|
Kandik
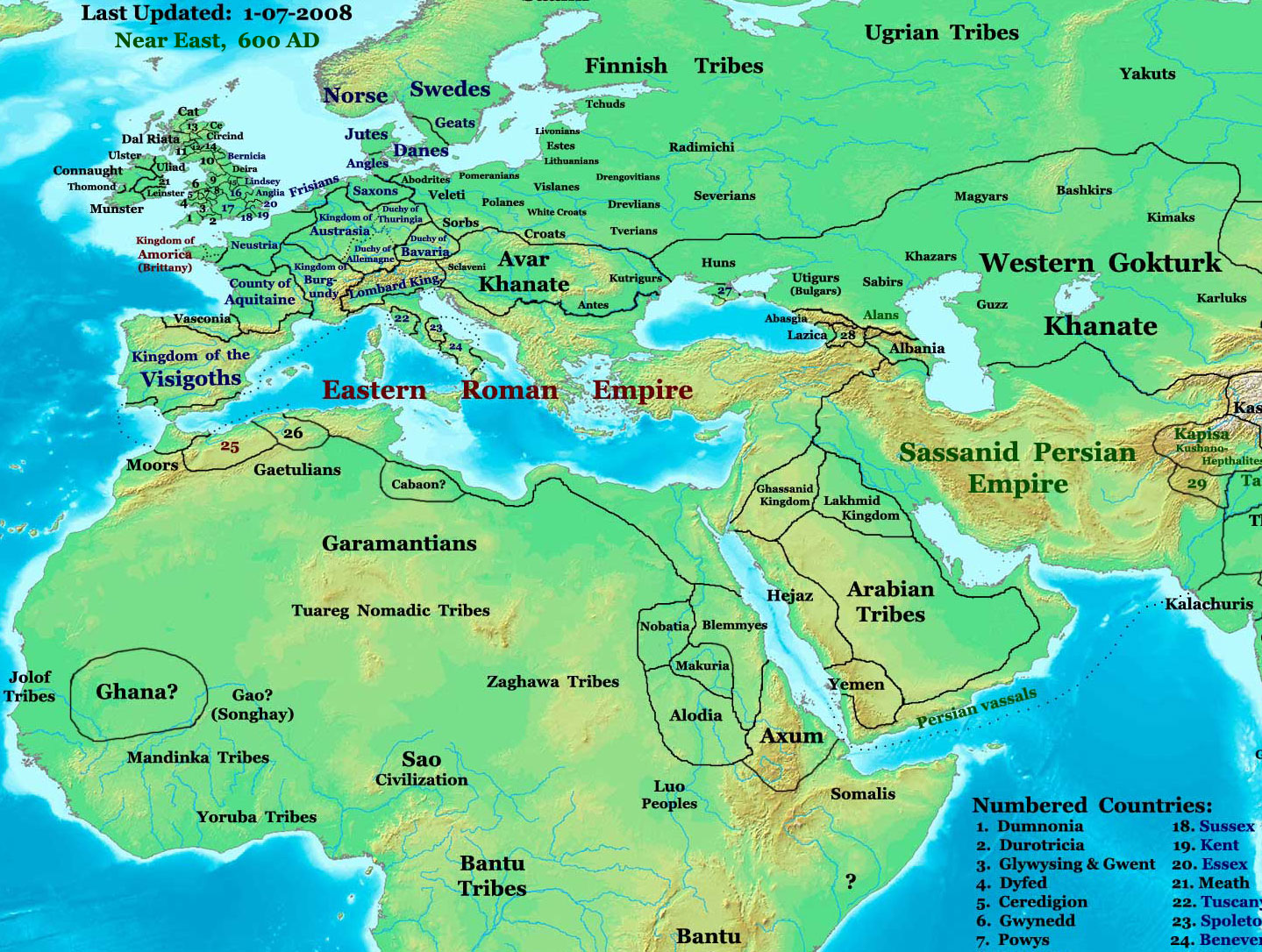
Kandik or Kazrig was one of the three Scythian brothers mentioned in the chronicle of Michael of Syria, the Jacobite Patriarch of Antioch. After leading their Iverian people as refugees away from the Turks as Pseudo-Avar khagans, Kazrig and his brothers Bolgaris and Bayan I approached Sarosius to mediate for him with the Byzantine Empire in 557. They soon conquered the remnant of the Akatziri Hunno-Bulgars also known as Kutrigurs from the time of Ernak Ernak was the last known ruler of the Huns, and the third son of Attila. After Attila's death in AD 453, his Empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He succeeded his older brother Ellac in AD 454, .... References {{reflist Year of death missing 6th-century monarchs in Europe Year of birth unknown Pannonian Avars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars (Caucasus), Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayan I
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602. As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'', ''Abaroi'' and ''Varchonites'') and the Bulgars migrated into Central and the Southeast Europe. Bayan I led the Avars (along with many Proto-Bulgarians) into Pannonia, where they established their khaganate from 568. Dealings with the Franks, Lombards and Gepids By 562, the Avars and Bulgars had reached the Lower Danube: it was most likely in that year that Bayan became their supreme Khagan in the stead of the previous ruler, the Kutrigur khan Zabergan. As allies of the Byzantine Empire of Justinian I (), the Avars had obtained a grant of gold to crush other nomads – the Sabirs, Utigurs, Kutrigurs and Saragurs – in the lands later known as Ukraine, a task they accomplished to the emperor's satisfaction. Bayan's Avars now dema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarosius
Sarosius (, ), also called Sarodius (Σαρώδιος ''Sarṓdios'') or Saroes {{IPAc-en, ˈ, s, æ, r, oʊ-, iː, z (Σαρόης ''Saróēs''), was the king of the Alans in the early 6th century while they were still in Ukraine. He acted as diplomatic negotiator between the Central Asian Pseudo-Avar refugees led by Kandik and the Byzantine emperor Justinian I in 557 and then again between Justin II and the Turks in 569. From the latter we learn that the Avars whom Sarosios helped in 557 were in fact renegades from the Hephthalites (who surrendered to the Göktürks and Sassanid Persia in 567) and apparently had no right to use the title of Avar Khagan Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im .... The diplomatic ties that Sarosios fostered led to the Göktürks' agreement wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythia
Scythia (, ) or Scythica (, ) was a geographic region defined in the ancient Graeco-Roman world that encompassed the Pontic steppe. It was inhabited by Scythians, an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people. Etymology The names and are themselves Latinisations of the Ancient Greek names () and (), which were themselves derived from the ancient Greek names for the Scythians, () and (), derived from the Scythian endonym . Geography Scythia proper The territory of the Scythian kingdom of the Pontic steppe extended from the Don river in the east to the Danube river in the west, and covered the territory of the treeless steppe immediately north of the Black Sea's coastline, which was inhabited by nomadic pastoralists, as well as the fertile black-earth forest-steppe area to the north of the treeless steppe, which was inhabited by an agricultural population. The northern border of this Scythian kingdom were the deciduous woodlands, while several rivers, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turan, Azerbaijan
Turan (known as Orconikidze until 1999) is a village and municipality in the Shaki Rayon of Azerbaijan Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by .... It has a population of 1,796. References Populated places in Shaki District {{Shaki-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, imperial rank in Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, and some other languages, equal to the status of emperor and someone who rules a khaganate (empire). The female equivalent is Khatun. It may also be translated as "Khan (title), Khan of Khans", equivalent to King of Kings. In Bulgarian, the title became known as ''Khan'', while in modern Turkic, the title became ''Khaan'' with the ''g'' sound becoming almost silent or non-existent; the ''ğ'' in modern Turkish language, Turkish ''Kağan'' is also silent. After the division of the Mongol Empire, monarchs of the Yuan dynasty and the Northern Yuan held the title of ''Khagan''. ''Kağan, Hakan'' and ''Kaan'', Turkish language, Turkish equivalents of the title are common Tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zabergan
Zabergan () was the chieftain of the Kutrigurs, a Turkic nomadic tribe of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, after Sinnion. His name is Iranian, meaning full moon. Either under pressure from incoming Avars,; or in revolt against the Byzantine Empire, in the winter of 558, he led a large Kutrigur army that crossed the frozen Danube. The army was divided into three sections: one raided south far as Thermopylae, while two others the Thracian Chersonesus and the periphery of Constantinople. In March 559 Zabergan attacked Constantinople, and one part of his forces consisted of 7,000 horsemen, but Belisarius defeated him at the Battle of Melantias and he was forced to withdraw. The transit of such big distances in a short period of time shows that the Kutrigurs were mounted warriors, and Zabergan's raiders were already encamped near the banks of the Danube. However, once again Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) managed to persuade the Utigur chieftain Sandilch to attack the Kutrigurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akatziri
The Akatziri, Akatzirs or Acatiri (, , , ; ) were a tribe that lived north of the Black Sea, though the Crimean city of Cherson seemed to be under their control in the sixth century. Jordanes ( 551) called them a mighty people, not agriculturalists but cattle-breeders and hunters. Their ethnicity is undetermined: the 5th-century historian Priscus describes them as ethnic () Scythians, but they are also referred to as Huns (''Akatiri Hunni''). Their name has also been connected to the Agathyrsi. However, according to E. A. Thompson, any conjectured connection between the Agathyrsi and the Akatziri should be rejected outright. History Roman emperor Theodosius II () sent an envoy to the Akatziri trying to detach them from their alliance with the Hunnic ruler Attila (435–453), an effort made to stir up fighting which also ensued. In 447 or 448 the Huns successfully campaigned against the Akatziri. In 448 or 449, as Priscus recounts " Onegesius along with the eldest of Attila' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutrigurs
The Kutrigurs were a Turkic nomadic equestrian tribe who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Türks. Etymology The name ''Kutrigur'', also recorded as ''Kwrtrgr'', ''Κουτρίγουροι'', ''Κουτούργουροι'', ''Κοτρίγουροι'', ''Κοτρίγοροι'', ''Κουτρίγοροι'', ''Κοτράγηροι'', ''Κουτράγουροι'', ''Κοτριαγήροι'', has been suggested as a metathecized form of Turkic ''*Toqur- Oğur'', with ''*quturoğur'' meaning "nine Oğur (tribes)". David Marshall Lang derived it from Turkic ''kötrügür'' (conspicuous, eminent, renowned). Few scholars support theories deriving the Kutrigurs from the Guti/Quti and the Utigurs from the Ud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernak
Ernak was the last known ruler of the Huns, and the third son of Attila. After Attila's death in AD 453, his Empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He succeeded his older brother Ellac in AD 454, and probably ruled simultaneously over Huns in dual kingship with his brother Dengizich, but in separate divisions in separate lands. Priscus, during his stay at Attila's court in AD 448 or 449, recorded a personal occasion between Attila and Ernak. At a banquet Attila looked on him with serene eyes, while taking small account of his other sons. He was Attila's favorite son, because as a certain Hun explained to him, the Hunnic prophets prophesied his ''genos'' would fail, but would be restored by this son. Ernak has often been identified with ''Irnik'' from the Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans, who is noted as a descendant of the Dulo clan and leader of the Bulgars for 150 years, starting approximately from AD 437. Etymology The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |