Photochemical Logic Gate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Photochemistry is the branch of
Photochemistry is the branch of
 Alternatively, it is possible for the excited state S1 to undergo spin inversion and to generate a triplet excited state T1 having two unpaired electrons with the same spin. This violation of the spin selection rule is possible by
Alternatively, it is possible for the excited state S1 to undergo spin inversion and to generate a triplet excited state T1 having two unpaired electrons with the same spin. This violation of the spin selection rule is possible by
 Photochemical reactions require a light source that emits wavelengths corresponding to an electronic transition in the reactant. In the early experiments (and in everyday life), sunlight was the light source, although it is polychromatic.
Photochemical reactions require a light source that emits wavelengths corresponding to an electronic transition in the reactant. In the early experiments (and in everyday life), sunlight was the light source, although it is polychromatic.
 Photochemistry is the branch of
Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
(wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
from 100 to 400 nm), visible (400–750 nm), or infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
radiation (750–2500 nm).
In nature, photochemistry is of immense importance as it is the basis of photosynthesis, vision, and the formation of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
with sunlight. It is also responsible for the appearance of DNA mutations leading to skin cancers.
Photochemical reactions proceed differently than temperature-driven reactions. Photochemical paths access high-energy intermediates that cannot be generated thermally, thereby overcoming large activation barriers in a short period of time, and allowing reactions otherwise inaccessible by thermal processes. Photochemistry can also be destructive, as illustrated by the photodegradation
Photodegradation is the alteration of materials by light. Commonly, the term is used loosely to refer to the combined action of sunlight and air, which cause oxidation and hydrolysis. Often photodegradation is intentionally avoided, since it dest ...
of plastics.
Concept
Grotthuss–Draper law and Stark–Einstein law
Photoexcitation
Photoexcitation in crystal
Photoexcitation is the production of an excited state of a quantum system by photon absorption. The excited state originates from the interaction between a photon and the quantum system. Photons carry energy that is ...
is the first step in a photochemical process where the reactant is elevated to a state of higher energy, an excited state
In quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Add ...
. The first law of photochemistry, known as the Grotthuss–Draper law
Photoelectrochemical processes are processes in photoelectrochemistry; they usually involve transforming light into other forms of energy.
These processes apply to photochemistry, optically pumped Laser pumping, lasers, sensitized solar cells, lu ...
(for chemists Theodor Grotthuss
Freiherr Christian Johann Dietrich Theodor von Grotthuss (20 January 1785 – 26 March 1822) was a Baltic German scientist known for establishing the first theory of electrolysis in 1806 and formulating the first law of photochemistry in 1817. Hi ...
and John W. Draper), states that light must be absorbed by a chemical substance in order for a photochemical reaction Organic photochemistry encompasses organic reactions that are induced by the action of light. The absorption of ultraviolet light by organic molecules often leads to reactions. In the earliest days, sunlight was employed, while in more modern times ...
to take place. According to the second law of photochemistry, known as the Stark–Einstein law (for physicists Johannes Stark
Johannes Stark (; 15 April 1874 – 21 June 1957) was a German physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1919 "for his discovery of the Doppler effect in canal rays and the splitting of spectral lines in electric fields". This phenom ...
and Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
), for each photon of light absorbed by a chemical system, no more than one molecule is activated for a photochemical reaction, as defined by the quantum yield
In particle physics, the quantum yield (denoted ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system.
\Phi(\lambda)=\frac
Applications
Fluorescence spectroscopy
The fluorescence ...
.
Fluorescence and phosphorescence
When a molecule or atom in theground state
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state ...
(S0) absorbs light, one electron is excited to a higher orbital level. This electron maintains its spin
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spin (physics) or particle spin, a fundamental property of elementary particles
* Spin quantum number, a number which defines the value of a particle's spin
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thr ...
according to the spin selection rule; other transitions would violate the law of conservation of angular momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total ang ...
. The excitation to a higher singlet state
In quantum mechanics, a singlet state usually refers to a system in which all electrons are paired. The term 'singlet' originally meant a linked set of particles whose net angular momentum is zero, that is, whose overall spin quantum number s=0. A ...
can be from HOMO
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
to LUMO
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for ''highest occupied molecular orbital'' and ''lowest unoccupied molecular orbital'', respectively. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the ''frontie ...
or to a higher orbital, so that singlet excitation states S1, S2, S3... at different energies are possible.
Kasha's rule
Kasha's rule is a principle in the photochemistry of electronically excited molecules. The rule states that photon emission (fluorescence or phosphorescence) occurs in appreciable yield only from the lowest excited state of a given multiplicity. ...
stipulates that higher singlet states would quickly relax by radiationless decay or internal conversion
Internal conversion is an atomic decay process where an excited nucleus interacts electromagnetically with one of the orbital electrons of an atom. This causes the electron to be emitted (ejected) from the atom. Thus, in internal conversion (o ...
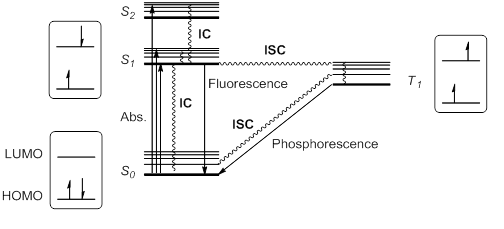
(IC) to S1. Thus, S1 is usually, but not always, the only relevant singlet excited state. This excited state S1 can further relax to S0 by IC, but also by an allowed radiative transition from S1 to S0 that emits a photon; this process is called fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
.
 Alternatively, it is possible for the excited state S1 to undergo spin inversion and to generate a triplet excited state T1 having two unpaired electrons with the same spin. This violation of the spin selection rule is possible by
Alternatively, it is possible for the excited state S1 to undergo spin inversion and to generate a triplet excited state T1 having two unpaired electrons with the same spin. This violation of the spin selection rule is possible by intersystem crossing
Intersystem crossing (ISC) is an isoenergetic radiationless process involving a transition between the two electronic states with different spin multiplicity.
Excited singlet and triplet states
When an electron in a molecule with a singlet grou ...
(ISC) of the vibrational and electronic levels of S1 and T1. According to Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity, this T1 state would be somewhat more stable than S1.
This triplet state can relax to the ground state S0 by radiationless ISC or by a radiation pathway called phosphorescence
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluor ...
. This process implies a change of electronic spin, which is forbidden by spin selection rules, making phosphorescence (from T1 to S0) much slower than fluorescence (from S1 to S0). Thus, triplet states generally have longer lifetimes than singlet states. These transitions are usually summarized in a state energy diagram or Jablonski diagram
In molecular spectroscopy, a Jablonski diagram is a diagram that illustrates the electronic states and often the vibrational levels of a molecule, and also the transitions between them. The states are arranged vertically by energy and grouped hor ...
, the paradigm of molecular photochemistry.
These excited species, either S1 or T1, have a half-empty low-energy orbital, and are consequently more oxidizing
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
than the ground state. But at the same time, they have an electron in a high-energy orbital, and are thus more reducing. In general, excited species are prone to participate in electron transfer processes.
Experimental setup
Mercury-vapor lamp
A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger soda lime or borosilicate gla ...
s are more common in the laboratory. Low-pressure mercury-vapor lamps mainly emit at 254 nm. For polychromatic sources, wavelength ranges can be selected using filters. Alternatively, laser beams are usually monochromatic (although two or more wavelengths can be obtained using nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in Nonlinearity, nonlinear media, that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity ...
), and LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresp ...
s have a relatively narrow band
Band or BAND may refer to:
Places
*Bánd, a village in Hungary
* Band, Iran, a village in Urmia County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran
* Band, Mureș, a commune in Romania
* Band-e Majid Khan, a village in Bukan County, West Azerbaijan Province, ...
that can be efficiently used, as well as Rayonet lamps, to get approximately monochromatic beams.
The emitted light must reach the targeted functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
without being blocked by the reactor, medium, or other functional groups
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
present. For many applications, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
is used for the reactors as well as to contain the lamp. Pyrex
Pyrex (trademarked as ''PYREX'' and ''pyrex'') is a brand introduced by Corning Inc. in 1915, initially for a line of clear, low-thermal-expansion borosilicate glass used for laboratory glassware and kitchenware. It was later expanded in the 1 ...
absorbs at wavelengths shorter than 275 nm. The solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
is an important experimental parameter. Solvents are potential reactants, and for this reason, chlorinated solvents are avoided because the C–Cl bond can lead to chlorination of the substrate. Strongly-absorbing solvents prevent photons from reaching the substrate. Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
solvents absorb only at short wavelengths and are thus preferred for photochemical experiments requiring high-energy photons. Solvents containing unsaturation absorb at longer wavelengths and can usefully filter out short wavelengths. For example, cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexan ...
and acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly Volatile organic compound, volatile, and flammable liquid with a charact ...
"cut off" (absorb strongly) at wavelengths shorter than 215 and 330 nm, respectively.
Typically, the wavelength employed to induce a photochemical process is selected based on the absorption spectrum
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, ...
of the reactive species, most often the absorption maximum. Over the last years, however, it has been demonstrated that, in the majority of bond-forming reactions, the absorption spectrum does not allow selecting the optimum wavelength to achieve the highest reaction yield based on absorptivity. This fundamental mismatch between absorptivity and reactivity has been elucidated with so-called photochemical action plots.
Photochemistry in combination with
flow chemistry
In flow chemistry, also called reactor engineering, a chemical reaction is run in a continuously flowing stream rather than in batch production. In other words, pumps move fluid into a reactor, and where tubes join one another, the fluids contac ...
Continuous-flow photochemistry offers multiple advantages over batch photochemistry. Photochemical reactions are driven by the number of photons that are able to activate molecules causing the desired reaction. The large surface-area-to-volume ratio
The surface-area-to-volume ratio or surface-to-volume ratio (denoted as SA:V, SA/V, or sa/vol) is the ratio between surface area and volume of an object or collection of objects.
SA:V is an important concept in science and engineering. It is use ...
of a microreactor maximizes the illumination, and at the same time allows for efficient cooling, which decreases the thermal side products.
Principles
In the case of photochemical reactions, light provides theactivation energy
In the Arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (k ...
. Simplistically, light is one mechanism for providing the activation energy required for many reactions. If laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
light is employed, it is possible to selectively excite a molecule so as to produce a desired electronic and vibrational state. Equally, the emission from a particular state may be selectively monitored, providing a measure of the population of that state. If the chemical system is at low pressure, this enables scientists to observe the energy distribution of the products of a chemical reaction before the differences in energy have been smeared out and averaged by repeated collisions.
The absorption of a photon by a reactant molecule may also permit a reaction to occur not just by bringing the molecule to the necessary activation energy, but also by changing the symmetry of the molecule's electronic configuration, enabling an otherwise-inaccessible reaction path, as described by the Woodward–Hoffmann selection rules. A +2cycloaddition
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more Unsaturated hydrocarbon, unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of th ...
reaction is one example of a pericyclic reaction
In organic chemistry, a pericyclic reaction is the type of organic reaction wherein the transition state of the molecule has a cyclic geometry, the reaction progresses in a concerted fashion, and the bond orbitals involved in the reaction overl ...
that can be analyzed using these rules or by the related frontier molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding ...
theory.
Some photochemical reactions are several orders of magnitude faster than thermal reactions; reactions as fast as 10−9 seconds and associated processes as fast as 10−15 seconds are often observed.
The photon can be absorbed directly by the reactant or by a photosensitizer
Photosensitizers are light absorbers that alter the course of a photochemical reaction. They usually are catalysts. They can function by many mechanisms; sometimes they abstract an electron from the substrate, and sometimes they abstract a hydro ...
, which absorbs the photon and transfers the energy to the reactant. The opposite process, when a photoexcited state is deactivated by a chemical reagent, is called quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
.
Most photochemical transformations occur through a series of simple steps known as primary photochemical processes. One common example of these processes is the excited state proton transfer.
Photochemical reactions
Examples of
photochemical reactions Organic photochemistry encompasses organic reactions that are induced by the action of light. The absorption of ultraviolet light by organic molecules often leads to reactions. In the earliest days, sunlight was employed, while in more modern times ...
*Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
: Plants use solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
to convert carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and water into glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
.
*Human formation of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
by exposure to sunlight.
*Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the emission of light during a chemiluminescence reaction by living organisms. Bioluminescence occurs in multifarious organisms ranging from marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some Fungus, fungi, microorgani ...
: ''e.g.'' In fireflies
The Lampyridae are a family of elateroid beetles with more than 2,000 described species, many of which are light-emitting. They are soft-bodied beetles commonly called fireflies, lightning bugs, or glowworms for their conspicuous production ...
, an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
in the abdomen catalyzes a reaction that produces light.
* Polymerizations started by photoinitiators, which decompose upon absorbing light to produce the free radicals for radical polymerization
In polymer chemistry, radical polymerization (RP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of a radical to building blocks ( repeat units). Radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms, usu ...
.
*Photodegradation
Photodegradation is the alteration of materials by light. Commonly, the term is used loosely to refer to the combined action of sunlight and air, which cause oxidation and hydrolysis. Often photodegradation is intentionally avoided, since it dest ...
of many substances, e.g. polyvinyl chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of ...
and Fp. Medicine bottles are often made from darkened glass to protect the drugs from photodegradation.
*Photochemical rearrangements, ''e.g.'' photoisomerization
In chemistry, photoisomerization is a form of isomerization induced by photoexcitation. Both reversible and irreversible photoisomerizations are known for photoswitchable compounds. The term "photoisomerization" usually, however, refers to a rev ...
, hydrogen atom transfer, and photochemical electrocyclic reactions.
*Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death ( phototoxicity).
PDT is used in treating acne, wet age-related macula ...
: Light is used to destroy tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
by the action of singlet oxygen
Singlet oxygen, systematically named dioxygen(singlet) and dioxidene, is a gaseous inorganic chemistry, inorganic chemical with the formula O=O (also written as or ), which is in a quantum state where all electrons are Radical (chemistry), spin p ...
generated by photosensitized reactions of triplet oxygen
Triplet oxygen, 3O2, refers to the ''S'' = 1 electronic ground state of molecular oxygen (dioxygen). Molecules of triplet oxygen contain two unpaired electrons, making triplet oxygen an unusual example of a stable and commonly encountered diradi ...
. Typical photosensitizers
Photosensitizers are light absorbers that alter the course of a photochemical reaction. They usually are catalysts. They can function by many mechanisms; sometimes they abstract an electron from the substrate, and sometimes they abstract a hydro ...
include tetraphenylporphyrin
Tetraphenylporphyrin, abbreviated TPP or H2TPP, is a synthetic heterocyclic compound that resembles naturally occurring porphyrins. Porphyrins are dyes and cofactors found in hemoglobin and cytochromes and are related to chlorophyll and vitamin ...
and methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia. It has previously been used for treating cyanide poisoning and urinary trac ...
. The resulting singlet oxygen is an aggressive oxidant, capable of converting C–H bonds into C–OH groups.
* Diazo printing process
*Photoresist
A photoresist (also known simply as a resist) is a light-sensitive material used in several processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving, to form a patterned coating on a surface. This process is crucial in the electronics industry.
T ...
technology, used in the production of microelectronic
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre- ...
components.
* Vision is initiated by a photochemical reaction of rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the ''RHO'' gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rod cells. Rhodopsin mediates dim ...
.
*Toray
is a multinational corporation headquartered in Japan that specializes in industrial products centered on technologies in organic synthetic chemistry, polymer chemistry, and biochemistry.
Its founding business areas were fibers and textiles, ...
photochemical production of ε-caprolactame.
*Photochemical production of artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for he ...
, an anti-malaria drug.
* Photoalkylation, used for the light-induced addition of alkyl groups to molecules.
*DNA: photodimerization leading to cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers.
Organic photochemistry
Examples of photochemicalorganic reactions
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical r ...
are electrocyclic reaction
In organic chemistry, an electrocyclic reaction is a type of pericyclic reaction, pericyclic, rearrangement reaction, rearrangement reaction where the net result is one pi bond being converted into one sigma bond or vice versa. These reactions are ...
s, radical reaction
A free-radical reaction is any chemical reaction involving free radicals. This reaction type is abundant in organic reactions. Two pioneering studies into free radical reactions have been the discovery of the triphenylmethyl radical by Moses Gomb ...
s, photoisomerization
In chemistry, photoisomerization is a form of isomerization induced by photoexcitation. Both reversible and irreversible photoisomerizations are known for photoswitchable compounds. The term "photoisomerization" usually, however, refers to a rev ...
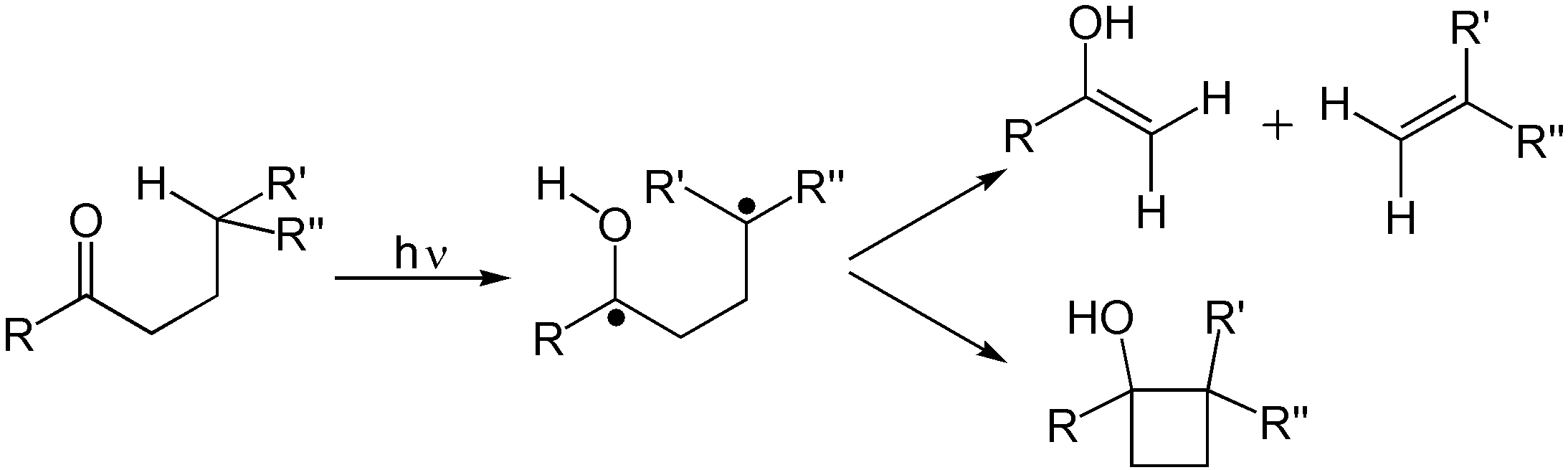
, and Norrish reaction
A Norrish reaction, named after Ronald George Wreyford Norrish, is a photochemical reaction taking place with ketones and aldehydes. Such reactions are subdivided into Norrish type I reactions and Norrish type II reactions. While of limited synthet ...
s.

Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
s undergo many important reactions that proceed via a photon-induced π to π* transition. The first electronic excited state of an alkene lacks the π-bond
In chemistry, pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, in each of which two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, and in which this overlap occurs laterally. Each of these atomic orbitals ...
, so that rotation about the C–C bond is rapid and the molecule engages in reactions not observed thermally. These reactions include cis-trans isomerization and cycloaddition to other (ground state) alkene to give cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and is commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commerc ...
derivatives. The cis-trans isomerization of a (poly)alkene is involved in retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use ret ...
, a component of the machinery of vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
. The dimerization
In chemistry, dimerization is the process of joining two identical or similar molecular entities by bonds. The resulting bonds can be either strong or weak. Many symmetrical chemical species are described as dimers, even when the monomer is u ...
of alkenes is relevant to the photodamage of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, where thymine dimer
Pyrimidine dimers represent molecular lesions originating from thymine or cytosine bases within DNA, resulting from photochemical reactions. These lesions, commonly linked to direct DNA damage, are induced by ultraviolet light (UV), particularl ...
s are observed upon illuminating DNA with UV radiation. Such dimers interfere with transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, often th ...
. The beneficial effects of sunlight are associated with the photochemically-induced retro-cyclization (decyclization) reaction of ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a mycosterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergostero ...
to give vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
. In the DeMayo reaction
The DeMayo reaction is a photochemical reaction in which the enol of a 1,3-diketone reacts with an alkene (or another species with a C=C bond) and the resulting cyclobutane ring undergoes a retro-aldol reaction to yield a 1,5-diketone:
The net e ...
, an alkene reacts with a 1,3-diketone reacts via its enol
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of functional group or intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula (R = many substituents). The term ''enol'' is an abbreviation of ''alkenol'', a portmanteau deriving from "-ene ...
to yield a 1,5-diketone. Still another common photochemical reaction is Howard Zimmerman
Howard E. Zimmerman (July 5, 1926 – February 12, 2012) was a professor of chemistry at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1980 and the recipient of the 1986 American Institute of Chemis ...
's di-π-methane rearrangement
In organic chemistry, the di-π-methane rearrangement is the Organic photochemistry, photochemical Rearrangement reaction, rearrangement of a molecule that contains two pi bond, π-systems separated by a saturated carbon atom. In the Aliphatic c ...
.
In an industrial application, about 100,000 tonnes of benzyl chloride
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.
Preparation
Benzyl chloride is prepared industrially ...
are prepared annually by the gas-phase photochemical reaction of toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water
Water is an inorganic compound with the c ...
with chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
. The light is absorbed by chlorine molecules, the low energy of this transition being indicated by the yellowish color of the gas. The photon induces homolysis of the Cl-Cl bond, and the resulting chlorine radical converts toluene to the benzyl radical:
:Cl2 + hν → 2 Cl·
:C6H5CH3 + Cl· → C6H5CH2· + HCl
:C6H5CH2· + Cl· → C6H5CH2Cl
Mercaptans
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
can be produced by photochemical addition of hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
(H2S) to alpha olefins
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.
The International Union of P ...
.
Inorganic and organometallic photochemistry
Coordination complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ' ...
es and organometallic compound
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and ...
s are also photoreactive. These reactions can entail cis-trans isomerization. More commonly, photoreactions result in dissociation of ligands, since the photon excites an electron on the metal to an orbital that is antibonding
In theoretical chemistry, an antibonding orbital is a type of molecular orbital that weakens the chemical bond between two atoms and helps to raise the energy of the molecule relative to the separated atoms. Such an orbital has one or more node ...
with respect to the ligands. Thus, metal carbonyl
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against n ...
s that resist thermal substitution undergo decarbonylation upon irradiation with UV light. UV-irradiation of a THF
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ma ...
solution of molybdenum hexacarbonyl
Molybdenum hexacarbonyl (also called molybdenum carbonyl) is the chemical compound with the formula Mo(CO)6. This colorless solid, like its chromium, tungsten, and seaborgium analogues, is noteworthy as a volatile, air-stable derivative of a metal ...
gives the THF complex, which is synthetically useful:
:Mo(CO)6 + THF → Mo(CO)5(THF) + CO
In a related reaction, photolysis of iron pentacarbonyl
Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula . Under standard conditions Fe( CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor t ...
affords diiron nonacarbonyl
Diiron nonacarbonyl is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2(CO)9. This metal carbonyl is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and of occasional use in organic synthesis. It is a more reactive source of Fe(0) than Fe(CO)5. This mica ...
(see figure):
:2 Fe(CO)5 → Fe2(CO)9 + CO
Select photoreactive coordination complexes can undergo oxidation-reduction processes via single electron transfer. This electron transfer can occur within the inner or outer
{{Short pages monitor