|
Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who had settled in the region before the archaic period. Ionia proper comprised a narrow coastal strip from Phocaea in the north near the mouth of the river Hermus (now the Gediz), to Miletus in the south near the mouth of the river Maeander, and included the islands of Chios and Samos. It was bounded by Aeolia to the north, Lydia to the east and Caria to the south. The cities within the region figured significantly in the strife between the Persian Empire and the Greeks. Ionian cities were identified by mythic traditions of kinship and by their use of the Ionic dialect, but there was a core group of twelve Ionian cities that formed the Ionian League and had a shared sanctuary and festival at Panionion. These twelve cities were (from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ἰωνία
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greeks, Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who had settled in the region before the Archaic Greece, archaic period. Ionia proper comprised a narrow coastal strip from Phocaea in the north near the mouth of the river Hermus (now the Gediz River, Gediz), to Miletus in the south near the mouth of the river Maeander, and included the islands of Chios and Samos. It was bounded by Aeolis, Aeolia to the north, Lydia to the east and Caria to the south. The cities within the region figured significantly in the strife between the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire and the Greeks. Ionian cities were identified by mythic traditions of kinship and by their use of the Ionic dialect, but there was a core group of twelve Ionian cities that formed the Ionian League and had a shared sanctuary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ἰωνίη
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who had settled in the region before the archaic period. Ionia proper comprised a narrow coastal strip from Phocaea in the north near the mouth of the river Hermus (now the Gediz), to Miletus in the south near the mouth of the river Maeander, and included the islands of Chios and Samos. It was bounded by Aeolia to the north, Lydia to the east and Caria to the south. The cities within the region figured significantly in the strife between the Persian Empire and the Greeks. Ionian cities were identified by mythic traditions of kinship and by their use of the Ionic dialect, but there was a core group of twelve Ionian cities that formed the Ionian League and had a shared sanctuary and festival at Panionion. These twelve cities were (from sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionians
The Ionians (; , ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the traditional four major tribes of Ancient Greece, alongside the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the Hellenic world, together with the Dorian and Aeolian dialects. When referring to populations, "''Ionian''" defines several groups in Classical Greece. In its narrowest sense, the term referred to the region of Ionia in Asia Minor. In a broader sense, it could be used to describe all speakers of the Ionic dialect, which in addition to those in Ionia proper also included the Greek populations of Euboea, the Cyclades, and many cities founded by Ionian colonists. Finally, in the broadest sense it could be used to describe all those who spoke languages of the East Greek group, which included Attic. The foundation myth which was current in the Classical period suggested that the Ionians were named after Ion, son of Xuthus, who lived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
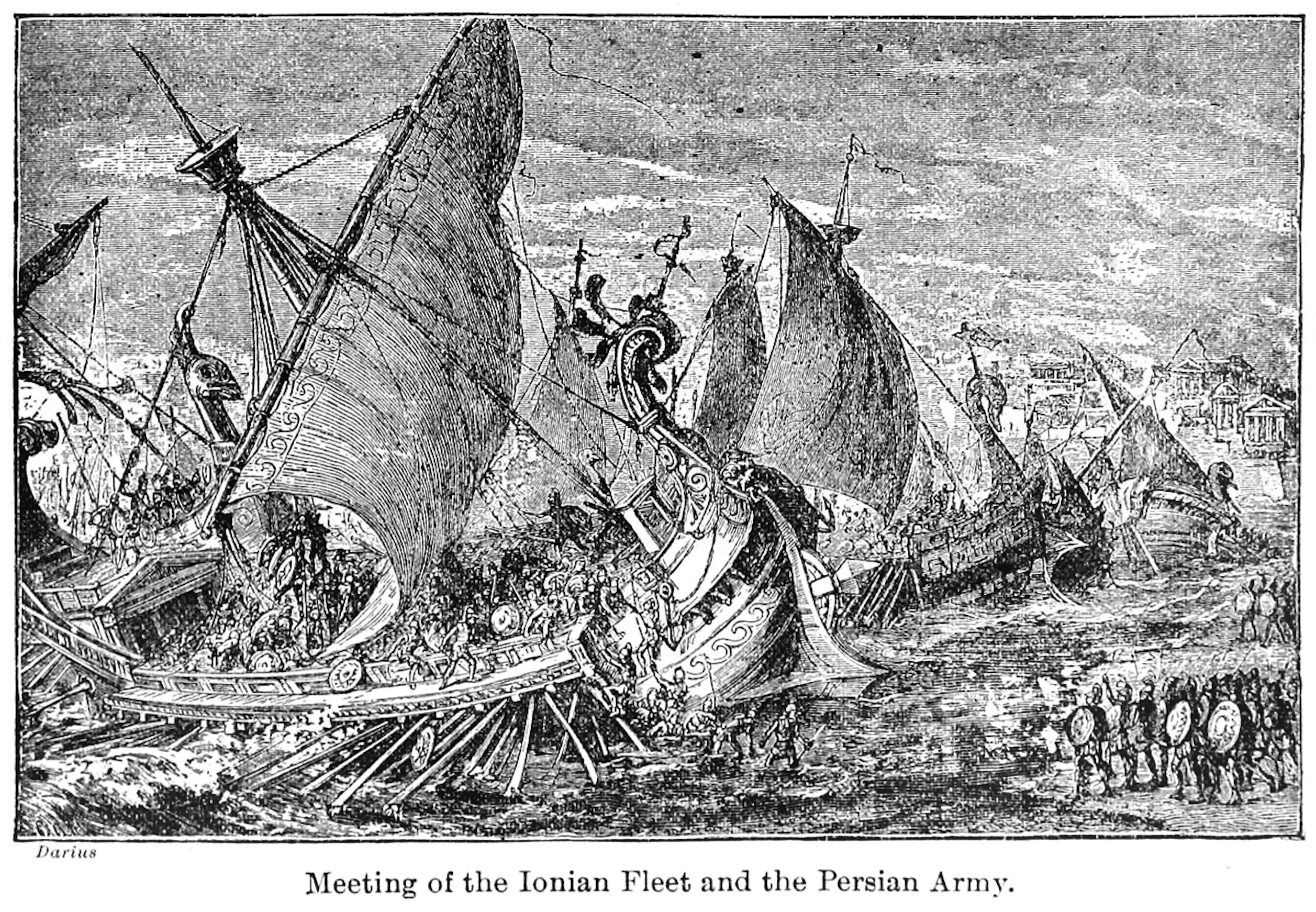
Ionia (satrapy)
Ionia, known in Old Persian as Ionians, Yauna (Wikt:𐎹𐎢𐎴, 𐎹𐎢𐎴), was a region within the Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of Lydia, with its capital at Sardis, within the Achaemenid Empire, First Persian Empire. The first mention of the Yauna is at the Behistun inscription. History Achaemenid conquest (c. 546 – 479 BC) In the mid-6th century BC, the Ionians were conquered by Cyrus the Great and according to Herodotus, they were placed in the same tax district (the first) as the Pamphylians, Lycians, Magnesians, Aeolians, Milyans, and Carians. It is unclear to what extent the Yauna were advantaged or disadvantaged by Persian rule, and what caused the Ionian Revolt which broke out in c. 499 BC and lasted until 494 BC. The main source, Herodotus, puts it down to the personal ambitions of two men of Miletus, Histiaeus and Aristagoras; modern scholars debate what the underlying reasons may have been; arguments for economic and political causes are variously put forward, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycale
Mycale () also Mykale and Mykali (, ''Mykálē''), called Samsun Dağı and Dilek Dağı ( Dilek Peninsula) in modern Turkey, is a mountain on the west coast of central Anatolia in Turkey, north of the mouth of the Maeander and divided from the Greek island of Samos by the 1.6 km wide Mycale Strait. The mountain forms a ridge, terminating in what was known anciently as the Trogilium promontory (Ancient Greek Τρωγίλιον or Τρωγύλιον). There are several beaches on the north shore ranging from sand to pebbles. The south flank is mainly escarpment. In the Late Bronze Age, it may have been known under the Hittite name Arrinnanda. In classical Greece nearly the entire ridge was a promontory enclosed by the Aegean Sea. Geopolitically it was part of Ionia with Priene placed on the coast on the south flank of the mountain and Miletus on the coast opposite to the south across the deep embayment into which the Maeander River drained. Somewhat further north wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephesus
Ephesus (; ; ; may ultimately derive from ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, in present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital, by Attica, Attic and Ionians, Ionian Greek colonists. During the Classical Greece, Classical Greek era, it was one of twelve cities that were members of the Ionian League. The city came under the control of the Roman Republic in 129 BC. The city was famous in its day for the nearby Temple of Artemis (completed around 550 BC), which has been designated one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Its many monumental buildings included the Library of Celsus and a theatre capable of holding 24,000 spectators. Ephesus was a recipient city of one of the Pauline epistles and one of the seven churches of Asia addressed in the Book of Revelation. The Gospel of John may have been written there,Stephen L Harris, Harris, Stephen L., ''Under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Dialect
Ionic or Ionian Greek () was a subdialect of the Eastern or Attic–Ionic dialect group of Ancient Greek. The Ionic group traditionally comprises three dialectal varieties that were spoken in Euboea (West Ionic), the northern Cyclades (Central Ionic), and from BC onward in Asiatic Ionia (East Ionic), where Ionian colonists from Athens founded their cities. Ionic was the base of several literary language forms of the Archaic and Classical periods, both in poetry and prose. The works of Homer and Hesiod are among the most popular poetic works that were written in a literary form of the Ionic dialect, known as Epic or Homeric Greek. The oldest Greek prose, including that of Heraclitus, Herodotus, Democritus, and Hippocrates, was also written in Ionic. By the end of the 5th century BC, Ionic was supplanted by Attic, which had become the dominant dialect of the Greek world. History The Ionic dialect appears to have originally spread from the Greek mainland across the Aegean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian League
The Ionian League (; , ; or , , in ), also called the Panionic League, was a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th century BC comprising twelve Ionian Greek city-states (a dodecapolis, of which there were many others), and eventually thirteen city-states with the admission of Smyrna. The earliest union of city-states in the area was the Ionian League. The League survived through the Hellenistic and Roman periods, until the 3rd century AD. Overview The twelve ancient city-states were listed by Herodotus as:Herodotus. ''The Histories''1.142 *Miletus, Myus, and Priene — all located in Caria (a region in Asia Minor). The three Greek cities spoke the same Ionic subdialect. Starting from the 7th century BC, Greek-Carian bilinguals in Caria suggest the Carians shared their former ancestral land amicably with the Greeks. The Carian language is not Greek but is a remnant of the Anatolian language group that dominated Anatolia before being pushed out b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Greek
Ionic or Ionian Greek () was a subdialect of the Eastern or Attic–Ionic dialect group of Ancient Greek. The Ionic group traditionally comprises three dialectal varieties that were spoken in Euboea (West Ionic), the northern Cyclades (Central Ionic), and from BC onward in Asiatic Ionia (East Ionic), where Ionian colonists from Athens founded their cities. Ionic was the base of several literary language forms of the Archaic and Classical periods, both in poetry and prose. The works of Homer and Hesiod are among the most popular poetic works that were written in a literary form of the Ionic dialect, known as Epic or Homeric Greek. The oldest Greek prose, including that of Heraclitus, Herodotus, Democritus, and Hippocrates, was also written in Ionic. By the end of the 5th century BC, Ionic was supplanted by Attic, which had become the dominant dialect of the Greek world. History The Ionic dialect appears to have originally spread from the Greek mainland across the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phocaea
Phocaea or Phokaia (Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: Φώκαια, ''Phókaia''; modern-day Foça in Turkey) was an ancient Ionian Ancient Greece, Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia. Colonies in antiquity, Greek colonists from Phocaea founded the colony of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, in France) in 600 BC, Emporion (modern-day Empúries, in Catalonia, Spain) in 575 BC and Elea (modern-day Velia, in Campania, Italy) in 540 BC. Geography Phocaea was the northernmost of the Ionian cities, on the boundary with Aeolis. It was located near the mouth of the river Hermus (now Gediz River, Gediz), and situated on the coast of the peninsula separating the Gulf of Cyme (Aeolis), Cyme to the north, named for the largest of the Aeolis, Aeolian cities, and the Gulf of Smyrna (now İzmir) to the south. Phocaea had two natural harbours within close range of the settlement, both containing a number of small islands. Phocaea's harbours allowed it to develop a thriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and extensive network of colonies, Miletus was a major center of trade, culture, and innovation from the Bronze Age through the Roman period. The city played a foundational role in the development of early Greek philosophy and science, serving as the home of the Milesian school with thinkers such as Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes. Miletus's prosperity was closely linked to its strategic coastal location and the productivity of its surrounding rural hinterland, which supported thriving agriculture and facilitated wide-ranging commercial activity. The city established dozens of colonies around the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Black Sea, significantly shaping the Ancient Greece, Greek world’s expansion. Archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |