Nemertines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nemertea is a
 The proboscis of the
The proboscis of the  In most of the class
In most of the class
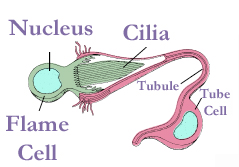 Nemertea use organs called
Nemertea use organs called
 The central nervous-system consists of a
The central nervous-system consists of a
 Most nemerteans are marine animals that burrow in sediments, lurk in crevices between shells, stones or the
Most nemerteans are marine animals that burrow in sediments, lurk in crevices between shells, stones or the
The Marine Biological Laboratory: Phylum Nemertea (Nemertinea, Nemertini, Rhynchocoela)Nemertea LifeDeskVideo of a Nemertea in Puget Sound
{{Authority control Protostome phyla Extant Ordovician first appearances
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms, consisting of about 1300 known species. Most ribbon worms are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. Many have patterns of yellow, orange, red and green coloration.
The foregut, stomach and intestine run a little below the midline of the body, the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
is at the tip of the tail, and the mouth is under the front. A little above the gut is the , a cavity which mostly runs above the midline and ends a little short of the rear of the body. All species have a proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a pr ...
which lies in the rhynchocoel when inactive but everts to emerge just above the mouth to capture the animal's prey with venom. A highly extensible muscle in the back of the rhynchocoel pulls the proboscis in when an attack ends. A few species with stubby bodies filter feed
Filter feeders are aquatic animals that acquire nutrients by feeding on organic matters, food particles or smaller organisms (bacteria, microalgae and zooplanktons) suspended in water, typically by having the water pass over or through a specia ...
and have suckers at the front and back ends, with which they attach to a host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
* Host Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica
People
* ...
.
The brain is a ring of four ganglia
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there a ...
, positioned around the rhynchocoel near the animal's front end. At least a pair of ventral nerve cord
The ventral nerve cord is a major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It is the functional equivalent of the vertebrate spinal cord. The ventral nerve cord coordinates neural signaling from the brain to the body and vice ve ...
s connect to the brain and run along the length of the body. Most nemerteans have various chemoreceptors
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance ( endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorece ...
, and on their heads some species have a number of pigment-cup ocelli
A simple eye or ocellus (sometimes called a pigment pit) is a form of eye or an optical arrangement which has a single lens without the sort of elaborate retina that occurs in most vertebrates. These eyes are called "simple" to distinguish the ...
, which can detect light but can not form an image. Nemerteans respire through the skin. They have at least two lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
vessels which are joined at the ends to form a loop, and these and the rhynchocoel are filled with fluid. There is no heart, and the flow of fluid depends on contraction of muscles in the vessels and the body wall. To filter out soluble waste products, flame cell
A flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in simple invertebrates, including flatworms ( Platyhelminthes), rotifers and nemerteans; these are the simplest animals to have a dedicated excretory system. Flame cells function like a kidney ...
s are embedded in the front part of the two lateral fluid vessels, and remove the wastes through a network of pipes to the outside.
All nemerteans move slowly, using their external cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
to glide on surfaces on a trail of slime
Slime or slimy may refer to:
Science and technology Biology
* Slime coat, the coating of mucus covering the body of all fish
* Slime mold, an informal name for several eukaryotic organisms
* Biofilm, or slime, a syntrophic community of micr ...
, while larger species use muscular waves to crawl, and some swim by dorso-ventral undulations. A few live in the open ocean while the rest find or make hiding places on the bottom. About a dozen species inhabit freshwater, mainly in the tropics and subtropics, and another dozen species live on land in cool, damp places. Most nemerteans are carnivores
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly mu ...
, feeding on annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s, clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
s and crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s. Some species of nemerteans are scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume Corpse decomposition, dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a he ...
s, and a few live commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
ly inside the mantle cavity of mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s.
In most species the sexes are separate, but all the freshwater species are hermaphroditic
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
. Nemerteans often have numerous temporary gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s (ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
or testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
), and build temporary gonoducts (ducts from which the ova or sperm are emitted) opening to a gonopore
A gonopore, sometimes called a gonadopore, is a genital pore in many invertebrates. Hexapods, including insects, have a single common gonopore, except mayflies, which have a pair of gonopores. More specifically, in the unmodified female, it is ...
, one per gonad, when the ova and sperm are ready. The eggs are generally fertilised externally. Some species shed them into the water, and others protect their eggs in various ways. The fertilized egg divides by spiral cleavage
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells the same siz ...
and grows by determinate development, in which the fate of a cell can usually be predicted from its predecessors in the process of division. The embryos of most taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
develop either directly to form juveniles (like the adult but smaller) or larvae that resemble the planula
A planula is the free-swimming, flattened, ciliated, bilaterally symmetric larval form of various cnidarian species and also in some species of Ctenophores, which are not related to cnidarians at all. Some groups of Nemerteans also produce larva ...
s of cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
ns. However, some form a pilidium larva, in which the developing juvenile has a gut which lies across the larva's body, and usually eats the remains of the larva when it emerges. The bodies of some species fragment readily, and even parts cut off near the tail can grow full bodies.
Traditional taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
divides the phylum in two classes, Anopla
Anopla (for changes in taxonomy, see reference from 2019) has long been used as name for a Class (biology), class of marine worms of the phylum Nemertea, characterized by the absence of stylet (anatomy), stylets on the proboscis, the mouth being ...
("unarmed" – their proboscises do not have a little dagger) with two orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* H ...
, and Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the proboscis.
Evolution and systematics
The record of nemerteans is extremely sparse, as would be expected ...
("armed" with a dagger) also with two orders. However, it is now accepted that Anopla are paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
, as one order of Anopla is more closely related to Enopla than to the other order of Anopla. The phylum Nemertea itself is monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
, its main synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
being the rhynchocoel and eversible proboscis. Traditional taxonomy says that nemerteans are closely related to flatworms
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates commonly called ...
, but both phyla are regarded as members of the Lophotrochozoa
Lophotrochozoa (, "crest/wheel animals") is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, and brach ...
, a very large clade, sometimes viewed as a superphylum that also includes mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s, brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear e ...
s, bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary Colony (biology), colonies. Typically about long, they have a spe ...
and many other protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's memb ...
s.
History
In 1555Olaus Magnus
Olaus Magnus (born Olof Månsson; October 1490 – 1 August 1557) was a Swedish writer, cartographer, and Catholic clergyman.
Biography
Olaus Magnus (a Latin translation of his Swedish birth name Olof Månsson) was born in Linköping in Octo ...
wrote of a marine worm which was apparently long ("40 cubits"), about the width of a child's arm, and whose touch made a hand swell. William Borlase
William Borlase (2 February 169631 August 1772), Cornish antiquary, geologist and naturalist. From 1722, he was Rector of Ludgvan, Cornwall, where he died. He is remembered for his works ''The Antiquities of Cornwall'' (1754; 2nd ed., 1769) a ...
wrote in 1758 of a "sea long worm", and in 1770 Gunnerus wrote a formal description of this animal, which he called ''Ascaris longissima''. Its current name, ''Lineus longissimus
The bootlace worm (''Lineus longissimus'') is a species of ribbon worm and one of the longest known animals, with specimens up to long being reported. Its mucus is highly toxic.
Taxonomy
The bootlace worm is in the phylum Nemertea or ribbon wor ...
'', was first used in 1806 by Sowerby. In 1995, a total of 1,149 species had been described and grouped into 250 genera.
Nemertea are named after the Greek sea-nymph
A nymph (; ; sometimes spelled nymphe) is a minor female nature deity in ancient Greek folklore. Distinct from other Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature; they are typically tied to a specific place, land ...
Nemertes, one of the daughters of Nereus
In Greek mythology, Nereus ( ; ) was the eldest son of Pontus (the Sea) and Gaia ( the Earth), with Pontus himself being a son of Gaia. Nereus and Doris became the parents of 50 daughters (the Nereids) and a son ( Nerites), with whom Nereus ...
and Doris. Alternative names for the phylum have included ''Nemertini'', ''Nemertinea'', and ''Rhynchocoela''. The Nemertodermatida
Nemertodermatida is a class of Acoelomorpha, comprising 18 species of millimetre-sized turbellariform, mostly interstitial worms.
Taxonomy
The order Nemertodermatida contains two families with 6 genera. The high level of cryptic diversity in ...
are a separate phylum, whose closest relatives appear to be the Acoela
Acoela, or the acoels, is an order of small and simple invertebrates in the subphylum Acoelomorpha of phylum Xenacoelomorpha, a deep branching bilaterian group of animals, which resemble flatworms. Historically they were treated as an order ...
.
Description
Body structure and major cavities
The typical nemertean body is very thin in proportion to its length. The smallest are a few millimeters long, most are less than , and several exceed . The longest animal ever found, at long, may be a specimen of ''Lineus longissimus
The bootlace worm (''Lineus longissimus'') is a species of ribbon worm and one of the longest known animals, with specimens up to long being reported. Its mucus is highly toxic.
Taxonomy
The bootlace worm is in the phylum Nemertea or ribbon wor ...
'', Ruppert, Fox and Barnes refer to a ''Lineus longissimus
The bootlace worm (''Lineus longissimus'') is a species of ribbon worm and one of the longest known animals, with specimens up to long being reported. Its mucus is highly toxic.
Taxonomy
The bootlace worm is in the phylum Nemertea or ribbon wor ...
'' long, washed ashore after a storm off St Andrews
St Andrews (; ; , pronounced ʰʲɪʎˈrˠiː.ɪɲ is a town on the east coast of Fife in Scotland, southeast of Dundee and northeast of Edinburgh. St Andrews had a recorded population of 16,800 , making it Fife's fourth-largest settleme ...
in Scotland. Other estimates are about . Zoologists find it extremely difficult to measure this species. For comparison:
* The longest recorded blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
was .
* The dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s ''Argentinosaurus
''Argentinosaurus'' (meaning "lizard from Argentina") is a genus of giant sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period in what is now Argentina. Although it is only known from fragmentary remains, ''Argentinos ...
'' and ''Patagotitan
''Patagotitan'' is a genus of titanosaurian sauropoda, sauropod dinosaur from the Cerro Barcino Formation in Chubut Province, Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species known from at least six young adult individuals, ''Patagotita ...
'' are estimated at approximately and respectively.
* A specimen of the Arctic giant jellyfish ''Cyanea capillata arctica
The lion's mane jellyfish (''Cyanea capillata'') is one of the largest known species of jellyfish. Its range is confined to cold, boreal waters of the Arctic, northern Atlantic, and northern Pacific Oceans. It is common in the English Channel, ...
'' was long.
''L. longissimus'', however, is usually only a few millimeters wide. The bodies of most nemerteans can stretch a lot, up to 10 times their resting length in some species, but reduce their length to 50% and increase their width to 300% when disturbed. A few have relatively short but wide bodies, for example ''Malacobdella grossa'' is up to long and wide, and some of these are much less stretchy. Smaller nemerteans are approximately cylindrical, but larger species are flattened dorso-ventrally. Many have visible patterns in various combinations of yellow, orange, red and green.
The outermost layer of the body has no cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
, but consists of a cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
ted and gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also funct ...
ular epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
containing rhabdite
Rhabdites (from Greek, ''rhabdos'', rod) are rodlike structures in the cells of the epidermis or underlying parenchyma in certain turbellarians, and in the epidermis of nemertea
Nemertea is a phylum of animals also known as ribbon worms or ...
s, which form the mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
in which the cilia glide. Each ciliated cell has many cilia and microvilli
Microvilli (: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, cellula ...
. The outermost layer rests on a thickened basement membrane
The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tis ...
, the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
. Next to the dermis are at least three layers of muscles, some circular and some longitudinal. The combinations of muscle types vary between the different classes, but these are not associated with differences in movement. Nemerteans also have dorso-ventral muscles, which flatten the animals, especially in the larger species. Inside the concentric tubes of these layers is mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
, a kind of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
. In pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
species this tissue is gelatinous and buoyant.
They are unsegmented, but at least one species, Annulonemertes minusculus, is segmented. But this is assumed to be a derived trait. The segmentation does not include the coelom and body wall, and is therefore referred to as pseudosegmentation.
The mouth is ventral and a little behind the front of the body. The foregut, stomach and intestine run a little below the midline of the body and the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
is at the tip of the tail. Above the gut and separated from the gut by mesenchyme is the rhynchocoel, a cavity which mostly runs above the midline and ends a little short of the rear of the body. The rhynchocoel of class Anopla
Anopla (for changes in taxonomy, see reference from 2019) has long been used as name for a Class (biology), class of marine worms of the phylum Nemertea, characterized by the absence of stylet (anatomy), stylets on the proboscis, the mouth being ...
has an orifice a little to the front of the mouth, but still under the front of the body. In the other class, Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the proboscis.
Evolution and systematics
The record of nemerteans is extremely sparse, as would be expected ...
, the mouth and the front of the rhynchocoel share an orifice. The rhynchocoel is a coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
, as it is lined by epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
.
Proboscis and feeding
Theproboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a pr ...
is an infolding of the body wall, and sits in the rhynchocoel when inactive. When muscles in the wall of the rhynchocoel compress the fluid inside, the pressure makes the proboscis jump inside-out along a canal called the rhynchodeum and through an orifice, the proboscis pore. The proboscis has a muscle which attaches to the back of the rhynchocoel, can stretch up to 30 times its inactive length and acts to retract the proboscis.
 The proboscis of the
The proboscis of the class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Anopla
Anopla (for changes in taxonomy, see reference from 2019) has long been used as name for a Class (biology), class of marine worms of the phylum Nemertea, characterized by the absence of stylet (anatomy), stylets on the proboscis, the mouth being ...
exits from an orifice which is separate from the mouth, coils around the prey and immobilizes it by sticky, toxic secretions. The Anopla can attack as soon as the prey moves into the range of the proboscis. Some Anopla have branched proboscises which can be described as "a mass of sticky spaghetti". The animal then draws its prey into its mouth.
 In most of the class
In most of the class Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the proboscis.
Evolution and systematics
The record of nemerteans is extremely sparse, as would be expected ...
, the proboscis exits from a common orifice of the rhynchocoel and mouth. A typical member of this class has a stylet, a calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime (mineral), lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of Science, scientific disciplines.
In zoology
''Calcare ...
barb, with which the animal stabs the prey many times to inject toxins and digestive secretions. The prey is then swallowed whole or, after partial digestion, its tissues are sucked into the mouth. The stylet is attached about one-third of the distance from the end of the evert
Evert is a Dutch and Swedish short form of the Germanic masculine name "Everhard" (alternative Eberhard).Evert
at the
ed proboscis, which extends only enough to expose the stylet. On either side of the active stylet are sacs containing back-up stylets to replace the active one as the animal grows or an active one is lost. Instead of one stylet, the at the
Polystilifera
Polystilifera is an suborder of worms belonging to the order Hoplonemertea.
Families:
* Armaueriidae
* Balaenanemertidae
* Brinkmanniidae
* Buergeriellidae
* Chuniellidae
* Dinonemertidae
* Drepanobandidae
* Drepanogigantidae
* Drepanophorellida ...
have a pad that bears many tiny stylets, and these animals have separate orifices for the proboscis and mouth, unlike other Enopla. The Enopla can only attack after contacting the prey.
Some nemerteans, such as ''L. longissimus'', absorb organic food in solution through their skins, which may make the long, slim bodies an advantage. Suspension feeding
Filter feeders are aquatic animals that acquire nutrients by feeding on organic matters, food particles or smaller organisms (bacteria, microalgae and zooplanktons) suspended in water, typically by having the water pass over or through a specia ...
is found only among the specialized symbiotic bdellonemerteans, which have a proboscis but no stylet, and use suckers to attach themselves to bivalve
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed b ...
s.
Respiration and circulatory system
Nemerteans lack specializedgills
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
, and respiration occurs over the surface of the body, which is long and sometimes flattened. Like other animals with thick body walls, they use fluid circulation rather than diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
to move substances through their bodies. The circulatory system consists of the rhynchocoel and peripheral vessels, while their blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
is contained in the main body cavity. The fluid in the rhynchocoel moves substances to and from the proboscis, and functions as a fluid skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
in everting the proboscis and in burrowing. The vessels circulate fluid round the whole body and the rhynchocoel provides its own local circulation. The circulatory vessels are a system of coeloms.
In the simplest type of circulatory system, two lateral vessels are joined at the ends to form a loop. However, many species have additional long-wise and cross-wise vessels. There is no heart nor pumping vessels, and the flow of fluid depends on contraction of both the vessels and the body wall's muscles. In some species, circulation is intermittent, and fluid ebbs and flows in the long-wise vessels. The fluid in the vessels is usually colorless, but in some species it contains cells that are yellow, orange, green or red. The red type contain hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
and carry oxygen, but the function of the other pigments is unknown.
Excretion
 Nemertea use organs called
Nemertea use organs called protonephridia
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia co ...
to excrete soluble waste products, especially nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
ous by-products of cellular metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. In nemertean protonephridia, flame cell
A flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in simple invertebrates, including flatworms ( Platyhelminthes), rotifers and nemerteans; these are the simplest animals to have a dedicated excretory system. Flame cells function like a kidney ...
s which filter out the wastes are embedded in the front part of the two lateral fluid vessels. The flame cells remove the wastes into two collecting ducts, one on either side, and each duct has one or more nephridiopore A nephridiopore is part of the nephridium, an excretory organ found in many organisms, such as flatworms and annelids. Polychaetes typically release their gametes into the water column using nephridiopores.
Nephridia are homologous to nephrons ...
s through which the wastes exit. Semiterrestrial and freshwater nemerteans have many more flame cells than marines, sometimes thousands. The reason may be that osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration ...
is more difficult in non-marine environments.
Nervous-system and senses
 The central nervous-system consists of a
The central nervous-system consists of a brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
and paired ventral nerve cord
The ventral nerve cord is a major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It is the functional equivalent of the vertebrate spinal cord. The ventral nerve cord coordinates neural signaling from the brain to the body and vice ve ...
s that connect to the brain and run along the length of the body. The brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
is a ring
(The) Ring(s) may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
Arts, entertainment, and media Film and TV
* ''The Ring'' (franchise), a ...
of four ganglia
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there a ...
, masses of nerve cells, positioned round the rhynchocoel near its front end – while the brains of most protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's memb ...
invertebrates encircle the foregut. Most nemertean species have just one pair of nerve cords, many species have additional paired cords, and some species also have a dorsal cord. In some species the cords lie within the skin, but in most they are deeper, inside the muscle layers. The central nervous-system is often red or pink because it contains hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
. This stores oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
for peak activity or when the animal experiences anoxia, for example while burrowing
An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of s ...
in oxygen-free sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s.
Some species have paired cerebral
Cerebral may refer to:
* Of or relating to the brain
* Cerebrum, the largest and uppermost part of the brain
* Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the cerebrum
* Retroflex consonant, also referred to as a cerebral consonant, a type of consonant so ...
organs, sacs whose only openings are to the outside. Others species have unpaired evertible organs on the front of their heads. Some have slits along the side of the head or grooves obliquely across the head, and these may be associated with paired cerebral organs. All of these are thought to be chemoreceptor
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance ( endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorece ...
s, and the cerebral organs may also aiding osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration ...
. Small pits in the epidermis appear to be sensors. On their head, some species have a number of pigment-cup ocelli
A simple eye or ocellus (sometimes called a pigment pit) is a form of eye or an optical arrangement which has a single lens without the sort of elaborate retina that occurs in most vertebrates. These eyes are called "simple" to distinguish the ...
, which can detect light but not form an image. Most nemerteans have two to six ocelli, although some have hundreds. A few tiny species that live between grains of sand have statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, crustaceans, and gastropods, A similar structure is also found in '' Xenoturbella''. T ...
s, which sense balance.
''Paranemertes peregrina
''Paranemertes peregrina'' is a species of Nemertea, or ribbon worm, in the family Neesiidae.
Description
''P. peregrina'' is usually dark dorsally, with a brown or purple coloration. It appears peach-colored due to its lighter ventral colorat ...
'', which feeds on polychaetes, can follow the prey's trails of mucus, and find its burrow by backtracking along its own trail of mucus.
Movement
Nemerteans generally move slowly, though they have occasionally been documented to successfully prey on spiders or insects. Most nemerteans use their external cilia to glide on surfaces on a trail ofslime
Slime or slimy may refer to:
Science and technology Biology
* Slime coat, the coating of mucus covering the body of all fish
* Slime mold, an informal name for several eukaryotic organisms
* Biofilm, or slime, a syntrophic community of micr ...
, some of which is produced by glands in the head. Larger species use muscular waves to crawl, and some aquatic species swim by dorso-ventral undulations. Some species burrow by means of muscular peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
, and have powerful muscles. Some species of the suborder
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized ...
Monostilifera
Monostilifera is a suborder of nemertean worms belonging to the class Hoplonemertea (formerly Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the p ...
, whose proboscis have one active stylet, move by extending the proboscis, sticking it to an object and pulling the animal toward the object.
Reproduction and life-cycle
Larger species often break up when stimulated, and the fragments often grow into full individuals. Some species fragment routinely and even parts near the tail can grow full bodies. But this kind of extreme regeneration is restricted to only a few types of nemerteans, and is assumed to be a derived feature. Allreproduce sexually
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex Biological life cycle, life cycle in which a gamete (haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to p ...
, and most species are gonochoric
In biology, gonochorism is a sexual system where there are two sexes and each individual organism is either male or female. The term gonochorism is usually applied in animal species, the vast majority of which are gonochoric.
Gonochorism contrast ...
(the sexes are separate), but all the freshwater forms are hermaphroditic
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
.
Nemerteans often have numerous temporary gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s (ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
or testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
), forming a row down each side of the body in the mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
. Temporary gonoducts (ducts from which the ova
, abbreviated as OVA and sometimes as OAV (original animation video), are Japanese animated films and special episodes of a series made specially for release in home video formats without prior showings on television or in theaters, though the ...
or sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
are emitted), one per gonad, are built when the ova and sperm are ready. The eggs are generally fertilised externally. Some species shed them into the water, some lay them in a burrow or tube, and some protect them by cocoons or gelatinous
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolysis, hydrolyzed col ...
strings. Some bathypelagic
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypela ...
(deep sea) species have internal fertilization
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For inte ...
, and some of these are viviparous
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juve ...
, growing their embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
s in the female's body.
The zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
(fertilised egg) divides by spiral cleavage
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells the same siz ...
and grows by determinate development, in which the fate of a cell can usually be predicted from its predecessors in the process of division. The embryos of most taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
develop either directly to form juveniles (like the adult but smaller) or to form planuliform larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e. The planuliform larva stage may be short-lived and lecithotrophic ("yolky") before becoming a juvenile, or may be planktotrophic
Marine larval ecology is the study of the factors influencing dispersing larvae, which many marine invertebrates and fishes have. Marine animals with a larva typically release many larvae into the water column, where the larvae develop before meta ...
, swimming for some time and eating prey larger than microscopic particles. However, many members of the order Heteronemertea
Heteronemertea is a Monophyly, monophyletic order (biology), order of about 500 species of nemertean worms. It contains genus, genera such as ''Lineus'' and ''Cerebratulus'', and includes the largest and most muscular nemerteans.
Almost all hete ...
and the palaeonemertea
Palaeonemertea is a class of primitive nemertean worm. It may be para- or polyphyletic, consisting of three to five clades and totalling about 100 species.
These worms have several apparently simple features and, as their name suggests, they ar ...
n family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Hubrechtiidae
Hubrechtiidae is a family of worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateria, bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limb (anatomy), limbs, and usually no eyes.
Worms vary in size from micro ...
form a pilidium larva, which can capture unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
and which Maslakova describes as like a deerstalker
A deerstalker is a type of cap that is typically worn in rural areas, often for hunting, especially deer stalking. Because of the cap's popular association with the fictional detective Sherlock Holmes, it has become stereotypical headgear f ...
cap with the ear flaps pulled down. It has a gut which lies across the body, a mouth between the "ear flaps", but no anus. A small number of imaginal disc
An imaginal disc is one of the parts of a holometabolous insect larva that will become a portion of the outside of the adult insect during the pupal transformation to the imago. Contained within the body of the larva, there are pairs of discs t ...
s form, encircling the archenteron
The archenteron, also called the gastrocoel, is the internal cavity formed in the gastrulation stage in early embryonic development that becomes the cavity of the primitive gut.
Formation in sea urchins
As primary mesenchyme cells detach fro ...
(developing gut) and coalesce to form the juvenile. When it is fully formed, the juvenile bursts out of the larva body and usually eats it during this catastrophic metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth transformation or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and different ...
. This larval stage is unique in that there are no Hox gene
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox, homeobox genes, are a gene cluster, group of related genes that Evolutionary developmental biology, specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the craniocaudal axis, head-tail axis of animals. Hox protein ...
s involved during development, which are only found in the juveniles developing inside the larvae.
The species ''Paranemertes peregrina
''Paranemertes peregrina'' is a species of Nemertea, or ribbon worm, in the family Neesiidae.
Description
''P. peregrina'' is usually dark dorsally, with a brown or purple coloration. It appears peach-colored due to its lighter ventral colorat ...
'' has been reported as having a life span of around 18 months.
Ecological significance
 Most nemerteans are marine animals that burrow in sediments, lurk in crevices between shells, stones or the
Most nemerteans are marine animals that burrow in sediments, lurk in crevices between shells, stones or the holdfast
Holdfast most often refers to:
*Holdfast (biology), a root-like structure that anchors aquatic sessile organisms to their substrate
*Holdfast (tool), a tool used to secure a workpiece to a workbench or anvil
Holdfast or hold fast may also refer t ...
s of algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
or sessile
Sessility, or sessile, may refer to:
* Sessility (motility), organisms which are not able to move about
* Sessility (botany), flowers or leaves that grow directly from the stem or peduncle of a plant
* Sessility (medicine), tumors and polyps that ...
animals. Some live deep in the open oceans, and have gelatinous bodies. Others build semi-permanent burrows lined with mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
or produce cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coate ...
-like tubes. Mainly in the tropics and subtropics, about 12 species appear in freshwater, and about a dozen species live on land in cool, damp places, for example under rotting logs.
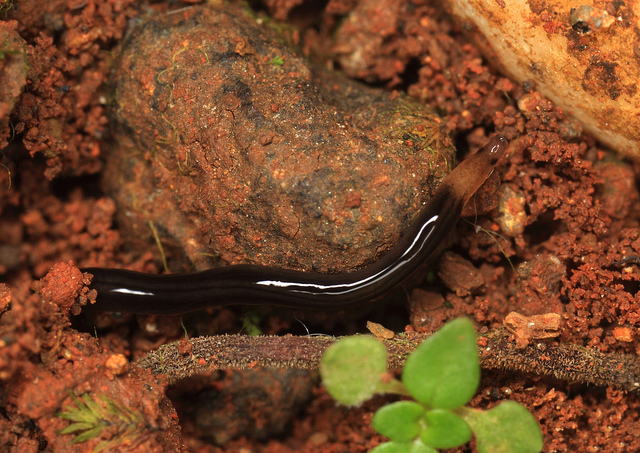
The terrestrial ''Argonemertes dendyi'' is a native of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
but has been found in the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
, in Sao Miguel in the Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
, in Gran Canaria
Gran Canaria (, ; ), also Grand Canary Island, is the third-largest and second-most-populous island of the Canary Islands, a Spain, Spanish archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa. the island had a population of that constitut ...
, and in a lava tube
A lava tube, more rarely called a pyroduct, is a 'roofed conduit through which molten lava travels away from its vent'. If lava in the tube drains out, it will leave an empty cave. Lava tubes are common in low-viscosity volcanic systems. La ...
at Kaumana on the Island of Hawaii
Hawaii is the List of islands of the United States by area, largest island in the United States, located in the Hawaii, state of Hawaii, the southernmost state in the union. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of volcani ...
. It can build a cocoon, which allows it to avoid desiccation while being transported, and it may be able to build populations quickly in new areas as it is a protandrous
Sequential hermaphroditism (called dichogamy in botany) is one of the two types of hermaphroditism, the other type being simultaneous hermaphroditism. It occurs when the organism's sex changes at some point in its life. A sequential hermaphrodit ...
hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
. Another terrestrial genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
, ''Geonemertes
''Geonemertes'' is a genus of nemerteans belonging to the family Prosorhochmidae.
The species of this genus are found in all world oceans.
Species:
*''Geonemertes caeca''
*''Geonemertes graffi''
*''Geonemertes pelaensis''
*''Geonemertes per ...
'', is mostly found in Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different context ...
but has species in the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
, widely across the Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
, in Tristan da Cunha
Tristan da Cunha (), colloquially Tristan, is a remote group of volcano, volcanic islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascensi ...
in the South Atlantic, in Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, in the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, in Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ...
and in the Azores. ''Geonemertes pelaensis
''Geonemertes pelaensis'' is a species of terrestrial Nemertea.Norenburg, J.; Gibson, R.; Herrera Bachiller, A.; Strand, M. (2021). World Nemertea Database. Geonemertes pelaensis Semper, 1863. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at ...
'' has been implicated in the decline of native arthropod species on the Ogasawara Islands
The Bonin Islands, also known as the , is a Japanese archipelago of over 30 subtropical and tropical islands located around SSE of Tokyo and northwest of Guam. The group as a whole has a total area of but only two of the islands are permanen ...
, where it was introduced in the 1980s.
Most are carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they ar ...
s, feeding on annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s, clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
s and crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, and may kill annelids of about their own size. They sometimes take fish, both living and dead. Insects and myriapod
Myriapods () are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.
Although molecular evidence and similar fossils suggests a diversifi ...
s are the only known prey of the two terrestrial species of ''Argonemertes''.
A few nemerteans are scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume Corpse decomposition, dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a he ...
s, and these generally have good distance chemoreception
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance (endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorecept ...
("smell") and are not selective about their prey. A few species live commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
ly inside the mantle cavity of molluscs and feed on micro-organisms filtered out by the host.
Near San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
the nemertean '' Carcinonemertes errans'' has consumed about 55% of the total egg production of its host, the dungeness crab
The Dungeness crab (''Metacarcinus magister'') makes up one of the most important seafood industries along the west coast of North America. Its typical range extends from Alaska's Aleutian Islands to Point Conception, near Santa Barbara, Califo ...
''Metacarcinus magister''. ''C. errans'' is considered a significant factor in the collapse of the dungeness crab fishery. Other coastal nemerteans have devastated clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
beds.
The few predators on nemerteans include bottom-feeding fish, some sea birds, a few invertebrates including horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only surviving xiphosurans. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or even crustaceans; they are chelicerates, more closely related to arachnids like spiders, ticks, and scor ...
s, and other nemerteans. Nemerteans' skins secrete toxins that deter many predators, but some crabs may clean nemerteans with one claw before eating them. The American ''Cerebratulus lacteus
''Cerebratulus lacteus'', the milky nemertean or milky ribbon worm, is a proboscis worm in the family Lineidae. This ribbon worm has a wide geographical range on both sides of the northern Atlantic Ocean.
Description
''Cerebratulus lacteus'' gr ...
'' and the South African ''Polybrachiorhynchus dayi'', both called "tapeworms" in their respective localities, are sold as fish bait.
Taxonomy
Traditional taxonomic classification has divided the group into two classes and four orders: *Class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Anopla
Anopla (for changes in taxonomy, see reference from 2019) has long been used as name for a Class (biology), class of marine worms of the phylum Nemertea, characterized by the absence of stylet (anatomy), stylets on the proboscis, the mouth being ...
("unarmed"). Includes animals with proboscis without stylet, and a mouth underneath and behind the brain.
** Order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Palaeonemertea
Palaeonemertea is a class of primitive nemertean worm. It may be para- or polyphyletic, consisting of three to five clades and totalling about 100 species.
These worms have several apparently simple features and, as their name suggests, they ar ...
. Comprises 100 marine species. Their body wall has outer circular and inner length-wise muscles. In addition, ''Carinoma tremaphoros'' has circular and inner length-wise muscles in the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
; the extra muscle layers seem to be needed for burrowing
An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of s ...
by peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
.
** Order Heteronemertea
Heteronemertea is a Monophyly, monophyletic order (biology), order of about 500 species of nemertean worms. It contains genus, genera such as ''Lineus'' and ''Cerebratulus'', and includes the largest and most muscular nemerteans.
Almost all hete ...
. Comprises about 400 species. The majority are marine, but three are freshwater. Their body-wall muscles are disposed in four layers, alternately circular and length-wise starting from the outermost layer. The order includes the strongest swimmers. Two genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
have branched proboscises.
* Class Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the proboscis.
Evolution and systematics
The record of nemerteans is extremely sparse, as would be expected ...
("armed"). All have stylets except order Bdellonemertea. Their mouth is located underneath and ahead of the brain. Their main nerve cords run inside body-wall muscles.
** Order Bdellonemertea. Includes seven species, of which six live as commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
s in the mantle of large clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
s and one in that of a freshwater snail. The hosts filter feed
Filter feeders are aquatic animals that acquire nutrients by feeding on organic matters, food particles or smaller organisms (bacteria, microalgae and zooplanktons) suspended in water, typically by having the water pass over or through a specia ...
and all the hosts steal food from them. These nemerteans have short, wide bodies and have no stylets but have a sucking pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
and a posterior stucker, with which they move like inchworm
The geometer moths are moths belonging to the family Geometridae of the insect order Lepidoptera, the moths and butterflies. Their scientific name derives from the Ancient Greek (derivative form of or "the earth"), and "measure" in referen ...
s.
** Order Hoplonemertea
Hoplonemertea is a class of ribbon worms. It contains two orders:
* Monostilifera
* Polystilifera
The proboscis is armed with one or more stylets; intestine straight, mostly with paired lateral diverticula
In medicine or biology, a div ...
. Comprises 650 species. They live in benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "the depths". ...
and pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
sea water, in freshwater and on land. They feed by commensalism and parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
, and are armed with stylet(s)
*** Suborder Monostilifera
Monostilifera is a suborder of nemertean worms belonging to the class Hoplonemertea (formerly Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the p ...
. Includes 500 species with a single central stylet. Some use the stylet for locomotion as well as for capturing prey.
*** Suborder Polystilifera
Polystilifera is an suborder of worms belonging to the order Hoplonemertea.
Families:
* Armaueriidae
* Balaenanemertidae
* Brinkmanniidae
* Buergeriellidae
* Chuniellidae
* Dinonemertidae
* Drepanobandidae
* Drepanogigantidae
* Drepanophorellida ...
. Includes about 100 pelagic and 50 benthic species. Their pads bear many tiny stylets.
Recent molecular phylogenetic studies divided the group into two superclasses, three classes, and eight orders:
*Superclass Pronemertea
**Class Palaeonemertea
Palaeonemertea is a class of primitive nemertean worm. It may be para- or polyphyletic, consisting of three to five clades and totalling about 100 species.
These worms have several apparently simple features and, as their name suggests, they ar ...
***Order Carinomiformes
***Order Tubulaniformes
''Tubulaniformes'' is an order of worms belonging to the class Palaeonemertea.
Families:
* Callineridae Bergendal, 1901
* Carinomellidae Chernyshev, 1995
* Tubulanidae
Tubulanidae is a family of primitive nemertean worms in the order Palaeo ...
***Order Archinemertea
*Superclass Neonemertea
**Class Pilidiophora
Heteronemertea is a monophyletic order of about 500 species of nemertean worms. It contains genera such as '' Lineus'' and '' Cerebratulus'', and includes the largest and most muscular nemerteans.
Almost all heteronemerteans have three primar ...
***Order Hubrechtiiformes
***Order Heteronemertea
Heteronemertea is a Monophyly, monophyletic order (biology), order of about 500 species of nemertean worms. It contains genus, genera such as ''Lineus'' and ''Cerebratulus'', and includes the largest and most muscular nemerteans.
Almost all hete ...
**Class Hoplonemertea
Hoplonemertea is a class of ribbon worms. It contains two orders:
* Monostilifera
* Polystilifera
The proboscis is armed with one or more stylets; intestine straight, mostly with paired lateral diverticula
In medicine or biology, a div ...
(= Enopla)
***Order Polystilifera
Polystilifera is an suborder of worms belonging to the order Hoplonemertea.
Families:
* Armaueriidae
* Balaenanemertidae
* Brinkmanniidae
* Buergeriellidae
* Chuniellidae
* Dinonemertidae
* Drepanobandidae
* Drepanogigantidae
* Drepanophorellida ...
***Order Monostilifera
Monostilifera is a suborder of nemertean worms belonging to the class Hoplonemertea (formerly Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the p ...
(includes Bdellonemertea)
*''incertae sedis''
** Order Arhynchonemertea (provisionally has been separated its own class Arhynchocoela in 1995)
Evolutionary history
Fossil record
As nemerteans are mostly soft-bodied, one would expect fossils of them to be extremely rare. One might expect the stylet of a nemertean to be preserved, since it is made ofcalcium phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white ...
, but no fossil stylets have yet been found. reported nemertean fossils and traces from the Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epoch (geology), epochs of the Triassic period (geology), period or the middle of three series (stratigraphy), series in which the Triassic system (stratigraphy), system is di ...
of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
.
The Middle Cambrian
Middle or The Middle may refer to:
* Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits.
Places
* Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man
* Middle Bay (disambiguation)
* Middle Brook (disambiguation)
* Middle Creek (di ...
fossil ''Amiskwia
''Amiskwia'' is a genus of soft-bodied marine animals known from fossils of the Middle Cambrian Lagerstätten both in the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada and the Maotianshan shales of Yunnan Province, China. It is interpreted as a membe ...
'' from the Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fos ...
has been classed as a nemertean, based on a resemblance to some unusual deep-sea swimming nemerteans, but few paleontologists accept this classification as the Burgess Shale fossils show no evidence of rhynchocoel nor intestinal caeca.
reported fossils of vermiform
Vermes (" vermin/vermes") is an obsolete taxon used by Carl Linnaeus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck for non-arthropod invertebrate animals.
Linnaeus
In Linnaeus's ''Systema Naturae'', the Vermes had the rank of class, occupying the 6th (and last) ...
organisms with a wide range of morphologies occurring on bedding planes from the Late Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
(Katian
The Katian is the second stage of the Upper Ordovician. It is preceded by the Sandbian and succeeded by the Hirnantian Stage. The Katian began million years ago and lasted for about 7.6 million years until the beginning of the Hirnantian mill ...
) Vauréal Formation (Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
). In the specimens preserving the anterior end of the body, this end is pointed or rounded, bearing a rhynchocoel with the proboscis, which is characteristic for nemerteans. The authors attributed these fossils to nemerteans and interpreted them as the oldest record of the group reported so far. However, Knaust & Desrochers cautioned that partly preserved putative nemertean fossils might ultimately turn out to be fossils of turbellaria
The Turbellaria are one of the traditional sub-divisions of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), and include all the sub-groups that are not exclusively parasitic. There are about 4,500 species, which range from to large freshwater forms mo ...
ns or annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s.
It has been suggested that '' Archisymplectes'', one of the Pennsylvanian Pennsylvanian may refer to:
* A person or thing from Pennsylvania
* Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, on the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timesc ...
-age animals from Mazon Creek
The Mazon Creek fossil beds are a conservation ' found near Morris, in Grundy County, Illinois. The fossils are preserved in ironstone concretions, formed approximately in the mid- Pennsylvanian epoch of the Carboniferous period. These concr ...
in northern and central Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, may be a nemertean.
This fossil, however, only preserves the outline of the "worm", and there is no evidence of a proboscis,
so there is no certainty that it represents a nemertean.
Within Nemertea
There is no doubt that the phylum Nemertea ismonophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
(meaning that the phylum includes all and only descendants of one ancestor that was also a member of the phylum). The synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
(trait shared by an ancestor and all its descendants, but not by other groups) include the eversible proboscis located in the rhynchocoel.
While treat the Palaeonemertea as monophyletic, regard them as paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
and basal (contains the ancestors of the more recent clades). The Anopla
Anopla (for changes in taxonomy, see reference from 2019) has long been used as name for a Class (biology), class of marine worms of the phylum Nemertea, characterized by the absence of stylet (anatomy), stylets on the proboscis, the mouth being ...
("unarmed") represent an evolutionary grade
A grade is a taxon united by a level of morphological or physiological complexity. The term was coined by British biologist Julian Huxley, to contrast with clade, a strictly phylogenetic unit.
Phylogenetics
The concept of evolutionary grades ...
of nemerteans without stylets (comprising the Heteronemertea
Heteronemertea is a Monophyly, monophyletic order (biology), order of about 500 species of nemertean worms. It contains genus, genera such as ''Lineus'' and ''Cerebratulus'', and includes the largest and most muscular nemerteans.
Almost all hete ...
and the Palaeonemerteans), while Enopla
Enopla is one of the classes of the worm phylum Nemertea, characterized by the presence of a peculiar armature of spines or plates in the proboscis.
Evolution and systematics
The record of nemerteans is extremely sparse, as would be expected ...
("armed") are monophyletic, but find that Palaeonemertea is doubly paraphyletic, having given rise to both the Heteronemertea and the Enopla. treat the Bdellonemertea as a clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
separate from the Hoplonemertea
Hoplonemertea is a class of ribbon worms. It contains two orders:
* Monostilifera
* Polystilifera
The proboscis is armed with one or more stylets; intestine straight, mostly with paired lateral diverticula
In medicine or biology, a div ...
, while believe the Bdellonemertea are a part of the Monostilifera (with one active stylet), which are within the Hoplonemertea – which implies that "Enopla" and "Hoplonemertea" are synonyms for the same branch of the tree. The Polystilifera (with many tiny stylets) are monophyletic.
Relationships with other phyla
English-language writings have conventionally treated nemerteans as acoelomate bilaterians that are most closely related to flatworms (Platyhelminthes). These pre-cladistics
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to Taxonomy (biology), biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesiz ...
analyses emphasised as shared features: multiciliated (with multiple cilia per cell), glandular epidermis; rod-shaped secretory bodies or rhabdites; frontal glands or organs; protonephridia
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia co ...
; and acoelomate body organization. However, multiciliated epidermal cells and epidermal gland cells are also found in Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; : ctenophore ) is a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are ...
, Annelida
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to variou ...
, Mollusca and other taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
. The rhabdites of nemertea have a different structure from those of flatworms at the microscopic scale. The frontal glands or organs of flatworms vary a lot in structure, and similar structures appear in small marine annelids and entoproct
Entoprocta (), or Kamptozoa , is a phylum of mostly sessile aquatic animals, ranging from long. Mature individuals are goblet-shaped, on relatively long stalks. They have a "crown" of solid tentacles whose cilia generate water currents that d ...
larvae. The protonephridia of nemertea and flatworms are different in structure, and in position – the flame cell
A flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in simple invertebrates, including flatworms ( Platyhelminthes), rotifers and nemerteans; these are the simplest animals to have a dedicated excretory system. Flame cells function like a kidney ...
s of nemertea are usually in the walls of the fluid vessels and are served by "drains" from which the wastes exit by a small number of tubes through the skin, while the flame cells of flatworms are scattered throughout the body.
Rigorous comparisons show no synapomorphies of nemertean and platyhelminth nephridia.
According to more recent analyses, in the development of nemertean embryos, ectomesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical ...
(outer part of the mesoderm, which is the layer in which most of the internal organs are built) is derived from cells labelled 3a and 3b, and endomesoderm (inner part of the mesoderm) is derived from the 4d cell. Some of the ectomesoderm in annelids
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
, echiurans and mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s is derived from cells 3a and 3b, while the ectomesoderm of polyclad
The Polycladida represents a highly diverse clade of free-living marine flatworms. They are known from the littoral to the sublittoral zone (extending to the deep hot vents), and many species are common from coral reefs. Only a few species are fo ...
flatworm
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), ...
s is derived from the 2b cell and acoel
Acoela, or the acoels, is an order of small and simple invertebrates in the subphylum Acoelomorpha of phylum Xenacoelomorpha, a deep branching bilaterian group of animals, which resemble flatworms. Historically they were treated as an order of ...
flatworms produce no ectomesoderm. In nemerteans the space between the epidermis and the gut is mainly filled by well-developed muscles embedded in noncellular connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
. This structure is similar to that found in larger flatworms such as polyclad
The Polycladida represents a highly diverse clade of free-living marine flatworms. They are known from the littoral to the sublittoral zone (extending to the deep hot vents), and many species are common from coral reefs. Only a few species are fo ...
s and triclad
Planarians (triclads) are free-living flatworms of the class Turbellaria, order Tricladida, which includes hundreds of species, found in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial habitats.pp 3., "Planarians (the popular name for the group as a whole ...
s, but a similar structure of body-wall muscles embedded in noncellular connective tissue is widespread among the Spiralia
The Spiralia are a morphologically diverse clade of protostome animals, including within their number the molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths and other Taxon, taxa. The term ''Spiralia'' is applied to those phyla that exhibit canonical spiral clea ...
(animals in which the early cell divisions make a spiral pattern) such as sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of marine annelid worms, that have secondarily lost their segmentation. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum of unsegmented ...
ns, echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of ocean, marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, but e ...
ns and many annelids.
Nemerteans' affinities with Annelida (including Echiura, Pogonophora, Vestimentifera and perhaps Sipuncula) and Mollusca make the ribbon-worms members of Lophotrochozoa
Lophotrochozoa (, "crest/wheel animals") is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, and brach ...
, which include about half of the extant animal phyla. Lophotrochozoa groups: those animals that feed using a lophophore
The lophophore () is a characteristic feeding organ possessed by four major groups of animals: the Brachiopoda, Bryozoa, Hyolitha, and Phoronida, which collectively constitute the protostome group Lophophorata.Brachiopoda
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear e ...
, Bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary Colony (biology), colonies. Typically about long, they have a spe ...
, Phoronida
Phoronids ( taxonomic name Phoronida, sometimes called horseshoe worms) are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore (a "crown" of tentacles), and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies ...
, Entoprocta
Entoprocta (), or Kamptozoa , is a phylum (biology), phylum of mostly Sessility (zoology), sessile aquatic animals, ranging from long. Mature individuals are goblet-shaped, on relatively long stalks. They have a "crown" of solid tentacles whos ...
); phyla in which most members' embryos develop into trochophore
A trochophore () is a type of free-swimming planktonic marine larva with several bands of cilia.
By moving their cilia rapidly, they make a water eddy to control their movement, and to bring their food closer in order to capture it more easily.
...
larvae (for example Annelida and Mollusca); and some other phyla (such as Platyhelminthes, Sipuncula, Gastrotricha, Gnathostomulida, Micrognathozoa, Nemertea, Phoronida
Phoronids ( taxonomic name Phoronida, sometimes called horseshoe worms) are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore (a "crown" of tentacles), and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies ...
, Platyhelminthes, and Rotifera
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first described by Rev. John Harris ...
).
These groupings are based on molecular phylogeny
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
, which compares sections of organisms DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
. While analyses by molecular phylogeny are confident that members of Lophotrochozoa are more closely related to each other than of non-members, the relationships between members are mostly unclear.
Most protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's memb ...
phyla outside the Lophotrochozoa are members of Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa () is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda (insects, chelicerates (including arachnids), crustaceans, and myriapods), Nematoda, and several smaller phylum (biology), phyla. The grouping of these animal phyla into a single ...
("animals that molt
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is a process by which an animal casts off parts of its body to serve some beneficial purpose, either at ...
"), which include Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
a, Nematoda
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitism, parasitic. Parasitic ...
and Priapulida
Priapulida (priapulid worms, from Gr. πριάπος, ''priāpos'' ' Priapus' + Lat. ''-ul-'', diminutive), sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertilit ...
. Most other bilaterian
Bilateria () is a large clade of animals characterised by bilateral symmetry during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left–r ...
phyla are in the Deuterostomia
Deuterostomes (from Ancient Greek, Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryogenesis, embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three Phyl ...
, which include Echinodermata
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, ...
and Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) th ...
. The Acoelomorpha
Acoelomorpha is a subphylum of very simple and small soft-bodied organism, soft-bodied animals with planula-like features which live in marine (ocean), marine or brackish waters. They usually live between grains of sediment, swimming as plankton, ...
, which are neither protostomes nor deuterostomes, are regarded as basal bilaterians.
See also
*''Emplectonema neesii
''Emplectonema neesii'' is a species of ribbon worm in the phylum Nemertea. It is found on the middle and lower regions of the shore, under stones and in shingle and is common round the coasts of Britain and Ireland.
Description
Like other ribbo ...
''
*''Lineus longissimus
The bootlace worm (''Lineus longissimus'') is a species of ribbon worm and one of the longest known animals, with specimens up to long being reported. Its mucus is highly toxic.
Taxonomy
The bootlace worm is in the phylum Nemertea or ribbon wor ...
''
*''Parborlasia corrugatus
''Parborlasia corrugatus'' is a proboscis worm in the family Lineidae. It was formerly placed in family Cerebratulidae. This species of proboscis or ribbon worm can grow to in length, and lives in marine environments down to . This scavenger an ...
''
Notes
References
External links
The Marine Biological Laboratory: Phylum Nemertea (Nemertinea, Nemertini, Rhynchocoela)
{{Authority control Protostome phyla Extant Ordovician first appearances