Pre-Norman Invasion Irish Celtic Kinship Groups on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Irish clans are traditional
 O'Rahilly's version of history has been questioned by archaeologists and historians who have played down the role of the Cruthin as invaders, including by
O'Rahilly's version of history has been questioned by archaeologists and historians who have played down the role of the Cruthin as invaders, including by
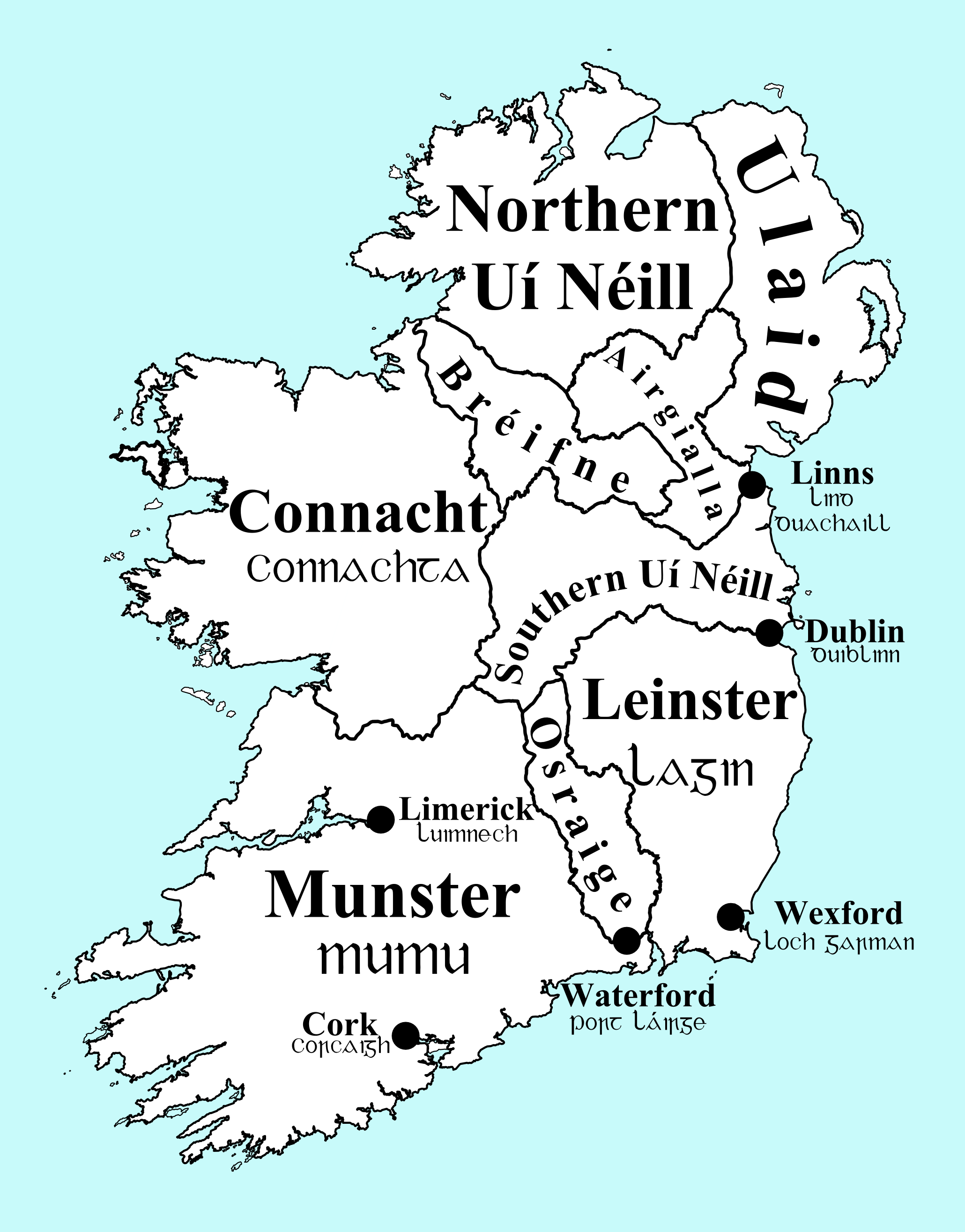
 Within the ''Gaeil'' there was distinction between the tribes of the south from those of the north, and also from those of the west. The tribes in the south called themselves the Eoghanacht and in about the year 400 AD they established at
Within the ''Gaeil'' there was distinction between the tribes of the south from those of the north, and also from those of the west. The tribes in the south called themselves the Eoghanacht and in about the year 400 AD they established at
kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
groups sharing a common surname and heritage and existing in a lineage-based society, originating prior to the 17th century. A clan (or in Irish, plural ) included the chief and his patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritanc ...
relatives; however, Irish clans also included unrelated clients of the chief. These unrelated clients and their agnatic descendants were ineligible to be elected chief, but nonetheless assumed the name of the leading lineage as a show of allegiance.
Beginning in the 8th century, various genealogical collections were compiled purporting to trace the ancestry of these clans. Among them are genealogies in Rawlinson B 502
Oxford, Bodleian Library, Rawlinson B 502 is a medieval Irish manuscript which currently resides in the Bodleian Library, Oxford. It ranks as one of the three major surviving Irish manuscripts to have been produced in pre-Norman Ireland, the t ...
, the Book of Ballymote
The ''Book of Ballymote'' (, RIA MS 23 P 12, 275 foll.), was written in 1390 or 1391 in or near the town of Ballymote, now in County Sligo, but then in the tuath of Corann.
According to David Sellar who was the Lord Lyon King of Arms in ...
, the Book of Lecan
The ''Great Book of Lecan'' or simply ''Book of Lecan'' () ( RIA, 23 P 2) is a late-medieval Irish manuscript written between 1397 and 1418 in Castle Forbes, Lecan (Lackan, Leckan; Irish ), in the territory of Tír Fhíacrach, near moder ...
, the ''Leabhar Mór na nGenealach'' compiled by Dubhaltach MacFhirbisigh, and the Ó Cléirigh Book of Genealogies
The O'Clery Book of Genealogies, also known as Royal Irish Academy Ms. 23 D 17, was written by Cú Choigcríche Ó Cléirigh, one of the Four Masters, who was transported in the 1650s to Ballyacroy, County Mayo, "under the guidance of Rory O'Donne ...
. In all of these cases, the genealogies listed state the agnatic descent of the chiefs and chieftains, and not necessarily every member of the clan. At least one genetic study has concluded that while these genealogies appear fairly accurate back to the Middle Ages, they are unreliable before the 7th century.
Definition of "clan"
The Irish word ''clann'' is a borrowing from the Latin ''planta'', meaning 'a plant, an offshoot, offspring, a single child or children, by extension race or descendants'. For instance, the O'Daly family were poetically known as ''Clann Dalaigh'', from a remote ancestor called Dalach. ''Clann'' was used in the later Middle Ages to provide a plural for surnames beginning with ''Mac'' meaning 'son of'. For example, "Clann Cárthaigh" meant the men of the MacCarthy family and "Clann Suibhne
Clan Sweeney is an Irish clan of Scotland, Scottish origin. The Mac Suibhne family did not permanently settle in Ireland before the beginning of the 14th century, when they became Gallowglass soldiers for the O'Donnell dynasty, Ua Domnaill dyn ...
" meant the men of the MacSweeny family. ''Clann'' was also used to denote a subgroup within a wider surname, the descendants of a recent common ancestor, such as the ''Clann Aodha Buidhe'' or the ''O'Neills
O'Neills Irish International Sports Company Ltd. is an Irish sporting goods manufacturer established in 1918. It is the largest manufacturer of sportswear in Ireland, with production plants located in Dublin and Strabane.
O'Neills has a long r ...
'' of Clandeboy, whose ancestor was Aodh Buidhe who died in 1298. Such a "clan", if sufficiently closely related, could have common interests in landownership, but any political power wielded by their chief was territorially based.
From ancient times, Irish society was organised around traditional kinship groups or clans. These clans traced their origins to larger pre-surname population groupings or clans such as Uí Briúin
The Uí Briúin were a royal dynasty of Connacht. Their eponymous apical ancestor was Brión, son of Eochaid Mugmedon and Mongfind, and an elder half brother of Niall of the Nine Hostages. They formed part of the Connachta, along with th ...
in Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, C ...
, Eóganachta
The Eóganachta (Modern , ) were an Irish dynasty centred on Rock of Cashel, Cashel which dominated southern Ireland (namely the Kingdom of Munster) from the 6/7th to the 10th centuries, and following that, in a restricted form, the Kingdom of De ...
and Dál gCais
The Dalcassians ( ) are a Gaels, Gaelic Irish clan, generally accepted by contemporary scholarship as being a branch of the Déisi Muman, that became very powerful in Ireland during the 10th century. Their genealogies claimed descent from Tál ...
in Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
, Uí Néill
The Uí Néill (; meaning "descendants of Niall") are Irish dynasties that claim descent from Niall Noígíallach (Niall of the Nine Hostages), a historical King of Tara who is believed to have died around c. 405. They are generally divided ...
in Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
, and Fir Domnann
The Fir Domnann were a people named in Irish legendary history.
The name ''Fir Domnann'' is based on the root ''dumno''-, which means both 'deep' and 'the world'. The suffix -''on''- often occurs in Gaulish and British divine names. The tribal n ...
in Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
. Within these larger groupings there tended to be one ''sept
A sept () is a division of a family, especially of a Scottish or Irish family. The term is used both in Scotland and in Ireland, where it may be translated as Irish , meaning "progeny" or "seed", and may indicate the descendants of a person ...
'' (division) who through war and politics became more powerful than others for a period of time and the leaders of some were accorded the status of royalty
Royalty may refer to:
* the mystique/prestige bestowed upon monarchs
** one or more monarchs, such as kings, queens, emperors, empresses, princes, princesses, etc.
*** royal family, the immediate family of a king or queen-regnant, and sometimes h ...
in Gaelic Ireland. Some of the more important septs to achieve this power were O'Connor O'Connor or O'Conor may refer to:
People
* O'Connor or O'Conor, an Irish clan
* O'Connor Sligo, a royal dynasty ruling the northern part of the Kingdom of Connacht
* O'Connor (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Places
* Burdett ...
in Connacht, MacCarthy McCarthy (also spelled MacCarthy or McCarty) may refer to:
* MacCarthy dynasty, a Gaelic Irish clan
* McCarthy, Alaska, United States
* McCarty, Missouri, United States
* McCarthy Road, a road in Alaska
* McCarthy (band), an indie pop band
* Châte ...
of Desmond and O'Brien of Thomond in Munster, Ó Neill of Clandeboy in Ulster, and MacMorrough Kavanagh in Leinster.
The largely symbolic role of High king of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and was later sometimes assigned anachronously or to leg ...
tended to rotate among the leaders of these royal clans. The larger or more important clans were led by a or chief who had the status of royalty and the smaller and more dependent clans were led by chieftains. Under Brehon law
Early Irish law, also called Brehon law (from the old Irish word breithim meaning judge), comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norman invasion of 1169, but underwe ...
, the leaders of Irish clans were appointed by their kinsmen as custodians of the clan and were responsible for maintaining and protecting their clan and its property. The clan system formed the basis of society up to the 17th century.
Origins
The O'Rahilly doctrine
According to T. F. O'Rahilly, in his works ''Goides and Their Predecessors'' and later ''Early Irish History'', there were a total of four waves of Celtic invasions of the British Isles and that the first three of these were pre-Gaelic.Brady, Ciaran; O'Dowd, Mary; Walter, Brian (1989). pp. 22 and 26Dillon, Myles; Chadwick, Nora (2000). p. 5 According to O'Rahilly, these were people who had largely remained unconquered by theRomans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
whose territory was mostly restricted to the broad plains of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. A larger part of England remained out of the control of the West Germanic people who invaded after the imperial collapse of Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.
Julius Caes ...
and who founded the English nation.
O'Rahilly's version of the origins of the Irish, as supported by C. Thomas Cairney and John Grenham is as follows: The first of the Celtic invaders of Ireland were known as the Cruthin
The Cruthin (; or ; ) were a people of early medieval Ireland. Their heartland was in Ulster and included parts of the present-day counties of Antrim, Down and Londonderry. They are also said to have lived in parts of Leinster and Connacht ...
who arrived between 800 and 500 BC.
The second wave of Celts to come to Ireland were known as the Erainn
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this se ...
and this is supposedly where the Gaelic name for Ireland, Erin
Erin is a personal name taken from the Hiberno-English word for Ireland, originating from the Irish word ''"Éirinn"''. "Éirinn" is the dative case of the Irish word for Ireland, "Éire", genitive "Éireann", the dative being used in preposi ...
, originated from. These people arrived between 500 and 100 BC. They came from the area which is today known as Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
and had superior iron weaponry, and thus eventually reduced the Irish Cruthin to tributary status. The third wave of Celtic settlement in Ireland came from Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by som ...
during the first century BC and this was probably because of pressure from the Romans on the south of Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
. These people were known as the Dumnonii
The Dumnonii or Dumnones were a Britons (historical), British List of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes, tribe who inhabited Dumnonia, the area now known as Cornwall and Devon (and some areas of present-day Dorset and Somerset) in the further pa ...
and gave their name to Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
in England. Their most powerful branch in Ireland was the Laigin
The Laigin, modern spelling Laighin (), were a Gaelic population group of early Ireland. They gave their name to the Kingdom of Leinster, which in the medieval era was known in Irish as ''Cóiced Laigen'', meaning "Fifth/province of the Leinste ...
who gave their name to Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
. A branch of the Irish group of the Dumnonii settled just to the south of Dumbarton
Dumbarton (; , or ; or , meaning 'fort of the Britons (historical), Britons') is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven, Dunbartonshire, River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. ...
in Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
and were the ancestors of the Strathclyde-Briton
Strathclyde (, "valley of the Clyde"), also known as Cumbria, was a Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland and North West England, a region the Welsh tribes referred ...
s.
The fourth and last major Celtic settlements in Ireland took place around 50 BC. This was directly because of Roman attempts to dominate the Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
of Continental Europe. This included, among others, a group known as the ''Feni'' who came to Ireland directly from the Continent and according to tradition landed in south Kerry and the Boyne estuary. The earlier inhabitants of the country fiercely resisted the newcomers who were referred to as the '' Gaeil'' because they spoke the Gaelic language
The Goidelic ( ) or Gaelic languages (; ; ) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically formed a dialect continuum stretching from Ireland through the Isle o ...
. The power and influence of the ''Gaeils'' gradually spread over the next three centuries, northwards, from Kerry into Tipperary and Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. W ...
, as well as to the west into Galway
Galway ( ; , ) is a City status in Ireland, city in (and the county town of) County Galway. It lies on the River Corrib between Lough Corrib and Galway Bay. It is the most populous settlement in the province of Connacht, the List of settleme ...
and Roscommon
Roscommon (; ; ) is the county town and the largest town in County Roscommon in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is roughly in the centre of Ireland, near the meeting of the N60 road (Ireland), N60, N61 road (Ireland), N61 and N63 road (Irelan ...
. By the 5th century they were dominant in most of Ireland and had established dynasties and tribal groups. These groups determined the Irish politics and culture until the Norman invasion of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land in Ireland over which the monarchs of England then claimed sovereignty. The Anglo-Normans ...
which took place during the late 12th century.Grenham, John (1993). pp. 18-19
Modern opinion
 O'Rahilly's version of history has been questioned by archaeologists and historians who have played down the role of the Cruthin as invaders, including by
O'Rahilly's version of history has been questioned by archaeologists and historians who have played down the role of the Cruthin as invaders, including by Ian Adamson
Ian Adamson OBE (28 June 1944 – 9 January 2019) was an Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) politician and paediatrician, who was the Lord Mayor of Belfast from 1996 to 1997, having been Deputy Lord Mayor from 1994 to 1995.
He additionally served as ...
.Brady, Ciaran; O'Dowd, Mary; Walter, Brian (1989). pp. 22 and 26. Quoting: Adamson, Ian (1974). ''Cruthin: The Ancient Kindred''. Newtownards. p. 12 O'Rahilly's history has been entirely unaccepted by some historians including Francis John Byrne
Francis John Byrne (1934 – 30 December 2017) was an Irish historian.
Born in Shanghai where his father, a Dundalk man, captained a ship on the Yellow River, Byrne was evacuated with his mother to Australia on the outbreak of World War II. A ...
.Brady, Ciaran; O'Dowd, Mary; Walter, Brian (1989). p. 22. Quoting: Byrne. F. J. (1965). ''The Ireland of Saint Columba''. Historical Studies, 5, p. 38 According to Myles Dillon
Myles Patrick Dillon (11 April 190018 June 1972) was an Irish scholar whose primary interests were comparative philology, Celtic studies, and Sanskrit.
Early life
Myles Dillon was born in Dublin on 11 April 1900, one of six children of John a ...
and Nora K. Chadwick
Nora Kershaw Chadwick CBE FSA FBA (28 January 1891 – 24 April 1972) was an English philologist who specialised in Anglo-Saxon, Celtic and Old Norse studies.
Early life and education
Nora Kershaw was born in Lancashire in 1891, the first da ...
, while O'Rahilly's version of history has been accepted by some scholars and dismissed by others, it is an entirely traditional history that he had sourced from ''Lebor Gabála Érenn
''Lebor Gabála Érenn'' (literally "The Book of Ireland's Taking"; Modern Irish spelling: ''Leabhar Gabhála Éireann'', known in English as ''The Book of Invasions'') is a collection of poems and prose narratives in the Irish language inten ...
'' which was a historic manuscript written in the 11th century, also known as the ''Book of the Invasions of Ireland'', and not historic facts based on contemporary evidence.Dillon, Myles; Chadwick, Nora (2000). pp. 5-6 J. P. Mallory
James Patrick Mallory (born October 25, 1945) is an American archaeologist and Indo-Europeanist. Mallory is an emeritus professor at Queen's University, Belfast; a member of the Royal Irish Academy, and the former editor of the '' Journal of ...
stated that O'Rahilly has argued that this manuscript showed that the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
people of Ireland had seen a series of invasions from whom various dynasties and families might have traced their origins to.
According to Mallory, Ireland may have been inhabited by Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
(Old Stone Age) hunters, but that the evidence for this is only a few pieces of flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
. The first actual evidence of human residence in Ireland dates to around 8000 BC. Evidence of the first Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
farmers in Ireland dates to around 4000 BC. There is little evidence of a warrior elite in Ireland before 1500 BC and evidence for this appears during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
where everyone of a wealthy class had weaponry. The Irish language first appeared from between 700/600 BC and 400 AD during the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
. During this time, the Irish people came into contact with Roman traders.
According to the writers of ''Ulster: An Illustrated History'', there is evidence for the Ulaid
(Old Irish, ) or (Irish language, Modern Irish, ) was a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic Provinces of Ireland, over-kingdom in north-eastern Ireland during the Middle Ages made up of a confederation of dynastic groups. Alternative names include , which ...
who are referred to as the Erainn
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this se ...
by some genealogists which is also the name given on Ptolemy's map of Ireland
Ptolemy's map of Ireland is a part of his "first European map" (depicting the British Isles) in the series of maps included in his ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which he compiled in the second century AD in Roman Egypt and which is the oldes ...
which dates from the second century AD for the Iverni
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this se ...
who lived in County Cork
County Cork () is the largest and the southernmost Counties of Ireland, county of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, named after the city of Cork (city), Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster ...
, as well as being the origin of the name for Ireland. The centre of the Ulaid's land was in the Diocese of Down. The main population group of the Ulaid was the Cruthin whose territory was in the Diocese of Connor and Dromore. There is also evidence for the Loígis
Loígis () is the name of an Irish tribe, as it is called by contemporary scholars. Formerly, scholars generally called the tribe ''Laoighis'' or ''Laeighis'' in Irish, ''Lagisia'' in Latin, and ''Leix'' in English. Loígis is also the name of the ...
in Leinster and the Cíarraige
The Ciarraige were a population-group recorded in the early historic era in Ireland.
Origins
The word Ciarraige means ''the people of Ciar''. Ciar was the illegitimate son of Fergus, the King of Ulster. After being banished from the Court of ...
in Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
who also belong to this group and it is possible that their ancestors in Ireland were pre-Celtic.Brady, Ciaran; O'Dowd, Mary; Walter, Brian (1989). p. 27 It is also possible to identify from Ptolemy's map the Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North ...
of County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, County Antrim, Antrim, ) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, located within the historic Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the c ...
who later founded a powerful kingdom in Argyll
Argyll (; archaically Argyle; , ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a Shires of Scotland, historic county and registration county of western Scotland. The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975 and most of the area ...
, Scotland. The 11th century ''Lebor Gabála Érenn'' or ''Book of the Invasions of Ireland'', describes a series of failed invasions of Ireland before settlement in the 8th century. However, by the 8th century battles in Ireland were not between the natives and invaders but between tribes and dynasties for control of different parts of the island. Donnchadh Ó Corráin
Donnchadh Ó Corráin (28 February 1942 – 25 October 2017) was an Republic of Ireland, Irish historian and professor emeritus of medieval history at University College Cork. He earned his BA in history and Irish from UCC, graduating in 1964.
...
put the evidence for the Irish naitional identity back to the 7th century emphasising the impact that Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
had on the people there.
In 1002, the Uí Néill
The Uí Néill (; meaning "descendants of Niall") are Irish dynasties that claim descent from Niall Noígíallach (Niall of the Nine Hostages), a historical King of Tara who is believed to have died around c. 405. They are generally divided ...
lost the high kingship of Ireland to the leader of the Dal gCais
The Dalcassians ( ) are a Gaels, Gaelic Irish clan, generally accepted by contemporary scholarship as being a branch of the Déisi Muman, that became very powerful in Ireland during the 10th century. Their genealogies claimed descent from Tál ...
or Dalcassians
The Dalcassians ( ) are a Gaelic Irish clan, generally accepted by contemporary scholarship as being a branch of the Déisi Muman, that became very powerful in Ireland during the 10th century. Their genealogies claimed descent from Tál Cas. ...
, Brian Boru. It was during the century of declining Uí Néill dominance that surnames first started being used in Ireland. This meant that Ireland was one of the first countries in Europe to start using surnames. Descendants of Niall of the Nine Hostages
Niall Noígíallach (; Old Irish "having nine hostages"), or Niall of the Nine Hostages, was a legendary, semi-historical Irish king who was the ancestor of the Uí Néill dynasties that dominated Ireland from the 6th to the 10th centuries. ...
, who was the ancestor of the Uí Néill dynasty, include people with the surnames O'Boyle
O'Boyle is a surname of Irish origin. It is anglicised from the Gaelic O'Boyle Donegal, Ó Baoighill/Ó Baoill.
The clan was founded by a County Donegal, Donegal chieftain, Aneisleis Ó Baoighill, the grandson of Baoghal. The derivation of the Ga ...
, O'Connor O'Connor or O'Conor may refer to:
People
* O'Connor or O'Conor, an Irish clan
* O'Connor Sligo, a royal dynasty ruling the northern part of the Kingdom of Connacht
* O'Connor (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Places
* Burdett ...
and O'Donnell
The O'Donnell dynasty ( or ''Ó Domhnaill,'' ''Ó Doṁnaill'' ''or Ua Domaill;'' meaning "descendant of Dónal") were the dominant Irish clan of the kingdom of Tyrconnell in Ulster in the north of medieval and early modern Ireland.
Naming ...
. From the Dal gCais or Dalcassians came the surnames O'Brien and Kennedy
Kennedy may refer to:
People
* Kennedy (surname), including any of several people with that surname
** Kennedy family, a prominent American political family that includes:
*** Joseph P. Kennedy Sr. (1888–1969), American businessman, investor, ...
.
Social structure
 Within the ''Gaeil'' there was distinction between the tribes of the south from those of the north, and also from those of the west. The tribes in the south called themselves the Eoghanacht and in about the year 400 AD they established at
Within the ''Gaeil'' there was distinction between the tribes of the south from those of the north, and also from those of the west. The tribes in the south called themselves the Eoghanacht and in about the year 400 AD they established at Cashel
Cashel (an Anglicised form of the Irish language word ''Caiseal'', meaning "stone fort") may refer to:
Places in Ireland
*Cashel, County Tipperary
**The Rock of Cashel, an ancient, hilltop fortress complex for which Cashel is named
** Archbishop ...
a dynasty which held power throughout most of southern Ireland from the 5th to 12th centuries. The Munster families of O'Sullivan O'Sullivan may refer to:
People
* O'Sullivan family, a gaelic Irish clan
* O'Sullivan (surname), a family name
* Sullivan (surname), a variation of the O'Sullivan family name
Places
* O'Sullivan Dam, Washington, United States
* O'Sullivan Army He ...
, MacCarthy McCarthy (also spelled MacCarthy or McCarty) may refer to:
* MacCarthy dynasty, a Gaelic Irish clan
* McCarthy, Alaska, United States
* McCarty, Missouri, United States
* McCarthy Road, a road in Alaska
* McCarthy (band), an indie pop band
* Châte ...
and O'Connell O'Connell may refer to:
People
*O'Connell (name), people with O'Connell as a last name or given name
Schools
* Bishop Denis J. O'Connell High School, a high school in Arlington, Virginia
Places
* Mount O'Connell National Park in Queensland ...
claim descent from the Eoghanacht.
In the midlands of Ireland, the ''Gaeil'' tribes were known as Connachta
The Connachta are a group of medieval Irish dynasty, dynasties who claimed descent from the legendary High King of Ireland, High King Conn of the Hundred Battles, Conn Cétchathach (Conn of the Hundred Battles). The modern western Provinces of ...
and their name continues in the modern province of Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, C ...
. The most important of the Connacta tribes was the Uí Néill who claimed descent from Niall of the Nine Hostages. Niall's brothers included Ailill
Ailill (Ailell, Oilioll) is a male name in Old Irish. It is a prominent name in Irish mythology, as for Ailill mac Máta, King of Connacht and husband of Queen Medb, on whom Shakespeare based the Fairy Queen Mab. Ailill was a popular given name in ...
, Brion and Fiachra
Fiachra is an Irish male given name. It may refer to:
Clerics
:
* Saint Fiacre of Breuil (died 670), missionary in France
* Fiachra mac Colmain (500-558) Bishop of Armagh
* Fiachra Ua Focarta (died 1006) abbot of Clonfert
* Fiachra Ó Cealla ...
who were founders of the important Connachta tribes of Ui Ailella, Uí Briúin
The Uí Briúin were a royal dynasty of Connacht. Their eponymous apical ancestor was Brión, son of Eochaid Mugmedon and Mongfind, and an elder half brother of Niall of the Nine Hostages. They formed part of the Connachta, along with th ...
and Uí Fiachrach
The Uí Fiachrach () were a royal dynasty who originated in, and whose descendants later ruled, the ''coicead'' or ''fifth'' of Connacht (a western province of Ireland) at different times from the mid-first millennium onwards. They claimed descen ...
.
Although the Eoghanacht and Uí Néill were the most powerful tribal groups in Ireland, there were others who were locally powerful including the Airgíalla
Airgíalla (; Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel, Latin: ''Ergallia'') was a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor kingdoms, all indepen ...
in the north-east where they controlled what is now the counties of Tyrone, Armagh
Armagh ( ; , , " Macha's height") is a city and the county town of County Armagh, in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Primates of All ...
, Fermanagh
Historically, Fermanagh (), as opposed to the modern County Fermanagh, was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland, associated geographically with present-day County Fermanagh. ''Fir Manach'' originally referred to a distinct kin group of alleged Laigin or ...
and Monaghan
Monaghan ( ; ) is the county town of County Monaghan, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It also provides the name of its Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish and Monaghan (barony), Monaghan barony.
The population of the town as of the 2022 cen ...
. There was also the Ulaid
(Old Irish, ) or (Irish language, Modern Irish, ) was a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic Provinces of Ireland, over-kingdom in north-eastern Ireland during the Middle Ages made up of a confederation of dynastic groups. Alternative names include , which ...
h who inhabited what is now the counties of Down
Down most often refers to:
* Down, the relative direction opposed to up
* Down (gridiron football), in North American/gridiron football, a period when one play takes place
* Down feather, a soft bird feather used in bedding and clothing
* Downland ...
and Antrim.
Within these large areas there were up to 150 small divisions known as túatha and the names of many of these are reflected today in the names of the Irish baronies that make up the modern counties. Each túath had a ruler or petty king
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into t ...
who owed allegiance to a more powerful king who was over-king of three or more túatha. This over-king would in turn be subordinate to the king of a province, usually either the Eoghanacht or Uí Néill.
The succession of kings or chiefs was governed by a system known as Tanistry
Tanistry is a Gaelic system for passing on titles and lands. In this system the Tanist (; ; ) is the office of heir-apparent, or second-in-command, among the (royal) Gaelic patrilineal dynasties of Ireland, Scotland and Mann, to succeed to ...
whereby after a chief had died, the new chief would be elected from all agnatic cousins descended from a patrilineal grandfather or great-grandfather. However, according to Eoin MacNeill
Eoin MacNeill (; born John McNeill; 15 May 1867 – 15 October 1945) was an Irish scholar, Irish language enthusiast, Gaelic revivalist, nationalist, and politician who served as Minister for Education from 1922 to 1925, Ceann Comhairle of D ...
, the system known as tanistry which also took place before the position of king or chief had become vacant is not found in records until the time of feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
in Ireland which was not until the time of the Normans, and it was preceded by the similar system known as ''Rigdomna'' but which took place only after the position of king or chief had become vacant. This theory however, was disputed by Gearóid Mac Niocaill
Gearóid Mac Niocaill (1932–2004) was one of the foremost twentieth-century scholars and interpreters of late medieval Irish tracts.
Life
Gearóid was born in Hull, England in 1932 to an Irish mother. His lifelong work in the Irish language b ...
who stated that there is no good evidence to support that the usage of the term ''Rigdomna'' in early medieval Ireland was any different to that of ''tanaise'' (Tanistry) in late medieval Ireland and that the two terms were synonymous with each other. Although Mac Niocaill did state that MacNeill was correct in identifying a number of cases where ''Rigdomna'' was limited to a four generation group in early medieval Ireland but in late medieval Ireland it was almost always the son, brother or nephew of the king.
Tribes of the Cruthin
As per O'Rahilly's doctrine, theCruthin
The Cruthin (; or ; ) were a people of early medieval Ireland. Their heartland was in Ulster and included parts of the present-day counties of Antrim, Down and Londonderry. They are also said to have lived in parts of Leinster and Connacht ...
were the first Celts to settle in Ireland between about 800 and 500 BC. In line with this, according to Cairney, from them descended the following Irish tribes. Although it is not possible to prove O'Rahilly's history of the four Celtic invasions of Ireland or that the Cruthin were the first of these invasions, or that the following Irish tribes descended from them, according to historian Sean Duffy, the existence of all three of the following Irish tribes in around the 7th century is supported by the literature of the time that came to Ireland with Christianity.Duffy (2011). pp. 14, 15, 18, 19: "This material, the most comprehensive to survive in any country of Dark Age
The ''Dark Ages'' is a term for the Early Middle Ages (–10th centuries), or occasionally the entire Middle Ages (–15th centuries), in Western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, which characterises it as marked by economic, int ...
Europe, enables us to reconstruct the political map of Ireland even at this early period".
*The Dal nAraide
Dal is a term in the Indian subcontinent for dried, split pulses.
Dal or DAL may also refer to:
Places
Cambodia
*Dal, Ke Chong
Finland
* Laakso, a neighbourhood of Helsinki
India
* Dal Lake, in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
* Dal L ...
. Irish surnames that came from this tribe include: O'Lynch, MacGenises, and MacCartan. The latter two later became tributaries of the O'Neills.
*The Soghain
The Soghain were a people of ancient Ireland. The 17th-century scholar Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh identified them as part of a larger group called the Cruithin. Mac Fhirbhisigh stated that the Cruithin included "the Dál Araidhi ál nAraidi ...
. Their chief was in later times known as O'Mannin or Mannions and this has sometimes become Manning.
*The Loígis
Loígis () is the name of an Irish tribe, as it is called by contemporary scholars. Formerly, scholars generally called the tribe ''Laoighis'' or ''Laeighis'' in Irish, ''Lagisia'' in Latin, and ''Leix'' in English. Loígis is also the name of the ...
. Irish surnames which came from this tribe include: O'Mores, O'Nolans, O'Dorans, O'Lawlors and O'Dowlings.
Tribes of the Erainn
As per O'Rahilly's doctrine, theErainn
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this se ...
were the second wave of Celts to settle in Ireland between about 500 and 100 BC. In line with this, according to Cairney, from them descended the following Irish tribes. Although it is not possible to prove O'Rahilly's history of the four Celtic invasions of Ireland or that the Erainn were the second of these invasions, or that the following Irish tribes descended from them, according to historian Sean Duffy, with the exception of the Clann Choinleagain, the existence of all of the following Irish tribes in around the 7th century is supported by the literature of the time that came to Ireland with Christianity.
*The Clann Choinleagain (or MacGifoyles). This was an ancient clan located in the territory of the O'Carrols of Ely.
*The Conmaicne
The Conmaicne (; ) were a people of early Ireland, perhaps related to the Laigin, who dispersed to various parts of Ireland. They settled in Connacht and Longford, giving their name to several Conmaicne territories. T. F. O'Rahilly's assertion ...
Rein. The chiefly families of this tribe were the MacRannalls, O'Cornyns, O'Farrell
O'Farrell is an anglicised form of the Old Irish patronym ''Ó Fearghail''. According to the historian C. Thomas Cairney, the O'Farrells were part of the Conmaicne Rein tribe in Ireland who came from the Erainn tribe who were the second wave of Cel ...
s, O'Moledys and O'Quins.
*The Corca Dhuibhne
The Dingle Peninsula (; anglicised as Corkaguiny or Corcaguiny, the name of the corresponding barony) is the northernmost of the major peninsulas in County Kerry. It ends beyond the town of Dingle at Dunmore Head, the westernmost point of ma ...
. The chiefly families of this tribe were the O'Connells and O'Shea
O'Shea is a surname and, less often, a given name. It is an anglicized form of the Irish patronymic name Ó Séaghdha or Ó Sé, originating in the Kingdom of Corcu Duibne in County Kerry. Historian C. Thomas Cairney states that the O'Sheas were ...
s.
*The Corca Laoghdne. The chiefly families of this tribe were the O'Coffey, O'Dinneen, O'Driscoll
O'Driscoll (and its derivative Driscoll) is an Irish surname. It is derived from the Gaelic ''Ó hEidirsceoil''. The O'Driscolls were rulers of the Dáirine sept of the Corcu Loígde until the early modern period; their ancestors were Kings ...
, O'Flynn
O'Flynn is a surname of Irish origin which may refer to:
* Andrew O'Flynn (born 1946), Irish retired hurler
* Audrey O'Flynn (born 1987), Ireland women's rugby sevens international
* Catherine O'Flynn (born 1970), British writer
* Críostóir Ó ...
, O'Hea
O'Hea may refer to:
* Charles O'Hea (1814-1903), Irish Catholic priest active in Australia
* John Fergus O'Hea (c. 1838–1922), Irish cartoonist
* Matt O'Hea, Australian basketball player
* Patrick O'Hea (1848-?), Irish politician
* Timothy ...
, O'Hennessy and O'Leary
O'Leary is an Irish surname derived from the Gaelic Ó Laoghaire, meaning "descendant of Laoghaire"—a personal name often interpreted as "keeper of the calves" or "calf herder." The name is historically associated with a prominent family lineage ...
.
*The Corco Modhruadh. The chiefly families of this tribe were the O'Connors of Corcomroe, MacCurtins, O'Loghlens or O'Loughlin
The surname
In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although ...
s, O'Davoren
The O'Davoren () family were a scholarly clan of Corcomroe, Thomond (modern-day County Clare), Ireland active since medieval times.
Famed for their sponsorship of schools and knowledge of history and Early Irish law, the Uí Dhuibh dá Bhoirea ...
s and the Corca Thine.
*The Dal Cairbre Arad. The chiefly family of this tribe was the O'Dwyers.
*The Dal gCais
The Dalcassians ( ) are a Gaels, Gaelic Irish clan, generally accepted by contemporary scholarship as being a branch of the Déisi Muman, that became very powerful in Ireland during the 10th century. Their genealogies claimed descent from Tál ...
(Dalcassians
The Dalcassians ( ) are a Gaelic Irish clan, generally accepted by contemporary scholarship as being a branch of the Déisi Muman, that became very powerful in Ireland during the 10th century. Their genealogies claimed descent from Tál Cas. ...
). The chiefly families of this tribe were the O'Brien dynasty
The O'Brien dynasty (; ; genitive ''Uí Bhriain'' ) was an Irish Clan and noble house of Munster, founded in the 10th century by Brian Boru of the Dál gCais (Dalcassians). After becoming King of Munster, through conquest he established hims ...
who were the main chiefs, but also the MacConsidine
Considine is an Irish surname anglicised from the Gaelic form Mac Consaidín meaning "son of Consaidín" being derived from a foreign Christian name; meaning "son of Constantine". According to historian C. Thomas Cairney, the MacConsidines were o ...
s, MacDonnells, MacLysaghts, MacMahons, O'Ahernes, O'Kennedy
The O'Kennedy family (Irish language, Irish: ''Ó Cinnéide''), sometimes Kennedy, were an Irish royal dynasty, a sept of the Dál gCais, founded in the Middle Ages who were Kings of Ormond. Their founder was the nephew of High King of Ireland ...
s, O'Shanahans, O'Duracks, MacGraths, O'Fogartys, O'Galvins, O'Gradys
The O'Grady family, also styled O'Grady of Kilballyowen, is one of Ireland's noble families and surviving Chiefs of the Name. Their title is ''The O'Grady'' in English and ''Ó Gráda'' in Irish.
Naming conventions
History
They belong to the ...
, O'Hanrahan
Hanrahan is an Irish surname shared by many Irish people and descendants of Irish emigrants. The name is most common in the area of the Shannon Estuary (counties Kerry, Limerick and Clare) in Ireland. Through emigration the name has become fairl ...
s, O'Hickeys, O'Mearas, O'Molonys, O'Moroneys, O'Hartagans, O'Lonergans, Creagh
Creagh is an Irish surname derived from the Gaelic ''Craobhach'', meaning "branch". The Creagh family was first found in County Clare, where they held a family seat from ancient times. According to historian C. Thomas Cairney, the Creaghs were on ...
s, O'Quins, MacNamara
MacNamara or McNamara ( Irish: ''Mac Con Mara'') is an Irish surname of a family of County Clare in Ireland. According to historian C. Thomas Cairney, the MacNamaras were one of the chiefly families of the Dal gCais or Dalcassians who were a tri ...
s, MacInerneys, O'Dea
O'Dea ( ; , formerly ), is an Irish surname derived from ', the name of a tenth-century clan chieftain. According to historian C. Thomas Cairney, the O'Deas were one of the chiefly families of the Dal gCais or Dalcassians who were a tribe of ...
s and O'Griffeys.
*The Déisi
The ''Déisi'' were a social class in Ireland between the ancient and early medieval period. The various peoples listed under the heading ''déis'' shared a similar status in Gaelic Ireland, and had little or no actual kinship, though they were ...
. Their chief was O'Phelan.
*The Partraige
The Partraige were a people of early historic Ireland.
Several attested branches were found in Ireland, including the following:
* Partraige Cera - located at the northern end of Lough Mask (Loch Mask) and the region of Lough Carra (Loch Corr ...
. Their chiefly family was the O'Malleys.
*The Uaithni
The Uaithni were a people of early Ireland, who in early medieval times lived in north-eastern County Limerick and the adjoining part of County Tipperary, and had traditions that they once lived west of the River Shannon. Their name derives from a ...
. Their chiefly family was the O'Heffermans.
*The Uí Bairrche
Uí Bairrche (, ) was an Irish kin-based group that originally held lands in the south of the ancient province of Leinster (or ''Cóiced Laigen'' "the Fifth of the Laigin"). Another south Leinster kin group associated with the Uí Bairrche were g ...
. Their chiefly families were the O'Tracys and MacGorman
MacGorman (Irish language, Irish: ''Mac Gormáin''), also known as McGorman, Gorman, or O'Gorman (Irish language, Irish: ''Ó Gormáin''), is an Irish people, Irish Gaels, Gaelic clan based most prominently in what is today County Clare. The pat ...
s.
*The Ui Fidgenti. Their chiefly families were the O'Cullanes, O'Kinneallys, O'Donovans and MacEnerys.
*The Ulaid
(Old Irish, ) or (Irish language, Modern Irish, ) was a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic Provinces of Ireland, over-kingdom in north-eastern Ireland during the Middle Ages made up of a confederation of dynastic groups. Alternative names include , which ...
. Their chiefly family was the MacDonlevy
Donlevy is an Irish surname derived from the Gaelic 'son/descendant of Donn Sléibhe'; a given name meaning 'Donn of the mountain', i.e. 'dark mountain'. The MacDonlevys were the hereditary rulers of Dál Fiatach and styled as the Kings of Ulaid, ...
s.
Tribes of the Dumnonii or Laigin
As per O'Rahilly's doctrine, theDumnonii
The Dumnonii or Dumnones were a Britons (historical), British List of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes, tribe who inhabited Dumnonia, the area now known as Cornwall and Devon (and some areas of present-day Dorset and Somerset) in the further pa ...
or Laigin
The Laigin, modern spelling Laighin (), were a Gaelic population group of early Ireland. They gave their name to the Kingdom of Leinster, which in the medieval era was known in Irish as ''Cóiced Laigen'', meaning "Fifth/province of the Leinste ...
were the third wave of Celts to settle in Ireland during the first century BC. In line with this, according to Cairney, from them descended the following Irish tribes. Although it is not possible to prove O'Rahilly's history of the four Celtic invasions of Ireland or that the Dumnonii or Laigin were the third of these invasions, or that the following Irish tribes descended from them, according to historian Sean Duffy, with the exception of the Ciarraighe Loch na nAirne and the Feara Cualann, the existence of all of the following Irish tribes in around the 7th century is supported by the literature of the time that came to Ireland with Christianity.
*The Cianacht. Their chiefly families were the O'Connors of Keenaght and the "race of Luighne
Muimne, Luigne and Laigne, sons of Érimón by his wife Odba, were, according to medieval Irish legends and historical traditions, joint High Kings of Ireland following the death of their father. They ruled for three years, until Muimne died of pl ...
" or "Lugh
Lugh or Lug (; ) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a saviour.Olmsted, Garrett. ''The Gods of the Celts and the I ...
" which in turn included the chiefly families of O'Hara and O'Gara.
*The Dealbhna Eathra and Delbhna Nuadat
The Delbhna Nuadat (Modern Irish: ''Dealbhna Nuad''; IPA:ˈdʲalˠəwnˠəˈn̪ˠuəd̪ˠ) were lords of a large section of what is now Athlone in County Roscommon, situated between the River Suck, Suca and River Shannon, Shannon rivers. A branch o ...
. Their chiefly families were the O'Hanlys, MaCoghlans and O'Conrahys.
*The Saithne. Their chiefly family was the O'Casey
O'Casey is a common variation of the Gaelic ''cathasaigh'', meaning ''vigilant'' or ''watchful'', with the added anglicized prefix '' O of the Gaelic ''Ó'', meaning ''grandson'' or ''descendant''. At least six different septs used this name, ...
s.
*The Ciarraighe Loch na nAirne. Their chiefly family was the O'Kierans.
*The Ciarraighe Luachra. Their chiefly family was the O'Connors of Kerry.
*The Eile. Their chiefly families were the O'Carrols of Ely, O'Mahers, O'Riordans, and O'Flanagans.
*The Ui Failghe. Their chiefly families were the O'Connors of Offaly, O'Mooneys, MacColgans, O'Hennesseys, O'Holohan Holohan (; feminine ') is a surname of Gaels, Irish Gaelic origin, from the Irish ' meaning "proud".
A version of the family crest depicts two white lions holding up a golden tower.
According to historian C. Thomas Cairney, the O'Holohans were on ...
s, O'Dempsey
Dempsey is a surname of Irish origin.
Background
Dempsey is an anglicised form of Ó Díomasaigh, 'descendant of Díomasach'; this personal name is the Irish adjective ''díomasach'' 'proud'. The family originated in the Kingdom of Uí Failghe ...
s, and O'Dunnes.
*The Feara Cualann. Their chiefly families were the O'Cullens and O'Mulryans.
*The Ui Ceinnsealaigh. Their chiefly families were the Kavanaghs, Kinsella
Kinsella is a surname of Irish language, Irish Gaelic origin, developed from the original form ''Cinnsealach'', meaning "proud". The Kinsella sept is native in part of the modern County Wexford in Leinster, a district formerly called the Kinsella ...
s, O'Murphys, and O'Morchoes.
*The Uí Dúnlainge
The Uí Dúnlainge, from the Old Irish "grandsons (or descendants) of Dúnlaing", were an Irish dynasty of Leinster kings who traced their descent from Dúnlaing mac Énda Niada, a fifth-century King of Leinster. He was said to be a cousin of ...
. Their chiefly families were the O'Byrnes and O'Tooles.
*The Ui Maine. Their chiefs were the O'Kellys but also included the O'Fahys, O'Horans, O'Sheehans, O'Donnellan
Donnellan is an Irish surname and refers to the clan name Ó Domhnalláin or O'Donnellan.
At least two unrelated families of the name existed in Gaelic Ireland. One in south-east Ulster, another in south-east Connacht in the kingdom of Ui Maine ...
s, O'Maddens, O'Concannons, O'Mullens, O'Malleys, O'Naghtens, and O'Houlihans.
*The Oirghialla (Airgíalla
Airgíalla (; Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel, Latin: ''Ergallia'') was a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor kingdoms, all indepen ...
or Oriel). Their chiefly families were the MacBradys, O'Boylan The O'Boylan ( Irish: ''Ó Baoigheallain'') or O'Boyland sept came from ''Airgíalla'', having their principal stronghold in the barony of Dartrey in County Monaghan. They soon spread to reach eastern County Fermanagh, across County Monaghan and so ...
s, O'Flanagans, O'Mulroonys or Moroneys, Maguires, MacKerans, MacAuleys, O'Cassidys, O'Corrigans, MacManuses, MacMahons, MacCann
McCann or MacCan is an Irish surname and Scottish surname. It is derived from the Gaelic ''Mac Cana'' meaning "son of Cana". The Irish given name ''Cana'' literally means "cub", specifically alluding to a "wolf cub" (i.e. a young warrior).Quinn, ...
s, O'Hanraghtys, O'Hanlon O'Hanlon is an Irish surname associated with the Ó hAnluain sept. As with other similar names, the added prefix "O'" means "son of" (Hanlon).
Notable people with that surname include:
* Ardal O'Hanlon (born 1965), Irish comedian
* Cressida O'Hanl ...
s, O'Lynns, MacEvoys, MacDonalds, MacDonells, MacAlisters, MacIans, MacSheeys, MacIntyres, MacDougals, and Conns.
Tribes of the Gaels or Gaeils
As per O'Rahilly's doctrine, theGaels
The Gaels ( ; ; ; ) are an Insular Celts, Insular Celtic ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. They are associated with the Goidelic languages, Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising ...
or ''Gaeils'' were the fourth and final wave of Celtic settlement in Ireland which took place during the first century BC. In line with this, according to Cairney, from them descended the following Irish tribes. Although it is not possible to prove O'Rahilly's history of the four Celtic invasions of Ireland or that the Gaels or Gaeils were the fourth of these invasions, or that the following Irish tribes descended from them, according to historian Sean Duffy, with the exception of the Clann Cholmáin
Clann Cholmáin is the dynasty descended from Colmán Már mac Diarmato, son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Part of the Southern Uí Néill — they were the kings of Mide (Meath) — they traced their descent to Niall Noígiallach and hi ...
, Cineal Laoghaire and the Muintear Tadhagain, the existence of all of the following Irish tribes in around the 7th century is supported by the literature of the time that came to Ireland with Christianity.
The North Gaels
*TheConnachta
The Connachta are a group of medieval Irish dynasty, dynasties who claimed descent from the legendary High King of Ireland, High King Conn of the Hundred Battles, Conn Cétchathach (Conn of the Hundred Battles). The modern western Provinces of ...
.
**The Uí Briúin
The Uí Briúin were a royal dynasty of Connacht. Their eponymous apical ancestor was Brión, son of Eochaid Mugmedon and Mongfind, and an elder half brother of Niall of the Nine Hostages. They formed part of the Connachta, along with th ...
. Their chiefly family was in Gaelic the ''Síol Muireadaigh
The Síol Muireadaigh or Síol Muireadhaigh (; Anglicized ''Sil Murray'' or ''Silmurray''), was a leading sept of the Connachta group of Gaelic dynasties in medieval Ireland. The name Síol Muireadaigh was also used to refer to the territory occu ...
'' which anglicized is Silmurray and which included a number of important families including the O'Connors (O Connor Donn
The O'Conor dynasty (Middle Irish: ''Ó Conchobhair''; Modern ) are an Irish noble dynasty and formerly one of the most influential and distinguished royal dynasties in Ireland. The O'Conor family held the throne of the Kingdom of Connacht up ...
and O'Connor Sligo
Ó Conchobhair Sligigh (anglicised as O'Conor Sligo) is a Gaelic- Irish family and Chief of the Name.
The Ó Conchobhair Sligigh were a junior branch of the Ó Conchobhair Kings of Connacht.
They were descended from Brian Luighnech Ua Conchobha ...
), the O'Malones, the O'Mulconrys, MacShanlys, MacGoverns, MacClancy
Clancy is an Irish name coming from the Gaelic ''Mac Fhlannchaidh/Mac Fhlannchadha'', meaning "Son of the red/ruddy warrior" (Mac being for sons, ''Ní Fhlannchaidh/Ní Fhlannchadha'' would be for daughters), or as a hypocorism for Clarence. ...
s, O'Rourke
O'Rourke () is an Irish Gaelic clan based most prominently in what is today County Leitrim. The family were the historic rulers of Breifne and later West Breifne until the 17th century. The O'Rourke Clan Chief was at odds with the O'Reilly Chie ...
s, O'Reilly
O'Reilly () is a common Irish surname. The O'Reillys were historically the kings of East Bréifne in what is today County Cavan. The clan were part of the Connachta's Uí Briúin Bréifne kindred and were closely related to the Ó Ruairc ( ...
s, O'Beirnes, O'Sheridans, O'Carrys, O'Flanagans, O'Crowleys, MacDermot
Mac Diarmada (anglicised as McDermott or MacDermot), also spelled Mac Diarmata, is an Irish surname, and the surname of the ruling dynasty of Moylurg, a kingdom that existed in Connacht from the 10th to 16th centuries. The last ruling king was T ...
s, MacDonaghs, O'Mulvihills, MacGeraghtys, and O'Flahertys.
**The Uí Fiachrach
The Uí Fiachrach () were a royal dynasty who originated in, and whose descendants later ruled, the ''coicead'' or ''fifth'' of Connacht (a western province of Ireland) at different times from the mid-first millennium onwards. They claimed descen ...
.
***The Uí Fiachrach Muaidhe
The Uí Fiachrach Muaidhe were a branch of the Uí Fiachrach dynasty of the Connachta in medieval Ireland. They were centred on the Moy River valley of modern-day County Mayo, Ireland. At its largest extent, their territory, Tír Fhíacrach Múai ...
(northern). Their main chiefs were the O'Dowd
O'Dowd () is an Irish Gaelic clan based most prominently in what is today County Mayo and County Sligo. The clan name originated in the 9th century as a derivative of its founder Dubda mac Connmhach. The O'Dowd clan can be traced to the Doonfe ...
s, but other chiefly families included the O'Finnegans, O'Keeves, O'Bolans, O'Kearneys, and O'Quigleys.
***The Uí Fiachrach Aidhne
Uí Fhiachrach Aidhne (also known as Hy Fiachrach) was a kingdom located in what is now the south of County Galway.
Legendary origins and geography
Originally known as Aidhne, it was said to have been settled by the mythical Fir Bolg. Dubhalta ...
(southern). Their main chiefs were the O'Shaughnessy
Ó Seachnasaigh, O'Shaughnessy, collectively Uí Sheachnasaigh, clan name Cinél nAedha na hEchtghe, is a family surname of Irish origin. The name is found primarily in County Galway and County Limerick. Their name derives from Seachnasach mac ...
s, but other chiefly families were the O'Heynes, O'Heyne, or Hynes
''Hynes'' is a surname, many examples of which originate as the anglicisation the Irish name ''Ó hEidhin''.
Etymology
According to the '' Oxford Dictionary of Family Names in Britain and Ireland'', the modern name ''Hynes'' and its variants de ...
, O'Clerys, O'Donnells, O'Houlihans which in some places became Holland and Nolan, and also the O'Scanlans.
*The Uí Néill
The Uí Néill (; meaning "descendants of Niall") are Irish dynasties that claim descent from Niall Noígíallach (Niall of the Nine Hostages), a historical King of Tara who is believed to have died around c. 405. They are generally divided ...
.
**Northern Uí Néill
The Northern Uí Néill was any of several dynasties in north-western medieval Ireland that claimed descent from a common ancestor, Niall of the Nine Hostages. Other dynasties in central and eastern Ireland who also claimed descent from Niall ar ...
.
*** Cineál Eoghain. The chiefly family was the O'Neill dynasty
The O'Neill dynasty ( Irish: ''Ó Néill'') are a lineage of Irish Gaelic origin that held prominent positions and titles in Ireland and elsewhere. As kings of Cenél nEógain, they were historically one of the most prominent family of the N ...
, but also included the MacLoughlins, O'Branigans, O'Rahillys of Kerry, MacMartins of Tyrone, O'Cahan
The O'Cahan ( Irish: ''Ó Catháin'' 'descendants of Cahan') were a powerful sept of the Northern Uí Néill's Cenél nEógain in medieval Ireland. The name is presently anglicized as O'Kane, Kane and Keane.
The O'Cahan's originated in Lagga ...
s, MacLachlans, Lamonts, MacSorleys, MacNeills, MacEwens, MacQueens, MacSweens, MacSweeneys of Ireland, O'Creans, Crean
Crehan or O'Crehan is a surname with origins in the west of Ireland. Historically, it was rendered as Crean, O'Crean, Cregan or O'Cregan. Creaghan and O'Creaghan are a mix of the English language and the Irish language. Cryan is another variant ...
s, Crehan
Crehan or O'Crehan is a surname with origins in the west of Ireland. Historically, it was rendered as Crean, O'Crean, Cregan or O'Cregan. Creaghan and O'Creaghan are a mix of the English language and the Irish language. Cryan is another variant ...
s, Creghans, O'Donnelly
Donnelly is an Irish surname. Also used as: O’Donnelly or Donley. It is derived from the Gaelic ''Ó Donnghaile'' meaning 'descendant of Donnghal', a given name composed of the elements ''donn'' ('dark, brown') and ''gal'' ('valour'). O'Donnell ...
s, O'Hegartys, O'Gormleys, O'Hagan
O'Hagan is an Irish surname originally from the pre 10th century Old Gaelic Ó hAodhagáin, meaning perhaps "Little Fire from the Sun", being derived from Aodh the pagan sun god and Og meaning young, they are the "male descendant of Aodh" the paga ...
s, and O'Beolans.
*** Cineal Chonaill. Their main chiefs were the O'Donnell dynasty
The O'Donnell dynasty ( or ''Ó Domhnaill,'' ''Ó Doṁnaill'' ''or Ua Domaill;'' meaning "descendant of Dónal") were the dominant Irish clan of the kingdom of Tyrconnell in Ulster in the north of medieval and early modern Ireland.
Naming ...
of Tyrconnell
Tyrconnell (), also spelled Tirconnell and Tirconaill, was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland. It is associated geographically with present-day County Donegal, which was officially named ''County Tirconaill'' between 1922 and 1927. At times it also i ...
(Tír Chonaill), but also included the O'Canannains or O'Canons, O'Muldonys, O'Mulderrys, O'Friel
O'Friel ( or ) is a surname of Tyrconnell (modern-day County Donegal).
The origin of the names comes from Firghil (Ó Fearghial or Fergal), a descendant of Eoghan, (son of Niall Noígíallach, the most prolific warrior in Irish history) brother o ...
s, O'Boyles, O'Cullinans, and O'Dohertys.
***Cineal Cairbre. Their main chiefs were the O'Brolans.
**Southern Uí Néill
The Southern Uí Néill (, ) were a branch of the Uí Néill dynasty that invaded and settled in the Kingdom of Mide and its associated kingdoms.
Two sons of Niall Noigiallach, Lóegaire () and Coirpre (), initially led the dynasty. As did th ...
.
***Clann Cholmáin
Clann Cholmáin is the dynasty descended from Colmán Már mac Diarmato, son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Part of the Southern Uí Néill — they were the kings of Mide (Meath) — they traced their descent to Niall Noígiallach and hi ...
. Their main chiefs were the O'Melaghlins who were later known as the MacLoughlins of Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County ...
.
*** Cineal Fiachach. Their main chiefs were the MacGeoghegan
Geoghegan () is a surname of Irish origin.
Often spelled without the prefix "Mac", the name has many variants, including Gehegan, Geoghan, Geohegan, Gahagan, Gagan, and Gagon which approximate the most common pronunciations of the name. It is ...
s or O'Molloys.
*** Cineal Laoghaire. Their main chiefs were the O'Quinlans.
*** Fir Teathbha. Their main chiefs were the O'Caharneys, O'Dallys, MacAwleys, MacCarons, O'Brennas, and O'Shiels.
*** Muintear Tadhagain. Their chiefs were the O'Caharneys and O'Kearnys or Foxes
Foxes are small-to-medium-sized omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull; upright, triangular ears; a pointed, slightly upturned snout; and a long, bushy tail ("brush").
Twelve species ...
.
***The Four Tribes of Tara
The Four Tribes of Tara was an alliance of powerful clans that consisted of the O'Harts, O'Kelly's, O'Connolly, and the O'Regan. The princes of Tara were also styled princes of Brega, consisting of territory in the modern day counties Meath, Louth ...
: O'Harts, O'Regans, Mackennas, O'Higgins.
The South Gaels
*The Eoghanacht. The chiefly family was theMacCarthy dynasty
MacCarthy (), also spelled Macarthy, McCarthy or McCarty, is an Irish Irish clans, clan originating from Kingdom of Munster, Munster, an area they ruled during the Middle Ages. It was divided into several septs (branches) of which the MacCarthy ...
, but other families included the O'Meehans, O'Keeffe
O'Keeffe () is an Irish Gaelic clan based most prominently in what is today County Cork, particularly around Fermoy and Duhallow. The name comes from ''caomh'', meaning "kind", "gentle", "noble" Some reformed spellings present it as ''Ó Cu� ...
s, O'Sullivans and McGillycuddy
Valentine Trant McGillycuddy (February 14, 1849 – June 6, 1939) was a surgeon who served with expeditions and United States military forces in the West. He was considered controversial for his efforts to build a sustainable relationship betw ...
s.
*The Ui Eachach Mumhan. Their main chiefs were the O'Callaghan
O'Callaghan or simply Callaghan without the prefix (anglicized from two separate surnames and clans, '' Ó Ceallacháin,'' Munster Clan. ''Ó Ceileacháin,'' Oriel Clan'')'' is an Irish surname.
Origin and meaning Munster
The surname means desc ...
s, O'Donoghue
Donoghue or O'Donoghue is an anglicised form of the Irish language surname Ó Donnchadha or Ó Donnchú.
Etymology
The name means "descendant of Donnchadh", a personal name composed of the elements ''donn'' "brown-haired an and ''cath'' "batt ...
s, and O'Mahony
O'Mahony (Old Irish: ''Ó Mathghamhna''; Modern Irish: ''Ó Mathúna'') is the original name of the clan, with breakaway clans also spelled O'Mahoney, or simply Mahony, Mahaney and Mahoney, without the prefix. Brodceann O'Mahony was the eldest of t ...
s.
Vikings and Normans in Ireland
Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
and Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
are ethnically populations, linked in ancestry. From the 9th to 11th centuries, the Vikings raided and settled in Britain and Ireland. In Ireland the Vikings became completely Gaelicized and established the first towns. The Normans invaded and conquered England in 1066 and later had similar success invading Ireland in the late 12th century. The Normans were the first people to introduce the mounted knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
. In Ireland, these "Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
" families were influenced just as much as they themselves influenced and have been described as having become "more Irish than the Irish themselves
"More Irish than the Irish themselves" (; ) is a phrase used in Irish historiography to describe a phenomenon of cultural assimilation in late medieval Norman Ireland.
History
The descendants of Anglo-Norman lords who had settled in Ireland i ...
".
Viking families in Ireland
At least the following three Irish families are believed to be of Viking descent: the Clan Fearghaill whose chiefs were theO'Halloran
O'Halloran is the surname of the ultimate and at least two distinct Gaelic- Irish families, one in County Galway and another in south-east County Clare linked to the Dál gCais. On occasions it is translated as "stranger" or "from across the sea" ...
s, the MacCotters, and the O'Doyles.
Norman families in Ireland
The following surnames found in Ireland are believed to be of Norman origin and to have arrived following the Norman invasion of Ireland:Barry Barry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Barry (name), including lists of people with the given name, nickname or surname, as well as fictional characters with the given name
* Dancing Barry, stage name of Barry Richards (born c. 195 ...
, Branne, Burke
Burke (; ) is a Normans in Ireland, Norman-Irish surname, deriving from the ancient Anglo-Norman and Hiberno-Norman noble dynasty, the House of Burgh. In Ireland, the descendants of William de Burgh (''circa'' 1160–1206) had the surname'' de B ...
, Butler
A butler is a person who works in a house serving and is a domestic worker in a large household. In great houses, the household is sometimes divided into departments, with the butler in charge of the dining room, wine cellar, and pantries, pantr ...
, Condon, Cusak, Dalton
Dalton may refer to:
Science
* Dalton (crater), a lunar crater
* Dalton (program), chemistry software
* Dalton (unit) (Da), a.k.a. unified atomic mass unit
* John Dalton, chemist, physicist and meteorologist
* 12292 Dalton, an asteroid
Ent ...
, Darcy, de Covcy, Dillon
Dillon may refer to:
People
*Dillon (surname)
* Dillon (given name)
*Dillon (singer) (born 1988), Brazilian singer
* J. J. Dillon, primary ring name of American professional wrestler James Morrison (born 1942)
Places Canada
* Dillon, Saskatchewa ...
, Fagun, Fitzgerald Fitzgerald may refer to:
People
* Fitzgerald (surname), a surname
* Fitzgerald Hinds, Trinidadian politician
* Fitzgerald Toussaint (born 1990), former American football running back
Place Australia
* Fitzgerald River National Park, a nati ...
, MacGibbon, French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
, Hackett, Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
, Keating, Lacy
Lacy is a surname and a unisex given name.
People with the name include:
People
Surname
* Alan J. Lacy (born 1953), American businessman
* Antonio Lacy (born 1957), Spanish doctor and surgeon
* Arthur J. Lacy (1876–1975), American poli ...
, Lynch
Lynch may refer to:
Places Australia
* Lynch Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica
* Lynch Point, Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica
* Lynch's Crater, Queensland, Australia
England
* River Lynch, Hertfordshire
* The Lynch, an island in the Rive ...
, MacCostello, Martin, Nugent, Power, Purcell
Henry Purcell (, rare: ; September 1659 – 21 November 1695) was an English composer of Baroque music, most remembered for his more than 100 songs; a tragic opera, ''Dido and Aeneas''; and his incidental music to a version of Shakespeare's ...
, Rothes, Sarsfield, Wall.
The following surnames are believed to have come to Ireland with the Norman invasion but are believed to have been of Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
origin: Tobin, Flemming
Flemming is a surname and a male given name referring, like the more common '' Fleming'', to an inhabitant (or descendant thereof) of Flanders,Prendergast.
The following surnames are believed to have come to Ireland with the Norman invasion but are believed to have been of
 In the 16th century,
In the 16th century,

Clans of Ireland
Fitzpatrick Clan SocietyThe Fitzpatrick – Mac Giolla Phádraig Clan Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:Irish Clans
Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, of or about Wales
* Welsh language, spoken in Wales
* Welsh people, an ethnic group native to Wales
Places
* Welsh, Arkansas, U.S.
* Welsh, Louisiana, U.S.
* Welsh, Ohio, U.S.
* Welsh Basin, during t ...
origin: Roche
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche (), is a Switzerland, Swiss multinational corporation, multinational holding healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, ...
, Blake
Blake or Blake's may refer to:
People
* Blake (given name), a given name of English origin (includes a list of people with the name)
* Blake (surname), a surname of English origin (includes a list of people with the name)
** William Blake (1757 ...
, Joyce, MacQuillan, Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, Taffe, Walsh
Walsh may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Walsh (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters
Places Australia
* Mount Walsh, Mount Walsh National Park
Canada
* Fort Walsh, one of the first Royal Canadian Mounted ...
, Savage.
End of the clan system
 In the 16th century,
In the 16th century, English common law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures. The judiciary is independent, and legal principles like fairness, equality bef ...
was introduced throughout Ireland, along with a centralised royal administration in which the county and the sheriff replaced the "country" and the clan chief.
When the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
was created in 1541, the Dublin administration wanted to involve the Gaelic chiefs into the new entity, creating new titles for them such as the Baron Upper Ossory
Baron Upper Ossory was a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created on 11 June 1541 for Barnaby Fitzpatrick. This was in pursuance of the Surrender and regrant policy of King Henry VIII. Under the policy, Gaelic chiefs were actively encou ...
, Earl of Tyrone
The Earl of Tyrone is a title created three times in the Peerage of Ireland, and once in the Spanish nobility. It was created for the final time in 1746 for Marcus Beresford, 1st Viscount Tyrone, son-in-law of the last de Poer earls. His son wa ...
, and Baron Inchiquin
Baron Inchiquin () is one of the older titles in the Peerage of Ireland. It was one of two titles created on 1 July 1543 for Murrough O'Brien, Prince of Thomond, who claimed descent from Brian Boru, a High King of Ireland. The English titles ...
. In the process, they were granted new coats of arms from 1552. The associated policy of surrender and regrant
During the Tudor conquest of Ireland (c.1540–1603), "surrender and regrant" was the legal mechanism by which Irish clans were to be converted from a power structure rooted in clan and kin loyalties, to a late-Feudalism, feudal system under t ...
involved a change to succession to a title by the European system of primogeniture
Primogeniture () is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn Legitimacy (family law), legitimate child to inheritance, inherit all or most of their parent's estate (law), estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some childre ...
, and not by the Irish tanistry
Tanistry is a Gaelic system for passing on titles and lands. In this system the Tanist (; ; ) is the office of heir-apparent, or second-in-command, among the (royal) Gaelic patrilineal dynasties of Ireland, Scotland and Mann, to succeed to ...
, where a group of male cousins of a chief were eligible to succeed by election.
The early 17th century was a watershed in Ireland. It marked the destruction of Ireland's ancient Gaelic aristocracy following the Tudor re-conquest and cleared the way for the Plantation of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster (; Ulster Scots dialects, Ulster Scots: ) was the organised Settler colonialism, colonisation (''Plantation (settlement or colony), plantation'') of Ulstera Provinces of Ireland, province of Irelandby people from Great ...
. In 1607 the senior Gaelic chiefs of Ulster left Ireland to recruit support in Spain but failed, and instead eventually arrived in Rome where they remained for the rest of their lives . After this point, the English authorities in Dublin established real control over all of Ireland for the first time, bringing a centralised government to the entire island, and successfully disarmed the native clans and their lordships.
Later developments and "revival"

Clans of Ireland
Clans of Ireland ( Irish: ''Finte na hÉireann'') is an Irish charity established to authenticate, represent and co-ordinate the activities of Irish clans. Founded in 1989, it has operated under the patronage of the President of Ireland since 2 ...
is an Irish non-governmental organisation established in 1989 with the aim of authenticating, representing and co-ordinating the activities of modern Irish clan organisations. It has operated under the patronage of the President of Ireland
The president of Ireland () is the head of state of Republic of Ireland, Ireland and the supreme commander of the Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish Defence Forces. The presidency is a predominantly figurehead, ceremonial institution, serving as ...
since 2012, and is accredited as a "civil society NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
" by the United Nations. It performs research, promotes clan rallies, and advances DNA studies.
The Standing Council of Scottish Chiefs
The Standing Council of Scottish Chiefs (SCSC) is an organisation that represents many prominent Scottish clan chief, clan chiefs and Scottish clan chief#Chief of the Name and Arms, Chiefs of the Name and Arms in Scotland. It claims to be the pr ...
signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Clans of Ireland in 2013 at Christchurch Cathedral, Dublin. As part of the agreement they agreed to mutually recognise each other's authority.
See also
* List of Irish clans in Ulster *Scottish clan
A Scottish clan (from Scottish Gaelic , literally 'children', more broadly 'kindred') is a kinship group among the Scottish people. Clans give a sense of shared heritage and descent to members, and in modern times have an official structure r ...
* List of Scottish clans
The following is a list of Scottish clans (with and without chiefs) – including, when known, their heraldic crest badges, tartans, mottoes, and other information.
The crest badges used by members of Scottish clans are based upon armoria ...
* List of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes
This is a list of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a large ...
* Celtic peoples
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
** Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
** Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
* Celtic nations
Sports ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Clans of Ireland
Fitzpatrick Clan Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:Irish Clans