|
Rotifera
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703. Most rotifers are around long (although their size can range from to over ), and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species. Some rotifers are free swimming and truly planktonic, others move by inchworming along a substrate, and some are sessile, living inside tubes or gelatinous holdfasts that are attached to a substrate. About 25 species are colonial (e.g., ''Sinantherina semibullata''), either sessile or planktonic. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton, being a major foodsource and with many species also contributing to the decomposition of soil organic matter. Genetic evidence indicates t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bdelloidea
Bdelloidea (from Greek language, Greek βδέλλα, ''bdella'' 'leech') is a Class (biology), class of rotifers found in freshwater habitats all over the world. There are over 450 described species of bdelloid rotifers (or 'bdelloids'), distinguished from each other mainly on the basis of Morphology (biology), morphology. The main characteristics that distinguish bdelloids from #Evolutionary Relationships, related groups of rotifers are exclusively parthenogenesis, parthenogenetic reproduction and the ability to survive in dry, harsh environments by entering a state of desiccation-induced dormancy (anhydrobiosis) at any life stage. They are often referred to as "ancient asexuals" due to their unique asexual history that spans back to over 25 million years ago through fossil evidence. Bdelloid rotifers are microscopic organisms, typically between 150 and 700 μm in length. Most are slightly too small to be seen with the naked eye, but appear as tiny white dots through even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachionus Calyciflorus
''Brachionus calyciflorus'' is a planktonic rotifer species occurring in freshwater. It is commonly used as a model organism in toxicology, ecology and evolutionary biology. Its advantages include the small size and short generation time (average generation time of ''B. calyciflorus'' is around 2.2 days at 24 °C). Taxonomy The taxonomy of Brachionus calyciflorus is well-established based on morphological and molecular characteristics. As a member of the phylum Rotifera, it shares many features with other rotifers, including a ciliated corona and a characteristic rotary motion. Within the genus Brachionus, there are several species, including B. plicatilis, which is also commonly used in research and aquaculture. Brachionus calyciflorus is distinct from other species in the genus due to its unique calyx-shaped lorica. Morphology Brachionus calyciflorus has a characteristic morphology that distinguishes it from other rotifer species. The body of Brachionus calyciflorus is elo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seisonidae
Seisonidae is a family of rotifers, found on the gills of '' Nebalia'', a marine crustacean. Peculiar among rotifers, they are gonochoric; males and females are both present and are equal in size. Both genders are similar with paired gonads. It is considered to have diverged from the other rotifers early on, and in one treatment is placed in a separate class Seisonoidea. They have a large and elongate body with reduced corona. Their muscular system is similar to that of other rotifers: they have longitudinal muscles as well as open annular muscles. Being attached for most of their life, they are semi-sessile, but are capable of detaching and crawl short distances if required. Feeding has never been observed directly, but the stomach in ''Seison nebaliae'' contained bacteria, while a substance that probably represents hemolymph of the ''Nebalia'' host was found in the stomach of ''Paraseison annulatus''. The latter prefer to settle beneath the carapace on the gills of the host's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it remains undifferentiated. In the past, and for practical purposes, coelom characteristics have been used to classify bilaterian animal phyla into informal groups. Etymology The term ''coelom'' derives from the Ancient Greek word () 'cavity'. Structure Development The coelom is the mesodermally lined cavity between the gut and the outer body wall. During the development of the embryo, coelom formation begins in the gastrulation stage. The developing digestive tube of an embryo forms as a blind pouch called the archenteron. In protostomes, the coelom forms by a process known as schizocoely. The archenteron initially forms, and the mesoderm splits into two layers: the first attaches to the body wall or ectoderm, forming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
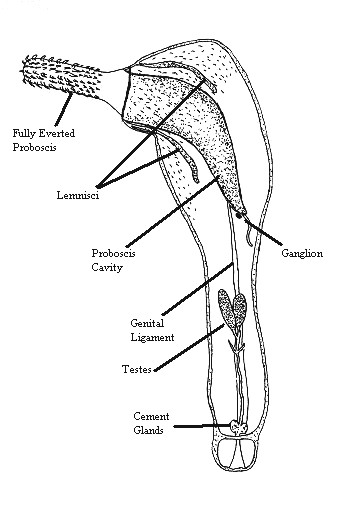
Acanthocephala
Acanthocephala ( Greek , ' 'thorn' + , ' 'head') is a group of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1,420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were long thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is sometimes known as Syndermata, or simply as Rotifera, with the acanthocephalans described as a subclass of a rotifer class Hemirotatoria. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684). In 1771 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogononta
Monogononta is a class of rotifers, found mostly in freshwater but also in soil and marine environments. They include both free-swimming and Sessility (zoology), sessile forms. Monogononts generally have a reduced Rotifer#Anatomy, corona, and each individual has a single gonad, which gives the group its name. Males are generally smaller than females, and are produced only during certain times of the year, with females otherwise reproducing through parthenogenesis. Their wikt:mastax, mastax is not designed for grinding. They produce mictic and amictic eggs. The class contains 1,570 species. Females are always diploid, and males are haploid. Diploid females produce two types of eggs. One type give rise to new females like themselves, and another that give rise to females that only produce haploid eggs. These will develop into males. When males, through hypodermic impregnation, inject sperm into the body cavity of females carrying a haploid egg, the fertilized egg will develop in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachionus Plicatilis
''Brachionus plicatilis'' is a euryhaline (tolerate a wide range of salinity) rotifer in the family '' Brachionidae'', and is possibly the only commercially important rotifer, being raised in the aquaculture industry as food for fish larvae. It has a broad distribution in salt lakes around the world and has become a model system for studies in ecology and evolution Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re .... Reproduction ''Brachionus'' species can normally reproduce asexually and sexually (cyclical parthenogenesis). Sexual reproduction (termed Mixis) is usually induced when population density increases. Mixis in Brachionus plicatilis has been shown to be induced by a density-dependent chemical cue. Genome size Haploid '1C' genome sizes in the ''Brachionus plicatilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
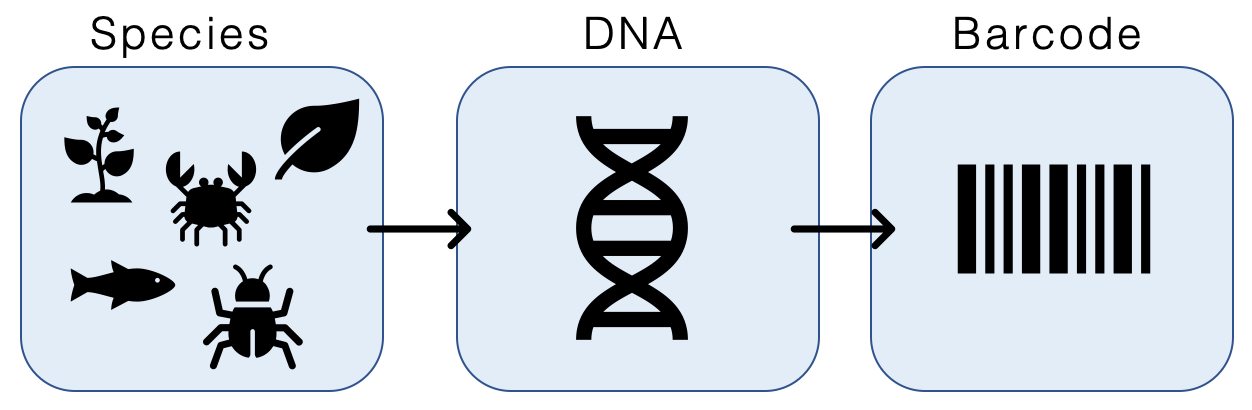
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called " sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (zoology)
Sessility is the biological property of an animal describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile animals for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile animals can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other organisms grow from a solid object, such as a rock, a dead tree trunk, or a human-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalodella Vittata
''Cephalodella'' is a genus of rotifers in the family Notommatidae, with 190 species worldwide. '' Cephalodella vittata'' is a species endemic to Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ....Hendrik Segers (2007). Annotated checklist of the rotifers (Phylum Rotifera), with notes on nomenclature, taxonomy Selected species * '' Cephalodella auritculata'' * '' Cephalodella catellina'' * '' Cephalodella elegans'' * '' Cephalodella forficata'' * '' Cephalodella forficula'' * '' Cephalodella gibba'' (Ehrenberg, 1830) * '' Cephalodella hoodi'' * '' Cephalodella marina'' Myers, 1924 * '' Cephalodella sterea'' * '' Cephalodella vittata'' References * O'Reilly, M. (2001). Rotifera, in: Costello, M.J. et al. (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across most or all of the surface of the Earth, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and environmental conditions, though this is not always so. Killer whales ( orcas) are among the most well-known cosmopolitan species on the planet, as they maintain several different resident and transient (migratory) populations in every major oceanic body on Earth, from the Arctic Circle to Antarctica and every coastal and open-water region in-between. Such a taxon (usually a species) is said to have a ''cosmopolitan'' distribution, or exhibit cosmopolitanism, as a species; another example, the rock dove (commonly referred to as a ' pigeon'), in addition to having been bred domestically for centuries, now occurs in most urban areas around the world. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic (native) species, or one foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |