|
Parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a Hematophagy, blood-feeding insect host (biology), host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue (often the liver) before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect (mosquitoes in majority cases), continuing the life cycle. ''Plasmodium'' is a member of the phylum Apicomplexa, a large group of parasitic eukaryotes. Within Apicomplexa, ''Plasmodium'' is in the order Haemosporida and family Plasmodiidae. Over 200 species of ''Plasmodium'' have been described, many of which have been subdivided into 14 subgenera based on parasite morphology and host range. Evolutionary relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleeping Sickness
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species '' Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two types, ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' (TbG) and ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' (TbR). TbG causes over 92% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas. Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis involves detecting the parasite in a blood smear or lymph node fluid. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease. Prevention of severe diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
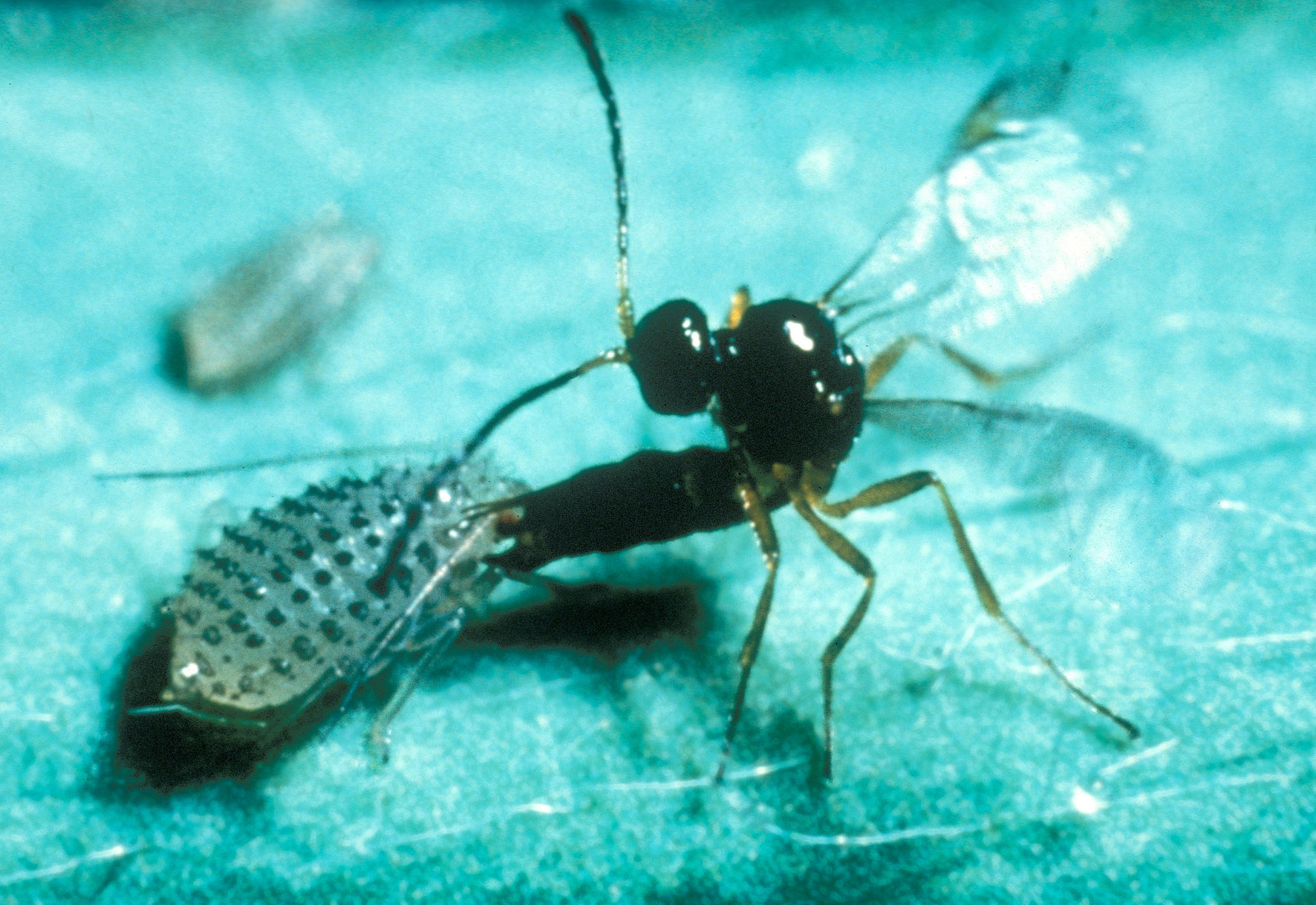
Parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation. Among parasitoids, strategies range from living inside the host (''endoparasitism''), allowing it to continue growing before emerging as an adult, to Paralysis, paralysing the host and living outside it (''ectoparasitism''). Hosts can include other parasitoids, resulting in hyperparasitism; in the case of oak galls, up to five levels of parasitism are possible. Some parasitoids Behavior-altering parasite, influence their host's behaviour in ways that favour the propagation of the parasitoid. Parasitoids are found in a variety of Taxon, taxa across the insect superorder Endopterygota, whose compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease Vector
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen such as a parasite or microbe, to another living organism. Agents regarded as vectors are mostly blood-sucking ( hematophagous) arthropods such as mosquitoes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected the stomach tissue of a mosquito. Arthropods Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects and ticks feed on blood, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways. The '' Anopheles'' mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses ( arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapeworms
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish-infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitic; many have complex life histories, including a stage in a definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, '' Diphyllobothrium'' has at least two intermediate hosts, a crustacean and then one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Castration
Parasitic castration is the strategy, by a parasite, of blocking reproduction by its host, completely or in part, to its own benefit. This is one of six major strategies within parasitism. Evolutionary strategy The parasitic castration strategy, which results in the reproductive death of the host, can be compared with the parasitoid strategy, which results in the host's death. Both parasitoids and parasitic castrators tend to be similar to their host in size, whereas most non-castrating parasites are orders of magnitude smaller than the host. In both strategies, an infected host is much less hospitable to new parasites than an uninfected one. A parasite that ends the reproductive life of its host theoretically liberates a significant fraction of the host's resources, which can now be used to benefit the parasite. The fraction of intact host energy spent on reproduction includes not just gonads and gametes but also secondary sexual characteristics, mate-seeking behavior, competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and specialized, highly elongated, piercing-sucking mouthparts. All mosquitoes drink nectar from flowers; females of some species have in addition adapted to drink blood. The group diversified during the Cretaceous period. Evolutionary biology, Evolutionary biologists view mosquitoes as micropredators, small animals that Parasitism, parasitise larger ones by drinking their blood without immediately killing them. Parasitology, Medical parasitologists view mosquitoes instead as Disease vector, vectors of disease, carrying protozoan parasites or bacterial or virus, viral pathogens from one Host (biology), host to another. The mosquito life cycle cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th-century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by changes in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebic Dysentery
Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba '' Entamoeba histolytica''. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ulcerations, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea. Complications can include inflammation and ulceration of the colon with tissue death or perforation, which may result in peritonitis. Anemia may develop due to prolonged gastric bleeding. Cysts of ''Entamoeba'' can survive for up to a month in soil or for up to 45 minutes under fingernails. Invasion of the intestinal lining results in bloody diarrhea. If the parasite reaches the bloodstream it can spread through the body, most frequently ending up in the liver where it can cause amoebic liver abscesses. Liver abscesses can occur without previous diarrhea. Diagnosis is made by stool examination using microscopy, but it can be difficult to distinguish ''E. histolytica'' fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
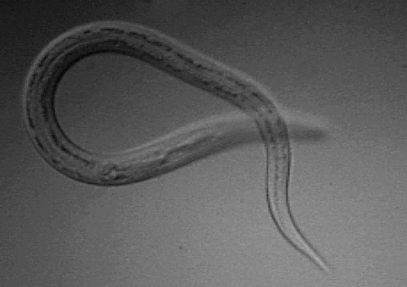
Hookworm
Hookworms are Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal, Hematophagy, blood-feeding, parasitic Nematode, roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera ''Ancylostoma'' and ''Necator (nematode), Necator''. In other animals the main parasites are species of ''Ancylostoma''. Hookworm is closely associated with poverty because it is most often found in impoverished areas, and its symptoms promote poverty through the educational and health effects it has on children. It is the leading cause of anemia and undernutrition in developing countries, while being one of the most commonly occurring diseases among poor people. Hookworm thrives in areas where rainfall is sufficient and keeps the soil from drying out, and where temperatures are higher, making r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |