Milete on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The city of Miletus became one of the twelve
The city of Miletus became one of the twelve
Megara and Miletos: Colonising with Apollo. A Structural Comparison of Religious and Political Institutions in Two Archaic Greek Polis States
see Abstract a
Alexander Herda research
/ref> Both cities acted under the leadership and sanction of an
 In 479 BC, the Greeks decisively defeated the Persians on the Greek mainland at the
In 479 BC, the Greeks decisively defeated the Persians on the Greek mainland at the
 During the
During the
 The first excavations in Miletus were conducted by the French archaeologist Olivier Rayet in 1873, followed by the German archaeologists
The first excavations in Miletus were conducted by the French archaeologist Olivier Rayet in 1873, followed by the German archaeologists
File:Fragment_of_a_terracotta_oinochoe_(jug)_MET_DP114676.jpg, The name Fikellura derives from a site on the island of Rhodes to which this fabric has been attributed. It is now established that the center of production was Miletus.
File:Fragment_of_a_terracotta_oinochoe_(jug)_MET_DP121651.jpg,
File:Terracotta_amphoriskos_(oil_flask)_MET_DP114678.jpg, Milesian Vase
File:Greek_-_Fikellura_Amphora_-_Walters_482114.jpg, Milesian Vase
File:Terracotta_amphoriskos_(oil_flask)_MET_DP114695.jpg, Milesian Vase
File:Terracotta_oinochoe_(jug)_MET_DP1864.jpg, Milesian Vase
 The ruins appear on satellite maps at 37°31.8'N 27°16.7'E, about 3 km north of Balat and 3 km east of Batıköy in
The ruins appear on satellite maps at 37°31.8'N 27°16.7'E, about 3 km north of Balat and 3 km east of Batıköy in
Miletus_Museum_04.jpg, Sculpture from Baths of Faustina
File:Milet_2013-03-25t.jpg, Faustina Baths in Miletus
File:Didyma sacred way.jpg, The Sacred Way from Miletus with the remains of the stoa
File:Miletus-_Temple_-_panoramio.jpg, The Ionic Stoa on the Sacred Way
File:Remains_of_the_stoa_connecting_the_main_Bath_of_Faustina_to_the_Palaestra_(Miletus).jpg, Remains of the stoa connecting the main Bath of Faustina to the Palaestra
File:Miletus, Illustration for La Terre-Sainte et les lieux illustrés par les apôtres, by Adrien Egron, 1837 (39).jpg, Illustration of Miletus
File:Miletus - Ancient Greek theatre 03.jpg, Right entrance of the ancient Greek theatre
File:The_Theater_of_Miletus.jpg, Ancient Greek theatre
 Miletus became known for the great number of colonies it founded. It was considered the greatest Greek metropolis and founded more colonies than any other Greek city.
Miletus became known for the great number of colonies it founded. It was considered the greatest Greek metropolis and founded more colonies than any other Greek city.
 *
*A Dictionary of Greek and Roman biography and mythology, Baccheius
/ref>
Official websiteAusgrabungen in Milet
official site of the excavations in Miletus by Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Ancient Coins of MiletusLivius picture archive: MiletusSome 250 pictures of site and museum
in English translation
* * ttp://www.fhw.gr/choros/miletus/en/index.php Details about most of the monumentsbr>Walking the sacred pagan path from Ancient Miletus to Didim
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Former populated places in Turkey Archaeological sites in the Aegean region Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey History of Aydın Province Tourist attractions in Aydın Province Ionian League Buildings and structures in Aydın Province Members of the Delian League Greek city-states Late Bronze Age collapse Populated places in ancient Caria New Testament cities Didim District
Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and ex ...
(Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and extensive network of colonies, Miletus was a major center of trade, culture, and innovation from the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
through the Roman period
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. The city played a foundational role in the development of early Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC. Philosophy was used to make sense of the world using reason. It dealt with a wide variety of subjects, including astronomy, epistemology, mathematics, political philosophy, ethics, metaphysic ...
and science, serving as the home of the Milesian school
The Ionian school of pre-Socratic philosophy refers to Ancient Greek philosophers, or a school of thought, in Ionia in the 6th century B.C, the first in the Western tradition.
The Ionian school included such thinkers as Thales, Anaximand ...
with thinkers such as Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
, Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
, and Anaximenes.
Miletus's prosperity was closely linked to its strategic coastal location and the productivity of its surrounding rural hinterland, which supported thriving agriculture and facilitated wide-ranging commercial activity. The city established dozens of colonies around the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, significantly shaping the Greek world’s expansion.
Archaeological investigations have revealed a rich material culture, including the sanctuary of Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
at Didyma
Didyma (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called ''Didymaion''. But it was home to both of the Ancient ...
, remnants of the city's distinctive grid plan, and evidence of long-term agricultural and rural management. Throughout its history, Miletus experienced periods of autonomy and foreign rule, serving as a cultural crossroads between Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Anatolian, and later Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
spheres. The city’s enduring legacy is reflected in its contributions to philosophy, urban planning, and the spread of Greek civilization.
History

Neolithic
The earliest available archaeological evidence indicates that the islands on which Miletus was originally placed were inhabited by aNeolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
population in 3500–3000 BC.Crouch (2004) page 183. Pollen in core samples from Lake Bafa in the Latmus region inland of Miletus suggests that a lightly grazed climax forest prevailed in the Maeander valley, otherwise untenanted. Sparse Neolithic settlements were made at springs, numerous and sometimes geothermal Geothermal is related to energy and may refer to:
* Geothermal energy, useful energy generated and stored in the Earth
* Geothermal activity, the range of natural phenomena at or near the surface, associated with release of the Earth's internal he ...
in this karst, rift valley topography. The islands offshore were settled perhaps for their strategic significance at the mouth of the Maeander, a route inland protected by escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
Due to the similarity, the term '' scarp'' may mistakenly be incorrectly used inte ...
s. The graziers in the valley may have belonged to them, but the location looked to the sea.
Middle Bronze Age
The prehistoric archaeology of the Early and Middle Bronze Age portrays a city heavily influenced by society and events elsewhere in the Aegean, rather than inland.Minoan period
The earliest Minoan settlement of Miletus dates to 2000 BC. Beginning at about 1900 BC artifacts of theMinoan civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe. The ruins of the Minoan palaces at K ...
acquired by trade arrived at the site. For some centuries the location received a strong impulse from that civilization, an archaeological fact that tends to support but not necessarily confirm the founding legend—that is, a population influx from Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
. According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
:Ephorus says: Miletus was first founded and fortified above the sea by Cretans, where the Miletus of olden times is now situated, being settled by Sarpedon, who brought colonists from the Cretan Miletus and named the city after that Miletus, the place formerly being in possession of theAccording to Pausanias, however, Miletus was a friend of Sarpedon fromLeleges The Leleges (; ) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean Sea, Aegean region, before the Greek people, Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are u ....
Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, after whom the city was named. Miletus had a son named Kelados, and the heroon of Kelados has been found at Panormos, a port of Miletus near Didyma
Didyma (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called ''Didymaion''. But it was home to both of the Ancient ...
.
The legends recounted as history by the ancient historians and geographers are perhaps the strongest; the late mythographers have nothing historically significant to relate.
Late Bronze Age
Recorded history at Miletus begins with the records of theHittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
and the Mycenaean records of Pylos
Pylos (, ; ), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of ...
and Knossos
Knossos (; , ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is a Bronze Age archaeological site in Crete. The site was a major centre of the Minoan civilization and is known for its association with the Greek myth of Theseus and the minotaur. It is located on th ...
, in the Late Bronze Age.
Mycenaean period
Miletus was aMycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and sou ...
an stronghold on the coast of Asia Minor from to 1100 BC. In , the city supported an anti-Hittite rebellion of Uhha-Ziti
Uhha-Ziti was the last independent king of Arzawa, a Bronze Age kingdom of western Anatolia around 1320 BC.
Family
Uhha-Ziti had two recorded children, Piyama-Kurunta and Tapalazunauli, who were of fighting age as of 1322 BC.
History Late Bronz ...
of nearby Arzawa
Arzawa was a region and political entity in Western Anatolia during the Late Bronze Age. In Hittite texts, the term is used to refer both to a particular kingdom and to a loose confederation of states. The chief Arzawan state, whose capital wa ...
. Muršili ordered his generals Mala-Ziti and Gulla to raid Millawanda, and they proceeded to burn parts of it; damage from LHIIIA found on-site has been associated with this raid. In addition the town was fortified according to a Hittite plan.
Miletus is then mentioned in the "Tawagalawa letter
The Tawagalawa letter (Catalogue des Textes Hittites, CTH 181) is a fragmentary Hittite text from the mid 13th century BC. It is notable for providing a window into relations between Hittites and Mycenaean Greece, Greeks during the Late Bronze Age ...
", part of a series including the Manapa-Tarhunta letter The Manapa-Tarhunta letter ( CTH 191; KUB 19.5 + KBo 19.79) is a fragmentary text in the Hittite language from the 13th century BC. The letter was sent to the Hittite king by Manapa-Tarhunta, client king of the Seha River Land. In the letter, Manap ...
and the Milawata letter
The Milawata letter ( CTH 182) is an item of diplomatic correspondence from a Hittite king at Hattusa to a client king in western Anatolia around 1240 BC. It constitutes an important piece of evidence in the debate concerning the historicity of H ...
, all of which are less securely dated. The Tawagalawa letter notes that Milawata had a governor, Atpa, who was under the jurisdiction of ''Ahhiyawa
The Achaeans or Akhaians (; , "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively.
The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwe ...
'' (a growing state probably in LHIIIB Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
); and that the town of Atriya was under Milesian jurisdiction. The Manapa-Tarhunta letter also mentions Atpa. Together the two letters tell that the adventurer Piyama-Radu
Piyamaradu (also spelled ''Piyama-Radu'', ''Piyama Radu'', ''Piyamaradus'', ''Piyamaraduš'') was a warlord mentioned in Hittite documents from the middle and late 13th century BC. As an ally of the Ahhiyawa, he led or supported insurrections aga ...
had humiliated Manapa-Tarhunta before Atpa (in addition to other misadventures); a Hittite king then chased Piyama-Radu into Millawanda and, in the Tawagalawa letter, requested Piyama-Radu's extradition to Hatti
Hatti may refer to
*Hatti (; Assyrian ) in Bronze Age Anatolia:
**the area of Hattusa, roughly delimited by the Halys bend
**the Hattians of the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC
**the Hittites of ''ca'' 1400–1200 BC
**the areas to the west of the Euphra ...
.
The Milawata letter mentions a joint expedition by the Hittite king and a Luwian
Luwian (), sometimes known as Luvian or Luish, is an ancient language, or group of languages, within the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The ethnonym Luwian comes from ''Luwiya'' (also spelled ''Luwia'' or ''Luvia'') – ...
vassal (probably Kupanta-Kurunta of Mira) against Miletus, and notes that the city (together with Atriya) was now under Hittite control.
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
mentions that during the time of the Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
, Miletus was an ally of Troy and was city of the Carians
The Carians (; , ''Kares'', plural of , ''Kar'') were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia, who spoke the Carian language.
Historical accounts Karkisa
It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is ...
, under Nastes and Amphimachus In Greek mythology, Amphimachus (; Ancient Greek: Ἀμφίμαχος derived from ἀμφί ''amphi'' "on both sides, in all directions, surrounding" and μαχη ''mache'' "battle") was a name attributed to multiple individuals.
* Amphimachus, so ...
.
In the last stage of LHIIIB, the citadel of Bronze Age Pylos
Pylos (, ; ), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of ...
counted among its female slaves a '' mi-ra-ti-ja'', Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the earliest attested form of the Greek language. It was spoken on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC). The language is preserved in inscriptions in Linear B, a script first atteste ...
for "women from Miletus", written in Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
syllabic script.
Fall of Miletus
During the collapse of Bronze Age civilization, Miletus was burnt again, presumably by theSea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Ancient Egypt, Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was proposed by the 19th-century Egyptology, Egyptologis ...
.
Dark Age
Mythographers told that Neleus, a son ofCodrus
Codrus (; ; Greek: , ''Kódros'') was the last of the semi-mythical Kings of Athens (r. ca 1089– 1068 BC). He was an ancient exemplar of patriotism and self-sacrifice. He was succeeded by his son Medon, who it is claimed ruled not as king bu ...
the last King of Athens
Before the Athenian democracy, the tyrants, and the Archons, the city-state of Athens was ruled by kings. Most of these are probably mythical or only semi-historical. The following lists contain the chronological order of the title King of Athens ...
, had come to Miletus after the " Return of the Heraclids" (so, during the Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
). A heroon for Neleus was allegedly located outside of the city wall of Roman Miletus, which probably marks the former city center contemporary to Neleus. The Ionians killed the men of Miletus and married their Carian widows. This is the mythical commencement of the enduring alliance between Athens and Miletus, which played an important role in the subsequent Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of th ...
.
Archaic period
 The city of Miletus became one of the twelve
The city of Miletus became one of the twelve Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
n city-states of Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
to form the Ionian League
The Ionian League (; , ; or , , in ), also called the Panionic League, was a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th century BC comprising twelve Ionian Greek city-states (a dodecapolis, of which there were many other ...
.
Miletus was one of the cities involved in the Lelantine War
The Lelantine War was a military conflict between the two ancient Greek city states Chalcis and Eretria in Euboea which took place in the early Archaic period, between c. 710 and 650 BC. The reason for war was, according to tradition, the strugg ...
of the 8th century BC.
Ties with Megara
Miletus is known to have early ties withMegara
Megara (; , ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken ...
in Greece. According to some scholars, these two cities had built up a "colonisation alliance". In the 7th/6th century BC they acted in accordance with each other.Alexander Herda (2015)Megara and Miletos: Colonising with Apollo. A Structural Comparison of Religious and Political Institutions in Two Archaic Greek Polis States
see Abstract a
Alexander Herda research
/ref> Both cities acted under the leadership and sanction of an
Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
oracle. Megara cooperated with that of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
. Miletus had her own oracle of Apollo ''Didymeus Milesios'' in Didyma
Didyma (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called ''Didymaion''. But it was home to both of the Ancient ...
. Also, there are many parallels in the political organisation of both cities.
According to Pausanias, the Megarians said that their town owed its origin to Car
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than cargo. There are around one billio ...
, the son of Phoroneus
In Greek mythology, Phoroneus (; Ancient Greek: Φορωνεύς means 'bringer of a price') was a culture-hero of the Argolid, fire-bringer, law giver, and primordial king of Argos.
Family
Phoroneus was the son of the river god Inachus and eit ...
, who built the city citadel called 'Caria'. This 'Car of Megara' may or may not be one and the same as the 'Car of the Carians', also known as Car (King of Caria).
In the late 7th century BC, the tyrant Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus (; ; 440 – 388 BC) was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a primary leader of the ultimat ...
preserved the independence of Miletus during a 12-year war fought against the Lydian Empire
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis.
At some point before 800 BC, the Lydia ...
. Thrasybulus was an ally of the famous Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
ian tyrant Periander
Periander (; ; died c. 585 BC) was the second tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made Corinth one of the wealthiest city ...
.
Miletus was an important center of philosophy and science, producing such men as Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
, Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
and Anaximenes. Referring to this period, religious studies
Religious studies, also known as religiology or the study of religion, is the study of religion from a historical or scientific perspective. There is no consensus on what qualifies as ''religion'' and definition of religion, its definition is h ...
professor F. E. Peters described '' pan-deism'' as "the legacy of the Milesians". As well as being a philosopher, Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
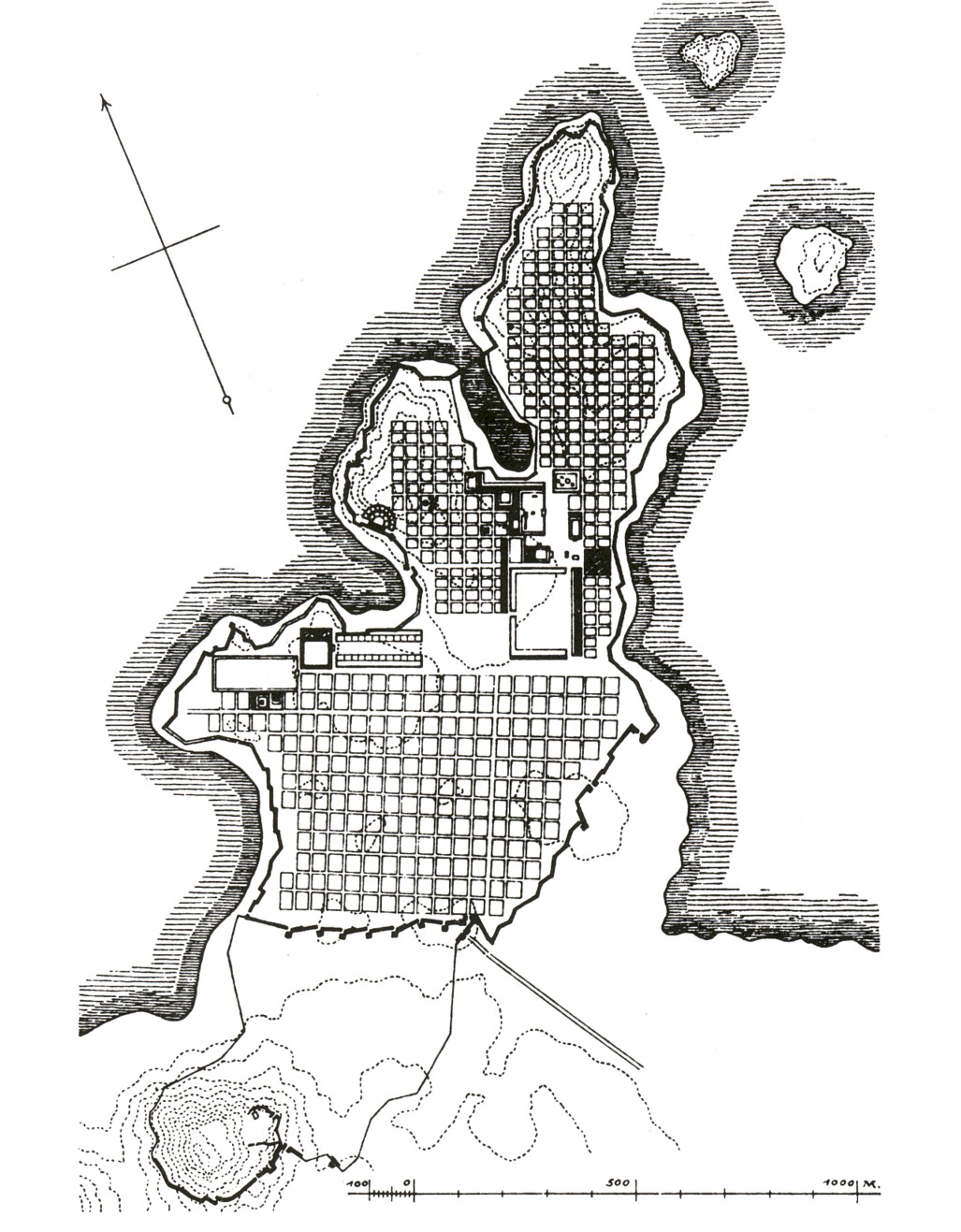
was also suggested to have initiated the famous grid plan of the city. An archaic orthogonal street system at Miletus has been confirmed by archaeological survey, but this system would not cover the entire urban center of Miletus until the classical period.
By the 6th century BC, Miletus had earned a maritime empire with many colonies, mainly scattered around the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
. Miletus and its numerous colonies were culturally tied by, for example, the cult of Aphrodite
Aphrodite (, ) is an Greek mythology, ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretism, syncretised Roman counterpart , desire, Sexual intercourse, sex, fertility, prosperity, and ...
, a deity associated with seafaring in the cultural context of Miletus. However, its maritime hegemony declined as a result of the Persian occupation in the early fourth century BC, and the vacuum of power was later filled by Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
.
First Achaemenid period
WhenCyrus
Cyrus () is a Persian-language masculine given name. It is historically best known as the name of several List of monarchs of Iran, Persian kings, most notably including Cyrus the Great, who founded the Achaemenid Empire in 550 BC. It remains wid ...
of Persia defeated Croesus
Croesus ( ; ; Latin: ; reigned:
)
was the Monarch, king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his Siege of Sardis (547 BC), defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. According to Herodotus, he reigned 14 years. Croesus was ...
of Lydia in the middle of the 6th century BC, Miletus fell under Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
rule. In 499 BC, Miletus's tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to ...
Aristagoras
Aristagoras of Miletus (), d. 497/496 BC, was the tyrant of the Ionian city of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC. He acted as one of the instigators of the Ionian Revolt against the Persian Achaemenid Empire. He was ...
became the leader of the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris (Asia Minor), Doris, Ancient history of Cyprus, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Achaemenid Empire, Persian rule, lasting from 499 ...
against the Persians, who, under Darius the Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
, quashed this rebellion in the Battle of Lade
The Battle of Lade () was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities (joined by the Lesbians) and the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, and resulted in a decisi ...
in 494 BC and punished Miletus by selling all of the women and children into slavery, killing the men, and expelling all of the young men as eunuchs, thereby assuring that no Miletus citizen would ever be born again. A year afterward, Phrynicus produced the tragedy ''The Capture of Miletus'' in Athens. The Athenians fined him for reminding them of their loss.
Classical Greek period
 In 479 BC, the Greeks decisively defeated the Persians on the Greek mainland at the
In 479 BC, the Greeks decisively defeated the Persians on the Greek mainland at the Battle of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Polis, Greek city-states (including Sparta, Cla ...
, and Miletus was freed from Persian rule. Although many sanctuaries of Miletus had been destroyed by the Persians, the restoration of them was prohibited by the "Oath of the Ionians", which aimed to retain the ruins as memorials. However, this oath was only partially observed by the Milesians, with some sanctuaries being restored back to their Archaic appearances. The city's gridlike layout was also constructed across all the area within the city wall, designed by Hippodamus of Miletus
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; c. 480– 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to ...
. It later became famous and was known as the "Hippodamian plan", serving as the basic layout for the new foundations of Hellenistic and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
cities.
Second Achaemenid period
In 387 BC, thePeace of Antalcidas
The King's Peace (387 BC) was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece. The treaty is also known as the Peace of Antalcidas, after Antalcidas, the Spartan diplomat who traveled to ...
gave the Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
under king Artaxerxes II
Arses (; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( ; ), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II () and his mother was Parysatis.
Soon after his accession, Ar ...
control of the Greek city-states of Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
, including Miletus.
In 358 BC, Artaxerxes II died and was succeeded by his son Artaxerxes III
Ochus ( ), known by his dynastic name Artaxerxes III ( ; ), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 359/58 to 338 BC. He was the son and successor of Artaxerxes II and his mother was Stateira.
Before ascending the throne Artaxerxes was ...
, who, in 355 BC, forced Athens to conclude a peace, which required its forces to leave Asia Minor (Anatolia) and acknowledge the independence of its rebellious allies.
Macedonian period
In 334 BC, theSiege of Miletus
The siege of Miletus was Alexander the Great's first siege and naval encounter with the Achaemenid Empire. This siege was directed against Miletus, a city in southern Ionia, which is now located in the Aydın province of modern-day Turkey. Durin ...
by the forces of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
of Macedonia conquered the city. The conquest of most of the rest of Asia Minor soon followed. In this period, the city reached its greatest extent, occupying within its walls an area of approximately .
When Alexander died in 323 BC, Miletus came under the control of Ptolemy, governor of Caria
Caria (; from Greek language, Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; ) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Carians were described by Herodotus as being Anatolian main ...
, and his satrap of Lydia, Asander
Asander or Asandros (; lived 4th century BC) was the son of Philotas (father of Parmenion), Philotas and brother of Parmenion and Agathon (son of Philotas), Agathon. He was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian general under Alexander the Great, a ...
, who had become autonomous. In 312 BC, Macedonian general Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( , "Antigonus the One-Eyed"; 382 – 301 BC) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control lar ...
sent Docimus and Medeius to free the city and grant autonomy, restoring the democratic patrimonial regime. In 301 BC, after Antigonus I was killed in the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus () was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his son Demetrius wer ...
by the coalition of Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek language, Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessaly, Thessalian officer and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became king of Thrace, Anatolia, Asia Minor and Mace ...
, Cassander
Cassander (; ; 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and '' de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
A son of Antipater and a contemporary of Alexander the ...
, and Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to fo ...
, founder of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
, Miletus maintained good relations with all the successors after Seleucus I Nicator made substantial donations to the sanctuary of Didyma and returned the statue of Apollo that had been stolen by the Persians in 494 BC.
In 295 BC, Antigonus I's son Demetrius Poliorcetes
Demetrius I Poliorcetes (; , , ; ) was a Macedonian Greek nobleman and military leader who became king of Asia between 306 and 301 BC, and king of Macedon between 294 and 288 BC. A member of the Antigonid dynasty, he was the son of its founder, ...
was the eponymous archon (stephanephorus) in the city, which allied with Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Pto ...
of Egypt, while Lysimachus assumed power in the region, enforcing a strict policy towards the Greek cities by imposing high taxes, forcing Miletus to resort to lending.
Seleucid period
Around 287/286 BC Demetrius Poliorcetes returned, but failed to maintain his possessions and was imprisoned in Syria. Nicocles of Sidon, the commander of Demetrius' fleet surrendered the city. Lysimachus dominated until 281 BC, when he was defeated by the Seleucids at the Battle of Corupedium. In 280/279 BC the Milesians adopted a new chronological system based on the Seleucids.Egyptian period
In 279 BC, the city was taken from Seleucid king Antiochus II by Egyptian kingPtolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
, who donated a large area of land to cement their friendship, and it remained under Egyptian sway until the end of the century.
Aristides of Miletus, founder of the bawdy Miletian school of literature, flourished in the 2nd century BC.
Roman period
After an alliance with Rome, in 133 BC the city became part of the province of Asia. Miletus benefited from Roman rule and most of the present monuments date to this period. TheNew Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
mentions Miletus as the site where the Apostle Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
in 57 AD met the elders of the church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
of Ephesus
Ephesus (; ; ; may ultimately derive from ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, in present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital ...
near the close of his Third Missionary Journey, as recorded in Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
(Acts 20:15–38). It is believed that Paul stopped by the Great Harbour Monument and sat on its steps. He might have met the Ephesian elders there and then bade them farewell on the nearby beach. Miletus is also the city where Paul left Trophimus
Trophimus (, ''Tróphimos'') or Trophimus the Ephesian (, ''Tróphimos ho Ephésios'') was a Christian who accompanied Paul during a part of his third missionary journey. He was with Paul in Jerusalem, and the Jews, supposing that the apostle ...
, one of his travelling companions, to recover from an illness (2 Timothy
The Second Epistle to Timothy is one of the three pastoral epistles traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle.. Addressed to Timothy, a fellow missionary, it is traditionally considered to be the last epistle Paul wrote before his death. T ...
4:20). Because this cannot be the same visit as Acts 20 (in which Trophimus accompanied Paul all the way to Jerusalem, according to Acts 21:29), Paul must have made at least one additional visit to Miletus, perhaps as late as 65 or 66 AD. Paul's previous successful three-year ministry in nearby Ephesus
Ephesus (; ; ; may ultimately derive from ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, in present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital ...
resulted in the evangelization of the entire province of Asia (see Acts 19:10, 20; 1 Corinthians
The First Epistle to the Corinthians () is one of the Pauline epistles, part of the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The epistle is attributed to Paul the Apostle and a co-author, Sosthenes, and is addressed to the Christian church in Anc ...
16:9). It is safe to assume that at least by the time of the apostle's second visit to Miletus, a fledgling Christian community was established in Miletus.
In 262 new city walls were built.
However the harbour was silting up and the economy was in decline. In 538 emperor Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
rebuilt the walls but it had become a small town.
Byzantine period
 During the
During the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
age the see of Miletus was raised to an archbishopric and later a metropolitan bishopric. The small Byzantine castle called Palation located on the hill beside the city, was built at this time. Miletus was headed by a curator
A curator (from , meaning 'to take care') is a manager or overseer. When working with cultural organizations, a curator is typically a "collections curator" or an "exhibitions curator", and has multifaceted tasks dependent on the particular ins ...
.
Turkish rule
Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persi ...
conquered the city in the 14th century and used Miletus as a port to trade with Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
.
In the 15th century, the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
utilized the city as a harbour during their rule in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. As the harbour became silted up, the city was abandoned. Due to ancient and subsequent deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature ...
(mostly by goat herds), erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
and soil degradation
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a soil health, stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession revert ...
, the ruins of the city lie some from the sea with sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s filling the plain and bare hill ridges without soils and trees, a maquis shrubland
220px, Low maquis in Corsica
220px, High ''macchia'' in Sardinia
( , , ) or ( , ; often in Italian; , ; ; ; ) is a savanna-like shrubland biome in the Mediterranean region, typically consisting of densely growing evergreen shrubs.
Maquis ...
remaining.
The Ilyas Bey Complex from 1403 with its mosque is a Europa Nostra
Europa Nostra (Latin for "Our Europe") is a pan-European Federation for cultural heritage, Cultural Heritage, representing citizens' organisations that work on safeguarding Europe's cultural and natural heritage. It is the voice of this movement ...
awarded cultural heritage site in Miletus.
Archaeological excavations
 The first excavations in Miletus were conducted by the French archaeologist Olivier Rayet in 1873, followed by the German archaeologists
The first excavations in Miletus were conducted by the French archaeologist Olivier Rayet in 1873, followed by the German archaeologists Julius Hülsen
Julius may refer to:
People
* Julius (name), a masculine given name and surname (includes a list of people with the name)
* Julius (nomen), the name of a Roman family (includes a list of Ancient Romans with the name)
** Julius Caesar (100– ...
and Theodor Wiegand
Theodor Wiegand (30 October 1864 – 19 December 1936) was a German archaeologist.
Wiegand was born in Bendorf, Rhenish Prussia. He studied at the universities of Munich, Berlin, and Freiburg. In 1894 he worked under Wilhelm Dörpfeld at th ...
between 1899 and 1931.
Excavations, however, were interrupted several times by wars and various other events.
Carl Weickart excavated for a short season in 1938 and again between 1955 and 1957.
He was followed by Gerhard Kleiner and then by Wolfgang Muller-Wiener.
Today, excavations are organized by the Ruhr University
The Ruhr University Bochum (, ) is a public research university located in the southern hills of the central Ruhr area, Bochum, Germany. It was founded in 1962 as the first new public university in Germany after World War II. Instruction began i ...
of Bochum
Bochum (, ; ; ; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia. With a population of 372,348 (April 2023), it is the sixth-largest city (after Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund, Essen and Duisburg) in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous German federa ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
.
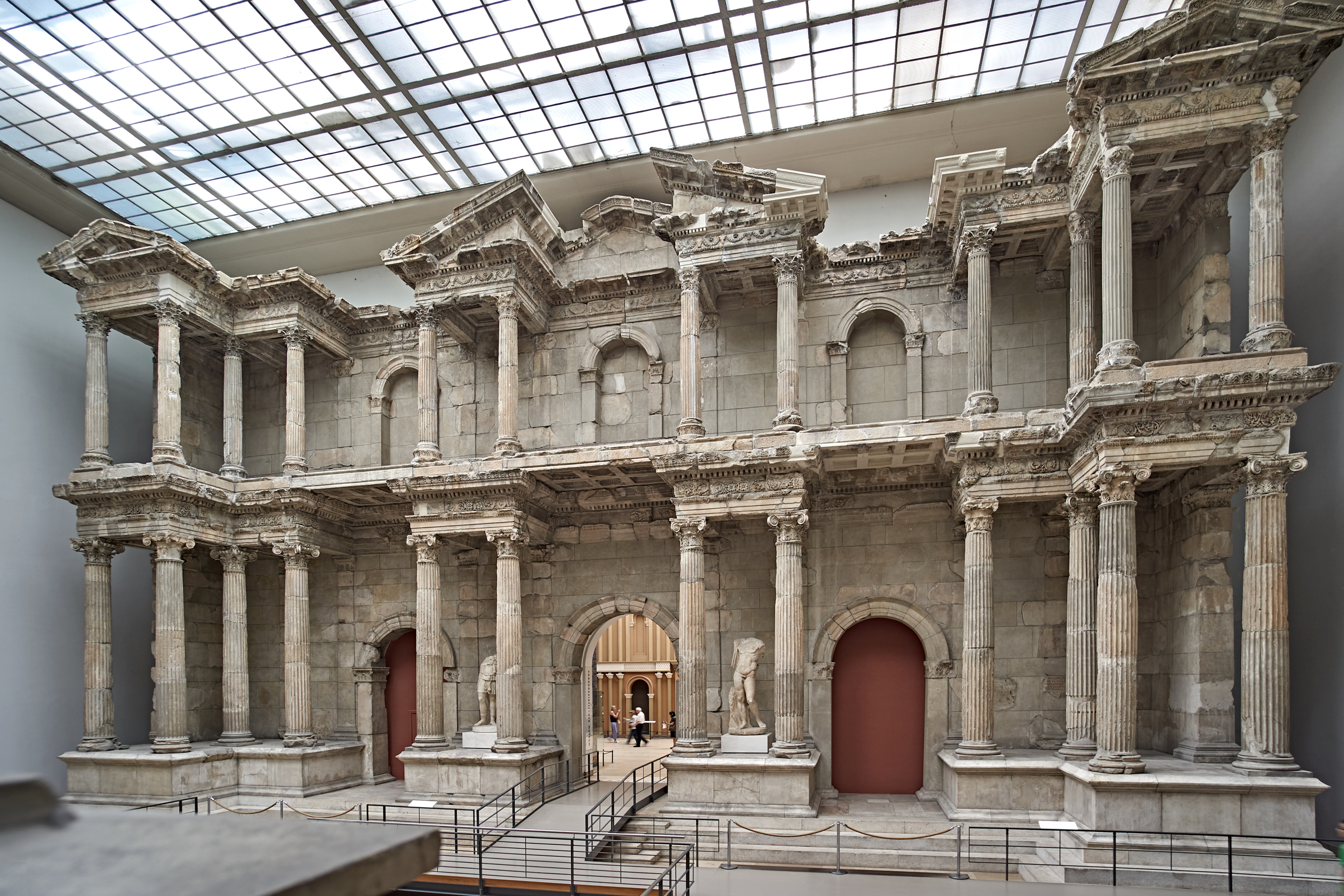
One remarkable artifact recovered from the city during the first excavations of the 19th century, the Market Gate of Miletus, was transported piece by piece to Germany and reassembled. It is currently exhibited at the Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum (; ) is a Kulturdenkmal , listed building on the Museum Island in the Mitte (locality), historic centre of Berlin, Germany. It was built from 1910 to 1930 by order of Emperor Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II and accordi ...
in Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
. The main collection of artifacts resides in the ''Miletus Museum'' in Didim
Didim is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Aydın Province, Turkey. Its area is 424 km2, and its population is 97,000 (2022). It is a popular seaside holiday resort on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of western Turkey, from t ...
, Aydın
Aydın ( ''EYE-din''; ; formerly named ''Güzelhisar; Greek: Τράλλεις)'' is a city in and the seat of Aydın Province in Turkey's Aegean Region. The city is located at the heart of the lower valley of Büyük Menderes River (ancient ...
, serving since 1973.
Archaeologists discovered a cave under the city's theatre and believe that it is a "sacred" cave which belonged to the cult of Asklepius.
Examples of the Milesian Vase
Geography
Aydın Province
Aydın Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality of southwestern Turkey, located in the Aegean Region. Its area is 8,116 km2, and its population is 1,148,241 (2022). T ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
.
In antiquity the city possessed a harbor
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be moored. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is ...
at the southern entry of a large bay, on which two more of the traditional twelve Ionian cities stood: Priene
Priene (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city of Ionia (and member of the Ionian League) located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of what was then the course of the Maeander River (now called the Büyük Menderes Rive ...
and Myus. The harbor of Miletus was additionally protected by the nearby small island of Lade. Over the centuries the gulf silted up with alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
carried by the Meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the Channel (geography), channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erosion, erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank (cut bank, cut bank or river cl ...
River. Priene and Myus had lost their harbors by the Roman era, and Miletus itself became an inland town in the early Christian era; all three were abandoned to ruin as their economies were strangled by the lack of access to the sea. There is a Great Harbor Monument where, according to the New Testament account, the apostle Paul stopped on his way back to Jerusalem by boat. He met the Ephesian Elders and then headed out to the beach to bid them farewell, recorded in the book of Acts 20:17-38.
Geology
During thePleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
epoch the Miletus region was submerged in the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
. It subsequently emerged slowly, the sea reaching a low level of about below present level at about 18,000 BP. The site of Miletus was part of the mainland.
A gradual rise brought a level of about below present at about 5500 BP, creating several karst
Karst () is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. Ther ...
block islands of limestone, the location of the first settlements at Miletus. At about 1500 BC the karst shifted due to small crustal movements and the islands consolidated into a peninsula. Since then the sea has risen 1.75 m but the peninsula has been surrounded by sediment from the Maeander river and is now land-locked. Sedimentation of the harbor began at about 1000 BC, and by 300 AD Lake Bafa
Lake Bafa () also known as Lake Çamiçi () and in earlier times the Vafi Sea () is a lake situated in southwestern Turkey, part of it within the boundaries of Milas district of Muğla Province and the northern part within Aydın Province's Söke ...
had been created.
Gallery
Economy and Land Use
The economic prosperity of Miletus during the Archaic and Classical periods depended heavily on its rural hinterland. Archaeological surveys and remote sensing analyses have revealed systems of terraces, field boundaries, and enclosures across the Milesian peninsula. These are interpreted as evidence of long-standing agro-pastoral activity, possibly dating as far back as the Archaic period and extending intoLate Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
.
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
, describing the tactics of Alyattes
Alyattes ( Lydian language: ; ; reigned c. 635 – c. 585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyattes, grandson of Ardys, and great-grandson of Gyges. He died after a r ...
against the Milesian countryside, writes: "He sent his army, marching to the sound of pipes and harps and bass and treble flutes, to invade when the crops in the land were ripe; and whenever he came to the Milesian territory, he neither demolished nor burnt nor tore the doors off the country dwellings, but let them stand unharmed; but he destroyed the trees and the crops of the land, and so returned to where he came from; for as the Milesians had command of the sea, it was of no use for his army to besiege their city. The reason that the Lydian did not destroy the houses was this: that the Milesians might have homes from which to plant and cultivate their land, and that there might be the fruit of their toil for his invading army to lay waste."
These rural systems supported olive cultivation, animal herding, and small-scale farming. Faunal remains suggest that herding was a major component of the rural economy. Excavations have shown a predominance of goat bones over sheep, possibly reflecting the influence of Cretan
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
animal husbandry techniques adopted in early Miletus.
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, citing Ephorus
Ephorus of Cyme (; , ''Ephoros ho Kymaios''; 330 BC) was an ancient Greek historian known for his universal history, now lost.
Biography
Information on his biography is limited. He was born in Cyme, Aeolia, and together with the historia ...
, relates: "Miletus was first founded and fortified by the Cretans on the spot above the sea-coast where at present the ancient Miletus is situated, and that Sarpedon
Sarpedon (; ) is the name of several figures in Greek mythology
* Sarpedon, a son of Zeus, who fought on the side of Troy in the Trojan War. Although in the ''Iliad'', he was the son of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Gre ...
conducted thither settlers from the Miletus in Crete, and gave it the same name; that Leleges
The Leleges (; ) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean Sea, Aegean region, before the Greek people, Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are u ...
were the former occupiers of the country, and that afterwards Neleus
Neleus (; ) was a mythological king of Pylos. In some accounts, he was also counted as an Argonaut instead of his son, Nestor.
Family
Neleus was the son of Poseidon and Tyro, and brother of Pelias. According to Pausanias, Neleus was the son o ...
built the present city."
Farmsteads, oil presses, cisterns, and possible pastoral installations such as shepherding stations have been identified in the countryside, suggesting a decentralized but productive economy. The northern plains and Maeander valley, both under Milesian control, were especially fertile, providing grain and supporting livestock crucial to the city’s sustenance and export economy.
In addition to grain and wool, Miletus likely exported surplus olive oil during favorable years. Archaic Milesian amphorae
An amphora (; ; English ) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storage rooms and packages, tied together with rope and delivered by land ...
, widely distributed and characterized by thickened rims, may have been used for oil transport.
Botanical evidence from the Milesian countryside also reveals the cultivation of figs and lentils. Carbonized fig remains have been found in large numbers, and fig trees were likely common along field margins, significantly influencing the diet in the region.
Both literary and archaeological evidence demonstrate that Miletus’ agricultural base was essential for sustaining its urban population, supporting rural life, and providing the surpluses that underpinned Milesian colonization and trade.
Colonies
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
(''Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
'', 5.31) says that Miletus founded over 90 colonies.
The extent of Milesian colonization was shaped by a convergence of economic, social, and political factors. Like other Greek poleis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
, Miletus faced pressures from population growth and competition for arable land, which drove many citizens to seek new opportunities overseas. Economic motivations included expanding trade networks and accessing new resources, especially along the Black Sea coast, which offered grain, fish, and raw materials not easily available in Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
. Political factors, such as stasis (internal conflict) and the impact of foreign powers like Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis.
At some point before 800 BC, ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, also contributed, sometimes prompting groups or exiles to establish new settlements abroad. Scholars note that Milesian colonization was characterized both by “proactive” ventures seeking commercial gain and “reactive” migrations resulting from disruptions at home.
The Black Sea region became a primary focus of Milesian colonial expansion from the seventh century BCE onward. Milesian foundations such as Sinope
Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
* Sinope (mythology), i ...
, Olbia
Olbia (, ; ; ) is a city and communes of Italy, commune of 61,000 inhabitants in the Italy, Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called in the Roman age, Civita in the Middle ...
, and Panticapaeum
Pantikapaion ( , from Scythian 'fish-path'; ) was an ancient Greek city on the eastern shore of Crimea, which the Greeks called Taurica. The city lay on the western side of the Cimmerian Bosporus, and was founded by Milesians in the late 7t ...
quickly grew into major trading hubs and centers for the exchange of goods between Greeks and indigenous populations. These colonies enabled Miletus to dominate regional commerce in grain, fish, and slaves, contributing significantly to the city’s wealth. The choice of the Black Sea also reflected both strategies to exploit new resources and responses to population and political pressures in Ionia.
Sinope, located on the southern coast of the Black Sea, was one of the earliest and most prosperous Milesian colonies, traditionally founded in the late seventh century BCE.
Olbia, on the northwestern Black Sea coast, likewise became a major economic center, especially for grain exports to the Greek world.
Milesian colonization not only expanded the city’s economic and political reach, but also established enduring cultural connections across the Mediterranean and Black Sea, with many settlements continuing to thrive and influence local societies for centuries.
While some Milesian colonies ultimately declined or were absorbed by neighboring powers, many—such as Sinope and Olbia—remained prominent centers of trade and Hellenic culture well into the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
and Roman periods. The archaeological remains and historical records of these colonies continue to shed light on the reach and legacy of Milesian influence throughout antiquity.
Some colonies founded include:
* Abydos
* Amisos
* Apollonia Pontica
* Borysthenites (Berezan)
*Cardia
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms re ...
*Cius
Cius (; ''Kios''), later renamed Prusias on the Sea (; ) after king Prusias I of Bithynia, was an ancient Greek city bordering the Propontis (now known as the Sea of Marmara), in Bithynia and in Mysia (in modern northwestern Turkey), and had a ...
*Colonae
Kolonai (; ) was an ancient Greek city in the south-west of the Troad region of Anatolia. It has been located on a hill by the coast known as Beşiktepe ('cradle hill'), about equidistant between Larisa to the south and Alexandreia Troas to th ...
* Cotyora
*Cyzicus
Cyzicus ( ; ; ) was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula (the classical Arctonnesus), a tombolo which is said to have or ...
*Dioscurias
Sukhumi or Sokhumi is a city in a wide bay on the Black Sea's eastern coast. It is both the capital and largest city of Abkhazia, a partially recognised state that most countries consider a part of Georgia. The city has been controlled by Abkh ...
* Hermonassa
* Histria
* Kepoi
* Kerasous
*Lampsacus
Lampsacus (; ) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in modern day Turkey, strategically situated on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been trans ...
*Leros
Leros (), also called Lero (from the Italian language), is a Greek island and municipality in the Dodecanese in the southern Aegean Sea. It lies from Athens's port of Piraeus, from which it can be reached by a nine-hour ferry ride or by a 45-min ...
* Limnae
*Miletopolis
Miletopolis () or Miletoupolis (Μιλητούπολις) was a town in the north of ancient Mysia, at the confluence of the rivers Macestus and Rhyndacus, and on the west of the lake which derives its name from the town. It was a Milesian colo ...
* Myrmekion (?)
* Nymphaion
* Odessos
*Olbia
Olbia (, ; ; ) is a city and communes of Italy, commune of 61,000 inhabitants in the Italy, Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called in the Roman age, Civita in the Middle ...
* Paesus
*Panticapaeum
Pantikapaion ( , from Scythian 'fish-path'; ) was an ancient Greek city on the eastern shore of Crimea, which the Greeks called Taurica. The city lay on the western side of the Cimmerian Bosporus, and was founded by Milesians in the late 7t ...
*Parium
Parium (or Parion; ) was a Greek city of Adrasteia in Mysia on the Hellespont. Its bishopric was a suffragan of Cyzicus, the metropolitan see of the Roman province of Hellespontus.
History
Founded in 709 B.C., the ancient city of Parion is lo ...
* Patraeus
*Phanagoria
Phanagoria (; ) was the largest ancient Greek city on the Taman peninsula, spread over two plateaus along the eastern shore of the Cimmerian Bosporus.
The city was a large emporium for all the traffic between the coast of the Maeotian marshe ...
* Phasis
*Pityus
Pitsunda or Bichvinta ( ka, ბიჭვინთა, ; ; ) is a resort town in the Gagra District of Abkhazia/Georgia. Founded by Greek colonists in the 5th century BC, Pitsunda became an important political and religious centre of the region i ...
*Priapus
In Greek mythology, Priapus (; ) is a minor rustic fertility god, protector of livestock, fruit plants, gardens, and male genitalia. Priapus is marked by his oversized, permanent erection, which gave rise to the medical term priapism. He becam ...
* Proconnesus
* Prusias (?)
*Sinope
Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
* Sinope (mythology), i ...
*Scepsis
Scepsis or Skepsis () was an ancient settlement in the Troad, Asia Minor that is at the present site of the village of Kurşunlutepe, near the town of Bayramiç in Turkey. The settlement is notable for being the location where the famous libra ...
*Tanais
Tanais ( ''Tánaïs''; ) was an ancient Greek city in the Don river delta, called the Maeotian marshes in classical antiquity. It was a bishopric as Tana and remains a Latin Catholic titular see as Tanais.
Location
The delta reaches into the ...
* Theodosia
* Tieion
* Tomis
*Tyras
Tyras () was an ancient Greek city on the northern coast of the Black Sea. It was founded by colonists from Miletus, probably about 600 BC. The city was situated some 10 km from the mouth of the Tyras River, which is now called the Dn ...
* Tyritake
*Trapezunt
Trabzon, historically known as Trebizond, is a city on the Black Sea coast of northeastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. The city was founded in 756 BC as "Trapezous" by colonists from Miletus. It was added into the Achaemenid Em ...
Philosophy
Miletus played a foundational role in the origins of Western philosophical inquiry. In the 6th century BCE, thinkers such asThales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
, Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
, and Anaximenes—collectively known as the Milesian school
The Ionian school of pre-Socratic philosophy refers to Ancient Greek philosophers, or a school of thought, in Ionia in the 6th century B.C, the first in the Western tradition.
The Ionian school included such thinkers as Thales, Anaximand ...
—began to investigate the material basis of the cosmos through rational, systematic inquiry rather than mythological narrative.
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
records that, “Thales, the founder of this kind of philosophy, stated it to be water. (This is why he declared that the earth rests on water.) …water is the principle of the nature of moist things.” Aristotle further notes, “Some say he earthrests on water. This is the oldest account that we have inherited, and they say that Thales of Miletus said this. It rests because it floats like wood or some other such thing…for nothing is by nature such as to rest on air, but on water.”
Thales’ student Anaximander introduced the concept of the apeiron
''Apeiron'' (; ) is a Greek word meaning '(that which is) unlimited; boundless; infinite; indefinite' from ''a-'' 'without' and ''peirar'' 'end, limit; boundary', the Ionic Greek form of ''peras'' 'end, limit, boundary'.
Origin of everything
...
(the infinite or indefinite) as a more abstract source of existence. According to Aristotle (via Simplicius): “Anaximander… said that the apeiron was the arkhē and element of things that are, and he was the first to introduce this name for the arkhē. …He says that the arkhē is neither water nor any of the other things called elements, but some other nature which is apeiron, out of which come to be all the heavens and the worlds in them. The things that are perish into the things from which they come to be, according to necessity, for they pay penalty and retribution to each other for their injustice in accordance with the ordering of time, as he says in rather poetical language.” Aristotle also states that for Anaximander, the apeiron “is deathless and indestructible…for it is divine.”
Anaximenes, in turn, posited air (''aēr'') as the basic element, suggesting it could transform into other forms of matter through rarefaction and condensation: “Anaximenes… declared that air is the underlying principle and that all the rest come to be from it by rarefaction and condensation. Fire, when air is rarefied; wind, then cloud, when condensed; water, then earth, then stones, and the rest come into being from these.”
The emergence of this rational mode of thinking was likely influenced by Miletus’s cosmopolitanism and its contact with the ancient cultures of the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
. These intellectual foundations laid the groundwork for later developments in Greek philosophy and science.
Religion and the Sacred Way
Miletus had several significant religious institutions, the most important of which was the sanctuary ofApollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
at Didyma
Didyma (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called ''Didymaion''. But it was home to both of the Ancient ...
, located roughly 18 kilometers south of the city. The sanctuary was connected to the city by a ceremonial road known as the Sacred Way
A sacred way, spirit way, spirit road, spirit path, etc. (, ''shéndào'') is the ornate road leading to a Chinese tomb of a major dignitary. The sacred way is lined on both sides by a succession of statues, pillars, and stelae. The statues al ...
, which served as a route for ritual processions and pilgrimage festivals.
Didyma was renowned for its oracle, second in prestige only to that of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
. Prophecies were delivered by a priestess within a richly adorned temple complex. Archaeological discoveries along the Sacred Way have uncovered rows of consecrated statues and inscriptions, often commissioned by Milesian elites and foreign notables.
The sanctuary was a hub for both religion and politics, reinforcing Miletus’ influence within Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
and the wider Aegean. Religious practices at Didyma, including oracular consultation and ritual dedication, reflected and shaped the city’s cultural identity and its connections with other Ionian communities.
Notable people
 *
*Arctinus of Miletus
Arctinus of Miletus or Arctinus Milesius () was a Greek epic poet whose reputation is purely legendary, as none of his works survive. Traditionally dated between 775 BC and 741 BC, he was said to have been a pupil of Homer. His father was Teleus s ...
(775 BC – 741 BC), epic poet
*Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
(c. 624 BC – c. 546 BC), Pre-Socratic
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of the ...
philosopher
*Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
(c. 610 BC – c. 546 BC), Pre-Socratic philosopher and geographer
*Cadmus
In Greek mythology, Cadmus (; ) was the legendary Phoenician founder of Boeotian Thebes, Greece, Thebes. He was, alongside Perseus and Bellerophon, the greatest hero and slayer of monsters before the days of Heracles. Commonly stated to be a ...
(fl. c. 550 BC), writer
* Anaximenes (c. 585 BC – c. 525 BC), Pre-Socratic philosopher
*Aristagoras
Aristagoras of Miletus (), d. 497/496 BC, was the tyrant of the Ionian city of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC. He acted as one of the instigators of the Ionian Revolt against the Persian Achaemenid Empire. He was ...
(fl. 6th-5th century BC), Tyrant of Miletus
*Phocylides
Phocylides (), Greek gnomic poet of Miletus, contemporary of Theognis of Megara, was born about 560 BC.
A few fragments of his " maxims" have survived (chiefly in the ''Florilegium'' of Stobaeus), in which he expresses his contempt for the po ...
(born c. 560 BC), Greek gnomic poet
* Hecataeus (c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), Greek historian
*Histiaeus
Histiaeus (, died 493 BC), the son of Lysagoras, was a Greek ruler of Miletus in the late 6th century BC. Histiaeus was tyrant of Miletus under Darius I, king of Persia, who had subjugated Miletus and the other Ionian states in Asia Mi ...
(died 493 BC), ruler of Miletus
*Leucippus
Leucippus (; , ''Leúkippos''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. He is traditionally credited as the founder of atomism, which he developed with his student Democritus. Leucippus divided the world into two entities: atoms, indivisible ...
(fl. first half of 5th century BC), philosopher and originator of Atomism (his association with Miletus is traditional, but disputed)
*Hippodamus
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; c.480 BCE, 480–408 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosophe ...
(c. 498 – 408 BC), urban planner
*Aspasia
Aspasia (; ; after 428 BC) was a ''metic'' woman in Classical Athens. Born in Miletus, she moved to Athens and began a relationship with the statesman Pericles, with whom she had a son named Pericles the Younger. According to the traditional h ...
(c. 470 – 400 BC) courtesan, and mistress of Pericles
Pericles (; ; –429 BC) was a Greek statesman and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed ...
, was born in Miletus
*Aristides
Aristides ( ; , ; 530–468 BC) was an ancient Athenian statesman. Nicknamed "the Just" (δίκαιος, ''díkaios''), he flourished at the beginning of Athens' Classical period and is remembered for his generalship in the Persian War. ...
(fl. 2nd century BC), writer
*Monime
Monime, sometimes known as Monima (; died 72/71 BC), was a Macedonian Greek noblewoman from Anatolia and one of the wives of King Mithridates VI of Pontus.
According to the ancient sources she was a citizen of either Miletus or Stratonicea, Cari ...
(died 72/71 BC), a Greek noblewoman and one of the wives of Mithridates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and ...
*Alexander Polyhistor
Lucius Cornelius Alexander Polyhistor (; flourished in the first half of the 1st century BC; also called Alexander of Miletus) was a Greek scholar who was enslaved by the Romans during the Mithridatic War and taken to Rome as a tutor. After his r ...
(fl. 1st century AD), Greek scholar, born in Miletus before being taken as a slave to Rome
* Aeschines of Miletus (fl. 1st century AD), a distinguished orator in the Asiatic style
*Isidore
Isidore ( ; also spelled Isador, Isadore and Isidor) is a masculine given name. The name is derived from the Greek name ''Isídōros'' (Ἰσίδωρος, latinized ''Isidorus'') and can literally be translated to 'gift of Isis'. The name has survi ...
(fl. 6th century AD), Greek architect
* Hesychius (fl. 6th century AD), Greek chronicler and biographer
*Timagenes or Timogenes, historian and rhetor
*Philiscus of Miletus, rhetor. Teacher of Neanthes of Cyzicus
Neanthes of Cyzicus (; ) was a Greek historian and rhetorician of Cyzicus in Anatolia living in the fourth and third centuries BC.
Biography
Neanthes was a pupil of Philiscus of Miletus ("who is reasonably certain to have died before 300 BC"Michae ...
*Hellanicus, historian
*Dionysicles () of Miletus, sculptor. One of his famous works was a statue, at Leonidaion, of Democrates of Tenedos
Tenedos (, ''Tenedhos''; ), or Bozcaada in Turkish language, Turkish, is an island of Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively, the island constitutes the Bozcaada, Çanakkale, Bozcaada district of Çanakkale Provinc ...
who was an ancient Olympic winner at wrestling
* Baccheius or Bacchius of Miletus (Βακχεῖος), a writer. He wrote a work on agriculture./ref>
See also
*Cities of the ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by ...
Notes
References and sources
;References ;Sources *Further reading
* *External links
Official website
official site of the excavations in Miletus by Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Ancient Coins of Miletus
in English translation
* * ttp://www.fhw.gr/choros/miletus/en/index.php Details about most of the monumentsbr>Walking the sacred pagan path from Ancient Miletus to Didim
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Former populated places in Turkey Archaeological sites in the Aegean region Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey History of Aydın Province Tourist attractions in Aydın Province Ionian League Buildings and structures in Aydın Province Members of the Delian League Greek city-states Late Bronze Age collapse Populated places in ancient Caria New Testament cities Didim District