|
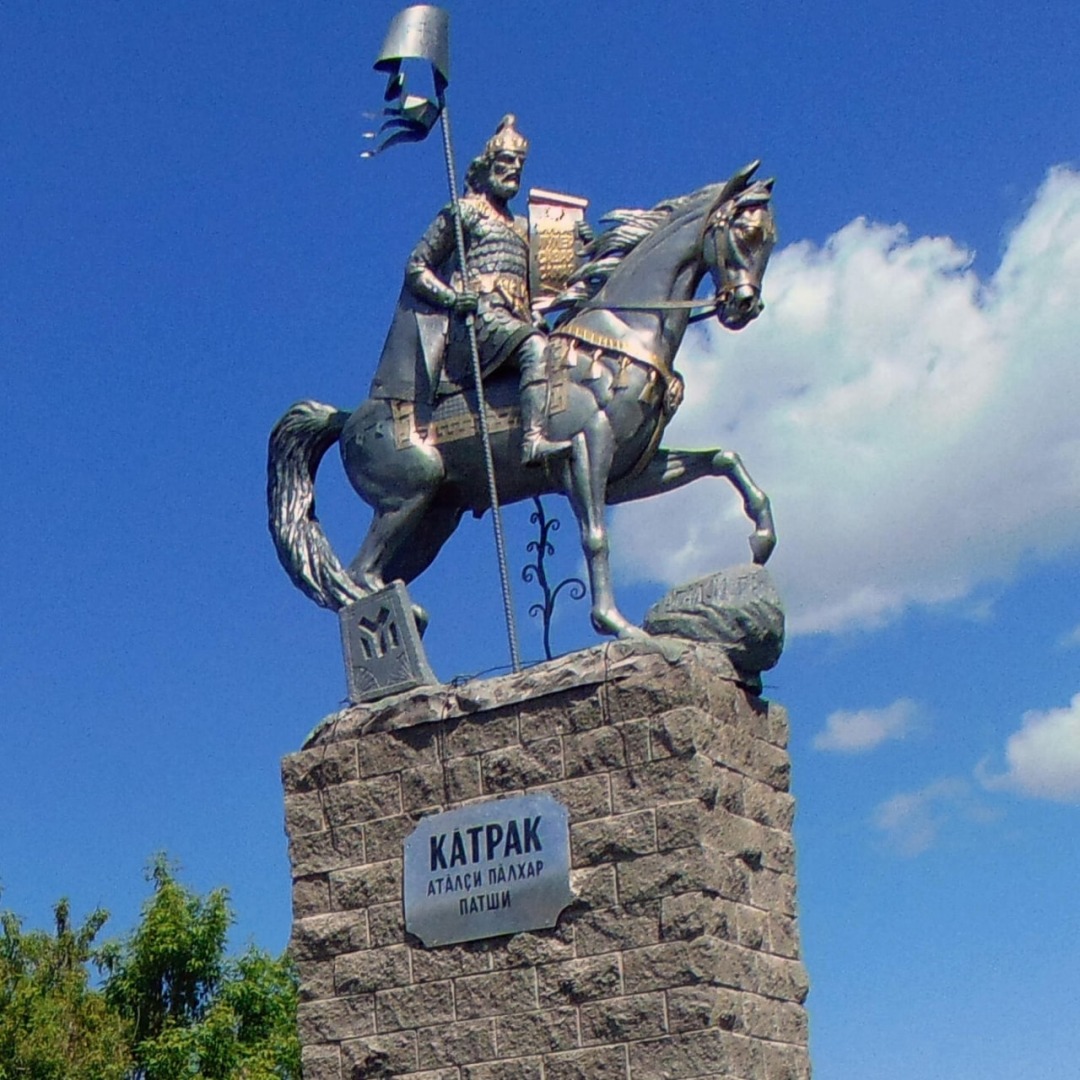
Kotrag
Kotrag was according to Nikephoros I of Constantinople a son of Kubrat of the Dulo clan of Bulgars. Following the death of his father, he began to extend the influence of his Bulgars to the Volga River. He is remembered as the founder of Volga Bulgaria. Honour * Kotrag Nunatak on Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is named after Kotrag. * In the Republic of Chuvashia in the village of Shemursha on June 12, 2022, a monument was erected to the founder of the Volga Bulgaria - Kotrag Name The possible origin of the name of khan Kotrag from the Chuvash name ''Kătrak'' and ''Kătrashka'', which in translation means ''Curly'', a common pre-Christian name among the Chuvash. In the Kipchak languages, the word ''Curly'' is translated as tat. Bodrә (''Бөдрә)'' on kaz.Buyra (''Бұйра)''. Perhaps the name Kotrag was given in honor of the great-grandfather Kobrat, who also bore the name Kotrag in honor of whom the whole tribe of Kutrigurs was named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotrag Nunatak
Kotrag Nunatak (Nunatak Kotrag \'nu-na-tak ko-'trag\) is a conspicuous rocky peak of elevation 290 m projecting from Murgash Glacier, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It was named after Khan Kotrag, founder of the Kingdom of Volga Bulgaria in the 7th Century AD. Location The peak is located at which is 540 m southwest of Lloyd Hill, 1.47 km east of Telerig Nunatak, and 970 m west of Altsek Nunatak (Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05 and mapping in 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. References Kotrag Nunatak.SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
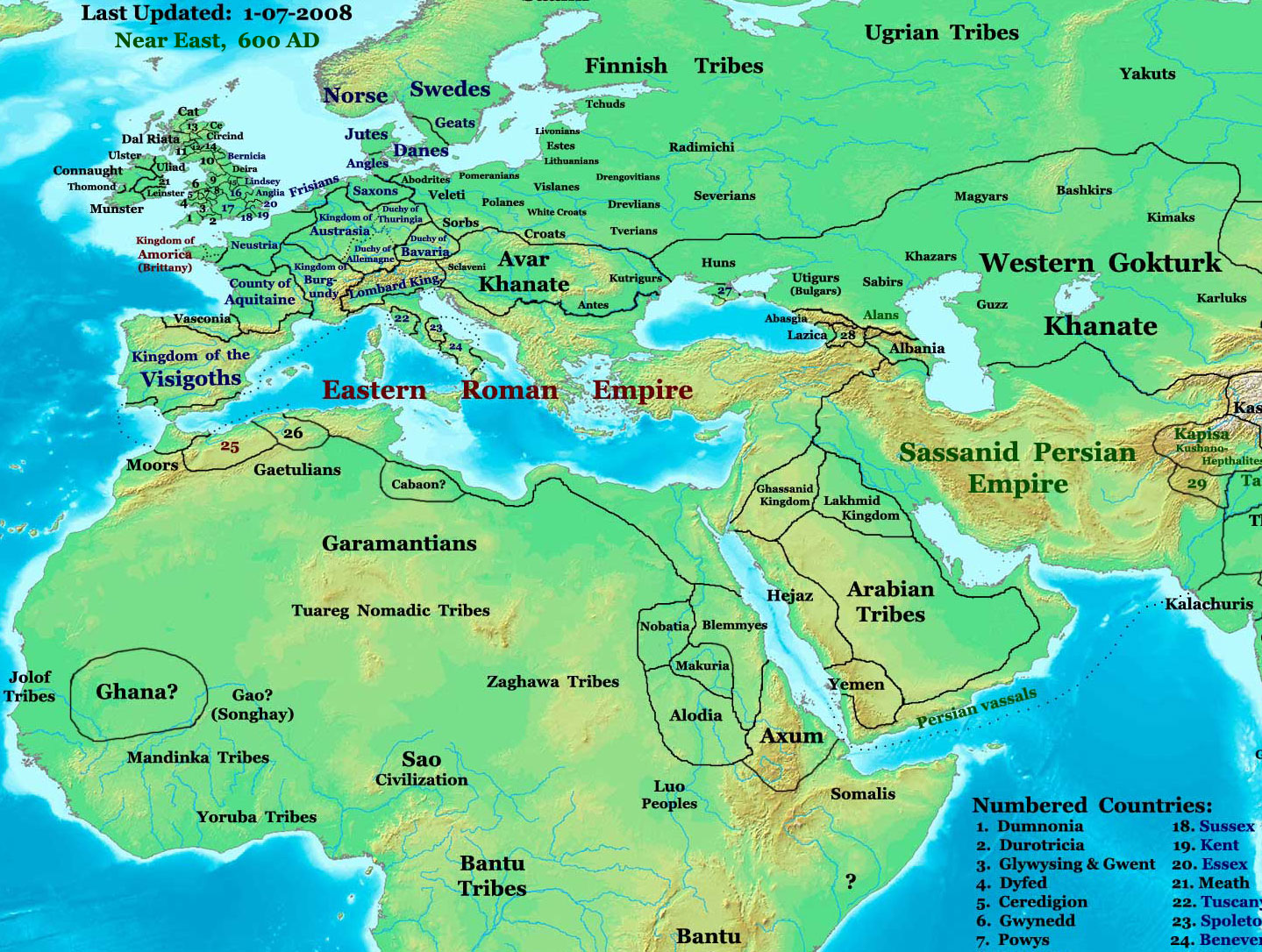
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kubrat
Kubrat ( el, Κοβρᾶτος, Kούβρατος; bg, Кубрат ) was the ruler of the Onogur–Bulgars, credited with establishing the confederation of Old Great Bulgaria in ca. 632. His name derived from the Turkic words ''qobrat'' — "to gather", or ''qurt'', i.e. "wolf". Origin In the '' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'' Kubrat is mentioned as ''Kurt'' (), being a member of the Dulo clan and reigning for 60 years having succeeded Gostun of the Ermi clan. Bulgars were Turkic nomadic people, who participated in the 5th-century Hunnic confederation. Upon Attila's death, the tribes that later formed the Bulgars had retreated east into the Black Sea-Caspian Steppe. The western Bulgar tribes joined the Avar Khaganate, while the eastern Bulgars came under the Western Turkic Khaganate by the end of the 6th century. Theophanes the Confessor called him "king of the Onogundur Huns". Patriarch Nikephoros I (758–828) called Kubrat "lord of the Onuğundur" and "ruler of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dulo
The Dulo clan was a ruling dynasty of the Bulgars. The origins of the Bulgars and Dulo clan are not known precisely, and there are many theories about their origin. It is generally considered that they – or at least the elite caste – were intimately related to the origin and activity of the Huns and Western Turkic Khaganate. Particularly, it is said that the Dulo descended from the rulers of Great Bulgaria, which was founded by Khan Asparuh's (681–701) father on the steppes of Ukraine. This state was a centralized monarchy from its inception, unlike previous Hunno-Turkic political entities, which were tribal confederations. The royal family and rulers of Old Great Bulgaria (632–668) and the first half of the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), in their prince lists ('' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'') claimed through Irnik, who was probably related to or was Attila's son Ernak himself, or at least of Attilid descent. During the pagan period, the succession of clan l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria, was a historic Bulgar state that existed between the 7th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state with large numbers of Turkic Bulgars, a variety of Finnic and Ugric peoples, and many East Slavs. Its strategic position of allowed it to create a monopoly between the trade of Arabs, Norse and Avars. History Origin and creation of the state The Bulgars were Turkic tribes of Oghuric origin, who settled north of the Black Sea. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, they came under the overlordship of the Khazars, leading other ethnic groups, including Finnic and Iranic peoples. In about 630 they founded Old Great Bulgaria, which was destroyed by the Khazars in 668. Kubrat's son and appointed heir, Batbayan Bezmer, moved from the Azov region in about AD 665, commanded by the Kazarig Khagan Kotrag, to whom he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dulo Clan
The Dulo clan was a ruling dynasty of the Bulgars. The origins of the Bulgars and Dulo clan are not known precisely, and there are many theories about their origin. It is generally considered that they – or at least the elite caste – were intimately related to the origin and activity of the Huns and Western Turkic Khaganate. Particularly, it is said that the Dulo descended from the rulers of Great Bulgaria, which was founded by Khan Asparuh's (681–701) father on the steppes of Ukraine. This state was a centralized monarchy from its inception, unlike previous Hunno-Turkic political entities, which were tribal confederations. The royal family and rulers of Old Great Bulgaria (632–668) and the first half of the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), in their prince lists ('' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans'') claimed through Irnik, who was probably related to or was Attila's son Ernak himself, or at least of Attilid descent. During the pagan period, the succession of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument To Kotrag
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, historical, political, technical or architectural importance. Some of the first monuments were dolmens or menhirs, megalithic constructions built for religious or funerary purposes. Examples of monuments include statues, (war) memorials, historical buildings, archaeological sites, and cultural assets. If there is a public interest in its preservation, a monument can for example be listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Etymology It is believed that the origin of the word "monument" comes from the Greek ''mnemosynon'' and the Latin ''moneo'', ''monere'', which means 'to remind', 'to advise' or 'to warn', however, it is also believed that the word monument originates from an Albanian word 'mani men' which in Albanian language means 'remembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of . It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average at delta – between and – and of |
Kutrigurs
Kutrigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Turks. Etymology The name ''Kutrigur'', also recorded as ''Kwrtrgr'', ''Κουτρίγουροι'', ''Κουτούργουροι'', ''Κοτρίγουροι'', ''Κοτρίγοροι'', ''Κουτρίγοροι'', ''Κοτράγηροι'', ''Κουτράγουροι'', ''Κοτριαγήροι'', has been suggested as a metathecized form of Turkic ''*Toqur- Oğur'', with ''*quturoğur'' meaning "nine Oğur (tribes)". David Marshall Lang derived it from Turkic ''kötrügür'' (conspicuous, eminent, renowned). Few scholars support theories deriving the Kutrigurs from the Guti/Quti and the Utigurs from the Udi/Uti, of ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utigurs
Utigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. They possibly were closely related to the Kutrigurs and Bulgars. Etymology The name ''Ut(r)igur'', recorded as , and , is generally considered as a metathesized form suggested by Gyula Németh of Turkic ''*Otur- Oğur'', thus the ''*Uturğur'' mean "Thirty Oğurs (tribes)". Lajos Ligeti proposed ''utur-'' (to resist), while Louis Bazin ''uturkar'' (the victors-conquerors), ''Quturgur'' and ''qudurmaq'' (the enrages). There has been little scholarly support for theories linking the names Kutrigur and Utigur to peoples such as the Guti/Quti and/or Udi/Uti, of Ancient Southwest Asia and the Caucasus respectively, which have been posited by scholars such as Osman Karatay, and Yury Zuev. No evidence has been presented that the Guti moved from their homeland in the Zagros Mountains (modern Iran/Iraq) to the Steppes, and they are widely believed to have spoken an Indo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Emperor Justinian's wars, Procopius became the principal Roman historian of the 6th century, writing the ''History of the Wars'', the ''Buildings'', and the ''Secret History''. Life Apart from his own writings the main source for Procopius's life was an entry in the ''Suda'',Suda pi.2479. See under 'Procopius' oSuda On Line a Byzantine Greek encyclopaedia written sometime after 975 which discusses his early life. He was a native of Caesarea in the province of '' Palaestina Prima''. He would have received a conventional upper class education in the Greek classics and rhetoric, perhaps at the famous school at Gaza. He may have attended law school, possibly at Berytus (present-day Beirut) or Constantinople (now Istanbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Language
The Kazakh or simply Qazaq ( Latin: or , Cyrillic: or , Arabic Script: or , , ) is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia by Kazakhs. It is closely related to Nogai, Kyrgyz and Karakalpak. It is the official language of Kazakhstan and a significant minority language in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang, north-western China and in the Bayan-Ölgii Province of western Mongolia. The language is also spoken by many ethnic Kazakhs throughout the former Soviet Union (some 472,000 in Russia according to the 2010 Russian Census), Germany, and Turkey. Like other Turkic languages, Kazakh is an agglutinative language and employs vowel harmony. ''Ethnologue'' recognizes three mutually intelligible dialect groups, Northeastern Kazakh, the most widely spoken variety which also serves as the basis for the standard language, Southern Kazakh and Western Kazakh. The language share a degree of mutual intelligiblity with closely related Karakal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |