddhist traditions use vocal music with instrumental accompaniment as part of their rituals and devotional practices. Buddhist vocal music and chanting is often part of Buddhist rituals
A ritual is a repeated, structured sequence of actions or behaviors that alters the internal or external state of an individual, group, or environment, regardless of conscious understanding, emotional context, or symbolic meaning. Traditionally ...
and festivals
A festival is an event celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, Melā, mela, or Muslim holidays, eid. A ...
in which they may be seen as offerings to the Buddha. Chants, songs and plays about the life of the Buddha by the Buddhists of Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
are sometimes called ''Buddha-samkirtan'' or ''Buddha kirtan.'' Instruments like the Indian harmonium, flute, dotara
The ''dotara'' or ''dotar''
( ''dütüra'', দোতৰা ''dütora'', ; ''dotora''), (literally, “Of r ‘having’two strings”) is a two- stringed, plucked musical instrument from South Asia, with most contemporary models having four ...
, khol
The ''khol'' is a terracotta two-sided drum used in northern and eastern India for accompaniment with devotional music ('' bhakti''). It is also known as a ''mridanga'' (<
 The famed Bengali saint
The famed Bengali saint
Kamini Natarajan
an
Sheela Bringi
Kirtan singing has also become popular among Westerners who consider themselves spiritual but who are not part of any specific religious institution or movement ("
online
/ref>
KirtanThe Braj Ras Lila
Darius Swann (1975)
The Washington Post, Michelle Boorstein (2013) {{Authority control Hindu prayer and meditation Bhakti movement Indian folk music Indian feminine given names Feminine given names Hindu music Performing arts in India Puja (Hinduism) Music of Bengal Indian styles of music
early Buddhism The term Early Buddhism can refer to at least two distinct periods in the History of Buddhism, mostly in the History of Buddhism in India:
* Pre-sectarian Buddhism, which refers to the teachings and monastic organization and structure, founded by ...
, as attested by artistic depictions in Indian sites like Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
. Early Buddhist sources often have a negative attitude towards music, possibly because it was considered sensual and inconsistent with its core monastic teachings. However, Mahayana
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, Buddhist texts#Mahāyāna texts, texts, Buddhist philosophy, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main ex ...
and Vajrayana
''Vajrayāna'' (; 'vajra vehicle'), also known as Mantrayāna ('mantra vehicle'), Guhyamantrayāna ('secret mantra vehicle'), Tantrayāna ('tantra vehicle'), Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, is a Mahāyāna Buddhism, Mahāyāna Buddhis ...
sources tend to be much more positive to music, seeing it as a suitable offering to the Buddhas and as a skillful means
In Buddhism, upaya (Sanskrit: उपाय, , ''expedient means'', ''pedagogy'') is an aspect of guidance along the Buddhist paths to liberation where a conscious, voluntary action "is driven by an incomplete reasoning" about its direction. Upa ...
to bring sentient beings to Buddhism. Buddhist songs and chants make use of the following genres: sutras
''Sutra'' ()Monier Williams, ''Sanskrit English Dictionary'', Oxford University Press, Entry fo''sutra'' page 1241 in Indian literary traditions refers to an aphorism or a collection of aphorisms in the form of a manual or, more broadly, a ...
, mantras
A mantra ( ; Pali: ''mantra'') or mantram (Devanagari: मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words (most often in an Indo-Iranian language like Sanskrit or Avestan) belie ...
, dharani
Dharanis (IAST: ), also known as (Skt.) ''vidyās'' and ''paritas'' or (Pal.) ''parittas'', are lengthier Buddhist mantras functioning as mnemonic codes, incantations, or recitations, and almost exclusively written originally in Sanskrit while Pa ...
, parittas, or verse compositions (such as gathas
The Gathas () are 17 hymns in the Avestan language from the Zoroastrian oral tradition of the Avesta. The oldest surviving text fragment dates from 1323 CE, but they are believed by scholars to have been composed before 1000 BCE and passed dow ...
, stotras
''Stotra'' (Sanskrit: स्तोत्र) is a Sanskrit word that means "ode, eulogy or a hymn of praise."Monier Williams, Monier Williams' Sanskrit-English Dictionary, Oxford University Press, Article on 'Stotra'' It is a literary genre of In ...
, and caryagitis).
Examples of Buddhist musical traditions include the Newari Buddhist Gunlā Bājan, Tibetan Buddhist music, Japanese Buddhist
Buddhism was first established in Japan in the 6th century CE. Most of the Japanese Buddhists belong to new schools of Buddhism which were established in the Kamakura period (1185-1333). During the Edo period (1603–1868), Buddhism was cont ...
Shōmyō
is a style of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the nort ...
, modern Indian Buddhist bhajans
Bhajan is an Indian term for any devotional song with a religious theme or spiritual ideas, specifically among Dharmic religions, in any language. The term bhajanam (Sanskrit: भजनम्) means ''reverence'' and originates from the root w ...
, and Cambodian Smot chanting. As there are many different traditions of Buddhist music and chanting, the musical instruments
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
used vary widely, from solely relying on the human voice
The human voice consists of sound Voice production, made by a human being using the vocal tract, including Speech, talking, singing, Laughter, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically ...
, to many types of classic instruments used in Asian music
Asian music encompass numerous musical styles, traditions, and forms originating in Asian countries.
Asian music traditions include:
*
** Music of China
** Music of Hong Kong
** Music of Japan
** Traditional music of Korea
*** Music of Nor ...
(such as the ancient Indian veena
The ''veena'', also spelled ''vina'' ( IAST: vīṇā), is any of various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps.
) as well as modern instruments (harmonium
The pump organ or reed organ is a type of organ that uses free reeds to generate sound, with air passing over vibrating thin metal strips mounted in a frame. Types include the pressure-based harmonium, the suction reed organ (which employs a va ...
, keyboards, guitars
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
, etc).
There are also some Western Buddhists who have recently adopted kirtan singing. One Western Buddhist kirtan artist is Lee Mirabai Harrington.
Judaism
TheBene Israel
The Bene Israel (), also referred to as the "Teli, Shanivar Teli" () or "History of the Jews in India, Native Jew" caste, are a community of Jews in India. It has been suggested that they are the descendants of one of the Ten Lost Tribes via t ...
, a Jewish community in the Indian subcontinent, adopted the devotional singing style Kirtan from their Marathi Hindu neighbors. Their main traditional musical instruments are the Indian Harmonium
file:Harmonium 20151009 (23914086965).jpg, A Delhi style Bina brand Indian harmonium with a built in suitcase for easy transport and with 9 Organ stop, air stop knobs (stops 2, 4, 6, 8 are drones).
file:Kathmandu-21.JPG, Musicians in Kathmandu, ...
and the Bulbul tarang.
In the modern era, kirtan has also been adopted by several jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
like Susan Deikman. These jewish kirtans replace Sanskrit Hindu lyrics with Hebrew songs and chants.
In the Western world
Krishna kirtan in Times Square Western kirtan performers at Bhakti Fest The famed Bengali saint
The famed Bengali saint Paramahansa Yogananda
Paramahansa Yogananda (born Mukunda Lal Ghosh; January 5, 1893March 7, 1952) was an Indian and American Hindu monk, yoga, yogi and guru who introduced millions to meditation and Kriya Yoga school, Kriya Yoga through his organization, Self ...
was an early proponent of kirtan in the West
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.
West or The West may also refer to:
Geography and locations
Global context
* The Western world
* Western culture and Western civilization in general
* The Western Bloc, countries allied with NAT ...
. He chanted Guru Nanak Dev
Guru ( ; IAST: ''guru'') is a Sanskrit term for a "mentor, guide, expert, or master" of certain knowledge or field. In pan-Indian traditions, a guru is more than a teacher: traditionally, the guru is a reverential figure to the disciple (or '' s ...
's ''Hey Hari Sundara'' ("Oh God Beautiful") with 3,000 people at Carnegie Hall
Carnegie Hall ( ) is a concert venue in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is at 881 Seventh Avenue (Manhattan), Seventh Avenue, occupying the east side of Seventh Avenue between 56th Street (Manhattan), 56th and 57th Street (Manhattan), 57t ...
in 1923.
Kirtan became more common with the spread of Indian religious movements in the West in the 1960s. Movements which were influential in bringing Indian kirtan to West include the International Society for Krishna Consciousness
The International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), commonly known as the Hare Krishna movement, is a religious organization that follows the Gaudiya Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism. It was founded on 13 July 1966 in New York City by ...
(ISKCON), 3HO
3HO (Healthy, Happy, Holy Organization), also known as Sikh Dharma of the Western Hemisphere or Sikh Dharma International, is a controversial American organization founded in 1969 by Harbhajan Singh Khalsa, also called "Yogi Bhajan".Yogi Bhajan
Yogi Bhajan (born Harbhajan Singh Puri) (August 26, 1929 – October 6, 2004), also known as Siri Singh Sahib to his followers, was an American entrepreneur, yoga guru, and putative spiritual teacher. He introduced his version of Kundalin ...
), the Ramakrishna mission
Ramakrishna Math and Ramakrishna Mission (RKM) is a spiritual and philanthropic organisation headquartered in Belur Math, West Bengal. The mission is named after the Indian Hindu spiritual guru and mystic Ramakrishna. The mission was founde ...
, the Divine Life Society
The Divine Life Society (DLS) is a Hinduism, Hindu spiritual organization and an ashram, founded by Swami Sivananda Saraswati in 1936, at Muni Ki Reti, Rishikesh, India. The Society has branches around the world, with its headquarters in Rishi ...
, and Yogananda's Self-Realization Fellowship
Self-Realization Fellowship (SRF) is a worldwide religious organization founded in 1920 by Paramahansa Yogananda, the Indian guru who authored '' Autobiography of a Yogi''. Before moving to the United States, Yogananda began his spiritual wo ...
.
Western kirtan singers, some of who learned in India, have also popularized the practice. Western kirtan performers include Krishna Das, Bhagavan Das, Nina Rao, Wah!
Peter James Wylie (born 22 March 1958) is an English singer-songwriter and guitarist, best known as the leader of the band variously known as Wah!, Wah! Heat, Shambeko! Say Wah!, JF Wah!, The Mighty Wah! and Wah! The Mongrel.
Career Early ba ...
, Jai Uttal
Jai Uttal (born June 12, 1951) is an American musician. He is a Grammy-nominated singer and “a pioneer in the world music community with his eclectic East-meets-West sound.”
Biography
Uttal grew up in New York City and lived in a home fille ...
, Snatam Kaur
Snatam Kaur Khalsa (born June 19, 1972 in Trinidad, Colorado), is an American singer, songwriter and author. Kaur performs new age Indian devotional music, kirtan, and tours the world as a peace activist. The surname "Kaur", meaning "princes ...
, Lokah Music, Deva Premal
Jolantha Fries (born 2 April 1970), known professionally as Deva Premal, is a German singer known for her performances of Sanskrit mantras. Her music is composed and produced with Prabhu Music. Her album ''Deva'' (2018) was nominated for a Gramm ...
, Jahnavi Harrison
Jahnavi Harrison, also known by her spiritual name, Jahnavi Jivana dasi, is a British musician known for her Hindu mantra meditation music (kirtan). She regularly appears as a presenter on BBC Radio 4's '' Something Understood'' programme and BB ...
, Jim Gelcer
Jim Gelcer (born December 16, 1961) is a Canadian jazz drummer, singer, musician, composer, and producer, also known for blending traditional kirtan, a genre of spiritual music from India, with modern influences like R&B, jazz, and rock.
Histor ...
, Jyoshna, Aindra Das, Gina Sala', and Gaura Vani & As Kindred Spirits. Western Yoga centers report an increase in attendance at kirtans; according to ''Pure Music''s Frank Goodman in conversation with Krishna Das in 2006, kirtan has taken on a wider popularity. Some Western kirtan singers have also adapted kirtan songs with influences from other styles, including rock music
Rock is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in the United States as "rock and roll" in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of styles from the mid-1960s, primarily in the United States and the United Kingdo ...
, new-age music
New-age is a genre of music intended to create artistic inspiration, relaxation, and optimism. It is used by listeners for yoga, massage, meditation, and reading as a method of stress management to bring about a state of ecstasy rather tha ...
, African music
The continent of Africa is vast and its music is diverse, with different regions and nations having many distinct musical traditions. African music includes the genres like makwaya, highlife, mbube, township music, jùjú, fuji, jaiva ...
and latin american music.Enstedt, Daniel; Plank, Katarina (2023). ''Eastern Practices and Nordic Bodies: Lived Religion, Spirituality and Healing in the Nordic Countries,'' p. 96, 101. Springer Nature. There are also Kirtan singers in the west who sing more traditional Indian style kirtan such aKamini Natarajan
an
Sheela Bringi
Kirtan singing has also become popular among Westerners who consider themselves spiritual but who are not part of any specific religious institution or movement ("
spiritual but not religious
"Spiritual but not religious" (SBNR), also known as "spiritual but not affiliated" (SBNA), or less commonly "more spiritual than religious", is a popular phrase and initialism used to self-identify a life stance of spirituality that does not reg ...
"). In this case, kirtan is seen as a social, expressive and holistic experience which helps one connect with the inner self. It is also considered egalitarian and manifests as an eclectic practice which draws on multiple cultures and is tolerant to most religions. Western spiritual kirtan can be found in Western yoga
Yoga as exercise is a physical activity consisting mainly of postures, often connected by flowing sequences, sometimes accompanied by breathing exercises, and frequently ending with relaxation lying down or meditation. Yoga in this form has ...
centers, new age
New Age is a range of Spirituality, spiritual or Religion, religious practices and beliefs that rapidly grew in Western world, Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclecticism, eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise d ...
groups, spiritual communes, and neo-shamanic circles.
For some Western practitioners, kirtan is seen as a way of socializing, relaxing, achieving meditative states, expressing oneself, attaining inner peace and positive emotions, getting to know one's inner self, and cultivating love for a deity and for others.
In the United States case law, the term ''sankirtana'' has also been used to specifically refer to the promotional activities of ISKCON. ISKCON had sought the right to perform ''sankirtana'' in California airports such as in Los Angeles. The court ruled that while ISKCON has a constitutional rights of protected speech, the Los Angeles airport also has a right to forbid any form of solicitation, out of "a legitimate interest in controlling pedestrian congestion and reducing the risk of fraud and duress attendant to repetitive, in-person solicitation of funds" by all groups including ISKCON.Supreme Court of California, opinion in ISKCON v. City of Los Angeles, pages 2, 12–2online
/ref>
Given name
The male given name Kirtan or Kirtana is used in South India for females as well, particularly inTelangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
, and Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
.
See also
*Adi Shankara
Adi Shankara (8th c. CE), also called Adi Shankaracharya (, ), was an Indian Vedanga, Vedic scholar, Hindu philosophy, philosopher and teacher (''acharya'') of Advaita Vedanta. Reliable information on Shankara's actual life is scant, and h ...
* Ananda Marga
Ānanda Mārga (, Schwa deletion in Indo-Aryan languages, also spelled Anand Marg and Ananda Marg), or officially Ānanda Mārga Pracāraka Saṃgha (organization for the propagation of the path of bliss), is a world-wide socio-spiritual orga ...
* Bhakti
''Bhakti'' (; Pali: ''bhatti'') is a term common in Indian religions which means attachment, fondness for, devotion to, trust, homage, worship, piety, faith, or love.See Monier-Williams, ''Sanskrit Dictionary'', 1899. In Indian religions, it ...
* Bhakti movement
The Bhakti movement was a significant religious movement in medieval Hinduism that sought to bring religious reforms to all strata of society by adopting the method of Bhakti, devotion to achieve salvation. Originating in Tamilakam during 6t ...
* Bhakti yoga
Bhakti yoga (), also called Bhakti marga (, literally the path of '' bhakti''), is a spiritual path or spiritual practice within Hinduism focused on loving devotion towards any personal deity.Karen Pechelis (2014), The Embodiment of Bhakti, ...
* Bhajan
Bhajan is an Indian term for any devotional song with a religious theme or spiritual ideas, specifically among Dharmic religions, in any language. The term bhajanam (Sanskrit: भजनम्) means ''reverence'' and originates from the root w ...
* Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
Chaitanya Mahaprabhu (; ), born Vishvambhara Mishra () (18 February 1486 – 14 June 1534), was an Indian Hindus, Hindu saint from Bengal and the founder of Gaudiya Vaishnavism. Chaitanya Mahaprabhu's mode of worshipping Krishna with bha ...
* Gaudiya Vaishnavism
Gaudiya Vaishnavism (), also known as Chaitanya Vaishnavism, is a Vaishnavism, Vaishnava Hindu denominations, Hindu religious movement inspired by Chaitanya Mahaprabhu (1486–1534) in India. "Gaudiya" refers to the Gaura or Gauḍa region o ...
* Gurbani
Gurbani (, pronunciation: , lit. the Guru's words) is a Sikh term, very commonly used by Sikhs to refer to various compositions by the Sikh Gurus and other writers of Guru Granth Sahib. In general, hymns in the central text of the Sikhs, the Gu ...
* Hindustani language
Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in North India and Pakistan as the lingua franca of the region. It is also spoken by the Deccani people, Deccani-speaking community in the Deccan plateau. Hindustani is a pluricentric language w ...
* Historical Vedic religion
The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedism or Brahmanism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontin ...
* Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east ...
* International Society for Krishna Consciousness
The International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), commonly known as the Hare Krishna movement, is a religious organization that follows the Gaudiya Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism. It was founded on 13 July 1966 in New York City by ...
** Hare Krishna (mantra)
The Hare Krishna mantra, also referred to reverentially as the (), is a 16-word Vaishnava mantra mentioned in the Kali-Saṇṭāraṇa Upaniṣad. In the 15th century, it rose to importance in the Bhakti movement following the teachings o ...
* :Kirtan performers
* Nama sankeerthanam
The namasamkirtana (), also rendered namajapa () is the Hindu practice of congregational chanting of the names and other sacred expressions associated with a given deity. More commonly practised by members of the Vaishnava tradition, the namasamk ...
* Raga
A raga ( ; , ; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a musical mode, melodic mode. It is central to classical Indian music. Each raga consists of an array of melodic structures with musical motifs; and, fro ...
* Sikh music
Sikh music, also known as Gurbani Sangeet (; meaning ''music of'' ''the speech of wisdom'')'','' and as Gurmat Sangeet (; meaning ''music of the counsel or tenets of the Guru'')'','' or even as Shabad Kirtan (), is the classical music style that i ...
* Substratum in Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit has a number of linguistic features which are alien to most other Indo-European languages. Prominent examples include: phonologically, the introduction of retroflexes, which alternate with dentals, and morphologically, the formati ...
* Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit, also simply referred as the Vedic language, is the most ancient known precursor to Sanskrit, a language in the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is atteste ...
* Vedic chant
The oral tradition of the Vedas () consists of several pathas, "recitations" or ways of chanting the Vedic mantras. Such traditions of Vedic chant are often considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition in existence, the fixation of the Vedic text ...
* Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
References
External links
Kirtan
Darius Swann (1975)
The Washington Post, Michelle Boorstein (2013) {{Authority control Hindu prayer and meditation Bhakti movement Indian folk music Indian feminine given names Feminine given names Hindu music Performing arts in India Puja (Hinduism) Music of Bengal Indian styles of music