Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
on the
Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spans . Thailand
is bordered to the northwest by
Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
, to the northeast and east by
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
, to the southeast by
Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, to the south by the
Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. ...
and
Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, and to the southwest by the
Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
; it also shares
maritime border
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of Earth's water surface areas using physiographical or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boun ...
s with
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
to the southeast and
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
and
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
to the southwest.
Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
is the state capital and
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metrop ...
.
Thai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 6th to 11th centuries.
Indianised kingdoms such as the
Mon,
Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was an empire in Southeast Asia, centered on Hydraulic empire, hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja (; ) by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilization of Chenla and lasted from 802 t ...
, and
Malay states
The monarchies of Malaysia exist in each of the nine Malay states under the constitutional monarchy system as practised in Malaysia. The political system of Malaysia is based on the Westminster parliamentary system in combination with features ...
ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as the Kingdoms of
Ngoenyang
Hiran Nakhon Ngoenyang (; ), also known as Chayaworanakhon Chiang Lao, Hiranyanakhon Ngoenyang Chiang Saen, Nakhon Yangkapura, or Thasai Ngoenyang was an early mueang or kingdom of the Northern Thai people from the 7th through 13th centuries A ...
,
Sukhothai,
Lan Na
The Lan Na kingdom or the Kingdom of Lanna (, , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; , , ), also known as Lannathai, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to the 18th centuries.
The cultural developmen ...
, and
Ayutthaya
Ayutthaya, Ayudhya, or Ayuthia may refer to:
* Ayutthaya Kingdom, a Thai kingdom that existed from 1350 to 1767
** Ayutthaya Historical Park, the ruins of the old capital city of the Ayutthaya Kingdom
* Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province (locall ...
, which also rivalled each other. European contact began in 1511 with a
Portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, which became a regional power by the end of the 15th century. Ayutthaya reached its peak during the 18th century, until it was destroyed in the
Burmese–Siamese War.
King Taksin the Great quickly reunified the fragmented territory and established the short-lived
Thonburi Kingdom
The Thonburi Kingdom was a major Thai people, Siamese kingdom which existed in Southeast Asia from 1767 to 1782, centered around the city of Thonburi, in Siam or present-day Thailand. The kingdom was founded by Taksin, who reunited Siam follow ...
(1767–1782), of which he was the only king. He was succeeded in 1782 by
Phutthayotfa Chulalok (Rama I), the first monarch of the current
Chakri dynasty
The Chakri dynasty is the current reigning dynasty of the Thailand, Kingdom of Thailand. The head of the house is the Monarchy of Thailand, king, who is head of state. The family has ruled Thailand since the founding of the Rattanakosin era and ...
. Throughout the era of
Western imperialism in Asia, Siam remained the only state in the region to avoid
colonisation
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
by foreign powers, although it was often forced to make
territorial
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
trade and legal concessions in unequal treaties. The Siamese system of government was centralised and transformed into a modern unitary
absolute monarchy during the 1868–1910 reign of
Chulalongkorn
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his death in 1910 was cha ...
(Rama V).
In
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Siam sided with
the Allies, a political decision made in order to amend the unequal treaties. Following a bloodless
revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
in 1932, it became a constitutional monarchy and changed its official name to Thailand,
becoming an ally of Japan in
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. In the late 1950s, a military coup under
Sarit Thanarat
Sarit Thanarat (also spelled Dhanarajata; ; born Siri (); 16 June 1908 – 8 December 1963) was a Thai politician and military commander. He served as commander-in-chief of the Royal Thai Army (from 1954) and as Minister of Defense during ...
revived the monarchy's historically influential role in politics. During the
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, Thailand became a
major non-NATO ally
A major non-NATO ally (MNNA) is a designation given by the Federal government of the United States, United States government to countries that have strategic working relationships with the United States Armed Forces while not being members of t ...
of the United States and played an
anti-communist role in the region as a member of
SEATO, which was disbanded in 1977.
Apart from a
brief period of parliamentary democracy in the mid-1970s and 1990s, Thailand has periodically alternated between
democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
and
military rule. Since the 2000s, the country has been in continual political conflict between supporters and opponents of twice-elected
Prime Minister of Thailand
The prime minister of Thailand (, , ; literally 'chief minister of state') is the head of government of Thailand. The prime minister is also the chair of the cabinet of Thailand. The post has existed since the Siamese Revolution of 1932, when ...
Thaksin Shinawatra
Thaksin Shinawatra (, ; born 26 July 1949) is a Thai businessman and politician who was the 23rd prime minister of Thailand from 2001 to 2006. Since 2009 he has also been a citizen of Montenegro.
Thaksin founded the mobile phone operator A ...
, which resulted in two
coups (in
2006
2006 was designated as the International Year of Deserts and Desertification.
Events
January
* January 1– 4 – Russia temporarily cuts shipment of natural gas to Ukraine during a price dispute.
* January 12 – A stampede during t ...
and
2014
The year 2014 was marked by the surge of the Western African Ebola epidemic, West African Ebola epidemic, which began in 2013, becoming the List of Ebola outbreaks, most widespread outbreak of the Ebola, Ebola virus in human history, resul ...
), along with the establishment of its
current constitution, a
nominally democratic government after the
2019 Thai general election
Nineteen or 19 may refer to:
* 19 (number)
* One of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019
Films
* ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film
* ''Nineteen'' (1987 film), a 1987 science fiction film
* '' 19-Nineteen'', a 2009 South Korean film
* '' D ...
, and
large pro-democracy protests in 2020–2021, which included unprecedented demands to reform the monarchy. Since 2019, it has been nominally a
parliamentary
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
; in practice, however, structural advantages in the constitution have ensured the military's continued influence in politics.
Thailand is a
middle power
A middle power is a state that is not a superpower or a great power, but still exerts influence and plays a significant role in international relations. These countries often possess certain capabilities, such as strong economies, advanced tech ...
in global affairs and a founding member of
ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
. It has the
second-largest economy in Southeast Asia and the
23rd-largest in the world by
PPP, and it ranks
29th by nominal GDP. Thailand is classified as a
newly industrialised economy, with manufacturing, agriculture, and
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
as leading sectors.
Etymology
Thailand was known by outsiders before 1939 as ''Siam''. According to
George Cœdès, the word ''Thai'' () means 'free man' in the Thai language, "differentiating the Thai from the natives encompassed in Thai society as serfs".
According to
Chit Phumisak, Thai () simply means 'people' or 'human being'; his investigation shows that some rural areas used the word "Thai" instead of the usual Thai word ''khon'' () for people.
According to
Michel Ferlus
Michel Ferlus (; 1935 – 10 March 2024) was a French linguistics, linguist who specialized in the historical phonology of languages of Southeast Asia. In addition to phonological systems, he also studied writing systems, in particular the evoluti ...
, the ethnonyms Thai-Tai (or Thay-Tay) would have evolved from the etymon ''*k(ə)ri:'' 'human being'.
Thais often refer to their country using the polite form ''prathet Thai'' (). They also use the more colloquial term ''mueang Thai'' () or simply ''Thai;'' the word ''
mueang
Mueang ( Ahom: 𑜉𑜢𑜤𑜂𑜫; ''mɯ̄ang'', ), Muang ( ''mɯ́ang'', ), Möng ( Tai Nuea: ᥛᥫᥒᥰ ''möeng''; ''móeng'', ), Meng ( zh, c=猛 or 勐) or Mường (Vietnamese) were pre-modern semi-independent city-states or princip ...
'', archaically referring to a
city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
, is commonly used to refer to a city or town as the centre of a region. ''Ratcha Anachak Thai'' () means 'kingdom of Thailand' or 'kingdom of Thai'.
Etymologically, its components are: ''ratcha'' (, ''
rājan
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long ...
'', 'king, royal, realm'), ''ana-'' (
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
''āṇā'' 'authority, command, power', itself from the Sanskrit , ''ājñā'', of the same meaning), and ''-chak'' (from Sanskrit ''cakra-'' 'wheel', a symbol of power and rule).
The
Thai National Anthem
The Thai National Anthem, also simply referred to as the National Anthem, is the national anthem of Thailand. It was officially adopted in its current form on 10 December 1939. It replaced "Sansoen Phra Barami" as the civilian anthem in 1932 (the ...
(), written by
Luang Saranupraphan during the patriotic 1930s, refers to the Thai nation as ''prathet Thai'' (). The first line of the national anthem is: ''prathet thai ruam lueat nuea chat chuea thai'' (), 'Thailand is founded on blood and flesh'.
The former name ''Siam'' may have originated from
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
श्याम (''śyāma'', 'dark')
or
Mon ရာမည (''rhmañña'', 'stranger'), probably the same root as ''
Shan'' and ''
Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
''. The word ''Śyâma'' is possibly not the true origin, but a pre-designed deviation from its proper, original meaning. Another theory is the name derives from the Chinese calling this region 'Xian'.
The ancient Khmers used the word ''Siam'' to refer to people settled in the west
Chao Phraya River
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
valley surrounding the ancient city of
Nakhon Pathom
Nakhon Pathom (, ) is a city (''thesaban nakhon'') in central Thailand, the former capital of Nakhon Pathom province. One of the most important landmarks is the giant Phra Pathommachedi. The city is also home to Thailand's only Bhikkhuni temple W ...
in the present-day
central Thailand
Central Thailand (Central Plain) (historically also known as Siam or Dvaravati) is one of the regions of Thailand, covering the broad alluvial plain of the Chao Phraya River. It is separated from northeast Thailand (Isan) by the Phetchabun Mount ...
; it may probably originate from the name of Lord
Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
, which also called ''Shyam'', as in the
Wat Sri Chum Inscription, dated 13th century CE, mentions came to restore
Phra Pathommachedi at the city of Lord Krishna (Nakhon Pathom) in the early era of the
Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom was a post-classical Siamese kingdom (Mandala (political model), ''maṇḍala'') in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai Historical Park, Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thaila ...
.
The signature of King
Mongkut
Mongkut (18 October 18041 October 1868) was the fourth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama IV. He reigned from 1851 until his death in 1868.
The reign of Mongkut was marked by significant modernization ini ...
(r. 1851–1868) reads ''SPPM'' (''Somdet Phra Poramenthra Maha'') ''Mongkut Rex Siamensium'' (Mongkut, King of the Siamese). This usage of the name in
the country's first international treaty gave the name ''Siam'' official status, until 24 June 1939 when it was changed to ''Thailand''.
History
Prehistory and origins
There is evidence of continuous human habitation in present-day Thailand from 20,000 years ago to the present day.
The earliest evidence of rice growing is dated at 2,000 BCE.
Areas comprising what is now Thailand participated in the
Maritime Jade Road
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Pri ...
, as ascertained by archeological research. The trading network existed for 3,000 years, between 2000 BCE to 1000 CE. Bronze appeared –1,000 BCE.
The site of
Ban Chiang in northeast Thailand currently ranks as the earliest known centre of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia. Iron appeared around 500 BCE.
The
Kingdom of Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartography, Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Greater India#Indianized kingdoms of South East Asia, Indianized state—or, rather a loose netwo ...
was the first and most powerful Southeast Asian kingdom at the time (2nd century BCE).
The
Mon people
The Mon (; Thai Mon: ဂကူမည်; , ; , ) are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand (mostly in Pathum Than ...
established the principalities of
Dvaravati and Kingdom of
Hariphunchai in the 6th century. The
Khmer people
The Khmer people (, Romanization of Khmer#UNGEGN, UNGEGN: , Romanization of Khmer#ALA-LC Romanization Tables, ALA-LC: ) are an Austroasiatic ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 95% of Cambodia's population of 17 million.https ...
established the
Khmer empire
The Khmer Empire was an empire in Southeast Asia, centered on Hydraulic empire, hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja (; ) by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilization of Chenla and lasted from 802 t ...
, centred in
Angkor
Angkor ( , 'capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura (; ),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-English Dictionary''. Bureau of Special Research in Modern Languages. The Catholic Uni ...
, in the 9th century.
, a Malay state controlling trade through the
Malacca Strait
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, long and from wide, between the Malay Peninsula to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pa ...
, rose in the 10th century.
The Indochina peninsula was heavily influenced by the
culture and religions of India from the time of the Kingdom of Funan to that of the Khmer Empire.
The
Thai people
Thai people, historically known as Siamese people, are an ethnic group native to Thailand. In a narrower and ethnic sense, the Thais are also a Tai peoples, Tai ethnic group dominant in Central Thailand, Central and Southern Thailand (Siam prope ...
are of the
Tai ethnic group, characterised by common linguistic roots.
Chinese chronicles first mention the Tai peoples in the 6th century BCE. While there are many assumptions regarding the origin of Tai peoples,
David K. Wyatt, a historian of Thailand, argued that their ancestors who at present inhabit Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, India, and China came from the
Điện Biên Phủ
Điện Biên Phủ (, vi-hantu, ) is a city in the Northwest (Vietnam), northwestern region of Vietnam. It is the capital of Điện Biên Province. The city is best known for the decisive Battle of Dien Bien Phu, Battle of Điện Biên Phủ ...
area between the 5th and the 8th century.
Thai people began migrating into present-day Thailand gradually from the 6th to 11th century, which Mon and Khmer people occupied at the time. Thus Thai culture was influenced by Indian, Mon, and Khmer cultures. Tai people intermixed with various ethnic and cultural groups in the region, resulting in many groups of present-day Thai people. Genetic evidences suggested that ethnolinguistics could not accurately predict the origins of the Thais.
argued that Thai is not a race or ethnicity but a culture group.
According to French historian
George Cœdès, "The Thai first enter history of
Farther India in the eleventh century with the mention of ''Syam'' slaves or prisoners of war in
Champa
Champa (Cham language, Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ, چمڤا; ; 占城 or 占婆) was a collection of independent Chams, Cham Polity, polities that extended across the coast of what is present-day Central Vietnam, central and southern Vietnam from ...
epigraphy", and "in the twelfth century, the
bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s of
Angkor Wat
Angkor Wat (; , "City/Capital of Wat, Temples") is a Buddhism and Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhist temple complex in Cambodia. Located on a site measuring within the ancient Khmer Empire, Khmer capital city of Angkor, it was originally constructed ...
" where "a group of warriors" are described as ''Syam'',
though Cham accounts do not indicate the origins of ''Syam'' or what ethnic group they belonged to.
The origins and ethnicity of the ''Syam'' remain unclear, with some literature suggesting that ''Syam'' refers to the
Shan people
The Shan people (, , or , ), also known as the Tai Long (တႆးလူင်, ) or Tai Yai, are a Tai ethnic group of Southeast Asia. The Shan are the biggest minority of Burma (Myanmar) and primarily live in the Shan State, but also inhabi ...
, the
Bru people
The Bru (also Bruu, or Bru-Vân Kiều; ; Lao: wikt:บรู, ບຣູ ; Thai: wikt:บรู, บรู; which literally means "people living in the woods") are an indigenous peoples, indigenous ethnic group living in Thailand, Laos, Vietna ...
, or the
Brau people.
However, mainland Southeast Asian sources from before the fourteenth century primarily used the word ''Syam'' as an
ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
, referring to those who belonged to a separate cultural category different from the Khmer, Cham, Bagan, or Mon. This contrasts with the Chinese sources, where ''Xian'' was used as a
toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''wikt:toponym, toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for ...
.
Early Tai confederate cities: (691 BCE – 13th century CE)

Theoretically,
Tai-Kadai-speaking people formed as early as the 12th century BCE in the middle of the
Yangtze basin. Some groups later migrated south to
Guangxi
Guangxi,; officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang Province, Hà Giang, Cao Bằn ...
.
However, after several bloody centuries against
Chinese influence in
Guangxi
Guangxi,; officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang Province, Hà Giang, Cao Bằn ...
between 333 BCE and the 11th century, hundreds of thousands of Tais were killed, thus,
Tai people began to move southwestward along the rivers and over the lower passes into the mountain north of
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
and river valleys in present-day
Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
of
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Some evidence indicates that the ancestors of Tai people migrated en masse southwestwards out of Yunnan only after the 1253
Mongol invasion of Dali; however, it is not generally accepted.
Tais defeated
indigenous tribes and emerged as the new power in the new region. As a result, several Tai city-states were established, scattered from
Điện Biên Phủ
Điện Biên Phủ (, vi-hantu, ) is a city in the Northwest (Vietnam), northwestern region of Vietnam. It is the capital of Điện Biên Province. The city is best known for the decisive Battle of Dien Bien Phu, Battle of Điện Biên Phủ ...
in present-day northwestern
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
and highland
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
to
northeastern India
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, M ...
.
According to the ''Simhanavati legend'' given in several chronicles, the first Tai city-state in northern Thailand,
Singhanavati, was founded around the 7th century.
However, several modern
geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth ...
and
archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
studies found that its centre, Yonok Nahaphan, dates from 691 BCE–545 CE;
this roughly coincides with the establishment of
Shan States
The Shan States were a collection of minor Shan people, Shan kingdoms called ''mueang, möng'' whose rulers bore the title ''saopha'' (''sawbwa''). In British rule in Burma, British Burma, they were analogous to the princely states of Britis ...
, another Tai's federated principalities in the present-day northeast
Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
. as well as
Muang Sua
Muang Sua (, ) was the name of Luang Phrabang following its conquest in 698 by a Tai peoples, Tai/Lao prince, Khun Lo, who seized his opportunity when the king of Kingdom of Nanzhao, Nanzhao was engaged elsewhere. Khun Lo had been awarded the tow ...
(
Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang (Lao language, Lao: wikt:ຫຼວງພະບາງ, ຫຼວງພະບາງ, pronounced ), historically known as Xieng Thong (ຊຽງທອງ) and alternatively spelled Luang Phabang or Louangphabang, is the capital of Lu ...
) in the east.
After Singhanavati was submerged below
Chiang Saen Lake
Chiang Saen Lake () is a natural freshwater lake in Thailand, it is located in Yonok Subdistrict, Chiang Saen District, Chiang Rai Province, northern Thailand, northernmost Thailand.
According to the Thai folklore, folklore, the legend of Sing ...
due to an
earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
in 545,
the survivors then founded a new seat at . The kingdom lasted for another 93 years.
In addition to
Singhanavati, another northern principality probably related to the Tai people,
Ngoenyang
Hiran Nakhon Ngoenyang (; ), also known as Chayaworanakhon Chiang Lao, Hiranyanakhon Ngoenyang Chiang Saen, Nakhon Yangkapura, or Thasai Ngoenyang was an early mueang or kingdom of the Northern Thai people from the 7th through 13th centuries A ...
, was established as the successor of Singhanavati in 638 by , also centred in (present-day
Mae Sai District,
Chiang Rai
Chiang Rai (, ; , ) is the northernmost major city in Thailand, with a population of about 200,000 people. It is located in Mueang Chiang Rai District, Chiang Rai Province. Chiang Rai was established as a capital city in the reign of King Ma ...
).
Its seat was moved to
Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai, sometimes written as Chiengmai or Chiangmai, is the largest city in northern Thailand, the capital of Chiang Mai province and the List of municipalities in Thailand#Largest cities by urban population, second largest city in Thailan ...
in 1262 by King
Mangrai
Mangrai (; ; c. 1238–1311) was the 25th king of Ngoenyang (r. 1261–1292) and the first king of Lanna (r. 1292–1311). He established a new city, Chiang Mai, as the capital of the Lanna Kingdom (1296–1558).Wyatt, D. K. Thailand, A Short Hi ...
, which considered the foundation of the
Lan Na
The Lan Na kingdom or the Kingdom of Lanna (, , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; , , ), also known as Lannathai, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to the 18th centuries.
The cultural developmen ...
kingdom. Mangrai unified the surrounding area and also created a network of states through political alliances to the east and north of the
Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of and a drainage area of , discharging of wat ...
. His dynasty would rule the kingdom continuously for the next two centuries.
Lan Na
The Lan Na kingdom or the Kingdom of Lanna (, , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; , , ), also known as Lannathai, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to the 18th centuries.
The cultural developmen ...
expanded its territory southward and annexed the
Mon Hariphunchai of
Dvaravati in 1292.
In the late tenth century, Tai people began to migrate further south to the present-day upper
central Thailand
Central Thailand (Central Plain) (historically also known as Siam or Dvaravati) is one of the regions of Thailand, covering the broad alluvial plain of the Chao Phraya River. It is separated from northeast Thailand (Isan) by the Phetchabun Mount ...
.
Around the 1100s period, several cities in this area, such as Songkwae, Sawankhalok, and Chakangrao, were ruled by the Tai people, and they eventually launched several battles against the pre-existing
Mon of
Lavo, who had been falling under
Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla ( zh, t=真臘, s=, 真腊, p=Zhēnlà, w=Chen-la; , ; ) is the Chinese designation for the vassal of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late 6th to the early 9th century in Indochina. ...
and
Khmer influences since the 7th century, thus bringing the establishment of the Tai people's independent state,
Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom was a post-classical Siamese kingdom (Mandala (political model), ''maṇḍala'') in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai Historical Park, Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thaila ...
, in the upper
Chao Phraya River
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
valley in 1238.
The earliest conflict between
Tai people and the preexisting ethnics was recorded in the mid-4th century when the ruler of
Singhanavati, , forcibly lost the seat at Yonok to King Khom from Umongasela (present-day
Fang). He then fled to Vieng Si Tuang (; present-day Wiang Phang Kham,
Mae Sai district) but had to send tributes to Yonok annually until his son,
Phrom, took back Yonok and expelled King Khom from Umongasela.
[ Some historians suggest that Lavo's capital, Lopburi, was once seized by Phrom.]royal intermarriage
Royal intermarriage is the practice of members of ruling dynasties marrying into other reigning families. It was more commonly done in the past as part of strategic diplomacy for national interest. Although sometimes enforced by legal requirem ...
s.[
]
Mon and Lavo Kingdoms: (5th century CE – 13th century CE)

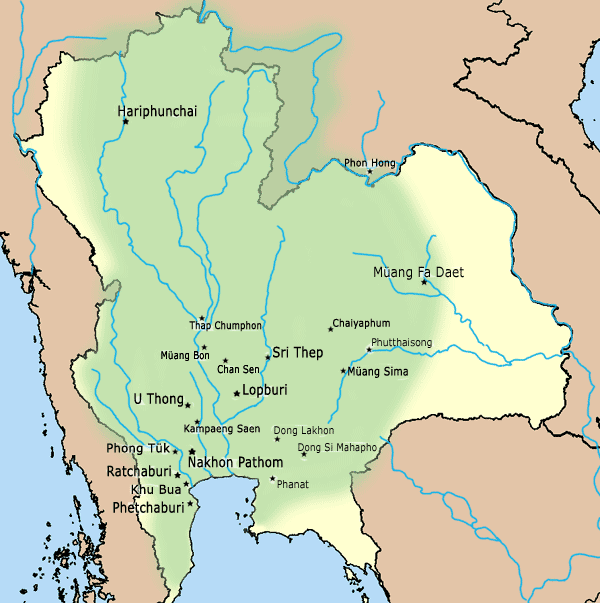 As is generally known, the present-day
As is generally known, the present-day Thai people
Thai people, historically known as Siamese people, are an ethnic group native to Thailand. In a narrower and ethnic sense, the Thais are also a Tai peoples, Tai ethnic group dominant in Central Thailand, Central and Southern Thailand (Siam prope ...
were previously called Siamese before the country was renamed Thailand in the mid-20th century.Mon people
The Mon (; Thai Mon: ဂကူမည်; , ; , ) are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand (mostly in Pathum Than ...
in Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
than the Tais of southern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions that display certain differences in terms of their geography, demographics, economy, and culture.
Extent
The Qinling–Daba Mountains serve as the transition zone between ...
,[Pittayaporn, Pittayawat (2014). Layers of Chinese Loanwords in Proto-Southwestern Tai as Evidence for the Dating of the Spread of Southwestern Tai](_blank)
. ''MANUSYA: Journal of Humanities'', Special Issue No 20: 47–64.Mon language
The Mon language, formerly known as Peguan and Talaing, is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Mon people. Mon, like the related Khmer language, but unlike most languages in mainland Southeast Asia, is not tonal. The Mon language is a recogn ...
, as well as Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
.Lan Na
The Lan Na kingdom or the Kingdom of Lanna (, , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; , , ), also known as Lannathai, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to the 18th centuries.
The cultural developmen ...
also called the southern region occupied by the Mon Haripuñjaya of Dvaravati as ''Shyam Pradesh'' (), which indicates that the ancient Siamese and the Mon people in central Thailand were probably the same ethnolinguistic group.
The earliest evidence to mention the Siam people are stone inscriptions found in Angkor Borei of Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in Mainland Southeast Asia covering ...
(K.557 and K.600), dated 661 CE, the slave's name is mentioned as "Ku Sayam" meaning "Sayam female slaves" (Ku is a prefix used to refer to female slaves in the pre-Angkorian era), and the Takéo inscriptions (K.79) written in 682 during the reign of Bhavavarman II of Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla ( zh, t=真臘, s=, 真腊, p=Zhēnlà, w=Chen-la; , ; ) is the Chinese designation for the vassal of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late 6th to the early 9th century in Indochina. ...
also mention Siam Nobel: ''Sāraṇnoya Poña Sayam'', which was transcribed into English as: ''the rice field that was given to the poña (noble rank) who was called Sayam (Siam)''.central Thailand
Central Thailand (Central Plain) (historically also known as Siam or Dvaravati) is one of the regions of Thailand, covering the broad alluvial plain of the Chao Phraya River. It is separated from northeast Thailand (Isan) by the Phetchabun Mount ...
and their state was called ''Xiān guó'' ( zh, 暹國), while the eastern plain belonged to the Mon of Lavo ( zh, 羅渦國),Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla ( zh, t=真臘, s=, 真腊, p=Zhēnlà, w=Chen-la; , ; ) is the Chinese designation for the vassal of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late 6th to the early 9th century in Indochina. ...
and Khmer hegemony around the 7th–9th centuries. Those Mon political entities, which also included Haripuñjaya in the north and several city-states in the northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—eac ...
, are collectively called Dvaravati.
However, the states of Siamese Mon and Lavo were later merged via the royal intermarriage
Royal intermarriage is the practice of members of ruling dynasties marrying into other reigning families. It was more commonly done in the past as part of strategic diplomacy for national interest. Although sometimes enforced by legal requirem ...
and became Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. Europe ...
in the mid-14th century,Isan
Northeast Thailand or Isan (Isan language, Isan/, ; ; also written as Isaan, Isarn, Issarn, Issan, Esan, or Esarn; from Pāli ''isāna'' or Sanskrit ईशान्य ''īśānya'' "northeast") consists of 20 provinces in northeastern Thai ...
principalities, centred in Phanom Rung and Phimai, later pledged allegiance to Siamese's Ayutthaya during the reign of Borommarachathirat II ( 1424–1448). The remaining principal city-states in Isan
Northeast Thailand or Isan (Isan language, Isan/, ; ; also written as Isaan, Isarn, Issarn, Issan, Esan, or Esarn; from Pāli ''isāna'' or Sanskrit ईशान्य ''īśānya'' "northeast") consists of 20 provinces in northeastern Thai ...
region became Lan Xang
Lan Xang () or Lancang was a Lao people, Lao kingdom that held the area of present-day Laos from 1353 to 1707. For three and a half centuries, Lan Xang was one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. The kingdom is the basis for Laos's nat ...
around 1353 after the twin cities of Muang Sua
Muang Sua (, ) was the name of Luang Phrabang following its conquest in 698 by a Tai peoples, Tai/Lao prince, Khun Lo, who seized his opportunity when the king of Kingdom of Nanzhao, Nanzhao was engaged elsewhere. Khun Lo had been awarded the tow ...
(Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang (Lao language, Lao: wikt:ຫຼວງພະບາງ, ຫຼວງພະບາງ, pronounced ), historically known as Xieng Thong (ຊຽງທອງ) and alternatively spelled Luang Phabang or Louangphabang, is the capital of Lu ...
) and ''Vieng Chan Vieng Kham'' (Vientiane
Vientiane (, ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of Laos. Situated on the banks of the Mekong, Mekong River at the Thailand, Thai border, it comprises the five urban districts of Vientiane Prefecture and had a population of 840,000 ...
) became independent following the death of the Sukhothai king Ram Khamhaeng
Ramkhamhaeng (, ) or commonly known as Pho Khun Ramkhamhaeng Maharat (, ) was the third king of the Phra Ruang Dynasty, ruling the Sukhothai Kingdom (a historical kingdom of Thailand) from 1279 to 1298, during its most prosperous era.
He is c ...
.
According to the Wat Kud Tae inscription (K.1105), dated c. 7th century, during the period that the eastern Mon entity, Lavo, was strongly influenced by the Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla ( zh, t=真臘, s=, 真腊, p=Zhēnlà, w=Chen-la; , ; ) is the Chinese designation for the vassal of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late 6th to the early 9th century in Indochina. ...
, the Siamese Mon in the west also established a royal intermarriage
Royal intermarriage is the practice of members of ruling dynasties marrying into other reigning families. It was more commonly done in the past as part of strategic diplomacy for national interest. Although sometimes enforced by legal requirem ...
with Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla ( zh, t=真臘, s=, 真腊, p=Zhēnlà, w=Chen-la; , ; ) is the Chinese designation for the vassal of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late 6th to the early 9th century in Indochina. ...
as Sri Chakatham, prince of Sambhuka (ศามภูกะ, in the present-day Ratchaburi province
Ratchaburi province (, ) or Rat Buri () is one of Thailand's seventy-six provinces (''changwat'') lies in Western Thailand. Neighbouring provinces are (from north clockwise) Kanchanaburi, Nakhon Pathom, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram and ...
), married to a princess of Isanavarman I, and two mandala
A mandala (, ) is a geometric configuration of symbols. In various spiritual traditions, mandalas may be employed for focusing attention of practitioners and adepts, as a spiritual guidance tool, for establishing a sacred space and as an aid ...
s then became an ally.Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla ( zh, t=真臘, s=, 真腊, p=Zhēnlà, w=Chen-la; , ; ) is the Chinese designation for the vassal of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late 6th to the early 9th century in Indochina. ...
sieged Funan
Funan (; , ; , Chữ Hán: ; ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Khmer-Mon Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''( Mandala)''—located in Mainland Southeast Asia covering ...
and moved the centre to Angkor
Angkor ( , 'capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura (; ),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-English Dictionary''. Bureau of Special Research in Modern Languages. The Catholic Uni ...
, both Siamese Mon and the Angkorian eventually marched the troops to attack Vijaya
Vijaya may refer to:
Places
* Vijaya (Champa), a city-state and former capital of the historic Champa in what is now Vietnam
* Vijayawada, a city in Andhra Pradesh, India
People
* Prince Vijaya of Sri Lanka (fl. 543–505 BC), earliest recorde ...
of Champa
Champa (Cham language, Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ, چمڤا; ; 占城 or 占婆) was a collection of independent Chams, Cham Polity, polities that extended across the coast of what is present-day Central Vietnam, central and southern Vietnam from ...
in 1201 during the reign of Jayavarman VII
Jayavarman VII (), known posthumously as Mahaparamasaugata (, c. 1122–1218), was king of the Khmer Empire. He was the son of King Dharanindravarman II (r. 1150–1160) and Queen Sri Jayarajacudamani.
He was the first king devoted to Buddhism, ...
, as recorded in the Cho-Dinh inscription (C.3).
Sukhothai Kingdom (1238 CE – 14th century CE)
After the decline of the Khmer Empire and Kingdom of Pagan in the early 13th century, various states thrived in their place. The domains of Tai people existed from the northeast of present-day India to the north of present-day Laos and to the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
.Lavo Kingdom
The Lavo Kingdom () was a political entity (Mandala (Southeast Asian political model), mandala) on the left bank of the Chao Phraya River in the Upper Chao Phraya valley from the end of Dvaravati civilization, in the 7th century, until 1388. The o ...
to Nakhon Si Thammarat
Nakhon Si Thammarat (, ; from ) is a city municipality (''thesaban nakhon'') located in Mueang Nakhon Si Thammarat, the capital of Nakhon Si Thammarat Province. Nakhon Si Thammarat Province is situated in the South of Thailand. It is about s ...
in the south. There are, however, no records detailing the arrival of the Tais.Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom was a post-classical Siamese kingdom (Mandala (political model), ''maṇḍala'') in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai Historical Park, Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thaila ...
in 1238.Ram Khamhaeng
Ramkhamhaeng (, ) or commonly known as Pho Khun Ramkhamhaeng Maharat (, ) was the third king of the Phra Ruang Dynasty, ruling the Sukhothai Kingdom (a historical kingdom of Thailand) from 1279 to 1298, during its most prosperous era.
He is c ...
(). However, it was mostly a network of local lords who swore fealty to Sukhothai, not directly controlled by it.Thai script
The Thai script (, , ) is the abugida used to write Thai language, Thai, Southern Thai language, Southern Thai and many other languages spoken in Thailand. The Thai script itself (as used to write Thai) has 44 consonant symbols (, ), 16 vowel s ...
and Thai ceramics were an important export in his era. Sukhothai embraced Theravada
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' (anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhi ...
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
in the reign of Maha Thammaracha I
Maha Thammaracha I (, ), born as Li Thai (, ), was a king of the Sukhothai Kingdom, and the first Buddhist philosopher to write in the Thai language. He reigned from roughly 1347 until his death in 1368. Li Thai was the son of Loe Thai and the g ...
(1347–1368).
Ayutthaya Kingdom (1351–1767)
According to the most widely accepted version of its origin, the Ayutthaya Kingdom rose from the earlier, nearby Lavo Kingdom
The Lavo Kingdom () was a political entity (Mandala (Southeast Asian political model), mandala) on the left bank of the Chao Phraya River in the Upper Chao Phraya valley from the end of Dvaravati civilization, in the 7th century, until 1388. The o ...
and Suvarnabhumi with Uthong as its first king. Ayutthaya was a patchwork of self-governing principalities and tributary provinces owing allegiance to the King of Ayutthaya under the mandala system. Its initial expansion was through conquest and political marriage.
Before the end of the 15th century, Ayutthaya invaded the Khmer Empire three times and sacked its capital Angkor
Angkor ( , 'capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura (; ),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-English Dictionary''. Bureau of Special Research in Modern Languages. The Catholic Uni ...
. Ayutthaya then became a regional power in place of the Khmer. Constant interference of Sukhothai effectively made it a vassal state of Ayutthaya and it was finally incorporated into the kingdom. Borommatrailokkanat brought about bureaucratic reforms which lasted into the 20th century and created a system of social hierarchy called '' sakdina'', where male commoners were conscripted as corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid forced labour that is intermittent in nature, lasting for limited periods of time, typically only a certain number of days' work each year. Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state (polity), state for the ...
labourers for six months a year.Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
but failed to conquer the Malacca Sultanate
The Malacca Sultanate (; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswara, also known as I ...
, which was supported by the Chinese Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
.envoy
Envoy or Envoys may refer to:
Diplomacy
* Diplomacy, in general
* Envoy (title)
* Special envoy, a type of Diplomatic rank#Special envoy, diplomatic rank
Brands
*Airspeed Envoy, a 1930s British light transport aircraft
*Envoy (automobile), an au ...
of Portuguese duke Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque, 1st Duke of Goa ( – 16 December 1515), was a Portuguese general, admiral, statesman and ''conquistador''. He served as viceroy of Portuguese India from 1509 to 1515, during which he expanded Portuguese influence across ...
in 1511. Portugal became an ally and ceded some soldiers to King Rama Thibodi II. The Portuguese were followed in the 17th century by the French, Dutch, and English. Rivalry for supremacy over Chiang Mai and the Mon people pitted Ayutthaya against the Burmese Kingdom. Several wars with its ruling Taungoo dynasty
''taungnguumainn saat''
, conventional_long_name = Toungoo dynasty
, common_name = Taungoo dynasty
, status = Empire/ Kingdom
, event_start = Independence from Ava Kingdom
, year_start = 15 ...
starting in the 1540s in the reign of Tabinshwehti and Bayinnaung
, title = King of Toungoo
, image = Bayinnaung.JPG
, caption = Statue of Bayinnaung in front of the National Museum of Myanmar
, reign = 30 April 1550 – 10 October 1581
, coronation = 11 January 1551 at Taungoo, ...
were ultimately ended with the capture of the capital in 1570.Naresuan
Naresuan (1555/1556 – 25 April 1605), commonly known as Naresuan the Great, or Sanphet II was the 18th Monarchy of Thailand, king of the Ayutthaya Kingdom and 2nd monarch of the List of monarchs of Thailand#Sukhothai dynasty (1569–1629), S ...
proclaimed independence in 1584 followed.Narai
King Narai the Great (, , ) or Ramathibodi III ( ) was the 27th monarch of Ayutthaya Kingdom, the 4th and last monarch of the Prasat Thong dynasty. He was the king of Ayutthaya Kingdom from 1656 to 1688 and arguably the most famous king of the ...
's reign (1656–1688), when some European travellers regarded Ayutthaya as an Asian great power, alongside China and India.Siamese revolution of 1688
The Siamese revolution of 1688 was a major popular uprising in the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom (modern Thailand) which led to the overthrow of the pro-French Siamese king Narai. Phetracha, previously one of Narai's trusted military advisors, took a ...
.golden age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during wh ...
", a relatively peaceful episode in the second quarter of the 18th century where art
Art is a diverse range of cultural activity centered around ''works'' utilizing creative or imaginative talents, which are expected to evoke a worthwhile experience, generally through an expression of emotional power, conceptual ideas, tec ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
, and learning flourished. There were seldom foreign wars, apart from conflict with the Nguyễn lords
The Nguyễn lords (, 主阮; 1558–1777, 1780–1802), also known as the Nguyễn clan (; ), were Nguyễn dynasty's forerunner and a feudal noble clan ruling southern Đại Việt in the Revival Lê dynasty. The Nguyễn lords were membe ...
for control of Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
starting around 1715. The last fifty years of the kingdom witnessed bloody succession crises, where there were purges of court officials and able generals for many consecutive reigns. In 1765, a combined 40,000-strong force of Burmese armies invaded it from the north and west. The Burmese under the new Alaungpaya
Alaungpaya (, ; also spelled Alaunghpaya or Alaung-Phra; 11 May 1760) was the founder and first emperor of the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. By the time of his death from illness during his Burmese–Siamese War (1759–60), campaign in Siam, this ...
dynasty quickly rose to become a new local power by 1759. After a 14-month siege, the capital city's walls fell and the city was burned in April 1767.
Thonburi Kingdom (1767–1782)
The capital and many of its territories lay in chaos after the war. The former capital was occupied by the Burmese garrison army and five local leaders declared themselves overlords, including the lords of Sakwangburi, Phitsanulok
Phitsanulok (, ) is a city municipality in northern Thailand and the capital of Phitsanulok province. It had a city population of 60,827 and an urban population of approximately 200,000 in 2024, making it Thailand's 19th-most populous city p ...
, Pimai, Chanthaburi
Chanthaburi (, ) is a town ('' thesaban mueang'') in the east of Thailand, on the banks of the Chanthaburi River. It is the capital of the Chanthaburi Province and the Mueang Chanthaburi District.
The town covers the two ''tambons'' Talat an ...
, and Nakhon Si Thammarat
Nakhon Si Thammarat (, ; from ) is a city municipality (''thesaban nakhon'') located in Mueang Nakhon Si Thammarat, the capital of Nakhon Si Thammarat Province. Nakhon Si Thammarat Province is situated in the South of Thailand. It is about s ...
. Chao Tak, a capable military leader, proceeded to make himself a lord by right of conquest
The right of conquest was historically a right of ownership to land after immediate possession via force of arms. It was recognized as a principle of international law that gradually deteriorated in significance until its proscription in the af ...
, beginning with the legendary sack of Chanthaburi
Chanthaburi (, ) is a town ('' thesaban mueang'') in the east of Thailand, on the banks of the Chanthaburi River. It is the capital of the Chanthaburi Province and the Mueang Chanthaburi District.
The town covers the two ''tambons'' Talat an ...
. Based at Chanthaburi, Chao Tak raised troops and resources, and sent a fleet up the Chao Phraya
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
to take the fort of Thonburi
__NOTOC__
Thonburi () is an area of modern Bangkok. During the era of the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Kingdom of Ayutthaya, its location on the right (west) bank at the mouth of the Chao Phraya River had made it an important garrison town, which is ref ...
. In the same year, Chao Tak was able to retake Ayutthaya from the Burmese only seven months after the fall of the city.
Chao Tak then crowned himself as Taksin and proclaimed Thonburi
__NOTOC__
Thonburi () is an area of modern Bangkok. During the era of the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Kingdom of Ayutthaya, its location on the right (west) bank at the mouth of the Chao Phraya River had made it an important garrison town, which is ref ...
as temporary capital in the same year. He also quickly subdued the other warlords. His forces engaged in wars with Burma, Laos, and Cambodia, which successfully Burmese–Siamese War (1774–1775), drove the Burmese out of Lan Na in 1775,Chakri dynasty
The Chakri dynasty is the current reigning dynasty of the Thailand, Kingdom of Thailand. The head of the house is the Monarchy of Thailand, king, who is head of state. The family has ruled Thailand since the founding of the Rattanakosin era and ...
and founder of the Rattanakosin Kingdom on 6 April 1782.
Rattanakosin Kingdom and modernization (1782 –1932)
Under Rama I (1782–1809), Rattanakosin successfully defended against Burmese attacks and put an end to Burmese incursions. He also created suzerainty over large portions of Laos and Cambodia. In 1821, Briton John Crawfurd was sent to negotiate a new trade agreement with Siam – the first sign of an issue which was to dominate 19th century Siamese politics. Bangkok signed the Burney Treaty in 1826, after the British victory in the First Anglo-Burmese War.Mongkut
Mongkut (18 October 18041 October 1868) was the fourth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama IV. He reigned from 1851 until his death in 1868.
The reign of Mongkut was marked by significant modernization ini ...
(1851–1868), who recognised the potential threat Western powers posed to Siam, his court contacted the Government of the United Kingdom, British government directly to defuse tensions.Chulalongkorn
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his death in 1910 was cha ...
, with Somdet Chaophraya Sri Suriwongse (Chuang Bunnag) acting as regent.corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid forced labour that is intermittent in nature, lasting for limited periods of time, typically only a certain number of days' work each year. Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state (polity), state for the ...
system. The Front Palace crisis of 1874 stalled attempts at further reforms.Chao Phraya
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
valley a buffer state. Not until the 20th century could Siam renegotiate every unequal treaty dating from the Bowring Treaty, including extraterritoriality. The advent of the ''monthon'' system marked the creation of the modern Thai nation-state.
Constitutional monarchy, World War II and Cold War (1932–1975)
 A Siamese revolution of 1932, bloodless revolution took place in 1932, in which Prajadhipok was forced to grant the country's first constitution, thereby ending centuries of feudal and absolute monarchy. The combined results of economic hardships brought on by the Great Depression, sharply falling rice prices, and a significant reduction in public spending caused discontent among aristocrats.
A Siamese revolution of 1932, bloodless revolution took place in 1932, in which Prajadhipok was forced to grant the country's first constitution, thereby ending centuries of feudal and absolute monarchy. The combined results of economic hardships brought on by the Great Depression, sharply falling rice prices, and a significant reduction in public spending caused discontent among aristocrats. In June 1946, young King Ananda was found dead under mysterious circumstances. His younger brother Bhumibol Adulyadej ascended to the throne. Thailand joined the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) to become an active ally of the United States in 1954.
In June 1946, young King Ananda was found dead under mysterious circumstances. His younger brother Bhumibol Adulyadej ascended to the throne. Thailand joined the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) to become an active ally of the United States in 1954.Sarit Thanarat
Sarit Thanarat (also spelled Dhanarajata; ; born Siri (); 16 June 1908 – 8 December 1963) was a Thai politician and military commander. He served as commander-in-chief of the Royal Thai Army (from 1954) and as Minister of Defense during ...
launched a coup in 1957, which removed Khana Ratsadon from politics. His rule (premiership 1959–1963) was autocratic; he built his legitimacy around the god-like status of the monarch and by channelling the government's loyalty to the king.
Contemporary history
Constant unrest and instability, as well as fear of a communist takeover after the fall of Saigon, made some ultra-right groups brand leftist students as communists.Thaksin Shinawatra
Thaksin Shinawatra (, ; born 26 July 1949) is a Thai businessman and politician who was the 23rd prime minister of Thailand from 2001 to 2006. Since 2009 he has also been a citizen of Montenegro.
Thaksin founded the mobile phone operator A ...
, governed from 2001 until 2006. His policies were successful in reducing rural poverty and initiated universal healthcare in the country. However, Thaksin was viewed as a corrupt populist who was destroying the middle class in order to favour himself and the rural poor. He also faced criticism over his response to a South Thailand insurgency which escalated starting from 2004. Additionally, his recommendations to the rural poor directly conflicted with King Bhumibol's recommendations, drawing the ire of royalists, a powerful faction in Thailand. In response, the royalists made up a story about how Thaskin and his "advisors gathered in Finland to plot the overthrow of the monarchy".
Meanwhile, massive protests against Thaksin led by the People's Alliance for Democracy (PAD) started in his second term as prime minister. Eventually, the monarchy and the military agree to oust the leader. In this case, the military first sought permission from the king to oust Thaksin, the permission was denied. But then, the king rejected Thaksin's choice to lead the army, allowing a military leader to be put into power who wanted the coup.1 Then, the army dissolved Thaksin's party with 2006 Thai coup d'état, a coup d'état in 2006 and banned over a hundred of its executives from politics. After the coup, a military government was installed which lasted a year. Coming back to democracy was a process that took very active participation of the people. The people frequently stormed government buildings and the military threatened yet another coup.
Coming back to democracy was a process that took very active participation of the people. The people frequently stormed government buildings and the military threatened yet another coup.
Geography
Totalling , Thailand is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 50th-largest country by total area.Isan
Northeast Thailand or Isan (Isan language, Isan/, ; ; also written as Isaan, Isarn, Issarn, Issan, Esan, or Esarn; from Pāli ''isāna'' or Sanskrit ईशान्य ''īśānya'' "northeast") consists of 20 provinces in northeastern Thai ...
, consists of the Khorat Plateau, bordered to the east by the Mekong River. The centre of the country is dominated by the predominantly flat Chao Phraya
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
river valley, which runs into the Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. ...
. Southern Thailand consists of the narrow Kra Isthmus that widens into the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
.
The Chao Phraya and the Mekong River are the indispensable water courses of rural Thailand. Industrial scale production of crops use both rivers and their tributaries. The Gulf of Thailand covers and is fed by the Chao Phraya, Mae Klong River, Mae Klong, Bang Pakong River, Bang Pakong, and Tapi River, Thailand, Tapi Rivers. It contributes to the tourism sector owing to its clear shallow waters along the coasts in the southern region and the Kra Isthmus. The eastern shore of the Gulf of Thailand has the kingdom's premier deepwater port in Sattahip District, Sattahip and its busiest commercial port, Laem Chabang. Phuket Province, Phuket, Krabi Province, Krabi, Ranong, Phang Nga and Trang Province, Trang, and their islands, all lay along the coasts of the Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
.
Climate
 Thailand's climate is influenced by monsoon winds that have a seasonal character (the southwest and northeast monsoon).
Thailand's climate is influenced by monsoon winds that have a seasonal character (the southwest and northeast monsoon).
Biodiversity and conservation
 List of national parks of Thailand, National parks in Thailand are defined as ''an area that contains natural resources of ecological importance or unique beauty, or flora and fauna of special importance''. Thailand's protected areas include 156 national parks, 58 wildlife sanctuaries, 67 non-hunting areas, and 120 forest parks. They cover almost 31 per cent of the kingdom's territory.
List of national parks of Thailand, National parks in Thailand are defined as ''an area that contains natural resources of ecological importance or unique beauty, or flora and fauna of special importance''. Thailand's protected areas include 156 national parks, 58 wildlife sanctuaries, 67 non-hunting areas, and 120 forest parks. They cover almost 31 per cent of the kingdom's territory.
Politics and government
Prior to 1932, Thai kings were feudal or absolute monarchy, absolute monarchs. During Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom was a post-classical Siamese kingdom (Mandala (political model), ''maṇḍala'') in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai Historical Park, Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thaila ...
, the king was seen as a ''Dharmaraja'' or 'king who rules in accordance with Dharma'. The system of government was a network of tributaries ruled by local lords. Modern absolute monarchy and statehood was established by Chulalongkorn when he transformed the decentralised protectorate system into a unitary state. On 24 June 1932, Khana Ratsadon (People's Party) carried out a bloodless revolution which marked the beginning of constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
.
Thailand has had 20 constitutions and charters since 1932, including the latest and current 2017 Constitution. All constitutions state that the politics is conducted within the framework of a constitutional monarchy, but the ''de facto'' form of government has ranged from military dictatorship to electoral democracy. Government is Separation of powers, separated into three branches:
* The legislative branch: the National Assembly of Thailand, National Assembly is composed of the Senate of Thailand, Senate, the 200-member indirectly elected upper house and House of Representatives of Thailand, House of Representatives, the elected 500-member lower house. Its most recent election is 2023 Thai general election, the 2023 general election. The coalition led by Pheu Thai Party currently holds the majority. The 2024 Thai Senate election was the first senate election held under the current constitution in the process criticized as "the most complicated election in the world". The senate is allegedly dominated by Bhumjaithai Party-affiliated senators.
* The executive branch consisting of the
Government is Separation of powers, separated into three branches:
* The legislative branch: the National Assembly of Thailand, National Assembly is composed of the Senate of Thailand, Senate, the 200-member indirectly elected upper house and House of Representatives of Thailand, House of Representatives, the elected 500-member lower house. Its most recent election is 2023 Thai general election, the 2023 general election. The coalition led by Pheu Thai Party currently holds the majority. The 2024 Thai Senate election was the first senate election held under the current constitution in the process criticized as "the most complicated election in the world". The senate is allegedly dominated by Bhumjaithai Party-affiliated senators.
* The executive branch consisting of the Prime Minister of Thailand
The prime minister of Thailand (, , ; literally 'chief minister of state') is the head of government of Thailand. The prime minister is also the chair of the cabinet of Thailand. The post has existed since the Siamese Revolution of 1932, when ...
, the head of government, and other cabinet members of up to 35 people. The Prime Minister was elected by the House of Representatives. The current constitution mandates that prime ministers are to be considered from candidates nominated by political parties before the election. The current prime minister is Paetongtarn Shinawatra, a member of the Pheu Thai Party.
* The judiciary is supposed to be independent of the executive and the legislative branches, although judicial rulings are suspected of being based on political considerations rather than on existing law.
Military and bureaucratic aristocrats fully controlled political parties between 1946 and the 1980s. Most parties in Thailand are short-lived.
Administrative divisions
Thailand is a unitary state; the administrative services of the executive branch are divided into three levels by ''National Government Organisation Act, BE 2534'' (1991): central, provincial and local. Thailand is composed of 76 Provinces of Thailand, provinces (, ''changwat''), which are first-level administrative divisions. There are also two specially governed districts: the capital Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
and Pattaya. Bangkok is at provincial level and thus often counted as a province. Each province is divided into Districts of Thailand, districts (, ''amphoe'') and the districts are further divided into sub-districts (, ''tambons''). The name of each province's capital city (, mueang) is the same as that of the province. For example, the capital of Chiang Mai Province (''Changwat Chiang Mai'') is ''Mueang Chiang Mai'' or ''Chiang Mai''. All provincial governors and district chiefs, which are administrators of provinces and districts respectively, are appointed by the central government. Thailand's provinces are sometimes grouped into four to six regions, depending on the source.
Foreign relations
 Siam's and Thailand's way of conducting foreign relations has long been described as "bamboo bending with the wind", of policies that are "always solidly rooted, but flexible enough to bend whichever way the wind blows in order to survive", or adaptable and pragmatic. In order to secure independence, it sought to pit one great power against the others so that it would be dominated by none.
During the
Siam's and Thailand's way of conducting foreign relations has long been described as "bamboo bending with the wind", of policies that are "always solidly rooted, but flexible enough to bend whichever way the wind blows in order to survive", or adaptable and pragmatic. In order to secure independence, it sought to pit one great power against the others so that it would be dominated by none.
During the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, Thailand sought to prevent the spread of communism so it joined the United States, including participating in SEATO alliance, sending expeditions to Korea and Vietnam, and offering the US to use its base. Thailand is one of the five founding members of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), initially to safeguard against communism. The end of Vietnam War was a turning point in Thai foreign policy and afterwards it sought to improve relations with Communist China and its now-Communist neighbours. Thailand remains an active member of ASEAN and seek to project its influence in it. Thailand has developed increasingly close ties with other members, with progressing regional co-operation in economic, trade, banking, political, and cultural matters.
In the 2000s, Thailand had taken an active role on the international stage and participated fully in international and regional organisations. It is a major non-NATO ally
A major non-NATO ally (MNNA) is a designation given by the Federal government of the United States, United States government to countries that have strategic working relationships with the United States Armed Forces while not being members of t ...
and Priority Watch List Special 301 Report of the United States. When East Timor gained independence from Indonesia, Thailand contributed troops to the international peacekeeping effort. As part of its effort to increase international ties, Thailand had reached out to such regional organisations as the Organization of American States (OAS) and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE).
During Thaksin Shinawatra
Thaksin Shinawatra (, ; born 26 July 1949) is a Thai businessman and politician who was the 23rd prime minister of Thailand from 2001 to 2006. Since 2009 he has also been a citizen of Montenegro.
Thaksin founded the mobile phone operator A ...
's premiership, negotiations for several free trade agreements with China, Australia, Bahrain, India, and the US were initiated. Thaksin sought to position Thailand as a regional leader, initiating various development projects in poorer neighbouring countries. More controversially, he established close, friendly ties with the Burmese dictatorship. Thailand joined the US-led 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of Iraq, sending a Thai Humanitarian Assistance Task Force 976 Thai-Iraq, humanitarian contingent until September 2004. Thailand also had contributed troops to reconstruction efforts in Afghanistan.
In April 2009, the Cambodian–Thai border dispute brought troops on territory immediately adjacent to the 900-year-old ruins of Cambodia's Preah Vihear Temple, Preah Vihear Hindu temple near the border.
After the 2014 coup, Thailand leaned more towards China. Growing Chinese influence and capital inflow caused some members of parliament to raise the concern about "economic colony" under China after many concessions.
During the Gaza war, Israel-Gaza war in 2023, at first Thailand's prime minister stated that his government strongly condemns the attack against Israel and extends its deepest condolences to the government and the people of Israel but the government later changed its position and announced that Thailand adopted a neutral stance in this conflict. 28 Thai nationals were killed in this conflict.
Armed forces
 The Royal Thai Armed Forces (กองทัพไทย; ) constitute the military of the Kingdom of Thailand. It consists of the Royal Thai Army (กองทัพบกไทย), the Royal Thai Navy (กองทัพเรือไทย), and the Royal Thai Air Force (กองทัพอากาศไทย). It also incorporates various paramilitary forces.
The Thai Armed Forces have a combined manpower of 306,000 active duty personnel and another 245,000 active reserve personnel. The Monarchy of Thailand, head of the Thai Armed Forces (จอมทัพไทย, ''Chom Thap Thai'') is the king, although this position is only nominal. The armed forces are managed by the Ministry of Defence (Thailand), Ministry of Defence of Thailand, which is headed by the Minister of Defence (a member of the cabinet of Thailand) and commanded by the Royal Thai Armed Forces Headquarters, which in turn is headed by the List of Commanders of the Royal Thai Armed Forces Headquarters, Chief of Defence Forces of Thailand. Thai annual defence budget almost tripled from US$1.98 billion in 2005 to US$5.88 billion in 2016, accounting for approximately 1.4% of GDP.
The Royal Thai Armed Forces (กองทัพไทย; ) constitute the military of the Kingdom of Thailand. It consists of the Royal Thai Army (กองทัพบกไทย), the Royal Thai Navy (กองทัพเรือไทย), and the Royal Thai Air Force (กองทัพอากาศไทย). It also incorporates various paramilitary forces.
The Thai Armed Forces have a combined manpower of 306,000 active duty personnel and another 245,000 active reserve personnel. The Monarchy of Thailand, head of the Thai Armed Forces (จอมทัพไทย, ''Chom Thap Thai'') is the king, although this position is only nominal. The armed forces are managed by the Ministry of Defence (Thailand), Ministry of Defence of Thailand, which is headed by the Minister of Defence (a member of the cabinet of Thailand) and commanded by the Royal Thai Armed Forces Headquarters, which in turn is headed by the List of Commanders of the Royal Thai Armed Forces Headquarters, Chief of Defence Forces of Thailand. Thai annual defence budget almost tripled from US$1.98 billion in 2005 to US$5.88 billion in 2016, accounting for approximately 1.4% of GDP.
Economy
The economy of Thailand is heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic product (GDP). Thailand exports over US$105 billion worth of goods and services annually.
Income and wealth disparities
 Thais have median wealth per one adult person of $1,469 in 2016,
Thais have median wealth per one adult person of $1,469 in 2016,
Exports and manufacturing
The economy of Thailand is heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic products (GDPs). Major exports include cars, computers, electrical appliances, Rice production in Thailand, rice, textiles and footwear, fishery products, rubber, and jewellery.Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
and the List of countries by motor vehicle production, 9th largest in the world.
Tourism
 Tourism makes up about 6% of the country's economy. Prior to the pandemic, Thailand was the world's eighth most visited country according to the World Tourism rankings compiled by the United Nations World Tourism Organization, United Nations World Tourism Organisation. In 2019, Thailand received 39.8 million international tourists, ahead of United Kingdom and Germany and was the fourth highest in international tourism earning 60.5 billion US dollars.
Thailand was the most visited country in Southeast Asia in 2013, according to the World Tourism Organisation. Estimates of tourism receipts directly contributing to the Thai GDP of 12 trillion baht range from 9 per cent (1 trillion baht) (2013) to 16 per cent. When including the indirect effects of tourism, it is said to account for 20.2 per cent (2.4 trillion baht) of Thailand's GDP.
Asian tourists primarily visit Thailand for Bangkok and the historical, natural, and cultural sights in its vicinity. Western tourists not only visit Bangkok and surrounding areas; many travel to the southern beaches and islands. The north is the chief destination for trekking and adventure travel with its diverse ethnic minority groups and forested mountains. The region hosting the fewest tourists is
Tourism makes up about 6% of the country's economy. Prior to the pandemic, Thailand was the world's eighth most visited country according to the World Tourism rankings compiled by the United Nations World Tourism Organization, United Nations World Tourism Organisation. In 2019, Thailand received 39.8 million international tourists, ahead of United Kingdom and Germany and was the fourth highest in international tourism earning 60.5 billion US dollars.
Thailand was the most visited country in Southeast Asia in 2013, according to the World Tourism Organisation. Estimates of tourism receipts directly contributing to the Thai GDP of 12 trillion baht range from 9 per cent (1 trillion baht) (2013) to 16 per cent. When including the indirect effects of tourism, it is said to account for 20.2 per cent (2.4 trillion baht) of Thailand's GDP.
Asian tourists primarily visit Thailand for Bangkok and the historical, natural, and cultural sights in its vicinity. Western tourists not only visit Bangkok and surrounding areas; many travel to the southern beaches and islands. The north is the chief destination for trekking and adventure travel with its diverse ethnic minority groups and forested mountains. The region hosting the fewest tourists is Isan
Northeast Thailand or Isan (Isan language, Isan/, ; ; also written as Isaan, Isarn, Issarn, Issan, Esan, or Esarn; from Pāli ''isāna'' or Sanskrit ईशान्य ''īśānya'' "northeast") consists of 20 provinces in northeastern Thai ...
. To accommodate foreign visitors, a separate tourism police with offices were set up in the major tourist areas and an emergency telephone number.
Thailand ranks as the worlds fifth largest medical tourism destination in spending, according to the World Travel and Tourism Council, attracting over 2.5 million visitors in 2018, and is number one in Asia. The country is popular for the growing practice of sex reassignment surgery (SRS) and cosmetic surgery. In 2010–2012, more than 90% of medical tourists travelled to Thailand for SRS. Prostitution in Thailand and sex tourism also form a ''de facto'' part of the economy. Campaigns promote Thailand as exotic to attract tourists. One estimate published in 2003 placed the trade at US$4.3 billion per year or about 3% of the Thai economy. It is believed that at least 10% of tourist dollars are spent on the sex trade.
Agriculture and natural resources
 Forty-nine per cent of Thailand's labour force is employed in agriculture in Thailand, agriculture.
Forty-nine per cent of Thailand's labour force is employed in agriculture in Thailand, agriculture.[Henri Leturque and Steve Wiggins 2010]
Thailand's progress in agriculture: Transition and sustained productivity growth
. London: Overseas Development Institute Between 1962 and 1983, the agricultural sector grew by 4.1% per year on average and continued to grow at 2.2% between 1983 and 2007.
Informal economy
In 2012, it was estimated that informal workers comprised 62.6% of the Thai workforce. The Ministry of Labour (Thailand), Ministry of Labour defines informal workers to be individuals who work in informal economies and do not have employee status under a given country's Labour Protection Act (LPA). The informal sector in Thailand has grown significantly over the past 60 years over the course of Thailand's gradual transition from an agriculture-based economy to becoming more industrialised and service-oriented.
Science and technology
Thailand ranked 41st in the Global Innovation Index in 2024. The Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation and Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation#Organization, its agencies oversees the development of science, technology, and research in Thailand. According to the National Research Council of Thailand, the country devoted 1.1% of its GDP to the research and development of science in 2019, with over 166,788 research and development personnel in full-time equivalent that year.
Infrastructure
Transportation
 The State Railway of Thailand (SRT) operates all of Thailand's national rail lines. Krung Thep Aphiwat Central Terminal and Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) railway station, Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) are the main termini of intercity routes. Phahonyothin and ICD Lat Krabang are the main freight terminals. SRT had of track, all of it meter gauge. Nearly all is single-track (2702.1 km), although some important sections around Bangkok are double () or triple-tracked (), and there are plans to extend this.
Rail transport in Bangkok includes long-distance services. There are four rapid transit rail systems in the capital: the BTS Skytrain, MRT (Bangkok), MRT, SRT Red Lines, and the Airport Rail Link (Bangkok), Airport Rail Link. In Bangkok, there were two failed rapid rail projects Lavalin Skytrain and Bangkok Elevated Road and Train System, before Mass Rapid Transit Master Plan in Bangkok Metropolitan Region was endorsed by the cabinet on 27 September 1994 and implemented from 1995 to the present.
The State Railway of Thailand (SRT) operates all of Thailand's national rail lines. Krung Thep Aphiwat Central Terminal and Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) railway station, Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) are the main termini of intercity routes. Phahonyothin and ICD Lat Krabang are the main freight terminals. SRT had of track, all of it meter gauge. Nearly all is single-track (2702.1 km), although some important sections around Bangkok are double () or triple-tracked (), and there are plans to extend this.
Rail transport in Bangkok includes long-distance services. There are four rapid transit rail systems in the capital: the BTS Skytrain, MRT (Bangkok), MRT, SRT Red Lines, and the Airport Rail Link (Bangkok), Airport Rail Link. In Bangkok, there were two failed rapid rail projects Lavalin Skytrain and Bangkok Elevated Road and Train System, before Mass Rapid Transit Master Plan in Bangkok Metropolitan Region was endorsed by the cabinet on 27 September 1994 and implemented from 1995 to the present.
Energy
75% of Thailand's electrical generation is powered by natural gas in 2014.
Demographics
Thailand has an estimated population of 71.7 million as of 2023; Thailand's first census in 1909 found the population to be 8.2 million. Thailand's population is largely rural, concentrated in the rice-growing areas of the central, northeastern, and northern regions. About 44.2% of Thailand's population lived in urban areas , slowly increasing from 29.4% in the 1990 census and 31.1% in the 2000 census.
Thailand's government-sponsored family planning programme resulted in a dramatic decline in population growth from 3.1% in 1960 to around 0.4% today. In 1970, an average of 5.7 people lived in a Thai household; in 2022, the average Thai household size was 3 people. Now, more than 20% of its population is aged over 60 and has a low birth rate, posing economic challenges. The sex ratio between male and female is 1.05, with Thailand having slightly more males.
Ethnic groups
As of 2010, Thai people make up the majority of Thailand's population (95.9%). The remaining 4.1% of the population are Burmese (2.0%), others (1.3%), and unspecified (0.9%).southern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions that display certain differences in terms of their geography, demographics, economy, and culture.
Extent
The Qinling–Daba Mountains serve as the transition zone between ...
, the northeastern group (Isan people) are mixed Tai and several Austroasiatic-speaking ethnic groups, while the central and southern groups (formerly called Siamese) strongly share genetic profiles with the Mon people
The Mon (; Thai Mon: ဂကူမည်; , ; , ) are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand (mostly in Pathum Than ...
.
Population centres
Language
Thai language, Thai is the official language. It is a Kra–Dai language closely related to Lao language, Lao, Shan language, Shan in Myanmar, and numerous smaller languages spoken in an arc from Hainan and Yunnan south to the Chinese border. It is the principal language of education and government and spoken throughout the country.
Religion
The country's most prevalent religion is Theravada
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' (anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhi ...
Buddhism, which is an integral part of Thai identity and culture. Active participation in Buddhism is among the highest in the world. Thailand has the second-largest number of Buddhists in the world after China. According to the 2018 National Statistical Office (Thailand), National Statistical Office data, 93.46% of the country's population self-identified as Buddhists. Islam in Thailand, Muslims constitute the second largest religious group in Thailand, comprising 5.37% of the population in 2018.
Islam in Thailand, Muslims constitute the second largest religious group in Thailand, comprising 5.37% of the population in 2018.
Education
 In 1995, as minister of education, Sukavich Rangsitpollaid let out his plans for educational reform in Thailand. The reform was considered a landmark movement after nearly 100 years of education under the previous system. Thailand's youth literacy rate was 98.1% in 2015. Education is provided by a school system of kindergartens, primary, lower secondary and upper secondary schools, numerous vocational colleges, and universities. Education is compulsory up to and including age 14, while the government is mandated to provide free education through to age 17. Issues concerning university entrance have been in constant upheaval for a number of years. The country is also one of the few that still mandates uniform up to the university years, which is still a subject of ongoing debate.
In 2013, the Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (Thailand), Ministry of Information and Communication Technology announced that 27,231 schools would receive classroom-level access to internet, high-speed internet. However, the country's educational infrastructure was still underprepared for online teaching, as smaller and more remote schools were particularly hindered by COVID-19 restrictions.
The number of higher education institutions in Thailand has grown over the past decades to 156 officially. The two top-ranking universities in Thailand are Chulalongkorn University and Mahidol University. Thai universities' research output is still relatively low, even though the country's journal publications increased by 20% between 2011 and 2016. Thailand has the second highest number of English-medium private international schools in ASEAN, Southeast Asian Nations.
In 1995, as minister of education, Sukavich Rangsitpollaid let out his plans for educational reform in Thailand. The reform was considered a landmark movement after nearly 100 years of education under the previous system. Thailand's youth literacy rate was 98.1% in 2015. Education is provided by a school system of kindergartens, primary, lower secondary and upper secondary schools, numerous vocational colleges, and universities. Education is compulsory up to and including age 14, while the government is mandated to provide free education through to age 17. Issues concerning university entrance have been in constant upheaval for a number of years. The country is also one of the few that still mandates uniform up to the university years, which is still a subject of ongoing debate.
In 2013, the Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (Thailand), Ministry of Information and Communication Technology announced that 27,231 schools would receive classroom-level access to internet, high-speed internet. However, the country's educational infrastructure was still underprepared for online teaching, as smaller and more remote schools were particularly hindered by COVID-19 restrictions.
The number of higher education institutions in Thailand has grown over the past decades to 156 officially. The two top-ranking universities in Thailand are Chulalongkorn University and Mahidol University. Thai universities' research output is still relatively low, even though the country's journal publications increased by 20% between 2011 and 2016. Thailand has the second highest number of English-medium private international schools in ASEAN, Southeast Asian Nations.
Health
Thailand ranks world's sixth, and Asia's first in the 2019 Global Health Security Index of global health security capabilities in 195 countries, making it the only developing country on the world's top ten. Thailand had 62 hospitals accredited by Joint Commission, Joint Commission International. In 2002, Bumrungrad International Hospital, Bumrungrad became the first hospital in Asia to meet the standard.
Health and medical care is overseen by the Ministry of Public Health (Thailand), Ministry of Public Health (MOPH), with total national expenditures on health amounting to 4.3 per cent of GDP in 2009. Non-communicable diseases form the major burden of morbidity and mortality, while infectious diseases including malaria and tuberculosis, as well as traffic accidents, are also important public health issues.
In December 2018, the interim parliament voted to legalise the use of cannabis for medical reasons, making Thailand the first Southeast Asian country to allow the use of medical cannabis.
Culture
 Thai culture and traditions incorporate influences from India, China, Cambodia, and the rest of Southeast Asia. Thailand's national religion, Theravada, Theravada Buddhism, is central to modern Thai identity. Buddhism in Thailand, Thai Buddhism has evolved over time to include many regional beliefs originating from Hinduism, animism, as well as ancestor worship. The Thai solar calendar, official calendar in Thailand is based on the Eastern version of the Buddhist calendar, Buddhist Era (BE). Thai identity today is a Thaification, social construct of the Phibun regime in the 1940s.
Several ethnic groups mediated change between their traditional local culture, national Thai, and global cultural influences. Overseas Chinese also form a significant part of Thai society, particularly in and around Bangkok. Thai Chinese businesses prosper as part of the larger bamboo network.
Thai culture and traditions incorporate influences from India, China, Cambodia, and the rest of Southeast Asia. Thailand's national religion, Theravada, Theravada Buddhism, is central to modern Thai identity. Buddhism in Thailand, Thai Buddhism has evolved over time to include many regional beliefs originating from Hinduism, animism, as well as ancestor worship. The Thai solar calendar, official calendar in Thailand is based on the Eastern version of the Buddhist calendar, Buddhist Era (BE). Thai identity today is a Thaification, social construct of the Phibun regime in the 1940s.
Several ethnic groups mediated change between their traditional local culture, national Thai, and global cultural influences. Overseas Chinese also form a significant part of Thai society, particularly in and around Bangkok. Thai Chinese businesses prosper as part of the larger bamboo network.
 Respect for elderly and superiors (by age, position, monks, or certain professions) is Thai mores, reflecting in many classes of Thai honorifics, honorifics. ''Thai greeting, Wai'' is a familiar Thai greeting, and is generally offered first by a person who is younger or lower in social status and position.
Respect for elderly and superiors (by age, position, monks, or certain professions) is Thai mores, reflecting in many classes of Thai honorifics, honorifics. ''Thai greeting, Wai'' is a familiar Thai greeting, and is generally offered first by a person who is younger or lower in social status and position.
Art
 The origins of Thai art were influenced by Buddhist art and by scenes from the Indian epics. Traditional Thai sculpture almost exclusively depicts Buddha image, images of the Buddha, being very similar with the other styles from
The origins of Thai art were influenced by Buddhist art and by scenes from the Indian epics. Traditional Thai sculpture almost exclusively depicts Buddha image, images of the Buddha, being very similar with the other styles from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. Traditional Thai paintings usually consist of book illustrations, and painted ornamentation of buildings such as palaces and temples.
Thai art was influenced by indigenous civilisations of the Dvaravati, Mon and other civilisations. By the Sukothai and Ayutthaya periods, Thai had developed into its own unique style and was later further influenced by the other Asian styles, mostly by Indian art, Sri Lankan and Chinese art, Chinese. Thai sculpture and painting, and the royal courts provided patronage, erecting temples and other religious shrines as acts of merit or to commemorate important events.
Architecture
The Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. Europe ...
movement is designed to display might and riches. The temples in Ayutthaya seldom built eaves stretching from the masterhead. Buddhist temples in Thailand are known as "wats", from the Pāḷi ''vāṭa'', meaning an enclosure: a temple has an enclosing wall that divides it from the secular world. Wat architecture demonstrates many differences in layout and style, but they all adhere to the same principles.
Literature
Thai literature has had a long history. Even before the establishment of the Sukhothai Kingdom there existed oral and written works.
During the Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom was a post-classical Siamese kingdom (Mandala (political model), ''maṇḍala'') in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai Historical Park, Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thaila ...
, most literary works were written in simple prose with certain alliteration schemes. Major works include King Ram Khamhaeng Inscription describing life at the time, which is considered the first literary work in Thai script, but some historians questioned its authenticity. ''Trai Phum Phra Ruang'', written in 1345 by King Maha Thammaracha I
Maha Thammaracha I (, ), born as Li Thai (, ), was a king of the Sukhothai Kingdom, and the first Buddhist philosopher to write in the Thai language. He reigned from roughly 1347 until his death in 1368. Li Thai was the son of Loe Thai and the g ...
, expounds Buddhist philosophy based on an extensive study with reference to over 30 sacred texts and could be considered the nation's first piece of research dissertation.
During the Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. Europe ...
, new Thai poetry, poetic forms were created, with different rhyme schemes and metres. It is common to find a combination of different poetic forms in one poetic work. ''Lilit Yuan Phai'' is a narrative poem describing Ayutthaya–Lan Na War (1441–1474), the war between King Borommatrailokkanat of Ayutthaya and Prince Tilokaraj of Lan Na
The Lan Na kingdom or the Kingdom of Lanna (, , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; , , ), also known as Lannathai, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to the 18th centuries.
The cultural developmen ...
. One literary work is ''Kap He Ruea'', composed by Prince Thammathibet in the ''nirat'' tradition. Traditionally, the verse is sung during the royal barge procession and has been the model for subsequent poets to emulate. The same prince also composed the greatly admired ''Kap Ho Khlong'' on the Visit to Than Thongdaeng and ''Kap Ho Khlong Nirat Phrabat''.
Music and dance
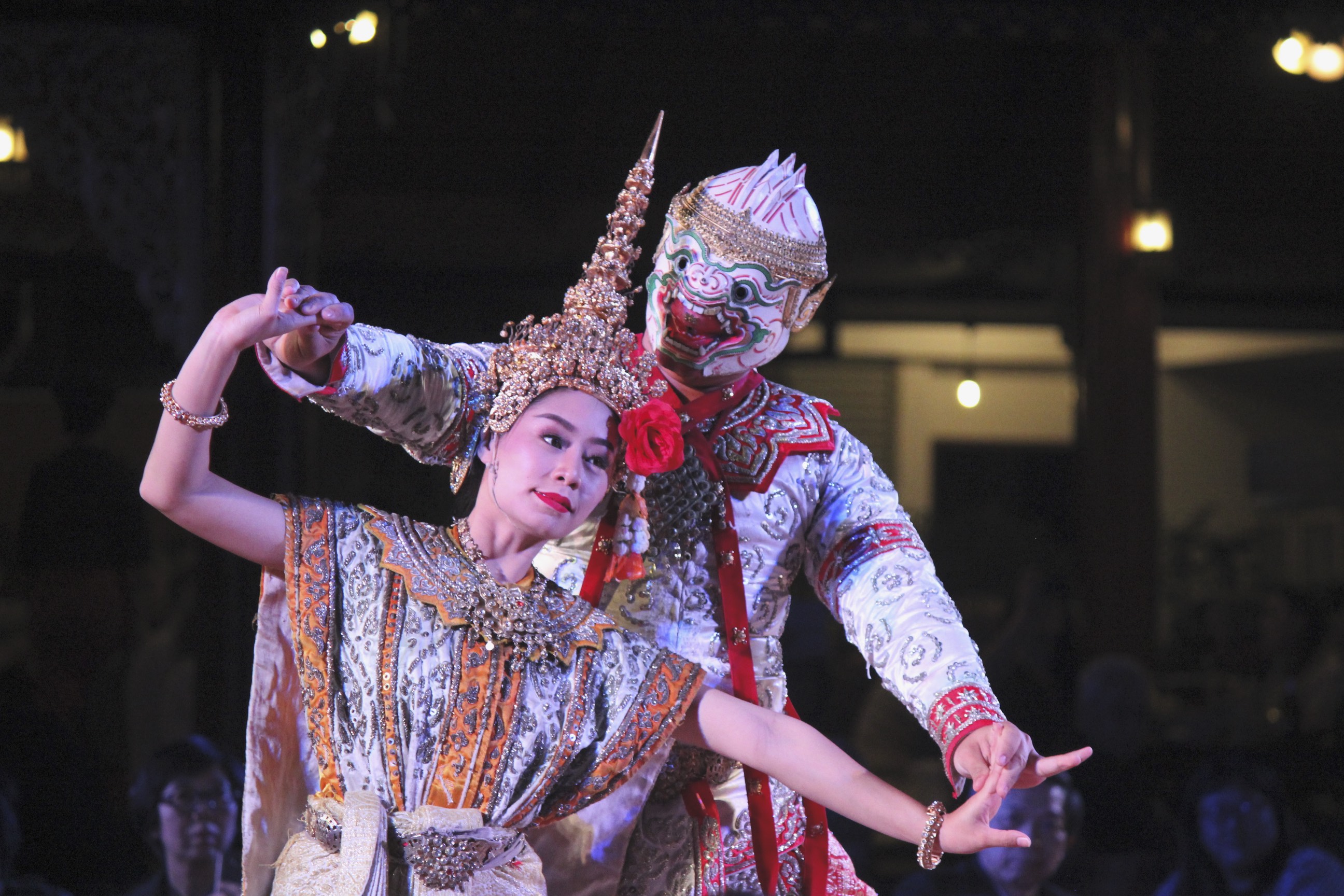 Aside from folk and regional dances (southern Thailand's Menora (dance), Menora and Ramwong, for example), the two major forms of Thai classical dance drama are Khon and Lakhon nai. In the beginning, both were exclusively court entertainments, and it was not until much later that a popular style of dance theatre, likay, evolved as a diversion for common folk. Folk dance forms include dance theater forms like likay, numerous regional dances (''ram''), the ritual dance ram muay, and homage to the teacher, Wai khru ram muay, wai khru. Both ram muay and wai khru take place before all traditional muay Thai matches.
The three primary classical ensembles are the Piphat, Khrueang sai, and Mahori. Mahori employ small ching hand cymbals.
Aside from folk and regional dances (southern Thailand's Menora (dance), Menora and Ramwong, for example), the two major forms of Thai classical dance drama are Khon and Lakhon nai. In the beginning, both were exclusively court entertainments, and it was not until much later that a popular style of dance theatre, likay, evolved as a diversion for common folk. Folk dance forms include dance theater forms like likay, numerous regional dances (''ram''), the ritual dance ram muay, and homage to the teacher, Wai khru ram muay, wai khru. Both ram muay and wai khru take place before all traditional muay Thai matches.
The three primary classical ensembles are the Piphat, Khrueang sai, and Mahori. Mahori employ small ching hand cymbals.
Entertainment
Thai films are exported and exhibited in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. Thai cinema has developed its own unique identity.
The Thai heist thriller film ''Bad Genius'' (2017) was one of the most internationally successful Thai films; it broke Thai film earning records in several Asian countries, Bad Genius won in 12 categories at the 27th Suphannahong National Film Awards, and also won the Jury Award at the 16th New York Asian Film Festival with a worldwide collection of more than $42 million.
''Shutter (2004 film), Shutter'' (2004) was one of the best-known Thai horror movies and was recognized worldwide. Films such as ''Ong-Bak: Muay Thai Warrior'' (2003) and ''Tom-Yum-Goong'' (2005), starring Tony Jaa, feature distinctive aspects of Thai martial arts "Muay Thai". Thailand television dramas, known as Thai television soap opera, Lakorn, have become popular in Thailand and regionally.
The entertainment industries are estimated to have directly contributed $2.1 billion in GDP to the Thai economy in 2011. They also directly supported 86,600 jobs. Amongst several dance-pop artists who have made internationally successful are "Lisa" Lalisa Manobal, Violette Wautier, and Tata Young.
Cuisine
Thai cuisine is one of the most popular in the world. Common ingredients include garlic, lemongrass, kaffir lime, galangal, turmeric, coriander, and coconut milk. Each region of Thailand has its specialities: ''kaeng khiao wan'' (green curry) in the central region, ''som tam'' (green papaya salad) in the northeast, ''khao soi'' in the north, and Massaman curry, ''massaman'' curry in the south.
In 2017, seven Thai dishes appeared on a list of the "World's 50 Best Foods"—an online worldwide poll by CNN Travel. Thailand had more dishes on the list than any other country. They were: ''tom yam goong'' (4th), ''pad Thai'' (5th), ''som tam'' (6th), ''massaman'' curry (10th), green curry (19th), Thai fried rice (24th) and ''nam tok mu'' (36th). Two desserts were also listed in CNN's 50 Best Desserts Around The World: mango sticky rice and tub tim krob.
The staple food in Thailand is rice, particularly jasmine rice, which forms part of almost every meal. Thailand is a leading exporter of rice, and Thais consume over 100 kg of milled rice per person per year. Thailand is also the world leader in edible insect industry and well known for its street food; Bangkok is sometimes called the street food capital of the world.
Units of measurement
Thailand generally uses the metric system, but Thai units of measurement, traditional units of measurement for land area are used, and imperial units of measurement are occasionally used for building materials. Years are numbered as B.E. (Thai solar calendar, Buddhist Era) in educational settings, civil service, government, contracts, and newspaper datelines. However, in banking, and increasingly in industry and commerce, standard Western year (Christian or Common Era) counting is the standard practice.
Sports
Muay Thai () is a combat sport that uses stand-up striking along with various clinch fighting, clinching techniques. Muay Thai became widespread internationally in the late-20th to 21st centuries. Famous practitioners include Buakaw Banchamek, Samart Payakaroon, and Apidej Sit-Hirun. Association football has overtaken Muay Thai as the most widely followed sport in Thailand. The Thailand national football team has played the AFC Asian Cup six times and reached the semifinals in 1972. The country has hosted the Asian Cup twice, in 1972 AFC Asian Cup, 1972 and in 2007 AFC Asian Cup, 2007 (along with Indonesia, Malaysia, and Vietnam for the 2007).
Volleyball is rapidly growing as one of the most popular sports. The Thailand women's national volleyball team, women's team has often participated in the FIVB Volleyball Women's World Championship, World Championship, FIVB Volleyball Women's World Cup, World Cup, and FIVB Volleyball World Grand Prix, World Grand Prix Asian Championship. They have won the Asian Women's Volleyball Championship, Asian Championship twice and the AVC Cup for Women, Asian Cup once. Takraw is a sport native to Thailand in which the players hit a rattan ball and are only allowed to use their feet, knees, chest, and head to touch the ball. Sepak takraw is a form of this sport which is similar to volleyball. A rather similar game but played only with the feet is buka ball.
Rugby football, Rugby is also a growing sport in Thailand with the Thailand national rugby union team rising to be ranked 61st in the world. Thailand became the first country in the world to host an international 80 welterweight rugby tournament in 2005. Thailand has also attracts golfers from Japan, Korea, and Western countries. There are more than 200 world-class golf courses nationwide. For basketball, the Chang Thailand Slammers won the 2011 ASEAN Basketball League Championship. The Thailand national basketball team had its most successful year at the Basketball at the 1966 Asian Games, 1966 Asian Games where it won the silver medal.
 The Lumpinee Boxing Stadium originally sited at Rama IV Road near Lumphini Park hosted its final Muay Thai boxing matches on 8 February 2014 after the venue first opened in December 1956. On 11 February 2014, the stadium was relocated to Ram Intra Road due to the new venue's capacity. Thammasat Stadium in Bangkok was built for the 1998 Asian Games. Rajamangala National Stadium is the biggest sporting arena in Thailand, with a capacity of around 50,000.
The Lumpinee Boxing Stadium originally sited at Rama IV Road near Lumphini Park hosted its final Muay Thai boxing matches on 8 February 2014 after the venue first opened in December 1956. On 11 February 2014, the stadium was relocated to Ram Intra Road due to the new venue's capacity. Thammasat Stadium in Bangkok was built for the 1998 Asian Games. Rajamangala National Stadium is the biggest sporting arena in Thailand, with a capacity of around 50,000.
See also
* International rankings of Thailand
* Outline of Thailand
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Government
Thaigov.go.th
– Government of Thailand
(archived 10 December 2008)
Mfa.go.th
– Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Thailand Internet information
– National Electronics and Computer Technology Center
Ministry of Culture
(archived 28 April 2015)
General information
Thailand
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Thailand
entry in Library of Congress Country Studies. 1987
Thailand
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' (archived 7 February 2009)
Thailand
from the BBC News
Thailand
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' entry
*
Longdo Map
– Thailand maps in English and Thai
Key Development Forecasts for Thailand
from International Futures
2010 Thailand population census by Economic and Social statistics Bureau
(archived 16 January 2013)
Travel
Tourism Authority of Thailand
– official tourism website
Other
Thailand Country Fact Sheet
from the Common Language Project (archived 31 July 2014)
*
{{coord, 15, 101, region:TH_type:country, display=title
Thailand,
1932 establishments in Asia
1932 establishments in Siam
1932 establishments in Southeast Asia
Countries in Asia
Kingdoms
Member states of ASEAN
Member states of the United Nations
Observer states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Southeast Asian countries
States and territories established in 1932
Tiger Cub Economies

 As is generally known, the present-day
As is generally known, the present-day  A Siamese revolution of 1932, bloodless revolution took place in 1932, in which Prajadhipok was forced to grant the country's first constitution, thereby ending centuries of feudal and absolute monarchy. The combined results of economic hardships brought on by the Great Depression, sharply falling rice prices, and a significant reduction in public spending caused discontent among aristocrats.
In 1933, Boworadet rebellion, a counter-revolutionary rebellion took place to reinstate absolute monarchy, but failed. Prajadhipok's conflict with the government eventually led to abdication. The government selected Ananda Mahidol, who was studying in Switzerland, to be the new king.
Later that decade, the army wing of Khana Ratsadon came to dominate Siamese politics. Plaek Phibunsongkhram who became premier in 1938, started political oppression and took an openly anti-royalist stance. His government adopted nationalism and Westernisation, Sinophobia, anti-Chinese and anti-French policies.
In 1939, there was a decree changing the name of the country from "Siam" to "Thailand". In 1941, Thailand was in Franco–Thai War, a brief conflict with Vichy France, resulting in Thailand gaining some Lao and Cambodian territories.
On 8 December 1941, Japanese invasion of Thailand, the Empire of Japan launched an invasion of Thailand, and fighting broke out shortly before Phibun ordered an armistice. Japan was granted free passage, and on 21 December Thailand and Japan signed a military alliance with a secret protocol, wherein the Japanese government agreed to help Thailand regain Territorial losses of Thailand, lost territories.
The Thai government then declared war on the United States and the United Kingdom. The United Kingdom, whose colony British Malaya, Malaya was under immediate threat from Thai forces, responded in kind, but the United States refused to declare war and ignored Thailand's declaration. The Free Thai Movement was launched both in Thailand and abroad to oppose the government and Japanese occupation. After the war ended in 1945, Thailand signed formal agreements to end the state of war with Allies of World War II, the Allies.
A Siamese revolution of 1932, bloodless revolution took place in 1932, in which Prajadhipok was forced to grant the country's first constitution, thereby ending centuries of feudal and absolute monarchy. The combined results of economic hardships brought on by the Great Depression, sharply falling rice prices, and a significant reduction in public spending caused discontent among aristocrats.
In 1933, Boworadet rebellion, a counter-revolutionary rebellion took place to reinstate absolute monarchy, but failed. Prajadhipok's conflict with the government eventually led to abdication. The government selected Ananda Mahidol, who was studying in Switzerland, to be the new king.
Later that decade, the army wing of Khana Ratsadon came to dominate Siamese politics. Plaek Phibunsongkhram who became premier in 1938, started political oppression and took an openly anti-royalist stance. His government adopted nationalism and Westernisation, Sinophobia, anti-Chinese and anti-French policies.
In 1939, there was a decree changing the name of the country from "Siam" to "Thailand". In 1941, Thailand was in Franco–Thai War, a brief conflict with Vichy France, resulting in Thailand gaining some Lao and Cambodian territories.
On 8 December 1941, Japanese invasion of Thailand, the Empire of Japan launched an invasion of Thailand, and fighting broke out shortly before Phibun ordered an armistice. Japan was granted free passage, and on 21 December Thailand and Japan signed a military alliance with a secret protocol, wherein the Japanese government agreed to help Thailand regain Territorial losses of Thailand, lost territories.
The Thai government then declared war on the United States and the United Kingdom. The United Kingdom, whose colony British Malaya, Malaya was under immediate threat from Thai forces, responded in kind, but the United States refused to declare war and ignored Thailand's declaration. The Free Thai Movement was launched both in Thailand and abroad to oppose the government and Japanese occupation. After the war ended in 1945, Thailand signed formal agreements to end the state of war with Allies of World War II, the Allies.
 In June 1946, young King Ananda was found dead under mysterious circumstances. His younger brother Bhumibol Adulyadej ascended to the throne. Thailand joined the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) to become an active ally of the United States in 1954. Field Marshal
In June 1946, young King Ananda was found dead under mysterious circumstances. His younger brother Bhumibol Adulyadej ascended to the throne. Thailand joined the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) to become an active ally of the United States in 1954. Field Marshal  List of national parks of Thailand, National parks in Thailand are defined as ''an area that contains natural resources of ecological importance or unique beauty, or flora and fauna of special importance''. Thailand's protected areas include 156 national parks, 58 wildlife sanctuaries, 67 non-hunting areas, and 120 forest parks. They cover almost 31 per cent of the kingdom's territory. The parks are administered by the Department of National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation, National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department (DNP) of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (Thailand), Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (MNRE).
Thailand has a mediocre but improving performance in the global Environmental Performance Index (EPI), with an overall ranking of 91 out of 180 countries in 2016. The environmental areas where Thailand performs worst (i.e., highest-ranking) are air quality (167), environmental effects of the agricultural industry (106), and the climate and energy sector (93), the later mainly because of a high CO2 emission, CO2 emission per kWh produced. Thailand performs best (i.e., lowest-ranking) in water resource management (66), with some major improvements expected for the future, and sanitation (68). The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.00/10, ranking it 88th globally out of 172 countries.
The population of elephants, the country's List of national animals, national symbol, has fallen from 100,000 in 1850 to an estimated 2,000. Poachers have long hunted elephants for ivory and hides, and now increasingly for Elephant meat, meat. Young elephants are often captured for use in tourist attractions or as work animals, where there have been claims of mistreatment. In 1989, the government banned the use of elephants for logging, leading many elephant owners to move their domesticated animals to the tourism industry.
Poaching of protected species remains a major problem. Tigers, leopards, and other large cats are hunted for their pelts. Many are farmed or hunted for their meat, which supposedly has medicinal properties. Although such trade is illegal, the well-known Bangkok market Chatuchak Weekend Market, Chatuchak is still known for the sale of endangered species. The practice of keeping wild animals as pets affects species such as Asiatic black bear, Malayan sun bear, Lar gibbon, white-handed lar, pileated gibbon, and binturong.
List of national parks of Thailand, National parks in Thailand are defined as ''an area that contains natural resources of ecological importance or unique beauty, or flora and fauna of special importance''. Thailand's protected areas include 156 national parks, 58 wildlife sanctuaries, 67 non-hunting areas, and 120 forest parks. They cover almost 31 per cent of the kingdom's territory. The parks are administered by the Department of National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation, National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department (DNP) of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (Thailand), Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (MNRE).
Thailand has a mediocre but improving performance in the global Environmental Performance Index (EPI), with an overall ranking of 91 out of 180 countries in 2016. The environmental areas where Thailand performs worst (i.e., highest-ranking) are air quality (167), environmental effects of the agricultural industry (106), and the climate and energy sector (93), the later mainly because of a high CO2 emission, CO2 emission per kWh produced. Thailand performs best (i.e., lowest-ranking) in water resource management (66), with some major improvements expected for the future, and sanitation (68). The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.00/10, ranking it 88th globally out of 172 countries.
The population of elephants, the country's List of national animals, national symbol, has fallen from 100,000 in 1850 to an estimated 2,000. Poachers have long hunted elephants for ivory and hides, and now increasingly for Elephant meat, meat. Young elephants are often captured for use in tourist attractions or as work animals, where there have been claims of mistreatment. In 1989, the government banned the use of elephants for logging, leading many elephant owners to move their domesticated animals to the tourism industry.
Poaching of protected species remains a major problem. Tigers, leopards, and other large cats are hunted for their pelts. Many are farmed or hunted for their meat, which supposedly has medicinal properties. Although such trade is illegal, the well-known Bangkok market Chatuchak Weekend Market, Chatuchak is still known for the sale of endangered species. The practice of keeping wild animals as pets affects species such as Asiatic black bear, Malayan sun bear, Lar gibbon, white-handed lar, pileated gibbon, and binturong.
 Government is Separation of powers, separated into three branches:
* The legislative branch: the National Assembly of Thailand, National Assembly is composed of the Senate of Thailand, Senate, the 200-member indirectly elected upper house and House of Representatives of Thailand, House of Representatives, the elected 500-member lower house. Its most recent election is 2023 Thai general election, the 2023 general election. The coalition led by Pheu Thai Party currently holds the majority. The 2024 Thai Senate election was the first senate election held under the current constitution in the process criticized as "the most complicated election in the world". The senate is allegedly dominated by Bhumjaithai Party-affiliated senators.
* The executive branch consisting of the
Government is Separation of powers, separated into three branches:
* The legislative branch: the National Assembly of Thailand, National Assembly is composed of the Senate of Thailand, Senate, the 200-member indirectly elected upper house and House of Representatives of Thailand, House of Representatives, the elected 500-member lower house. Its most recent election is 2023 Thai general election, the 2023 general election. The coalition led by Pheu Thai Party currently holds the majority. The 2024 Thai Senate election was the first senate election held under the current constitution in the process criticized as "the most complicated election in the world". The senate is allegedly dominated by Bhumjaithai Party-affiliated senators.
* The executive branch consisting of the  Siam's and Thailand's way of conducting foreign relations has long been described as "bamboo bending with the wind", of policies that are "always solidly rooted, but flexible enough to bend whichever way the wind blows in order to survive", or adaptable and pragmatic. In order to secure independence, it sought to pit one great power against the others so that it would be dominated by none.
During the
Siam's and Thailand's way of conducting foreign relations has long been described as "bamboo bending with the wind", of policies that are "always solidly rooted, but flexible enough to bend whichever way the wind blows in order to survive", or adaptable and pragmatic. In order to secure independence, it sought to pit one great power against the others so that it would be dominated by none.
During the  Thais have median wealth per one adult person of $1,469 in 2016, increasing from $605 in 2010. In 2016, Thailand was List of countries by Human Development Index, ranked 87th in Human Development Index, and List of countries by inequality-adjusted HDI, 70th in the inequality-adjusted HDI.
In 2017, Thailand's median household income was ฿26,946 per month. Top quintile households had a 45.0% share of all income, while bottom quintile households had 7.1%. There were 26.9 million persons who had the bottom 40% of income earning less than ฿5,344 per person per month. During the 2013–2014 Thai political crisis, a survey found that anti-government People's Democratic Reform Committee, PDRC mostly (32%) had a monthly income of more than ฿50,000, while pro-government United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship, UDD mostly (27%) had between ฿10,000 and ฿20,000.
In 2014, Credit Suisse reported that Thailand was the world's third most unequal country, behind Russia and India. The top 10% richest held 79% of the country's assets. The top 1% held 58% of the assets. The 50 richest Thai families had a total net worth accounting to 30% of GDP. Bank of Thailand reported that during 2006–16, Thailand's top 5% largest companies had 85% of all corporate revenue in the nation, and only 6% of the country's companies were in export industries, which made up 60% of the country's GDP.
In 2016, 5.81 million people lived in poverty, or 11.6 million people (17.2% of population) if "near poor" is included. The proportion of the poor relative to total population in each region was 12.96% in the Northeast, 12.35% in the South, and 9.83% in the North. In 2017, there were 14 million people who applied for social welfare (yearly income of less than ฿100,000 was required). In the first quarter of 2023, Thai household debts totaled 14.6 trillion baht or 89.2% of GDP; the average debt per household was approximately 500,000 baht. In 2016, there were estimated 30,000 homeless persons in the country.
Thais have median wealth per one adult person of $1,469 in 2016, increasing from $605 in 2010. In 2016, Thailand was List of countries by Human Development Index, ranked 87th in Human Development Index, and List of countries by inequality-adjusted HDI, 70th in the inequality-adjusted HDI.
In 2017, Thailand's median household income was ฿26,946 per month. Top quintile households had a 45.0% share of all income, while bottom quintile households had 7.1%. There were 26.9 million persons who had the bottom 40% of income earning less than ฿5,344 per person per month. During the 2013–2014 Thai political crisis, a survey found that anti-government People's Democratic Reform Committee, PDRC mostly (32%) had a monthly income of more than ฿50,000, while pro-government United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship, UDD mostly (27%) had between ฿10,000 and ฿20,000.
In 2014, Credit Suisse reported that Thailand was the world's third most unequal country, behind Russia and India. The top 10% richest held 79% of the country's assets. The top 1% held 58% of the assets. The 50 richest Thai families had a total net worth accounting to 30% of GDP. Bank of Thailand reported that during 2006–16, Thailand's top 5% largest companies had 85% of all corporate revenue in the nation, and only 6% of the country's companies were in export industries, which made up 60% of the country's GDP.
In 2016, 5.81 million people lived in poverty, or 11.6 million people (17.2% of population) if "near poor" is included. The proportion of the poor relative to total population in each region was 12.96% in the Northeast, 12.35% in the South, and 9.83% in the North. In 2017, there were 14 million people who applied for social welfare (yearly income of less than ฿100,000 was required). In the first quarter of 2023, Thai household debts totaled 14.6 trillion baht or 89.2% of GDP; the average debt per household was approximately 500,000 baht. In 2016, there were estimated 30,000 homeless persons in the country.
 Tourism makes up about 6% of the country's economy. Prior to the pandemic, Thailand was the world's eighth most visited country according to the World Tourism rankings compiled by the United Nations World Tourism Organization, United Nations World Tourism Organisation. In 2019, Thailand received 39.8 million international tourists, ahead of United Kingdom and Germany and was the fourth highest in international tourism earning 60.5 billion US dollars.
Thailand was the most visited country in Southeast Asia in 2013, according to the World Tourism Organisation. Estimates of tourism receipts directly contributing to the Thai GDP of 12 trillion baht range from 9 per cent (1 trillion baht) (2013) to 16 per cent. When including the indirect effects of tourism, it is said to account for 20.2 per cent (2.4 trillion baht) of Thailand's GDP.
Asian tourists primarily visit Thailand for Bangkok and the historical, natural, and cultural sights in its vicinity. Western tourists not only visit Bangkok and surrounding areas; many travel to the southern beaches and islands. The north is the chief destination for trekking and adventure travel with its diverse ethnic minority groups and forested mountains. The region hosting the fewest tourists is
Tourism makes up about 6% of the country's economy. Prior to the pandemic, Thailand was the world's eighth most visited country according to the World Tourism rankings compiled by the United Nations World Tourism Organization, United Nations World Tourism Organisation. In 2019, Thailand received 39.8 million international tourists, ahead of United Kingdom and Germany and was the fourth highest in international tourism earning 60.5 billion US dollars.
Thailand was the most visited country in Southeast Asia in 2013, according to the World Tourism Organisation. Estimates of tourism receipts directly contributing to the Thai GDP of 12 trillion baht range from 9 per cent (1 trillion baht) (2013) to 16 per cent. When including the indirect effects of tourism, it is said to account for 20.2 per cent (2.4 trillion baht) of Thailand's GDP.
Asian tourists primarily visit Thailand for Bangkok and the historical, natural, and cultural sights in its vicinity. Western tourists not only visit Bangkok and surrounding areas; many travel to the southern beaches and islands. The north is the chief destination for trekking and adventure travel with its diverse ethnic minority groups and forested mountains. The region hosting the fewest tourists is  Forty-nine per cent of Thailand's labour force is employed in agriculture in Thailand, agriculture. This is down from 70% in 1980. Rice is the most important crop in the country and Thailand had long been the world's leading exporter of rice, until recently falling behind both India and Vietnam. Thailand has the highest percentage of arable land, 27.25%, of any state in the Greater Mekong Subregion. About 55% of the arable land area is used for rice production.
Agriculture has been experiencing a transition from labour-intensive and transitional methods to a more industrialised and competitive sector.Henri Leturque and Steve Wiggins 2010
Forty-nine per cent of Thailand's labour force is employed in agriculture in Thailand, agriculture. This is down from 70% in 1980. Rice is the most important crop in the country and Thailand had long been the world's leading exporter of rice, until recently falling behind both India and Vietnam. Thailand has the highest percentage of arable land, 27.25%, of any state in the Greater Mekong Subregion. About 55% of the arable land area is used for rice production.
Agriculture has been experiencing a transition from labour-intensive and transitional methods to a more industrialised and competitive sector.Henri Leturque and Steve Wiggins 2010 The State Railway of Thailand (SRT) operates all of Thailand's national rail lines. Krung Thep Aphiwat Central Terminal and Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) railway station, Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) are the main termini of intercity routes. Phahonyothin and ICD Lat Krabang are the main freight terminals. SRT had of track, all of it meter gauge. Nearly all is single-track (2702.1 km), although some important sections around Bangkok are double () or triple-tracked (), and there are plans to extend this.
Rail transport in Bangkok includes long-distance services. There are four rapid transit rail systems in the capital: the BTS Skytrain, MRT (Bangkok), MRT, SRT Red Lines, and the Airport Rail Link (Bangkok), Airport Rail Link. In Bangkok, there were two failed rapid rail projects Lavalin Skytrain and Bangkok Elevated Road and Train System, before Mass Rapid Transit Master Plan in Bangkok Metropolitan Region was endorsed by the cabinet on 27 September 1994 and implemented from 1995 to the present.
Thailand has of highways. , Thailand has over 462,133 roads and 37 million registered vehicles, 20 million of them motorbikes. A number of undivided two-lane highways have been converted into divided four-lane highways. Within the Bangkok Metropolitan Region, there are a number of Controlled-access highways in Thailand, controlled-access highways. There are 4,125 public vans operating on 114 routes from Bangkok alone. Other forms of road transport includes Auto rickshaw, tuk-tuks, taxis—with over 80,647 registered taxis nationwide as of 2018, vans (minibus), motorbike taxis, and songthaews.
, Thailand has 103 airports with 63 paved runways, in addition to 6 heliports. The busiest airport in the country is Bangkok's Suvarnabhumi Airport.
The State Railway of Thailand (SRT) operates all of Thailand's national rail lines. Krung Thep Aphiwat Central Terminal and Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) railway station, Bangkok (Hua Lamphong) are the main termini of intercity routes. Phahonyothin and ICD Lat Krabang are the main freight terminals. SRT had of track, all of it meter gauge. Nearly all is single-track (2702.1 km), although some important sections around Bangkok are double () or triple-tracked (), and there are plans to extend this.
Rail transport in Bangkok includes long-distance services. There are four rapid transit rail systems in the capital: the BTS Skytrain, MRT (Bangkok), MRT, SRT Red Lines, and the Airport Rail Link (Bangkok), Airport Rail Link. In Bangkok, there were two failed rapid rail projects Lavalin Skytrain and Bangkok Elevated Road and Train System, before Mass Rapid Transit Master Plan in Bangkok Metropolitan Region was endorsed by the cabinet on 27 September 1994 and implemented from 1995 to the present.
Thailand has of highways. , Thailand has over 462,133 roads and 37 million registered vehicles, 20 million of them motorbikes. A number of undivided two-lane highways have been converted into divided four-lane highways. Within the Bangkok Metropolitan Region, there are a number of Controlled-access highways in Thailand, controlled-access highways. There are 4,125 public vans operating on 114 routes from Bangkok alone. Other forms of road transport includes Auto rickshaw, tuk-tuks, taxis—with over 80,647 registered taxis nationwide as of 2018, vans (minibus), motorbike taxis, and songthaews.
, Thailand has 103 airports with 63 paved runways, in addition to 6 heliports. The busiest airport in the country is Bangkok's Suvarnabhumi Airport.
 In 1995, as minister of education, Sukavich Rangsitpollaid let out his plans for educational reform in Thailand. The reform was considered a landmark movement after nearly 100 years of education under the previous system. Thailand's youth literacy rate was 98.1% in 2015. Education is provided by a school system of kindergartens, primary, lower secondary and upper secondary schools, numerous vocational colleges, and universities. Education is compulsory up to and including age 14, while the government is mandated to provide free education through to age 17. Issues concerning university entrance have been in constant upheaval for a number of years. The country is also one of the few that still mandates uniform up to the university years, which is still a subject of ongoing debate.
In 2013, the Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (Thailand), Ministry of Information and Communication Technology announced that 27,231 schools would receive classroom-level access to internet, high-speed internet. However, the country's educational infrastructure was still underprepared for online teaching, as smaller and more remote schools were particularly hindered by COVID-19 restrictions.
The number of higher education institutions in Thailand has grown over the past decades to 156 officially. The two top-ranking universities in Thailand are Chulalongkorn University and Mahidol University. Thai universities' research output is still relatively low, even though the country's journal publications increased by 20% between 2011 and 2016. Thailand has the second highest number of English-medium private international schools in ASEAN, Southeast Asian Nations. Cram schools are especially popular for university entrance exams.
Students in ethnic minority areas score consistently lower in standardised national and international tests. This is likely due to unequal allocation of educational resources, weak teacher training, poverty, and low Thai language skill, the language of the tests. , Thailand was ranked 89th out of 100 countries globally for English proficiency. Thailand is the third most popular study destination in ASEAN. The number of international degree students in Thailand increased by 9.7 times between 1999 and 2012, from 1,882 to 20,309 students. Most of international students come from neighbor countries like China, Myanmar, Cambodia and Vietnam.
In 1995, as minister of education, Sukavich Rangsitpollaid let out his plans for educational reform in Thailand. The reform was considered a landmark movement after nearly 100 years of education under the previous system. Thailand's youth literacy rate was 98.1% in 2015. Education is provided by a school system of kindergartens, primary, lower secondary and upper secondary schools, numerous vocational colleges, and universities. Education is compulsory up to and including age 14, while the government is mandated to provide free education through to age 17. Issues concerning university entrance have been in constant upheaval for a number of years. The country is also one of the few that still mandates uniform up to the university years, which is still a subject of ongoing debate.
In 2013, the Ministry of Information and Communication Technology (Thailand), Ministry of Information and Communication Technology announced that 27,231 schools would receive classroom-level access to internet, high-speed internet. However, the country's educational infrastructure was still underprepared for online teaching, as smaller and more remote schools were particularly hindered by COVID-19 restrictions.
The number of higher education institutions in Thailand has grown over the past decades to 156 officially. The two top-ranking universities in Thailand are Chulalongkorn University and Mahidol University. Thai universities' research output is still relatively low, even though the country's journal publications increased by 20% between 2011 and 2016. Thailand has the second highest number of English-medium private international schools in ASEAN, Southeast Asian Nations. Cram schools are especially popular for university entrance exams.
Students in ethnic minority areas score consistently lower in standardised national and international tests. This is likely due to unequal allocation of educational resources, weak teacher training, poverty, and low Thai language skill, the language of the tests. , Thailand was ranked 89th out of 100 countries globally for English proficiency. Thailand is the third most popular study destination in ASEAN. The number of international degree students in Thailand increased by 9.7 times between 1999 and 2012, from 1,882 to 20,309 students. Most of international students come from neighbor countries like China, Myanmar, Cambodia and Vietnam.
 Thai culture and traditions incorporate influences from India, China, Cambodia, and the rest of Southeast Asia. Thailand's national religion, Theravada, Theravada Buddhism, is central to modern Thai identity. Buddhism in Thailand, Thai Buddhism has evolved over time to include many regional beliefs originating from Hinduism, animism, as well as ancestor worship. The Thai solar calendar, official calendar in Thailand is based on the Eastern version of the Buddhist calendar, Buddhist Era (BE). Thai identity today is a Thaification, social construct of the Phibun regime in the 1940s.
Several ethnic groups mediated change between their traditional local culture, national Thai, and global cultural influences. Overseas Chinese also form a significant part of Thai society, particularly in and around Bangkok. Thai Chinese businesses prosper as part of the larger bamboo network.
Thai culture and traditions incorporate influences from India, China, Cambodia, and the rest of Southeast Asia. Thailand's national religion, Theravada, Theravada Buddhism, is central to modern Thai identity. Buddhism in Thailand, Thai Buddhism has evolved over time to include many regional beliefs originating from Hinduism, animism, as well as ancestor worship. The Thai solar calendar, official calendar in Thailand is based on the Eastern version of the Buddhist calendar, Buddhist Era (BE). Thai identity today is a Thaification, social construct of the Phibun regime in the 1940s.
Several ethnic groups mediated change between their traditional local culture, national Thai, and global cultural influences. Overseas Chinese also form a significant part of Thai society, particularly in and around Bangkok. Thai Chinese businesses prosper as part of the larger bamboo network.
 Respect for elderly and superiors (by age, position, monks, or certain professions) is Thai mores, reflecting in many classes of Thai honorifics, honorifics. ''Thai greeting, Wai'' is a familiar Thai greeting, and is generally offered first by a person who is younger or lower in social status and position. Older siblings have duties to younger ones.
Taboos in Thai culture include touching someone's head or pointing with the feet, as the head is considered the most sacred and the foot the lowest part of the body.
Respect for elderly and superiors (by age, position, monks, or certain professions) is Thai mores, reflecting in many classes of Thai honorifics, honorifics. ''Thai greeting, Wai'' is a familiar Thai greeting, and is generally offered first by a person who is younger or lower in social status and position. Older siblings have duties to younger ones.
Taboos in Thai culture include touching someone's head or pointing with the feet, as the head is considered the most sacred and the foot the lowest part of the body.
 Aside from folk and regional dances (southern Thailand's Menora (dance), Menora and Ramwong, for example), the two major forms of Thai classical dance drama are Khon and Lakhon nai. In the beginning, both were exclusively court entertainments, and it was not until much later that a popular style of dance theatre, likay, evolved as a diversion for common folk. Folk dance forms include dance theater forms like likay, numerous regional dances (''ram''), the ritual dance ram muay, and homage to the teacher, Wai khru ram muay, wai khru. Both ram muay and wai khru take place before all traditional muay Thai matches.
The three primary classical ensembles are the Piphat, Khrueang sai, and Mahori. Mahori employ small ching hand cymbals.
Aside from folk and regional dances (southern Thailand's Menora (dance), Menora and Ramwong, for example), the two major forms of Thai classical dance drama are Khon and Lakhon nai. In the beginning, both were exclusively court entertainments, and it was not until much later that a popular style of dance theatre, likay, evolved as a diversion for common folk. Folk dance forms include dance theater forms like likay, numerous regional dances (''ram''), the ritual dance ram muay, and homage to the teacher, Wai khru ram muay, wai khru. Both ram muay and wai khru take place before all traditional muay Thai matches.
The three primary classical ensembles are the Piphat, Khrueang sai, and Mahori. Mahori employ small ching hand cymbals.
 The Lumpinee Boxing Stadium originally sited at Rama IV Road near Lumphini Park hosted its final Muay Thai boxing matches on 8 February 2014 after the venue first opened in December 1956. On 11 February 2014, the stadium was relocated to Ram Intra Road due to the new venue's capacity. Thammasat Stadium in Bangkok was built for the 1998 Asian Games. Rajamangala National Stadium is the biggest sporting arena in Thailand, with a capacity of around 50,000.
The Lumpinee Boxing Stadium originally sited at Rama IV Road near Lumphini Park hosted its final Muay Thai boxing matches on 8 February 2014 after the venue first opened in December 1956. On 11 February 2014, the stadium was relocated to Ram Intra Road due to the new venue's capacity. Thammasat Stadium in Bangkok was built for the 1998 Asian Games. Rajamangala National Stadium is the biggest sporting arena in Thailand, with a capacity of around 50,000.