|
Mammalian Teeth
Teeth are common to most vertebrates, but mammalian teeth are distinctive in having a variety of shapes and functions. This feature first arose among early therapsids during the Permian, and has continued to the present day. All therapsid groups with the exception of the mammals are now extinct, but each of these groups possessed different tooth patterns, which aids with the classification of fossils. Most extant mammals including humans are diphyodonts, i.e. they have an early set of deciduous teeth and a later set of permanent teeth, permanent or "adult" teeth. Notable exceptions are elephants, kangaroos, and manatees, all of which are polyphyodonts, i.e. having teeth that are continuously being replaced. Mammal teeth include incisors, Canine tooth, canines, premolars, and Molar (tooth), molars, not all of which are present in all mammals. Various evolutionary modifications have occurred, such as the lack of canines in Glires, the development of tusks from either incisors (elep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa - Cheetah Experience (48974093898) (cropped)
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', ), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). South is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutheria
Eutheria (from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ), also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of Placentalia, placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials. Eutherians are distinguished from non-eutherians by various phenotypic traits of the feet, ankles, jaws and teeth. All extant eutherians lack epipubic bones, which are present in all other living mammals (marsupials and monotremes). This allows for expansion of the abdomen during pregnancy, though epipubic bones are present in many primitive eutherians. Eutheria was named in 1872 by Theodore Gill; in 1880, Thomas Henry Huxley defined it to encompass a more broadly defined group than Placentalia. The earliest unambiguous eutherians are known from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation of China, dating around 120 million years ago. Two tribosphenic mammals, ''Durlstodon'' and ''Durlstotherium'' from the Berriasian age (~145–140 million years ago) of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
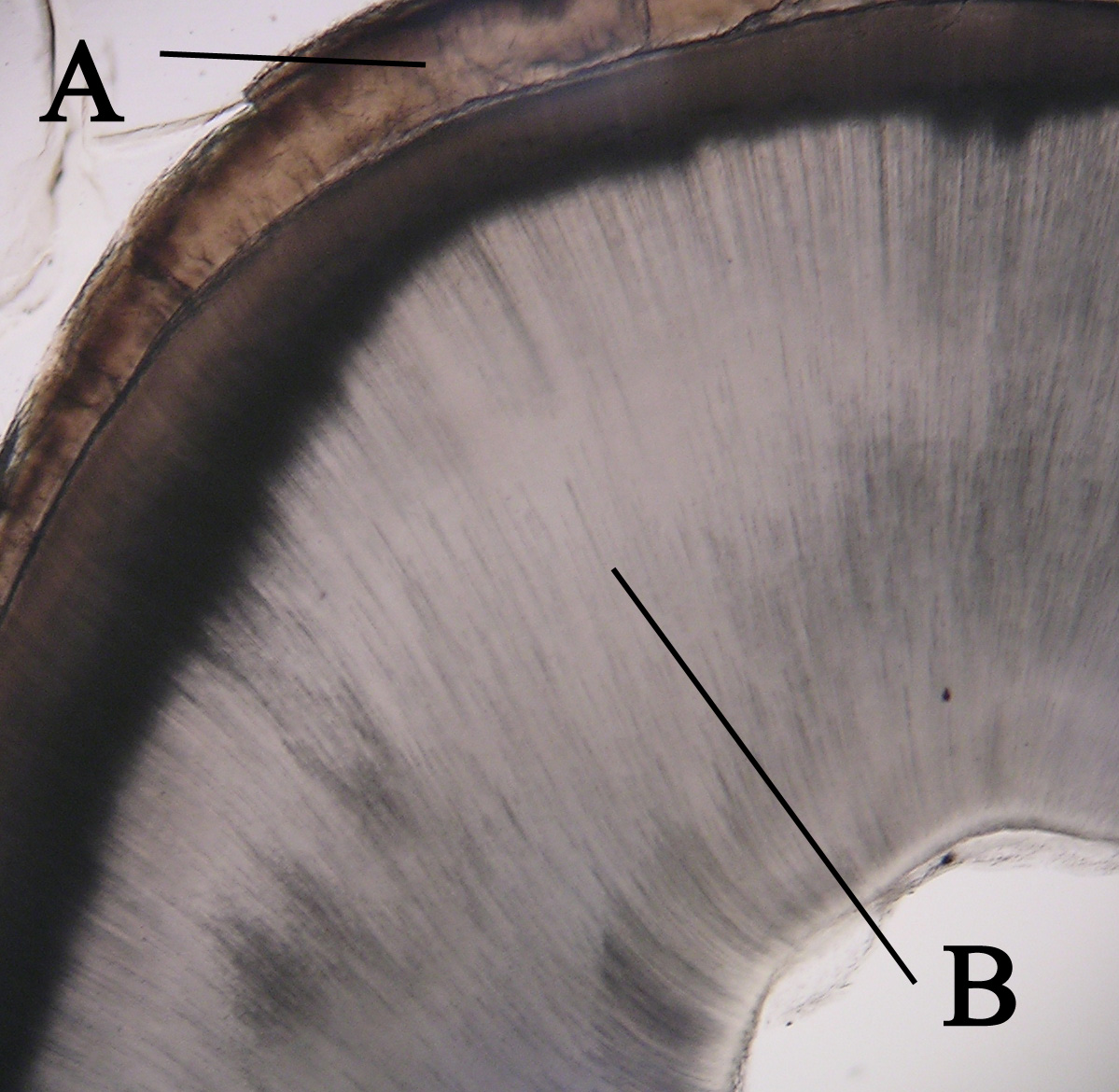
Dentin
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue (biology), tissue of the body and, along with tooth enamel, enamel, cementum, and pulp (tooth), pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Tooth Development
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stages of fetal development. Primary (baby) teeth start to form between the sixth and eighth week of prenatal development, and permanent teeth begin to form in the twentieth week.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nanci, Elsevier, 2013, pages 70-94 If teeth do not start to develop at or near these times, they will not develop at all, resulting in hypodontia or anodontia. A significant amount of research has focused on determining the processes that initiate tooth development. It is widely accepted that there is a factor within the tissues of the first pharyngeal arch that is necessary for the development of teeth. Overview The tooth germ is an aggregation of cells that eventually forms a tooth.University of Texas Medical Branch. These cells are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblasts
Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown. Structure Each ameloblast is a columnar cell approximately 4 micrometers in diameter, 40 micrometers in length and is hexagonal in cross section. The secretory end of the ameloblast ends in a six-sided pyramid-like projection known as the Tomes' process. The angulation of the Tomes' process is significant in the orientation of enamel rods, the basic unit of tooth enamel. Distal terminal bars are junctional complexes that separate the Tomes' processes from ameloblast proper. Development Ameloblasts are derived from oral epithelium tissue of ectodermal origin. Their differentiation from preameloblasts (whose origin is from inner enamel epithelium) is a result of signaling from the ectomesenchymal cells of the dental papilla. Initially the preameloblasts will differentiate into presecretory ameloblasts and then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, Cavia, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (tooth)
In dentistry, the crown is the visible part of the tooth above the gingival margin and is an essential component of dental anatomy. Covered by Tooth enamel, enamel, the crown plays a crucial role in cutting, tearing, and grinding food. Its shape and structure vary depending on the type and function of the tooth (incisors, Canine tooth, canines, premolars, or Molar (tooth), molars), and differ between Deciduous teeth, primary dentition and Permanent teeth, permanent dentition. The crown also contributes to facial aesthetics, speech, and oral health. Anatomical crown vs clinical crown The anatomical crown refers to the portion of the tooth covered by enamel, regardless of whether it is visible. The clinical crown is the part of the tooth that is visible in the mouth. In a healthy young adult, the gums typically follow the contour where enamel meets the root, so the clinical and anatomical crowns are similar in size. However, with age or periodontal disease, this may change. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypsodont
Hypsodont is a pattern of dentition characterized by with high crowns, providing extra material for wear and tear. Some examples of animals with hypsodont dentition are cows and horses; all animals that feed on gritty, fibrous material. The opposite condition is called brachydont. Evolution Since the morphology of the hypsodont tooth is suited to a more abrasive diet, hypsodonty was thought to have evolved concurrently with the spread of grasslands. Grass contains phytoliths, silica-rich granules, which wear away dental tissue more quickly. Analysis has shown, however, that the development of this morphology is out of sync with the spread and flourishing of grasslands. Instead, the ingestion of grit and soil is hypothesized to be the primary driver of hypsodonty, a hypothesis termed the grit, not grass hypothesis. Morphology Hypsodont dentition is characterized by: * high-crowned teeth * A rough, flattish occlusal surface adapted for crushing and grinding * Cementum both ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagomorph
The lagomorphs () are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae (rabbits and hares) and the Ochotonidae ( pikas). There are 110 recent species of lagomorph, of which 109 species in twelve genera are extant, including ten genera of rabbits (42 species); one genus of hare (33 species) and one genus of pika (34 species). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek (, "hare") + (, "form"). Taxonomy and evolutionary history Other names used for this order, now considered synonymous, include: ''Duplicidentata'' (Illiger, 1811); ''Leporida'' (Averianov, 1999); ''Neolagomorpha'' (Averianov, 1999); ''Ochotonida'' (Averianov, 1999); and ''Palarodentia'' (Haeckel, 1895; Lilian, 2016). The evolutionary history of the lagomorphs is still not well understood. In the late 20th century, it was generally agreed that '' Eurymylus'', which lived in eastern Asia and dates back to the late Paleocene or early Eocene, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbit
Rabbits are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also includes the hares), which is in the order Lagomorpha (which also includes pikas). They are familiar throughout the world as a small herbivore, a prey animal, a domesticated form of livestock, and a pet, having a widespread effect on ecologies and cultures. The most widespread rabbit genera are '' Oryctolagus'' and '' Sylvilagus''. The former, ''Oryctolagus'', includes the European rabbit, ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'', which is the ancestor of the hundreds of breeds of domestic rabbit and has been introduced on every continent except Antarctica. The latter, ''Sylvilagus'', includes over 13 wild rabbit species, among them the cottontails and tapetis. Wild rabbits not included in ''Oryctolagus'' and ''Sylvilagus'' include several species of limited distribution, including the pygmy rabbit, volcano rabbit, and Sumatran striped rabbit. Rabbits are a paraphyletic grouping, and do not constitute a clade, as ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a relatively undeveloped state and then nurtured within a pouch on their mother's abdomen. Extant marsupials encompass many species, including Kangaroo, kangaroos, Koala, koalas, Opossum, opossums, Phalangeriformes, possums, Tasmanian devil, Tasmanian devils, Wombat, wombats, Wallaby, wallabies, and Bandicoot, bandicoots. Marsupials constitute a clade stemming from the last common ancestor of extant Metatheria, which encompasses all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to Placentalia, placentals. The evolutionary split between placentals and marsupials occurred 125-160 million years ago, in the Middle Jurassic-Early Cretaceous period. Presently, close to 70% of the 334 extant marsupial species are concentrated on the Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |