Phosphate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In
File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png,
Phosphoric
acid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png,
Dihydrogen
phosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png,
Hydrogen
phosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png,
Phosphate or orthophosphate
In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the trivalent functional group in such esters. Phosphates may contain sulfur in place of one or more oxygen atoms ( thiophosphates and organothiophosphates).
Orthophosphates are especially important among the various phosphates because of their key roles in biochemistry,
 In water solution, orthophosphoric acid and its three derived anions coexist according to the dissociation and recombination equilibria below
Values are at 25°C and 0 ionic strength.
The p''K''''a'' values are the pH values where the concentration of each species is equal to that of its conjugate bases. At pH 1 or lower, the phosphoric acid is practically undissociated. Around pH 4.7 (mid-way between the first two p''K''''a'' values) the dihydrogen phosphate ion, , is practically the only species present. Around pH 9.8 (mid-way between the second and third p''K''''a'' values) the monohydrogen phosphate ion, , is the only species present. At pH 13 or higher, the acid is completely dissociated as the phosphate ion, .
This means that salts of the mono- and di-phosphate ions can be selectively crystallised from aqueous solution by setting the pH value to either 4.7 or 9.8.
In effect, , and behave as separate weak acids because the successive p''K''''a'' differ by more than 4.
Phosphate can form many polymeric ions such as pyrophosphate, , and triphosphate, . The various metaphosphate ions (which are usually long linear polymers) have an empirical formula of and are found in many compounds.
In water solution, orthophosphoric acid and its three derived anions coexist according to the dissociation and recombination equilibria below
Values are at 25°C and 0 ionic strength.
The p''K''''a'' values are the pH values where the concentration of each species is equal to that of its conjugate bases. At pH 1 or lower, the phosphoric acid is practically undissociated. Around pH 4.7 (mid-way between the first two p''K''''a'' values) the dihydrogen phosphate ion, , is practically the only species present. Around pH 9.8 (mid-way between the second and third p''K''''a'' values) the monohydrogen phosphate ion, , is the only species present. At pH 13 or higher, the acid is completely dissociated as the phosphate ion, .
This means that salts of the mono- and di-phosphate ions can be selectively crystallised from aqueous solution by setting the pH value to either 4.7 or 9.8.
In effect, , and behave as separate weak acids because the successive p''K''''a'' differ by more than 4.
Phosphate can form many polymeric ions such as pyrophosphate, , and triphosphate, . The various metaphosphate ions (which are usually long linear polymers) have an empirical formula of and are found in many compounds.
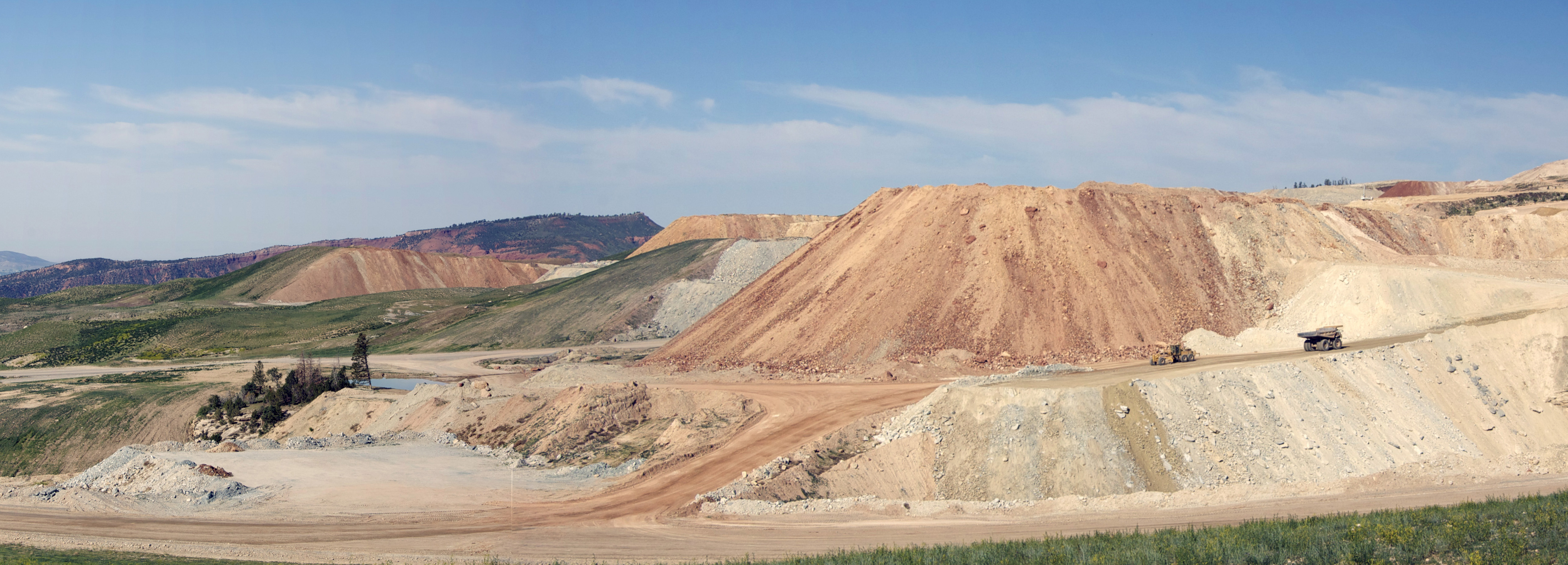 Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus, found in many phosphate minerals. In mineralogy and geology, phosphate refers to a rock or ore containing phosphate ions. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in agriculture and industry.
The largest global producer and exporter of phosphates is
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus, found in many phosphate minerals. In mineralogy and geology, phosphate refers to a rock or ore containing phosphate ions. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in agriculture and industry.
The largest global producer and exporter of phosphates is
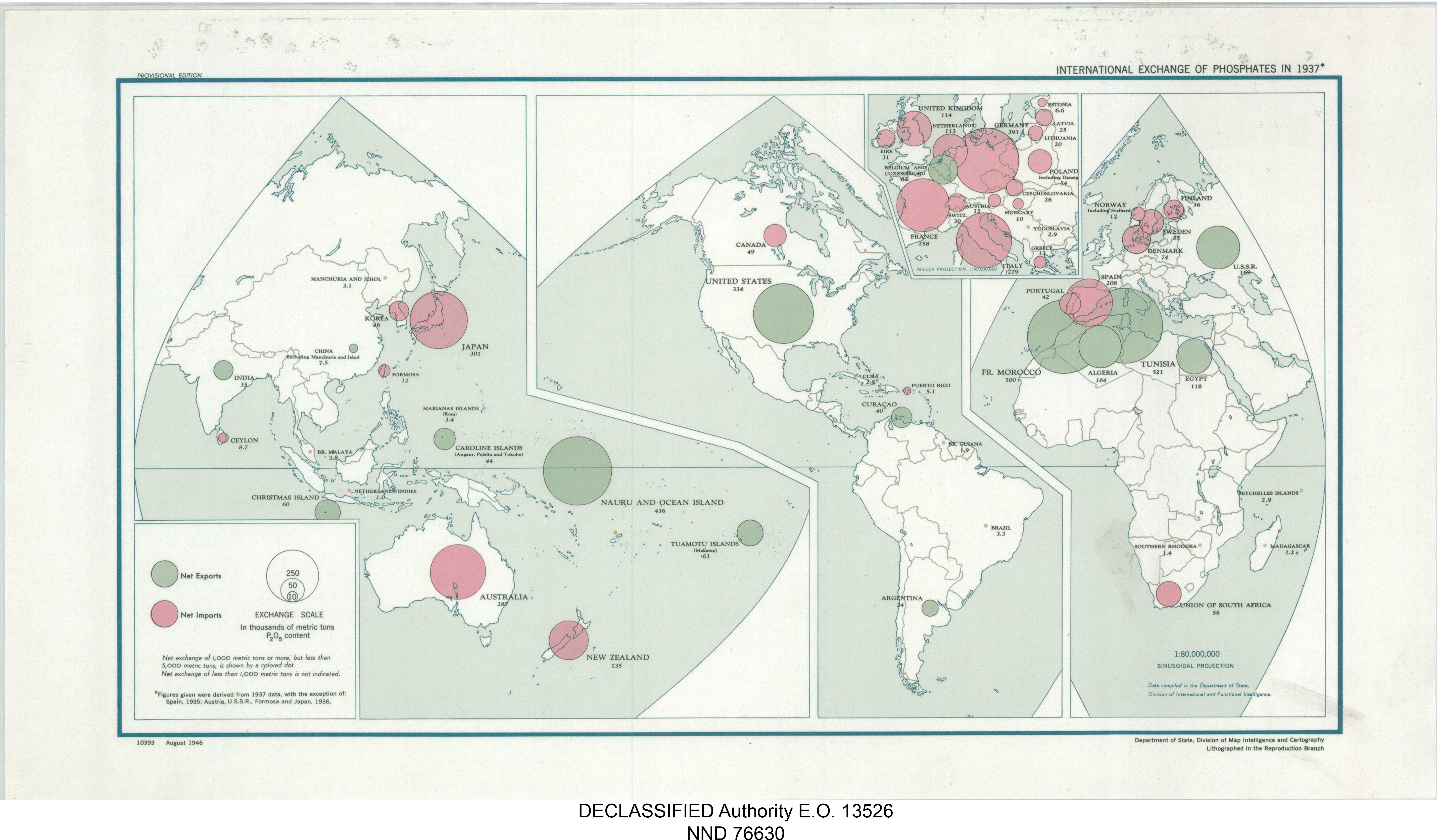 The three principal phosphate producer countries (China, Morocco and the United States) account for about 70% of world production.
The three principal phosphate producer countries (China, Morocco and the United States) account for about 70% of world production.
US Minerals Databrowser
provides data graphics covering consumption, production, imports, exports and price for phosphate and 86 other minerals
Phosphate: analyte monograph
– The Association for Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine * {{Authority control Functional groups Phosphorus oxyanions Industrial minerals Concrete admixtures Phosphorus(V) compounds
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid, phosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one proton gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion while removal of two protons gives the hydrogen phosphate ion . These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate.
Phosphoric
acid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png,
Dihydrogen
phosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png,
Hydrogen
phosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png,
Phosphate or orthophosphate
biogeochemistry
Biogeochemistry is the Branches of science, scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemistry, chemical, physics, physical, geology, geological, and biology, biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natu ...
, and ecology, and their economic importance for agriculture and industry. The addition and removal of phosphate groups ( phosphorylation and dephosphorylation) are key steps in cell metabolism.
Orthophosphates can condense to form pyrophosphates.
Chemical properties
The phosphate ion has a molar mass of 94.97 g/mol, and consists of a central phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. It is the conjugate base of the hydrogen phosphate ion , which in turn is the conjugate base of the dihydrogen phosphate ion , which in turn is the conjugate base of orthophosphoric acid, . Many phosphates are soluble in water at standard temperature and pressure. The sodium, potassium, rubidium,caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only f ...
, and ammonium phosphates are all water-soluble. Most other phosphates are only slightly soluble or are insoluble in water. As a rule, the hydrogen and dihydrogen phosphates are slightly more soluble than the corresponding phosphates.
Equilibria in solution
Biochemistry of phosphates
Inbiological system
A biological system is a complex Biological network inference, network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is ...
s, phosphorus can be found as free phosphate anions in solution (inorganic phosphate) or bound to organic molecules as various organophosphates.
Inorganic phosphate is generally denoted Pi and at physiological ( homeostatic) pH primarily consists of a mixture of and ions. At a neutral pH, as in the cytosol (pH = 7.0), the concentrations of the orthophosphoric acid and its three anions have the ratios
Thus, only the and ions are present in significant amounts in the cytosol (62% , 38% ). In extracellular fluid (pH = 7.4), this proportion is inverted (61% , 39% ).
Inorganic phosphate can also be present as pyrophosphate anions , which give orthophosphate by hydrolysis:
:
Organic phosphates are commonly found in the form of esters as nucleotides (e.g. AMP, ADP, and ATP) and in DNA and RNA. Free orthophosphate anions can be released by the hydrolysis of the phosphoanhydride bonds in ATP or ADP. These phosphorylation and dephosphorylation reactions are the immediate storage and source of energy for many metabolic processes. ATP and ADP are often referred to as high-energy phosphates, as are the phosphagens in muscle tissue. Similar reactions exist for the other nucleoside diphosphates and triphosphates.
Bones and teeth
An important occurrence of phosphates in biological systems is as the structural material of bone and teeth. These structures are made of crystalline calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite. The hard dense enamel of mammalian teeth may contain fluoroapatite, a hydroxy calcium phosphate where some of the hydroxyl groups have been replaced by fluoride ions.Medical and biological research uses
Phosphates are medicinal salts of phosphorus. Some phosphates, which help cure many urinary tract infections, are used to make urine more acidic. To avoid the development of calcium stones in the urinary tract, some phosphates are used. For patients who are unable to get enough phosphorus in their daily diet, phosphates are used as dietary supplements, usually because of certain disorders or diseases. Injectable phosphates can only be handled by qualified health care providers.Plant metabolism
Plants take up phosphorus through several pathways: the arbuscular mycorrhizal pathway and the direct uptake pathway.Adverse health effects
Hyperphosphatemia, or a high blood level of phosphates, is associated with elevated mortality in the general population. The most common cause of hyperphosphatemia in people, dogs, and cats is kidney failure. In cases of hyperphosphatemia, limiting consumption of phosphate-rich foods, such as some meats and dairy items and foods with a high phosphate-to-protein ratio, such as soft drinks, fast food, processed foods, condiments, and other products containing phosphate-salt additives is advised. Phosphates induce vascular calcification, and a high concentration of phosphates in blood was found to be a predictor of cardiovascular events.Production
Geological occurrence
 Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus, found in many phosphate minerals. In mineralogy and geology, phosphate refers to a rock or ore containing phosphate ions. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in agriculture and industry.
The largest global producer and exporter of phosphates is
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus, found in many phosphate minerals. In mineralogy and geology, phosphate refers to a rock or ore containing phosphate ions. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in agriculture and industry.
The largest global producer and exporter of phosphates is Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
. Within North America, the largest deposits lie in the Bone Valley region of central Florida, the Soda Springs region of southeastern Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
, and the coast of North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
. Smaller deposits are located in Montana, Tennessee, Georgia, and South Carolina. The small island nation of Nauru and its neighbor Banaba Island, which used to have massive phosphate deposits of the best quality, have been mined excessively. Rock phosphate can also be found in Egypt, Israel, Palestine, Western Sahara, Navassa Island, Tunisia, Togo, and Jordan, countries that have large phosphate-mining industries.
Phosphorite mines are primarily found in:
* North America: United States, especially Florida, with lesser deposits in North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
, and Tennessee
* Africa: Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, Algeria, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Niger, Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, Togo, Tunisia, Mauritania
* Middle East: Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Iraq, at the town of Akashat, near the Jordanian border.
* Central Asia: Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
* Oceania: Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Makatea, Nauru, and Banaba Island
In 2007, at the current rate of consumption, the supply of phosphorus was estimated to run out in 345 years. However, some scientists thought that a " peak phosphorus" would occur in 30 years and Dana Cordell from Institute for Sustainable Futures said that at "current rates, reserves will be depleted in the next 50 to 100 years". Reserves refer to the amount assumed recoverable at current market prices. In 2012 the USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geograp ...
estimated world reserves at 71 billion tons, while 0.19 billion tons were mined globally in 2011. Phosphorus comprises 0.1% by mass of the average rock (while, for perspective, its typical concentration in vegetation is 0.03% to 0.2%), and consequently there are quadrillions of tons of phosphorus in Earth's 3×1019-ton crust, albeit at predominantly lower concentration than the deposits counted as reserves, which are inventoried and cheaper to extract. If it is assumed that the phosphate minerals in phosphate rock are mainly hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite, phosphate minerals contain roughly 18.5% phosphorus by weight. If phosphate rock contains around 20% of these minerals, the average phosphate rock has roughly 3.7% phosphorus by weight.
Some phosphate rock deposits, such as Mulberry in Florida, are notable for their inclusion of significant quantities of radioactive uranium isotopes. This is a concern because radioactivity can be released into surface waters from application of the resulting phosphate fertilizer.
In December 2012, Cominco Resources announced an updated JORC compliant resource of their Hinda project in Congo-Brazzaville of 531 million tons, making it the largest measured and indicated phosphate deposit in the world.
Around 2018, Norway discovered phosphate deposits almost equal to those in the rest of Earth combined.
In July 2022 China announced quotas on phosphate exportation.
The largest importers in millions of metric tons of phosphate are Brazil 3.2, India 2.9 and the USA 1.6.
Mining
 The three principal phosphate producer countries (China, Morocco and the United States) account for about 70% of world production.
The three principal phosphate producer countries (China, Morocco and the United States) account for about 70% of world production.
Ecology
In ecological terms, because of its important role in biological systems, phosphate is a highly sought after resource. Once used, it is often a limiting nutrient in environments, and its availability may govern the rate of growth of organisms. This is generally true of freshwater environments, whereas nitrogen is more often the limiting nutrient in marine (seawater) environments. Addition of high levels of phosphate to environments and to micro-environments in which it is typically rare can have significant ecological consequences. For example, blooms in the populations of some organisms at the expense of others, and the collapse of populations deprived of resources such as oxygen (see eutrophication) can occur. In the context of pollution, phosphates are one component of total dissolved solids, a major indicator of water quality, but not all phosphorus is in a molecular form that algae can break down and consume. Calcium hydroxyapatite and calcite precipitates can be found aroundbacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
in alluvial topsoil. As clay minerals promote biomineralization, the presence of bacteria and clay minerals resulted in calcium hydroxyapatite and calcite precipitates.
Phosphate deposits can contain significant amounts of naturally occurring heavy metals. Mining operations processing phosphate rock can leave tailings piles containing elevated levels of cadmium, lead, nickel, copper, chromium, and uranium. Unless carefully managed, these waste products can leach heavy metals into groundwater or nearby estuaries. Uptake of these substances by plants and marine life can lead to concentration of toxic heavy metals in food products.
See also
* Diammonium phosphate – * Disodium phosphate – * Metaphosphate – * Monosodium phosphate – * Organophosphorus compounds * Ouled Abdoun Basin * Phosphate conversion coatingReferences
External links
US Minerals Databrowser
provides data graphics covering consumption, production, imports, exports and price for phosphate and 86 other minerals
Phosphate: analyte monograph
– The Association for Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine * {{Authority control Functional groups Phosphorus oxyanions Industrial minerals Concrete admixtures Phosphorus(V) compounds