Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
religious and political leader and the founder of
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
.
According to Islam, he was a prophet who was
divinely inspired
Divine inspiration is the concept of a supernatural force, typically a deity, causing a person or people to experience a creative desire. It has been a commonly reported aspect of many religions, for thousands of years. Divine inspiration is ofte ...
to preach and confirm the
monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
teachings of
Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam).
According to Christianity, Adam ...
,
Noah
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian Patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5–9), the Quran and Baháʼí literature, ...
,
Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
,
Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
,
Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
, and other
prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
. He is believed to be the
Seal of the Prophets
Seal of the Prophets (; or ) is a title used in the Qur'an and by Muslims to designate the Islamic prophet Muhammad as the last of the prophets sent by God.
The title is applied to Muhammad in verse 33:40 of the Qur'an, with the popular Yu ...
in Islam, and along with the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
, his teachings and
normative examples form the basis for Islamic religious belief.
Muhammad was born in
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
to the aristocratic
Banu Hashim
Banu Hashim () is an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe to which the Islamic prophet Muhammad belonged, named after Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf.
Members of this clan, and especially their descendants, are also referred ...
clan of the
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By ...
. He was the son of
Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib
Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib (; ; ) was the father of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.Ibn Hisham note 97.Muhammad ibn Saad, ''Tabaqat'' vol. 8. Translated by Bewley, A. (1995). ''The Women of Madina''. London: Ta-Ha Publishers. He was the son of A ...
and
Amina bint Wahb
Amina bint Wahb ibn Abd Manaf al-Zuhriyya (, ) was the mother of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. She belonged to the Banu Zuhra tribe.
Early life and marriage
Aminah was born to Wahb ibn Abd Manaf and Barrah bint 'Abd al-'Uzzā ibn 'Uthmān ib ...
. His father, Abdullah, the son of tribal leader
Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, died around the time Muhammad was born. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal uncle,
Abu Talib. In later years, he would periodically seclude himself in a mountain cave named
Hira
Hira may refer to:
Places
*Cave of Hira, a cave associated with Muhammad
*Al-Hirah, an ancient Arab city in Iraq
** Battle of Hira, 633AD, between the Sassanians and the Rashidun Caliphate
* Hira Mountains, Japan
* Hira, New Zealand, settlement ...
for several nights of prayer. When he was 40, in , Muhammad reported being visited by
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Chris ...
in the cave and receiving
his first revelation from God. In 613, Muhammad started
preaching
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. E ...
these revelations publicly,
Muhammad Mustafa Al-A'zami
Muhammad Mustafa Al-A'zami (; 1930 – 20 December 2017) was an Indian-born Saudi Arabian contemporary hadith scholar best known for his critical investigation of the theories of fellow Islamic scholars Ignác Goldziher, David Margoliouth, an ...
(2003), ''The History of The Qur'anic Text: From Revelation to Compilation: A Comparative Study with the Old and New Testaments'', pp. 26–27. UK Islamic Academy. . proclaiming that "God is One", that complete "submission" () to
God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
() is the right way of life (), and that he was a prophet and messenger of God, similar to other
prophets in Islam
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, mos ...
.
Muhammad's followers were initially few in number, and experienced
persecution by Meccan polytheists for 13 years. To escape ongoing persecution, he
sent some of his followers to
Abyssinia
Abyssinia (; also known as Abyssinie, Abissinia, Habessinien, or Al-Habash) was an ancient region in the Horn of Africa situated in the northern highlands of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea.Sven Rubenson, The survival of Ethiopian independence, ...
in 615, before he and his followers migrated from Mecca to
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
(then known as Yathrib) later in 622. This event, the , marks the beginning of the
Islamic calendar
The Hijri calendar (), also known in English as the Islamic calendar, is a lunar calendar consisting of 12 lunar months in a year of 354 or 355 days. It is used to determine the proper days of Islamic holidays and rituals, such as the Ramad ...
, also known as the Hijri calendar. In Medina, Muhammad united the tribes under the
Constitution of Medina
The Constitution of Medina (; or ; also known as the Umma Document), is a document dealing with tribal affairs during the Islamic prophet Muhammad's time in Medina and formed the basis of the First Islamic State, a multi-religious polity under his ...
. In December 629, after eight years of intermittent fighting with Meccan tribes, Muhammad gathered an army of 10,000 Muslim converts and
marched on the city of Mecca. The conquest went largely uncontested, and Muhammad seized the city with minimal casualties. In 632, a few months after returning from the
Farewell Pilgrimage
The Farewell Pilgrimage () refers to the one Hajj pilgrimage that Muhammad performed in the Islamic year 10 AH, following the Conquest of Mecca. Muslims believe that verse 22:27 of the Quran brought about the intent to perform Hajj in Muhammad tha ...
, he fell ill and died. By the time of his death, most of the
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
had
converted to Islam
Reversion to Islam, also known within Islam as reversion, is adopting Islam as a religion or faith. Conversion requires a formal statement of the '' shahādah'', the credo of Islam, whereby the prospective convert must state that "there is none w ...
.
The revelations () that Muhammad reported receiving until his death form the verses () of the Quran, upon which Islam is based, are regarded by Muslims as the verbatim word of God and his final revelation. Besides the Quran, Muhammad's teachings and practices, found in transmitted reports, known as
hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
, and in his biography (), are also upheld and used as
sources of Islamic law
Various sources of Islamic Laws are used by Islamic jurisprudence to elaborate the body of Islamic law, which are called Masdar (مصادر) or Dalil (دليل). In Sunni Islam, the scriptural sources of traditional jurisprudence are the Holy Q ...
. Apart from Islam, Muhammad has received praise in
Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
as an inspirational figure, in the
Druze faith
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arab esoteric religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and syncretic religion whose main tenets assert th ...
as one of the seven main
prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
, and in the
Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
as a
Manifestation of God.
Biographical sources

Quran
The
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
is the central
religious text
Religious texts, including scripture, are texts which various religions consider to be of central importance to their religious tradition. They often feature a compilation or discussion of beliefs, ritual practices, moral commandments and ...
of Islam. Muslims believe it represents the words of
God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
revealed by the archangel
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Chris ...
to Muhammad. The Quran is mainly addressed to a single "Messenger of God" who is referred to as Muhammad in a number of verses. The Quranic text also describes the settlement of his followers in
Yathrib
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
after their expulsion by the Quraysh, and briefly mentions military encounters such as the
Muslim victory at Badr.
The Quran, however, provides minimal assistance for Muhammad's chronological biography; most Quranic verses do not provide significant historical context and timeline. Almost none of
Muhammad's companions
The Companions of the Prophet () were the Muslim disciples and followers of the Islamic prophet Muhammad who saw or met him during his lifetime. The companions played a major role in Muslim battles, society, hadith narration, and governance ...
are mentioned by name in the Quran, hence not providing sufficient information for a concise biography.
The
Birmingham Quran manuscript
The Birmingham Quran manuscript comprises two leaves of parchment from an early Quranic manuscript or muṣḥaf. In 2015, the manuscript, which is held by the University of Birmingham in England, was radiocarbon dated to between 568 and 6 ...
has been
radiocarbon dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
to between 568 and 645, though the manuscript's discoverer has asserted that the text on the parchment is from a later date.
Early biographies

Important sources regarding Muhammad's life may be found in the historic works by writers of the 2nd and 3rd centuries of the
Hijri era
Hijra, Hijrah, Hegira, Hejira, Hijrat or Hijri may refer to:
Islam
* Hijrah (also ''Hejira'' or ''Hegira''), the migration of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE
* Migration to Abyssinia or First Hegira, of Muhammad's followers in 615 CE
* L ...
(mostly overlapping with the 8th and 9th centuries CE respectively). These include traditional Muslim biographies of Muhammad, which provide additional information about his life.
The earliest written (biographies of Muhammad and quotes attributed to him) is
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
's ''
Life of God's Messenger'' written (150 AH). Although the original work was lost, this survives as extensive excerpts in works by
Ibn Hisham
Abu Muhammad Abd al-Malik ibn Hisham ibn Ayyub al-Himyari (; died 7 May 833), known simply as Ibn Hisham, was a 9th-century Abbasid historian and scholar. He grew up in Basra, in modern-day Iraq and later moved to Egypt.
Life
Ibn Hisham has ...
and to a lesser extent by
al-Tabari
Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr ibn Yazīd al-Ṭabarī (; 839–923 CE / 224–310 AH), commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Sunni Muslim scholar, polymath, historian, exegete, jurist, and theologian from Amol, Tabaristan, present- ...
. However, Ibn Hisham wrote in the preface to his biography of Muhammad that he omitted matters from Ibn Ishaq's biography that "would distress certain people". Another early historical source is the history of Muhammad's campaigns by
al-Waqidi
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Umar ibn Waqid al-Aslami () ( – 207 AH; commonly referred to as al-Waqidi (Arabic: ; c. 747 – 823 AD) was an early Arab Muslim historian and biographer of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, specializing in his military ...
( AH), and
the work of Waqidi's secretary
Ibn Sa'd al-Baghdadi
Abū ‘Abd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Sa‘d ibn Manī‘ al-Baṣrī al-Hāshimī or simply Ibn Sa'd () and nicknamed ''Scribe of Waqidi'' (''Katib al-Waqidi''), was a scholar and Arabian biographer. Ibn Sa'd was born in 784/785 CE (168 AH) and die ...
( AH). Due to these early biographical efforts, more is known about Muhammad than almost any other founder of a major religion. Many scholars accept these early biographies as authentic. However, Waqidi's biography has been widely
criticized by Islamic scholars for his methods, in particular his decision to omit his sources. Recent studies have led scholars to distinguish between traditions touching legal matters and purely historical events. In the legal group, traditions could have been subject to invention while historic events, aside from exceptional cases, may have been subject only to "tendential shaping". Other scholars have criticized the reliability of this method, suggesting that one cannot neatly divide traditions into purely legal and historical categories.
Western historians describe the purpose of these early biographies as largely to convey a message, rather than to strictly and accurately record history.
Hadith

Other important sources include the
hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
collections, accounts of verbal and physical teachings and traditions attributed to Muhammad. Hadiths were compiled several generations after his death by Muslims including
Muhammad al-Bukhari
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Ismāʿīl ibn Ibrāhīm al-Juʿfī al-Bukhārī (; 21 July 810 – 1 September 870) was a 9th-century Persian Muslim '' muhaddith'' who is widely regarded as the most important ''hadith'' scholar in the histor ...
,
Muslim ibn al-Hajjaj
Abū al-Ḥusayn Muslim ibn al-Ḥajjāj ibn Muslim ibn Ward al-Qushayrī an-Naysābūrī (; after 815 – May 875 CE / 206 – 261 AH), commonly known as Imam Muslim, was an Islamic scholar from the city of Nishapur, particularly known as a ' ...
,
Muhammad ibn Isa at-Tirmidhi
Muhammad ibn Isa al-Tirmidhi (; 824 – 9 October 892 CE / 209–279 AH), often referred to as Imām at-Termezī/Tirmidhī, was an Islamic scholar, and collector of hadith from Termez (early Khorasan and in present-day Uzbekistan). He w ...
,
Abd ar-Rahman al-Nasai,
Abu Dawood
Abū Dāwūd (Dā’ūd) Sulaymān ibn al-Ash‘ath ibn Isḥāq al-Azdī al-Sijistānī (), commonly known as Abū Dāwūd al-Sijistānī, was a scholar of prophetic hadith who compiled the third of the six "canonical" hadith collections recogn ...
,
Ibn Majah
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Yazīd Ibn Mājah al-Rabʿī al-Qazwīnī (; (b. 209/824, d. 273/887) commonly known as Ibn Mājah, was a Middle Ages, medieval scholar of hadith of Persian people, Persian origin. He compiled the last of Sunni ...
,
Malik ibn Anas
Malik ibn Anas (; –795) also known as Imam Malik was an Arab Islamic scholar and traditionalist who is the eponym of the Maliki school, one of the four schools of Islamic jurisprudence in Sunni Islam.Schacht, J., "Mālik b. Anas", in: ''E ...
,
al-Daraqutni
Ali ibn Umar al-Daraqutni (; 918–995 CE / 306–385 AH), was a Sunni Muslim scholar and traditionist best known for compiling the hadith collection '' Sunan al-Daraqutni''. He is commonly celebrated in Sunni tradition with titles such as "Im ...
.
Muslim scholars have typically placed a greater emphasis on the hadith instead of the biographical literature, since hadith maintain a traditional chain of transmission (); the lack of such a chain for the biographical literature makes it unverifiable in their eyes. The hadiths generally present an idealized view of Muhammad.
Western scholars have expressed skepticism regarding the verifiability of these chains of transmission. It is widely believed by Western scholars that there was widespread fabrication of hadith during the early centuries of Islam to support certain theological and legal positions,
and it has been suggested that it is "very likely that a considerable number of that can be found in the collections did not actually originate with the Prophet".
In addition, the meaning of a hadith may have drifted from its original telling to when it was finally written down, even if the chain of transmission is authentic.
Overall, some Western academics have cautiously viewed the hadith collections as accurate historical sources,
while the "dominant paradigm" in Western scholarship is to consider their reliability suspect.
Scholars such as
Wilferd Madelung
Wilferd Ferdinand Madelung FBA (26 December 1930 – 9 May 2023) was a German author and scholar of Islamic history widely recognised for his contributions to the fields of Islamic and Iranian studies. He was appreciated in Iran for his "know ...
do not reject the hadith which have been compiled in later periods, but judge them in their historical context.
Meccan years
Early life

Muhammad ibn Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim was born in
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
, and
his birthday is believed to be in the month of
Rabi' al-Awwal
Rabiʽ al-Awwal (, also known as Rabi' al-Ula (), or Rabi' I) is the third month of the Islamic calendar. The name ''Rabī‘ al-awwal'' means "''the first month'' or ''beginning of Spring (season), spring''", referring to its position in the ...
. He belonged to the
Banu Hashim
Banu Hashim () is an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe to which the Islamic prophet Muhammad belonged, named after Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf.
Members of this clan, and especially their descendants, are also referred ...
clan of the
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By ...
tribe, which was a dominant force in western Arabia. While his clan was one of the more distinguished in the tribe, it seems to have experienced a lack of prosperity during his early years.
According to Muslim tradition, Muhammad was a , someone who professed
monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
in
pre-Islamic Arabia
Pre-Islamic Arabia is the Arabian Peninsula and its northern extension in the Syrian Desert before the rise of Islam. This is consistent with how contemporaries used the term ''Arabia'' or where they said Arabs lived, which was not limited to the ...
. He is also claimed to have been a descendant of
Ishmael
In the Bible, biblical Book of Genesis, Ishmael (; ; ; ) is the first son of Abraham. His mother was Hagar, the handmaiden of Abraham's wife Sarah. He died at the age of 137. Traditionally, he is seen as the ancestor of the Arabs.
Within Isla ...
, son of
Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
.
The name Muhammad means "praiseworthy" in Arabic and it appears four times in the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
. He was also known as "al-Amin" () when he was young; however, historians differ as to whether it was given by people as a reflection of his nature or was simply a given name from his parents, i.e., a masculine form of his mother's name "Amina". Muhammad acquired the of Abu al-Qasim later in his life after the birth of his son Qasim, who died two years afterwards.
Islamic tradition states that Muhammad's birth year coincided with the
Year of the Elephant
The ʿām al-fīl (, Year of the Elephant) is the name in Islamic history for the year approximately equating to 570–571 CE. According to Islamic resources, it was in this year that prophet Mohammad was born.Hajjah Adil, Amina, "''Prophet ...
, when
Abraha
Abraha ( Ge’ez: አብርሃ) (also spelled Abreha, died presumably 570 CE) was an Aksumite military leader who controlled the Kingdom of Himyar (modern-day Yemen) and a large part of Arabia for over 30 years in the 6th century. Originally ...
, the
Aksumite
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging ...
viceroy in the former
Himyarite Kingdom
Himyar was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qataban, Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According ...
, unsuccessfully attempted to conquer Mecca. Recent studies, however, challenge this notion, as other evidence suggests that the expedition, if it had occurred, would have transpired substantially before Muhammad's birth. Later Muslim scholars presumably linked Abraha's renowned name to the narrative of Muhammad's birth to elucidate the unclear passage about "the men of elephants" in Quran 105:1–5. ''The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity'' deems the tale of Abraha's war elephant expedition as a myth.
Muhammad's father,
Abdullah
Abdullah may refer to:
* Abdullah (name), a list of people with the given name or surname
* Abdullah, Kargı, Turkey, a village
* ''Abdullah'' (film), a 1980 Bollywood film directed by Sanjay Khan
* '' Abdullah: The Final Witness'', a 2015 Pakis ...
, died almost six months before he was born. Muhammad then stayed with his foster mother,
Halima bint Abi Dhu'ayb
Halima bint Abi Dhu'ayb al-Sa'diyya () was the foster-mother of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Halimah and her husband were from the tribe of Sa'd b. Bakr, a subdivision of Hawazin (a large North Arabian tribe or group of tribes).
Relationship ...
, and her husband until he was two years old. At the age of six, Muhammad lost his biological mother
Amina
Amina (or Aminah) is the loose transcription of two different Arabic female given names:
* ʾĀmina (Arabic: آمنة, also anglicized as ''Aaminah'' or ''Amna'') meaning "safe one, protected"
* ʾAmīna (Arabic: أمينة, also anglicized as ''Am ...
to illness and became an orphan. For the next two years, until he was eight years old, Muhammad was under the guardianship of his paternal grandfather,
Abd al-Muttalib
Shayba ibn Hāshim (; ), better known as ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib, () was the fourth chief of the Quraysh tribal confederation and grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Early life
His father was Hashim ibn 'Abd Manaf,Muhammad ibn Sa ...
, until the latter's death. He then came under the care of his uncle,
Abu Talib, the new leader of the Banu Hashim. Abu Talib's brothers assisted with Muhammad's learning
Hamza
The hamza ( ') () is an Arabic script character that, in the Arabic alphabet, denotes a glottal stop and, in non-Arabic languages, indicates a diphthong, vowel, or other features, depending on the language. Derived from the letter '' ʿayn'' ( ...
, the youngest, trained Muhammad in
archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a Bow and arrow, bow to shooting, shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting ...
,
swordsmanship
Swordsmanship or sword fighting refers to the skills and techniques used in combat and training with any type of sword. The term is modern, and as such was mainly used to refer to smallsword fencing, but by extension it can also be applied to an ...
, and
martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defence; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; ...
. Another uncle,
Abbas
Abbas may refer to:
People
* Abbas (name), list of people with the name, including:
**Abbas ibn Ali (645–680), popularly known as ''Hazrat-e-Abbas'', the son of Ali ibn Abi Talib (the first imam in Shia Islam)
**Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (567 ...
, provided Muhammad with a job leading
caravans on the northern segment of the route to Syria.
The historical record of Mecca during Muhammad's early life is limited and fragmentary, making it difficult to distinguish between fact and legend. Several Islamic narratives relate that Muhammad, as a child, went on a trading trip to Syria with his uncle Abu Talib and met a monk named
Bahira
Bahira (, ) is the name in Islamic tradition of a Christian monk who is said to have foretold Muhammad's prophethood when they met while Muhammad was accompanying his uncle Abu Talib on a trading trip.Abel, A.Baḥīrā. ''Encyclopaedia of Isla ...
, who is said to have then foretold his prophethood. There are multiple versions of the story with details that contradict each other. All accounts of Bahira and his meeting with Muhammad have been considered fictitious by modern historians as well as by some medieval Muslim scholars such as
al-Dhahabi
Shams ad-Dīn adh-Dhahabī (), also known as Shams ad-Dīn Abū ʿAbdillāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn ʿUthmān ibn Qāymāẓ ibn ʿAbdillāh at-Turkumānī al-Fāriqī ad-Dimashqī (5 October 1274 – 3 February 1348) was an Atharism, Athari ...
.
Sometime later in his life, Muhammad proposed marriage to his cousin and first love,
Fakhitah bint Abi Talib
Fākhitah bint Abī Ṭālib (), also known as Hind and better known by her kunya Umm Hānī, was a cousin and companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Early life
She was the eldest daughter of Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Fatima bi ...
. But likely owing to his poverty, his proposal was rejected by her father, Abu Talib, who chose a more illustrious suitor. When Muhammad was 25, his fortunes turned around; his business reputation caught the attention of his 40-year-old distant relative
Khadija
Khadija, Khadeeja or Khadijah () is an Arabic feminine given name, the name of Khadija bint Khuwaylid, first wife of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In 1995, it was one of the three most popular Arabic feminine names in the Muslim world, along wi ...
, a wealthy businesswoman who had staked out a successful career as a merchant in the caravan trade industry. She asked him to take one of her caravans into Syria, after which she was so impressed by his competence in the expedition that she proposed marriage to him; Muhammad accepted her offer and remained monogamous with her until her death.
In 605, the Quraysh decided to roof the
Kaaba
The Kaaba (), also spelled Kaba, Kabah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaba al-Musharrafa (), is a stone building at the center of Islam's most important mosque and Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site, the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, Sa ...
, which had previously consisted only of walls. A complete rebuild was needed to accommodate the new weight. Amid concerns about upsetting the deities, a man stepped forth with a pickaxe and exclaimed, "O goddess! Fear not! Our intentions are only for the best." With that, he began demolishing it. The anxious Meccans awaited divine retribution overnight, but his unharmed continuation the next day was seen as a sign of heavenly approval. According to a narrative collected by
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
, when it was time to reattach the
Black Stone
The Black Stone () is a rock set into the eastern corner of the Kaaba, the ancient building in the center of the Masjid al-Haram, Grand Mosque in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is revered by Muslims as an Islamic relic which, according to Muslim tradi ...
, a dispute arose over which clan should have the privilege. It was determined that the first person to step into the Kaaba's court would arbitrate. Muhammad took on this role, asking for a cloak. He placed the stone on it, guiding clan representatives to jointly elevate it to its position. He then personally secured it within the wall.
Beginnings of the Quran

The financial security Muhammad enjoyed from
Khadija
Khadija, Khadeeja or Khadijah () is an Arabic feminine given name, the name of Khadija bint Khuwaylid, first wife of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In 1995, it was one of the three most popular Arabic feminine names in the Muslim world, along wi ...
, his wealthy wife, gave him plenty of free time to spend in solitude in the
cave of Hira
Jabal al-Nour ( or 'Hill of the Illumination') is a mountain near Mecca in the Hejaz region of Saudi Arabia. The mountain houses the grotto or cave of Hira (), which holds tremendous significance for Muslims throughout the world, as it is here w ...
. According to Islamic tradition, in 610, when he was 40 years old, the angel
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Chris ...
appeared to him during his visit to the cave. The angel showed him a cloth with
Quranic verses
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
on it and instructed him to read. When Muhammad confessed his illiteracy, Gabriel choked him forcefully, nearly suffocating him, and repeated the command. As Muhammad reiterated his inability to read, Gabriel choked him again in a similar manner. This sequence took place once more before Gabriel finally recited the verses, allowing Muhammad to memorize them. These verses later constituted
Quran 96:1-5.
When Muhammad came to his senses, he felt scared; he started to think that after all of this spiritual struggle, he had been visited by a
jinn
Jinn or djinn (), alternatively genies, are supernatural beings in pre-Islamic Arabian religion and Islam.
Their existence is generally defined as parallel to humans, as they have free will, are accountable for their deeds, and can be either ...
, which made him no longer want to live. In desperation, Muhammad fled from the cave and began climbing up towards the top of the mountain to jump to his death. But when he reached the summit, he experienced another
vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, this time seeing a mighty being that engulfed the horizon and stared back at Muhammad even when he turned to face a different direction. This was the
spirit of revelation (), which Muhammad later referred to as
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Chris ...
; it was not a naturalistic
angel
An angel is a spiritual (without a physical body), heavenly, or supernatural being, usually humanoid with bird-like wings, often depicted as a messenger or intermediary between God (the transcendent) and humanity (the profane) in variou ...
, but rather a
transcendent presence that resisted the ordinary limits of humanity and space.
Frightened and unable to understand the experience, Muhammad hurriedly staggered down the mountain to his wife Khadija. By the time he got to her, he was already crawling on his hands and knees, shaking wildly and crying "Cover me!", as he thrust himself onto her lap. Khadija wrapped him in a cloak and tucked him in her arms until his fears dissipated. She had absolutely no doubts about his revelation; she insisted it was real and not a jinn. Muhammad was also reassured by Khadija's Christian cousin
Waraqah ibn Nawfal
Waraqah ibn Nawfal ibn Asad ibn Abd-al-Uzza ibn Qusayy Al-Qurashi (Arabic ) was a Christian Arabian ascetic who was the paternal first cousin of Khadijah bint Khuwaylid, the first wife of Muhammad. He was considered to be a ''hanif'', who practi ...
, who jubilantly exclaimed "Holy! Holy! If you have spoken the truth to me, O Khadijah, there has come to him the great divinity who came to Moses aforetime, and lo, he is the prophet of his people." Khadija instructed Muhammad to let her know if Gabriel returned. When he appeared during their private time, Khadija conducted tests by having Muhammad sit on her left thigh, right thigh, and lap, inquiring Muhammad if the being was still present each time. After Khadija removed her clothes with Muhammad on her lap, he reported that Gabriel left at that moment. Khadija thus told him to rejoice as she concluded it was not
Satan
Satan, also known as the Devil, is a devilish entity in Abrahamic religions who seduces humans into sin (or falsehood). In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the '' yetzer hara'', or ' ...
but an angel visiting him.
Muhammad's demeanor during his moments of inspiration frequently led to allegations from his contemporaries that he was under the influence of a jinn, a soothsayer, or a magician, suggesting that his experiences during these events bore resemblance to those associated with such figures widely recognized in ancient Arabia. Nonetheless, these enigmatic seizure events might have served as persuasive evidence for his followers regarding the divine origin of his revelations. Some historians posit that the graphic descriptions of Muhammad's condition in these instances are likely genuine, as they are improbable to have been concocted by later Muslims.
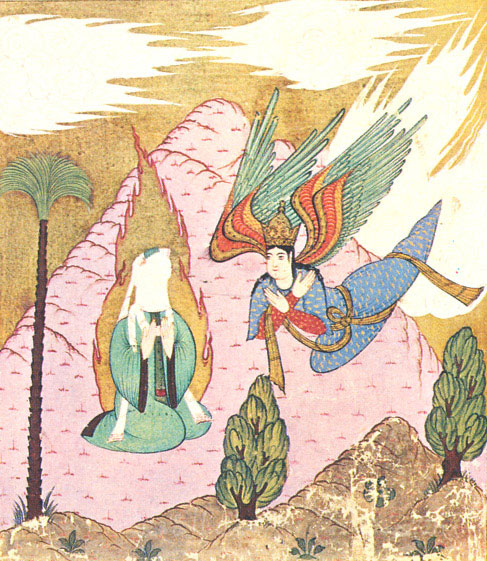

Shortly after Waraqa's death, the revelations ceased for a period, causing Muhammad great distress and thoughts of suicide. On one occasion, he reportedly climbed a mountain intending to jump off. However, upon reaching the peak, Gabriel appeared to him, affirming his status as the true Messenger of God. This encounter soothed Muhammad, and he returned home. Later, when there was another long break between revelations, he repeated this action, but Gabriel intervened similarly, calming him and causing him to return home.
Muhammad was confident that he could distinguish his own thoughts from these messages. The early Quranic revelations utilized approaches of cautioning non-believers with divine punishment, while promising rewards to believers. They conveyed potential consequences like famine and killing for those who rejected Muhammad's God and alluded to past and future calamities. The verses also stressed the imminent final judgment and the threat of hellfire for skeptics. Due to the complexity of the experience, Muhammad was initially very reluctant to tell others about his revelations; at first, he confided in only a few select family members and friends. According to Muslim tradition, Muhammad's wife Khadija was the first to believe he was a prophet. She was followed by Muhammad's ten-year-old cousin
Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
, close friend
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
, and adopted son
Zayd
Zaid or Zayd (; ) is an Arabic given name and surname.
Zaid
*Zaid Abbas (born 1983), Jordanian basketball player
* Zaid Abdul-Aziz (born 1946), American basketball player
*Zaid Al-Harb (1887–1972), Kuwaiti poet
*Zaid al-Rifai (1936-2024), Jord ...
. As word of Muhammad's revelations continued to spread throughout the rest of his family, they became increasingly divided on the matter, with the youth and women generally believing in him, while most of the men in the elder generations were staunchly opposed.
Opposition in Mecca
Around 613, Muhammad began to preach to the public;
many of his first followers were women,
freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, slaves were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self- ...
, servants, slaves, and other members of the
lower social class
A social class or social stratum is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the working class and the capitalist class. Membership of a social class can for example be dependent on education, w ...
. These converts keenly awaited each new revelation from Muhammad; when he recited it, they all would repeat after him and memorize it, and the literate ones recorded it in writing. Muhammad also introduced rituals to his group which included prayer () with physical postures that embodied complete surrender () to
God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
, and almsgiving () as a requirement of the Muslim community (). By this point, Muhammad's religious movement was known as ('purification').
Initially, he had no serious opposition from the inhabitants of
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
, who were indifferent to his proselytizing activities, but when he started to attack their beliefs, tensions arose. The
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By ...
challenged
him to perform miracles, such as bringing forth springs of water, yet he declined, reasoning that the regularities of nature already served as sufficient proof of God's majesty. Some satirized his lack of success by wondering why God had not bestowed treasure upon him. Others called on him to visit Paradise and return with tangible parchment scrolls of the
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
. But Muhammad asserted that the Quran, in the form he conveyed it, was already an extraordinary proof.
According to
Amr ibn al-As
Amr ibn al-As ibn Wa'il al-Sahmi (664) was an Arab commander and companion of Muhammad who led the Muslim conquest of Egypt and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Qurayshite, Amr embraced Islam in and was ...
, several of the Quraysh gathered at
Hijr and discussed how they had never faced such serious problems as they were facing from Muhammad. They said that he had derided their culture, denigrated their ancestors, scorned their faith, shattered their community, and cursed their gods. Sometime later, Muhammad came, kissing the
Black Stone
The Black Stone () is a rock set into the eastern corner of the Kaaba, the ancient building in the center of the Masjid al-Haram, Grand Mosque in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is revered by Muslims as an Islamic relic which, according to Muslim tradi ...
and performing the ritual . As Muhammad passed by them, they reportedly said hurtful things to him. The same happened when he passed by them a second time. On his third pass, Muhammad stopped and said, "Will you listen to me, O Quraysh? By Him (God), who holds my life in His hand, I bring you slaughter." They fell silent and told him to go home, saying that he was not a violent man. The next day, a number of Quraysh approached him, asking if he had said what they had heard from their companions. He answered yes, and one of them seized him by his cloak.
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
intervened, tearfully saying, "Would you kill a man for saying God is my Lord?" And they left him.
The Quraysh attempted to entice Muhammad to quit preaching by giving him admission to the merchants' inner circle as well as an advantageous marriage, but he refused both of the offers. A delegation of them then, led by the leader of the
Makhzum
The Banu Makhzum () was one of the wealthy clans of the Quraysh. They are regarded as being among the three most powerful and influential clans in Mecca before the advent of Islam, the other two being the Banu Hashim (the tribe of the Islamic prop ...
clan, known by the Muslims as
Abu Jahl
Amr ibn Hisham (), better known as Abū Jahl (; ) was the Meccan Quraysh polytheist leader of the Mushrikites known for his opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the most prominent flag-bearer of opposition towards Islam.
A promine ...
, went to Muhammad's uncle
Abu Talib, head of the
Hashim
Hashim () is a common male Arabic given name.
Notable people with the name include:
*Hashim ibn Abd Manaf
* Hashim Amir Ali
* Hashim Shah
* Hashim Amla
* Hashim Thaçi
* Hashim Khan
* Hashim Qureshi
* Mir Hashim Ali Khan
*Hashim al-Atassi
* Hashi ...
clan and Muhammad's caretaker, giving him an ultimatum to disown Muhammad:
Abu Talib politely dismissed them at first, thinking it was just a heated talk. But as Muhammad grew more vocal, Abu Talib requested Muhammad to not burden him beyond what he could bear, to which Muhammad wept and replied that he would not stop even if they put the sun in his right hand and the moon in his left. When he turned around, Abu Talib called him and said, "Come back nephew, say what you please, for by God I will never give you up on any account."
Quraysh delegation to Yathrib
The leaders of the Quraysh sent
Nadr ibn al-Harith
Al-Naḍr ibn al-Ḥārith ibn ʿAlqama ibn Kalada ibn ʿAbd Manāf ibn Abd al-Dār ibn Quṣayy (, d. 624 CE) was an Arab pagan physician who is considered one of the greatest Qurayshi opponents to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was captured a ...
and
Uqba ibn Abi Mu'ayt
Uqba ibn Abi Mu'ayt () (died 624) was one of the principal adversaries of Islam. He was a Quraysh leader and a member of the Banu 'Abdu Shams clan of Quraish tribe.
Family Family lineage
He was 'Uqba, son of Abi Mu'ayt, son of Abi 'Amru, so ...
to
Yathrib
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
to seek the opinions of the Jewish
rabbi
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as ''semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of t ...
s regarding Muhammad. The rabbis advised them to ask Muhammad three questions: recount the tale of young men who ventured forth in the first age; narrate the story of a traveler who reached both the eastern and western ends of the earth; and provide details about the spirit. If Muhammad answered correctly, they stated, he would be a Prophet; otherwise, he would be a liar. When they returned to Mecca and asked Muhammad the questions, he told them he would provide the answers the next day. However, 15 days passed without a response from his God, leading to gossip among the Meccans and causing Muhammad distress. At some point later, the angel
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Chris ...
came to Muhammad and provided him with the answers.
In response to the first query, the Quran tells a story about a group of men sleeping in a cave (Quran 18:9–25), which scholars generally link to the legend of the
Seven Sleepers
The Seven Sleepers (; ), also known in Christendom as Seven Sleepers of Ephesus, and in Islam as Aṣḥāb al-Kahf (اصحاب الکهف, ''aṣḥāb al-kahf'', lit. Companions of the Cave), is a Late antiquity, late antique Christianity, ...
of Ephesus. For the second query, the Quran speaks of
Dhu al-Qarnayn
, (, ; "The Owner of Two-Horns") is a leader who appears in the Qur'an, Surah al-Kahf (18), Ayahs 83–101, as one who travels to the east and west and sets up a barrier between a certain people and Gog and Magog (). Elsewhere, the Qur'an t ...
, literally 'he of the two horns' (Quran 18:93–99), a tale that academics widely associate with the
Alexander Romance. As for the third query, concerning the nature of the spirit, the Quranic revelation asserted that it was beyond human comprehension. Neither the Jews who devised the questions nor the Quraysh who posed them to Muhammad converted to Islam upon receiving the answers. Nadr and Uqba were later executed on Muhammad's orders after the
Battle of Badr
The Battle of Badr or sometimes called The Raid of Badr ( ; ''Ghazwahu Badr''), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ; ''Yawm al-Furqan'') in the Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the pre ...
, while other captives were held for ransom. As Uqba pleaded, "But who will take care of my children, Muhammad?" Muhammad responded, "Hell!"
Migration to Abyssinia and the incident of Satanic Verses
In 615, Muhammad sent some of his followers to
emigrate
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
to the Abyssinian
Kingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging ...
and found a small colony under the protection of the Christian Ethiopian emperor
Aṣḥama ibn Abjar
The ''Najashi'' () was the Arabic term for the ruler of the Kingdom of Aksum () who reigned from 614 to 630. It is agreed by Muslim scholars that Najashi gave shelter to early Muslim refugees from Mecca, around 615–616 at Aksum.
Reign
The ...
. Among those who departed were
Umm Habiba
Ramla bint Abi Sufyan ibn Harb (; ), commonly known by her Umm Habiba (), was a wife of Muhammad.
Early life
She was born in circa 589 or 594. She was the daughter of Abu Sufyan ibn Harb and Safiyyah bint Abi al-'As. Abu Sufyan was the chief o ...
, the daughter of one of the Quraysh chiefs,
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
, and her husband. The Quraysh then sent two men to retrieve them. Because leatherwork at the time was highly prized in Abyssinia, they gathered a lot of skins and transported them there so they could distribute some to each of the kingdom's generals. But the king firmly rejected their request.
While
Tabari
Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr ibn Yazīd al-Ṭabarī (; 839–923 CE / 224–310 AH), commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Sunni Muslim scholar, polymath, historian, exegete, jurist, and theologian from Amol, Tabaristan, present-day ...
and
Ibn Hisham
Abu Muhammad Abd al-Malik ibn Hisham ibn Ayyub al-Himyari (; died 7 May 833), known simply as Ibn Hisham, was a 9th-century Abbasid historian and scholar. He grew up in Basra, in modern-day Iraq and later moved to Egypt.
Life
Ibn Hisham has ...
mentioned only one migration to Abyssinia, there were two sets according to
Ibn Sa'd
Abū ‘Abd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Sa‘d ibn Manī‘ al-Baṣrī al-Hāshimī or simply Ibn Sa'd () and nicknamed ''Scribe of Waqidi'' (''Katib al-Waqidi''), was a scholar and Arabian biographer. Ibn Sa'd was born in 784/785 CE (168 AH) and di ...
. Of these two, the majority of the first group returned to Mecca before the event of , while the majority of the second group remained in Abyssinia at the time and went directly to
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
after the event of . These accounts agree that persecution played a major role in Muhammad sending them there. According to
W. Montgomery Watt, the episodes were more complex than the traditional accounts suggest; he proposes that there were divisions within the embryonic Muslim community, and that they likely went there to trade in competition with the prominent merchant families of Mecca. In
Urwa's letter preserved by Tabari, these emigrants returned after the conversion to Islam of a number of individuals in positions such as
Hamza
The hamza ( ') () is an Arabic script character that, in the Arabic alphabet, denotes a glottal stop and, in non-Arabic languages, indicates a diphthong, vowel, or other features, depending on the language. Derived from the letter '' ʿayn'' ( ...
and
Umar
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Mu ...
.
Along with many others,
Tabari recorded that Muhammad was desperate, hoping for an accommodation with his tribe. So, while he was in the presence of a number of Quraysh, after delivering verses mentioning three of their favorite deities (Quran 53:19–20),
Satan
Satan, also known as the Devil, is a devilish entity in Abrahamic religions who seduces humans into sin (or falsehood). In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the '' yetzer hara'', or ' ...
put upon his tongue two short verses: "These are the high flying ones / whose intercession is to be hoped for." This led to a general reconciliation between Muhammad and the Meccans, and the Muslims in Abyssinia began to return home. However, the next day, Muhammad retracted these verses at the behest of
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Chris ...
, claiming that they had been cast by Satan to his tongue and God had abrogated them. Instead, verses that revile those goddesses were then revealed. The returning Muslims thus had to make arrangements for clan protection before they could re-enter Mecca.
This
Satanic Verses
The Satanic Verses are words of "satanic suggestion" which the Islamic prophet Muhammad is alleged to have mistaken for divine revelation. The first use of the expression in English is attributed to Sir William Muir in 1858.
The words praise the ...
incident was reported en masse and documented by nearly all of the major biographers of Muhammad in Islam's first two centuries, which according to them corresponds to Quran 22:52. But since the rise of the
hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
movement and systematic theology with its new doctrines, including the , which claimed that Muhammad was infallible and thus could not be fooled by Satan, the historical memory of the early community has been reevaluated. By the 20th century, Muslim scholars unanimously rejected this incident.
On the other hand, most European biographers of Muhammad recognize the veracity of this incident of satanic verses on the basis of the
criterion of embarrassment
The criterion of embarrassment is a type of biblical historical analysis in which a historical account is deemed more likely to be true if the author would have no reason to invent a historical account which might embarrass them. Certain Biblical ...
. Historian Alfred T. Welch proposes that the period of Muhammad's turning away from strict monotheism was likely far longer but was later encapsulated in a story that made it much shorter and implicated Satan as the culprit.
In 616, an agreement was established whereby all other Quraysh clans were to enforce a ban on the
Banu Hashim
Banu Hashim () is an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe to which the Islamic prophet Muhammad belonged, named after Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf.
Members of this clan, and especially their descendants, are also referred ...
, prohibiting trade and marriage with them. Nevertheless, Banu Hashim members could still move around Mecca freely. Despite facing increasing verbal abuse, Muhammad continued to navigate the streets and engage in public debates without being physically harmed. At a later point, a faction within Quraysh, sympathizing with Banu Hashim, initiated efforts to end the sanctions, resulting in a general consensus in 619 to lift the ban.
Attempt to establish himself in Ta'if
In 619, Muhammad faced a period of sorrow. His wife,
Khadija
Khadija, Khadeeja or Khadijah () is an Arabic feminine given name, the name of Khadija bint Khuwaylid, first wife of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In 1995, it was one of the three most popular Arabic feminine names in the Muslim world, along wi ...
, a crucial source of his financial and emotional support, died. In the same year, his uncle and guardian,
Abu Talib, also died. Despite Muhammad's persuasions to Abu Talib to embrace Islam on his deathbed, he clung to his polytheistic beliefs until the end. Muhammad's other uncle,
Abu Lahab, who succeeded the
Banu Hashim
Banu Hashim () is an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe to which the Islamic prophet Muhammad belonged, named after Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf.
Members of this clan, and especially their descendants, are also referred ...
clan leadership, was initially willing to provide Muhammad with protection. However, upon hearing from Muhammad that Abu Talib and
Abd al-Muttalib
Shayba ibn Hāshim (; ), better known as ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib, () was the fourth chief of the Quraysh tribal confederation and grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Early life
His father was Hashim ibn 'Abd Manaf,Muhammad ibn Sa ...
were destined for hell due to not believing in Islam, he withdrew his support.
Muhammad then went to
Ta'if
Taif (, ) is a city and governorate in Mecca Province in Saudi Arabia. Located at an elevation of in the slopes of the Hijaz Mountains, which themselves are part of the Sarawat Mountains, Sarat Mountains, the city has a population of 563,282 pe ...
to try to establish himself in the city and gain aid and protection against the Meccans, but he was met with a response: "If you are truly a prophet, what need do you have of our help? If God sent you as his messenger, why doesn't He protect you? And if
Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
wished to send a prophet, couldn't He have found a better person than you, a weak and fatherless orphan?" Realizing his efforts were in vain, Muhammad asked the people of Ta'if to keep the matter a secret, fearing that this would embolden the hostility of the Quraysh against him. However, instead of accepting his request, they pelted him with stones, injuring his limbs. He eventually evaded this chaos and persecution by escaping to the garden of
Utbah ibn Rabi'ah
Utba ibn Rabi'a () (), also known as Abu al-Walid () was one of the prominent pagan leaders of the Quraysh during the era of Muhammad. He was the father of Abu Hudhayfa, al-Walid, Hind and father-in-law of Abu Sufyan ibn Harb. Utba was kill ...
, a Meccan chief with a summer residence in Ta'if. Muhammad felt despair due to the unexpected rejection and hostility he received in the city; at this point, he realized he had no security or protection except from God, so he began praying. Shortly thereafter, Utbah's Christian slave
Addas Addas () was a young Christian slave boy who lived in Taif, a mountainous area south of Mecca, during the times of Muhammad, the prophet of Islam. Originally from Nineveh, he was supposedly the first person from the western province of Taif to conv ...
stopped by and offered grapes, which Muhammad accepted. By the end of the encounter, Addas felt overwhelmed and kissed Muhammad's head, hands, and feet in recognition of his prophethood.
On Muhammad's return journey to Mecca, news of the events in Ta'if had reached the ears of
Abu Jahl
Amr ibn Hisham (), better known as Abū Jahl (; ) was the Meccan Quraysh polytheist leader of the Mushrikites known for his opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the most prominent flag-bearer of opposition towards Islam.
A promine ...
, and he said, "They did not allow him to enter Ta'if, so let us deny him entry to Mecca as well." Knowing the gravity of the situation, Muhammad asked a passing horseman to deliver a message to
Akhnas ibn Shariq
Al-Akhnas ibn Shurayq al-Thaqafī (Arabic: الأخنس بن شريق الثقفي) was a contemporary to Muhammad and one of the leaders of Mecca.
Biography
Late life — ?-610
He was a rich man and an ally of Banu Zuhrah.
Muhammad's era ...
, a member of his mother's clan, requesting his protection so that he could enter in safety. But Akhnas declined, saying that he was only a confederate of the house of
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By ...
. Muhammad then sent a message to
Suhayl ibn Amir
Suhayl ibn ʿAmr (), also known as Abū Yazīd, was a contemporary of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a prominent leader among the Quraysh tribe of Mecca. Clever and articulate, he was known as the ''Khatib'' (orator) of his tribe, and his opi ...
, who similarly declined on the basis of tribal principle. Finally, Muhammad dispatched someone to ask
Mut'im ibn 'Adiy, the chief of the
Banu Nawfal
Banu Nawfal () is a notable Arabic sub-clan of the Quraish tribe. Its progenitor is Nawfal ibn Abd Manaf.
References
Nawfal
{{islam-stub ...
. Mut'im agreed, and after equipping himself, he rode out in the morning with his sons and nephews to accompany Muhammad to the city. When Abu Jahl saw him, he asked if Mut'im was simply giving him protection or if he had already converted to his religion. Mut'im replied, "Granting him protection, of course." Then Abu Jahl said, "We will protect whomever you protect."
Isra' and Mi'raj

It is at this low point in Muhammad's life that the accounts in the lay out the famous Isra' and Mi'raj. Nowadays, Isra' is believed by Muslims to be the journey of Muhammad from Mecca to
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, while Mi'raj is from Jerusalem to the heavens. There is considered no substantial basis for the Mi'raj in the Quran, as the Quran does not address it directly.
Verse 17:1 of the Quran recounts Muhammad's night journey from a revered place of prayer to the most distant place of worship. The
Kaaba
The Kaaba (), also spelled Kaba, Kabah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaba al-Musharrafa (), is a stone building at the center of Islam's most important mosque and Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site, the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, Sa ...
, holy enclosure in Mecca, is widely accepted as the starting point, but there is disagreement among Islamic traditions as to what constitutes "the farthest place of worship". Some modern scholars maintain that the earliest tradition saw this faraway site as a celestial twin of the Kaaba, so that Muhammad's journey took him directly from Mecca through the heavens. A later tradition, however, refers to it as , which is generally associated with Jerusalem. Over time, these different traditions merged to present the journey as one that began in Mecca, passed through Jerusalem, and then ascended to heaven.
The dating of the events also differs from account to account.
Ibn Sa'd
Abū ‘Abd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Sa‘d ibn Manī‘ al-Baṣrī al-Hāshimī or simply Ibn Sa'd () and nicknamed ''Scribe of Waqidi'' (''Katib al-Waqidi''), was a scholar and Arabian biographer. Ibn Sa'd was born in 784/785 CE (168 AH) and di ...
recorded that Muhammad's Mi'raj took place first, from near the Kaaba to the heavens, on the 27th of
Ramadan
Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar. It is observed by Muslims worldwide as a month of fasting (''Fasting in Islam, sawm''), communal prayer (salah), reflection, and community. It is also the month in which the Quran is believed ...
, 18 months before the , while the Isra' from Mecca to took place on the 17th night of the
Last Rabi’ul before the . As is well known, these two stories were later combined into one. In
Ibn Hisham
Abu Muhammad Abd al-Malik ibn Hisham ibn Ayyub al-Himyari (; died 7 May 833), known simply as Ibn Hisham, was a 9th-century Abbasid historian and scholar. He grew up in Basra, in modern-day Iraq and later moved to Egypt.
Life
Ibn Hisham has ...
's account, the Isra' came first and then the Mi'raj, and he put these stories before the deaths of Khadija and Abu Talib. In contrast,
al-Tabari
Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr ibn Yazīd al-Ṭabarī (; 839–923 CE / 224–310 AH), commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Sunni Muslim scholar, polymath, historian, exegete, jurist, and theologian from Amol, Tabaristan, present- ...
included only the story of Muhammad's ascension from the sanctuary in Mecca to "the earthly heaven". Tabari placed this story at the beginning of Muhammad's public ministry, between his account of Khadija becoming "the first to believe in the Messenger of God" and his account of "the first male to believe in the Messenger of God".
Migration to Medina
As resistance to his proselytism in Mecca grew, Muhammad began to limit his efforts to non-Meccans who attended fairs or made pilgrimages. During this period, Muhammad had an encounter with six individuals from the Banu Khazraj. These men had a history of raiding Jews in their locality, who in turn would warn them that a prophet would be sent to punish them. On hearing Muhammad's religious message, they said to each other, "This is the very prophet of whom the Jews warned us. Don't let them get to him before us!" Upon embracing Islam, they returned to Medina and shared their encounter, hoping that by having their people—the Khazraj and the Aws, who had been at odds for so long—accept Islam and adopt Muhammad as their leader, unity could be achieved between them.
The next year, five of the earlier converts revisited Muhammad, bringing with them seven newcomers, three of whom were from the Banu Aws. At Aqaba, near Mecca, they pledged their loyalty to him. Muhammad then entrusted
Mus'ab ibn Umayr
Muṣʿab ibn ʿUmayr () also known as Muṣʿab al-Khayr ("the Good") was a '' sahabi'' (companion) of Muhammad. From the Banū ʿAbd al-Dār branch of the Quraysh, he embraced Islam in 614 CE and was the first ambassador of Islam. He died in ...
to join them on their return to Medina to promote Islam. Come June 622, a significant clandestine meeting was convened, again at Aqaba. In this gathering, seventy-five individuals from Medina (then Yathrib) attended, including two women, representing all the converts of the oases. Muhammad asked them to protect him as they would protect their wives and children. They concurred and gave him their oath, commonly referred to as the
second pledge at al-Aqabah
The second pledge at al-ʿAqabah () was an important event in Islam where 75 residents of the city of Medina pledged their loyalty to Muhammad as their leader in an oath of allegiance known as a '' bay'ah''. It preceded the Hijrah, or migration ...
or the pledge of war. Paradise was Muhammad's promise to them in exchange for their loyalty.
Subsequently, Muhammad called upon the Meccan Muslims to relocate to Medina. This event is known as the , literally meaning 'severing of kinship ties'. The departures spanned approximately three months. To avoid arriving in Medina by himself with his followers remaining in Mecca, Muhammad chose not to go ahead and instead stayed back to watch over them and persuade those who were reluctant. Some were held back by their families from leaving, but in the end, there were no Muslims left in Mecca.
Islamic tradition recounts that in light of the unfolding events,
Abu Jahl
Amr ibn Hisham (), better known as Abū Jahl (; ) was the Meccan Quraysh polytheist leader of the Mushrikites known for his opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the most prominent flag-bearer of opposition towards Islam.
A promine ...
proposed a joint assassination of Muhammad by representatives of each clan. Having been informed about this by the angel Gabriel, Muhammad asked his cousin
Ali
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until his assassination in 661, as well as the first Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Born to Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib an ...
to lie in his bed covered with his green hadrami mantle, assuring that it would safeguard him.
That night
''That Night'' (originally titled ''One Hot Summer'') is a 1992 American coming-of-age romantic drama film written and directed by Craig Bolotin and starring C. Thomas Howell and Juliette Lewis. It is based on the 1987 novel of the same name ...
, the group of planned assassins approached Muhammad's home to carry out the attack but changed their minds upon hearing the voices of
Sawdah and some of Muhammad's daughters, since it was considered shameful to kill a man in front of the women in his family. They instead chose to wait until Muhammad left the house the next morning; one of the men peeked into a window and saw what he believed to be Muhammad (but was actually Ali dressed in Muhammad's cloak), though unbeknownst to them, Muhammad had previously escaped from the back of the residence. When Ali went outside to go for a walk the following morning, the men realized they had been fooled, and the Quraysh consequently offered a 100-camel bounty for the return of Muhammad's body, dead or alive. After staying hidden for three days, Muhammad subsequently departed with
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
for Medina, which at the time was still named Yathrib; the two men arrived in Medina on 4 September 622. The Meccan Muslims who undertook the migration were then called the
Muhajirun
The ''Muhajirun'' (, singular , ) were the converts to Islam and the Islamic prophet Muhammad's advisors and relatives, who emigrated from Mecca to Medina; the event is known in Islam as the '' Hijra''. The early Muslims from Medina are called the ...
, while the Medinan Muslims were dubbed the
Ansar.
Medinan years
Building the religious community in Medina
A few days after settling in Medina, Muhammad negotiated for the purchase of a piece of land; upon this plot, the Muslims began constructing a building that would become Muhammad's residence as well as a community gathering place () for prayer (). Tree trunks were used as pillars to hold up the roof, and there was no fancy pulpit; instead, Muhammad stood on top of a small stool to speak to the congregation. The structure was completed after about seven months in April 623, becoming the first Muslim building and mosque; its northern wall had a stone marking the direction of prayer () which was Jerusalem at that time. Muhammad used the building to host public and political meetings, as well as a place for the poor to gather to receive alms, food, and care. Christians and Jews were also allowed to participate in community worship at the mosque. Initially, Muhammad's religion had no organized way to call the community to prayer in a coordinated manner. To resolve this, Muhammad had considered using a ram's horn () like the Jews or a wooden clapper like the Christians, but one of the Muslims in the community had a dream where a man in a green cloak told him that someone with a loud booming voice should announce the service by crying out "
allahu akbar
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), although the term was used in pre-Islamic Arabia ...
" ('God is greater') to remind Muslims of their top priority; when Muhammad heard about this dream, he agreed with the idea and selected
Bilal __NOTOC__
Bilal may refer to:
People
* Bilal (name), or Belal or Bilel, including a list of people with the name
* Bilal ibn Rabah, a companion of Muhammad, made calls for prayers
* Bilal (American singer)
* Bilal (Lebanese singer)
Places
* Bi ...
, a former Abyssinian slave known for his loud voice.
Constitution of Medina
The
Constitution of Medina
The Constitution of Medina (; or ; also known as the Umma Document), is a document dealing with tribal affairs during the Islamic prophet Muhammad's time in Medina and formed the basis of the First Islamic State, a multi-religious polity under his ...
was a
legal covenant written by Muhammad. In the constitution, Medina's Arab and Jewish tribes promised to live peacefully alongside the Muslims and to refrain from making a separate treaty with Mecca. It also guaranteed the Jews freedom of religion. In the agreement, everyone under its jurisdiction was required to defend and protect the oasis if attacked. Politically, the agreement helped Muhammad better understand which people were on his side.
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
, following his narration of the , maintains that Muhammad penned the text and divulges its assumed content without supplying any or corroboration. The appellation is generally deemed imprecise, as the text neither established a state nor enacted Quranic statutes, but rather addressed tribal matters. While scholars from both the West and the Muslim world agree on the text's authenticity, disagreements persist on whether it was a treaty or a unilateral proclamation by Muhammad, the number of documents it comprised, the primary parties, the specific timing of its creation (or that of its constituent parts), whether it was drafted before or after Muhammad's removal of the three leading Jewish tribes of Medina, and the proper approach to translating it.
Beginning of armed conflict
Following the emigration, the people of Mecca seized property of Muslim emigrants to Medina. War would later break out between the people of Mecca and the Muslims. Muhammad delivered Quranic verses permitting Muslims to fight the Meccans. According to the traditional account, on 11 February 624, while praying in the
Masjid al-Qiblatayn
The Masjid al-Qiblatayn (, , ), also spelt Masjid al-Qiblatain, is a Sunni Islam mosque in Medina, Saudi Arabia. The mosque is believed by Muslims to be the place where the final Islamic prophet, Muhammad, received the command to change the ''Q ...
in Medina, Muhammad received revelations from God that he should be facing Mecca rather than Jerusalem during prayer. Muhammad adjusted to the new direction, and his companions praying with him followed his lead, beginning the tradition of facing Mecca during prayer.
Muhammad ordered a number of raids to capture Meccan caravans, but only the 8th of them, the
Raid on Nakhla
The Raid on Nakhla () was a raid that was initially unplanned by the companions of Muhammad, but is considered to be the first successful raid against the Meccans, since it was carried out during an espionage event. This raid took place at Nakhl ...
, resulted in actual fighting and capture of booty and prisoners.
In March 624, Muhammad led some three hundred warriors in a raid on a Meccan merchant caravan. The Muslims set an ambush for the caravan at Badr. Aware of the plan, the Meccan caravan eluded the Muslims. A Meccan force was sent to protect the caravan and went on to confront the Muslims upon receiving word that the caravan was safe. Due to being outnumbered more than three to one, a spirit of fear ran throughout the Muslim camp; Muhammad tried to boost their morale by telling them he had a dream in which God promised to send 1,000 angels to fight with them. From a tactical standpoint, Muhammad placed troops in front of all of the wells so the Quraysh would have to fight for water, and positioned other troops in such a way that would require the Quraysh to fight uphill while also facing the sun. The
Battle of Badr
The Battle of Badr or sometimes called The Raid of Badr ( ; ''Ghazwahu Badr''), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ; ''Yawm al-Furqan'') in the Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the pre ...
commenced, and the Muslims ultimately won, killing at least forty-five Meccans with fourteen Muslims dead. They also succeeded in killing many Meccan leaders, including
Abu Jahl
Amr ibn Hisham (), better known as Abū Jahl (; ) was the Meccan Quraysh polytheist leader of the Mushrikites known for his opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the most prominent flag-bearer of opposition towards Islam.
A promine ...
. Seventy prisoners had been acquired, many of whom were ransomed. Muhammad and his followers saw the victory as confirmation of their faith and Muhammad ascribed the victory to the assistance of an invisible host of angels. The Quranic verses of this period, unlike the Meccan verses, dealt with practical problems of government and issues like the distribution of spoils.
The victory strengthened Muhammad's position in Medina and dispelled earlier doubts among his followers. As a result, the opposition to him became less vocal. Pagans who had not yet converted were very bitter about the advance of Islam. Two pagans,
Asma bint Marwan
ʻAṣmāʼ bint Marwān ( "Ãsma, daughter of Marwan") a female Arab poet said to have lived in Medina in 7th-century Arabia. There is debate whether Muhammad ordered her assassinated for her agitating against Muhammad.
Islamic sources Family ...
of the Aws Manat tribe and
Abu 'Afak of the 'Amr b. 'Awf tribe, had composed verses taunting and insulting the Muslims. They were killed by people belonging to their own or related clans, and Muhammad did not disapprove of the killings. This report, however, is considered by some to be a fabrication. Most members of those tribes converted to Islam, and little pagan opposition remained.
Muhammad expelled from Medina the
Banu Qaynuqa
The Banu Qaynuqa (; also spelled Banu Kainuka, Banu Kaynuka, Banu Qainuqa, Banu Qaynuqa) was one of the three main Jewish tribes that originally lived in Medina (now part of Saudi Arabia) before being expelled by Muhammad. They were merchants an ...
, one of three main Jewish tribes, but some historians contend that the expulsion happened after Muhammad's death. According to
al-Waqidi
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Umar ibn Waqid al-Aslami () ( – 207 AH; commonly referred to as al-Waqidi (Arabic: ; c. 747 – 823 AD) was an early Arab Muslim historian and biographer of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, specializing in his military ...
, after
Abd Allah ibn Ubayy
Abd-Allah ibn Ubayy (, died 631), also called Ibn Salul in reference to his grandmother, was a chief of the Arab tribe Banu Khazraj and one of the leading men of Medina (then known as Yathrib). Upon the arrival of Muhammad, Ibn Ubayy became a Musl ...
spoke for them, Muhammad refrained from executing them and commanded that they be exiled from Medina. Following the Battle of Badr, Muhammad also made mutual-aid alliances with a number of Bedouin tribes to protect his community from attacks from the northern part of
Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
.
Conflicts with Jewish tribes
Once the ransom arrangements for the Meccan captives were finalized, he initiated a siege on the
Banu Qaynuqa
The Banu Qaynuqa (; also spelled Banu Kainuka, Banu Kaynuka, Banu Qainuqa, Banu Qaynuqa) was one of the three main Jewish tribes that originally lived in Medina (now part of Saudi Arabia) before being expelled by Muhammad. They were merchants an ...
, regarded as the weakest and wealthiest of Medina's three main Jewish tribes. Muslim sources provide different reasons for the siege, including an altercation involving
Hamza
The hamza ( ') () is an Arabic script character that, in the Arabic alphabet, denotes a glottal stop and, in non-Arabic languages, indicates a diphthong, vowel, or other features, depending on the language. Derived from the letter '' ʿayn'' ( ...
and Ali in the Banu Qaynuqa market, and another version by
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
, which tells the story of a Muslim woman being pranked by a Qaynuqa goldsmith. Regardless of the cause, the Banu Qaynuqa sought refuge in their fort, where Muhammad blockaded them, cutting off their access to food supplies. The Banu Qaynuqa requested help from their Arab allies, but the Arabs refused since they were supporters of Muhammad. After roughly two weeks, the Banu Qaynuqa capitulated without engaging in combat.
Following the surrender of the Qaynuqa, Muhammad was moving to execute the men of the tribe when
Abdullah ibn Ubayy
Abd-Allah ibn Ubayy (, died 631), also called Ibn Salul in reference to his grandmother, was a chief of the Arab tribe Banu Khazraj and one of the leading men of Medina (then known as Yathrib). Upon the arrival of Muhammad, Ibn Ubayy became a Mus ...
, a Muslim
Khazraj
The Banu Khazraj () is a large Arab tribe based in Medina. They were also in Medina during Muhammad's era.
The Banu Khazraj are a South Arabian Qahtanite tribe that were pressured out of South Arabia as a result of the destruction of the Marib ...
chieftain who had been aided by the Qaynuqa in the past encouraged Muhammad to show leniency. In a narrated incident, Muhammad turned away from Ibn Ubayy, but undeterred, the chieftain grasped Muhammad's cloak, and refused to let go until Muhammad agreed to treat the tribe leniently. Despite being angered by the incident, Muhammad spared the Qaynuqa, stipulating that they must depart Medina within three days and relinquish their property to the Muslims, with a fifth () being retained by Muhammad.
Back in Medina,
Ka'b ibn al-Ashraf
Ka'b ibn al-Ashraf (; died ) was, according to Islamic texts, a pre-Islamic Arabic poet and contemporary of Muhammad in Medina. Scholars identify him as a Jewish leader.
Biography
Ka'b was born to a father from the Arab Tayy tribe and a mother ...
, a wealthy half-Jewish man from
Banu Nadir
The Banu Nadir (, ) were a Jewish Arab tribe that lived in northern Arabia at the oasis of Medina until the 7th century. They were probably a part of the Constitution of Medina, which was formed after Muhammad's Hijrah. Tensions rose between th ...
and staunch critic of Muhammad, had just returned from Mecca after producing poetry that mourned the death of the Quraysh at Badr and aroused them to retaliate. When Muhammad learned of this incitement against the Muslims, he asked his followers, "Who is ready to kill Ka'b, who has hurt God and His apostle?"
Ibn Maslamah offered his services, explaining that the task would require deception. Muhammad did not contest this. He then gathered accomplices, including Ka'b's foster brother, Abu Naila. They pretended to complain about their post-conversion hardships, persuading Ka'b to lend them food. On the night of their meeting with Ka'b, they murdered him when he was caught off-guard.
Meccan retaliation
In 625, the Quraysh, wearied by Muhammad's continuous attacks on their caravans, decided to take decisive action. Led by
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
, they assembled an army to oppose Muhammad. Upon being alerted by his scout about the impending threat, Muhammad convened a war council. Initially, he considered defending from the city center, but later decided to meet the enemy in open battle at
Mount Uhud
Mount Uhud (, ) is a mountain north of Medina, in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia. It is high and long. It was the site of the second battle between the Prophets of Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad and the Shirk (Islam), polytheists of his T ...
, following the insistence of the younger faction of his followers. As they prepared to depart, the remaining Jewish allies of
Abdullah ibn Ubayy
Abd-Allah ibn Ubayy (, died 631), also called Ibn Salul in reference to his grandmother, was a chief of the Arab tribe Banu Khazraj and one of the leading men of Medina (then known as Yathrib). Upon the arrival of Muhammad, Ibn Ubayy became a Mus ...
offered their help, which Muhammad declined. Despite being outnumbered, the Muslims initially held their ground but lost advantage when some archers disobeyed orders. As rumors of Muhammad's death spread, the Muslims started to flee, but he had only been injured and managed to escape with a group of loyal adherents. Satisfied they had restored their honor, the Meccans returned to Mecca. Mass casualties suffered by the Muslims in the Battle of Uhud resulted in many wives and daughters being left without a male protector, so after the battle, Muhammad received
revelation
Revelation, or divine revelation, is the disclosing of some form of Religious views on truth, truth or Knowledge#Religion, knowledge through communication with a deity (god) or other supernatural entity or entities in the view of religion and t ...
allowing Muslim men to have up to four wives each, marking the beginning of
polygyny in Islam
Traditional Sunni and Shia Islamic marital jurisprudence allows Muslim men to be married to multiple women (a practice known as polygyny) -- up to four wives at a time under Islamic law -- with the stipulation that if the man fears he's unable to ...
.
Sometime later, Muhammad found himself needing to pay blood money to
Banu Amir
The Banu Amir () was a large and ancient Arab tribe originating from Western Arabia that dominated Najd for centuries after the rise of Islam. It was an independent branch of the Hawazin confederation, and its original homeland was the border are ...
. He sought monetary help from the Jewish tribe of
Banu Nadir
The Banu Nadir (, ) were a Jewish Arab tribe that lived in northern Arabia at the oasis of Medina until the 7th century. They were probably a part of the Constitution of Medina, which was formed after Muhammad's Hijrah. Tensions rose between th ...
, and they agreed to his request. However, while waiting, he departed from his companions and disappeared. When they found him at his home, according to
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
, Muhammad disclosed that he had received a divine revelation of a planned assassination attempt on him by the Banu Nadir, which involved dropping a boulder from a rooftop. Muhammad then initiated a siege on the tribe; during this time he also commanded the felling and burning of their palm groves, which was an unambiguous symbol of declaring war in Arabia. After a fortnight or so, the Banu Nadir capitulated. They were directed to vacate their land and permitted to carry only one camel-load of goods for every three people. From the spoils, Muhammad claimed a fertile piece of land where barley sprouted amongst palm trees.
Raid on the Banu Mustaliq
Upon receiving a report that the
Banu Mustaliq
The Banu Mustaliq () is an Arab tribe. The tribe is a sub-clan of the Banu Khuza'a, descended from Azdi Qahtani. They occupied the territory of Qadid on the Red Sea shore between Jeddah and Rabigh.
History
The Banu al Mustaliq, allied to the ...
were planning an attack on Medina, Muhammad's troops executed a surprise attack on them at their watering place, causing them to flee rapidly. In the confrontation, the Muslims lost one man, while the enemy suffered ten casualties. As part of their triumph, the Muslims seized 2,000 camels, 500 sheep and goats, and 200 women from the tribe. The Muslim soldiers desired the captive women, but they also sought ransom money. They asked Muhammad about using to prevent pregnancy, to which Muhammad replied, "You are not under any obligation to forbear from that..." Later, envoys arrived in Medina to negotiate the ransom for the women and children. Despite having the choice, all of them chose to return to their country instead of staying.
Battle of the Trench
With the help of the exiled
Banu Nadir
The Banu Nadir (, ) were a Jewish Arab tribe that lived in northern Arabia at the oasis of Medina until the 7th century. They were probably a part of the Constitution of Medina, which was formed after Muhammad's Hijrah. Tensions rose between th ...
, the Quraysh military leader
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
mustered a force of 10,000 men. Muhammad prepared a force of about 3,000 men and adopted a form of defense unknown in Arabia at that time; the Muslims dug a trench wherever Medina lay open to cavalry attack. The idea is credited to a Persian convert to Islam,
Salman the Persian
Salman Farsi (; ) was a Persian religious scholar and one of the companions of Muhammad. As a practicing Zoroastrian, he dedicated much of his early life to studying to become a magus, after which he began travelling extensively throughout Weste ...
. The siege of Medina began on 31 March 627 and lasted two weeks. Abu Sufyan's troops were unprepared for the fortifications, and after an ineffectual siege, the coalition decided to return home. The Quran discusses this battle in sura Al-Ahzab, in verses 33:9–27.
[Uri Rubin, ''Quraysh'', ]Encyclopaedia of the Quran
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alp ...
.
During the battle, the Jewish tribe of
Banu Qurayza
The Banu Qurayza (; alternate spellings include Quraiza, Qurayzah, Quraytha, and the archaic Koreiza) were a Jewish tribe which lived in northern Arabia, at the oasis of Yathrib (now known as Medina). They were one of the three major Jewish ...
, located to the south of Medina, entered into negotiations with Meccan forces to revolt against Muhammad. Although the Meccan forces were swayed by suggestions that Muhammad was sure to be overwhelmed, they desired reassurance in case the confederacy was unable to destroy him. No agreement was reached after prolonged negotiations, partly due to sabotage attempts by Muhammad's scouts. After the coalition's retreat, the Muslims accused the Banu Qurayza of treachery and besieged them in their forts for 25 days. The Banu Qurayza eventually surrendered; according to
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
, all the men apart from a few converts to Islam were beheaded, while the women and children were enslaved. Walid N. Arafat and
Barakat Ahmad
Barakat Ahmad (died 1988) was an Ahmadi scholar and Indian diplomat. He had a doctorate in Arab history from the American University of Beirut and a doctorate in literature from the University of Tehran.Leon Nemoy, ''Barakat Ahmad's "Muhammad and ...
have disputed the accuracy of Ibn Ishaq's narrative. Arafat believes that Ibn Ishaq's Jewish sources, speaking over 100 years after the event, conflated this account with memories of earlier massacres in Jewish history; he notes that Ibn Ishaq was considered an unreliable historian by his contemporary
Malik ibn Anas
Malik ibn Anas (; –795) also known as Imam Malik was an Arab Islamic scholar and traditionalist who is the eponym of the Maliki school, one of the four schools of Islamic jurisprudence in Sunni Islam.Schacht, J., "Mālik b. Anas", in: ''E ...
, and a transmitter of "odd tales" by the later
Ibn Hajar Ibn Hajar may refer to:
*Ibn Hajar al-Asqalani (1372–1449), Shafi'i and Hadith scholar
*Ibn Hajar al-Haytami
Sheikhul Islam Shihāb al-Dīn Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī ibn Ḥajar al-Haytamī al-Makkī al-Anṣārī kn ...
. Ahmad argues that only some of the tribe were killed, while some of the fighters were merely enslaved. Watt finds Arafat's arguments "not entirely convincing", while
Meir J. Kister has refuted the arguments of Arafat and Ahmad.
In the siege of Medina, the Meccans exerted the available strength to destroy the Muslim community. The failure resulted in a significant loss of prestige; their trade with Syria vanished. Following the Battle of the Trench, Muhammad made two expeditions to the north, both ended without any fighting. While returning from one of these journeys (or some years earlier according to other early accounts), an
accusation of adultery was made against
Aisha
Aisha bint Abi Bakr () was a seventh century Arab commander, politician, Muhaddith, muhadditha and the third and youngest wife of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Aisha had an important role in early Islamic h ...
, Muhammad's wife. Aisha was exonerated from accusations when Muhammad announced he had received a revelation confirming Aisha's innocence and directing that charges of adultery be supported by four eyewitnesses (sura 24,
An-Nur
An-Nur () is the List of chapters in the Quran, 24th chapter of the Quran with 64 verse (poetry), verses. The surah takes its name, An Nur, from verse 35.
Summary
*1 This Surah, chapter Waḥy, revealed from Jannah, heaven
*2-3 Law relating t ...
).
Invasion of the Banu Qurayza
On the day the Quraysh forces and their allies withdrew, Muhammad, while bathing at his wife's abode, received a visit from the angel Gabriel, who instructed him to attack the Jewish tribe of
Banu Qurayza
The Banu Qurayza (; alternate spellings include Quraiza, Qurayzah, Quraytha, and the archaic Koreiza) were a Jewish tribe which lived in northern Arabia, at the oasis of Yathrib (now known as Medina). They were one of the three major Jewish ...
. Islamic sources recount that during the
preceding Meccan siege, the Quraysh leader
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
incited the Qurayza to attack the Muslims from their compound, but the Qurayza demanded the Quraysh to provide 70 hostages from among themselves to ascertain their commitment to their plans, as proposed by Muhammad's secret agent
Nuaym ibn Masud
Nuaym ibn Masud ''al-Ghatafani'' () was a companion of Muhammad hailing from Najd in the northern highlands of Arabia, belonging to the powerful Ghatafan tribe. His first exposure to Muhammad was when Abu Sufyan sent him to Medina to convince the M ...
. Abu Sufyan refused their requirement. Nevertheless, later accounts claim that 11 Jewish individuals from the Qurayza were indeed agitated and acted against Muhammad, though the course of event may have been dramatized within the tradition.
Citing the intrigue of the Qurayza, Muhammad besieged the tribe, though the tribe denied the charges. However, there are sources that say the
Banu Qurayza
The Banu Qurayza (; alternate spellings include Quraiza, Qurayzah, Quraytha, and the archaic Koreiza) were a Jewish tribe which lived in northern Arabia, at the oasis of Yathrib (now known as Medina). They were one of the three major Jewish ...
broke the treaty with Muhammad and assisted the enemies of Muslims during the Battle of the Trench. As the situation turned against the Qurayza, the tribe proposed to leave their land with one loaded camel each, but Muhammad refused. They then offered to leave without taking anything, but this was rejected as well, with Muhammad insisting on their unconditional surrender. The Qurayza subsequently requested to confer with one of their
Aws allies who had embraced Islam, leading to the arrival of
Abu Lubaba. When asked about Muhammad's intentions, he gestured towards his throat, indicating an imminent massacre. He immediately regretted his indiscretion and tied himself to one of the Mosque pillars as a form of penance.
After a 25-day siege, the Banu Qurayza surrendered. The Muslims of Banu Aws entreated Muhammad for leniency, prompting him to suggest that one of their own should serve as the judge, which they accepted. Muhammad assigned the role to
Sa'd ibn Mu'adh
Saʿd ibn Muʿādh al-Ansari () () was the chief of the Aws tribe in Medina and one of the prominent companions of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He died shortly after the Battle of the Trench.
Family
Sa'd was born in Medina 590 CE, the son o ...
, a man nearing death from an infection in his wounds from the previous Meccan siege. He pronounced that all the men should be put to death, their possessions to be distributed among Muslims, and their women and children to be taken as captives. Muhammad approved this pronouncement saying it aligned with the God's judgement. Consequently, 600–900 men of Banu Qurayza were executed. The women and children were distributed as slaves, with some being transported to
Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
to be sold. The proceeds were then utilized to purchase weapons and horses for the Muslims.
Incidents with the Banu Fazara
A few months after the conflict with the Banu Qurayza, Muhammad organized a caravan to conduct trade in Syria.
Zayd ibn Haritha
Zayd ibn Ḥāritha al-Kalbī () (), was an early Muslim, Sahabi and the adopted son of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad. He is commonly regarded as the fourth person to have accepted Islam, after Muhammad's wife Khadija, Muhammad's cousin Ali, a ...
was tasked with guarding the convoy. When they journeyed through the territory of
Banu Fazara
The Banu Fazara or Fazzara or Fezara or Fezzara () were an Arab tribe whose original homeland was Najd.
Origins
According to Arab genealogical tradition, the progenitor of the Banu Fazara was Fazāra ibn Dhubyān ibn Baghīḍ ibn Rayth ibn G ...
, whom Zayd had raided in the past, the tribe seized the opportunity for revenge, attacking the caravan and injuring him. Upon his return to Medina, Muhammad ordered Zayd to lead a punitive operation against the Fazara in which their matriarch
Umm Qirfa
The Banu Fazara or Fazzara or Fezara or Fezzara () were an Arab tribe whose original homeland was Najd.
Origins
According to Arab genealogical tradition, the progenitor of the Banu Fazara was Fazāra ibn Dhubyān ibn Baghīḍ ibn Rayth ibn Gha ...
was captured and brutally executed.
Treaty of Hudaybiyya

Early in 628, following a dream of making an unopposed pilgrimage to Mecca, Muhammad embarked on the journey. He was dressed in his customary pilgrim attire and was accompanied by a group of followers. Upon reaching
Hudaybiyya, they encountered Quraysh emissaries who questioned their intentions. Muhammad explained they had come to venerate the Kaaba, not to fight. He then sent
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable companion of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, played a major role ...
,
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
's second cousin, to negotiate with the Quraysh. As the negotiations were prolonged, rumors of Uthman's death began to spark, prompting Muhammad to call his followers to renew their oaths of loyalty. Uthman returned with news of a negotiation impasse. Muhammad remained persistent. In the end, the Quraysh sent
Suhayl ibn Amr
Suhayl ibn ʿAmr (), also known as Abū Yazīd, was a contemporary of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a prominent leader among the Quraysh tribe of Mecca. Clever and articulate, he was known as the '' Khatib'' (orator) of his tribe, and his o ...
, an envoy with full negotiation powers. Following lengthy discussions, a treaty was finally enacted, with terms:
# A ten-year truce was established between both parties.
# If a Qurayshite came to Muhammad's side without his guardian's allowance, he was to be returned to the Quraysh; yet, if a Muslim came to the Quraysh, he would not be surrendered to Muhammad.
# Any tribes interested in forming alliances with Muhammad or the Quraysh were free to do so. These alliances were also protected by the ten-year truce.
# Muslims were then required to depart back to Medina, however, they were permitted to make the
Umrah
The Umrah () is an Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, the holiest city for Muslims, located in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia. It can be undertaken at any time of the year, in contrast to the '' Ḥajj'' (; "pilgrimage"), which has specific d ...
pilgrimage in the coming year.
Invasion of Khaybar
Roughly ten weeks subsequent to his return from Hudaybiyya, Muhammad expressed his plan to invade
Khaybar
KhaybarOther Arabic transliteration, standardized Arabic transliterations: / . Anglicized pronunciation: , . (, ) is an oasis in Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province, Saudi Arabia, situated some north of the city of Medina. Prior to ...
, a flourishing oasis about north of Medina. The city was populated by Jews, including those from the
Banu Nadir
The Banu Nadir (, ) were a Jewish Arab tribe that lived in northern Arabia at the oasis of Medina until the 7th century. They were probably a part of the Constitution of Medina, which was formed after Muhammad's Hijrah. Tensions rose between th ...
, who had previously been expelled by Muhammad from Medina. With the prospect of rich spoils from the mission, numerous volunteers answered his call. To keep their movements hidden, the Muslim military chose to march during the nighttime. As dawn arrived and the city folks stepped out of their fortifications to harvest their dates, they were taken aback by the sight of the advancing Muslim forces. Muhammad cried out, "
Allahu Akbar
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), although the term was used in pre-Islamic Arabia ...
! Khaybar is destroyed. For when we approach a people's land, a terrible morning awaits the warned ones." After a strenuous battle lasting more than a month, the Muslims successfully captured the city.
The spoils, inclusive of the wives of the slain warriors, were distributed among the Muslims. The chief of the Jews,
Kenana ibn al-Rabi, to whom the treasure of Banu al-Nadir was entrusted, denied knowing its whereabouts. After a Jew disclosed his habitual presence around a particular ruin, Muhammad ordered excavations, and the treasure was found. When questioned about the remaining wealth, Kenana refused to divulge it. Kinana was then put through torture by Muhammad's decree and subsequently beheaded by
Muhammad ibn Maslamah
Muhammad ibn Maslamah al-Ansari (; 588 or 591 – 663 or 666) was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was known as "The Knight of Allah's Prophet".Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir'' vol. 3. Translated by Bewley, A. ( ...
in revenge for his brother. Muhammad took Kinana's wife,
Safiyya bint Huyayy
Safiyya bint Huyayy ( ) was a Jewish convert to Islam from the Banu Nadir tribe. After the Battle of Khaybar in 628, she was widowed and taken captive by the early Muslims and subsequently became Muhammad's tenth wife. Like all other wome ...
, as his own slave and later advised her to convert to Islam. She accepted and agreed to become Muhammad's wife.
Following their defeat by the Muslims, some of the Jews proposed to Muhammad that they stay and serve as tenant farmers, given the Muslims' lack of expertise and labor force for date palm cultivation. They agreed to give half of the annual produce to the Muslims. Muhammad consented to this arrangement with the caveat that he could displace them at any time. While they were allowed to farm, he demanded the surrender of all gold or silver, executing those who secreted away their wealth. Taking a cue from what transpired in Khaybar, the Jews in
Fadak
Fadak () was a village with fertile land in an oasis near Medina. The takeover of Fadak by Muslims in 629 CE was peaceful and a share of it thus belonged to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. After Muhammad died in 632, Fadak was confiscated from h ...
immediately sent an envoy to Muhammad and agreed to the same terms of relinquishing 50% of their annual harvest. However, since no combat occurred, the rank and file had no claim to a portion of the spoils. Consequently, all the loot became Muhammad's exclusive wealth.
At the feast following the battle, the meal served to Muhammad was reportedly poisoned. His companion, Bishr, fell dead after consuming it, while Muhammad himself managed to vomit it out after tasting it. The perpetrator was
Zaynab bint al-Harith, a Jewish woman whose father, uncle, and husband had been killed by the Muslims. When asked why she did it, she replied, "You know what you've done to my people... I said to myself: If he is truly a prophet, he will know about the poison. If he's merely a king, I'll be rid of him." Muhammad suffered illness for a period due to the poison he ingested, and he endured sporadic pain from it until his death.
Final years
Conquest of Mecca
The
truce of Hudaybiyyah
The Treaty of al-Hudaybiya () was an event that took place during the lifetime of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was a pivotal treaty between Muhammad, representing the state of Medina, and the tribe of the Quraysh in Mecca in March 628 (corres ...
was enforced for two years. The tribe of
Banu Khuza'ah
The Banū Khuzāʿah (, singular ''Khuzāʿī'') are an Azdite, Qahtanite tribe, one of the main ancestral tribes of Arabia. They ruled Mecca and were the Kings of Hejaz for 500 years, before the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and many members of t ...
had good relations with Muhammad, whereas their enemies, the
Banu Bakr
The Banu Bakr bin Wa'il ( '), or simply Banu Bakr, today known as Bani Bakr is an Arabian tribe belonging to the large Rabi'ah, a branch of Adnanite tribe. It is registered as one of the oldest and most ancient Arab gatherings. The tribe is rep ...
, had allied with the Meccans. A clan of the Bakr made a night raid against the Khuza'ah, killing a few of them. The Meccans helped the Banu Bakr with weapons and, according to some sources, a few Meccans also took part in the fighting. After this event, Muhammad sent a message to Mecca with three conditions, asking them to accept one of them. These were: either the Meccans would pay
blood money
Blood money may refer to:
* Blood money (restitution), money paid to the family of a murder victim
* A stream of revenue used by boarding masters for placing many seaman on ships
* Money obtained from crime, especially at the cost of another's lif ...
for the slain among the Khuza'ah tribe, they disavow themselves of the Banu Bakr, or they should declare the truce of Hudaybiyyah null.
[Khan 1998, pp. 274–275.]
The Meccans replied that they accepted the last condition.
Soon they realized their mistake and sent
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
to renew the Hudaybiyyah treaty, a request that was declined by Muhammad.
Muhammad began to prepare for a campaign. In 630, Muhammad marched on Mecca with 10,000 Muslim converts. With minimal casualties, Muhammad seized control of Mecca. He declared an amnesty for past offences, except for ten men and women who were "guilty of murder or other offences or had sparked off the war and disrupted the peace". Some of these were later pardoned Most Meccans converted to Islam and Muhammad proceeded to destroy all the statues of
Arabian gods
Deities formed a part of the polytheistic religious beliefs in pre-Islamic Arabia, with many of the deities' names known. Up until about the time between the fourth century AD and the emergence of Islam, polytheism was the dominant form of reli ...
in and around the Kaaba. According to reports collected by
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic proph ...
and
al-Azraqi
Muhammad ibn 'Abd Allah Al-Azraqi () was a 9th-century Islamic commentator and historian, and author of the '' Book of Reports about Mecca'' (''Kitab Akhbar Makka'').
Al-Azraqi was from a family who lived in Mecca for hundreds of years. He gave ...
, Muhammad personally spared paintings or frescos of
Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religion
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blesse ...
and Jesus, but other traditions suggest that all pictures were erased. The Quran discusses the conquest of Mecca.
Subduing the Hawazin and Thaqif and the expedition to Tabuk

Upon learning that Mecca had fallen to the Muslims, the
Banu Hawazin gathered their entire tribe, including their families, to fight. They are estimated to have around 4,000 warriors. Muhammad led 12,000 soldiers to raid them, but they surprised him at the
valley of Hunayn. The Muslims overpowered them and took their women, children and animals. Muhammad then turned his attention to
Taif
Taif (, ) is a city and governorate in Mecca Province in Saudi Arabia. Located at an elevation of in the slopes of the Hijaz Mountains, which themselves are part of the Sarat Mountains, the city has a population of 563,282 people in 2022, mak ...
, a city that was famous for its vineyards and gardens. He ordered them to be destroyed and besieged the city, which was surrounded by walls. After 15–20 days of failing to breach their defenses, he abandoned the attempts.
When he divided the plentiful loot acquired at Hunayn among his soldiers, the rest of the Hawazin converted to Islam and implored Muhammad to release their children and women, reminding him that he had been nursed by some of those women when he was a baby. He complied but held on to the rest of the plunder. Some of his men opposed giving away their portions, so he compensated them with six camels each from subsequent raids. Muhammad distributed a big portion of the booty to the new converts from the Quraysh.
Abu Sufyan
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; ), commonly known by his ' Abu Sufiyan (), was a prominent opponent-turned companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the father of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I () and namesake of the S ...
and two of his sons,
Mu'awiya
Mu'awiya I (–April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and immediately after the four Rashid ...
and
Yazid
Yazīd (, "increasing", "adding more") is an Arabic name and may refer to:
Given name
* Yazid I (647–683), second Umayyad Caliph upon succeeding his father Muawiyah
* Yazid II (687–724), Umayyad caliph
* Yazid III (701–744), Umayyad caliph ...
, got 100 camels individually. The
Ansar, who had fought bravely in the battle, but received close to nothing, were unhappy with this. One of them remarked, "It is not with such gifts that one seeks God's face." Disturbed by this utterance, Muhammad retorted, "He changed color."
Roughly 10 months after he captured Mecca, Muhammad took his army to attack the wealthy border provinces of
Byzantine Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great, who had become the protector of the Hellenistic kingdom of Syria.
...
. Several motives are proposed, including avenging the defeat at Mu'tah and earning vast booty. Because of the drought and severe heat at that time, some of the Muslims refrained from participating. This led to the revelation of Quran 9:38 which rebuked those slackers. When Muhammad and his army reached
Tabuk
Tabuk may refer to:
*Tabuk, Kalinga, the capital city of Kalinga province of the Philippines
*Tabuk Province, a province of Saudi Arabia
**Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, capital city of the province
** Tabuk Regional Airport
*Expedition of Tabuk, a military ...
, there were no hostile forces present. However, he was able to force some of the local chiefs to accept his rule and pay . A group under
Khalid ibn Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career servi ...
that he sent for a raid also managed to acquire some booty including 2,000 camels and 800 cattle.
The Hawazin's acceptance of Islam resulted in Taif losing its last major ally. After enduring a year of unrelenting thefts and terror attacks from the Muslims following the siege, the people of Taif, known as the
Banu Thaqif
The Banu Thaqif () is an Arab tribe which inhabited, and still inhabits, the city of Ta'if and its environs, in modern Saudi Arabia, and played a prominent role in early Islamic history.
During the pre-Islamic period, the Thaqif rivaled and co ...
, finally reached a tipping point and acknowledged that embracing Islam was the most sensible path for them.
Farewell pilgrimage

On February 631, Muhammad received a revelation granting idolaters four months of grace, after which the Muslims would attack, kill, and plunder them wherever they met.
During the 632 pilgrimage season, Muhammad personally led the ceremonies and gave a sermon. Among the key points highlighted are said to have been the prohibition of usury and vendettas related to past murders from the pre-Islamic era; the brotherhood of all Muslims; and the adoption of twelve lunar months without
intercalation.
Death

After praying at the burial site in June 632, Muhammad suffered a dreadful headache that made him cry in pain. He continued to spend the night with each of his wives one by one, but he fainted in
Maymunah's hut. He requested his wives to allow him to stay in
Aisha
Aisha bint Abi Bakr () was a seventh century Arab commander, politician, Muhaddith, muhadditha and the third and youngest wife of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Aisha had an important role in early Islamic h ...
's hut. He could not walk there without leaning on Ali and
Fadl ibn Abbas, as his legs were trembling. His wives and his uncle
al-Abbas fed him an Abyssinian remedy when he was unconscious. When he came to, he inquired about it, and they explained they were afraid he had
pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (Pulmonary pleurae, pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant d ...
. He replied that God would not afflict him with such a vile disease, and ordered all the women to also take the remedy. According to various sources, including , Muhammad said that he felt his aorta being severed because of the food he ate at Khaybar. On 8 June 632, Muhammad died. In his last moments, he reportedly uttered:
Historian Alfred T. Welch speculates that Muhammad's death was caused by Medinan fever, which was aggravated by physical and mental fatigue.
Tomb
Muhammad was buried where he died in Aisha's house. During the reign of the Umayyad caliph
al-Walid I
Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan (; – 23 February 715), commonly known as al-Walid I (), was the sixth Umayyad caliph, ruling from October 705 until his death in 715. He was the eldest son of his predecessor, Caliph Abd al-Malik (). As ...
, the
Prophet's Mosque
The Prophet's Mosque () is the List of the oldest mosques, second mosque built by the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad in Medina, after the Quba Mosque, as well as the second List of large mosques, la ...
was expanded to include the site of Muhammad's tomb. The
Green Dome
The Green Dome (, ) is a green-coloured dome built above the tombs of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad and the early Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun Caliphs Abu Bakr () and Umar, Omar (), which used to be the chamber ...
above the tomb was built by the
Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
sultan
Al Mansur Qalawun
(, – November 10, 1290) was the seventh Turkic Bahri Mamluk sultan of Egypt; he ruled from 1279 to 1290. He was called (, "Qalāwūn the Victorious"). After having risen in power in the Mamluk court and elite circles, Qalawun eventually hel ...
in the 13th century, although the green color was added in the 16th century, under the reign of
Ottoman sultan
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I (; , ; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver () in his own realm, was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan between 1520 a ...
. Among tombs adjacent to that of Muhammad are those of his companions (), the first two Muslim caliphs
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
and
Umar
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Mu ...
, and an empty one that
Muslims believe awaits Jesus.
When
Saud bin Abdul-Aziz took Medina in 1805, Muhammad's tomb was stripped of its gold and jewel ornamentation. Adherents to
Wahhabism
Wahhabism is an exonym for a Salafi revivalist movement within Sunni Islam named after the 18th-century Hanbali scholar Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. It was initially established in the central Arabian region of Najd and later spread to oth ...
, Saud's followers, destroyed nearly every tomb dome in Medina in order to prevent their veneration,
and the one of Muhammad is reported to have narrowly escaped.
Similar events took place in 1925, when the
Saudi militias retook—and this time managed to keep—the city. In the Wahhabi interpretation of Islam, burial is to take place in unmarked graves.
Although the practice is frowned upon by the Saudis, many pilgrims continue to practice a —a ritual visit—to the tomb.
Succession

With Muhammad's death, disagreement broke out over who his successor would be.
Umar ibn al-Khattab
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muh ...
, a prominent companion of Muhammad, nominated
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
, Muhammad's friend and collaborator. With additional support, Abu Bakr was confirmed as the first
caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
. This choice was disputed by some of Muhammad's companions, who held that Ali ibn Abi Talib, his cousin and son-in-law, had been designated the successor by Muhammad at
Ghadir Khumm
The Ghadīr Khumm () was a gathering of Muslims to attend a sermon delivered by the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad on 16 March 632 Common Era, CE. The gathering is said to have taken place by the ''ghadir'' () in the ...
. Abu Bakr immediately moved to strike against the forces of the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
because of the previous defeat, although he first had to put down a rebellion by Arab tribes in an event that Muslim historians later referred to as the
Ridda wars
The Ridda Wars were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes, some of which were led by rival prophet claimants. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in ...
, or "Wars of Apostasy".
The pre-Islamic Middle East was dominated by the
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
and
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
empires. The
Roman–Persian Wars between the two had devastated the region, making the empires unpopular amongst local tribes. Furthermore, in the lands that would be conquered by Muslims, many Christians (
Nestorians
Nestorianism is a term used in Christian theology and Church history to refer to several mutually related but doctrinary, doctrinarily distinct sets of teachings. The first meaning of the term is related to the original teachings of Christian t ...
,
Monophysite
Monophysitism ( ) or monophysism ( ; from Greek , "solitary" and , "nature") is a Christological doctrine that states that there was only one nature—the divine—in the person of Jesus Christ, who was the incarnated Word. It is rejected as ...
s,
Jacobites and
Copt
Copts (; ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptian population, descended from the ancient Egyptians. Copts pre ...
s) were disaffected from the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
which deemed them heretics. Within a decade Muslims conquered
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
,
Byzantine Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great, who had become the protector of the Hellenistic kingdom of Syria.
...
,
Byzantine Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, l ...
, large parts of
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, and established the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
.
Household

Muhammad's life is traditionally defined into two periods:
pre-hijra in Mecca (570–622), and
post-hijra in Medina (622–632). Muhammad is said to have had thirteen wives in total (although two have ambiguous accounts,
Rayhana bint Zayd
Rayhana bint Zayd (; died ) was a Jewish convert to Islam from the Banu Nadir. Through marriage, she was also a part of the Banu Qurayza, another local Jewish tribe. During the siege of Banu Qurayza in 627, she was widowed and taken captive ...
and
Maria al-Qibtiyya
, better known as or (), or Maria the Copt, died 637, was an Egyptian woman who, along with her sister Sirin bint Shamun, was given as a slave to the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 628 by Al-Muqawqis, a Christian governor of Alexandria, during ...
, as wife or concubine
[Barbara Freyer Stowasser, ''Wives of the Prophet'', ]Encyclopedia of the Quran
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alp ...
.).
At the age of 25, Muhammad married the wealthy Khadija who was 40 years old. The marriage lasted for 25 years and was a happy one. Muhammad did not enter into marriage with another woman during this marriage. After Khadija's death, Khawla bint Hakim suggested to Muhammad that he should marry
Sawdah bint Zam'ah
Sawdah bint Zamah () was the second wife of Muhammad and regarded as "Umm-ul-Mu'mineen" (Arabic: أمّ المؤمنين, romanized: ''ʾumm al- muʾminīn''), "Mother of the Believers".
Early life
Sawdah was born and raised in Mecc ...
, a Muslim widow, or
Aisha
Aisha bint Abi Bakr () was a seventh century Arab commander, politician, Muhaddith, muhadditha and the third and youngest wife of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Aisha had an important role in early Islamic h ...
, daughter of
Umm Ruman
Zaynab bint ʿĀmir ibn ʿUwaymir ibn ʿAbd Shams ibn ʿAttāb al-Farāsīyya al-Kinānīyya, known by her '' kunya'' "Umm Rūmān" () was among the followers or companions of Muhammad. She was a wife of Abu Bakr and the mother of Aisha, which m ...
and
Abu Bakr
Abd Allah ibn Abi Quhafa (23 August 634), better known by his ''Kunya (Arabic), kunya'' Abu Bakr, was a senior Sahaba, companion, the closest friend, and father-in-law of Muhammad. He served as the first caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruli ...
of Mecca. Muhammad is said to have asked for arrangements to marry both.
[Watt, ''Aisha'', ]Encyclopaedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is a reference work that facilitates the Islamic studies, academic study of Islam. It is published by Brill Publishers, Brill and provides information on various aspects of Islam and the Muslim world, Isl ...
. According to classical sources, Muhammad married Aisha when she was 6–7 years old; the marriage was consummated later, when she was 9 years old and he was 53 years old.
Muhammad performed household chores such as preparing food, sewing clothes, and repairing shoes. He is also said to have had accustomed his wives to dialogue; he listened to their advice, and the wives debated and even argued with him.
Khadija is said to have had four daughters with Muhammad (
Ruqayya bint Muhammad
Ruqayya bint Muhammad (; –March 624) was the second eldest daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Khadija. She married the third caliph Uthman and the couple had a son Abd Allah. In 624, Ruqayya died from an illness.
Early life
Born ...
,
Umm Kulthum bint Muhammad
Umm Kulthūm bint Muḥammad () (–630) was the third daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad by his first wife Khadija bint Khuwaylid.
Conversion to Islam
She was born in Mecca, the fifth of their six children.Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-T ...
,
Zainab bint Muhammad
Zainab bint Muhammad () (598/599–629 CE) was the eldest daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad by his first wife Khadijah.
Marriage
She married her maternal cousin, Abu al-As ibn al-Rabi', before December 610, and Khadija gave her a weddin ...
,
Fatimah Zahra) and two sons (
Qasim ibn Muhammad
Al-Qāsim ibn Muḥammad () was the eldest of the sons of Muhammad and Khadija bint Khuwaylid. He died in 601 CE (before the declaration of his father's prophethood in 609), after his third birthday, and is buried in Jannat al-Mu'alla cemetery, ...
and
Abd Allah ibn Muhammad
ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad () also known as al-Ṭāhir () and al-Ṭayyib () was one of the sons of Muhammad and Khadija. He died in childhood.
Biography
His full name was Abd Allah ibn Muhammad ibn Abd Allah ibn Shaiba. His father became a s ...
, who both died in childhood). All but one of his daughters, Fatimah, died before him.
Some Shia scholars contend that Fatimah was Muhammad's only daughter.
Maria al-Qibtiyya
, better known as or (), or Maria the Copt, died 637, was an Egyptian woman who, along with her sister Sirin bint Shamun, was given as a slave to the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 628 by Al-Muqawqis, a Christian governor of Alexandria, during ...
bore him a son named
Ibrahim ibn Muhammad
Ibrāhīm ibn Muḥammad () was the son of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Maria al-Qibtiyya. He died at the age of 2.
Birth, illness and death
200px, Grave of Ibrahim at Jannat-ul-Baqi, Medina
According to Ibn Kathir, quoting Ibn Sa'd ...
, who died at two years old.
Nine of Muhammad's wives survived him.
Aisha, who became known as Muhammad's favorite wife in Sunni tradition, survived him by decades and was instrumental in helping assemble the scattered sayings of Muhammad that form the hadith literature for the Sunni branch of Islam.
Zayd ibn Haritha
Zayd ibn Ḥāritha al-Kalbī () (), was an early Muslim, Sahabi and the adopted son of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad. He is commonly regarded as the fourth person to have accepted Islam, after Muhammad's wife Khadija, Muhammad's cousin Ali, a ...
was a slave that Khadija gave to Muhammad. He was bought by her nephew
Hakim ibn Hizam
Ḥakīm ibn Ḥizām (Arabic: حكيم بن حزام) was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a nephew of Khadija. Born 13 years before the event of elephants ( Aam-ul-Feel) in Mecca, Arabia, he was the son of Khadija's brother, H ...
at the market in
Ukaz
In Imperial Russia, a ukase () or ukaz ( ) was a proclamation of the tsar, government, or a religious leadership (e.g., Patriarch of Moscow and all Rus' or the Most Holy Synod) that had the force of law. " Edict" and "decree" are adequate transla ...
. Zayd then became the couple's adopted son, but was later disowned when Muhammad was about to marry Zayd's ex-wife,
Zaynab bint Jahsh
Zaynab bint Jaḥsh (; ), was the first cousin and the seventh wife of Muhammad and therefore, considered by Muslims to be a Mother of the Believers. Abdulmalik ibn Hisham. ''Notes to Ibn Ishaq's "Life of the Prophet"'', Note 918. Translated by ...
. According to a BBC summary, "the Prophet Muhammad did not try to abolish slavery, and bought, sold, captured, and owned slaves himself. But he insisted that slave owners treat their slaves well and stressed the virtue of freeing slaves. Muhammad treated slaves as human beings and clearly held some in the highest esteem".
Legacy
Islamic tradition
Following the attestation to the
oneness of God
''Tawhid'' () is the concept of monotheism in Islam, it is the religion's central and single most important concept upon which a Muslim's entire religious adherence rests. It unequivocally holds that God is indivisibly one (''ahad'') and si ...
, the belief in Muhammad's prophethood is the main aspect of the
Islamic faith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or concept. In the context of religion, faith is "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
According to the Merriam-Webster's Dictionary, faith has multiple definitions, includ ...
. Every Muslim proclaims in the : "I testify that there is no god but God, and I testify that Muhammad is a Messenger of God". The is the basic creed or tenet of Islam. Islamic belief is that ideally the is the first words a newborn will hear; children are taught it immediately and it will be recited upon death. Muslims repeat the shahadah in the call to prayer () and the prayer itself. Non-Muslims wishing to
convert to Islam
Reversion to Islam, also known within Islam as reversion, is adopting Islam as a religion or faith. Conversion requires a formal statement of the ''Shahada, shahādah'', the credo of Islam, whereby the prospective convert must state that "there i ...
are required to recite the creed.

In Islamic belief, Muhammad is regarded as the last prophet sent by God. Writings such as
hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
and attribute several miracles or supernatural events to Muhammad. One of these is the
splitting of the Moon
The Splitting of the Moon () is a miracle in the Muslim faith attributed to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It is derived from and mentioned by Muslim traditions such as the (context of revelation).
Origin
The earliest available compil ...
, which according to earliest available compilations is a literal splitting of the Moon.
The
sunnah
is the body of traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time supposedly saw, followed, and passed on to the next generations. Diff ...
represents the actions and sayings of Muhammad preserved in hadith and covers a broad array of activities and beliefs ranging from religious rituals, personal hygiene, and burial of the dead to the mystical questions involving the love between humans and God. The sunnah is considered a model of emulation for pious Muslims and has to a great degree influenced the Muslim culture. Many details of major Islamic rituals such as daily prayers, the fasting and the annual pilgrimage are only found in the sunnah and not the Quran.

Muslims have traditionally expressed love and veneration for Muhammad. Stories of Muhammad's life, his intercession and of his miracles have permeated popular Muslim thought and poetry (). Among Arabic odes to Muhammad, ("Poem of the Mantle") by the Egyptian
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
al-Busiri
Al-Būṣīrī (; 1212–1294) was a Sanhaji Sufi Sunni Muslim poet belonging to the Shadhili, and a direct disciple of the Sufi saint Abu al-Abbas al-Mursi. His magnum opus, the ''Qaṣīda al-Burda'' "Poem of the Mantle" in praise of ...
(1211–1294) is particularly well-known, and widely held to possess a healing, spiritual power. The Quran refers to Muhammad as "a mercy () to the worlds". The association of rain with mercy in Oriental countries has led to imagining Muhammad as a rain cloud dispensing blessings and stretching over lands, reviving the dead hearts, just as rain revives the seemingly dead earth.
Muhammad's birthday
The Mawlid () is an annual festival commemorating the birthday of the Islamic prophet Muhammad on the traditional date of 12 Rabi' al-Awwal, the third month of the Islamic calendar. A day central to the traditions of some Sunnis, Mawlid is also ...
is celebrated as a major feast throughout the
Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, excluding Wahhabi-dominated Saudi Arabia where these public celebrations are discouraged. When Muslims say or write the name of Muhammad, they usually follow it with the Arabic phrase (''may God honor him and grant him peace'') or the English phrase ''peace be upon him''. In casual writing, the abbreviations SAW (for the Arabic phrase) or PBUH (for the English phrase) are sometimes used; in printed matter, a small calligraphic rendition is commonly used ().
Appearance and depictions
Various sources present a probable description of Muhammad in the prime of his life. He was slightly above average in height, with a sturdy frame and wide chest. His neck was long, bearing a large head with a broad forehead. His eyes were described as dark and intense, accentuated by long, dark eyelashes. His hair, black and not entirely curly, hung over his ears. His long, dense beard stood out against his neatly trimmed mustache. His nose was long and aquiline, ending in a fine point. His teeth were well-spaced. His face was described as intelligent, and his clear skin had a line of hair from his neck to his navel. Despite a slight stoop, his stride was brisk and purposeful. Muhammad's lip and cheek were ripped by a slingstone during the Battle of Uhud. The wound was later Cauterization, cauterized, leaving a scar on his face.
However, since the Aniconism in Islam, hadith prohibits the creation of images of sentient living beings, Islamic religious art mainly focuses on calligraphy.
Muslims generally avoid depictions of Muhammad, and instead decorate mosques with calligraphy, Quranic inscriptions, or geometrical designs.
Today, the interdiction against images of Muhammad—designed to prevent worship of Muhammad, rather than God—is much more strictly observed in Sunni Islam (85–90% of Muslims) and Ahmadiyya Islam (1%) than among Shias (10–15%). While both Sunnis and Shias have created images of Muhammad in the past,
Islamic depictions of Muhammad are rare.
They have mostly been limited to the private and elite medium of the miniature, and since about 1500 most depictions show Muhammad with his face veiled, or symbolically represent him as a flame.
The earliest extant depictions come from 13th century Sultanate of Rum, Anatolian Seljuk and Ilkhanid Persian miniatures, typically in literary genres describing the life and deeds of Muhammad.
During the Ilkhanid period, when Persia's Mongol rulers converted to Islam, competing Sunni and Shia groups used visual imagery, including images of Muhammad, to promote their particular interpretation of Islam's key events.
Influenced by the Buddhist tradition of representational religious art predating the Mongol elite's conversion, this innovation was unprecedented in the Islamic world, and accompanied by a "broader shift in Islamic artistic culture away from abstraction toward representation" in "mosques, on tapestries, silks, ceramics, and in glass and metalwork" besides books. In the Persian lands, this tradition of realistic depictions lasted through the Timurid dynasty until the Safavids took power in the early 16th century.
The Safavaids, who made Shia Islam the state religion, initiated a departure from the traditional Ilkhanid and Timurid artistic style by covering Muhammad's face with a veil to obscure his features and at the same time represent his luminous essence. Concomitantly, some of the unveiled images from earlier periods were defaced.
Later images were produced in
Ottoman Turkey and elsewhere, but mosques were never decorated with images of Muhammad.
Illustrated accounts of the night journey () were particularly popular from the Ilkhanid period through the Safavid era.
During the 19th century, Iran saw a boom of printed and illustrated books, with Muhammad's face veiled, aimed in particular at illiterates and children in the manner of graphic novels. Reproduced through lithography, these were essentially "printed manuscripts".
Today, millions of historical reproductions and modern images are available in some Muslim-majority countries, especially Turkey and Iran, on posters, postcards, and even in coffee-table books, but are unknown in most other parts of the Islamic world, and when encountered by Muslims from other countries, they can cause considerable consternation and offense.
Islamic social reforms
According to
W. Montgomery Watt, religion for Muhammad was not a private and individual matter but "the total response of his personality to the total situation in which he found himself. He was responding [not only]... to the religious and intellectual aspects of the situation but also to the economic, social, and political pressures to which contemporary Mecca was subject." Bernard Lewis says there are two important political traditions in Islam—Muhammad as a statesman in Medina, and Muhammad as a rebel in Mecca. In his view, Islam is a great change, akin to a revolution, when introduced to new societies.
[Lewi]
(1998)
Historians generally agree that Islamic social changes in areas such as social security, family structure, slavery and the rights of women and children improved on the status quo of Arab society.
For example, according to Lewis, Islam "from the first denounced Aristocracy (class), aristocratic privilege, rejected hierarchy, and adopted a formula of the career open to the talents".
Muhammad's message transformed society and Islamic ethics, moral orders of life in the Arabian Peninsula; society focused on the changes to perceived identity, worldview, and the hierarchy of values. Economic reforms addressed the plight of the poor, which was becoming an issue in Jahiliyyah, pre-Islamic Mecca. The Quran requires payment of an alms tax () for the benefit of the poor; as Muhammad's power grew he demanded that tribes who wished to ally with him implement the zakat in particular.
European appreciation

Guillaume Postel was among the first to present a more positive view of Muhammad when he argued that Muhammad should be esteemed by Christians as a valid prophet. Gottfried Leibniz praised Muhammad because "he did not deviate from the natural religion". Henri de Boulainvilliers, in his which was published posthumously in 1730, described Muhammad as a gifted political leader and a just lawmaker. He presents him as a divinely inspired messenger whom God employed to confound the bickering Oriental Christians, to liberate the Orient from the despotic rule of the Romans and Persians, and to spread the knowledge of the unity of God from India to Spain. Voltaire had a mixed opinion on Muhammad: in his play he vilifies Muhammad as a symbol of fanaticism, and in an essay in 1748 he calls him "a sublime and hearty charlatan". But in Voltaire's historical survey , he presents Mohammed as a legislator and conqueror and calls him an "enthusiast". Jean-Jacques Rousseau, in his ''The Social Contract, Social Contract'' (1762), "brushing aside hostile legends of Muhammad as a trickster and impostor, presents him as a sage legislator who wisely fused religious and political powers". In Claude-Emmanuel de Pastoret, Emmanuel Pastoret's 1787 ''Zoroaster, Confucius and Muhammad'', he presents the lives of these three "great men", "the greatest legislators of the universe", and compares their careers as religious reformers and lawgivers. Pastoret rejects the common view that Muhammad is an impostor and argues that the Quran proffers "the most sublime truths of cult and morals"; it defines the unity of God with an "admirable concision". Pastoret writes that the common accusations of his immorality are unfounded: on the contrary, his law enjoins sobriety, generosity, and compassion on his followers: the "legislator of Arabia" was "a great man". Napoleon Bonaparte admired Muhammad and Islam, and described him as a model lawmaker and conqueror. Thomas Carlyle in his book ''On Heroes, Hero-Worship, & the Heroic in History'' 1841 describes "Mahomet" as "A silent great soul; he was one of those who cannot
but be in earnest". Carlyle's interpretation has been widely cited by Muslim scholars as a demonstration that Western scholarship validates Muhammad's status as a great man in history.
Ian Almond says that German Romantic writers generally held positive views of Muhammad: "Goethe's 'extraordinary' poet-prophet, Johann Gottfried Herder, Herder's nation builder (...) Karl Wilhelm Friedrich Schlegel, Schlegel's admiration for Islam as an aesthetic product, enviably authentic, radiantly holistic, played such a central role in his view of Mohammed as an exemplary world-fashioner that he even used it as a scale of judgement for the classical (the dithyramb, we are told, has to radiate pure beauty if it is to resemble 'a Koran of poetry')". After quoting Heinrich Heine, who said in a letter to some friend that "I must admit that you, the great prophet of Mecca, are the greatest poet and that your Quran... will not easily escape my memory", John V. Tolan, John Tolan goes on to show how Jews in Europe in particular held more nuanced views about Muhammad and Islam, being an ethnoreligious minority feeling discriminated, they specifically lauded Al-Andalus, and thus, "writing about Islam was for Jews a way of indulging in a fantasy world, far from the persecution and pogroms of nineteenth-century Europe, where Jews could live in harmony with their non-Jewish neighbors".
Recent writers such as William Montgomery Watt and Richard Bell (Arabist), Richard Bell dismiss the idea that Muhammad deliberately deceived his followers, arguing that Muhammad "was absolutely sincere and acted in complete good faith" and Muhammad's readiness to endure hardship for his cause, with what seemed to be no rational basis for hope, shows his sincerity. Watt, however, says that sincerity does not directly imply correctness: in contemporary terms, Muhammad might have mistaken his subconscious for divine revelation. Watt and Bernard Lewis argue that viewing Muhammad as a self-seeking impostor makes it impossible to understand Islam's development. Alford T. Welch holds that Muhammad was able to be so influential and successful because of his firm belief in his vocation.
Criticism
Criticism of Muhammad has existed since the 7th century, when Muhammad was decried by his Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, non-Muslim Arab contemporaries for preaching monotheism, and by the Jewish tribes of Arabia for his perceived appropriation of Biblical narratives and List of biblical names, figures and proclamation of himself as the "
Seal of the Prophets
Seal of the Prophets (; or ) is a title used in the Qur'an and by Muslims to designate the Islamic prophet Muhammad as the last of the prophets sent by God.
The title is applied to Muhammad in verse 33:40 of the Qur'an, with the popular Yu ...
". In the Middle Ages, Western and Byzantine Christians labeled him a False prophet#Christianity, false prophet, the Antichrist, or portrayed him as a Heresy in Christianity, heretic. Contemporary criticism involves questioning Muhammad's legitimacy as a prophet, his moral conduct, Muhammad's wives, marriages, Slavery in Islam, ownership of slaves, treatment of enemies, approach to doctrinal matters, and psychological well-being.
Sufism
The sunnah contributed much to the development of Islamic law, particularly from the end of the first Islamic century. Muslim mystics, known as
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
s, who were seeking for the inner meaning of the Quran and the inner nature of Muhammad, viewed the prophet of Islam not only as a prophet but also as a perfect human being. All Sufi orders trace their chain of spiritual descent back to Muhammad.
Other religions
Muhammad Sahib is honored by Sikhs as one of the divine messengers sent to mankind, along with Moses, Jesus and others.
Guru Granth Sahib, the holiest book of Sikhism, states that a true Muslim who follows the faith of Muhammad would put aside the "delusion of death and life." The founder of Sikhism, Guru Nanak, is specifically said to have praised Muhammad as a source of divine experience having a personal influence on his life, as stated in the of Bhai Bala.
Followers of the
Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
venerate Muhammad as one of a number of prophets or "Manifestation of God (Baháʼí Faith), Manifestations of God". He is thought to be the final manifestation, or seal of the Progressive revelation (Baháʼí), Adamic cycle, but consider his teachings to have been superseded by those of Bahá'u'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí faith, and the first manifestation of the current cycle.
Druze tradition honors several "mentors" and "prophets", and Muhammad is considered an important prophet of God in the Druze faith, being among the seven prophets who appeared in different periods of history.
See also
* Ashtiname of Muhammad
* Arabian tribes that interacted with Muhammad
* Glossary of Islam
* List of biographies of Muhammad
* List of founders of religious traditions
* List of notable Hijazis
* Muhammad and the Bible
* Muhammad in film
* Muhammad's views on Christians
* Muhammad's views on Jews
* Possessions of Muhammad
* Relics of Muhammad
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Encyclopaedia of Islam
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
{{Authority control
570s births
632 deaths
6th-century Arab people
7th-century Arab people
7th-century Islamic religious leaders
7th-century merchants
7th-century military personnel
7th-century Asian people
Adoptees
Angelic visionaries
Arab generals
Arab Muslims
Arab politicians
Arab prophets
Arab slave owners
7th-century diplomats
Entering heaven alive
Founders of religions
Medina
Miracle workers
Muhammad,
People from Mecca
Prophets of the Quran
Prophets in the Druze faith
Quraysh
The Fourteen Infallibles
Characters in the Divine Comedy

 Important sources regarding Muhammad's life may be found in the historic works by writers of the 2nd and 3rd centuries of the
Important sources regarding Muhammad's life may be found in the historic works by writers of the 2nd and 3rd centuries of the  Other important sources include the
Other important sources include the  Muhammad ibn Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim was born in
Muhammad ibn Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim was born in 
 The financial security Muhammad enjoyed from
The financial security Muhammad enjoyed from  Shortly after Waraqa's death, the revelations ceased for a period, causing Muhammad great distress and thoughts of suicide. On one occasion, he reportedly climbed a mountain intending to jump off. However, upon reaching the peak, Gabriel appeared to him, affirming his status as the true Messenger of God. This encounter soothed Muhammad, and he returned home. Later, when there was another long break between revelations, he repeated this action, but Gabriel intervened similarly, calming him and causing him to return home.
Muhammad was confident that he could distinguish his own thoughts from these messages. The early Quranic revelations utilized approaches of cautioning non-believers with divine punishment, while promising rewards to believers. They conveyed potential consequences like famine and killing for those who rejected Muhammad's God and alluded to past and future calamities. The verses also stressed the imminent final judgment and the threat of hellfire for skeptics. Due to the complexity of the experience, Muhammad was initially very reluctant to tell others about his revelations; at first, he confided in only a few select family members and friends. According to Muslim tradition, Muhammad's wife Khadija was the first to believe he was a prophet. She was followed by Muhammad's ten-year-old cousin
Shortly after Waraqa's death, the revelations ceased for a period, causing Muhammad great distress and thoughts of suicide. On one occasion, he reportedly climbed a mountain intending to jump off. However, upon reaching the peak, Gabriel appeared to him, affirming his status as the true Messenger of God. This encounter soothed Muhammad, and he returned home. Later, when there was another long break between revelations, he repeated this action, but Gabriel intervened similarly, calming him and causing him to return home.
Muhammad was confident that he could distinguish his own thoughts from these messages. The early Quranic revelations utilized approaches of cautioning non-believers with divine punishment, while promising rewards to believers. They conveyed potential consequences like famine and killing for those who rejected Muhammad's God and alluded to past and future calamities. The verses also stressed the imminent final judgment and the threat of hellfire for skeptics. Due to the complexity of the experience, Muhammad was initially very reluctant to tell others about his revelations; at first, he confided in only a few select family members and friends. According to Muslim tradition, Muhammad's wife Khadija was the first to believe he was a prophet. She was followed by Muhammad's ten-year-old cousin  It is at this low point in Muhammad's life that the accounts in the lay out the famous Isra' and Mi'raj. Nowadays, Isra' is believed by Muslims to be the journey of Muhammad from Mecca to
It is at this low point in Muhammad's life that the accounts in the lay out the famous Isra' and Mi'raj. Nowadays, Isra' is believed by Muslims to be the journey of Muhammad from Mecca to  Early in 628, following a dream of making an unopposed pilgrimage to Mecca, Muhammad embarked on the journey. He was dressed in his customary pilgrim attire and was accompanied by a group of followers. Upon reaching Hudaybiyya, they encountered Quraysh emissaries who questioned their intentions. Muhammad explained they had come to venerate the Kaaba, not to fight. He then sent
Early in 628, following a dream of making an unopposed pilgrimage to Mecca, Muhammad embarked on the journey. He was dressed in his customary pilgrim attire and was accompanied by a group of followers. Upon reaching Hudaybiyya, they encountered Quraysh emissaries who questioned their intentions. Muhammad explained they had come to venerate the Kaaba, not to fight. He then sent 
 Muhammad began to prepare for a campaign. In 630, Muhammad marched on Mecca with 10,000 Muslim converts. With minimal casualties, Muhammad seized control of Mecca. He declared an amnesty for past offences, except for ten men and women who were "guilty of murder or other offences or had sparked off the war and disrupted the peace". Some of these were later pardoned Most Meccans converted to Islam and Muhammad proceeded to destroy all the statues of
Muhammad began to prepare for a campaign. In 630, Muhammad marched on Mecca with 10,000 Muslim converts. With minimal casualties, Muhammad seized control of Mecca. He declared an amnesty for past offences, except for ten men and women who were "guilty of murder or other offences or had sparked off the war and disrupted the peace". Some of these were later pardoned Most Meccans converted to Islam and Muhammad proceeded to destroy all the statues of 
 After praying at the burial site in June 632, Muhammad suffered a dreadful headache that made him cry in pain. He continued to spend the night with each of his wives one by one, but he fainted in Maymunah's hut. He requested his wives to allow him to stay in
After praying at the burial site in June 632, Muhammad suffered a dreadful headache that made him cry in pain. He continued to spend the night with each of his wives one by one, but he fainted in Maymunah's hut. He requested his wives to allow him to stay in  Muhammad's life is traditionally defined into two periods: pre-hijra in Mecca (570–622), and post-hijra in Medina (622–632). Muhammad is said to have had thirteen wives in total (although two have ambiguous accounts,
Muhammad's life is traditionally defined into two periods: pre-hijra in Mecca (570–622), and post-hijra in Medina (622–632). Muhammad is said to have had thirteen wives in total (although two have ambiguous accounts,  Muslims have traditionally expressed love and veneration for Muhammad. Stories of Muhammad's life, his intercession and of his miracles have permeated popular Muslim thought and poetry (). Among Arabic odes to Muhammad, ("Poem of the Mantle") by the Egyptian
Muslims have traditionally expressed love and veneration for Muhammad. Stories of Muhammad's life, his intercession and of his miracles have permeated popular Muslim thought and poetry (). Among Arabic odes to Muhammad, ("Poem of the Mantle") by the Egyptian 