Pannonian Avars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of
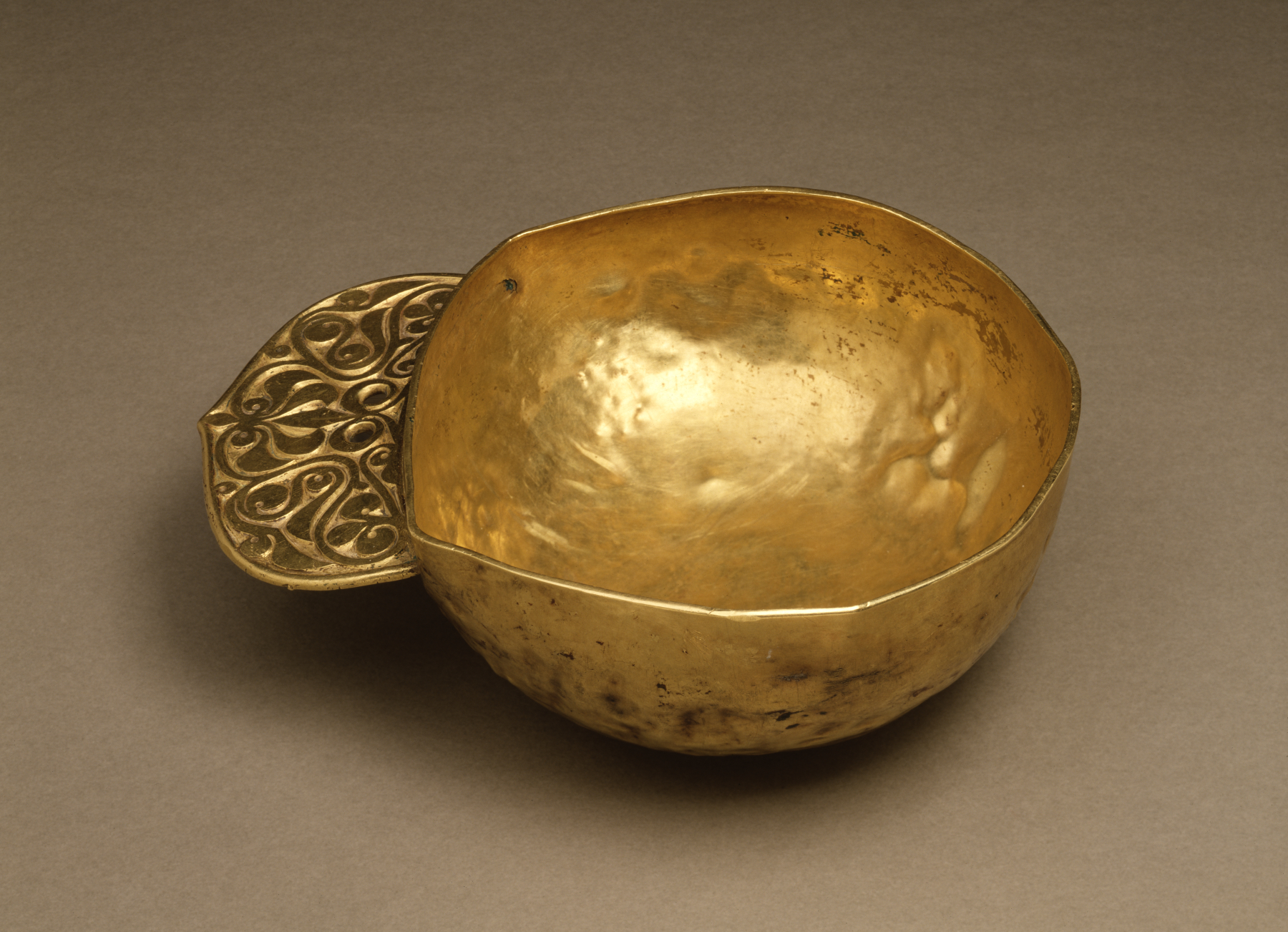
 According to the interpretation of Dobrovits and Nechaeva, the Turks insisted that the Avars were only "pseudo-Avars", so as to boast that they were the only formidable power in the Eurasian steppe. The Göktürks claimed that the "real Avars" remained loyal subjects of the Turks, farther east. A political name *''(A)Par'' 𐰯𐰻 was indeed mentioned in inscriptions honoring Kul Tigin and Bilge Qaghan, yet in Armenian sources ( Egishe Vardapet, Ghazar Parpetsi, and Sebeos) ''Apar'' seemingly indicated "a geographical area ( Khorasan), which might also intimate a political formation once there"; additionally, "'Apar-shar', that is, ''the country of the Apar''" was named after possibly
According to the interpretation of Dobrovits and Nechaeva, the Turks insisted that the Avars were only "pseudo-Avars", so as to boast that they were the only formidable power in the Eurasian steppe. The Göktürks claimed that the "real Avars" remained loyal subjects of the Turks, farther east. A political name *''(A)Par'' 𐰯𐰻 was indeed mentioned in inscriptions honoring Kul Tigin and Bilge Qaghan, yet in Armenian sources ( Egishe Vardapet, Ghazar Parpetsi, and Sebeos) ''Apar'' seemingly indicated "a geographical area ( Khorasan), which might also intimate a political formation once there"; additionally, "'Apar-shar', that is, ''the country of the Apar''" was named after possibly
Eurasian nomads
Eurasian nomads form groups of nomad, nomadic peoples who have lived in various areas of the Eurasian Steppe. History largely knows them via frontier historical sources from Europe and Asia.
The steppe nomads had no permanent abode, but travelle ...
of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks
The Göktürks (; ), also known as Türks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks, were a Turkic people in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and his sons, succeeded the Rouran Khaganate as the main powe ...
. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorpholog ...
and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
from the late 6th to the early 9th century.
The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian Steppe is a steppe extending across Eastern Europe to Central Asia, formed by the Caspian and Pontic steppes. It stretches from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the ''Pontus Euxinus'' of antiquity) to the northern a ...
as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and destruction in the Avar–Byzantine wars
The Avar–Byzantine wars were a series of conflicts between the Byzantine Empire and the Avar Khaganate. The conflicts were initiated in 568, after the Avars arrived in Pannonia, and claimed all the former land of the Gepids and Lombards as the ...
from 568 to 626 and influence on the Slavic migrations to Southeastern Europe
Early Slavs began mass migrating to Southeastern Europe between the first half of the 6th and 7th century in the Early Middle Ages. The rapid demographic spread of the Slavs was followed by a population exchange, mixing and language shift to and ...
.
Recent archaeogenetic studies indicate that the Pannonian Avars were of primarily Ancient Northeast Asian ancestry similar to those of modern-day people from Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
and the Amur River
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ''proper'' is ...
region in Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
, pointing to an initial rapid migration of nomadic tribes into the centre of Europe from the Eastern Eurasian Steppe. The Pannonian Avars' core may have been descended from the remnants of the Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
, which were accompanied by other Steppe groups.
Origins
Avars and pseudo-Avars
The earliest clear reference to the Avar ethnonym comes from Priscus the Rhetor (420s–after 472), who recounts that in c. 463 the Šaragurs and Onogurs were attacked by the Sabirs, who had been attacked by the Avars. In turn, the Avars had been driven off by people fleeing "man-eatinggriffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (; Classical Latin: ''gryps'' or ''grypus''; Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk ...
s" coming from "the ocean" (''Priscus Fr 40''). Whilst Priscus' accounts provide some information about the ethno-political situation in the Don-Kuban
Kuban ( Russian and Ukrainian: Кубань; ) is a historical and geographical region in the North Caucasus region of southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Don Steppe, the Volga Delta and separated fr ...
-Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
region after the demise of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, no unequivocal conclusions can be reached. Denis Sinor
Denis Sinor (born Dénes Zsinór, April 17, 1916 in Kolozsvár (Austria-Hungary, now Cluj-Napoca, Romania) – January 12, 2011 in Bloomington, Indiana) was a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Central Asian Studies at the Department of C ...
has argued that whoever the "Avars" referred to by Priscus were, they differed from the Avars who appear a century later, during the time of Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
(r. 527–565).
The next author to discuss the Avars, Menander Protector, appeared during the 6th century and wrote of Göktürk embassies to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
in 565 and 568. The Turks appeared angry at the Byzantines for having made an alliance with the Avars, whom the Turks saw as their subjects and slaves. Turxanthos, a Turk prince, calls the Avars "Varchonites" and "escaped slaves of the Turks", who numbered "about 20 thousand" (''Menander Fr 43'').
Many more, but somewhat confusing, details come from Theophylact Simocatta, who in c. 629, describes the final two decades of the 6th century. In particular, he claims to quote a triumph letter from Turxanthos:

 According to the interpretation of Dobrovits and Nechaeva, the Turks insisted that the Avars were only "pseudo-Avars", so as to boast that they were the only formidable power in the Eurasian steppe. The Göktürks claimed that the "real Avars" remained loyal subjects of the Turks, farther east. A political name *''(A)Par'' 𐰯𐰻 was indeed mentioned in inscriptions honoring Kul Tigin and Bilge Qaghan, yet in Armenian sources ( Egishe Vardapet, Ghazar Parpetsi, and Sebeos) ''Apar'' seemingly indicated "a geographical area ( Khorasan), which might also intimate a political formation once there"; additionally, "'Apar-shar', that is, ''the country of the Apar''" was named after possibly
According to the interpretation of Dobrovits and Nechaeva, the Turks insisted that the Avars were only "pseudo-Avars", so as to boast that they were the only formidable power in the Eurasian steppe. The Göktürks claimed that the "real Avars" remained loyal subjects of the Turks, farther east. A political name *''(A)Par'' 𐰯𐰻 was indeed mentioned in inscriptions honoring Kul Tigin and Bilge Qaghan, yet in Armenian sources ( Egishe Vardapet, Ghazar Parpetsi, and Sebeos) ''Apar'' seemingly indicated "a geographical area ( Khorasan), which might also intimate a political formation once there"; additionally, "'Apar-shar', that is, ''the country of the Apar''" was named after possibly Hephthalites
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian languages, Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to ...
, who were known as 滑 MC *''ɦˠuɛt̚'' > Ch.''Huá'' in Chinese sources. Even so, *''Apar'' could not be linked to the European Avars, notwithstanding any link, if there were, between the Hephthalites and Rourans. Furthermore, Dobrovits has questioned the authenticity of Theophylact's account. As such, he has argued that Theophylact borrowed information from Menander's accounts of Byzantine–Turk negotiations to meet political needs of his time–i.e. to castigate and deride the Avars during a time of strained political relations between the Byzantines and Avars (coinciding with Emperor Maurice's northern Balkan campaigns).
Paul the Deacon
Paul the Deacon
Paul the Deacon ( 720s 13 April in 796, 797, 798, or 799 AD), also known as ''Paulus Diaconus'', ''Warnefridus'', ''Barnefridus'', or ''Winfridus'', and sometimes suffixed ''Cassinensis'' (''i.e.'' "of Monte Cassino"), was a Benedictine monk, sc ...
in his ''History of the Lombards
The ''History of the Lombards'' or the ''History of the Langobards'' () is the chief work by Paul the Deacon, written in the late 8th century. This incomplete history in six books was written after 787 and at any rate no later than 796, maybe at ...
'' insisted that Avars were known previously as Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
and he conflated the two groups.
Uar, Rouran and other Central Asian peoples
According to some scholars, the Pannonian Avars originated from a confederation formed in theAral Sea
The Aral Sea () was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan to its north and Uzbekistan to its south, which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up into desert by the 2010s. It was in the Aktobe and Kyzylorda regions of Kazakhst ...
region, by the Uar (also known as the ''Ouar'', ''Warr'' or ''Var'') and the Xionites. The Xionites had likely been speakers of Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
and/or Turkic languages. The Hephthalites, affiliated previously to the Uar and Xionites, had remained in Central and northern South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. The Pannonian Avars were also known by names including ''Uarkhon'' or ''Varchonites''which may have been a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
combining ''Var'' and ''Chunni''.
The 18th-century historian Joseph de Guignes postulates a link between the Avars of European history with the Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
of Inner Asia
Inner Asia refers to the northern and landlocked regions spanning North Asia, North, Central Asia, Central, and East Asia. It includes parts of Western China, western and northeast China, as well as southern Siberia. The area overlaps with some d ...
based on a coincidence between Tardan Khan's letter to Constantinople and events recorded in Chinese sources, notably the '' Wei Shu'' and '' Bei Shi''. Chinese sources state that Bumin Qaghan, founder of the First Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of Bu ...
, defeated the Rouran, some of whom fled and joined the Western Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Western Wei (), was an imperial dynasty of China that followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei. One of the Northern dynasties during the era of the Northern and Southern dynasties, it ruled the weste ...
. Later, Bumin's successor Muqan Qaghan defeated the Hephthalites as well as the Turkic Tiele. Superficially these victories over the Tiele, Rouran and Hephthalites echo a narrative in the ''Theophylact'', boasting of Tardan's victories over the Hephthalites, Avars and Oghurs. However, the two series of events are not synonymous: the events of the latter took place during Tardan's rule, c. 580–599, whilst Chinese sources referring to the Turk defeat of the Rouran and other Central Asian peoples occurred 50 years earlier, at the founding of the First Turkic Khaganate. It is for this reason that the linguist János Harmatta rejected the identification of the Avars with the Rouran on this basis.
According to Edwin G. Pulleyblank, the name Avar is the same as the prestigious name Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', <
Tungusic origin. A study by Emil Heršak and Ana Silić (2002) suggests that the Avars were of heterogeneous origin, including mostly Turkic (Oghuric) and Mongolic groups. Later in Europe some Germanic and Slavic groups were assimilated into the Avars. Heršak and Silić concluded that their exact origin is unknown but stated that it is likely that the Avars were originally mainly composed of Turkic (Oghuric) tribes.
Increasing evidence supports a relationship between the elite of the Pannonian Avars and the Inner Asian
 In 2003, Walter Pohl summarized the formation of
In 2003, Walter Pohl summarized the formation of
 A genetic study published in scientific journal '' Cell'' in April 2022 analyzed 48 Pannonian Avar samples from the early, middle and late period, and found nearly all of them to have a high level of Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA) ancestry. The paternal lineage N1a1a1a1a3a-F4205 was most common (today highest percent of haplogroup N-F4205 was found in Dukha people of Mongolia with 52.2%), with Q1a, Q1b, R1a, R1b and E1b subclades present in smaller numbers. The samples had a strong affinity with modern peoples inhabiting the region from
A genetic study published in scientific journal '' Cell'' in April 2022 analyzed 48 Pannonian Avar samples from the early, middle and late period, and found nearly all of them to have a high level of Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA) ancestry. The paternal lineage N1a1a1a1a3a-F4205 was most common (today highest percent of haplogroup N-F4205 was found in Dukha people of Mongolia with 52.2%), with Q1a, Q1b, R1a, R1b and E1b subclades present in smaller numbers. The samples had a strong affinity with modern peoples inhabiting the region from  A genetic study published in scientific journal ''
A genetic study published in scientific journal ''
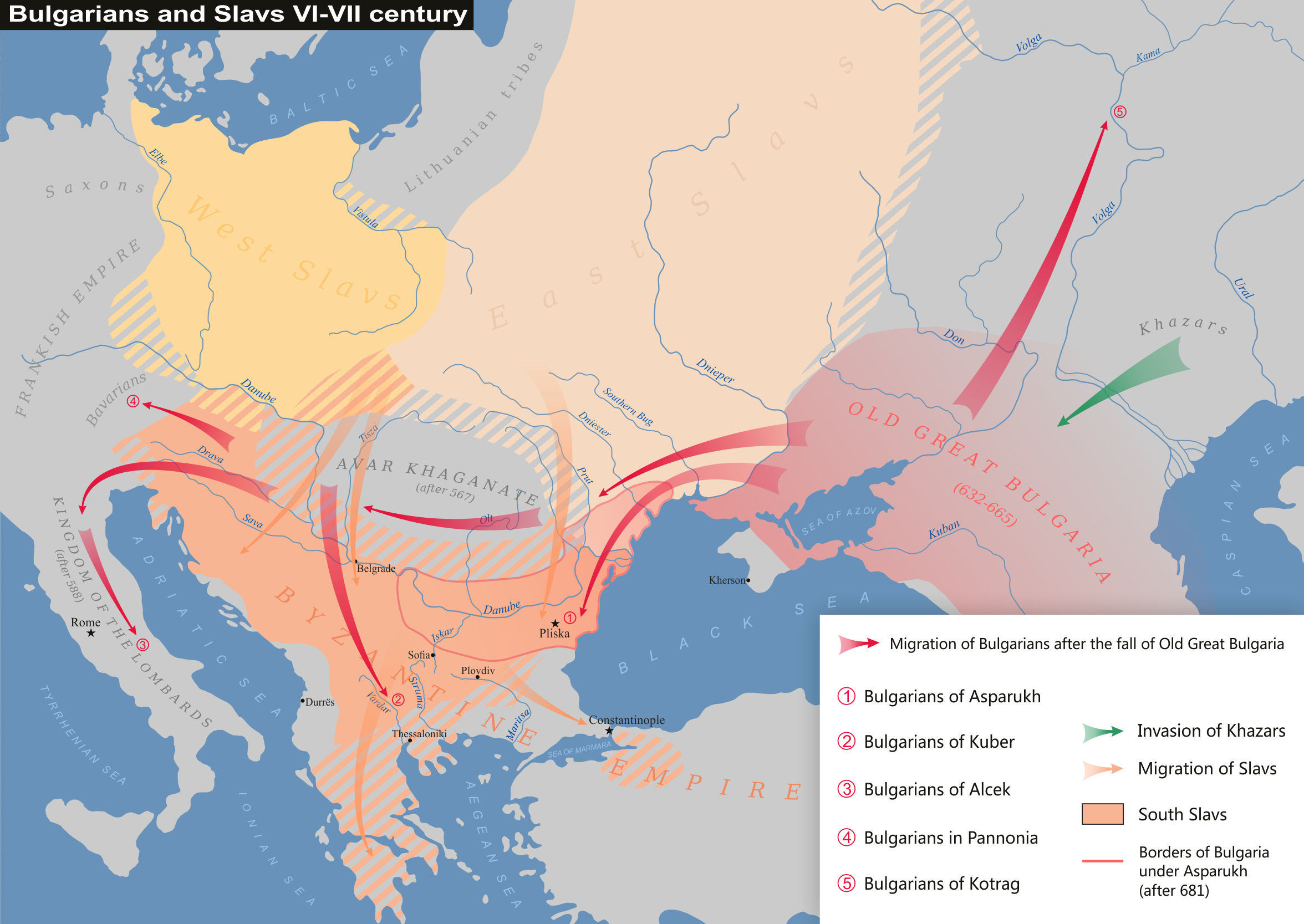
 With the death of Samo in 658 and Kubrat in 665, some Slavic tribes again came under Avar rule. Despite their father's advice, Kubrat's sons failed to maintain cohesion in Old Great Bulgaria which began to disintegrate. A few years later in the time of Batbayan, Old Great Bulgaria dissolved into five branches. From western Onoguria the first group of folk moved to Ravenna under Alzeco in the 650s. According to Book II of the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', a certain Avar Chagan seized his opportunity to coalesce in the regions further north in response to the secession of the Diocese of
With the death of Samo in 658 and Kubrat in 665, some Slavic tribes again came under Avar rule. Despite their father's advice, Kubrat's sons failed to maintain cohesion in Old Great Bulgaria which began to disintegrate. A few years later in the time of Batbayan, Old Great Bulgaria dissolved into five branches. From western Onoguria the first group of folk moved to Ravenna under Alzeco in the 650s. According to Book II of the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', a certain Avar Chagan seized his opportunity to coalesce in the regions further north in response to the secession of the Diocese of 
 A new type of ceramics—the so-called "
A new type of ceramics—the so-called "
 The gradual decline of Avar power accelerated to a rapid fall. A series of Frankish campaigns, beginning from 788, ended with the conquest of the Avar realm within a decade. Initial conflict between Avars and Franks occurred soon after the Frankish deposition of Bavarian duke Tassilo III and the establishment of direct Frankish rule over
The gradual decline of Avar power accelerated to a rapid fall. A series of Frankish campaigns, beginning from 788, ended with the conquest of the Avar realm within a decade. Initial conflict between Avars and Franks occurred soon after the Frankish deposition of Bavarian duke Tassilo III and the establishment of direct Frankish rule over
 The Pannonian Basin was the centre of the Avar power base. The Avars resettled captives from the peripheries of their empire to more central regions. Avar material culture is found south to Macedonia. However, to the east of the Carpathians, there are next to no Avar archaeological finds, suggesting that they lived mainly in the
The Pannonian Basin was the centre of the Avar power base. The Avars resettled captives from the peripheries of their empire to more central regions. Avar material culture is found south to Macedonia. However, to the east of the Carpathians, there are next to no Avar archaeological finds, suggesting that they lived mainly in the
– YouTube
Documentary with Gyula László in Hungarian, on state television channel Duna. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * p. 221 * * * *
{{DEFAULTSORT:Avar States and territories established in the 560s States and territories disestablished in the 820s Medieval history of Bulgaria Medieval history of Russia Medieval history of Ukraine Hungary in the Early Middle Ages Romania in the Early Middle Ages Moldova in the Early Middle Ages Avars Migration Period Medieval ethnic groups of Europe Barbarian kingdoms Turco-Mongol 6th-century establishments in Europe 9th-century disestablishments in Europe 560s establishments 820s disestablishments
Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
; however it remains unclear to what extent the European Avars descent from the Rouran population. It is argued that the initial elite core of the Pannonian Avars spoke a Para-Mongolic language (Serbi-Avar), which is a sister lineage to contemporary Mongolic languages
The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in North Asia, East Asia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this languag ...
.Shimunek, Andrew (2017). ''Languages of Ancient Southern Mongolia and North China: a Historical-Comparative Study of the Serbi or Xianbei Branch of the Serbi-Mongolic Language Family, with an Analysis of Northeastern Frontier Chinese and Old Tibetan Phonology''. Wiesbaden
Wiesbaden (; ) is the capital of the German state of Hesse, and the second-largest Hessian city after Frankfurt am Main. With around 283,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 24th-largest city. Wiesbaden form ...
: Harrassowitz Verlag. . OCLC
OCLC, Inc. See also: is an American nonprofit cooperative organization "that provides shared technology services, original research, and community programs for its membership and the library community at large". It was founded in 1967 as the ...
993110372.
Steppe empire dynamics and ethnogenesis
 In 2003, Walter Pohl summarized the formation of
In 2003, Walter Pohl summarized the formation of nomadic empire
Nomadic empires, sometimes also called steppe empires, Central or Inner Asian empires, were the empires erected by the bow-wielding, horse-riding, nomadic people in the Eurasian Steppe, from classical antiquity (Scythia) to the early modern era ...
s:
1. Many steppe empires were founded by groups who had been defeated in previous power struggles but had fled from the dominion of the stronger group. The Avars were likely a losing faction previously subordinate to the Ashina clan in the Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate () was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after the split of the First Turkic Khaganate (founded in the 6th century o ...
, and they fled west of the Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with ...
.
2. These groups usually were of mixed origin, and each of its components was part of a previous group.
3. Crucial in the process was the elevation of a khagan, which signified a claim to independent power and an expansionist
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who ...
strategy. This group also needed a new name that would give all of its initial followers a sense of identity.
4. The name for a new group of steppe riders was often taken from a repertoire of prestigious names which did not necessarily denote any direct affiliation to or descent from groups of the same name; in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, Avars, Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
, and Ogurs, or names connected with -(o)gur ( Kutrigurs, Utigurs, Onogurs, etc.), were most important. In the process of name-giving, both perceptions by outsiders and self-designation played a role. These names were also connected with prestigious traditions that directly expressed political pretensions and programmes, and had to be endorsed by success. In the world of the steppe, where agglomerations of groups were rather fluid, it was vital to know how to deal with a newly-emergent power. The symbolical hierarchy of prestige expressed through names provided some orientation for friend and foe alike.
Such views are mirrored by . "The ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is the formation and development of an ethnic group. This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th-century neologism that was later introduce ...
of early medieval peoples of steppe origin cannot be conceived in a ''single linear'' fashion due to their great and constant mobility", with no ethnogenetic "point zero", theoretical "proto-people" or proto-language. Moreover, Avar identity was strongly linked to Avar political institutions. Groups who rebelled or fled from the Avar realm could never be called "Avars", but were rather termed "Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
". Similarly, with the final demise of Avar power in the early 9th century, Avar identity disappeared almost instantaneously.
Savelyev and Jeong (2020) in "''Early nomads of the Eastern Steppe and their tentative connections in the West''" concluded that the initial Pannonian Avars formed in Central Asia from various ethno-linguistic groups, including Iranian peoples
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European langu ...
, Ugrians, Oghur-Turks, and Rouran
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
tribes. They further note that "the broadly East Asian component in the archaeological record of the European Avars is limited even in the earlier period of their history; elements originating from West Asia, the Caucasus, the Southern Russian steppes and the local Central European cultures can be traced alongside each other".
Subsequent analyses from 2022 on Avar remains however confirmed their Ancient Northeast Asian origin, and support a possible ethnogenesis of the Avar Elite from the former Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
.
Anthropology
In the Stuttgart Psalter there is an image of mounted archers riding backwards on their horses, a noted "Asian" tactic, which may depict the Avars. According to mid-20th century physical anthropologists such as Pál Lipták, human remains from the early Avar (7th century) period had mostly " Europoid" features, whilegrave goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are items buried along with a body.
They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into an afterlife, or offerings to gods. Grave goods may be classed by researche ...
indicated cultural links to the Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan, Siberia, Europea ...
. Cemeteries dated to the late Avar period (8th century) included many human remains with physical features typical of East Asian people
East Asian people (also East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% ...
or Eurasians (i.e., people with both East Asian and European ancestry). Remains with East Asian or Eurasian features were found in about one third of the Avar graves from the 8th century. According to Lipták, 79% of the population of the Danube-Tisza region during the Avar period showed Europoid characteristics. However, Lipták used racial terms later deprecated or regarded as obsolete, such as "Mongoloid
Mongoloid () is an obsolete racial grouping of various peoples indigenous to large parts of Asia, the Americas, and some regions in Europe and Oceania. The term is derived from a now-disproven theory of biological race. In the past, other terms ...
" for northeast Asian and " Turanid" for individuals of mixed ancestry. Several theories suggest that the ruling class of the Avars were of Northern East Asian origin resembling the "Tungid type" (common among Tungusic speaking peoples).
Archaeogenetics
A genetic study published in ''Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely ...
'' in September 2016 examined the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of 31 people buried in the Carpathian Basin between the 7th and 9th centuries. They were found to be mostly carrying European haplogroups such as H, K, T and U, while about 15% carried Asian haplogroups such as C, M6, D4c1 and F1a. Their mtDNA were found to be primarily characteristic of Eastern and Southern Europe.
A genetic study published in the ''American Journal of Physical Anthropology
The ''American Journal of Biological Anthropology''Info pages about the renaming are: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/page/journal/26927691/homepage/productinformation.html and https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/26927691 (previously known as ...
'' in 2018 examined 62 individuals buried in the 8th and 9th centuries at an Avar-Slavic burial in Cífer‐Pác, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
. Of the 46 samples of mtDNA extracted, 93% belonged to west Eurasian lineages, while 6% belonged to east Eurasian lineages. The amount of east Eurasian lineages was higher than among modern European populations, but lower than what has been found in other genetic studies on the Avars. The mtDNA of the examined individuals was found to be quite similar to medieval and modern Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
, and it was suggested that the mixed population examined had emerged through intermarriage between Avar males and Slavic females.
A genetic study published in ''Scientific Reports'' in November 2019 examined the remains of fourteen Avar males. Eleven of them were dated to the early Avar period, and three were dated to the middle and late Avar period. The eleven early Avar males were found to be carrying the paternal haplogroups N1a1a1a1a3 (four samples), N1a1a (two samples), R1a1a1b2a (two samples), C2, G2a, and I1. The three males dated to the middle and late Avar period carried the paternal haplogroups C2, N1a1a1a1a3 and E1b1b1a1b1a. In short, most carried "East Eurasian Y haplogroups typical for modern north-eastern Siberian and Buryat populations". The Avars studied were all determined to have had dark eyes and dark hair, and the majority of them were found to be primarily of East Asian origin.
A genetic study published in ''Scientific Reports'' in January 2020 examined the remains of 26 individuals buried at various elite Avar cemeteries in the Pannonian Basin dated to the 7th century. The mtDNA of these Avars belonged mostly to East Asian haplogroups, while the Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the Y ...
was exclusively of East Asian origin and "strikingly homogenous", belonging to haplogroups N-M231 and Q-M242. The evidence suggests that the Avar elite were largely patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritanc ...
and endogamous for centuries, and entered the Pannonian Basin through migrations from East Asia involving both men and women. Another 2020 study, but of Xiongnu remains in East Asia, found that the Xiongnu shared certain paternal (N1a, Q1a, R1a-Z94 and R1a-Z2124) and maternal haplotypes with the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
and Avars, and says on this basis that they were descended from Xiongnu, who they in turn suggested were descended from Scytho-Siberians.
 A genetic study published in scientific journal '' Cell'' in April 2022 analyzed 48 Pannonian Avar samples from the early, middle and late period, and found nearly all of them to have a high level of Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA) ancestry. The paternal lineage N1a1a1a1a3a-F4205 was most common (today highest percent of haplogroup N-F4205 was found in Dukha people of Mongolia with 52.2%), with Q1a, Q1b, R1a, R1b and E1b subclades present in smaller numbers. The samples had a strong affinity with modern peoples inhabiting the region from
A genetic study published in scientific journal '' Cell'' in April 2022 analyzed 48 Pannonian Avar samples from the early, middle and late period, and found nearly all of them to have a high level of Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA) ancestry. The paternal lineage N1a1a1a1a3a-F4205 was most common (today highest percent of haplogroup N-F4205 was found in Dukha people of Mongolia with 52.2%), with Q1a, Q1b, R1a, R1b and E1b subclades present in smaller numbers. The samples had a strong affinity with modern peoples inhabiting the region from Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
to the Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
, with a historical Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate ( Chinese: zh, c=, p=Róurán, label=no), also known as Ruanruan or Juan-juan ( zh, c=, p=Ruǎnruǎn, label=no) (or variously ''Jou-jan'', ''Ruruan'', ''Ju-juan'', ''Ruru'', ''Ruirui'', ''Rouru'', ''Rouruan'' or ''Tantan'') ...
sample, and with samples from Xiongnu-Xianbei periods in the eastern Asian steppe. The Avar individuals showed their highest genetic affinity with present-day Mongolic and Tungusic peoples, as well as Nivkhs.
 A genetic study published in scientific journal ''
A genetic study published in scientific journal ''Current Biology
''Current Biology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers all areas of biology, especially molecular biology, cell biology, genetics, neurobiology, ecology, and evolutionary biology. The journal includes research artic ...
'' in May 2022 examined 143 Avar samples from various periods, including Avar elites and local commoners. It confirmed the Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA) paternal and maternal origin for the Avar elite, with N1a-F4205 being their predominant and characteristic paternal lineage, alongside incorporated Q1a2a1 and R1a-Z94 Hunnic-Iranian remnants, and the rest belonging to local haplogroups found among surrounding populations. Autosomally, the Elite Avar samples "''preserved very ancient Mongolian pre-Bronze Age genomes, with ca 90% ncient North-East Asianancestry''", shared deep ancestry with European Huns, but although since Early Avar period started mixing with local and immigrant Hunnic-Iranian related populations, "''people with different genetic ancestries were seemingly distinguished, as samples with Hun-related genomes were buried in separate cemeteries''". The majority of the Avar Khaganate general population consisted of local European peoples (EU_core) but did not display Northeast Asian admixture, supporting a model of elite dominance of arriving horse nomads over a large sedentary population, with at least some subsequent admixture events. Genetic data on later Avar elite samples showed continuity with earlier Avars and the long-term presence of Northeast Asian ancestry among the Avar elite, suggesting a possible endogamous social system. There was however an increase of Northeast Asian and Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian ...
associated ancestry among the total population, suggesting either further migration from the Eurasian Steppe and admixture between local and Avar groups, or substructure among the overall population not observed before.
Wang et al. 2025 analyzed 722 remains from the periphery of the Avar Khaganate in Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
dating to 650–800 CE, specifically from sites in present-day Leobersdorf and Mödling
Mödling () is the capital of the Austrian Mödling (district), district of the same name located approximately 15 km south of Vienna.
Mödling lies in Lower Austria's industrial zone (Industrieviertel). The Mödlingbach, a brook which rises ...
, Lower Austria
Lower Austria ( , , abbreviated LA or NÖ) is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Major cities are Amstetten, Lower Austria, Amstetten, Krems an der Donau, Wiener Neustadt and Sankt Pölten, which ...
. Although both sites displayed a shared material culture, the remains from Leobersdorf displayed mostly East Asian
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
ancestry, while the remains from Mödling displayed mostly European-like ancestry. The archaeogenetic data revealed that even after 200 years since the arrival of the 'core Avars' from present-day Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, East Asian ancestry remained dominant among their elite, but apparently also among non-elite groups in periphery areas, as is the case for Leobersdorf. According to the authors, this can primarily be explained via "systematically choosing partners with similar ancestry from other sites in the Avar realm", until the assimilation of the Avar Khaganate into the Frankish empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
starting at 800 CE, with the last Avar prince being mentioned in 822 CE. The male Avar remains from Leobersdorf carried primarily the paternal haplogroup C-M217, while a minority carried haplogroup O-M175 and haplogroup R1a, in contrast, the male remains from Mödling displayed a more heterogeneous variation, including mostly local haplogroups, and only a minority carrying haplogroup C-M217 or N1a. The authors note that "what the evidence from Leobersdorf crucially shows is that entire groups of mostly Asian ancestry did not display elite or warrior status any more in the 8th century, and had moved out of the core area of the Avar realm", beyond that, non-Asian locals were fully assimilated into 'Avar culture', indistinguishable in terms of material culture.
History
Arrival in Europe
In 557, the Avars sent an embassy toConstantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, presumably from the northern Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
. This marked their first contact with the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. In exchange for gold, they agreed to subjugate the "unruly ''gentes''" on behalf of the Byzantines: subsequently they conquered and incorporated various nomadic tribes Kutrigurs and Sabirsand defeated the Antes.
By 562 the Avars controlled the lower Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
basin and the steppes north of the Black Sea. By the time they arrived in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, the Avars formed a heterogeneous group of about 20,000 horsemen. After the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
bought them off, they pushed northwestwards into Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
. However, Frankish opposition halted the Avars' expansion in that direction. Seeking rich pastoral lands, the Avars initially demanded land south of the Danube in present-day Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, but the Byzantines refused, using their contacts with the Göktürks as a threat against Avar aggression. The Avars turned their attention to the Carpathian Basin and to the natural defenses it afforded. The Carpathian Basin was occupied by the Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the G ...
. In 567 the Avars formed an alliance with the Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
enemies of the Gepidsand together they destroyed much of the Gepid kingdom. The Avars then persuaded the Lombards to move into northern Italy
Northern Italy (, , ) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four Northwest Italy, northwestern Regions of Italy, regions of Piedmo ...
, an invasion that marked the last Germanic mass-movement in the Migration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories ...
.
Continuing their successful policy of turning the various barbarians against each other, the Byzantines persuaded the Avars to attack the Sclavenes in Scythia Minor, a land rich with goods. After devastating much of the Sclavenes' land, the Avars returned to Pannonia after many of the khagan's subjects deserted to the Byzantine emperor.
Early Avar period (580–670)
By about 580, the Avar KhaganBayan I
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602.
As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'', ...
had established supremacy over most of the Slavic, Germanic and Bulgar tribes living in Pannonia and the Carpathian Basin. When the Byzantine Empire was unable to pay subsidies or hire Avar mercenaries, the Avars raided their Balkan territories. According to Menander, Bayan I commanded an army of 10,000 Kutrigur Bulgars and sacked Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
in 568, effectively cutting the Byzantine terrestrial link with northern Italy and western Europe.
In the 580s and 590s, many of the imperial armies were busy fighting the Persians, and the remaining troops in the Balkans were no match for the Avars. By 582, the Avars had captured Sirmium, an important fort in Pannonia. When the Byzantines refused to increase the stipend amount as requested by Bayan's son and successor Bayan II, the Avars proceeded to capture Singidunum
Singidunum ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Сингидунум, Singidunum) was an ancient city which later evolved into modern Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. The name is of Celtic origin, going back to the time when the Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the a ...
(Belgrade) and Viminacium
Viminacium (also ''Viminatium)'' was a major city, military camp, and the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman province of Moesia (modern-day Serbia). Following the division of Moesia in 87, following Domitian's Domitian's Dacian War, Dacian War, i ...
. They suffered setbacks, however, during Maurice's Balkan campaigns
Maurice's Balkan campaigns were a series of military expeditions conducted by Byzantine emperor, Roman Emperor Maurice (emperor), Maurice (reigned 582–602) in an attempt to defend the Balkans, Balkan provinces of the Byzantine Empire, Roman Empi ...
in the 590s.
By 600 the Avars had established a nomadic empire ruling over a multitude of peoples and stretching from modern Austria in the west to the Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian Steppe is a steppe extending across Eastern Europe to Central Asia, formed by the Caspian and Pontic steppes. It stretches from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the ''Pontus Euxinus'' of antiquity) to the northern a ...
in the east. After being defeated at the Battles of Viminacium
The Battles of Viminacium were a series of three battles fought against the Avars by the Eastern Roman Empire. They were decisive Roman successes, which were followed by an invasion of Pannonia.
In summer 599, the East Roman Emperor Maurice ...
in their homeland, some Avars defected to the Byzantines in 602, but Emperor Maurice decided not to return home as was customary. He maintained his army camp beyond the Danube throughout the winter, but the hardship caused the army to revolt, giving the Avars a desperately needed respite and they attempted an invasion of northern Italy in 610. The Byzantine civil war prompted a Persian invasion in the Byzantine–Sasanian War, and after 615 the Avars enjoyed a free hand in the undefended Balkans.
While negotiating with Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
beneath the walls of Constantinople in 617, the Avars launched a surprise attack. While they were unable to capture the city centre, they pillaged the suburbs and took 270,000 captives. Payments in gold and goods to the Avars reached a sum of 200,000 '' solidi'' shortly before 626. In 626, the Avars cooperated with the Sassanid
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
force in the failed siege of 626. After the defeat, the political and military power of the Avars declined. Byzantine and Frankish sources documented a war between the Avars and their western Slav clients, the Wends
Wends is a historical name for Slavs who inhabited present-day northeast Germany. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying ...
.
In the 630s, Samo
Samo (–) was the founder and sole ruler of the first recorded political union of Slavs, Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire ("realm", "kingdom", or "tribal union"), ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to Fredegarius, the only ...
, the ruler of the first Slavic polity known as Samo's Tribal Union or Samo's realm, increased his authority over lands to the north and west of the Khaganate at the expense of the Avars, ruling until his death in 658. The ''Chronicle of Fredegar
The ''Chronicle of Fredegar'' is the conventional title used for a 7th-century Frankish chronicle that was probably written in Burgundy. The author is unknown and the attribution to Fredegar dates only from the 16th century.
The chronicle begi ...
'' records that during Samo's rebellion in 631, 9,000 Bulgars led by Alciocus left Pannonia to modern-day Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
where Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the ...
massacred most of them. The remaining 700 joined the Wends.
At about the time of Samo's realm, Bulgar leader Kubrat of the Dulo clan led a successful uprising to end Avar authority over the Pannonian Plain, establishing Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria (Medieval Greek: Παλαιά Μεγάλη Βουλγαρία, ''Palaiá Megálē Voulgaría''), also often known by the Latin names ''Magna Bulgaria'' and ''Patria Onoguria'' (" Onogur land"), was a 7th-century Turkic noma ...
, or Patria Onoguria, "the homeland of Onogurs". The civil war, possibly a succession struggle in Onoguria between the Kutrigurs under Alciocus on one side and Utigur forces on the other, raged from 631 to 632. After Alciocus fled to Bavaria, the power of the Avars' Kutrigur forces was shattered, and Kubrat established peace between the Avars and Byzantium in 632. According to Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Byzantine emperor of the Macedonian dynasty, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, an ...
's 10th century work ''De Administrando Imperio
(; ) is a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. It is a domestic and foreign policy manual for the use of Constantine's son and successor, the Emperor Romanos II. It is a prominent example of Byz ...
,'' a group of Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
who had separated from the White Croats
The White Croats (; ; ; ), also known simply as Croats, were a group of Early Slavs, Early Slavic tribes that lived between East Slavs, East Slavic and West Slavs, West Slavic tribes in the historical region of Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia n ...
in White Croatia
White Croatia (also Great Croatia or Chrobatia; , also ) is the region from which part of the White Croats emigrated to the area of modern-day Croatia and lived between 7-10th century.
According to recent archaeological and historiographical res ...
had also fought against the Avars, after which they organized the Duchy of Croatia
The Duchy of Croatia (Modern ; also Duchy of the Croats, Modern ; ; ) was a medieval state that was established by White Croats who migrated into the area of the former Roman province of Dalmatia 7th century AD. Throughout its existence the Duch ...
. The Unknown Archon
In the first half of the 7th century, there was a ruler of the Serbs who led half of the Serbs from their homeland (White Serbia) to settle in the Balkans during the reign of Byzantine Emperor Heraclius (610–641), as mentioned in Emperor Constant ...
's people from Samo's realm were also resettled at this time.
Middle (670–720) and late (720–822) Avar periods
 With the death of Samo in 658 and Kubrat in 665, some Slavic tribes again came under Avar rule. Despite their father's advice, Kubrat's sons failed to maintain cohesion in Old Great Bulgaria which began to disintegrate. A few years later in the time of Batbayan, Old Great Bulgaria dissolved into five branches. From western Onoguria the first group of folk moved to Ravenna under Alzeco in the 650s. According to Book II of the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', a certain Avar Chagan seized his opportunity to coalesce in the regions further north in response to the secession of the Diocese of
With the death of Samo in 658 and Kubrat in 665, some Slavic tribes again came under Avar rule. Despite their father's advice, Kubrat's sons failed to maintain cohesion in Old Great Bulgaria which began to disintegrate. A few years later in the time of Batbayan, Old Great Bulgaria dissolved into five branches. From western Onoguria the first group of folk moved to Ravenna under Alzeco in the 650s. According to Book II of the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', a certain Avar Chagan seized his opportunity to coalesce in the regions further north in response to the secession of the Diocese of Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous province of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians ...
in the 670s by a " Kuber" Chagan.
:"Finally, the (Avar) Chagan, considering them to constitute a people with an identity of its own put, in accordance to the custom of his race, a chieftain upon them, a man by the name of Kouver. When Kouver (Chagan) learned from some of his most intimate associates the desire of the exiled Romans for their ancestral homes, he gave the matter some thought, then took them together with other peoples, i.e., the foreigners who had joined them, s is said in the Book of Moses about the Jews at the time of their exodus,with all their baggage and arms. According to what is said, they rebelled and separated themselves from the (Avar) Chagan. The (Avar) Chagan, when he learned this, set himself in pursuit of them, met them in five or six battles and, being defeated in each one by them, took flight and retired to the regions further north. After the victory, Kouver (Chagan), together with the aforementioned people, crossed the aforementioned river Danube, came to our regions and occupied the Keramesion plain."
About this time, '' Mark of Kalt'' records that in 677, the principality of Ungvar (Ung fortress) was established in the regions further north where Kotrag's group also fled following the chaos, and a third group of Onogur-Bulgarians led by Batayan was subdued by Ziebel
Tong Yabghu Qaghan (r. 618–628 or 630) was the khagan of the Western Turkic Khaganate from 618 to 628 AD. Tong Yabghu was the brother of Sheguy (r. 611–618), the previous khagan of the western Göktürks, and was a member of the Ashina ...
's emerging Khazar Empire according to Nikephoros I of Constantinople. Under Mauros, a fourth group of folk eventually settled in the present-day region of North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
. The fifth group from Onogur, Bulgaria, led by Khan Asparukh—the father of Khan Tervel—settled permanently along the Danube (c. 679–681), establishing the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northe ...
, stabilized by the victory at the battle of Ongal south of the eastern Carpathians. The Bulgarians turned on Byzantium who had established an alliance with Ziebel's Khazars.
Although the Avar empire had diminished to half its original size, the Avar-Slav alliance consolidated their rule west from the central parts of the mid-Danubian basin and extended their sphere of influence west to the Vienna Basin. The new ethnic element marked by hair clips for pigtails; curved, single-edged sabres; and broad, symmetrical bows marks the middle Avar-Bulgar period (670–720). New regional centers, such as those near Ozora
Ozora is a village in Tolna, Hungary, Tolna, Hungary. It has been notable since the Middle Ages, when Pipo of Ozora built a castle at this site by permission of Sigismund of Hungary in 1416. Artúr Görgei won an important victory in this area a ...
and Igar appeared. This strengthened the Avars' power base, although most of the Balkans lay in the hands of Slavic tribes since neither the Avars nor Byzantines were able to reassert control.
There are very few sources that cover the last century of Avar history. They only talk about the relations between the Avars and Lombards but little about the internals of the khaganate, so information about the Carpathian Basin is mostly from archaeology. Even here, elites are almost invisible, and there is little evidence of nomadic behavior. This transformation is little understood, but may have something to do with population growth.


 A new type of ceramics—the so-called "
A new type of ceramics—the so-called "Devínska Nová Ves
Devínska Nová Ves (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia. Its western borders are formed by the Morava River, which also forms the national border between Slovakia and Austria.
Devínska Nová Ves is notable mainly for its ...
" pottery—emerged at the end of the 7th century in the region between the Middle Danube and the Carpathians. These vessels were similar to the hand-made pottery of the previous period, but wheel-made items were also found in Devínska Nová Ves sites. Large inhumation cemeteries found at Holiare, Nové Zámky
Nové Zámky (; ) is a town in Nové Zámky District in the Nitra Region of southwestern Slovakia.
Geography
The town is located on the Danubian Lowland, on the Nitra River, at an altitude of 119 metres. It is located around 100 km fr ...
and other places in Slovakia, Hungary and Serbia from the period beginning around 690 show that the settlement network of the Carpathian Basin became more stable in the Late Avar period. The most popular Late Avar motifs—griffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (; Classical Latin: ''gryps'' or ''grypus''; Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk ...
s and tendril
In botany, a tendril is a specialized Plant stem, stem, leaf or Petiole (botany), petiole with a thread-like shape used by climbing plants for support and attachment, as well as cellular invasion by parasitic plants such as ''Cuscuta''. There ar ...
s decorating belts, mounts and a number of other artifacts connected to warriors—may either represent nostalgia for the lost nomadic past or evidence a new wave of nomads arriving from the Pontic steppes at the end of the 7th century. According to historians who accept the latter theory, the immigrants may have been either Onogurs or Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
. Anthropological studies of the skeletons point at the presence of a population with mongoloid features.
In the early 8th century, a new archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
—the so-called "griffin and tendril" culture—appeared in the Carpathian Basin. Some theories, including the "double conquest" theory of archaeologist Gyula László, attribute it to the arrival of new settlers, such as early Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the ...
, but this is still under debate. Hungarian archaeologists Laszló Makkai and András Mócsy attribute this culture to an internal evolution of Avars resulting from the integration of the Bulgar émigrés from the previous generation of the 670s. According to Makkai and Mócsy, "the material culture—art, clothing, equipment, weapons—of the late Avar/Bulgar period evolved autonomously from these new foundations". Many regions that had once been important centers of the Avar Empire had lost their significance while new ones arose. Although Avaric material culture
Material culture is culture manifested by the Artifact (archaeology), physical objects and architecture of a society. The term is primarily used in archaeology and anthropology, but is also of interest to sociology, geography and history. The fie ...
found over much of the northern Balkans may indicate an existing Avar presence, it probably represents the presence of independent Slavs who had adopted Avaric customs. Radovan Bunardžić dated Avar-Bulgar graves excavated in Čelarevo (near Sirmium), containing skulls with Mongolian features and Judaic symbols, to the late 8th century and 9th century.
Collapse
 The gradual decline of Avar power accelerated to a rapid fall. A series of Frankish campaigns, beginning from 788, ended with the conquest of the Avar realm within a decade. Initial conflict between Avars and Franks occurred soon after the Frankish deposition of Bavarian duke Tassilo III and the establishment of direct Frankish rule over
The gradual decline of Avar power accelerated to a rapid fall. A series of Frankish campaigns, beginning from 788, ended with the conquest of the Avar realm within a decade. Initial conflict between Avars and Franks occurred soon after the Frankish deposition of Bavarian duke Tassilo III and the establishment of direct Frankish rule over Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
in 788. At that time, the border between Bavarians and Avars was situated on the river Enns. An initial Avarian incursion into Bavaria was repelled, and Franco-Bavarian forces responded by taking the war to neighbouring Avarian territories, situated along the Danube, east of Enns. The two sides collided near the river Ybbs, on Ybbs Field (), where the Avars suffered a defeat in 788. This heralded the rise of Frankish power and Avarian decline in the region.
In 790, the Avars tried to negotiate a peace settlement with the Franks, but no agreement was reached. A Frankish campaign against the Avars, initiated in 791, ended successfully for the Franks. A large Frankish army, led by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
, crossed from Bavaria into the Avarian territory beyond the Enns, and started to advance along the Danube in two columns, but found no resistance and soon reached the region of the Vienna Woods, near the Pannonian Plain. No pitched battle was fought, since the Avars had fled before the advancing Carolingian army, while disease left most of the Avar horses dead. Tribal infighting began, showing the weakness of the khaganate.
The Franks had been supported by the Slavs, who established polities on former Avar territory. Charlemagne's son Pepin of Italy
Pepin or Pippin (born Carloman), (777 – 8 July 810) was King of Italy from 781 until his death in 810. He was the third son of Charlemagne (and his second with Queen Hildegard). Upon his baptism in 781, Carloman was renamed Pepin, where he wa ...
captured a large, fortified encampment known as "the Ring", which contained much of the spoils from earlier Avar campaigns. The campaign against the Avars again gathered momentum. By 796, the Avar chieftains had surrendered and became open to the acceptance of Christianity. In the meantime, all of Pannonia was conquered. According to the ''Annales Regni Francorum
The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales regni Francorum''), also called the ''Annales Laurissenses maiores'' ('Greater Lorsch Annals'), are a series of annals composed in Latin in Carolingian Francia, recording year-by-year the state of ...
'', the Avars began to submit to the Franks in 796. The song "'' De Pippini regis Victoria Avarica''" celebrating the defeat of the Avars at the hands of Pepin of Italy
Pepin or Pippin (born Carloman), (777 – 8 July 810) was King of Italy from 781 until his death in 810. He was the third son of Charlemagne (and his second with Queen Hildegard). Upon his baptism in 781, Carloman was renamed Pepin, where he wa ...
in 796 still survives. The Franks baptized many Avars and integrated them into the Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
. In 799, some Avars revolted.
In 804, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
conquered the southeastern Avar lands in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
and southeastern Pannonia up to the Middle Danube, and many Avars became subjects of the Bulgarian Empire Bulgarian Empire may refer to:
* First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led b ...
. Khagan Theodorus, a convert to Christianity, died after asking Charlemagne for help in 805; he was succeeded by Khagan Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
, who was baptized as the new Frankish client (and should not be assumed from his name alone to have been Khavar rather than Pseudo-Avar). Abraham was succeeded by Khagan (or Tudun
A tudun was a governor resident in a town or other settlement in the ancient Bulgar, Avar or Gokturk empires, particularly those of the Bulgars and the Khazars. The tudun was the personal representative of the imperial government and could ...
) Isaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
(Latin ''Canizauci''), about whom little is known. The Franks turned the Avar lands under their control into a frontier march. The March of Pannonia
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 ...
the eastern half of the Avar Marchwas then granted to the Slavic Prince Pribina, who established the Lower Pannonia principality in 840.
Whatever was left of Avar power was effectively ended when the Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
expanded their territory into the central and eastern portions of traditional Avar lands around 829. According to Pohl, an Avar presence in Pannonia is certain in 871, but thereafter the name is no longer used by chroniclers. Pohl wrote, "It simply proved impossible to keep up an Avar identity after Avar institutions and the high claims of their tradition had failed", although Regino wrote about them in 889. The growing amount of archaeological evidence in Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( ; , or ', ) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Traditional interpretation
The borders of Transdanubia are the Danube River (north and ...
also presumes an Avar population in the Carpathian Basin in the late 9th century. Archaeological findings suggest a substantial, late Avar presence on the Great Hungarian Plain
The Great Hungarian Plain (also known as Alföld or Great Alföld, or ) is a plain occupying the majority of the modern territory of Hungary. It is the largest part of the wider Pannonian Plain (however, the Great Hungarian Plain was not par ...
; however, it is difficult to determine their proper chronology. The preliminary results of the new excavations also imply that the known and largely accepted theory of the destruction of the Avar settlement area is outdated; a disastrous depopulation of the Avar Khaganate never happened.
Byzantine records, including the "''Notitia episcopatuum''", the "''Additio patriarchicorum thronorum''" by Neilos Doxapatres Neilos Doxapatres () was a Byzantine Greek monk, theologian, and writer active in Constantinople and Sicily during the first half of the 12th century.
Biography
Born into a native Greeks, Greek family of Constantinople, he made his career there, ...
, the "''Chronica''" by Petrus Alexandrinus and the "''Notitia patriarchatuum''" mention the 9th century Avars as an existing Christian population. The Avars had already been mixing with the more numerous Slavs for generations, and they later came under the rule of external polities, such as the Franks, Bulgaria, and Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
. Fine presumes that Avar descendants who survived the Hungarian Conquest in the 890s were likely absorbed by the Hungarian population. After the mid to late 8th-century Frankish conquest of Pannonia, Avar and Bulgar refugees migrated to settle in the area of Bulgaria and along its western periphery. The Avars in the region known as ''solitudo avarorum''currently called the Great Hungarian Plainvanished in an arc of three generations. They slowly merged with the Slavs to create a bilingual Turkic-Slavic-speaking people who were subjected to Frankish domination; the invading Magyars found this composite people in the late 9th century. The ''De Administrando Imperio
(; ) is a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. It is a domestic and foreign policy manual for the use of Constantine's son and successor, the Emperor Romanos II. It is a prominent example of Byz ...
'', written around 950 and based on older documents, states that "there are still descendants of the Avars in Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, and are recognized as Avars". Modern historians and archaeologists until now proved the opposite, that Avars never lived in Dalmatia proper (including Lika
Lika () is a traditional region of Croatia proper, roughly bound by the Velebit mountain from the southwest and the Plješevica mountain from the northeast. On the north-west end Lika is bounded by Ogulin-Plaški basin, and on the south-east by t ...
), that statement occurred somewhere in Pannonia, and the information belongs to the 9th century. There has been speculation that the modern Avar people of the Caucasus might have an uncertain connection to the historical Avars, but direct descent from them is rejected or doubted by many scholars.
List of known khagans
The recorded Avar khagans were: * Shaush (? – c. 552) * Kandik (c. 552 – c. 562) *Bayan I
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602.
As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'', ...
(562–602)
* Bayan II (602–617)
* Bayan III (617–630)
* Kouver Chagan (677–?)
* Theodorus (795–805)
* Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
(805–?)
* Isaac (?–835)
Social and tribal structure
 The Pannonian Basin was the centre of the Avar power base. The Avars resettled captives from the peripheries of their empire to more central regions. Avar material culture is found south to Macedonia. However, to the east of the Carpathians, there are next to no Avar archaeological finds, suggesting that they lived mainly in the
The Pannonian Basin was the centre of the Avar power base. The Avars resettled captives from the peripheries of their empire to more central regions. Avar material culture is found south to Macedonia. However, to the east of the Carpathians, there are next to no Avar archaeological finds, suggesting that they lived mainly in the western Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
. Scholars propose that a highly structured and hierarchical Avar society existed, having complex interactions with other "barbarian" groups. The khagan was the paramount figure, surrounded by a minority of nomadic aristocracy.
A few exceptionally rich burials have been uncovered, confirming that power was limited to the khagan and a close-knit class of "elite warriors". In addition to hoards of gold coins that accompanied the burials, the men were often buried with symbols of rank, such as decorated belts, weapons, stirrups resembling those found in central Asia, as well as their horse. The Avar army was composed from numerous other groups: Slavic, Gepidic and Bulgar military units. There also appeared to have existed semi-independent "client" (predominantly Slavic) tribes which served strategic roles, such as engaging in diversionary attacks and guarding the Avars' western borders abutting the Frankish Empire.
Initially, the Avars and their subjects lived mostly separately. Eventually, the Germanic and Slavic peoples were included in the Avaric social order and culture, which was Persian-Byzantine in fashion. Scholars have identified a fused Avar-Slavic culture, characterized by ornaments such as half-moon-shaped earrings, Byzantine-styled buckles, beads, and bracelets with horn-shaped ends. Paul Fouracre notes, " ere appears in the seventh century a mixed Slavic-Avar material culture, interpreted as peaceful and harmonious relationships between Avar warriors and Slavic peasants. It is thought possible that at least some of the leaders of the Slavic tribes could have become part of the Avar aristocracy". Apart from the assimilated Gepids, a few graves of Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
peoples have been found in the Avar lands. They perhaps served as mercenaries.
Language
The language or languages spoken by the Avars are unknown. Classicalphilologist
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of ...
Samu Szádeczky-Kardoss said that most of the Avar words used in contemporaneous Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
or Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
texts appear to have their origins in possibly Mongolian or Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic langua ...
. Other theories propose a Tungusic origin. According to Szádeczky-Kardoss, many of the titles and ranks used by the Pannonian Avars were also used by Turks, Proto-Bulgars, Uighurs and/or Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
, including ''khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im ...
'' (or ''kagan''), '' khan, kapkhan, tudun
A tudun was a governor resident in a town or other settlement in the ancient Bulgar, Avar or Gokturk empires, particularly those of the Bulgars and the Khazars. The tudun was the personal representative of the imperial government and could ...
, tarkhan
Tarkhan (, or ; ; zh, c=達干/達爾罕/答剌罕; ; ; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján, Tarxan'') is an ancient Central Asian title used by various ...
'', and ''khatun
Khatun ( ) is a title of the female counterpart to a Khan (title), khan or a khagan of the Göktürks, Turkic Khaganates and in the subsequent Mongol Empire.
Etymology and history
Before the advent of Islam in Central Asia, Khatun was the title of ...
''. There is evidence, however, that ruling and subject clans spoke a variety of languages. Proposals by scholars include Caucasian, Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
, Tungusic, Hungarian and Turkic.
Historian Gyula László has suggested that the late 9th-century Pannonian Avars spoke a variety of Old Hungarian, thereby forming an Avar-Hungarian continuity with then-newly arrived Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
. Based on archeologic and linguistic data, Florin Curta and Johanna Nichols
Johanna Nichols (born 1945, Iowa City, Iowa) is an American linguist and professor emerita in the Department of Slavic Languages and Literatures at the University of California, Berkeley.
Career
She earned her Ph.D. in Linguistics at the Univer ...
considered that there is no convincing evidence for the presence of any Turkic or Mongolic languages among the Avars, but evidence for the presence of Iranian languages
The Iranian languages, also called the Iranic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian langu ...
, further strengthened by Iranian-derived loanwords and toponyms in the region and among languages within the range of the Avars. Shimunek (2017) proposes that the elite core of the Avars spoke a " Para-Mongolic language" of the "Serbi–Awar" group, that is a sister branch of the Mongolic languages
The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in North Asia, East Asia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this languag ...
. Together, the Serbi–Awar and Mongolic languages make up the '' Serbi–Mongolic'' languages.
Some scholars like Omeljan Pritsak
Omeljan Yosypovych Pritsak (; 7 April 1919 – 29 May 2006) was the first Mykhailo Hrushevsky Professor of History of Ukraine, Ukrainian History at Harvard University and the founder and first director (1973–1989) of the Harvard Ukrainian Rese ...
, Horace Lunt, Florin Curta speculate that Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th ...
became the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
of the Avar Khaganate, which helped spreading the Slavic language in the Southeastern Europe. The assumption is problematic for several reasons, as Alan Timberlake notes that there was no "radical loss of grammar that accompanies creolization
Creolization is the process through which creole languages and cultures emerge. Creolization was first used by linguists to explain how contact languages become creole languages, but now scholars in other social sciences use the term to describe ...
" neither the Avars and Slavs had specific social and economical mechanisms for spreading ''lingua franca''. Jouko Lindstedt
Jouko Lindstedt (born 15 July 1955) is a Finnish linguist and a professor at the University of Helsinki. Lindstedt is a member of the Academy of Esperanto and was nominated as the Esperantist of the Year in 2000 (with Hans Bakker and Mauro La ...
asserts that Late Proto-Slavic/Common Slavic had a complex morphological and accentological system because of which "shows no trace of a possible lingua-franca function".
Warfare
The Avars were skilled warriors and almost exclusively fought on horseback. They often used light horse archers armed with powerful composite bows, as many other steppe peoples. These archers wore little to no armour, besides occasional helmets or knee guards. The Avars also employed the use of heavy cavalry, fully armoured in chainmail or scale armour as well as helmets. These heavier troops were armed with long lances, swords, and daggers. Upon subjugating the Slavic tribes in Pannonia, they often allied with the Slavs and employed them as foot soldiers even together laying siege to Constantinople, along with large numbers of Persians. These Slav warriors were usually armed with bows, axes, various types of spears, and round shields. The Byzantine Emperor Maurice wrote of the Avars and other nomad peoples in the Strategikon:Avar-Hungarian continuity theory
Gyula László says that the late Avars, arriving to the khaganate in 670 in great numbers, lived through the time between the destruction and plunder of the Avar state by the Franks during 791–795 and the arrival of the Magyars in 895. László points out that the settlements of theHungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
(Magyars) complemented, rather than replaced, those of the Avars. Avars remained on the plough fields, good for agriculture, while Hungarians took the river banks and river flats, suitable for pasturage. He notes that while the Hungarian graveyards consist of 40–50 graves on average, those of the Avars contain 600–1,000. According to these findings, the Avars not only survived the end of the Avar polity but lived in great masses and far outnumbered the Hungarian conquerors of Árpád
Árpád (; 845 – 907) was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or '' kende'' of the Hungarians, or their military leader or '' g ...
.
He also shows that Hungarians occupied only the centre of the Carpathian basin, but Avars lived in a larger territory. Looking at those territories where only the Avars lived, there are only Hungarian geographical names, not Slavic or Turkic as would be expected interspersed among them. This is further evidence for the Avar-Hungarian continuity. Names of the Hungarian tribes, chieftains and the words used for the leaders, etc., suggest that at least the leaders of the Hungarian conquerors were Turkic speaking. However, Hungarian is not a Turkic language, rather Uralic, and so they must have been assimilated by the Avars that outnumbered them.
László's Avar-Hungarian continuity theory posits that the modern Hungarian language
Hungarian, or Magyar (, ), is an Ugric language of the Uralic language family spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighboring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Out ...
descends from that spoken by the Avars rather than the conquering Magyars. Based on DNA evidence from graves, the original Magyars most resembled modern Bashkirs
The Bashkirs ( , ) or Bashkorts (, ; , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a Republics of Russia, republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of B ...
, a Turkic people located near the Urals, whereas the Khanty and Mansi, whose languages most resemble Hungarian, live some ways to the northeast of the Bashkirs.
See also
*Keszthely culture
The Keszthely culture was a mixed Romanised population-Germanic peoples, Germanic-Pannonian Avars, Avar, Christians, Christian enclave located in present-day Hungary, from the 6th century until the first half of the 7th century. These people could ...
* Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós
* Pannonian Romance
Pannonian Latin (also known as Pannonian Romance) was a variant of Vulgar Latin that developed in Pannonia, but became extinct after the loss of the province.
History
Most likely the bigger part of the indigenous population spoke P-Celtic. ...
* Székelys
The Székelys (, Old Hungarian script, Székely runes: ), also referred to as Szeklers, are a Hungarians, Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. In addition to their native villages in Suceava County in Bukovina, a ...
* Alattyán
* Palóc People
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *– YouTube
Documentary with Gyula László in Hungarian, on state television channel Duna. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * p. 221 * * * *
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Avar States and territories established in the 560s States and territories disestablished in the 820s Medieval history of Bulgaria Medieval history of Russia Medieval history of Ukraine Hungary in the Early Middle Ages Romania in the Early Middle Ages Moldova in the Early Middle Ages Avars Migration Period Medieval ethnic groups of Europe Barbarian kingdoms Turco-Mongol 6th-century establishments in Europe 9th-century disestablishments in Europe 560s establishments 820s disestablishments