Recurrent Pneumonia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the
 Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and
Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and
 Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include ''
Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include ''
 In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include
In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include
 Pneumonia frequently starts as an
Pneumonia frequently starts as an
 A
A
File:UOTW 34 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm, Pneumonia seen by ultrasound
File:UOTW 34 - Ultrasound of the Week 2.webm, Pneumonia seen by ultrasound
File:UOTW 34 - Ultrasound of the Week 3.jpg, Pneumonia seen by ultrasound
File:RtPneuKidMark.png, Right middle lobe pneumonia in a child as seen on plain X-ray
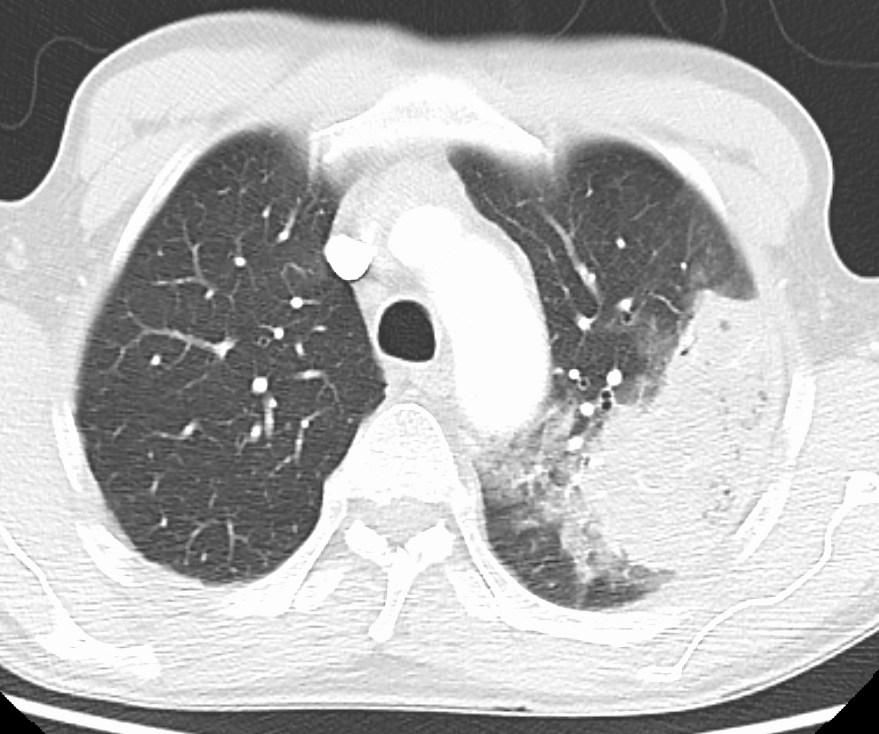
 In pneumonia, a collection of fluid may form in the space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (
In pneumonia, a collection of fluid may form in the space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (

 Pneumonia is a common illness affecting approximately 450 million people a year and occurring in all parts of the world. It is a major cause of death among all age groups resulting in 4 million deaths (7% of the world's total death) yearly. Rates are greatest in children less than five, and adults older than 75 years. It occurs about five times more frequently in the
Pneumonia is a common illness affecting approximately 450 million people a year and occurring in all parts of the world. It is a major cause of death among all age groups resulting in 4 million deaths (7% of the world's total death) yearly. Rates are greatest in children less than five, and adults older than 75 years. It occurs about five times more frequently in the
 Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by
Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by
lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable.
Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
. Chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
s, blood tests, and culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
of the sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked-eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections, and Cytopathology, cytological ...
may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia.
Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
(COPD), sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited Hemoglobinopathy, haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the ...
, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
, a history of smoking, a poor ability to cough (such as following a stroke), and immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that aff ...
.
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s to prevent certain types of pneumonia (such as those caused by ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, hemolysis (microbiology), alpha-hemolytic member of the genus ''Streptococcus''. ''S. pneumoniae'' cells are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not f ...
'' bacteria, influenza viruses
''Orthomyxoviridae'' () is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes nine genera: '' Alphainfluenzavirus'', '' Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', '' Isavirus'', '' Mykissvirus'', '' Quaranjavir ...
, or SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
) are available. Other methods of prevention include hand washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap, soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to th ...
to prevent infection, prompt treatment of worsening respiratory symptoms, and not smoking.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Pneumonia believed to be due to bacteria is treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s. If the pneumonia is severe, the affected person is generally hospitalized. Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy, also referred to as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Supplemental oxygen can also refer to the use of oxygen enriched air at altitude. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood o ...
may be used if oxygen levels are low.
Each year, pneumonia affects about 450 million people globally (7% of the population) and results in about 4 million deaths. With the introduction of antibiotics and vaccines in the 20th century, survival has greatly improved. Nevertheless, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death in developing countries, and also among the very old, the very young, and the chronically ill. Pneumonia often shortens the period of suffering among those already close to death and has thus been called "the old man's friend".
Signs and symptoms
People with infectious pneumonia often have aproductive cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ...
, fever accompanied by shaking chills, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, sharp or stabbing chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
during deep breaths, and an increased rate of breathing. In elderly people, confusion may be the most prominent sign.
The typical signs and symptoms in children under five are fever, cough, and fast or difficult breathing. Fever is not very specific, as it occurs in many other common illnesses and may be absent in those with severe disease, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
or in the elderly. In addition, a cough is frequently absent in children less than 2 months old. More severe signs and symptoms in children may include blue-tinged skin, unwillingness to drink, convulsions, ongoing vomiting, extremes of temperature, or a decreased level of consciousness.
Bacterial and viral cases of pneumonia usually result in similar symptoms. Some causes are associated with classic, but non-specific, clinical characteristics. Pneumonia caused by ''Legionella
''Legionella'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative bacteria that can be seen using a silver stain or grown in a special media that contains cysteine, an amino acid. It is known to cause legionellosis (all illnesses caused by ''Legi ...
'' may occur with abdominal pain, diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, or confusion. Pneumonia caused by ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, hemolysis (microbiology), alpha-hemolytic member of the genus ''Streptococcus''. ''S. pneumoniae'' cells are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not f ...
'' is associated with rusty colored sputum. Pneumonia caused by ''Klebsiella
''Klebsiella'' is a genus of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule.
''Klebsiella'' is named after German-Swiss microbiologist Edwin Klebs (1834–1913). Carl Friedlander described ' ...
'' may have bloody sputum often described as "currant jelly". Bloody sputum (known as hemoptysis
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the discharge of blood or blood-stained sputum, mucus through the mouth coming from the bronchi, larynx, vertebrate trachea, trachea, or lungs. It does not necessarily involve coughing. In other words, it is the airw ...
) may also occur with tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, Gram-negative pneumonia, lung abscess
Lung abscess is a type of liquefactive necrosis of the lung tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm) containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection.
This pus-filled cavity is often caused by aspiration, which m ...
es and more commonly acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis, also known as a chest cold, is short-term bronchitis – inflammation of the bronchus, bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) of the lungs. The most common symptom is a cough. Other symptoms include sputum, coughing up mucus, ...
. Pneumonia caused by ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae
''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' is a species of very small-cell bacteria that lack a cell wall, in the class Mollicutes. ''M. pneumoniae'' is a human pathogen that causes the disease Mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia related ...
'' may occur in association with swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, joint pain
Arthralgia () literally means 'joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutic ...
, or a middle ear infection. Viral pneumonia presents more commonly with wheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
than bacterial pneumonia. Pneumonia was historically divided into "typical" and "atypical" based on the belief that the presentation predicted the underlying cause. However, evidence has not supported this distinction, therefore it is no longer emphasized.
Cause
 Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and
Pneumonia is due to infections caused primarily by bacteria or viruses and less commonly by fungi and parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
. Although more than 100 strains of infectious agents have been identified, only a few are responsible for the majority of cases. Mixed infections with both viruses and bacteria may occur in roughly 45% of infections in children and 15% of infections in adults. A causative agent may not be isolated in about half of cases despite careful testing. In an active population-based surveillance for community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization in five hospitals in Chicago and Nashville from January 2010 through June 2012, 2259 patients were identified who had radiographic evidence of pneumonia and specimens that could be tested for the responsible pathogen. Most patients (62%) had no detectable pathogens in their sample, and unexpectedly, respiratory viruses were detected more frequently than bacteria. Specifically, 23% had one or more viruses, 11% had one or more bacteria, 3% had both bacterial and viral pathogens, and 1% had a fungal or mycobacterial infection. "The most common pathogens were human rhinovirus (in 9% of patients), influenza virus (in 6%), and ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (in 5%)."
The term ''pneumonia'' is sometimes more broadly applied to any condition resulting in inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the lungs (caused for example by autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
s, chemical burns or drug reactions); however, this inflammation is more accurately referred to as pneumonitis
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicide ...
.
Factors that predispose to pneumonia include smoking, immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that aff ...
, alcoholism, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
, sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited Hemoglobinopathy, haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the ...
(SCD), asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three mo ...
, liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Liver diseases
File:Ground gla ...
, and biological aging
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. Whole organism senescence involves an increase in death rates or a decrease in fecundity with increasing age, at least in the l ...
. Additional risks in children include not being breastfed, exposure to cigarette smoke and other air pollution, malnutrition, and poverty. The use of acid-suppressing medications – such as proton-pump inhibitors or H2 blockers – is associated with an increased risk of pneumonia. Approximately 10% of people who require mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
develop ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of lung infection that occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation breathing machines in hospitals. As such, VAP typically affects critically ill persons that are in an intensive care unit (I ...
, and people with a gastric feeding tube have an increased risk of developing aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may incl ...
. Moreover, the misplacement of a feeding tube can lead to aspiration pneumonia. 28% of tube malposition results in pneumonia. As with Avanos Medical
Avanos Medical, Inc. is a medical technology company making clinical medical devices. The company consists of two franchises – Pain Management and Chronic Care – that address reducing the use of opioids while helping patients recover faster ...
's feeding tube placement system, the CORTRAK* 2 EAS, which was recalled in May 2022 by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
due to adverse events reported, including pneumonia, caused a total of 60 injuries and 23 patient deaths, as communicated by the FDA. For people with certain variants of the FER gene, the risk of death is reduced in sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
caused by pneumonia. However, for those with TLR6
Toll-like receptor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR6'' gene. TLR6 is a transmembrane protein, member of toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. TLR6 acts in a heterodimer for ...
variants, the risk of getting Legionnaires' disease
Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of ''Legionella'' bacteria, quite often ''Legionella pneumophila''. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, myalgia, muscle pains, and headach ...
is increased.
Bacteria
 Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include ''
Bacteria are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' isolated in nearly 50% of cases. Other commonly isolated bacteria include ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophili ...
'' in 20%, '' Chlamydophila pneumoniae'' in 13%, and ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in 3% of cases; ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
''; ''Moraxella catarrhalis
''Moraxella catarrhalis'' is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system, middle ear, eye, central nervous system, and joints of humans. It causes the in ...
''; and ''Legionella pneumophila
''Legionella pneumophila'', the primary causative agent for Legionnaires' disease, Legionnaire's disease, is an Aerobic organism, aerobic, pleomorphic, Flagellum, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative bacterium. ' ...
''. A number of drug-resistant
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, ...
versions of the above infections are becoming more common, including drug-resistant ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (DRSP) and methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA).
The spreading of organisms is facilitated by certain risk factors. Alcoholism is associated with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen, molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an o ...
s, and ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''; smoking facilitates the effects of ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Haemophilus influenzae'', ''Moraxella catarrhalis'', and ''Legionella pneumophila''. Exposure to birds is associated with ''Chlamydia psittaci
''Chlamydia psittaci'' is a lethal intracellular bacterial species that may cause endemic avian chlamydiosis, epizootic outbreaks in other mammals, and respiratory psittacosis in humans. Potential hosts include feral birds and domesticated po ...
''; farm animals with '' Coxiella burnetti''; aspiration of stomach contents with anaerobic organisms; and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
with ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
'' and ''Staphylococcus aureus''. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' is more common in the winter, and it should be suspected in persons aspirating a large number of anaerobic organisms.
Viruses
 In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include
In adults, viruses account for about one third of pneumonia cases, and in children for about 15% of them. Commonly implicated agents include rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the ) is a Positive-sense single stranded RNA virus, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus ''Enterovirus'' in the family ''Picornaviridae''. Rhinoviru ...
es, coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es, influenza virus
''Orthomyxoviridae'' () is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes nine genera: '' Alphainfluenzavirus'', '' Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', '' Isavirus'', '' Mykissvirus'', '' Quaranjavir ...
, respiratory syncytial virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derive ...
(RSV), adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
, and parainfluenza. Herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
rarely causes pneumonia, except in groups such as newborns, persons with cancer, transplant recipients, and people with significant burns. After organ transplantation
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be trans ...
or in otherwise immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affe ...
persons, there are high rates of cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
pneumonia. Those with viral infections may be secondarily infected with the bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Staphylococcus aureus'', or ''Haemophilus influenzae'', particularly when other health problems are present. Different viruses predominate at different times of the year; during flu season
Flu season is an annually recurring time period characterized by the prevalence of an outbreak of influenza (flu). The season occurs during the cold half of the year in each hemisphere. It takes approximately two days to show symptoms. Influen ...
, for example, influenza may account for more than half of all viral cases. Outbreaks of other viruses also occur occasionally, including hantaviruses
''Orthohantavirus'' is a genus of viruses that includes all hantaviruses (family ''Hantaviridae'') that cause disease in humans. Orthohantaviruses, hereafter referred to as hantaviruses, are naturally found primarily in rodents. In general, each ...
and coronaviruses. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
(SARS-CoV-2) can also result in pneumonia.
Fungi
Fungal pneumonia is uncommon, but occurs more commonly in individuals with weakened immune systems due to AIDS,immunosuppressive drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classifie ...
s, or other medical problems. It is most often caused by ''Histoplasma capsulatum
''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is a species of dimorphic fungus. Its sexual form is called ''Ajellomyces capsulatus''. It can cause pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis.
''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is "distributed worldwide, except in Antarc ...
'', '' Blastomyces'', ''Cryptococcus neoformans
''Cryptococcus neoformans'' is an encapsulated basidiomycetous yeast belonging to the class Tremellomycetes and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is a filamentous fungus, formerly referred to ''Filob ...
'', '' Pneumocystis jiroveci'' (pneumocystis pneumonia
''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia (PCP), also known as ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia (PJP), is a form of pneumonia that is caused by the yeast-like fungus '' Pneumocystis jirovecii''.
''Pneumocystis'' specimens are commonly found in the lungs o ...
, or PCP), and ''Coccidioides immitis
''Coccidioides immitis'' is a pathogenic fungus that resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, northern Mexico, and a few other areas in the Western Hemisphere.
Epidemiology
''C. immitis'', along with its relativ ...
''. Histoplasmosis is most common in the Mississippi River basin
The Mississippi River is the primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, ...
, and coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis (, ) is a mammalian mycosis, fungal disease caused by ''Coccidioides immitis'' or ''Coccidioides posadasii''. It is commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, California fever, desert rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley fever. Cocci ...
is most common in the Southwestern United States. The number of cases of fungal pneumonia has been increasing in the latter half of the 20th century due to increasing travel and rates of immunosuppression in the population. For people infected with HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, PCP is a common opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection that occurs most commonly in individuals with an immunodeficiency disorder and acts more severe on those with a weakened immune system. These types of infections are considered serious and can be caused b ...
.
Parasites
A variety ofparasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s can affect the lungs, including ''Toxoplasma gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is a species of parasitic alveolate that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but members of the cat family (felidae) are the only known d ...
'', ''Strongyloides stercoralis
''Strongyloides stercoralis'' is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term ''threadworm'' can also refer to nematodes of t ...
'', ''Ascaris lumbricoides
''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is a large parasitic worm, parasitic Nematoda, roundworm of the genus ''Ascaris.'' It is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' ...
'', and ''Plasmodium malariae
''Plasmodium malariae'' is a parasitic protozoan that causes malaria in humans. It is one of several species of ''Plasmodium'' parasites that infect other organisms as pathogens, also including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and '' Plasmodium vivax' ...
''.Murray and Nadel (2010). Chapter 37. These organisms typically enter the body through direct contact with the skin, ingestion, or via an insect vector. Except for ''Paragonimus westermani
''Paragonimus westermani'' (Japanese lung fluke or oriental lung fluke) is the most common species of lung fluke that infects humans, causing paragonimiasis. Human infections are most common in eastern Asia and in South America. Paragonimiasis ...
'', most parasites do not specifically affect the lungs but involve the lungs secondarily to other sites. Some parasites, in particular those belonging to the ''Ascaris'' and ''Strongyloides'' genera, stimulate a strong eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix '' -phil'', meaning ''eosin-loving'') describes the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye commonly used in histological staining.
Eosin is an acidic dye for stainin ...
reaction, which may result in eosinophilic pneumonia
Eosinophilic pneumonia is a disease in which an eosinophil, a type of white blood cell, accumulates in the lungs. These cells cause disruption of the normal air spaces ( alveoli) where oxygen is extracted from the atmosphere. Several different k ...
. In other infections, such as malaria, lung involvement is due primarily to cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
-induced systemic inflammation. In the developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
, these infections are most common in people returning from travel or in immigrants. Around the world, parasitic pneumonia is most common in the immunodeficient.
Noninfectious
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia or noninfectious pneumonia is a class of diffuse lung diseases. They includediffuse alveolar damage
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is a Histology, histologic term used to describe specific changes that occur to the structure of the lungs during injury or Respiratory disease, disease. Most often DAD is described in association with the early stag ...
, organizing pneumonia
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles (bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pne ...
, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
Symptoms
Symptoms include cough, difficulty breathing, and fatigue.
Causes
It has been suggested that idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia has ...
, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, desquamative interstitial pneumonia
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) is a type of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia featuring elevated numbers of macrophages within the alveoli of the lung. DIP is a chronic disorder with an insidious onset. Its common symptoms include shor ...
, respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease, and usual interstitial pneumonia
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring ( pulmonary fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium (the supporting framework of the lung). UIP is thus classifi ...
. Lipoid pneumonia Lipoid pneumonia, also known as lipid pneumonia, is a rare form of lung inflammation (pneumonia) that develops when lipids (fats) enter the bronchial tree through aspiration or inhalation.
Signs and symptoms
Lipoid pneumonia can present as a fore ...
is another rare cause due to lipids
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins Vitamin A, A, Vitamin D, D, Vitamin E, E and Vitamin K, K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The fu ...
entering the lung. These lipids can either be inhaled or spread to the lungs from elsewhere in the body.
Mechanisms
 Pneumonia frequently starts as an
Pneumonia frequently starts as an upper respiratory tract infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat ...
that moves into the lower respiratory tract. It is a type of pneumonitis (lung inflammation). The normal flora of the upper airway give protection by competing with pathogens for nutrients. In the lower airways, reflexes of the glottis, actions of complement proteins and immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
s are important for protection. Micro aspiration of contaminated secretions can infect the lower airways and cause pneumonia. The progress of pneumonia is determined by the virulence of the organism; the amount of organism required to start an infection; and the body's immune response against the infection.
Bacterial
Most bacteria enter the lungs via small aspirations of organisms residing in the throat or nose. Half of normal people have these small aspirations during sleep. While the throat always contains bacteria, potentially infectious ones reside there only at certain times and under certain conditions. A minority of types of bacteria such as ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
'' and ''Legionella pneumophila'' reach the lungs via contaminated airborne droplets. Bacteria can also spread via the blood. Once in the lungs, bacteria may invade the spaces between cells and between alveoli, where the macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s and neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in differe ...
s (defensive white blood cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
s) attempt to inactivate the bacteria. The neutrophils also release cytokines, causing a general activation of the immune system. This leads to the fever, chills, and fatigue common in bacterial pneumonia. The neutrophils, bacteria, and fluid from surrounding blood vessels fill the alveoli, resulting in the consolidation seen on chest X-ray.
Viral
Viruses may reach the lung by a number of different routes. Respiratory syncytial virus is typically contracted when people touch contaminated objects and then touch their eyes or nose.Murray and Nadel (2010). Chapter 31. Other viral infections occur when contaminated airborne droplets are inhaled through the nose or mouth. Once in the upper airway, the viruses may make their way into the lungs, where they invade the cells lining the airways, alveoli, orlung parenchyma
file:emphysema, bullous, subpleural and honeycomb fibrosis (4563270966).jpg, upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural Focal lung pneumatosis, bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal org ...
. Some viruses such as measles and herpes simplex may reach the lungs via the blood. The invasion of the lungs may lead to varying degrees of cell death. When the immune system responds to the infection, even more lung damage may occur. Primarily white blood cells, mainly mononuclear cell
In immunology, agranulocytes (also known as nongranulocytes or mononuclear leukocytes) are one of the two types of leukocytes (white blood cells), the other type being granulocytes. Agranular cells are noted by the absence of Granule (cell biol ...
s, generate the inflammation. As well as damaging the lungs, many viruses simultaneously affect other organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
and thus disrupt other body functions. Viruses also make the body more susceptible to bacterial infections; in this way, bacterial pneumonia can occur at the same time as viral pneumonia.
Diagnosis
Pneumonia is typically diagnosed based on a combination of physical signs and often achest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
. In recent years, however, the role of lung ultrasonography has gained prominence, with substantial evidence demonstrating that, in expert hands, it surpasses radiography in accuracy. In adults with normal vital signs and a normal lung examination, the diagnosis is unlikely. However, the underlying cause can be difficult to confirm, as there is no definitive test able to distinguish between bacterial and non-bacterial cause. The overall impression of a physician appears to be at least as good as decision rules for making or excluding the diagnosis.
Diagnosis in children
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
has defined pneumonia in children clinically based on either a cough or difficulty breathing and a rapid respiratory rate, chest indrawing, or a decreased level of consciousness. A rapid respiratory rate is defined as greater than 60 breaths per minute in children under 2 months old, greater than 50 breaths per minute in children 2 months to 1 year old, or greater than 40 breaths per minute in children 1 to 5 years old.
In children, low oxygen levels and lower chest indrawing are more sensitive than hearing chest crackles
Crackles are the clicking, rattling, or crackling noises that may be made by one or both lungs of a human or animal with a respiratory disease during inhalation, and occasionally during exhalation. They are usually heard only with a stethosco ...
with a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medicine, medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected t ...
or increased respiratory rate. Grunting and nasal flaring may be other useful signs in children less than five years old.
Lack of wheezing is an indicator of ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' in children with pneumonia, but as an indicator it is not accurate enough to decide whether or not macrolide
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. ...
treatment should be used. The presence of chest pain in children with pneumonia doubles the probability of ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae''.
Diagnosis in adults
In general, in adults, investigations are not needed in mild cases. There is a very low risk of pneumonia if allvital sign
Vital signs (also known as vitals) are a group of the four to six most crucial medical signs that indicate the status of the body's vital (life-sustaining) functions. These measurements are taken to help assess the general physical health of a ...
s and auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and resp ...
are normal. C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin ...
(CRP) may help support the diagnosis. For those with CRP less than 20 mg/L without convincing evidence of pneumonia, antibiotics are not recommended.
Procalcitonin may help determine the cause and support decisions about who should receive antibiotics. Antibiotics are encouraged if the procalcitonin level reaches 0.25 μg/L, strongly encouraged if it reaches 0.5 μg/L, and strongly discouraged if the level is below 0.10 μg/L. In people requiring hospitalization, pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring blood oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of art ...
, chest radiography and blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s – including a complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
, serum electrolytes, C-reactive protein level, and possibly liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial ...
– are recommended.
The diagnosis of influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss ...
can be made based on the signs and symptoms; however, confirmation of an influenza infection requires testing. Thus, treatment is frequently based on the presence of influenza in the community or a rapid influenza test.
Adults 65 years old or older, as well as cigarette smokers and people with ongoing medical conditions are at increased risk for pneumonia.
Physical exam
Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
may sometimes reveal low blood pressure, high heart rate, or low oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the g ...
. The respiratory rate may be faster than normal, and this may occur a day or two before other signs. Examination of the chest may be normal, but it may show decreased expansion on the affected side. Harsh breath sounds from the larger airways that are transmitted through the inflamed lung are termed bronchial
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts Atmosphere of Earth, air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the Carina of trachea, carina are the right main b ...
breathing and are heard on auscultation with a stethoscope. Crackles (rales) may be heard over the affected area during inspiration. Percussion
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a percussion mallet, beater including attached or enclosed beaters or Rattle (percussion beater), rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or ...
may be dulled over the affected lung, and increased, rather than decreased, vocal resonance distinguishes pneumonia from a pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilog ...
.
Imaging
 A
A chest radiograph
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
L ...
is frequently used in diagnosis. In people with mild disease, imaging is needed only in those with potential complications, those not having improved with treatment, or those in which the cause is uncertain. If a person is sufficiently sick to require hospitalization, a chest radiograph is recommended. Findings do not always match the severity of disease and do not reliably separate between bacterial and viral infection.
X-ray presentations of pneumonia may be classified as lobar pneumonia, bronchopneumonia
Bronchopneumonia is a subtype of pneumonia. It is the acute inflammation of the Bronchus, bronchi, accompanied by inflamed patches in the nearby lobules of the lungs. citing: Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fifth Edition, Copyright 2014
...
, lobular pneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns Pulmonar ...
. Bacterial, community-acquired pneumonia classically show lung consolidation of one lung segmental lobe, which is known as lobar pneumonia. However, findings may vary, and other patterns are common in other types of pneumonia. Aspiration pneumonia may present with bilateral opacities primarily in the bases of the lungs and on the right side. Radiographs of viral pneumonia may appear normal, appear hyper-inflated, have bilateral patchy areas, or present similar to bacterial pneumonia with lobar consolidation. Radiologic findings may not be present in the early stages of the disease, especially in the presence of dehydration, or may be difficult to interpret in the obese
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when ...
or those with a history of lung disease. Complications such as pleural effusion may also be found on chest radiographs. Laterolateral chest radiographs can increase the diagnostic accuracy of lung consolidation and pleural effusion.
A CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
can give additional information in indeterminate cases and provide more details in those with an unclear chest radiograph (for example occult pneumonia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). They can be used to exclude pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
and fungal pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is an infection of the lungs by fungi. It can be caused by either endemic or opportunistic fungi or a combination of both. Case mortality in fungal pneumonias can be as high as 90% in immunocompromised patients, though immunoc ...
, and detect lung abscesses in those who are not responding to treatments. However, CT scans are more expensive, have a higher dose of radiation, and cannot be done at bedside.
Lung ultrasound may also be useful in helping to make the diagnosis. Ultrasound is radiation free and can be done at bedside. However, ultrasound requires specific skills to operate the machine and interpret the findings. It may be more accurate than chest X-ray.
Microbiology
In people managed in the community, determining the causative agent is not cost-effective and typically does not alter management. For people who do not respond to treatment,sputum culture
A sputum culture is a test to detect and identify bacteria or fungi that infect the lungs or breathing passages. Sputum is a thick fluid produced in the lungs and in the adjacent airways. Normally, fresh morning sample is preferred for the bac ...
should be considered, and culture for ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' should be carried out in persons with a chronic productive cough. Microbiological evaluation is also indicated in severe pneumonia, alcoholism, asplenia, immunosuppression, HIV infection, and those being empirically treated for MRSA of pseudomonas. Although positive blood culture
A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or ...
and pleural fluid
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable ...
culture definitively establish the diagnosis of the type of micro-organism involved, a positive sputum culture has to be interpreted with care for the possibility of colonisation
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
of respiratory tract. Testing for other specific organisms may be recommended during outbreaks, for public health reasons. In those hospitalized for severe disease, both sputum and blood cultures
A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or ...
are recommended, as well as testing the urine for antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
s to ''Legionella'' and ''Streptococcus''. Viral infections, can be confirmed via detection of either the virus or its antigens with culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
or polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
(PCR), among other techniques. ''Mycoplasma'', ''Legionella'', ''Streptococcus'', and ''Chlamydia'' can also be detected using PCR techniques on bronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), also known as bronchoalveolar washing, is a diagnostic method of the lower respiratory system in which a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into an appropriate airway in the lungs, with a measured amou ...
and nasopharyngeal swab
A nasopharyngeal swab is a device used for collecting a sample of Mucus#Respiratory system, nasal secretions from the back of the nose and throat. The sample is then analyzed for the presence of organisms or other clinical markers for disease. Th ...
. The causative agent is determined in only 15% of cases with routine microbiological tests.
Classification
''Pneumonitis'' refers to lung inflammation; pneumonia refers to pneumonitis, usually due to infection but sometimes non-infectious, that has the additional feature of pulmonary consolidation. Pneumonia is most commonly classified by where or how it was acquired: community-acquired, aspiration, healthcare-associated, hospital-acquired, and ventilator-associated pneumonia. It may also be classified by the area of the lung affected: lobar, bronchial pneumonia andacute interstitial pneumonia
Acute interstitial pneumonitis (also known as acute interstitial pneumonia) is a rare, severe lung disease that usually affects otherwise healthy individuals. There is no known cause or cure.
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is often categorized a ...
; or by the causative organism. Pneumonia in children may additionally be classified based on signs and symptoms as non-severe, severe, or very severe.
The setting in which pneumonia develops is important to treatment, as it correlates to which pathogens are likely suspects, which mechanisms are likely, which antibiotics are likely to work or fail, and which complications can be expected based on the person's health status.
Community
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is acquired in the community, outside of health care facilities. Compared with healthcare-associated pneumonia, it is less likely to involve multidrug-resistant bacteria. Although the latter are no longer rare in CAP, they are still less likely. Prior stays in healthcare-related environments such as hospitals, nursing homes, or hemodialysis centers or a history of receiving domiciliary care can increase patients' risk for CAP caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria.Healthcare
Health care–associated pneumonia (HCAP) is an infection associated with recent exposure to the health care system, including hospitals, outpatient clinics,nursing home
A nursing home is a facility for the residential care of older people, senior citizens, or disabled people. Nursing homes may also be referred to as care homes, skilled nursing facilities (SNF), or long-term care facilities. Often, these terms ...
s, dialysis centers, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
treatment, or home care
Homecare (home care, in-home care, care at home), also known as domiciliary care, personal care, community care, or social care, is health care or supportive care provided in the individual home where the patient or client is living, generally focu ...
. HCAP is sometimes called MCAP (medical care–associated pneumonia).
People may become infected with pneumonia in a hospital; this is defined as pneumonia not present at the time of admission (symptoms must start at least 48 hours after admission). It is likely to involve hospital-acquired infection
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care, healthcare facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital sett ...
s, with higher risk of multidrug-resistant pathogens. People in a hospital often have other medical conditions, which may make them more susceptible to pathogens in the hospital.
Ventilator-associated pneumonia occurs in people breathing with the help of mechanical ventilation. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is specifically defined as pneumonia that arises more than 48 to 72 hours after endotracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently ...
.
Differential diagnosis
Several diseases can present with similar signs and symptoms to pneumonia, such as: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma,pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
, bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the bronchi, airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with sputum, mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, hemoptysis, co ...
, lung cancer, and pulmonary emboli
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathin ...
. Unlike pneumonia, asthma and COPD typically present with wheezing, pulmonary edema presents with an abnormal electrocardiogram, cancer and bronchiectasis present with a cough of longer duration, and pulmonary emboli present with acute onset sharp chest pain and shortness of breath. Mild pneumonia should be differentiated from upper respiratory tract infection (URTI). Severe pneumonia should be differentiated from acute heart failure. Pulmonary infiltrates that resolved after giving mechanical ventilation should point to heart failure and atelectasis
Atelectasis is the partial collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absence in gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli are deflated down to l ...
rather than pneumonia. For recurrent pneumonia, underlying lung cancer, metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
, tuberculosis, a foreign bodies, immunosuppression, and hypersensitivity should be suspected.
Prevention
Prevention includesvaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
, environmental measures, and appropriate treatment of other health problems. It is believed that, if appropriate preventive measures were instituted globally, mortality among children could be reduced by 400,000; and, if proper treatment were universally available, childhood deaths could be decreased by another 600,000.
Vaccination
Vaccination prevents against certain bacterial and viral pneumonias both in children and adults.Influenza vaccine
Influenza vaccines, colloquially known as flu shots or the flu jab, are vaccines that protect against infection by influenza viruses. New versions of the vaccines are developed twice a year, as the influenza virus rapidly changes. While their ...
s are modestly effective at preventing symptoms of influenza, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) recommends yearly influenza vaccination for every person 6 months and older. Immunizing health care workers decreases the risk of viral pneumonia among their patients.
Vaccinations against ''Haemophilus influenzae'' and ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' have good evidence to support their use. There is strong evidence for vaccinating children under the age of 2 against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is a pneumococcal vaccine made with the conjugate vaccine method and used to protect infants, young children, and adults against disease caused by the bacterium '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (pneumococcus). It c ...
). Vaccinating children against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' has led to a decreased rate of these infections in adults, because many adults acquire infections from children. A ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' vaccine is available for adults, and has been found to decrease the risk of invasive pneumococcal disease by 74%, but there is insufficient evidence to suggest using the pneumococcal vaccine to prevent pneumonia or death in the general adult population. The CDC recommends that young children and adults aged 50 or older receive the pneumococcal vaccine, as well as older children or younger adults who have an increased risk of getting pneumococcal disease. In October 2024, the CDC lowered the age for adult pneumococcal vaccination from 65 to 50 years old to give more adults the opportunity to protect themselves from pneumococcal disease at the age when risk of infection substantially increases. The pneumococcal vaccine has been shown to reduce the risk of community acquired pneumonia in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but does not reduce mortality or the risk of hospitalization for people with this condition. People with COPD are recommended by a number of guidelines to have a pneumococcal vaccination. Other vaccines for which there is support for a protective effect against pneumonia include pertussis
Whooping cough ( or ), also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable bacterial disease. Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with a runny nose, fever, and mild cough, bu ...
, varicella, and measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
.
Medications
When influenza outbreaks occur, medications such asamantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended because ...
or rimantadine
Rimantadine (INN, sold under the trade name Flumadine) is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can short ...
may help prevent the condition, but they are associated with side effects. Zanamivir or oseltamivir
Oseltamivir, sold under the brand name Tamiflu among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B, viruses that cause the flu. Many medical organizations recommend it in people who have complicati ...
decrease the chance that people who are exposed to the virus will develop symptoms; however, it is recommended that potential side effects are taken into account.
Other
Smoking cessation
Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is Addiction, addictive and can cause Substance dependence, dependence. As a resu ...
and reducing indoor air pollution
Indoor air quality (IAQ) is the air quality within buildings and structures. Poor indoor air quality due to indoor air pollution is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. It has also been linked to sick build ...
, such as that from cooking indoors with wood, crop residues or dung, are both recommended. Smoking appears to be the single biggest risk factor for pneumococcal pneumonia
Pneumococcal pneumonia is a type of bacterial pneumonia that is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). It is the most common bacterial pneumonia found in adults, the most common type of community-acquired pneumonia, and one of the co ...
in otherwise-healthy adults. Hand hygiene and coughing into one's sleeve may also be effective preventative measures. Wearing surgical masks by the sick may also prevent illness.
Appropriately treating underlying illnesses (such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, and malnutrition) can decrease the risk of pneumonia. In children less than 6 months of age, exclusive breast feeding reduces both the risk and severity of disease. In people with HIV/AIDS and a CD4 count of less than 200 cells/uL the antibiotic trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacte ...
decreases the risk of ''Pneumocystis pneumonia'' and is also useful for prevention in those that are immunocompromised but do not have HIV.
Testing pregnant women for Group B Streptococcus and ''Chlamydia trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an ...
'', and administering antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
treatment, if needed, reduces rates of pneumonia in infants; preventive measures for HIV transmission from mother to child may also be efficient. Suctioning the mouth and throat of infants with meconium
Meconium is the earliest stool of a mammalian infant resulting from defecation. Unlike later feces, meconium is composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus: intestinal epithelial cells, lanugo, mucus, am ...
-stained amniotic fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products betwee ...
has not been found to reduce the rate of aspiration pneumonia and may cause potential harm, thus this practice is not recommended in the majority of situations. In the frail elderly good oral health care may lower the risk of aspiration pneumonia, even though there is no good evidence that one approach to mouth care is better than others in preventing nursing home acquired pneumonia. Zinc supplementation
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient body levels of zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a zinc blood level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in blood concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe ...
in children 2 months to five years old appears to reduce rates of pneumonia.
For people with low levels of vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
in their diet or blood, taking vitamin C supplements may be suggested to decrease the risk of pneumonia, although there is no strong evidence of benefit. There is insufficient evidence to recommend that the general population take vitamin C to prevent or treat pneumonia.
For adults and children in the hospital who require a respirator, there is no strong evidence indicating a difference between heat and moisture exchangers and heated humidifiers for preventing pneumonia. There is tentative evidence that laying flat on the back compared to semi-raised increases pneumonia risks in people who are intubated.
Management
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
by mouth, rest, simple analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in s ...
, and fluids usually suffice for complete resolution. Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
therapy for children aged 2 to 59 months with non‐severe pneumonia with wheeze may reduce of treatment failure by 20%, however results in little or no difference to clinical cure, in little or no difference to relapse, and treatment harms. However, those with other medical conditions, the elderly, or those with significant trouble breathing may require more advanced care. If the symptoms worsen, the pneumonia does not improve with home treatment, or complications occur, hospitalization may be required. Worldwide, approximately 7–13% of cases in children result in hospitalization, whereas in the developed world between 22 and 42% of adults with community-acquired pneumonia are admitted. The CURB-65 score is useful for determining the need for admission in adults. If the score is 0 or 1, people can typically be managed at home; if it is 2, a short hospital stay or close follow-up is needed; if it is 3–5, hospitalization is recommended. In children those with respiratory distress
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that c ...
or oxygen saturations of less than 90% should be hospitalized. The utility of chest physiotherapy in pneumonia has not yet been determined. Over-the-counter cough medicine has not been found to be effective, nor has the use of zinc supplementation in children. There is insufficient evidence for mucolytics. There is no strong evidence to recommend that children who have non-measles related pneumonia take vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
supplements. Vitamin D, as of 2023, is of unclear benefit in children. Vitamin C administration in pneumonia needs further research, despite found lower mortality and reduced severity for most ill patient, although it can be given to patient of low plasma vitamin C because it is not expensive and low risk.
Pneumonia can cause severe illness in a number of ways, and pneumonia with evidence of organ dysfunction may require intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
An inten ...
admission for observation and specific treatment. The main impact is on the respiratory and the circulatory system. Respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
not responding to normal oxygen therapy may require heated humidified high-flow therapy
Heated humidified high-flow therapy, often simply called high flow therapy , is a medical treatment providing respiratory support by delivering a flow of oxygen of up to 60 liters per minute to a patient through a large-bore or high-flow nasal c ...
delivered through nasal cannulae, non-invasive ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alte ...
, or in severe cases mechanical ventilation through an endotracheal tube. Regarding circulatory problems as part of sepsis, evidence of poor blood flow or low blood pressure is initially treated with 30 mL/kg of crystalloid infused intravenously. In situations where fluids alone are ineffective, vasopressor medication may be required.
For adults with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin co ...
(ARDS) undergoing mechanical ventilation, there is a reduction in mortality when people lie on their front for at least 12 hours a day. However, this increases the risk of endotracheal tube obstruction and pressure sores.
Bacterial
Antibiotics improve outcomes in those with bacterial pneumonia. The first dose of antibiotics should be given as soon as possible. Increased use of antibiotics, however, may lead to the development of antimicrobial resistant strains of bacteria. Antibiotic choice depends initially on the characteristics of the person affected, such as age, underlying health, and the location the infection was acquired. Antibiotic use is also associated with side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, taste distortion, or headaches. In the UK, treatment before culture results withamoxicillin
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication belonging to the aminopenicillin class of the penicillin family. The drug is used to treat bacterial infections such as middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, odontogenic inf ...
is recommended as the first line for community-acquired pneumonia, with doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
or clarithromycin
Clarithromycin, sold under the brand name Biaxin among others, is an antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. This includes strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, '' H. pylori'' infection, and Lyme disease, among others. Clari ...
as alternatives. In North America, amoxicillin, doxycycline, and in some areas a macrolide (such as azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes otitis media, middle ear infections, strep throa ...
or erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used ...
) is the first-line outpatient treatment in adults. In children with mild or moderate symptoms, amoxicillin taken by mouth is the first line. The use of fluoroquinolones
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic molecule, bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-Quinolone, 4-quinolone. They are used in human and ve ...
in uncomplicated cases is discouraged due to concerns about side-effects and generating resistance in light of there being no greater benefit.
For those who require hospitalization and caught their pneumonia in the community the use of a β-lactam such as cephazolin plus a macrolide such as azithromycin is recommended. A fluoroquinolone
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well ...
may replace azithromycin but is less preferred. Antibiotics by mouth and by injection appear to be similarly effective in children with severe pneumonia.
The duration of treatment has traditionally been seven to ten days, but increasing evidence suggests that shorter courses (3–5 days) may be effective for certain types of pneumonia and may reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance. Research in children showed that a shorter, 3-day course of amoxicillin was as effective as a longer, 7-day course for treating pneumonia in this population. For pneumonia that is associated with a ventilator caused by non-fermenting Gram-negative bacilli (NF-GNB), a shorter course of antibiotics increases the risk that the pneumonia will return. Recommendations for hospital-acquired pneumonia include third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotic ...
, carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Si ...
s, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycoside
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer ...
s, and vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat certain bacterial infections. It is administered intravenously ( injection into a vein) to treat complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone an ...
. These antibiotics are often given intravenously
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
and used in combination. In those treated in hospital, more than 90% improve with the initial antibiotics. For people with ventilator-acquired pneumonia, the choice of antibiotic therapy will depend on the person's risk of being infected with a strain of bacteria that is multi-drug resistant. Once clinically stable, intravenous antibiotics should be switched to oral antibiotics. For those with '' Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) or ''Legionella'' infections, prolonged antibiotics may be beneficial.
The addition of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s to standard antibiotic treatment appears to improve outcomes, reducing death and morbidity for adults with severe community acquired pneumonia, and reducing death for adults and children with non-severe community acquired pneumonia. A 2017 review therefore recommended them in adults with severe community acquired pneumonia. A 2019 guideline however recommended against their general use, unless refractory shock was present. Side effects associated with the use of corticosteroids include high blood sugar. There is some evidence that adding corticosteroids to the standard PCP pneumonia treatment may be beneficial for people who are infected with HIV.
The use of granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) along with antibiotics does not appear to reduce mortality and routine use for treating pneumonia is not supported by evidence.
Viral
Neuraminidase inhibitors may be used to treatviral pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is a pneumonia caused by a virus. Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in one or both lungs. The pulmonary alveoli fill with fluid or pus making it difficult to breathe. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, ...
caused by influenza viruses (influenza A
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as c ...
and influenza B). No specific antiviral
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
medications are recommended for other types of community acquired viral pneumonias including SARS coronavirus
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1), previously known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illn ...
, adenovirus, hantavirus
''Orthohantavirus'' is a genus of viruses that includes all hantaviruses (family ''Hantaviridae'') that cause disease in humans. Orthohantaviruses, hereafter referred to as hantaviruses, are naturally found primarily in rodents. In general, each ...
, and parainfluenza virus. Influenza A may be treated with rimantadine or amantadine, while influenza A or B may be treated with oseltamivir, zanamivir or peramivir. These are of most benefit if they are started within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms. Many strains of H5N1
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which causes the disease avian influenza (often referred to as "bird flu"). It is enzootic (maintained in the population) in many bird populations, and also panzoo ...
influenza A, also known as avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
or "bird flu", have shown resistance to rimantadine and amantadine. The use of antibiotics in viral pneumonia is recommended by some experts, as it is impossible to rule out a complicating bacterial infection. The British Thoracic Society recommends that antibiotics be withheld in those with mild disease. The use of corticosteroids is controversial.
Aspiration
In general, aspiration pneumonitis is treated conservatively with antibiotics indicated only for aspiration pneumonia. The choice of antibiotic will depend on several factors, including the suspected causative organism and whether pneumonia was acquired in the community or developed in a hospital setting. Common options includeclindamycin
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (mi ...
, a combination of a beta-lactam antibiotic and metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl and Metrogyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vagino ...
, or an aminoglycoside.
Corticosteroids are sometimes used in aspiration pneumonia, but there is limited evidence to support their effectiveness.
Follow-up
The British Thoracic Society recommends that a follow-up chest radiograph be taken in people with persistent symptoms, smokers, and people older than 50. American guidelines vary, from generally recommending a follow-up chest radiograph to not mentioning any follow-up.Prognosis
With treatment, most types of bacterial pneumonia will stabilize in 3–6 days. It often takes a few weeks before most symptoms resolve. X-ray findings typically clear within four weeks and mortality is low (less than 1%). In the elderly or people with other lung problems, recovery may take more than 12 weeks. In persons requiring hospitalization, mortality may be as high as 10%, and in those requiring intensive care it may reach 30–50%. Pneumonia is the most commonhospital-acquired infection
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care, healthcare facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital sett ...
that causes death.Murray and Nadel (2010). Chapter 32. Before the advent of antibiotics, mortality was typically 30% in those that were hospitalized. However, for those whose lung condition deteriorates within 72 hours, the problem is usually due to sepsis. If pneumonia deteriorates after 72 hours, it could be due to nosocomial infection or excerbation of other underlying comorbidities. About 10% of those discharged from hospital are readmitted due to underlying co-morbidities such as heart, lung, or neurological disorders, or due to new onset of pneumonia.
Complications may occur in particular in the elderly and those with underlying health problems. This may include, among others: empyema, lung abscess, bronchiolitis obliterans
Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO), also known as obliterative bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis and popcorn lung, is a disease that results in obstruction of the smallest airways of the lungs (bronchioles) due to inflammation. Symptoms inclu ...
, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and worsening of underlying health problems.Cunha (2010). pp. 6–18.
Clinical prediction rules
Clinical prediction rules have been developed to more objectively predict outcomes of pneumonia. These rules are often used to decide whether to hospitalize the person. * CURB-65 score, which takes into account the severity of symptoms, any underlying diseases, and age *Pneumonia severity index
The pneumonia severity index (PSI) or PORT Score is a clinical prediction rule that medical practitioners can use to calculate the probability of morbidity and mortality among patients with community acquired pneumonia.
The PSI/PORT score is of ...
(or ''PSI Score'')
Pleural effusion, empyema, and abscess
 In pneumonia, a collection of fluid may form in the space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (
In pneumonia, a collection of fluid may form in the space that surrounds the lung. Occasionally, microorganisms will infect this fluid, causing an empyema. To distinguish an empyema from the more common simple parapneumonic effusion, the fluid may be collected with a needle (thoracentesis
Thoracentesis , also known as thoracocentesis (), pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, or needle decompression (often used term), is an invasive medical procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. ...
), and examined. If this shows evidence of empyema, complete drainage of the fluid is necessary, often requiring a drainage catheter. In severe cases of empyema, surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
may be needed. If the infected fluid is not drained, the infection may persist, because antibiotics do not penetrate well into the pleural cavity. If the fluid is sterile, it must be drained only if it is causing symptoms or remains unresolved.
In rare circumstances, bacteria in the lung will form a pocket of infected fluid called a lung abscess. Lung abscesses can usually be seen with a chest X-ray but frequently require a chest CT scan to confirm the diagnosis. Abscesses typically occur in aspiration pneumonia, and often contain several types of bacteria. Long-term antibiotics are usually adequate to treat a lung abscess, but sometimes the abscess must be drained by a surgeon or radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide treatment within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but tod ...
.
Respiratory and circulatory failure
Pneumonia can cause respiratory failure by triggering acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which results from a combination of infection and inflammatory response. The lungs quickly fill with fluid and become stiff. This stiffness, combined with severe difficulties extracting oxygen due to the alveolar fluid, may require long periods of mechanical ventilation for survival. Other causes of circulatory failure arehypoxemia
Hypoxemia (also spelled hypoxaemia) is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia is usually caused by pulmonary disease. Sometimes the concentration of oxygen in the ...
, inflammation, and increased coagulability.
Sepsis is a potential complication of pneumonia but usually occurs in people with poor immunity or hyposplenism. The organisms most commonly involved are ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Haemophilus influenzae'', and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae''. Other causes of the symptoms should be considered such as a myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
or a pulmonary embolism.Cunha (2010). pp. 250–51.
Epidemiology
developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
than in the developed world. Viral pneumonia accounts for about 200 million cases. In the United States, , pneumonia is the 8th leading cause of death.
Children
In 2008, pneumonia occurred in approximately 156 million children (151 million in the developing world and 5 million in the developed world). In 2010, it resulted in 1.3 million deaths, or 18% of all deaths in those under five years, of which 95% occurred in the developing world. Countries with the greatest burden of disease include India (43 million), China (21 million) and Pakistan (10 million). It is the leading cause of death among children inlow income countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreemen ...
. Many of these deaths occur in the newborn
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
period. The World Health Organization estimates that one in three newborn infant deaths is due to pneumonia. Approximately half of these deaths can be prevented, as they are caused by the bacteria for which an effective vaccine is available. The IDSA has recommended that children and infants with symptoms of CAP should be hospitalized so they have access to pediatric nursing care. In 2011, pneumonia was the most common reason for admission to the hospital after an emergency department visit in the U.S. for infants and children.
History
 Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by
Pneumonia has been a common disease throughout human history. The word is from Greek πνεύμων (pneúmōn) meaning "lung". The symptoms were described by Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
(–370 BC): "Peripneumonia, and pleuritic affections, are to be thus observed: If the fever be acute, and if there be pains on either side, or in both, and if expiration be if cough be present, and the sputa expectorated be of a blond or livid color, or likewise thin, frothy, and florid, or having any other character different from the common... When pneumonia is at its height, the case is beyond remedy if he is not purged, and it is bad if he has dyspnoea, and urine that is thin and acrid, and if sweats come out about the neck and head, for such sweats are bad, as proceeding from the suffocation, rales, and the violence of the disease which is obtaining the upper hand." However, Hippocrates referred to pneumonia as a disease "named by the ancients". He also reported the results of surgical drainage of empyemas. Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah schola ...
(1135–1204 AD) observed: "The basic symptoms that occur in pneumonia and that are never lacking are as follows: acute fever, sticking pleuritic
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other sy ...
pain in the side, short rapid breaths, serrated pulse
In medicine, the pulse refers to the rhythmic pulsations (expansion and contraction) of an artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be felt ( palpated) in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surfac ...
and cough."Maimonides, ''Fusul Musa'' ("''Pirkei Moshe''"). This clinical description is quite similar to those found in modern textbooks, and it reflected the extent of medical knowledge through the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
into the 19th century.
Edwin Klebs was the first to observe bacteria in the airways of persons having died of pneumonia in 1875. Initial work identifying the two common bacterial causes, ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' and ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', was performed by Carl Friedländer
Carl Friedländer (19 November 1847, Brieg (Brzeg), Silesia – 13 May 1887, Meran (Merano), County of Tyrol) was a German pathologist and microbiologist who helped discover the bacterial cause of pneumonia in 1882. He also first described thro ...
and Albert Fraenkel in 1882 and 1884, respectively. Friedländer's initial work introduced the Gram stain
Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes ...
, a fundamental laboratory test still used today to identify and categorize bacteria. Christian Gram's paper describing the procedure in 1884 helped to differentiate the two bacteria, and showed that pneumonia could be caused by more than one microorganism. In 1887, Jaccond demonstrated pneumonia may be caused by opportunistic bacteria always present in the lung.
Sir William Osler
Sir William Osler, 1st Baronet, (; July 12, 1849 – December 29, 1919) was a Canadian physician and one of the "Big Four" founding professors of Johns Hopkins Hospital. Osler created the first Residency (medicine), residency program for speci ...
, known as "the father of modern medicine", appreciated the death and disability caused by pneumonia, describing it as the "captain of the men of death" in 1918, as it had overtaken tuberculosis as one of the leading causes of death at the time. This phrase was originally coined by John Bunyan
John Bunyan (; 1628 – 31 August 1688) was an English writer and preacher. He is best remembered as the author of the Christian allegory ''The Pilgrim's Progress'', which also became an influential literary model. In addition to ''The Pilgrim' ...
in reference to "consumption" (tuberculosis). Osler also described pneumonia as "the old man's friend" as death was often quick and painless when there were much slower and more painful ways to die.
Viral pneumonia was first described by Hobart Reimann in 1938. Reimann, Chairman of the Department of Medicine at Jefferson Medical College
Thomas Jefferson University is a private research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Established in its earliest form in 1824, the university officially combined with Philadelphia University in 2017. The university is ...
, had established the practice of routinely typing the pneumococcal organism in cases where pneumonia presented. Out of this work, the distinction between viral and bacterial strains was noticed.
Several developments in the 1900s improved the outcome for those with pneumonia. With the advent of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
and other antibiotics, modern surgical techniques, and intensive care in the 20th century, mortality from pneumonia, which had approached 30%, dropped precipitously in the developed world. Vaccination of infants against ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type B began in 1988 and led to a dramatic decline in cases shortly thereafter. Vaccination against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' in adults began in 1977, and in children in 2000, resulting in a similar decline.
Society and culture
Awareness
Due to the relatively low awareness of the disease, 12 November was declared in 2009 as the annual World Pneumonia Day, a day for concerned citizens and policy makers to take action against the disease.Costs
The global economic cost of community-acquired pneumonia has been estimated at $17 billion annually. Other estimates are considerably higher. In 2012 the estimated aggregate costs of treating pneumonia in the United States were $20 billion; the median cost of a single pneumonia-related hospitalization is over $15,000. According to data released by theCenters for Medicare and Medicaid Services
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is a federal agency within the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) that administers the Medicare program and works in partnership with state governments to administer ...
, average 2012 hospital charges for inpatient treatment of uncomplicated pneumonia in the U.S. were $24,549 and ranged as high as $124,000. The average cost of an emergency room consult for pneumonia was $943 and the average cost for medication was $66. Aggregate annual costs of treating pneumonia in Europe have been estimated at €10 billion.
References
Footnotes CitationsBibliography
* *External links
{{Authority control Articles containing video clips Coronavirus-associated diseases Infectious diseases Respiratory and cardiovascular disorders specific to the perinatal period Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate