Saint Lawrence Valley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international



 Large
Large
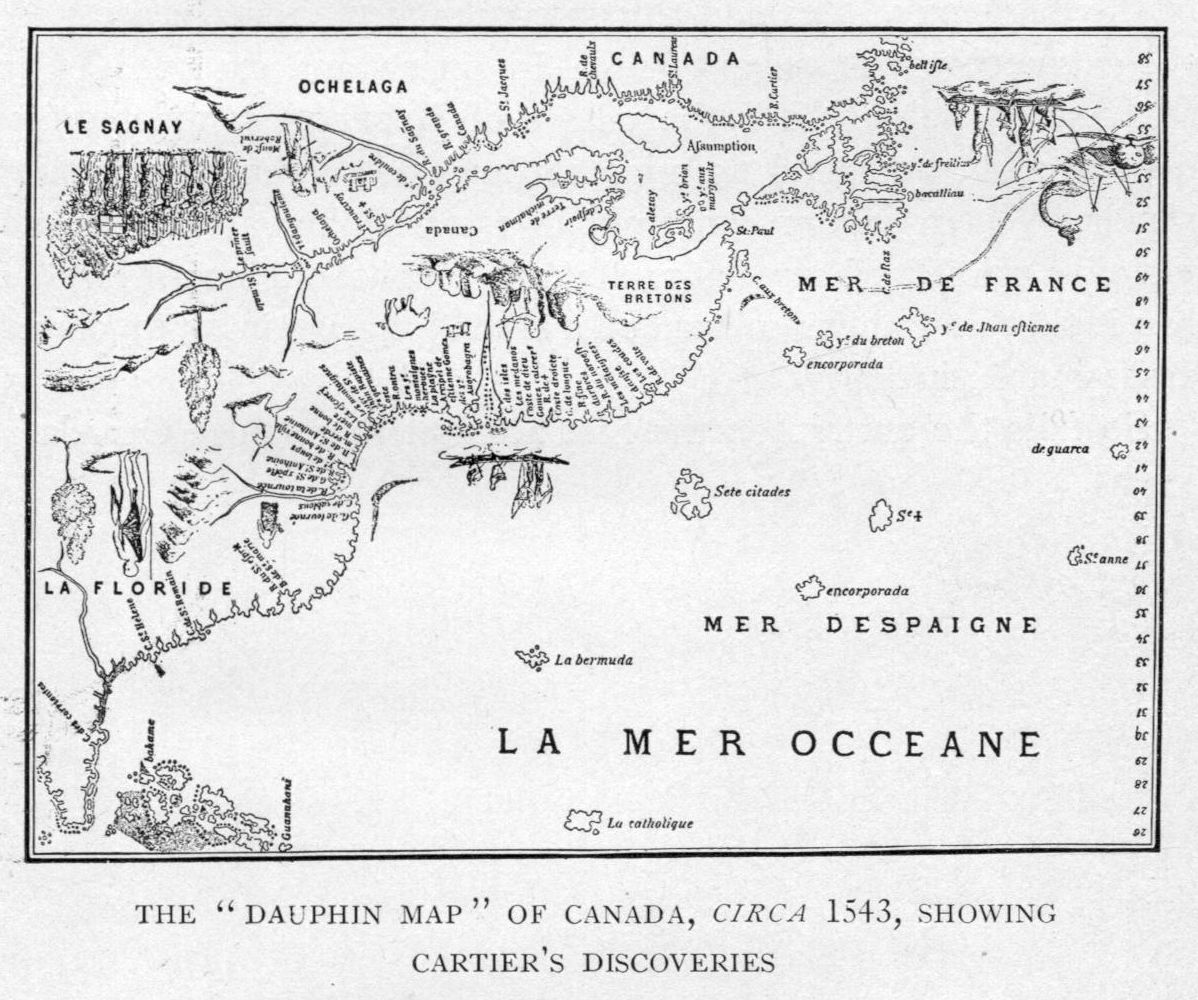

 *
*
Fur Trade Canoe Routes of Canada/Then and Now
1969, Eric W. Morse, M.A.;F.R.G.S, 121 p.
The Saint Lawrence Its Basin & Border-Lands
1905, Dr. S. E. Dawson, 584 p.
St. Lawrence Parks Commission (Ontario)
Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway SystemRadio Aids to Marine Navigation 2024
Radio Aids to Marine Navigation 2024, (Atlantic, St. Lawrence, Great Lakes, Lake Winnipeg, Arctic and Pacific)
Safe Passage: Aids to Navigation on the St. Lawrence
– Historical essay, illustrated with drawings and photographs
Annotated Bibliography on St. Lawrence County and Northern New York region.
International St. Lawrence River Board of Control
Saint Lawrence River, The Canadian Encyclopedia
Watch the Jacques Cousteau documentary, ''St. Lawrence: Stairway to the Sea''
Timing and position of late Wisconsinan ice-margins on the upper slope seaward of Laurentian Channel
David J. W. Piper et Adam Macdonald, 2001, 11 page {{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Lawrence River Physiographic provinces International rivers of North America Rivers of New York (state) Rivers of Ontario Canada–United States border Rivers of Montérégie Rivers of Capitale-Nationale Rivers of St. Lawrence County, New York Regions of New York (state)
river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
in the middle latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
s of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
connecting the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
to the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The Canada–United Sta ...
to the Gulf of St. Lawrence, traversing Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
and Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
in Canada and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
in the United States. A section of the river demarcates the Canada–U.S. border.
As the primary drainage outflow of the Great Lakes Basin, the St. Lawrence has the second-highest discharge of any river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
(after the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
) and the 16th-highest in the world. The estuary of the St. Lawrence is often cited by scientists as the largest in the world. Significant natural landmarks of the river and estuary include the 1,864 river islands of the Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (, ) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for about downstream fr ...
, the endangered whales of Saguenay–St. Lawrence Marine Park, and the limestone monoliths of the Mingan Archipelago.
Long a transportation route to Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
, the St. Lawrence River has played a key role in the history of Canada
The history of Canada covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Indians to North America thousands of years ago to the present day. The lands encompassing present-day Canada have been inhabited for millennia by Indigenous peoples, with d ...
and in the development of cities such as Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
. The river remains an important shipping route as the backbone of the St. Lawrence Seaway, a lock and canal system that enables world marine traffic to access the inland ports of the Great Lakes Waterway
The Great Lakes Waterway (GLW) is a system of natural channels and artificial locks and canals that enable navigation between the North American Great Lakes. Although all of the lakes are naturally connected as a chain, water travel between the ...
.
Etymology
The river has historically been given a variety of different names by localFirst Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
. Beginning in the 16th century, French explorers visited what is now Canada and gave the river names such as the ''Grand fleuve de Hochelaga'' and the ''Grande rivière du Canada'', where ''fleuve'' and ''rivière'' are two French words (''fleuve'' being a river that flows into the sea).
The river's present name has been used since 1604 when it was recorded on a map by Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
. Champlain opted for the names ''Grande riviere de sainct Laurens'' and ''Fleuve sainct Laurens'' in his writings, supplanting the earlier names. In contemporary French, the name is rendered as the ''fleuve Saint-Laurent''. The name ''Saint-Laurent'' (Saint Lawrence) was originally applied to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, eponymous bay by Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
upon his arrival into the region on the 10th of August feast day
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does n ...
for Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence (; 31 December 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, persecution of the Christians that the Roman Empire, Rom ...
in 1535.
Indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
use the following names:
*Innu-aimun
Innu-aimun or Montagnais is an Algonquian language spoken by over 10,000 Innu in Labrador and Quebec in Eastern Canada. It is a member of the Cree–Montagnais–Naskapi dialect continuum and is spoken in various dialects depending on the com ...
, the language of Nitassinan
Nitassinan () is the ancestral homeland of the Innu, an indigenous people of Eastern Quebec and Labrador, Canada. Nitassinan means "our land" in the Innu language. The territory covers the eastern portion of the Labrador peninsula.'' Nitassi ...
, refer to it as ''Wepistukujaw Sipo''/''Wepìstùkwiyaht sīpu''.
*the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
call it ''Moliantegok''/''Moliantekw'' ("Montréal River"), ''Kchitegw''/''Ktsitekw''/''Gicitegw'' ("Great River"), or ''Oss8genaizibo''/''Ws8genaisibo''/''Wsogenaisibo'' ("River of the Algonquins").
*in Mohawk language
Mohawk () or (' anguageof the Flint Place') is an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian language currently spoken by around 3,500 people of the Mohawk people, Mohawk nation, located primarily in current or former Haudenosaunee territories, predomin ...
it is ''Roiatatokenti'', ''Raoteniateara'', ''Ken’tarókwen'', or ''Kaniatarowanénhne''.
*Tuscarora people
The Tuscarora (in Tuscarora language, Tuscarora ''Skarù:ręˀ'') are an indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands in Canada and the United States. They are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian Native Americans in the United States, Native Amer ...
call it ''Kahnawáˀkye'' or ''Kaniatarowanenneh'' ("Big Water Current").
*Algonquin people
The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada and parts of the United States. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely ...
call it "the Walking Path" or ''Magtogoek'', or ''Kitcikanii sipi'', the "Large Water River".
*the Huron-Wendat Nation
The Huron-Wendat Nation (or Huron-Wendat First Nation) is an Iroquoian-speaking nation that was established in the 17th century. In the French language, used by most members of the First Nation, they are known as the . The French gave the nickn ...
call it ''Lada8anna'' or ''Laooendaooena.
*the Atikamekw
The Atikamekw are an Indigenous people in Canada. Their historic territory, ('Our Land'), is in the upper Saint-Maurice River valley of Quebec (about north of Montreal). One of the main communities is Manawan, about northeast of Montreal. ...
of Nitaskinan refer to it as '' Micta sipi'' ("Huge River").
Geography



Marine weather
In winter, the St. Lawrence River begins producing ice in December betweenMontreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
. The prevailing winds and currents push this ice towards the estuary, and it reaches the east of Les Méchins at the end of December. Ice covers the entire Gulf of St. Lawrence in January and February.
Ice helps navigation by preventing the formation of waves, and therefore spray, and prevents the icing of ships.
Watershed
With the draining of theChamplain Sea
The Champlain Sea () was a prehistoric inlet of the Atlantic Ocean into the North American continent, created by the retreating ice sheets during the closure of the last glacial period. The inlet once included lands in what are now the Canadi ...
, due to a rebounding continent from the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
, the St. Lawrence River was formed. The Champlain Sea lasted from about 13,000 years ago to about 10,000 years ago and was continuously shrinking during that time, a process that continues today. The head of the St. Lawrence River, near Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The Canada–United Sta ...
, is home to the Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (, ) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for about downstream fr ...
.
Today, the St. Lawrence River begins at the outflow of Lake Ontario and flows adjacent to Cape Vincent, Gananoque, Clayton, Alexandria Bay, Brockville
Brockville is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada, in the Thousand Islands region. Although it is the seat of the United Counties of Leeds and Grenville, it is politically Independent city, independent of the county. It is included with Leeds and ...
, Morristown, Ogdensburg, Massena, Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
, Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
, Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières (, ; ) is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice River, Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence River, Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Sain ...
, and Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
before draining into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, often given as the largest estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
in the world. The estuary begins at the eastern tip of Île d'Orléans
Île d'Orléans (; ) is an island located in the Saint Lawrence River about east of downtown Quebec City, Quebec, Canada. It was one of the first parts of the province to be colonized by the French, and a large percentage of French Canadians c ...
, just downstream from Quebec City. The river becomes tidal around Quebec City.
The St. Lawrence River runs from the farthest headwater to the mouth and from the outflow of Lake Ontario. These numbers include the estuary; without the estuary, the length from Lake Ontario is c. 500 km (c. 300 mi). The farthest headwater is the North River in the Mesabi Range
The Mesabi Iron Range is a mining district and mountain range in northeastern Minnesota following an elongate trend containing large deposits of iron ore. It is the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iro ...
at Hibbing, Minnesota. Its drainage area, which includes the Great Lakes, the world's largest system of freshwater lakes, is , of which is in Canada and is in the United States. The basin covers parts of Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
and Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
in Canada, parts of Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
, Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
, and nearly the entirety of the state of Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
in the United States. The average discharge below the Saguenay River is . At Quebec City, it is . The average discharge at the river's source, the outflow of Lake Ontario, is .
The St. Lawrence River includes Lake Saint Francis at Salaberry-de-Valleyfield, Lake Saint-Louis south of Montreal and Lake Saint Pierre east of Montreal. It encompasses four archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
es: the Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (, ) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for about downstream fr ...
chain near Alexandria Bay, New York and Kingston, Ontario
Kingston is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the northeastern end of Lake Ontario. It is at the beginning of the St. Lawrence River and at the mouth of the Cataraqui River, the south end of the Rideau Canal. Kingston is near the Thousand Islands, ...
; the Hochelaga Archipelago, including the Island of Montreal
The Island of Montreal (, ) is an island in southwestern Quebec, Canada, which is the site of a number of municipalities, including most of the city of Montreal, and is the most populous island in Canada. It is the main island of the Hochelag ...
and Île Jésus ( Laval); the Lake St. Pierre Archipelago (classified a biosphere world reserve by the UNESCO in 2000) and the smaller Mingan Archipelago. Other islands include Île d'Orléans near Quebec City and Anticosti Island north of the Gaspé. It is the second longest river in Canada.
Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain ( ; , ) is a natural freshwater lake in North America. It mostly lies between the U.S. states of New York (state), New York and Vermont, but also extends north into the Canadian province of Quebec.
The cities of Burlington, Ve ...
and the Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
, Richelieu, Saint-Maurice, Saint-François, Chaudière and Saguenay rivers drain into the St. Lawrence.
The St. Lawrence River is in a seismically active zone where fault reactivation is believed to occur along late Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozo ...
to early Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
normal faults related to the opening of the Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). It was in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalon ...
. The faults in the area are rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
-related and comprise the Saint Lawrence rift system.
According to the United States Geological Survey, the St. Lawrence Valley is a physiographic province
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific characte ...
of the larger Appalachian division, containing the Champlain section. However, in Canada, where most of the valley is, it is instead considered part of a distinct St. Lawrence Lowlands physiographic division, and not part of the Appalachian division.
Sources
The source of the North River in theMesabi Range
The Mesabi Iron Range is a mining district and mountain range in northeastern Minnesota following an elongate trend containing large deposits of iron ore. It is the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iro ...
in Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
(Seven Beaver Lake) is considered to be the source of the St. Lawrence River. Because it crosses so many lakes, the water system frequently changes its name. From source to mouth, the names are:
The St. Lawrence River also passes through Lake Saint-Louis and Lake Saint-Pierre in Quebec.
Tributaries
The St. Lawrence River and the largest tributaries of theGreat Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
.
The St. Lawrence River tributaries are listed upstream from the mouth. The major tributaries of the inter-lake sections are also shown, as well as the major rivers that flow into the Great Lakes. Great Lakes tributaries are listed in alphabetical order.
The list includes all tributaries with a drainage area
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, th ...
of at least 1,000 square kilometres and an average flow of more than 10 cubic metres per second.
Discharge
Biodiversity
The diversity of the St. Lawrence River includes: * 19 species ofmarine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s
* More than 230 species of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s
* Nearly 35 species of amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s and reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s
* 200 species of freshwater and saltwater fish (including 19 shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s and rays)
* 2200 invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s in the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
and its gulf
A gulf is a large inlet from an ocean or their seas into a landmass, larger and typically (though not always) with a narrower opening than a bay (geography), bay. The term was used traditionally for large, highly indented navigable bodies of s ...
(sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and a ...
s, jellyfish
Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies or simply jellies, are the #Life cycle, medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animal ...
, coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, etc.)
* Nearly 2000 vascular plants
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes (, ) or collectively tracheophyta (; ), are plants that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue ( ...
Marine mammals
 Large
Large marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s travel in all the seas of the earth, the research and observations of these giants concern fishermen
A fisherman or fisher is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.
Worldwide, there are about 38 million commercial and subsistence fishers and fish farmers. Fishermen may be professional or recr ...
and shipping industry
Maritime transport (or ocean transport) or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people (passengers or goods (cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by watercraft has been widely used throughout recorded history, as it provi ...
, exercise a fascination and a keen interest for laymen and, subjects of endless studies for scientists from Quebec, Canada and around the world.
Thirteen species of cetaceans frequent the waters of the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
and the Gulf of St. Lawrence:
# Northern bottlenose whale
# Delphinapterus leucas (Beluga Whale)
# Sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the Genus (biology), genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the s ...
# Atlantic white-sided dolphin
# White-beaked dolphin
# Orca
The orca (''Orcinus orca''), or killer whale, is a toothed whale and the largest member of the oceanic dolphin family. The only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'', it is recognizable by its black-and-white-patterned body. A cosmopol ...
# Long-finned pilot whale
The long-finned pilot whale, or pothead whale (''Globicephala melas'') is a large species of oceanic dolphin. It shares the genus ''Pilot whale, Globicephala'' with the short-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala macrorhynchus''). Long-finned pilo ...
# Phocoena phocoena
The harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena'') is one of eight extant species of porpoise. It is one of the smallest species of cetacean. As its name implies, it stays close to coastal areas or river estuaries, and as such, is the most familiar ...
(Harbour Porpoise)
# North Atlantic right whale
The North Atlantic right whale (''Eubalaena glacialis'') is a baleen whale, one of three right whale species belonging to the genus ''Eubalaena'', all of which were formerly classified as a single species. Because of their docile nature, their sl ...
# Common minke whale
The common minke whale or northern minke whale (''Balaenoptera acutorostrata'') is a species of minke whale within the suborder of baleen whales.
It is the smallest species of the rorquals and the second smallest species of baleen whale. Althoug ...
# Blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
# Humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh u ...
# Fin whale
The fin whale (''Balaenoptera physalus''), also known as the finback whale or common rorqual, is a species of baleen whale and the second-longest cetacean after the blue whale. The biggest individual reportedly measured in length, wi ...
History


First Nations
Flowing through and adjacent to numerous Indigenous homelands, the river was a primary thoroughfare for many peoples. Beginning in Dawnland at the Gulf of St. Lawrence, the river bordersMi'kma'ki
Mi'kma'ki or Mi'gma'gi is composed of the traditional and current territories, or country, of the Mi'kmaq people, in what is now Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and eastern Quebec, Canada. It is shared by an Non-governmental ...
in the South (what is today known as the Canadian Maritimes), and Nitassinan
Nitassinan () is the ancestral homeland of the Innu, an indigenous people of Eastern Quebec and Labrador, Canada. Nitassinan means "our land" in the Innu language. The territory covers the eastern portion of the Labrador peninsula.'' Nitassi ...
in the North, the national territory of the Innu people
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer t ...
. On the south shore beyond the Mi'kmaw
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Bru ...
district of Gespe'gewa'ki, the river passes Wolastokuk (the Maliseet
The Wolastoqiyik, (, also known as the Maliseet or Malecite () are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the Indigenous people of the Wolastoq ( Saint John River) valley and its tributaries. Their terri ...
homeland), Pαnawαhpskewahki (the Penobscot
The Penobscot (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic p ...
homeland), and Ndakinna (the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
homeland). Continuing, the river passes through the former country of the St. Lawrence Iroquois and then three of the six homelands of the Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( ), also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the Endonym and exonym, endonym Haudenosaunee ( ; ) are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Ind ...
: the Mohawk or Kanienʼkehá꞉ka, the Oneida or Onyota'a:ka, and the Onondaga or Onöñda’gaga’.
In the early 17th century, the Huron-Wendat Nation
The Huron-Wendat Nation (or Huron-Wendat First Nation) is an Iroquoian-speaking nation that was established in the 17th century. In the French language, used by most members of the First Nation, they are known as the . The French gave the nickn ...
migrated from their original country of Huronia to what is now known as Nionwentsïo centred around Wendake. Nionwentsïo occupies both the north and south shores of the river, overlapping with Nitassinan and the more western Wabanaki or Dawnland countries. Adjacent on the north shore is the Atikamekw territorial homeland of Nitaskinan and, upstream, the further reaches of Anishinaabewaki, specifically the homelands of the Algonquin and Mississauga
Mississauga is a Canadian city in the province of Ontario. Situated on the north-western shore of Lake Ontario in the Regional Municipality of Peel, it borders Toronto (Etobicoke) to the east, Brampton to the north, Milton to the northwest, ...
Nations.
European exploration
The Norse explored the Gulf of St. Lawrence in the 11th century and were followed by fifteenth- and early sixteenth-century European mariners, such asJohn Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
, and the brothers Gaspar and Miguel Corte-Real. The first European explorer known to have sailed up the St. Lawrence River itself was Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
. At that time, the land along the river described as "about two leagues, a mountain as tall as a heap of wheat" was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians. During Cartier's second voyage in 1535, because Cartier arrived in the estuary on Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence (; 31 December 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, persecution of the Christians that the Roman Empire, Rom ...
's feast day 10 August, he named it the ''Gulf of Saint Lawrence''.
The St. Lawrence River is today partly within the U.S. and as such is that country's sixth oldest surviving European place-name.
Early colonists
The earliest regular Europeans in the area were theBasques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
, who came to the St Lawrence Gulf and River in pursuit of whales from the early 16th century. The Basque whalers and fishermen traded with indigenous Americans and set up settlements, leaving vestiges all over the coast of eastern Canada and deep into the St. Lawrence River. Basque commercial and fishing activity reached its peak before the '' Armada Invencibles disaster (1588), when the Basque whaling fleet was confiscated by King Philip II of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He ...
. Initially, the whaling galleons from Labourd
Labourd (; ; ; ) is a former French province and part of the present-day Pyrénées Atlantiques '' département'' of Nouvelle-Aquitaine region. It is one of the traditional Basque provinces, and identified as one of the territorial component pa ...
were not affected by the Spanish defeat.
Until the early 17th century, the French used the name ''Rivière du Canada'' to designate the St. Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The St. Lawrence River served as the main route for European exploration of the North American interior, first pioneered by French explorer Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
.
Colonial control
Control of the river was crucial to Great Britain in the Seven Years War, British strategy to capture New France in theSeven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
. Having captured Louisbourg in 1758, the British sailed up to Quebec the following year thanks to charts drawn up by James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
. British troops were ferried via the St. Lawrence to attack the city from the west, which they successfully did at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham
The Battle of the Plains of Abraham, also known as the Battle of Quebec (), was a pivotal battle in the Seven Years' War (referred to as the French and Indian War to describe the North American theatre). The battle, which took place on 13 Sept ...
. The river was used again by the British to defeat the French siege of Quebec under the Chevalier de Lévis
Chevalier may refer to:
Honours Belgium
* a rank in the Belgian Order of the Crown (Belgium), Order of the Crown
* a rank in the Belgian Order of Leopold (Belgium), Order of Leopold
* a rank in the Belgian Order of Leopold II
* a title in the Be ...
in 1760.
In 1809, the first steamboat to ply its trade on the St. Lawrence was built and operated by John Molson
John Molson (28 December 1763 – 11 January 1836) was an English people, English-born brewer and entrepreneur in colonial Province of Quebec (1763–91), Quebec, which during his lifetime became Lower Canada. In addition to founding Molson Brewe ...
and associates, a scant two years after Fulton's steam-powered navigation of the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
. The '' Accommodation'' with ten passengers made her maiden voyage from Montreal to Quebec City in 66 hours, for 30 of which she was at anchor. She had a keel of 75 feet, and a length overall of 85 feet. The cost of a ticket was eight dollars upstream, and nine dollars down. She had berths that year for twenty passengers.
Within a decade, daily service was available in the hotly-contested Montreal-Quebec route.
Because of the virtually impassable Lachine Rapids
The Lachine Rapids () are a series of rapids on the Saint Lawrence River, between the Island of Montreal and the South Shore. They are confusingly located near the borough of Lasalle and not Lachine.
The Lachine Rapids contain large standi ...
, the St. Lawrence was once continuously navigable only as far as Montreal. Opened in 1825, the Lachine Canal
The Lachine Canal (, ) is a canal passing through the southwestern part of the Island of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, running 14.5 kilometres (9 miles) from the Old Port of Montreal to Lake Saint-Louis, through the boroughs of Lachine (borough), L ...
was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids. An extensive system of canals and locks, known as the St. Lawrence Seaway, was officially opened on 26 June 1959 by Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
(representing Canada) and President Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
(representing the United States). The Seaway (including the Welland Canal
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, and part of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. The canal traverses the Niagara Peninsula between Port Weller, Ontario, Port Weller on Lake Ontario, and Port Colborne on Lak ...
) now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. Lake Michigan–Huron has a larger combined surface area than Superior, but is normally considered tw ...
.
Modern Canada
Alcoa
Alcoa Corporation (an acronym for "Aluminum Company of America") is an American industrial corporation. It is the world's eighth-largest producer of aluminum. Alcoa conducts operations in 10 countries. Alcoa is a major producer of primary alu ...
, Reynolds Metals Company, and General Motors (GM) Central Foundry operated along the St. Lawrence River and its tributaries for decades. The Alcoa plant opened in 1903, and Reynolds and GM began operations in the late 1950s. These facilities released toxic substances into the St. Lawrence River and the surrounding area, including PCBs, PAHs, cyanide
In chemistry, cyanide () is an inorganic chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom.
Ionic cyanides contain the cyanide anion . This a ...
, fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
, and dioxins.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Battle of the St. Lawrence involved submarine and anti-submarine actions throughout the lower St. Lawrence River and the entire Gulf of St. Lawrence, Strait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle ( ; ) is a waterway in eastern Canada, that separates Labrador from the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is located in the southeast of the ...
and Cabot Strait from May to October 1942, September 1943, and again in October and November 1944. During this time, German U-boat
U-boats are Submarine#Military, naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the World War I, First and Second World Wars. The term is an Anglicization#Loanwords, anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the G ...
s sank several merchant marine ships and three Canadian warships.
In the late 1970s, the river was the subject of a successful ecological campaign (called "Save the River"), originally responding to planned development by the United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wo ...
. The campaign was organized, among others, by Abbie Hoffman
Abbot Howard Hoffman (November 30, 1936 – April 12, 1989) was an American political and social activist who co-founded the Youth International Party ("Yippies") and was a member of the Chicago Seven. He was also a leading proponent of the ...
.
In popular culture
 *
* Gatien Lapointe
Gatien Lapointe (December 18, 1931 - September 15, 1983) was a Canadian poet from Quebec.Cloutier-Wojciechowska C. (1985) "The St. Lawrence in the Poetry of Gatien Lapointe". In: Tymieniecka AT. (eds) Poetics of the Elements in the Human Condition: ...
, ''Ode au Saint-Laurent'', Éditions du Jour, Montréal, 1963, Paradis, A. (1963), report, 3 pages.
* The river was the setting for the Canadian television drama series '' Seaway''.
* It is the namesake of '' Saint-Laurent Herald''.
* In 1980, Jacques Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (, also , ; 11 June 191025 June 1997) was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called the ...
filmed '' Cries from the Deep'' and ''St. Lawrence: Stairway to the Sea''.
*The 1993 Canadian animated short film '' The Mighty River'' was about the river.
*The novel and film '' Black Robe'' are set primarily on the St. Lawrence River during the 17th century.
*The 1941 children's book '' Paddle-to-the-Sea'', and the film '' Paddle to the Sea'', involve passage through the St. Lawrence River.
*The St. Lawrence River is mentioned in the 1967 single Canadian Railroad Trilogy by Gordon Lightfoot
Gordon Meredith Lightfoot Jr. (November 17, 1938 – May 1, 2023) was a Canadian singer-songwriter who achieved worldwide success and helped define the singer-songwriter era of the 1970s. Widely considered one of Canada's greatest songwriters, ...
.
See also
References
Bibliography
External links
Fur Trade Canoe Routes of Canada/Then and Now
1969, Eric W. Morse, M.A.;F.R.G.S, 121 p.
The Saint Lawrence Its Basin & Border-Lands
1905, Dr. S. E. Dawson, 584 p.
St. Lawrence Parks Commission (Ontario)
Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway System
Radio Aids to Marine Navigation 2024, (Atlantic, St. Lawrence, Great Lakes, Lake Winnipeg, Arctic and Pacific)
Fisheries and Oceans Canada
Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO; ) is a department of the Government of Canada that is responsible for developing and implementing policies and programs in support of Canada's economic, ecological and scientific interests in oceans and inland ...
, 298 pages
Safe Passage: Aids to Navigation on the St. Lawrence
– Historical essay, illustrated with drawings and photographs
Annotated Bibliography on St. Lawrence County and Northern New York region.
International St. Lawrence River Board of Control
Saint Lawrence River, The Canadian Encyclopedia
Watch the Jacques Cousteau documentary, ''St. Lawrence: Stairway to the Sea''
Timing and position of late Wisconsinan ice-margins on the upper slope seaward of Laurentian Channel
David J. W. Piper et Adam Macdonald, 2001, 11 page {{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Lawrence River Physiographic provinces International rivers of North America Rivers of New York (state) Rivers of Ontario Canada–United States border Rivers of Montérégie Rivers of Capitale-Nationale Rivers of St. Lawrence County, New York Regions of New York (state)