Munster Plantation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The first Plantations of Ireland occurred during the Tudor conquest. The
The first Plantations of Ireland occurred during the Tudor conquest. The

Essex's Enterprise
''
 The second major influence on the plantation of Ulster was the political negotiation among the interest groups on the British side. The principal landowners were to be English Undertakers, wealthy men from England and Scotland who undertook to import tenants from their own estates. The planters were granted around each, on condition that they settle there a minimum of 48 adult males (including at least 20 families), who had to be
The second major influence on the plantation of Ulster was the political negotiation among the interest groups on the British side. The principal landowners were to be English Undertakers, wealthy men from England and Scotland who undertook to import tenants from their own estates. The planters were granted around each, on condition that they settle there a minimum of 48 adult males (including at least 20 families), who had to be
 In addition to the Ulster plantation, several other small plantations occurred under the reign of the Stuart Kings
In addition to the Ulster plantation, several other small plantations occurred under the reign of the Stuart Kings Since most land-owning families in Ireland had taken their estates by force in the previous four hundred years, very few of them, with the exception of the New English planters, had proper legal titles for them. As a result, in order to obtain such titles, they were required to forfeit a quarter of their lands. This policy was used against the Kavanaghs in Wexford and subsequently elsewhere, to break up Catholic Irish estates (especially the Gaelic ones) around the country. Following the precedent set in Wexford, small plantations were established in
Since most land-owning families in Ireland had taken their estates by force in the previous four hundred years, very few of them, with the exception of the New English planters, had proper legal titles for them. As a result, in order to obtain such titles, they were required to forfeit a quarter of their lands. This policy was used against the Kavanaghs in Wexford and subsequently elsewhere, to break up Catholic Irish estates (especially the Gaelic ones) around the country. Following the precedent set in Wexford, small plantations were established in  The Irish Catholic upper classes were unable to stop the continued plantations in Ireland because they had been barred from public office on religious grounds. By 1615 they comprised a minority in the Irish Parliament, as a result of the creation of "pocket boroughs" (where Protestants were in the majority) in planted areas. In 1625, they gained a temporary halt to land confiscations by agreeing to pay for England's war with France and Spain.
In addition to the plantations, thousands of independent settlers arrived in Ireland in the early 17th century, from the
The Irish Catholic upper classes were unable to stop the continued plantations in Ireland because they had been barred from public office on religious grounds. By 1615 they comprised a minority in the Irish Parliament, as a result of the creation of "pocket boroughs" (where Protestants were in the majority) in planted areas. In 1625, they gained a temporary halt to land confiscations by agreeing to pay for England's war with France and Spain.
In addition to the plantations, thousands of independent settlers arrived in Ireland in the early 17th century, from the
 Over 12,000 veterans of the
Over 12,000 veterans of the
 The plantations and their related agricultural development also radically altered Ireland's physical environment and ecology. In 1600, most of Ireland was heavily wooded and undeveloped, apart from the bogs. Most of the population lived in small, semi-nomadic townlands, many migrating seasonally to pastures for their cattle. By 1700, Ireland's native woodland had been reduced to a fraction of its former size; it was intensively logged and sold for profit by the plantation settlers for commercial ventures such as shipbuilding, as much of the English forests had been overlogged to total depletion, and the navy was becoming a great power. Several native animal species, such as the
The plantations and their related agricultural development also radically altered Ireland's physical environment and ecology. In 1600, most of Ireland was heavily wooded and undeveloped, apart from the bogs. Most of the population lived in small, semi-nomadic townlands, many migrating seasonally to pastures for their cattle. By 1700, Ireland's native woodland had been reduced to a fraction of its former size; it was intensively logged and sold for profit by the plantation settlers for commercial ventures such as shipbuilding, as much of the English forests had been overlogged to total depletion, and the navy was becoming a great power. Several native animal species, such as the
The Munster Plantation and the MacCarthys, 1583–1597
at The Irish Story {{DEFAULTSORT:Plantations of Ireland

Plantations
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tobacco ...
in 16th- and 17th-century Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
() involved the confiscation of Irish-owned land by the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
Crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
and the colonisation
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
of this land with settler
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a Human settlement, settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among ...
s from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
.
The main plantations took place from the 1550s to the 1620s, the biggest of which was the plantation of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster (; Ulster Scots dialects, Ulster Scots: ) was the organised Settler colonialism, colonisation (''Plantation (settlement or colony), plantation'') of Ulstera Provinces of Ireland, province of Irelandby people from Great ...
. The plantations led to the founding of many towns, massive demographic, cultural and economic changes, changes in land ownership and the landscape, and also to centuries of ethnic
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
and sectarian
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism a ...
conflict.
The Plantations took place before and during the earliest British colonization of the Americas
The British colonization of the Americas is the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and, after 1707, Kingdom of Grea ...
, and a group known as the West Country Men
The West Country Men were a group of influential individuals in Elizabethan England who advocated the English colonisation of Munster, attacks on the Spanish Empire, and the expansion of the English Empire. The group included Sir Humphrey Gilb ...
were involved in both Irish and American colonization.
There had been small-scale immigration from Britain since the 12th century, after the Anglo-Norman invasion. By the 15th century, direct English control had shrunk to an area called the Pale
The Pale ( Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast s ...
. In the 1540s the English Tudor conquest of Ireland
Ireland was conquered by the Tudor monarchs of England in the 16th century. The Anglo-Normans had Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, conquered swathes of Ireland in the late 12th century, bringing it under Lordship of Ireland, English rule. In t ...
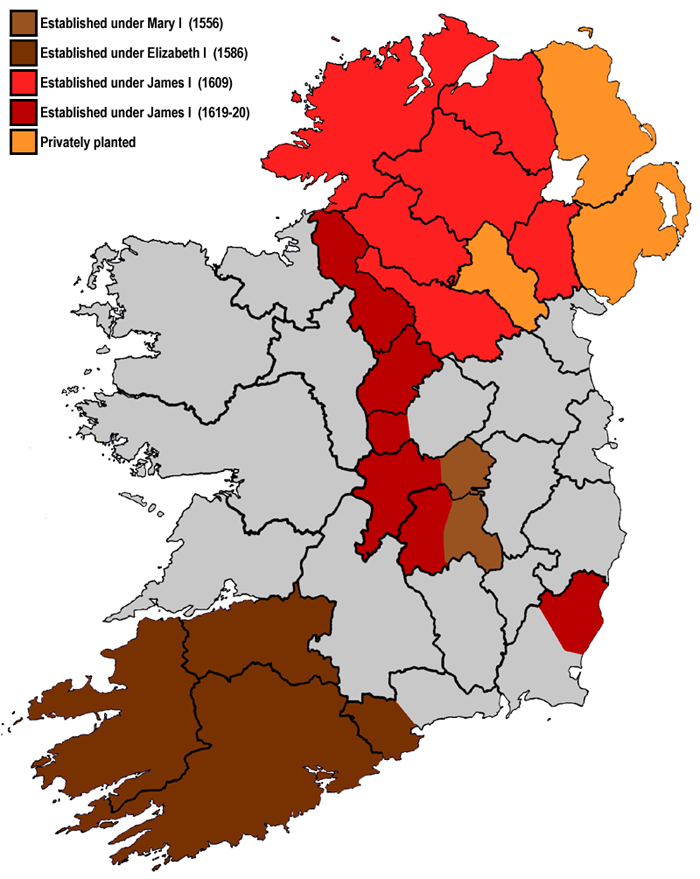
began. The first plantations were in the 1550s, during the reign of Queen Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain as the wife of King Philip II from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She made vigorous a ...
, in Laois
County Laois ( ; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and in the province of Leinster. It was known as Queen's County from 1556 to 1922. The modern county takes its name from Loígis, a medieval kingdom. Hist ...
(' Queen's County') and Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain ...
(' King's County'). These plantations were based around existing frontier
A frontier is a political and geographical term referring to areas near or beyond a boundary.
Australia
The term "frontier" was frequently used in colonial Australia in the meaning of country that borders the unknown or uncivilised, th ...
forts, but they were largely unsuccessful due to fierce resistance from native Irish clans.
The next plantations were during the reign of Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
. In 1568 there was an attempt to establish the first joint stock colony in Kerrycurrihy
Kerrycurrihy () is a historical barony in central County Cork, Ireland.
Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by ...
barony, but it was destroyed by the Irish. In the 1570s a privately funded plantation of east Ulster was attempted, but it also sparked conflict with the local Irish lord and ended in failure. The Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
plantation of the 1580s followed the Desmond Rebellions
The Desmond Rebellions occurred in 1569–1573 and 1579–1583 in the Irish province of Munster. They were rebellions by the Earl of Desmond, the head of the FitzGerald dynasty in Munster, and his followers, the Geraldines and their allies, ...
. Businessmen were encouraged to invest in the scheme and English colonists were settled on land confiscated from the defeated rebel lords. However, the settlements were scattered and attracted far fewer settlers than was hoped for. When the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
broke out in the 1590s, most of these settlements were abandoned, although English settlers began to return following the war.
The plantation of Ulster began in the 1610s, during the reign of James I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
* James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
* James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
* James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334� ...
. Following their defeat in the Nine Years' War, many rebel Ulster lords fled Ireland and their lands were confiscated. This was the biggest and most successful of the plantations and comprised most of the province of Ulster. While the province was mainly Irish-speaking and Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, the new settlers were required to be English-speaking Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
s,: "Advisors to King James VI/I, notably Arthur Chichester, Lord Deputy from 1604, and Sir John Davies, the lawyer, favoured the plantation as a definitive response to the challenges of ruling Ireland. ... Undertakers, servitors and natives were granted large blocks of land as long as they planted English-speaking Protestants". with most coming from the Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
and Northern England
Northern England, or the North of England, refers to the northern part of England and mainly corresponds to the Historic counties of England, historic counties of Cheshire, Cumberland, County Durham, Durham, Lancashire, Northumberland, Westmo ...
. This created a distinct Ulster Protestant
Ulster Protestants are an ethnoreligious group in the Irish province of Ulster, where they make up about 43.5% of the population. Most Ulster Protestants are descendants of settlers who arrived from Britain in the early 17th century Ulster Pl ...
community..
The Ulster plantation was one cause of the 1641 Irish Rebellion, during which thousands of settlers were killed, expelled or fled. After the Irish Catholics were defeated in the Cromwellian conquest of 1652, most remaining Catholic-owned land was confiscated and thousands of English soldiers settled in Ireland. Scottish settlement in Ulster resumed and intensified during the Scottish famine of the 1690s. By the 1720s, British Protestants were the majority in Ulster.
The plantations changed the demography of Ireland
Demography () is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analysis examine ...
by creating large communities with British and Protestant identities. The ruling classes of these communities replaced the older Catholic ruling class, which had shared with the general population a common Irish identity and set of political attitudes.
Background
There had been small-scale immigration from Britain in the 12th century, after the Anglo-Norman invasion, creating a small Anglo-Norman, English, Welsh and Flemish community in Ireland, under the Crown of England. By the 15th century, English control had shrunk to an area called The English Pale. By theTudor period
In England and Wales, the Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603, including the Elizabethan era during the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603). The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England, which began with ...
, however, Irish culture and language had regained most of the territory initially lost to the Anglo-Normans: "even in the Pale, all the common folk ... for the most part are of Irish birth, Irish habit and of Irish language". At a higher social level, there was intermarriage between the Gaelic Irish
The Gaels ( ; ; ; ) are an Insular Celtic ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx, and Scottish Gaeli ...
aristocracy and Anglo-Norman lords. To varying degrees inside and especially outside of the Pale, the 'Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
' had integrated into Irish society. Edmund Spenser
Edmund Spenser (; – 13 January 1599 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) was an English poet best known for ''The Faerie Queene'', an epic poem and fantastical allegory celebrating the House of Tudor, Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I. He is re ...
wrote of the ''old English'': "they are more sharpely to be chastised and reformed … for they are more stubborne, and disobedient to the law and government, than the Irish". English discourse on Ireland largely viewed the Gaelic Irish outside the Pale as savages, and compared them with the Native Americans in 1580.
In 1174 Rory O’Connor (Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair) defeated the Anglo-Norman army at Thurles
Thurles (; ''Durlas Éile'') is a town in County Tipperary, Ireland. It is located in the civil parish of the same name in the barony of Eliogarty and in the ecclesiastical parish of Thurles. The cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Arch ...
and began making incursions into the Pale itself forcing Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
to come to talks, the treaty of Windsor was drafted which was agreed upon that the Anglo-Normans would have mostly the Pale but couldn't make incursions into Irish held lands. Henry II would later disavow the treaty he agreed to and make incursions into Irish kingdoms, forfeiting his title as lord of Ireland and his right to the Pale itself, meaning subsequent claims by the English monarchy to Ireland such as Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
's lordship or later kingship were illegitimate.
Laudabiliter
was a papal bull, bull issued in 1155 by Pope Adrian IV, the only Englishman to have served in that office. Existence of the bull has been disputed by scholars over the centuries; no copy is extant but scholars cite the many references to it a ...
was a decree issued by the Pope that made Ireland's people the subjects of Henry II, however there is some debate on whether the Laudabiliter was legitimate or a forgery. The Laudabiliter could be compared to the Papal Bull "Inter Caetera," issued by Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI (, , ; born Roderic Llançol i de Borja; epithet: ''Valentinus'' ("The Valencian"); – 18 August 1503) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 11 August 1492 until his death in 1503.
Born into t ...
, which gave the Spanish the exclusive right to rule the lands discovered by Columbus, making the native Americans their "subjects". Despite this the Laudabiliter had a continuing political relevance into the 16th century. Henry VIII of England was excommunicated by Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III (; ; born Alessandro Farnese; 29 February 1468 – 10 November 1549) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 October 1534 to his death, in November 1549.
He came to the papal throne in an era follo ...
on 17 December 1538, causing his opponents to question his continuing claim to be Lord of Ireland, which was based ultimately on Laudabiliter. Henry established the Kingdom of Ireland in 1542.
Gerald of Wales
Gerald of Wales (; ; ; ) was a Cambro-Norman priest and historian. As a royal clerk to the king and two archbishops, he travelled widely and wrote extensively. He studied and taught in France and visited Rome several times, meeting the Pope. He ...
argued that the English crown has the right to rule Ireland because of a mission to civilise a barbarous people. His writings shaped English and European views of Ireland for centuries. He says: The idle woodland people the Irish reject agriculture, cities, the rights and privileges of citizenship and hence civilisation itself, the mission is to civilise and truly Christianise the Irish. The Irish rejected the Laudabiliter.
Early plantations (1556–1576)
 The first Plantations of Ireland occurred during the Tudor conquest. The
The first Plantations of Ireland occurred during the Tudor conquest. The Dublin Castle administration
Dublin Castle was the centre of the government of Ireland under English and later British rule. "Dublin Castle" is used metonymically to describe British rule in Ireland. The Castle held only the executive branch of government and the Privy Cou ...
intended to pacify and anglicise
Anglicisation or anglicization is a form of cultural assimilation whereby something non-English becomes assimilated into or influenced by the culture of England. It can be sociocultural, in which a non-English place adopts the English language ...
Irish territories controlled by the Crown and incorporate the Gaelic Irish aristocracy into the English-controlled Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
by using a policy of surrender and regrant
During the Tudor conquest of Ireland (c.1540–1603), "surrender and regrant" was the legal mechanism by which Irish clans were to be converted from a power structure rooted in clan and kin loyalties, to a late-Feudalism, feudal system under t ...
. The administration intended to develop Ireland as a peaceful and reliable possession, without risk of rebellion or foreign invasion. Wherever the policy of surrender and regrant failed, land was confiscated and English plantations were established. To this end, two forms of plantation were adopted in the second half of the 16th century. The first was the "exemplary plantation", in which small colonies of English would provide model farming communities that the Irish could emulate and be taxed.
Laois and Offaly
The second form set the trend for future English policy in Ireland. It was punitive/commercial in nature, as it provided for the plantation of English settlers on lands confiscated following the suppression of rebellions. The first such scheme was the Plantation of King's County (nowOffaly
County Offaly (; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain ...
) and Queen's County (now Laois
County Laois ( ; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and in the province of Leinster. It was known as Queen's County from 1556 to 1922. The modern county takes its name from Loígis, a medieval kingdom. Hist ...
) in 1556, naming them after the new Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
monarchs Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
and Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain as the wife of King Philip II from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She made vigorous a ...
respectively. The new county town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in ...
s were named Philipstown (now Daingean
Daingean (; or ), formerly Philipstown, named after King Philip II of Spain (then King of Ireland by ), is a small town in east County Offaly, Ireland. It is situated midway between the towns of Tullamore and Edenderry on the R402 regiona ...
) and Maryborough (now Portlaoise
Portlaoise ( ), or Port Laoise (), is the county town of County Laois, Republic of Ireland, Ireland.
It is in the Midland Region, Ireland, South Midlands in the province of Leinster.
Portlaoise was the fastest growing of the top 20 largest town ...
). An act, the Counties of Leix and Offaly Act 1556
The Settlement of Laois and Offaly Act 1556 (3 & 4 Phil. & Mar. c. 2 (I)) was an Act of the Parliament of Ireland passed in 1556 which resulted in the creation of Queen's County and King's County in the midlands of Ireland, and the establi ...
(3 & 4 Phil. & Mar. c. 2 (I)), was passed "whereby the King and Queen's Majesties, and the Heires and Successors of the Queen, be entitled to the Counties of Leix, Slewmarge, Irry, Glinmaliry, and Offaily, and for making the same Countries Shire Grounds.". The act was repealed in 1962. This plantation initiated the colonial settlement pattern for extending English control in hostile regions. The Leix-Offaly plantation also demonstrated to the Crown high cost of colonialism, leading them to encourage private financial participation in colonial ventures.
The O'Moore and O'Connor clans, which occupied the area, had traditionally raided the English-ruled Pale
Pale may refer to:
Jurisdictions
* Medieval areas of English conquest:
** Pale of Calais, in France (1360–1558)
** The Pale, or the English Pale, in Ireland
*Pale of Settlement, area of permitted Jewish settlement, western Russian Empire (179 ...
around Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
. The Lord Deputy of Ireland
The Lord Deputy was the representative of the monarch and head of the Irish executive (government), executive under English rule, during the Lordship of Ireland and then the Kingdom of Ireland. He deputised prior to 1523 for the Viceroy of Ireland ...
, the Earl of Sussex
Earl of Sussex is a title that has been created several times in the Peerages of England, Great Britain, and the United Kingdom. The early Earls of Arundel (up to 1243) were often also called Earls of Sussex.
The fifth creation came in the Pee ...
, ordered that they be dispossessed and replaced with an English settlement. However, the plantation was not a great success. The O'Moores and O'Connors retreated to the hills and bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and musk ...
s and fought a local insurgency against the settlement for much of the following 40 years. In 1578, the English finally subdued the displaced O'Moore clan by massacring most of their ''fine'' (or ruling families) at Mullaghmast
Mullaghmast (; modern English spelling: ''Mullamast'') is a hill in the south of County Kildare, Ireland, near the village of Ballitore and near the borders with counties Wicklow, Laois and Carlow. It was an important site in prehistory, in ea ...
in Laois, having invited them there for peace talks. Rory Oge O'More
Rory Oge O'More (; – 30 June 1578) was an Irish noble and chief of the O'More clan. As the Lord of Laois, he rebelled against the Tudors' sixteenth-century conquest of Gaelic Ireland.
Irish nationalists Patrick Pearse and Philip O'Sul ...
, the leader of rebellion in the area, was hunted down and killed later that year. The ongoing violence meant that the authorities had difficulty in attracting people to settle in their new plantation. Settlement ended up clustered around a series of military fortifications.

Kerrycurrihy
In 1568–1569,Warham St Leger
Sir Warham St Leger PC (Ire) ( – 1597) was an English soldier, administrator, and politician, who sat in the Irish House of Commons in the Parliament of 1585–1586.
Birth and origins
Warham was probably born in 1525 in England, the second so ...
and Richard Grenville
Sir Richard Grenville ( – ), also spelt Greynvile, Greeneville, and Greenfield, was an English privateer and explorer. Grenville was lord of the manors of Stowe, Cornwall and Bideford, Devon. He subsequently participated in the plantat ...
tried to establish a small English joint stock colony in the barony of Kerrycurrihy
Kerrycurrihy () is a historical barony in central County Cork, Ireland.
Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by ...
, by Cork Harbour
Cork Harbour () is a natural harbour and river estuary at the mouth of the River Lee (Ireland), River Lee in County Cork, Ireland. It is one of several which lay claim to the title of "second largest natural harbour in the world by navigational ...
, on land leased from the Earl of Desmon. They then proposed establishing larger corporate colonies in late 1568 creating a consortium of English merchants to fund a colony in Baltimore, west Co. Cork, mainly for exploiting the fisheries in Munster. The scheme was privately funded but also received a stipend from the English crown At about this time as part of the joint stock scheme Grenville also seized lands from the native Irish for colonization at Tracton
Tracton () is a civil parish in southeast County Cork in Ireland. Lying roughly 7 kilometres south of Carrigaline, it lies within the Dáil constituency of Cork South-Central. The area is named after Tracton Abbey, a Cistercian monastery that ...
, to the west of Cork harbour creating the first English joint stock colony in history. After Richard Greenville had departed from Ireland the fledging colony of Tracton was sacked by Donald McCarthy, 1st Earl of Clancare and Fitzmaurice along with the native inhabitants. The colony was small and quickly overwhelmed and all the English colonial inhabitants were killed except three or four English soldiers, who were promptly executed the next day. Sir Peter Carew had also asserted his claim to lands in south Leinster. The plantations in the south of Ireland led to bitter disputes with local Irish. However, in June 1569 the fledgling colonies were destroyed by the Irish under James FitzMaurice
James Michael Christopher Fitzmaurice DFC (6 January 1898 – 26 September 1965) was an Irish aviation pioneer. He was a member of the crew of the ''Bremen'', which made the first successful trans-Atlantic aircraft flight from East to West o ...
when the first Desmond Rebellion
The Desmond Rebellions occurred in 1569–1573 and 1579–1583 in the Irish province of Munster. They were rebellions by the Earl of Desmond, the head of the FitzGerald dynasty in Munster, and his followers, the Geraldines and their allies, a ...
began.
Dr Hiram Morgan
Hiram Morgan (born 1960) is an Irish historian. He is an expert on the Nine Years War (1594–1603), the career of Hugh O'Neill (1550–1616) and Ireland's connections with Europe and beyond. He was chairman of the Royal Irish Academy Committe ...
has stated that the Plantations of Munster starting with St leger were the prototype for the American colonies, the joint stock Irish model became the model for the Virginia Company
The Virginia Company was an English trading company chartered by King James I on 10 April 1606 with the objective of colonizing the eastern coast of America. The coast was named Virginia, after Elizabeth I, and it stretched from present-day ...
.
East Ulster
In the 1570s, there was an attempt to colonize parts of eastUlster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
, which had formerly been part of the English Earldom of Ulster
The Earldom of Ulster was an Anglo-Norman lordship in north-eastern Ireland during the Middle Ages, ruled by the Earls of Ulster and part of the Lordship of Ireland. The Norman knight John de Courcy invaded the Gaelic Irish kingdom of Ulaid ...
. It was known as the "Enterprise of Ulster". During the conflict between the English and Shane O'Neill, there were proposals to colonize parts of east Ulster, but Crown support was not forthcoming. Following Shane O'Neill's death, an act of attainder
A bill of attainder (also known as an act of attainder, writ of attainder, or bill of pains and penalties) is an act of a legislature declaring a person, or a group of people, guilty of some crime, and providing for a punishment, often without a ...
was passed on him for rebellion against the Crown. As O'Neill had claimed lordship over most of Ulster, the act declared most of the province to be forfeit to the Crown.
In 1571, Queen Elizabeth granted Sir Thomas Smith a large portion of Clannaboy
Clandeboye or Clannaboy ( Irish ''Clann Aodha Buí'', "family of Hugh the Blond") was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland, comprising what is now south County Antrim, north County Down, and the barony of Loughinsholin. The entity was relatively late in ...
and the Ards
Ards (or ARDS, ARDs) may refer to:
Medical
* ARDS, Acute respiratory distress syndrome
* ARDs, age-related diseases
Places
* Ards Peninsula, Northern Ireland
** Ards (territory), several historical territorial divisions on the Ards Peninsula
...
to colonize. Smith envisaged a colony led by the younger sons of English gentlemen, in which the native Irish would be employed as labourers. The scheme was partly privately funded and partly state-sponsored by way of military support. In 1572 Smith's son landed in the Ards with 100 men. They were opposed by the Lord of Clannaboy, Brian McPhelim O'Neill
Sir Brian McPhelim Bacagh O'Neill (died 1574) was Chief of the Name of Clan O'Neill List of rulers of Clandeboye#Lords of Lower Clandeboye, 1556—1600, Lower Clandeboye, an Irish clan in north-eastern Ireland during the Tudor conquest of Ireland ...
, who complained the grant was illegal. As the English often commandeered Irish church buildings for garrisons, McPhelim burned all church buildings in the Ards to prevent this. The colonists hastily built a fort near Comber
Comber ( , , locally ) is a town in County Down, Northern Ireland. It lies south of Newtownards, at the northern end of Strangford Lough. It is situated in the townland of Town Parks, the civil parish of Comber and the historic barony of Cas ...
, but the plantation fell apart after Smith's son was killed by Irishmen in 1573.
The plantation scheme was taken over by Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex
Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex (16 September 1539 – 22 September 1576), was an English nobleman and general. From 1573 until his death he fought in Ireland in connection with the Plantations of Ireland, most notably the Rathlin Island ...
, who set out to colonize much of County Antrim. He provided most of the funding, with the state providing some of the military support. He landed at Carrickfergus in 1573 with 1,100 men,Ellis, Steven. ''Ireland in the Age of the Tudors, 1447–1603''. Routledge, 2014. p. 303 but their numbers dwindled following an outbreak of plague in the town.Heffernan, DavidEssex's Enterprise
''
History Ireland
''History Ireland'' is a magazine with a focus on the history of Ireland. The first issue of the magazine appeared in Spring 1993. It went full-colour in 2004 and since 2005 it is published bi-monthly. It features articles by a range of writers ...
'', Volume 27, Issue 2 (March/April 2019). The colonists were opposed by McPhelim, Turlough Luineach O'Neill
Sir Turlough Lynagh O'Neill (also known as Turlough Luineach) ( Irish: ''An Ridire Toirdhealbhach Luineach mac Néill Chonnalaigh Ó Néill''; – September 1595) was an Irish Gaelic lord of Tír Eoghain in early modern Ireland. He was inau ...
of Tyrone, and Sorley Boy MacDonnell
Somhairle Buíodh MacDonnell (Scottish Gaelic: ''Somhairle Buidhe Mac Domhnaill''), known as Sorley Boy MacDonnell, whose last name was also given as MacDonald (c. 1505 – 1590), was a Gaelic chief, the son of Alexander Carragh MacDonnell, ...
of the Glens, who asserted they were opposing Essex rather than the Crown. In September 1574, Essex led a military expedition deep into Tyrone, burning crops. That November, Essex's men massacred 200 of McPhelim's company during a parley
A parley (from – "to speak") is a discussion or conference, especially one designed to end an argument or hostilities between two groups of people. As a verb, the term can be used in both past and present tense; in present tense the term ...
at Belfast Castle, and Essex then had McPhelim executed for treason. The MacDonnells called in reinforcements from their kinsmen in the Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gae ...
. In July 1575, Essex sent Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( 1540 – 28 January 1596) was an English Exploration, explorer and privateer best known for making the Francis Drake's circumnavigation, second circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition between 1577 and 1580 (bein ...
and John Norris to attack the MacDonnells. This ended with the massacre of 600 MacDonnell men, women and children on Rathlin Island
Rathlin Island (, ; Local Irish dialect: ''Reachraidh'', ; Scots: ''Racherie'') is an island and civil parish off the coast of County Antrim (of which it is part) in Northern Ireland. It is Northern Ireland's northernmost point. As of the 2021 ...
. By this time, Elizabeth had called an end to the scheme. It was a failure which had cost Essex and the Crown dearly.
Munster Plantation (1583 onwards)
The Munster Plantation of the 1580s was the first mass plantation in Ireland. It was instituted as punishment for theDesmond Rebellions
The Desmond Rebellions occurred in 1569–1573 and 1579–1583 in the Irish province of Munster. They were rebellions by the Earl of Desmond, the head of the FitzGerald dynasty in Munster, and his followers, the Geraldines and their allies, ...
, when the Geraldine Earl of Desmond
Earl of Desmond ( meaning Earl of South Munster) is a title of nobility created by the English monarch in the peerage of Ireland. The title has been created four times. It was first awarded in 1329 to Maurice FitzGerald, 1st Earl of Desmond, Maur ...
had rebelled against English interference in Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
. The Desmond dynasty was annihilated in the aftermath of the Second Desmond Rebellion
The Second Desmond Rebellion (1579–1583) was the more widespread and bloody of the two Desmond Rebellions in Ireland launched by the FitzGerald Dynasty of County Desmond, Desmond in Munster against English rule. The second rebellion began in ...
(1579–83) and their estates were confiscated by the Crown. The English authorities took the opportunity to settle the province with colonists from England and Wales, who, it was hoped, would be a bulwark against further rebellions. In 1584, the Surveyor General of Ireland, Sir Valentine Browne
Sir Valentine Browne (died 1589), of Croft, Lincolnshire, was auditor, treasurer and victualler of Berwick-upon-Tweed. He acquired large estates in Ireland during the Plantation of Munster, in particular the seignory of Molahiffe. He lived at ...
and a commission surveyed Munster, to allocate confiscated lands to English Undertakers (wealthy colonists who "undertook" to import tenants from England to work their new lands). The English Undertakers were obligated to develop new towns and provide for the defence of planted districts from attack.
However, the colonial plans were complicated by surveys showing less land available than previously imagined, as well as lawsuits influenced by the earl of Ormond. It was agreed that ninety-one families would be settled on 12,000 acres and further smaller grants of 8,000, 6,000 and 4,000 acres families were to be planted. In 1611 it has been estimated that 94,000 acres originally assigned to undertakers had been reclaimed. Out of the eighty-six, original volunteers only fifteen ultimately took out patents, although these were supplemented by another twenty individuals not associated with the initial scheme. On the outbreak of the Nine Years' War, one contemporary estimate was that the plantation had attracted about 5,000 English settlers, but it is more commonly surmised that the total English population in the colony stood at c. 4000 at the first overthrow in 1598. This was well short of the 11,375 people that the original plans had envisaged.
There was an enterprising capitalist element to the Munster plantations. Privateers and the enterprising public could buy land in Munster at pennies an acre as undertakers, sometimes backed by private investors. Sir Walter Raleigh owned large estates in Munster and harvested the forests around his estate to make tobacco pipes and wine barrels, although his company proved unprofitable. However, other investors made a fortune off the plantations.Canny p. 211 Businessman Robert Payne advocated for settlers to come to the Munster colonies. He bought land holdings in Munster for his venture, recruiting 25 business partners and partnering with industrialist Francis Willoughby. Willoughby was a sleeping partner in a project aimed at establishing an ironworks
An ironworks or iron works is an industrial plant where iron is smelted and where heavy iron and steel products are made. The term is both singular and plural, i.e. the singular of ''ironworks'' is ''ironworks''.
Ironworks succeeded bloome ...
in the Munster colonies. Daniel Gookin, a Munster colonist, sold his lands in Carrigaline
Carrigaline (; ) is a town and civil parish in County Cork, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, situated on the River Owenabue. Located about south of Cork (city), Cork city, and with a population of 18,239 people, it is one of the largest commuter ...
and his company in Munster to the ultimate capitalist-colonialist of the period, the newly created Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork
Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork (13 October 1566 – 15 September 1643), also known as 'the Great Earl of Cork', was an English politician who served as Lord Treasurer of the Kingdom of Ireland.
Lord Cork was an important figure in the continu ...
. He then partnered with another Munster colonist, Captain William Newce, to invest in the newlyformed Virginia Company and helped establish the colony at Jamestown in North America.
As well as the former Geraldine estates (spread through the modern counties of Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. W ...
, Cork
"Cork" or "CORK" may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Stopper (plug), or "cork", a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
*** Wine cork an item to seal or reseal wine
Places Ireland
* ...
, Kerry and Tipperary), the survey took in the lands belonging to other families and clans that had supported the rebellions in Kerry and southwest Cork. However, the settlement here was rather piecemeal because the ruling clan – the MacCarthy Mór
MacCarthy (), also spelled Macarthy, McCarthy or McCarty, is an Irish clan originating from Munster, an area they ruled during the Middle Ages. It was divided into several septs (branches) of which the MacCarthy Reagh, MacCarthy of Muskerry, and ...
line – argued that the rebel landowners were their subordinates and that the lords actually owned the land. In this area, lands once granted to some English Undertakers was taken away again when native lords, such as the MacCarthys, appealed the dispossession of their dependants.
Other sectors of the plantation were equally chaotic. John Popham imported 70 tenants from Somerset
Somerset ( , ), Archaism, archaically Somersetshire ( , , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east ...
, only to find that the land had already been settled by another undertaker, and he was obliged to send them home. Nevertheless, were planted with English colonists. The Crown hoped that the settlement would attract in the region of 15,000 colonists, but a report from 1589 showed that the English Undertakers had imported only about 700 English tenants between them. Historians have noted that each tenant was the head of a household and that he therefore likely represented at least 4–5 other people. This would put the English population in Munster at nearer to three or four thousand persons, but it was still substantially below the projected figure.
The Munster Plantation was supposed to develop compact defensible settlements, but the English settlers were spread in pockets across the province, wherever land had been confiscated. Initially, the English Undertakers were given detachments of English soldiers to protect them, but these were abolished in the 1590s. As a result, when the Nine Years War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between France and the Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial possessions in the Americas, India, and West Africa. Relat ...
– an Irish rebellion against English rule – reached Munster in 1598, most of the settlers were chased off their lands without a fight. They took refuge in the province's walled towns or fled back to England. However, when the rebellion was put down in 1601–03, the Plantation was re-constituted by the Governor of Munster, George Carew. The English settler population in the 1620s was four times greater than in the earlier Munster plantation and powerful enough to control a considerable area after the Irish Rebellion of 1641
The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was an uprising in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, initiated on 23 October 1641 by Catholic gentry and military officers. Their demands included an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and ...
.
Ulster Plantation (1606 onwards)
Prior to its conquest in theNine Years War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between France and the Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial possessions in the Americas, India, and West Africa. Relat ...
of the 1590s, Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
was the most Irish-Gaelic part of Ireland and the only province that was completely outside English control. The war, of 1594–1603, ended with the surrender of the O'Neill and O'Donnell lords to the English crown, but it was also a hugely costly and humiliating episode for the English government in Ireland. In the short term the war failed, and generous surrender terms given to the rebels re-granted them much of their former land, but under English law.
But when Hugh O'Neill and the other rebel earls left Ireland in the so-called 1607 Flight of the Earls
On 14 September ld Style and New Style dates, O.S. 4 September1607, Irish earls Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone, and Rory O'Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, permanently departed Rathmullan in Ireland for mainland Europe, accompanied by their fa ...
to seek help from the Spanish Crown for a new rebellion, the Lord Deputy Arthur Chichester
Arthur Chichester, 1st Baron Chichester (May 1563 – 19 February 1625), known between 1596 and 1613 as Sir Arthur Chichester, of Carrickfergus in Ireland, was an English administrator and soldier who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland from 1605 ...
seized the opportunity to colonise the province and declared the lands of O'Neill, O'Donnell and their followers forfeit. Initially, Chichester planned a fairly modest plantation, including large grants to Irish-born lords who had sided with the English during the war. However, in 1608 Cahir O'Doherty
Sir Cahir O'Doherty ( or ; 1587 – 5 July 1608) was the last Gaelic Irish chief of the O'Doherty clan, who in 1608 launched a failed rebellion against the English crown.
O'Doherty was the eldest son of clan chief John O'Doherty, ruler of ...
's rebellion in County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county of the Republic of Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster and is the northernmost county of Ireland. The county mostly borders Northern Ireland, sharing only a small b ...
interrupted implementation of this plan. O'Doherty was a former ally of the English who felt he had not been fairly rewarded for his role in the war. The rebellion was swiftly put down and O'Doherty killed, but these events gave Chichester a justification for expropriating all of the original landowners in the province.
In 1603 James VI of Scotland
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
also became James I of England, uniting these two crowns and also gaining possession of the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
, at that time an English Crown possession. The Plantation of Ulster was promoted to him as a joint "British", i.e. English and Scottish, venture to pacify and civilise Ulster. It was agreed that at least half of the settlers would be Scots. Six counties made up his official plantation of Ulster:
The plan was determined by two factors: first, the Crown wanted to protect the settlement from being destroyed by rebels like the Munster plantation. So rather than settling the planters in isolated pockets of land confiscated from convicted rebels, they confiscated all of the land and redistributed it, creating concentrations of British settlers around new towns and garrisons. The new landowners were explicitly banned from taking on Irish tenants, and had to import their tenant farmers from England and Scotland. The remaining Irish landowners were granted one quarter of the land in Ulster. The common Irish residents were to be relocated to live near garrisons and Protestant churches, the more ready for Protestant control. The Planters were barred from selling their lands to any Irishman.
 The second major influence on the plantation of Ulster was the political negotiation among the interest groups on the British side. The principal landowners were to be English Undertakers, wealthy men from England and Scotland who undertook to import tenants from their own estates. The planters were granted around each, on condition that they settle there a minimum of 48 adult males (including at least 20 families), who had to be
The second major influence on the plantation of Ulster was the political negotiation among the interest groups on the British side. The principal landowners were to be English Undertakers, wealthy men from England and Scotland who undertook to import tenants from their own estates. The planters were granted around each, on condition that they settle there a minimum of 48 adult males (including at least 20 families), who had to be English-speaking
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language ...
Protestants. However, veterans of the war in Ireland (known as Servitors) led by Arthur Chichester
Arthur Chichester, 1st Baron Chichester (May 1563 – 19 February 1625), known between 1596 and 1613 as Sir Arthur Chichester, of Carrickfergus in Ireland, was an English administrator and soldier who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland from 1605 ...
, successfully lobbied for land grants of their own. Since these former officers did not have enough private capital to fund the colonisation, their involvement was subsidised by the City of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, his ...
(the financial sector in London). The city was granted their own town, and lands. The final major recipient of lands was the Protestant Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland (, ; , ) is a Christian church in Ireland, and an autonomy, autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the Christianity in Ireland, second-largest Christian church on the ...
, which was granted all churches and lands previously owned by the Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
church. The Crown intended that clerics from England and the Pale
The Pale ( Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast s ...
convert the population to Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
.
The Plantation of Ulster was a mixed success for the English. By the 1630s, there were 20,000 adult male English and Scottish settlers in Ulster, which meant that the total settler population could have been as high as 80,000 to 150,000. They formed local majorities of the population in the Finn and Foyle valleys (around modern Derry and east County Donegal), north County Armagh
County Armagh ( ) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the traditional thirty-two counties of Ireland. It is located in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster and adjoins the southern shore of Lough Neagh. It borders t ...
and east County Tyrone
County Tyrone (; ) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the thirty-two traditional counties of Ireland. Its county town is Omagh.
Adjoined to the south-west shore of Lough Neagh, the cou ...
. Planters had achieved substantial settlement on unofficially planted lands in north Down, led by James Hamilton James Hamilton may refer to:
Dukes
*James Hamilton, 1st Duke of Hamilton (1606–1649), heir to the throne of Scotland
*James Hamilton, 4th Duke of Hamilton (1658–1712), Scottish nobleman
*James Hamilton, 5th Duke of Hamilton (1703–1743), Sco ...
and Hugh Montgomery, A. T. Q. Stewart: ''The Narrow Ground: The Roots of Conflict in Ulster.'' London, Faber and Faber Ltd. New Edition, 1989. p. 38. Cyril Falls
Cyril Bentham Falls CBE (2 March 1888 – 23 April 1971) was a British military historian, journalist, and academic, noted for his works on the First World War. He was born in Ireland and spent most of his life in England.
Early life
Falls was ...
: ''The Birth of Ulster''. London, Constable and Company Ltd. 1996. pp. 156–157. M. Perceval-Maxwell: ''The Scottish Migration to Ulster in the Reign of James 1.'' Belfast: Ulster Historical Foundation. 1999. p. 55. and in south Antrim under Sir Randall MacDonnell. The settler population increased rapidly, as just under half of the migrants were women – a very high ratio compared, for instance, to contemporary Spanish settlement in Latin America or English settlement in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
. New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
attracted more families, but still was predominately male in its early years.
But the Irish population was neither removed nor Anglicised. In practise, the settlers did not stay on poorer lands, but clustered around towns and the best land. This meant that many English and Scottish landowners had to take Irish tenants, contrary to the terms of the Plantation of Ulster. In 1609, Chichester deported 1300 former Irish soldiers from Ulster to serve in the Swedish Army
The Swedish Army () is the army, land force of the Swedish Armed Forces of the Kingdom of Sweden. Beginning with its service in 1521, the Swedish Army has been active for more than 500 years.
History
Svea Life Guards dates back to the year 1 ...
.
The attempted conversion of the Irish to Protestantism also had few successes; at first the clerics sent to Ireland were all English speakers, whereas the native population were usually monoglot
Monoglottism (Greek μόνος ''monos'', "alone, solitary", + γλῶττα , "tongue, language") or, more commonly, monolingualism or unilingualism, is the condition of being able to speak only a single language, as opposed to multilingualism. ...
speakers of Irish Gaelic
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigeno ...
. Later, the Catholic Church made a determined effort to retain its followers among the native population.
Later plantations (1610–1641)
 In addition to the Ulster plantation, several other small plantations occurred under the reign of the Stuart Kings
In addition to the Ulster plantation, several other small plantations occurred under the reign of the Stuart KingsJames I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
* James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
* James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
* James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334� ...
and his son Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
in the early 17th century. The first of these took place in north county Wexford
County Wexford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was ba ...
in 1610, where lands were confiscated from the MacMurrough-Kavanagh clan.
 Since most land-owning families in Ireland had taken their estates by force in the previous four hundred years, very few of them, with the exception of the New English planters, had proper legal titles for them. As a result, in order to obtain such titles, they were required to forfeit a quarter of their lands. This policy was used against the Kavanaghs in Wexford and subsequently elsewhere, to break up Catholic Irish estates (especially the Gaelic ones) around the country. Following the precedent set in Wexford, small plantations were established in
Since most land-owning families in Ireland had taken their estates by force in the previous four hundred years, very few of them, with the exception of the New English planters, had proper legal titles for them. As a result, in order to obtain such titles, they were required to forfeit a quarter of their lands. This policy was used against the Kavanaghs in Wexford and subsequently elsewhere, to break up Catholic Irish estates (especially the Gaelic ones) around the country. Following the precedent set in Wexford, small plantations were established in Laois
County Laois ( ; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and in the province of Leinster. It was known as Queen's County from 1556 to 1922. The modern county takes its name from Loígis, a medieval kingdom. Hist ...
and Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain ...
, Longford
Longford () is the county town of County Longford in Ireland. It had a population of 10,952 at the 2022 census. It is the biggest town in the county and about one third of the county's population lives there. Longford lies at the meeting of ...
, Leitrim and north Tipperary.
In Laois and Offally, the Tudor plantation had consisted of a chain of military garrisons. In the new, more peaceful climate of the 17th century, it attracted large numbers of landowners, tenants and labourers. Prominent planters in Leinster in this period include Charles Coote, Adam Loftus, and William Parsons.
In Munster, during the peaceful early years of the 17th century, thousands more English and Welsh settlers arrived in the province. There were many small plantations in Munster in this period, as Irish lords were required to forfeit up to one third of their estates to get their deeds to the remainder recognised by the English authorities. The settlers became concentrated in towns along the south coast – especially Youghal
Youghal ( ; ) is a seaside resort town in County Cork, Ireland. Located on the estuary of the Munster Blackwater, River Blackwater, the town is a former military and economic centre. Located on the edge of a steep riverbank, the town has a long ...
, Bandon, Kinsale
Kinsale ( ; ) is a historic port and fishing town in County Cork, Ireland. Located approximately south of Cork (city), Cork City on the southeast coast near the Old Head of Kinsale, it sits at the mouth of the River Bandon, and has a populatio ...
and Cork city
Cork ( ; from , meaning 'marsh') is the second-largest city in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the county town of County Cork, the largest city in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland ...
. Notable English Undertakers of the Munster Plantation include Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebell ...
, Edmund Spenser
Edmund Spenser (; – 13 January 1599 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) was an English poet best known for ''The Faerie Queene'', an epic poem and fantastical allegory celebrating the House of Tudor, Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I. He is re ...
, and Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork
Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork (13 October 1566 – 15 September 1643), also known as 'the Great Earl of Cork', was an English politician who served as Lord Treasurer of the Kingdom of Ireland.
Lord Cork was an important figure in the continu ...
. The latter especially made huge fortunes out of amassing Irish lands and developing them for industry and agriculture.
 The Irish Catholic upper classes were unable to stop the continued plantations in Ireland because they had been barred from public office on religious grounds. By 1615 they comprised a minority in the Irish Parliament, as a result of the creation of "pocket boroughs" (where Protestants were in the majority) in planted areas. In 1625, they gained a temporary halt to land confiscations by agreeing to pay for England's war with France and Spain.
In addition to the plantations, thousands of independent settlers arrived in Ireland in the early 17th century, from the
The Irish Catholic upper classes were unable to stop the continued plantations in Ireland because they had been barred from public office on religious grounds. By 1615 they comprised a minority in the Irish Parliament, as a result of the creation of "pocket boroughs" (where Protestants were in the majority) in planted areas. In 1625, they gained a temporary halt to land confiscations by agreeing to pay for England's war with France and Spain.
In addition to the plantations, thousands of independent settlers arrived in Ireland in the early 17th century, from the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
and France as well as Britain. Many of them became chief tenants of Irish land-owners; others set up in the towns (especially Dublin) – notably as bankers and financiers. By 1641, there were calculated to be up to 125,000 Protestant settlers in Ireland, though they were still outnumbered by native Catholics by around 15 to 1.
Not all of the early 17th century English Planters were Protestants. A considerable number of English Catholics settled in Ireland between 1603 and 1641, in part for economic reasons but also to escape persecution in England. In the time of Elizabeth and James I, the Catholics of England suffered a greater degree of persecution than English Catholics in Ireland. In England, Catholics were greatly outnumbered by Protestants and lived under constant fear of betrayal by their fellows. In Ireland they could blend in with the local majority-Catholic population in a way that was not possible in England. English Catholic planters were most common in County Kilkenny
County Kilkenny () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. It is named after the City status in Ir ...
, where they may have made up half of all the English and Scottish planters to arrive in this region.
Plantations stayed off the political agenda until the appointment of Thomas Wentworth, a Privy Councilor of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, to the position of Lord Deputy of Ireland
The Lord Deputy was the representative of the monarch and head of the Irish executive (government), executive under English rule, during the Lordship of Ireland and then the Kingdom of Ireland. He deputised prior to 1523 for the Viceroy of Ireland ...
in 1632. Wentworth's job was to raise revenue for Charles and to cement Royal control over Ireland – which meant, among other things, more plantations, both to raise money and to break the political power of the Irish Catholic gentry. Wentworth confiscated land in Wicklow
Wicklow ( ; , meaning 'church of the toothless one'; ) is the county town of County Wicklow in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is located on the east of Ireland, south of Dublin. According to the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, it had ...
and planned a full-scale Plantation of Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, C ...
– where all Catholic landowners would lose between a half and a quarter of their estates. The local juries were intimidated into accepting Wentworth's settlement; when a group of Connacht landowners complained to Charles I, Wentworth had them imprisoned. However, settlement proceeded only in County Sligo
County Sligo ( , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Northern and Western Region and is part of the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in ...
and County Roscommon
County Roscommon () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is part of the province of Connacht and the Northern and Western Region. It is the List of Irish counties by area, 11th largest Irish county by area and Li ...
. Next, Wentworth surveyed the major Catholic landowners in Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland.
The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century ...
for similar treatment, including members of the powerful Butler dynasty. Wentworth's plans were interrupted by the outbreak of the Bishops Wars
The Bishops' Wars were two separate conflicts fought in 1639 and 1640 between Scotland and England, with Scottish Royalists allied to England. They were the first of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which also include the First and Second Eng ...
in Scotland, which eventually resulted in Wentworth's execution by the English Parliament and civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
in England and Ireland. Wentworth's constant questioning of Catholic land titles was one of the major causes of the 1641 Rebellion
The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was an uprising in Ireland, initiated on 23 October 1641 by Catholic gentry and military officers. Their demands included an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and return of confiscat ...
, and the principal reason why it was joined by Ireland's wealthiest and most powerful Catholic families.
1641 Rebellion
In October 1641, after a bad harvest and in a threatening political climate,Phelim O'Neill
Sir Phelim Roe O'Neill of Kinard ( Irish: ''Sir Féilim Rua Ó Néill na Ceann Ard''; 1604–1653) was an Irish politician and soldier who started the Irish rebellion in Ulster on 23 October 1641. He joined the Irish Catholic Confede ...
launched a rebellion, hoping to rectify various grievances of Irish Catholic landowners. However, once the rebellion was underway, the resentment of the native Irish in Ulster boiled over into indiscriminate attacks on the settler population in the Irish Rebellion of 1641
The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was an uprising in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, initiated on 23 October 1641 by Catholic gentry and military officers. Their demands included an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and ...
. Irish Catholics attacked the plantations all around the country, but especially in Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
. English writers at the time put the Protestant victims at over 100,000. William Petty
Sir William Petty (26 May 1623 – 16 December 1687) was an English economist, physician, scientist and philosopher. He first became prominent serving Oliver Cromwell and the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth in Cromwellian conquest of I ...
, in his survey of the 1650s, estimated the death toll at around 30,000. More recent research, however, based on close examination of the depositions of the Protestant refugees collected in 1642, suggests a figure of 4,000 settlers were killed directly; and up to 12,000 may have died of causes also related to disease (always a cause of high fatalities during wartime) or privation after being expelled from their homes.
Ulster was worst hit by the wars, with massive loss of civilian life and mass displacement of people. The atrocities committed by both sides further poisoned the relationship between the settler and native communities in the province. Although peace was eventually restored to Ulster, the wounds opened in the plantation and civil war years were very slow to heal and arguably still fester in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
in the early 21st century.
In the 1641 Rebellion, the Munster Plantation was temporarily destroyed, just as it had been during the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
. Ten years of warfare took place in Munster between the planters and their descendants and the native Irish Catholics. But the ethnic/religious divisions were less stark in Munster than in Ulster. Some of the earlier English Planters in Munster had been Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
and their descendants largely sided with the Irish in the 1640s. Conversely, some Irish noblemen who had converted to Protestantism – notably Earl Inchiquin – sided with the settler community.
Cromwellian land confiscation (1652)
 Over 12,000 veterans of the
Over 12,000 veterans of the New Model Army
The New Model Army or New Modelled Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 t ...
were awarded land in Ireland in place of their wages due, which the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
was unable to pay. Many of these soldiers sold their land grants to other Protestants rather than settle in war-ravaged Ireland, but 7,500 soldiers did settle in Ireland. They were required to keep their weapons to act as a reserve militia in case of future rebellions. Taken together with the Merchant Adventurers, probably over 10,000 Parliamentarians settled in Ireland after the civil wars. In addition to the Parliamentarians, thousands of Scottish Covenanter
Covenanters were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. It originated in disputes with James VI and his son C ...
soldiers, who had been stationed in Ulster during the war, settled there permanently after its end.
Some Parliamentarians had argued that all the Irish should be deported to west of the River Shannon
The River Shannon ( or archaic ') is the major river on the island of Ireland, and at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of I ...
and replaced with English settlers. However, this would have required hundreds of thousands of English settlers willing to come to Ireland, and such numbers of aspirant settlers were never recruited. Rather, a land-owning class of British Protestants was created in Ireland, and they ruled over mostly Irish Catholic tenants. A minority of the "Cromwellian" landowners were Parliamentarian soldiers or creditors. Most were pre-war Protestant settlers, who took the opportunity to obtain confiscated lands. Before the wars, Catholics had owned 60% of the land in Ireland. During the Commonwealth period, Catholic landownership fell to 8–9%. After some restitution in the Restoration Act of Settlement 1662
The Act of Settlement 1662 ( 14 & 15 Chas. 2. Sess. 4. c. 2 (I)) was an act of the Irish Parliament in Dublin. It was a partial reversal of the Cromwellian Act for the Settlement of Ireland 1652, which punished Irish Catholics and Royalists ...
, it rose to 20% again.Lenihan, ''Confederate Catholics at War'', p. 111
In Ulster, the Cromwellian period eliminated those native landowners who had survived the Ulster plantation. In Munster and Leinster, the mass confiscation of Catholic-owned land after the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the Commonwealth of England, initially led by Oliver Cromwell. It forms part of the 1641 to 1652 Irish Confederate Wars, and wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three ...
, meant that English Protestants acquired almost all of the land holdings for the first time in these territories. In addition, under the Commonwealth regime, some 12,000 Irish people were sold into indentured servitude to the Caribbean and North American colonies. Another 34,000 Irish Catholics went into exile on the Continent, mostly in the Catholic countries of France or Spain.
Recent research has shown that although the native Irish land-owning class was subordinated in this period, it never totally disappeared. Many of its members found niches in trade or as chief tenants on their families' ancestral lands.
Subsequent settlement
For the remainder of the 17th century, Irish Catholics tried to get the Cromwellian Act of Settlement reversed. They briefly achieved this under James II during theWilliamite war in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland took place from March 1689 to October 1691. Fought between Jacobitism, Jacobite supporters of James II of England, James II and those of his successor, William III of England, William III, it resulted in a Williamit ...
, but the Jacobite defeat there led to another round of land confiscations. During the 1680s and 90s, another major wave of settlement took place in Ireland (though not another plantation in terms of land confiscation). At this time, the new settlers were principally Scots, tens of thousands of whom fled a famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
in the lowlands and border regions of Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
to come to Ulster. At this point Protestants and people of Scottish descent (who were mainly Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
s) became an absolute majority of the population in Ulster.
French Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
, who were Protestant, were also encouraged to settle in Ireland; they had been expelled from France after the Crown's revocation of the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was an edict signed in April 1598 by Henry IV of France, King Henry IV and granted the minority Calvinism, Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was predominantl ...
in 1685. Many of the Frenchmen were former soldiers, who had fought on the Williamite side in the Williamite war in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland took place from March 1689 to October 1691. Fought between Jacobitism, Jacobite supporters of James II of England, James II and those of his successor, William III of England, William III, it resulted in a Williamit ...
. This community settled mainly in Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
, as some had already been established as merchants in London. Their communal graveyard can still be seen off St Stephen's Green
St Stephen's Green () is a garden square and public park located in the city centre of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by ...
. The total population of this community may have reached 10,000.
Long-term results and suppression of Irish culture
The English banned and discouraged the use of the Irish language in 1537 with The Statute of Ireland – An Act for the English Order Habit and Language (28. Hen. 8. c. 15 (I)). Irish clothing was also banned throughout the centuries. On 14 February 1588, William Herbert wrote to Francis Walsingham that he desired to show posterity his affection for his God and his prince 'by a volume of my writing,' by 'a colony of my planting,' and by 'a college of my erecting.' Moderate in treating the Irish, he put into execution clauses of the statute against Irish customs, particularly forbidding the wearing of the native mantle. The Plantations had profound effects on Ireland. They resulted in the removal and/or execution of Catholic ruling classes and their replacement with what became known as theProtestant Ascendancy
The Protestant Ascendancy (also known as the Ascendancy) was the sociopolitical and economical domination of Ireland between the 17th and early 20th centuries by a small Anglicanism, Anglican ruling class, whose members consisted of landowners, ...
, Anglican landowners mostly originating from Great Britain. Their position was reinforced by the Penal Laws
Penal law refers to criminal law.
It may also refer to:
* Penal law (British), laws to uphold the establishment of the Church of England against Catholicism
* Penal laws (Ireland)
In Ireland, the penal laws () were a series of Disabilities (C ...
. These denied political and most land-owning rights to Catholics and non-Anglican Protestant denominations, they also brought in harsh punishments for use of the Irish language and limited Catholics ability to practice their religion. The forced dominance of the Protestant class in Irish life persisted until the late 18th century when they reluctantly voted for the Act of Union with Britain in 1800. It abolished their parliament, making their government part of Britain's. The plantations and their related agricultural development also radically altered Ireland's physical environment and ecology. In 1600, most of Ireland was heavily wooded and undeveloped, apart from the bogs. Most of the population lived in small, semi-nomadic townlands, many migrating seasonally to pastures for their cattle. By 1700, Ireland's native woodland had been reduced to a fraction of its former size; it was intensively logged and sold for profit by the plantation settlers for commercial ventures such as shipbuilding, as much of the English forests had been overlogged to total depletion, and the navy was becoming a great power. Several native animal species, such as the
The plantations and their related agricultural development also radically altered Ireland's physical environment and ecology. In 1600, most of Ireland was heavily wooded and undeveloped, apart from the bogs. Most of the population lived in small, semi-nomadic townlands, many migrating seasonally to pastures for their cattle. By 1700, Ireland's native woodland had been reduced to a fraction of its former size; it was intensively logged and sold for profit by the plantation settlers for commercial ventures such as shipbuilding, as much of the English forests had been overlogged to total depletion, and the navy was becoming a great power. Several native animal species, such as the wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, includin ...
, were hunted to extinction during this period. Most of the settler population was urbanized, living in permanent towns or villages. Some of the Irish people continued their traditional practices and culture under the shadow of heavy control and punishments. By the end of the plantation period, almost all of Ireland had become integrated into a market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production, and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a mark ...
. But many of the poorer classes had no access to money, still paying rent in kind
The term in kind (or in-kind) generally refers to goods, services, and transactions not involving money or not measured in monetary terms. It is a part of many spheres, mainly economics, finance, but also politics, work career, food, health and o ...
or in service. The plantations also introduced a new measurement system to Ireland called the Irish measure or plantation measure
Irish measure or plantation measure was a system of units of land measurement used in Ireland from the 16th century plantations until the 19th century, with residual use into the 20th century. The units were based on " English measure" but u ...
which had some residual use even into the 20th century.
See also
*British colonisation of the Americas
The British colonization of the Americas is the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by England, Scotland, and, after 1707, Great Britain. Colonization efforts began in the late 16 ...
* Down Survey
The Down Survey was a cadastral survey of Ireland, carried out by English scientist William Petty in 1655 and 1656. It was created to provide for precise re-allocation of land confiscated from the Irish.
The survey was apparently called the "Do ...
– William Petty
Sir William Petty (26 May 1623 – 16 December 1687) was an English economist, physician, scientist and philosopher. He first became prominent serving Oliver Cromwell and the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth in Cromwellian conquest of I ...
's survey of Irish land and population before the Cromwellian Plantations
* History of Ireland (1536–1691)
The history of Ireland between 1536 and 1691 saw the conquest and colonisation of the island by the English state and the settlement of tens of thousands of Protestant settlers from England, Wales and Scotland. Ireland had been partially conqu ...
* English colonial empire
The English overseas possessions comprised a variety of overseas territories that were colonised, conquered, or otherwise acquired by the Kingdom of England before 1707. (In 1707 the Acts of Union made England part of the Kingdom of Great Br ...
* Protestant Ascendancy
The Protestant Ascendancy (also known as the Ascendancy) was the sociopolitical and economical domination of Ireland between the 17th and early 20th centuries by a small Anglicanism, Anglican ruling class, whose members consisted of landowners, ...
* Irish question
References
Further reading
* *Robert Dunlop
Stephen Robert Dunlop (25 November 1960 – 15 May 2008) was a Northern Irish motorcycle racer. He was the younger brother of fellow road racer Joey Dunlop and the father of racers William Dunlop and Michael Dunlop. Like his brother, Dunlop ...
, "The Plantation of Munster, 1584–1589", ''English Historical Review
''The English Historical Review'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal that was established in 1886 and published by Oxford University Press (formerly by Longman). It publishes articles on all aspects of history – British, European, a ...
'' 3 (1888), 250–269
Sources
* Canny, Nicholas P., ''Making Ireland British 1580–1650'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001 * A newer edition (8th, 2002) is available. * Ford & McCafferty, ''The Origins of Sectarianism in Early Modern Ireland'', Cambridge University Press, 2005 * Lennon, Colm, ''Sixteenth Century Ireland – The Incomplete Conquest'', Dublin: Gill & Macmillan. 1994 * Lenihan, Padraig, ''Confederate Catholics at War'', Cork: Cork University Press, 2000 * McCarthy, Daniel, ''The Life and Letter book of Florence McCarthy Reagh, Tanist of Carberry'', Dublin, 1867 * MacCarthy-Morrogh, Michael, ''The Munster Plantation – English migration to Southern Ireland 1583–1641'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1986 * * Scot-Wheeler, James, ''Cromwell in Ireland'', New York, 1999External links
The Munster Plantation and the MacCarthys, 1583–1597
at The Irish Story {{DEFAULTSORT:Plantations of Ireland
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
Former English colonies
Human migration
16th century in Ireland
17th century in Ireland
Tudor England
Stuart England